Activity of Potassium Channel BmK-NSPK Inhibitor Regulated by Basic Amino Acid Residues: Novel Insight into the Diverse Peptide Pharmacology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
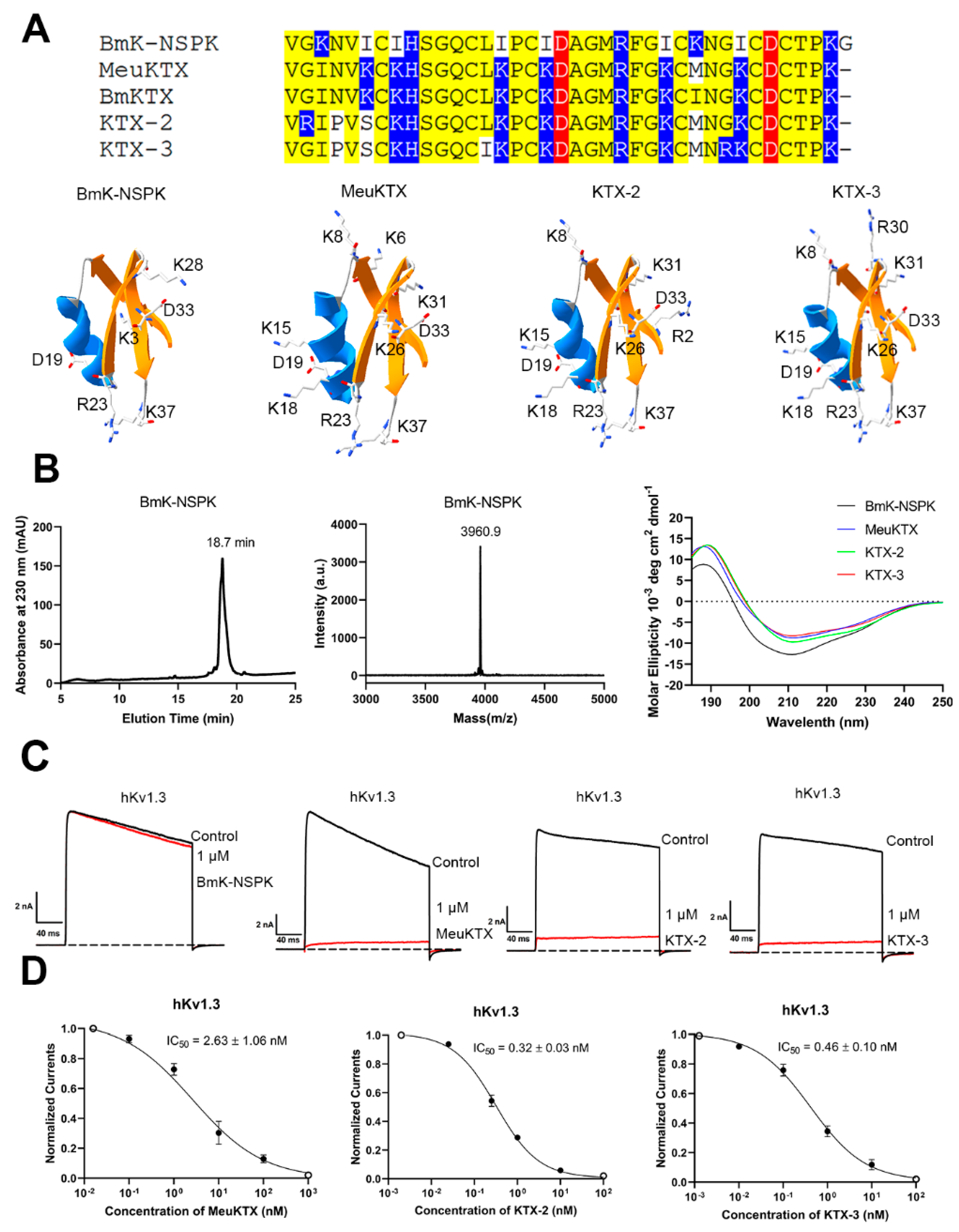
2.1. Similar Structure and Functional Loss of BmK-NSPK Peptide Due to Fewer Basic Residues
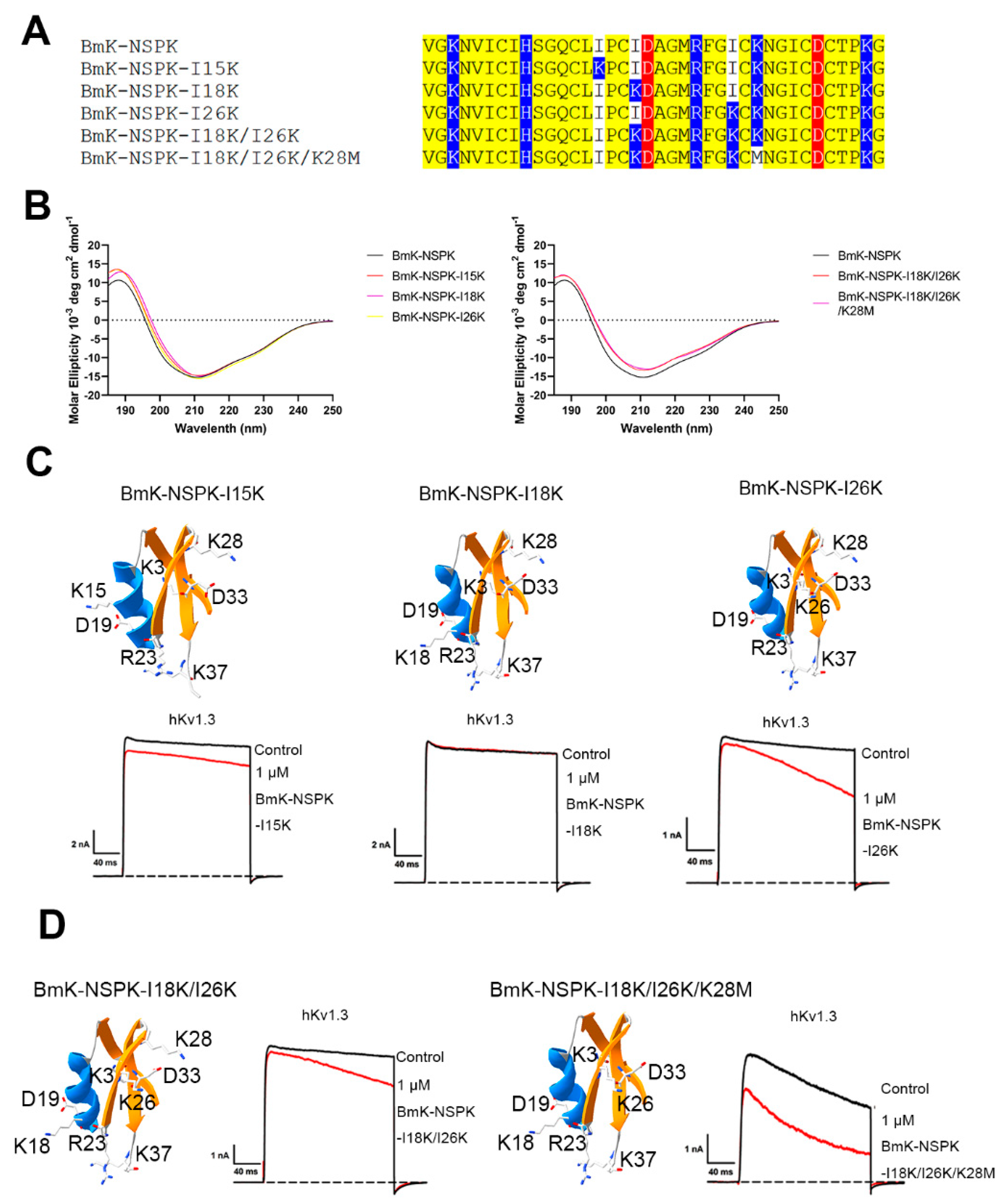
2.2. Less Effect of One and Two Basic Residue Introduction on BmK-NSPK Function
2.3. Significant Effect of Several Basic Residue Introduction on BmK-NSPK Function
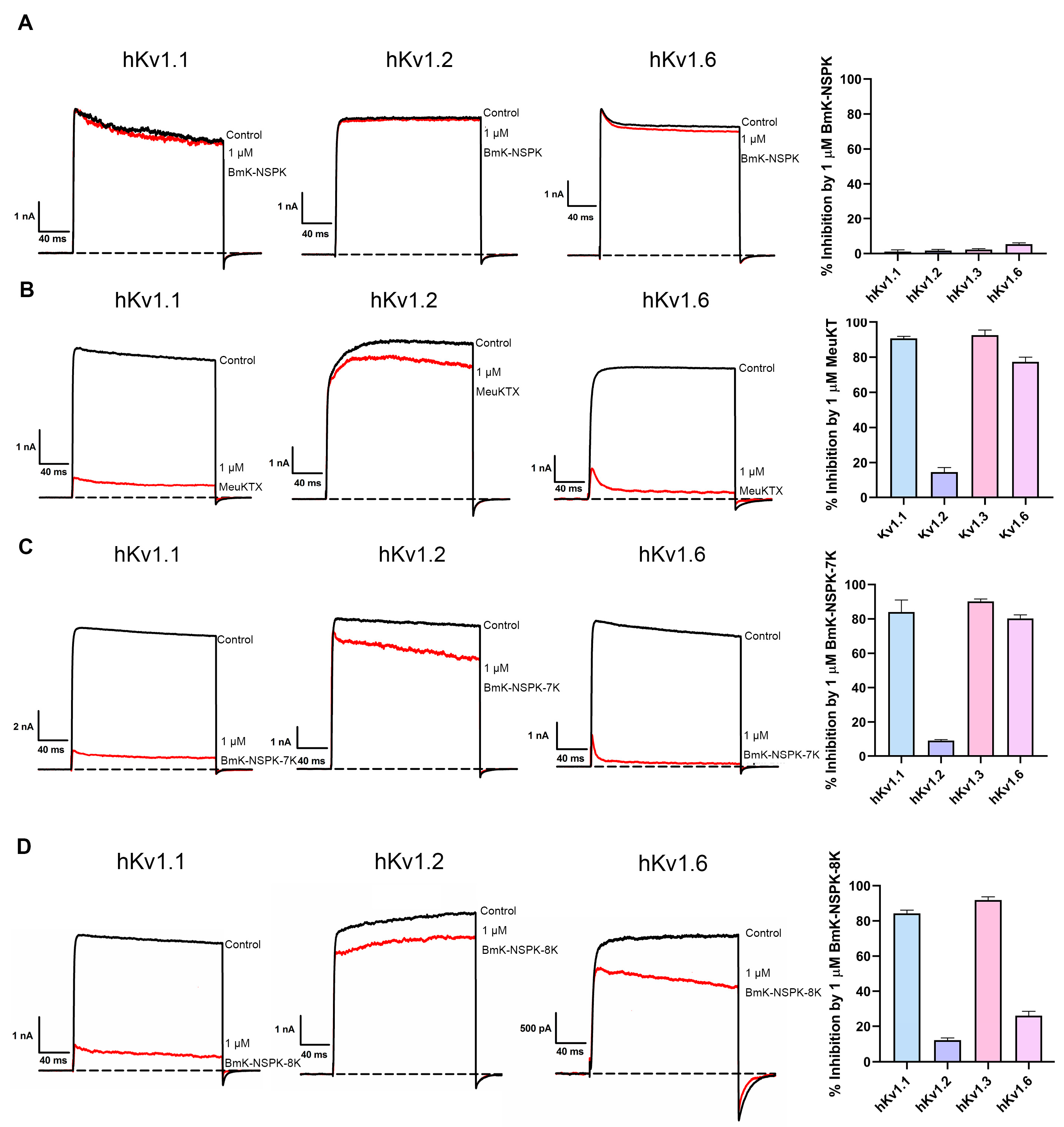
2.4. Importance of Basic Residue on BmK-NSPK Inhibition of Other Potassium Channels
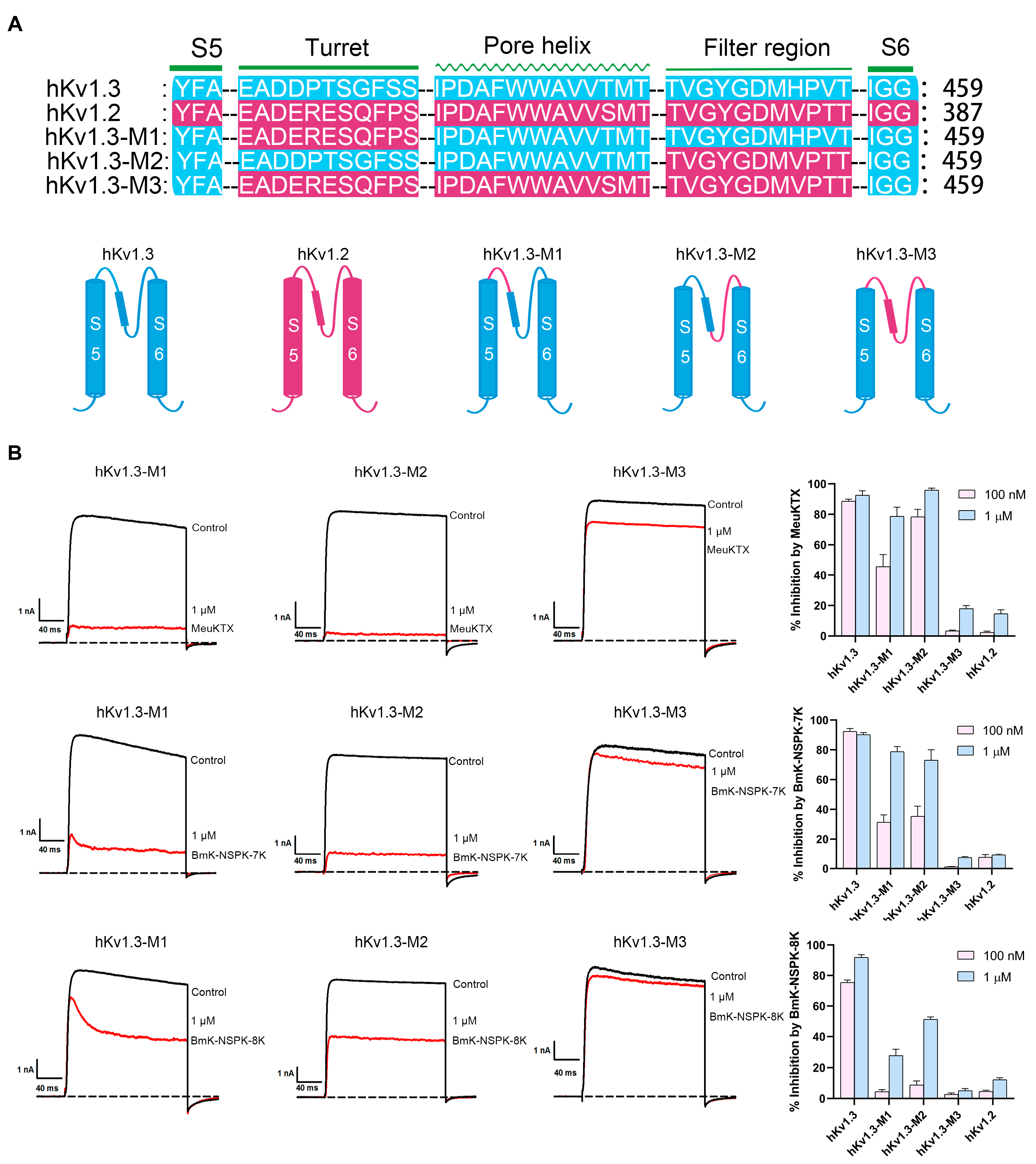
2.5. Differential Effects of Basic Residue Introduction on BmK-NSPK Inhibition of Potassium Channel Chimeras
3. Discussion
4. Method and Materials
4.1. Construction of Expression Vectors for Fusion Proteins
4.2. Expression, Purification and Identification of Peptides
4.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
4.4. Structural Analysis of Peptides
4.5. Potassium Channel Expression Vectors
4.6. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.7. Electrophysiological Recordings
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashcroft, F.M. From molecule to malady. Nature 2006, 440, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; Jouirou, B.; Sabatier, J.M. Animal toxins acting on voltage-gated potassium channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, R.; Heginbotham, L.; Abramson, T. Mapping the receptor site for charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking potassium channel inhibitor. Neuron 1990, 5, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, P.; Mackinnon, R. Revealing the architecture of a K+ channel pore through mutant cycles with a peptide inhibitor. Science 1995, 268, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Mackinnon, R. Agitoxin footprinting the shaker potassium channel pore. Neuron 1996, 16, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, R.; Cohen, S.L.; Kuo, A.L.; Lee, A.; Chait, B.T. Structural conservation in prokaryotic and eukaryotic potassium channels. Science 1998, 280, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, V.; Jiang, Y.X.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Mackinnon, R. Functional analysis of an archaebacterial voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 2003, 422, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Klem, A.M.; Ramu, Y. Ion conduction pore is conserved among potassium channels. Nature 2001, 413, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais, C.J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; Mackinnon, R. The structure of the potassium channel: Molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.B.; Campbell, E.B.; Mackinnon, R. Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent shaker family K+ channel. Science 2005, 309, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeton, C.; Wulff, H.; Standifer, N.E.; Azam, P.; Mullen, K.M.; Pennington, M.W.; Kolski-Andreaco, A.; Wei, E.; Grino, A.; Counts, D.R.; et al. Kv1.3 channels are a therapeutic target for T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17414–17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Yi, H.; Yin, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, W. Structural basis of a potent peptide inhibitor designed for Kv1.3 channel, a therapeutic target of autoimmune disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 19058–19065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Beeton, C.; Galea, C.A.; Smith, B.J.; Chi, V.; Monaghan, K.P.; Garcia, A.; Rangaraju, S.; Giuffrida, A.; Plank, D.; et al. Engineering a stable and selective peptide blocker of the Kv1.3 channel in T lymphocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Han, S.; Peng, B.; Yin, J.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Li, W. Selective inhibition of CCR7− effector memory T cell activation by a novel peptide targeting Kv1.3 channel in a rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29479–29494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, S.; Pheasant, D.J.; Miller, C. The charybdotoxin receptor of a shaker K+ channel-peptide and channel residues mediating molecular recognition. Neuron 1994, 12, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauer, H.; Pennington, M.; Cahalan, M.; Chandy, K.G. Structural conservation of the pores of calcium-activated and voltage-gated potassium channels determined by a sea anemone toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21885–21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, S.; Danse, J.M.; Lecoq, A.; Pinkasfeld, S.; Zinn-Justin, S.; Young, L.C.; de Medeiros, C.C.; Rowan, E.G.; Harvey, A.L.; Menez, A. Delineation of the functional site of alpha-dendrotoxin. The functional topographies of dendrotoxins are different but share a conserved core with those of other Kv1 potassium channel-blocking toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 25393–25403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yi, H.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, W. Molecular information of charybdotoxin blockade in the large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wu, Y. Molecular mechanism of the sea anemone toxin Shk recognizing the Kv1.3 channel explored by docking and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Lee, A.; Campbell, E.; Mackinnon, R. Structure of a pore-blocking toxin in complex with a eukaryotic voltage-dependent K+ channel. eLife 2013, 2, e00594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, P.; Fernandez-Marino, A.I.; Khanra, N.; He, C.; Paquette, A.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Smider, V.V.; Rice, W.J.; Swartz, K.J.; et al. Structures of the T cell potassium channel Kv1.3 with immunoglobulin modulators. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Rivetta, A.; Allen, K.; Sigworth, F.J. Cryo-em structures of Kv1.2 potassium channels, conducting and non-conducting. eLife 2024, 12, RP89459. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Q.; Dong, F.; Zhou, H.X. Electrostatic recognition and induced fit in the kappa-PVIIA toxin binding to shaker potassium channel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6836–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Shen, J.H.; Briggs, J.M.; Luo, X.M.; Tan, X.J.; Jiang, H.L.; Chen, K.X.; Ji, R.Y. Brownian dynamics simulations of interaction between scorpion toxin Lq2 and potassium ion channel. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Cui, M.; Briggs, J.M.; Huang, X.Q.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Luo, X.M.; Shen, J.H.; Ji, R.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; et al. Brownian dynamics simulations of the recognition of the scorpion toxin maurotoxin with the voltage-gated potassium ion channels. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2370–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Yin, S.; Yi, H.; Mouhat, S.; Qiu, S.; Cao, Z.; Sabatier, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, W. Protein - protein recognition control by modulating electrostatic interactions. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Sabatier, J.; De Waard, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Han, S.; Wu, Y. Unusual binding mode of scorpion toxin BmKTX onto potassium channels relies on its distribution of acidic residues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hong, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Xiang, F.; Yang, F.; Xie, Z.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Toxin acidic residue evolutionary function-guided design of de novo peptide drugs for the immunotherapeutic target, the Kv1.3 channel. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Na, R.; Yang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Huang, X. The binding process of BmKTX and BmKTX -D33H toward to Kv1.3 channel: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zou, X.; Li, S.; He, J.; Xi, C.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z. BmK NSPK, a potent potassium channel inhibitor from scorpion buthus martensii karsch, promotes neurite outgrowth via NGF/TrkA signaling pathway. Toxins 2021, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, K.G.; Wulff, H.; Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.; Gutman, G.A.; Cahalan, M.D. K+ channels as targets for specific immunomodulation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Sabatier, J.; Wu, Y. Treating autoimmune disorders with venom-derived peptides. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Vargas, J.M.; Possani, L.D.; Luna-Ramirez, K. Arthropod toxins acting on neuronal potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Wan, X.; Li, S.; Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Zuo, Z.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y. Different pharmacological properties between scorpion toxin BmKcug2 and its degraded analogs highlight the diversity of K+ channel blockers from thermally processed scorpions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 178, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, G.; Huang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Sun, F.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y. Functional characterization of a new degradation peptide BmTX4-P1 from traditional chinese scorpion medicinal material. Toxins 2023, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, D.; Xie, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Cao, Z.; et al. Ion channel modulation by scorpion hemolymph and its defensin ingredients highlights origin of neurotoxins in telson formed in paleozoic scorpions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y. Scorpion potassium channel-blocking defensin highlights a functional link with neurotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7097–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Jiang, L.; Yi, H.; Han, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, W. Different residues in channel turret determining the selectivity of ADWX-1 inhibitor peptide between Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4890–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.S.; Chandy, K.G. Venom-derived peptide inhibitors of voltage-gated potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilquin, B.; Racapé, J.; Wrisch, A.; Visan, V.; Lecoq, A.; Grissmer, S.; Ménez, A.; Gasparini, S. Structure of the BgK-Kv1.1 complex based on distance restraints identified by double mutant cycles: Molecular basis for convergent evolution of Kv1 channel blockers. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37406–37413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Mosbah, A.; Visan, V.; Wulff, H.; Delepierre, M.; Darbon, H.; Grissmer, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. The ‘functional’ dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1.2 potassium channels. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huys, I.; Xu, C.Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Vacher, H.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Chi, C.W.; Tytgat, J. BmTX3, a scorpion toxin with two putative functional faces separately active on A-type K+ and herg currents. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Contribution of the functional dyad of animal toxins acting on voltage-gated Kv1-type channels. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Qin, C.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Y. Activity of Potassium Channel BmK-NSPK Inhibitor Regulated by Basic Amino Acid Residues: Novel Insight into the Diverse Peptide Pharmacology. Molecules 2025, 30, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030450
Zuo Z, Yang X, Zhang H, Qin C, Cao Z, Wu Y. Activity of Potassium Channel BmK-NSPK Inhibitor Regulated by Basic Amino Acid Residues: Novel Insight into the Diverse Peptide Pharmacology. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030450
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Zheng, Xuhua Yang, Haozhen Zhang, Chenhu Qin, Zhijian Cao, and Yingliang Wu. 2025. "Activity of Potassium Channel BmK-NSPK Inhibitor Regulated by Basic Amino Acid Residues: Novel Insight into the Diverse Peptide Pharmacology" Molecules 30, no. 3: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030450
APA StyleZuo, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, H., Qin, C., Cao, Z., & Wu, Y. (2025). Activity of Potassium Channel BmK-NSPK Inhibitor Regulated by Basic Amino Acid Residues: Novel Insight into the Diverse Peptide Pharmacology. Molecules, 30(3), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030450




