Histological Insights into the Neuroprotective Effects of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules in Cerebral Ischemia
Abstract
1. Discovery Phase
1.1. Prevalence and Impact of Cerebral Ischemia
1.2. Role of Oxidative Stress in Pathogenesis
1.3. Rationale for the Use of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules
1.4. Objectives of the Review
- To summarize histological outcomes (neuronal survival, apoptosis markers, and structural preservation) associated with these compounds.
- To correlate histological evidence with the biochemical markers of oxidative stress and functional outcomes.
- To compare the relative contributions of peptide-based versus small-molecule antioxidants.
- To identify gaps in the literature and highlight opportunities for translational and clinical research.
2. Analytical Framework
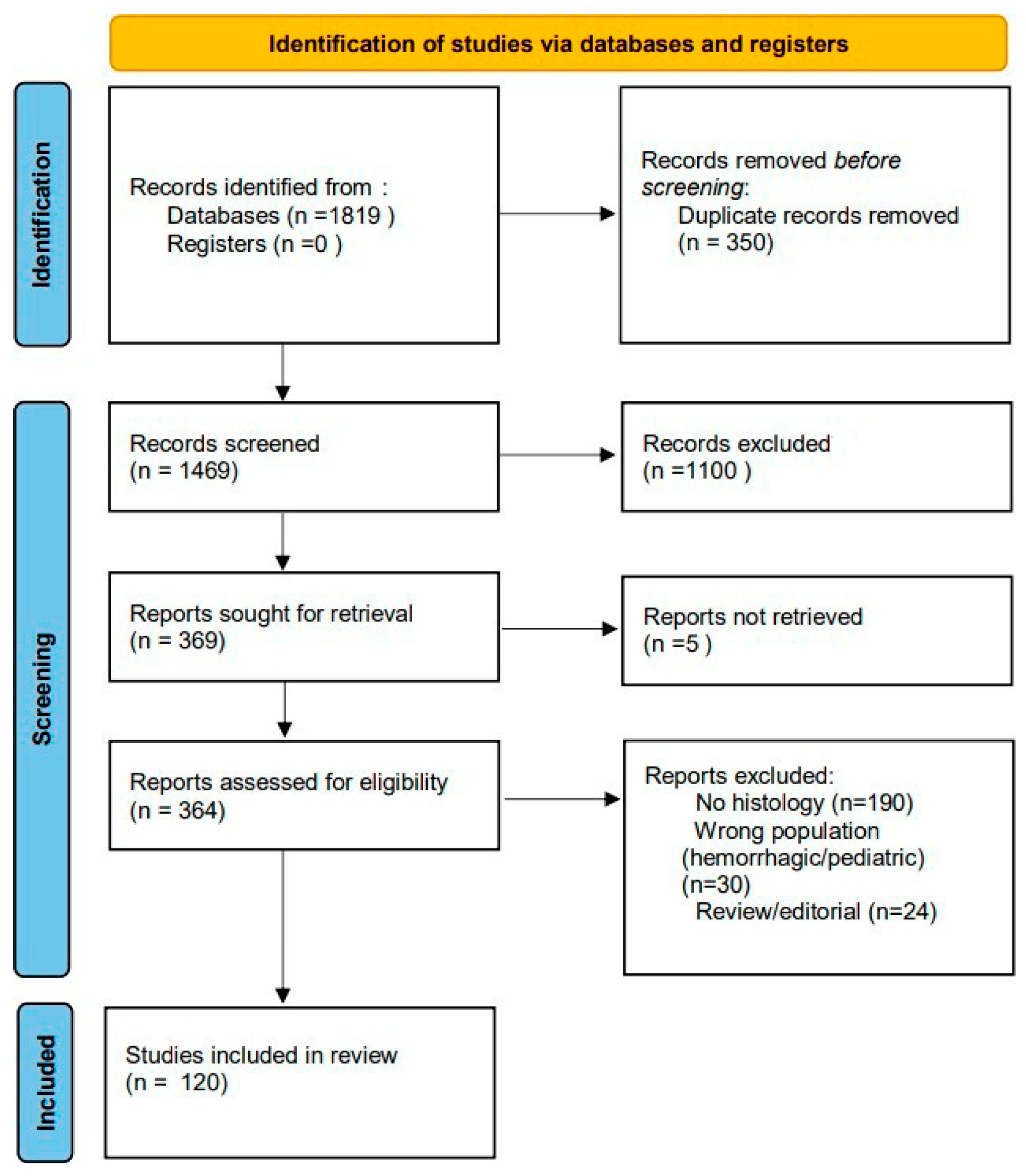
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria (PICO Framework)
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Data Extraction
3. Molecular and Histological Pathophysiology of Cerebral Ischemia
4. Empirical Evidence
4.1. Data Synthesis and Rationale for Tabular Presentation
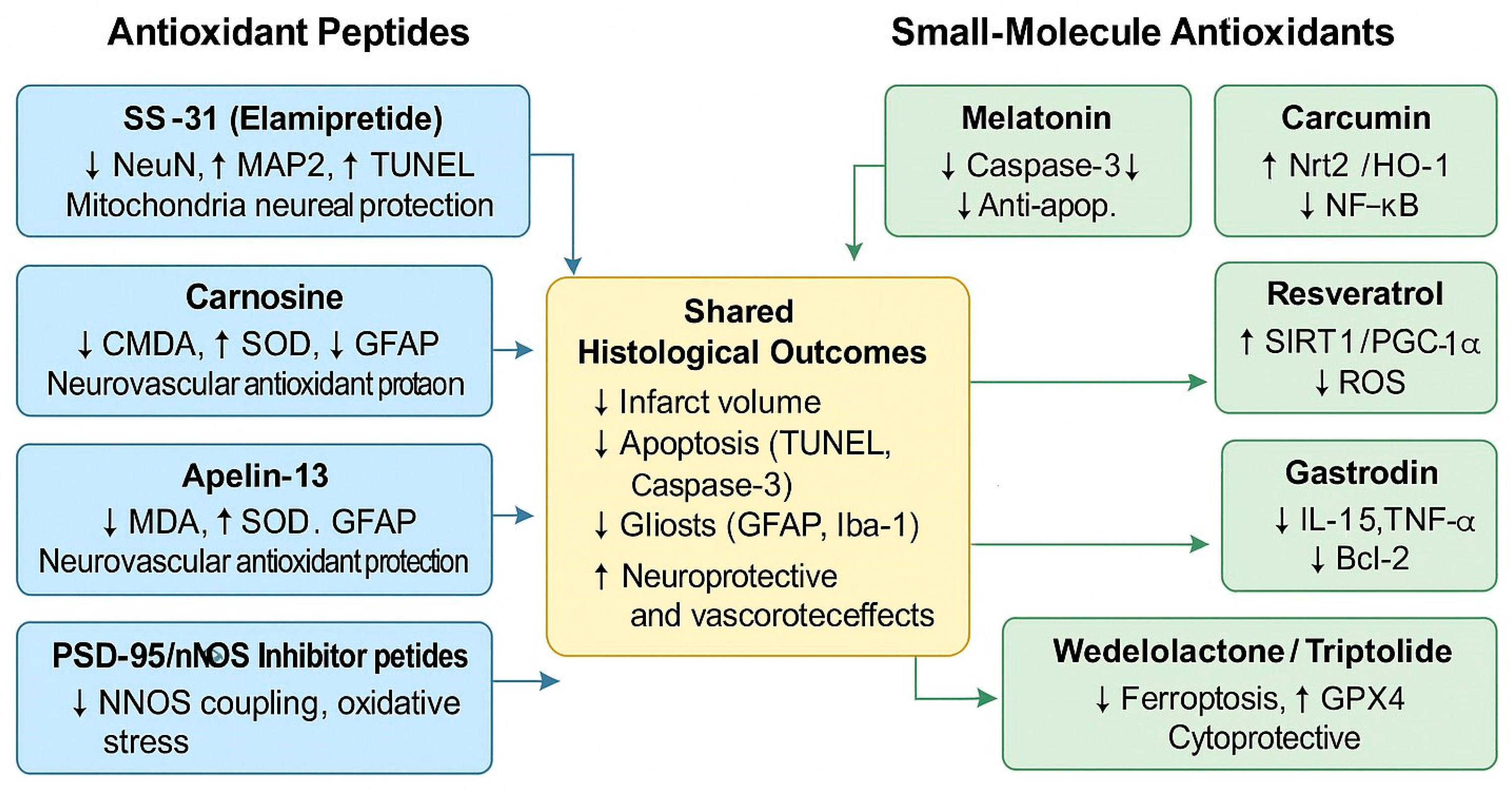
4.2. Antioxidant Peptides as Neuroprotective Agents
4.3. Small-Molecule Antioxidants
4.3.1. Melatonin
4.3.2. Resveratrol
4.3.3. Curcumin
4.3.4. Puerarin
4.3.5. Gastrodin
4.3.6. Wedelolactone
4.3.7. Triptolide
4.3.8. Sevoflurane Postconditioning
4.4. Antioxidant-Related Strategy
4.4.1. DGAT1 Inhibition
4.4.2. Epigenetic Modulation via ALKBH5 and Gastrodin
4.4.3. ATF3 Knockdown and Nrf2/HO-1 Activation
4.4.4. HMOX1/PPAR-γ/FABP4 Modulators
4.4.5. Integration with Microglial Remodeling
4.5. Comparative Histological Efficiency
4.6. Critical Analysis of Various Histological Effects
Consistent Effects Across Compounds
4.7. Critical Analysis: Consistent Versus Contradictory Histological Effects
5. Critical Evaluation
5.1. Interpretation of the Main Histological Findings
5.2. Mechanisms Involved: Mitigation of Oxidative Stress, Inhibition of Apoptosis, and Suppression of Inflammation
5.3. Key Challenges in Translating Data from Preclinical to Clinical Settings
5.4. Limitations of the Studies
5.5. Clinical Implications and Future Directions
6. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Acute Ischemic Stroke |
| MCAO | Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| EDB | Edaravone–Dexborneol |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin Gallate |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.O.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P.; Grupper, M.F.; Rautalin, I. World Stroke Organization: Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2025. Int. J. Stroke 2025, 20, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Harmon, E.; Gutierrez, M.; Kim, S.; Vance, L.; Burrous, H.; Stephenson, J.M.; Chauhan, A.; Banerjee, A.; Wise, Z.; et al. Single-cell analysis identifies Ifi27l2a as a regulator in ischemic stroke. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Ortega, G.; Torres-Campos, E.; Díaz-Moreno, M. Retrograde transport of neurotrophin receptor TrkB-FL induced by excitotoxicity regulates Golgi stability and is a target for stroke neuroprotection. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Tai, S.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Lo, K.H.; Lee, A.-H.; Chen, Y.-N.; Lee, A.-C.; Tseng, C.-S.; Lee, E.-J. Remote ischemic preconditioning enhances antioxidant capacity and reduces oxidative damage in experimental stroke. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 168010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, N.; Tai, C.; Yang, Y.; Ling, C.; Zhang, B.; Wei, L.; Yao, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, C. MT2A promotes angiogenesis in chronically ischemic brains through a copper–mitochondria regulatory mechanism. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liang, R.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Guo, X.; Ju, H.; Zhou, J.; Dong, M. Development of cell-permeable and plasma-stable peptidomimetic inhibitors against PSD-95/nNOS interaction as potential anti-ischemic stroke agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 299, 118062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, X.; Yang, S.; Zuo, H.; Guo, T.; Xiao, R.; Li, Y.; et al. Gastrodin promotes Alkbh5 nuclear localization and attenuates oxidative stress in ischemic stroke models. Phytomedicine 2025, 147, 157177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sure, V.N.; Sakamuri, S.S.V.P.; Orgunati, L.; Ageeli, R.; Murfee, W.L.; Katakam, P.V.G. Paradoxical mitochondrial effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition following oxygen-glucose deprivation-reoxygenation (OGD/R) in endothelial cells and neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahire, K.L.; Małuhins, R.; Bello, F.; Valero Freitag, S.; Jełisejevs, I.; Gile, R.; Upīte, J.; Plesnila, N.; Jansone, B. Hemispheric analysis of mitochondrial Complex I and II activity in the mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury. Mitochondrion 2023, 69, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhao, M.; Gao, K.; Zhang, W.; Xu, D.; Li, W.; Mu, F.; Lin, R.; Guo, C.; Li, R.; et al. Wedelolactone ameliorates ischemic stroke by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2025, ume 19, 6849–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.Q.; Bai, L.-Y.; Cao, X.; Xu, Y. The novel compound CP-10 suppresses microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in ischemic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 2025, 277, 110528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.J.; Shah, F.A.; Koh, P.O. Quercetin attenuates neuronal cells damage in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 80, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Delgado, A.; Ortiz, G.G.; Delgado-Lara, D.L.; González-Usigli, H.A.; González-Ortiz, L.J.; Cid-Hernández, M.; Cruz-Serrano, J.A.; Pacheco-Moisés, F.P. Effect of Melatonin Administration on Mitochondrial Activity and Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5577541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungu, C.N.; Mangalagiu, I.I.; Romila, A.; Nechita, A.; Putz, M.V.; Mehedinti, M.C. Molecular Mediated Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medala, V.K.; Dewanjee, B.G.S.; Ogunnokun, G.; Kandimalla, R.; Vallamkondu, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy, and role of dynamin-related protein 1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Elamipretide (SS-31) improves mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic and memory impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanikant, G.K.; Zemke, D.; Senut, M.C.; Frenkel, M.B.; Chen, A.F.; Gupta, R.; Majid, A. Carnosine is neuroprotective against permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 2007, 38, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Fukui, Y.; Feng, T.; Bian, Z.; Yu, H.; Morihara, R.; Hu, R.; Bian, X.; Sun, Y.; Takemoto, H.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of carnosine in a mice stroke model concerning oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 447, 120608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y. The beneficial roles of apelin-13/APJ system in cerebral ischemia: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 903151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.S.; Ma, Y.P.; Han, B.; Duan, W.L.; Meng, S.C.; Bai, M.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Duan, M.Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Apelin-13-Loaded Macrophage Membrane-Encapsulated Nanoparticles for Targeted Ischemic Stroke Therapy via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 14, 9175–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, D.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, D.; et al. OL-FS13 alleviates experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 357, 114180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wan, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Sun, G.; Ji, Y.; Lu, J.; et al. The Neurovascular Protective Effect of S14G-Humanin in a Murine MCAO Model and Brain Endothelial Cells. IUBMB Life 2020, 70, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, L.R.; Li, Z.L.; Ma, K.G.; Chang, K.W.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, P.B.; Ji, S.F.; Ma, Y.B.; Han, H.; et al. Thymosin 4 reverses phenotypic polarization of glial cells and cognitive impairment via negative regulation of NF-B signaling axis in APP/PS1 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreanu-Pirjol, B.S.; Oprea, O.C.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Roncea, F.N.; Prelipcean, A.M.; Craciunescu, O.; Iosageanu, A.; Artem, V.; Ranca, A.; Motelica, L. Health Benefits of Antioxidant Bioactive Compounds in the Fruits and Leaves of Lonicera caerulea L. and Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliot. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, U.; Tanbek, K.; Gul, S.; Gul, M.; Koc, A.; Sandal, S. Melatonin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inducing Autophagy. Neuroendocrinology 2023, 113, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpooya, M.; Mazdeh, M.; Rahmani, E.; Khazaie, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, D. Melatonin supplementation may benefit patients with acute ischemic stroke not eligible for reperfusion therapies: Results of a pilot study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 106, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negreanu-Pirjol, B.S.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Busuricu, F.; Jurja, S.; Craciunescu, O.; Oprea, O.; Motelica, L.; Oprita, E.I.; Roncea, F.N. The Role of Antioxidant Plant Extracts’ Composition and Encapsulation in Dietary Supplements and Gemmo-Derivatives, as Safe Adjuvants in Metabolic and Age-Related Conditions: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurja, S.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Vasile, M.; Mehedinti Hincu, M.; Coviltir, V.; Negreanu-Pirjol, B.S. Xanthophyll pigments dietary supplements administration and retinal health in the context of increasing life expectancy trend. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1226686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Tian, M.; Ren, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol pretreatment protects neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation and ischemic injury through inhibiting ferroptosis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, N.D.; Armas, G.V.; Fernández, M.A.; Grijalvo, S.; Díaz, D.D. Neuroprotective Effects of Resveratrol in Ischemic Brain Injury. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalu, A.M.; Grigorescu, C.C.; Serban, D.; Tudor, C.; Alexandrescu, C.; Stana, D.; Jurja, S.; Costea, A.C.; Alius, C.; Tribus, L.C.; et al. Complement Inhibitors for Geographic Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration—A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.J.; Gu, A.P.; Cai, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, R.C. Curcumin protects neural cells against ischemic injury in N2a cells and mouse brain with ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. 2020, 8, e00921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Shao, C.; Wu, H.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; et al. Puerarin mitigates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (CIR)-induced ferroptosis by suppressing Ser15 phosphorylation-mediated p53 activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 237, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Fu, X.; Ma, Q.; He, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, D.; Yan, S. Gastrodin: Modulating the xCT/GPX4 and ACSL4/LPCAT3 pathways to inhibit ferroptosis after ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, T.; Shao, C.; Wan, H. Puerarin Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis Through SLC7A11/GPX4/ACSL4 Axis and Alleviate Pyroptosis Through Caspase-1/GSDMD Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 8931–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Chang, Q. Triptolide alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulating the Fractalkine/CX3CR1 signaling pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 211, 110939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Qing, W.; Yang, H.; et al. Inhibition of diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 provides neuroprotection by inhibiting ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, G. Knockdown of ATF3 alleviates ischemic stroke and inhibits ferroptosis via activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 11224–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, K.; Cao, J.; Guo, M.; Dong, H.; Ye, W.; Zeng, S.; Wei, J.; Xi, Q. Silencing Hmox1 Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Inhibits Inflammation and Ferroptosis Via the PPAR-/FABP4 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 11164–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Jo, H.; Sonn, S.K.; Jeong, S.J.; Seo, S.; Suh, J.; Jin, J.; Kweon, H.Y.; Kim, T.K.; et al. The Antioxidant Enzyme Peroxiredoxin-1 Controls Stroke-Associated Microglia Against Acute Ischemic Stroke. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Xue, H.; Gao, Q.; Kuai, S.; Zhao, P. Influence of Sevoflurane Postconditioning on Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury via Nrf2-Regulated Ferroptosis in Neonatal Rats. Anesth. Analg. 2025, 141, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Cai, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Baicalin Prevents Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting ACSL4 Mediated Ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Y.; Qie, S.; Gao, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Tian, G.; Liu, Z.; Xi, J. Baicalein ameliorates ischemic brain damage through suppressing proinflammatory microglia polarization via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and STAT1 pathway. Brain Res. 2021, 1770, 147626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, Y.R.; Hu, M.S.; Gong, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lv, P. Edaravone dexborneol protects cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in mice. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Zhao, Z.A.; Shen, X.Y.; Qiu, S.Q.; Cui, Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.H.; Wang, L.H.; et al. Edaravone dexborneol for ischemic stroke with sufficient recanalization after thrombectomy: A randomized phase II trial. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Yu, X.; Zhao, R.; Song, J.; Du, G. Edaravone dexborneol alleviates cerebral ischemic injury via MKP-1-mediated inhibition of MAPKs and activation of Nrf2. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4013707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyar, M.; Ghadirzadeh, E.; Nezhadnaderi, P.; Moayedi, Z.; Maboud, P.; Ebrahimi, A.; Siahposht-Khachaki, A.; Karimi, N. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin on hippocampal CA1 neurons following middle cerebral artery ischemia–reperfusion in male rats: A behavioral, biochemical, and histological study. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.J.; Kang, J.B.; Koh, P.O. Epigallocatechin gallate alleviates neuronal cell damage against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B.; Du, Y.; Shi, S. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury due to inhibition of NOX2-mediated calcium homeostasis dysregulation in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, P.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. Luteolin alleviates inflammation and autophagy of hippocampus induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion by activating PPARγ in rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xia, F.; Gao, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, X. Kaempferol Mediated AMPK/mTOR Signal Pathway Has a Protective Effect on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inducing Autophagy. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Peng, C.; Lv, M.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Wei, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Preparation and Pharmacokinetics of Brain-Targeted Nanoliposome Loaded with Rutin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasan, H.; Singh, D.; Joshi, B.; Upadhyay, D.; Sharma, U.; Dinda, A.K.; Reeta, K.H. Dihydromyricetin alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating apoptosis and astrogliosis in peri-infarct cortex. Neurol. Res. 2022, 44, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Xia, X.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Shen, Z.; Chen, P. Geraniin Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via Regulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2152746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, X.; Yu, J. Total Flavonoids of Chuju Decrease Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis in Ischemic Stroke Rats: Network and Experimental Analyses. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 772401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, W. Resveratrol Alleviates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Neuronal Damage by Inhibiting NR3C2-Mediated TRIM28 Expression. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2025, 24, e31375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelanotte, S.; Staessens, S.; François, O.; De Wilde, M.; Desender, L.; De Sloovere, A.S.; Dewaele, T.; Tersteeg, C.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Vanacker, P.; et al. Association between thrombus composition and first-pass recanalization after thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 22, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Vandelanotte, S.; François, O.; Boulleaux, E.; Bretzner, M.; Casolla, B.; Corseaux, D.; Puy, L.; Denorme, F.; De Wilde, M.; et al. Association Between Thrombus Composition and Etiology in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated by Thrombectomy. Stroke 2025, 56, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujijantarat, N.; Templeton, K.A.; Antonios, J.P.; Renedo, D.; Koo, A.B.; Haynes, J.O.; Matouk, C.C. Is Clot Composition Associated with Cause of Stroke? A Multicenter Study. Stroke Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, K.H.; Nam, H.S.; Heo, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D.J.; Baik, M.; Yoo, J.; et al. Thrombus composition and distribution patterns by thrombus volume in acute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1619683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorany, M.; Bielle, F.; Chiaroni, P.M.; Allard, J.; Premat, K.; Lenck, S.; Shotar, E.; Li, M.; Gerschenfeld, G.; Rosso, C.; et al. Thrombus histopathological composition in distal versus proximal vessel occlusions treated by mechanical thrombectomy. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2025. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapostolle, A.; Loyer, C.; Elhorany, M.; Chaigneau, T.; Bielle, F.; Alamowitch, S.; Clarençon, F.; Elbim, C. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Ischemic Stroke Thrombi Are Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome. Stroke Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2023, 3, e000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkipeddi, S.M.K.; Rahmani, R.; Schartz, D.; Chittaranjan, S.; Ellens, N.R.; Kohli, G.S.; Bhalla, T.; Mattingly, T.K.; Welle, K.; Morrell, C.N.; et al. Stroke emboli from patients with atrial fibrillation enriched with neutrophil extracellular traps. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 8, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabrah, D.; Rossi, R.; Molina, S.; Douglas, A.; Pandit, A.; McCarthy, R.; Gilvarry, M.; Ceder, E.; Fitzgerald, S.; Dunker, D.; et al. White blood cell subtypes and neutrophil extracellular traps content as biomarkers for stroke etiology in acute ischemic stroke clots retrieved by mechanical thrombectomy. Thromb. Res. 2024, 234, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denorme, F.; Portier, I.; Rustad, J.L.; Cody, M.J.; de Araujo, C.V.; Hoki, C.; Alexander, M.D.; Grandhi, R.; Dyer, M.R.; Neal, M.D.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate ischemic stroke brain injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Larco, J.A.; Mereuta, M.O.; Liu, Y.; Fitzgerald, S.; Dai, D.; Kadirvel, R.; Savastano, L.; Kallmes, D.F.; Brinjikji, W. Diverse thrombus composition in thrombectomy stroke patients with longer time to recanalization. Thromb. Res. 2022, 209, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, H.; He, J.; Lai, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, X. Melatonin alleviates ischemic stroke by inhibiting ferroptosis through the CYP1B1/ACSL4 pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, R.; Bahadir, S.; Basar, I.; Aslanoglu, B.; Atlas, B.; Kaya, S.; Güzel, B.C.; Turan, Y. Neuroprotective effects of the combined treatment of resveratrol and urapidil in experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2024, 39, e395329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Luteolin-7-O-β-d-glucuronide Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemic Injury: Involvement of RIP3/MLKL Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2024, 29, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; You, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, C.; Hai, D.; Cai, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Isoliquiritigenin alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction via activating the Nrf2 pathway. Redox Biol. 2024, 77, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Triptolide promotes nerve repair after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by regulating the NogoA/NgR/ROCK pathway. Folia Neuropathol. 2024, 62, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessari, F.A.; Sharifi, M.; Yousefifard, M.; Gholamzadeh, R.; Nazarinia, D.; Aboutaleb, N. Apelin-13 attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating inflammation and targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2022, 126, 102171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. The effects and mechanisms of AM1241 in alleviating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 215, 111025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, L. Quantitative histopathologic profiling of arterial dissection-related thrombi in acute ischemic stroke: Etiological comparisons. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1640562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, R.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z. Edaravone dexborneol protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier damage by inhibiting ferroptosis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 217, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, L.; Duan, X. Metabolomic analysis and pharmacological validation of the cerebral protective effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Si, M.; Jia, H.-Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.-W.; Li, X.-Y.; Dai, X.-R.; Gong, P.; Luo, S.-Y. Anfibatide alleviates inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 axis in ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 926, 175032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Eriocalyxin B alleviated ischemic cerebral injury by limiting microglia-mediated excessive neuroinflammation in mice. Exp. Anim. 2024, 73, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liang, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Song, B.; Xu, Y. Edaravone dexborneol provides neuroprotective benefits by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-induced microglial pyroptosis in experimental ischemic stroke. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113 Pt A, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, T.; Tang, H.; Lu, Z.-W.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Yang, X.-L.; Zhao, L.-L.; Dang, M.-J.; Li, Y.; et al. Edaravone Dexborneol provides neuroprotective effect by inhibiting neurotoxic activation of astrocytes through inhibiting NF-κB signaling in cortical ischemia. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 218, 111097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hua, Y.; Fan, Y. Minocycline promotes functional recovery in ischemic stroke by modulating microglia polarization through STAT1/STAT6 pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 186, 114464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Jiang, W.; Huang, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Cao, C.; et al. Edaravone dexborneol alleviates ischemic injury and neuroinflammation by modulating microglial and astrocyte polarization while inhibiting leukocyte infiltration. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 130, 111700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Gong, D. Edaravone dexborneol promotes M2 microglia polarization against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 6647–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Cao, Q.; Xia, S.; Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Bao, X.; Xu, Y. A newly-synthesized compound CP-07 alleviates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injury via inhibiting STAT3 phosphorylation. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2023, 11, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yun, H.J.; Ding, Y.; Du, H.; Geng, X. Montelukast sodium protects against focal cerebral ischemic injury by regulating inflammatory reaction via promoting microglia polarization. Brain Res. 2023, 1817, 148498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of edaravone dexborneol on functional outcome and inflammatory response in patients with acute ischemic stroke. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Q. Relationship between thrombus composition and prognosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2024, 126, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Meng, X.; Yalkun, G.; Xu, A.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Ji, Y.; Xu, J.; Geng, D.; et al. Edaravone Dexborneol Versus Edaravone Alone for the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Comparative Trial. Stroke 2021, 52, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Mo, R.; Yao, X.; Nguyen, T.N.; Song, Z.; Xie, W.; Yuan, G.; Zuo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lei, S.; et al. Clinical and Safety Outcomes of Edaravone Dexborneol in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology 2025, 105, e213949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Akiyama, H.; Horii, T.; Mihara, K. Association Between Edaravone Use and Activities of Daily Living in Older Patients with Atherothrombotic Stroke: An observational study using Japanese real-world data. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shu, Z.G.; Liu, S.C.; Li, D.Z. Effect of Edaravone Dexborneol Combined with Interventional Thrombectomy in Elderly Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2025, 76, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, L.; Xu, B.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, W. Edaravone Dexborneol Reduces Early Post-Stroke Depression and Inflammation: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1451060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komakula, S.; Bhatia, R.; Sahib, A.; Upadhyay, A.S.L.J.; Garg, A.; Pandit, A.K.; Vibha, D.; Singh, M.B.; Tripathi, M.; Srivastava, M.V.P. Safety and Efficacy of N-Acetylcysteine as an Adjunct to Standard Treatment in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled PilotTrial (NACTLYS). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivien, D. NAC-Safety Investigators. N-Acetylcysteine as an Adjunct to Intravenous Fibrinolysis in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single-Group Study (NAC-Safety). Neuroscience 2025, 584, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kang, H.G.; Ahn, S.H.; Song, T.-J.; Shin, D.-I.; Bae, H.-J.; Kim, C.H.; Heo, S.H.; Cha, J.-K.; Lee, Y.B.; et al. Nelonemdaz and Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Mechanical Reperfusion: The RODIN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2456535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.D.; Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; Nogueira, R.G.; McTaggart, R.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Poppe, A.Y.; Buck, B.H.; Field, T.S.; Dowlatshahi, D.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nerinetide for the Treatment of Acute Ischaemic Stroke (ESCAPE-NA1): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juega, J.; Requena, M.; Pinana, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Camacho, J.; Vidal, M.; Moline, T.; Serna, G.; Palacio-Garcia, C.; Rubiera, M. Intracranial thrombus composition is associated with occlusion location and endovascular treatment outcomes: Results from ITACAT multicenter study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Deng, J.; Lu, H.; Wei, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Mono antiplatelet therapy for cardioembolic and undetermined etiological stroke after receiving successful mechanical thrombectomy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 201, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Fang, J.; He, L. Lower serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio as a predictor of poor functional outcome after mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischaemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, W.; Lu, Q.; Lei, Z.; Liu, P.; Liu, T.; Peng, L.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, M.; et al. Association of serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio with 1-year stroke outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A multicenter observational cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.F.; Castonguay, A.C.; Zaidat, O.O.; Jadhav, A.P.; Sheth, S.A.; Haussen, D.C.; Nguyen, T.N.; Burgess, R.E.; Alhajala, H.S.; Gharaibeh, K.; et al. Safety of Adjunctive Intraarterial Tenecteplase Following Mechanical Thrombectomy: The ALLY Pilot Trial. Stroke 2025, 56, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calinescu, M.; Fiastru, M.; Bala, D.; Mihailciuc, C.; Negreanu-Pîrjol, T.; Jurca, B. Synthesis, characterization, electrochemical behavior and antioxidant activity of new copper(II) coordination compounds with curcumin derivatives. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pîrvu, A.S.; Andrei, A.M.; Stănciulescu, E.C.; Baniță, I.M.; Pisoschi, C.G.; Jurja, S.; Ciuluvica, R. NAD+ metabolism and retinal degeneration (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuparu, A.Z.; Jurja, S.; Stuparu, A.F.; Axelerad, A. Narrative Review Concerning the Clinical Spectrum of Ophthalmological Impairments in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 140–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Counts (n) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule/Peptide | Total | Animal | Clinical | Histological Outcomes Reported (Increase↑/Decrease↓) |
| Triptolide | 8 | 8 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ TUNEL+; ↑ NeuN |
| Melatonin | 12 | 10 | 2 | ↓ GFAP (astrogliosis); ↑ MAP2 integrity; ↓ infarct volume |
| Quercetin | 7 | 7 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; H&E preservation |
| Wedelolactone | 4 | 4 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ apoptotic neurons |
| Elamipretide (SS–31) | 3 | 3 | 0 | ↑ NeuN survival; ↓ oxidative stress markers |
| Resveratrol | 9 | 9 | 0 | ↓ GFAP; ↓ infarct volume; improved neuronal survival |
| Curcumin | 8 | 8 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ apoptosis; preserved neuronal morphology |
| Edaravone | 10 | 7 | 3 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ TUNEL+; improved neuronal survival |
| Carnosine | 3 | 3 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↑ neuronal Survival |
| Apelin–13 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↑ NeuN+ |
| Hydroxysafflor Yellow A | 2 | 2 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; improved Nissl Staining |
| Gastrodin | 2 | 2 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ oxidative stress |
| Carbon dots | 2 | 2 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; reduced Apoptosis |
| Alpinetin | 2 | 2 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ inflammation |
| Remote ischemic preconditioning | 4 | 4 | 0 | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ GFAP; preserved neuronal integrity |
| Other small molecules/mixed antioxidants | 41 | 39 | 2 | General ↓ infarct size; ↓ oxidative stress; ↓ apoptosis |
| Total | 120 | 113 | 7 | |
| Molecule/Peptide | Histological Outcomes Reported | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| ↑ NeuN+ neuronal | Mitochondrial | |
| Elamipretide (SS–31) | survival; ↓ oxidative stress markers | stabilization; attenuation of oxidative stress |
| Carnosine | ↓ infarct volume; ↑ neuronal survival; ↓ caspase–mediated apoptosis | ROS scavenging; caspase inhibition; anti–apoptotic activity |
| Apelin–13 | ↓ infarct size; ↑ NeuN+ immunoreactivity (neuronal preservation) | Neuroprotective signaling; promotion of neuronal survival |
| OL–FS13 | Preserved MAP2+ dendritic integrity; ↓ microglial activation | Anti–inflammatory activity; attenuation of neuroinflammation |
| Humanin | Preserved neuronal ultrastructure; ↓ TUNEL+ cells; ↓ lipid peroxidation; restored mitochondrial enzyme activity | Mitochondrial protection; restoration of respiratory enzyme function |
| Thymosin–β4 | ↓ GFAP+ astrocytic proliferation; reduced glial scar; ↑ NeuN+ neuronal density | Anti–gliosis; modulation of neuroinflammation |
| Peptidomimetics (PSD–95/nNOS inhibitors) | ↓ infarct volume; ↓ neuronal apoptosis; preserved cortical lamination | Inhibition of excitotoxicity via disruption of PSD–95/nNOS coupling; ↓ nitric oxide overproduction |
| Structure | Small Molecule/Intervention | Histological Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
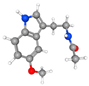 | Melatonin N-(2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)acetamide | Smaller infarct; preserved cortical layering; more intact neurons (Nissl); less cytoplasmic vacuolization and nuclear pyknosis (H&E). |
 | Resveratrol (E)-3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene | Fewer Fluoro–Jade B+ and TUNEL+ cells; better cortical thickness and laminar organization. |
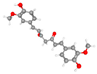 | Curcumin 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione | Less neuronal loss; preserved CA1/cortical layers (Nissl); reduced Iba1 and GFAP; improved mitochondrial and synaptic ultrastructure (EM). |
 | Puerarin daidzein-8-C-β-D-glucopyranoside | Lower chromatolysis; higher neuronal survival (H&E, Nissl); preserved synaptic density and mitochondrial integrity. |
 | Gastrodin 4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside | More intact hippocampal neurons (Nissl); reduced edema; preserved hippocampal lamination; attenuation of ferroptosis markers. |
 | Wedelolactone 1,8,9-trihydroxy-3-methoxybenzofuro [3,2-c]chromen-6-one | Smaller infarct; less cortical necrosis; decreased neuronal swelling/vacuolation (H&E); better neuronal morphology (Nissl). |
 | Triptolide | Smaller infarct; less neuronal necrosis in cortex/striatum; fewer Fluoro–Jade B+ cells. |
 | Sevoflurane postconditioning | Preserved CA1 neuronal density; improved cortical cytoarchitecture; reduced chromatolysis; attenuated glial reactivity. |
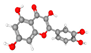 | Quercetin 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one | Reduced neuronal loss; preserved hippocampal neurons (Nissl); decreased microglial reactivity (Iba1) and astrogliosis (GFAP); improved mitochondrial ultrastructure (EM). |
| Domain/Intervention | Dose/Route | Tissue Readouts |
|---|---|---|
| Melatonin | 5–10 mg/kg i.p. | TUNEL↓; NeuN loss↓; lipid peroxidation↓; TEM: cristae preserved [67]. |
| Resveratrol ± urapidil | 30 mg/kg ± 5 mg/kg | H&E: pyknosis↓; IHC: caspase-3↓, Bcl-2↑, TNF-α↓; WM edema↓ [68]. |
| Luteolin | 25–50 mg/kg/day p.o. (7 d) | Iba1↓, GFAP↓; NeuN preserved; LC3B↓; TEM: mitochondrial vacuoles↓ [69]. |
| Luteolin-7-O-βD-glucuronide | 0.24–2.16 mg/kg | RIP3/MLKL↓; ∆Ψm improved; neuronal preservation [70]. |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 5–20 mg/kg | TUNEL↓; Nissl/H&E morphology restored; TEM: mitochondria healthier [71]. |
| Triptolide | 0.1–0.2 mg/kg | Infarct↓; PSD-95/GAP43↑; neuronal loss↓; M2 shift [72]. |
| Apelin-13 | 10–40 µg/kg i.v. | Infarct↓; IL-6 IHC↓; dose-dependent neuronal preservation [73]. |
| DGAT1 inhibition | 10 µL ICV of 50 µM A922500, 2 h pre-MCAO | Degenerating neurons↓; 4-HNE; infarct [74]. xCT/GPX4↑; |
| Gastrodin (ALKBH5 axis) | 15/30/60 mg/kg p.o., 7 d pre- and 7 d post-I/R | ACSL4/LPCAT3↓; apoptosis/edema↓; layers preserved [75]. |
| CB2 agonist AM1241 | 10 mg/kg i.p. | TUNEL↓; NeuN preserved; oxidative stress↓ [76]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurja, S.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Mehedinți, M.C.; Hincu, M.-A.; Lepadatu, A.C.; Negreanu-Pirjol, B.-S. Histological Insights into the Neuroprotective Effects of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules in Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules 2025, 30, 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234529
Jurja S, Negreanu-Pirjol T, Mehedinți MC, Hincu M-A, Lepadatu AC, Negreanu-Pirjol B-S. Histological Insights into the Neuroprotective Effects of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules in Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234529
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurja, Sanda, Ticuta Negreanu-Pirjol, Mihaela Cezarina Mehedinți, Maria-Andrada Hincu, Anca Cristina Lepadatu, and Bogdan-Stefan Negreanu-Pirjol. 2025. "Histological Insights into the Neuroprotective Effects of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules in Cerebral Ischemia" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234529
APA StyleJurja, S., Negreanu-Pirjol, T., Mehedinți, M. C., Hincu, M.-A., Lepadatu, A. C., & Negreanu-Pirjol, B.-S. (2025). Histological Insights into the Neuroprotective Effects of Antioxidant Peptides and Small Molecules in Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules, 30(23), 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234529







