Synthesis and Evaluation of Radiogallium-Labeled Peptide Probes for In Vivo Imaging of Legumain Activity
Abstract
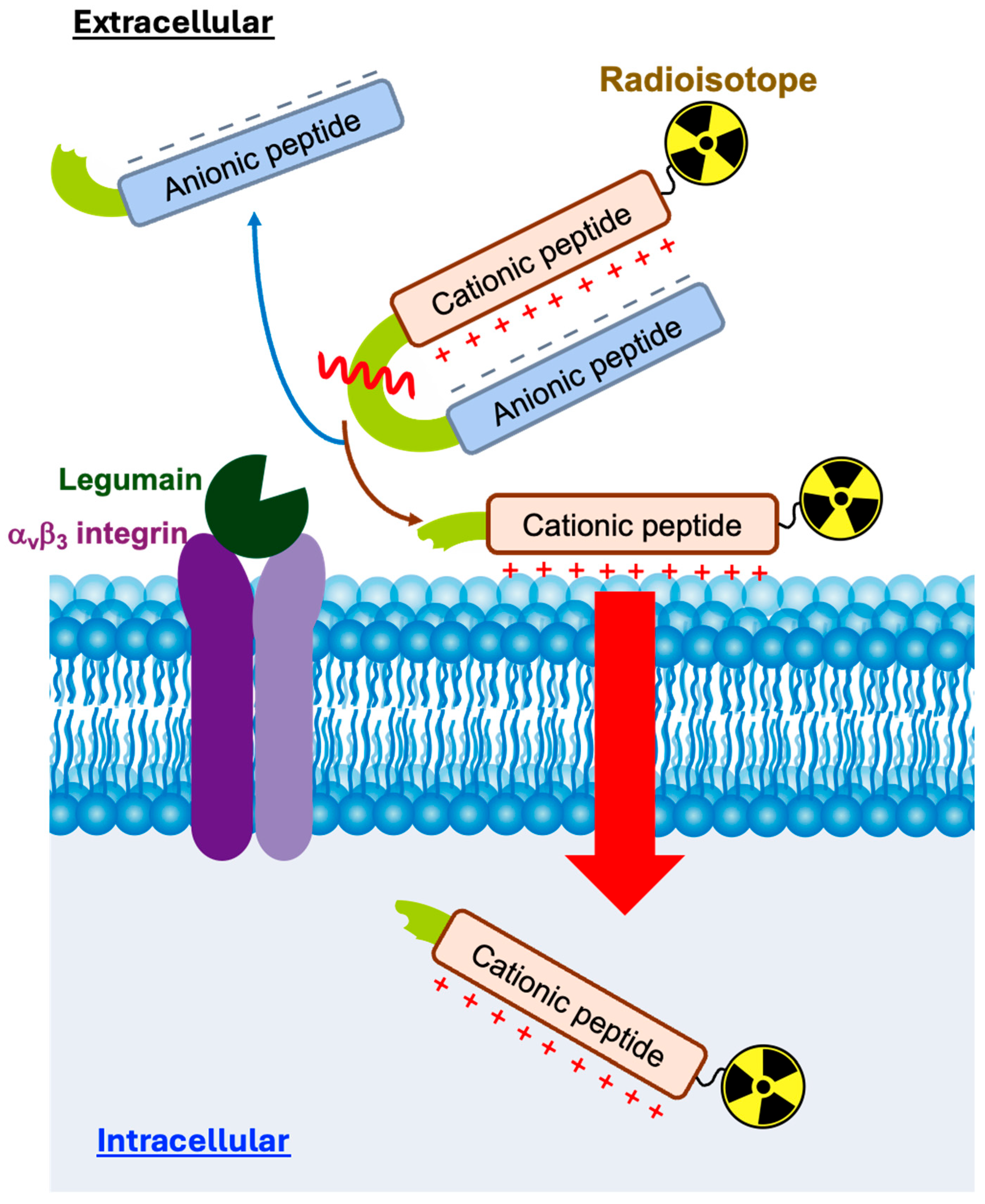
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
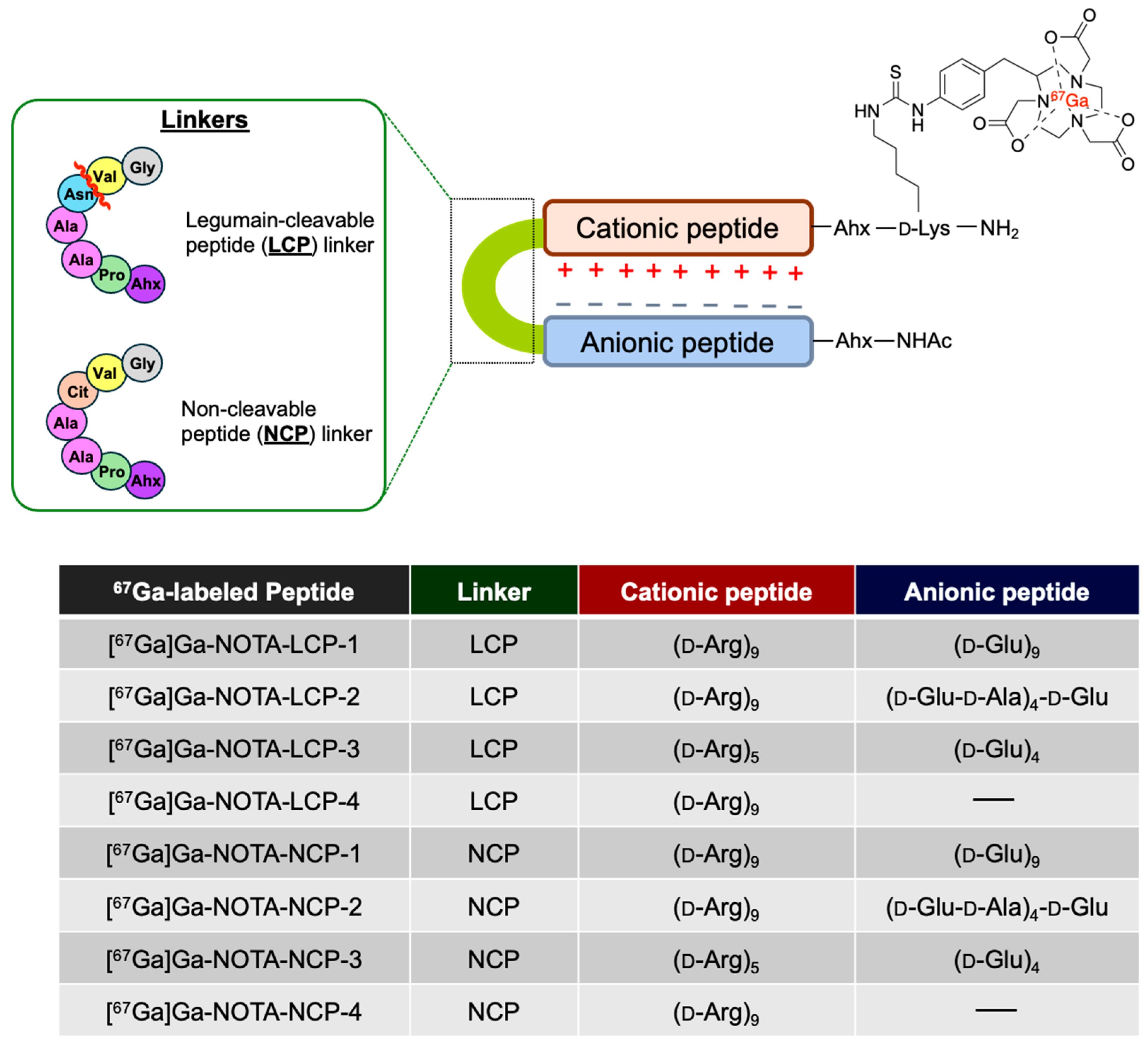
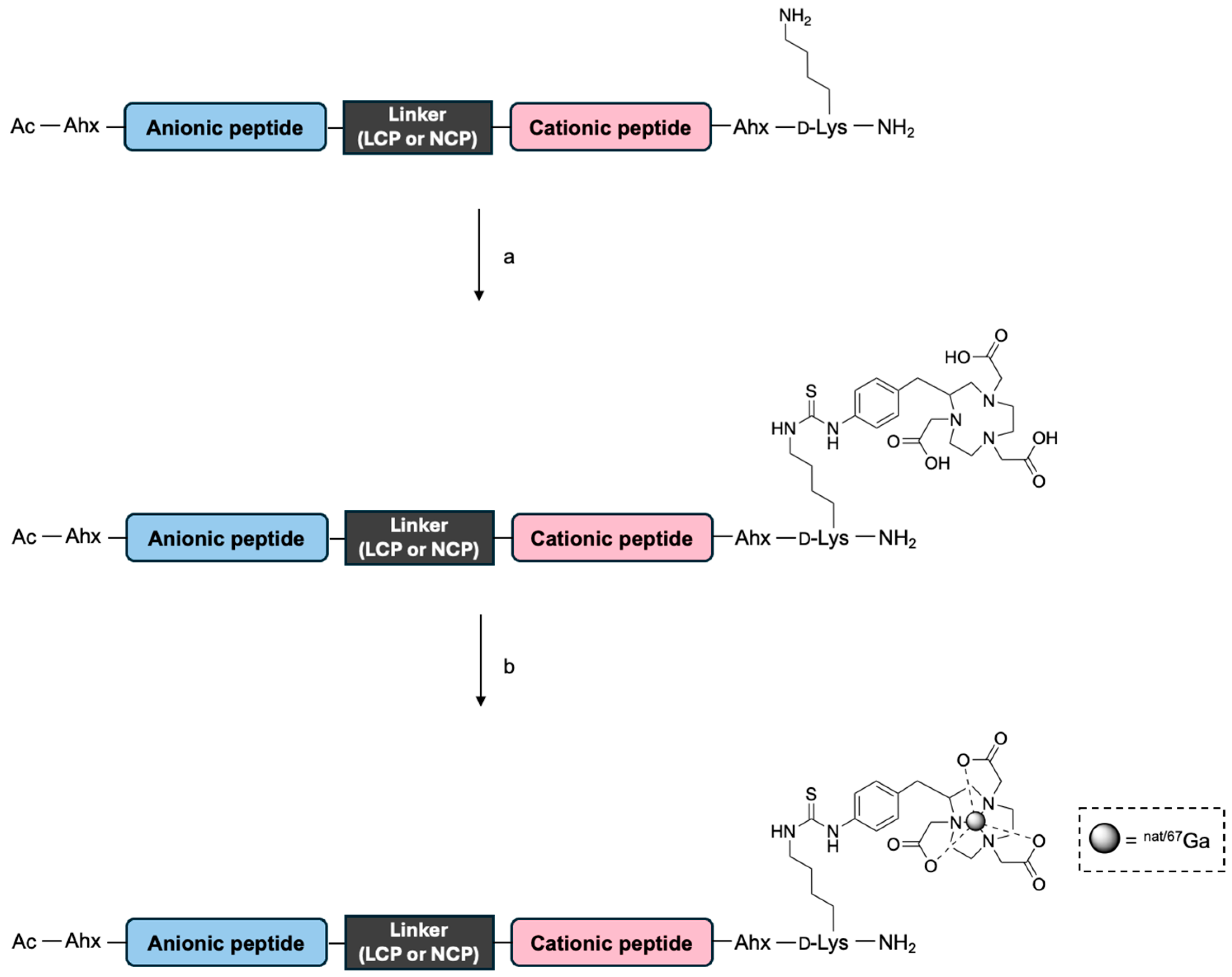
2.1. Preparation of NOTA- and Ga-NOTA-Peptides
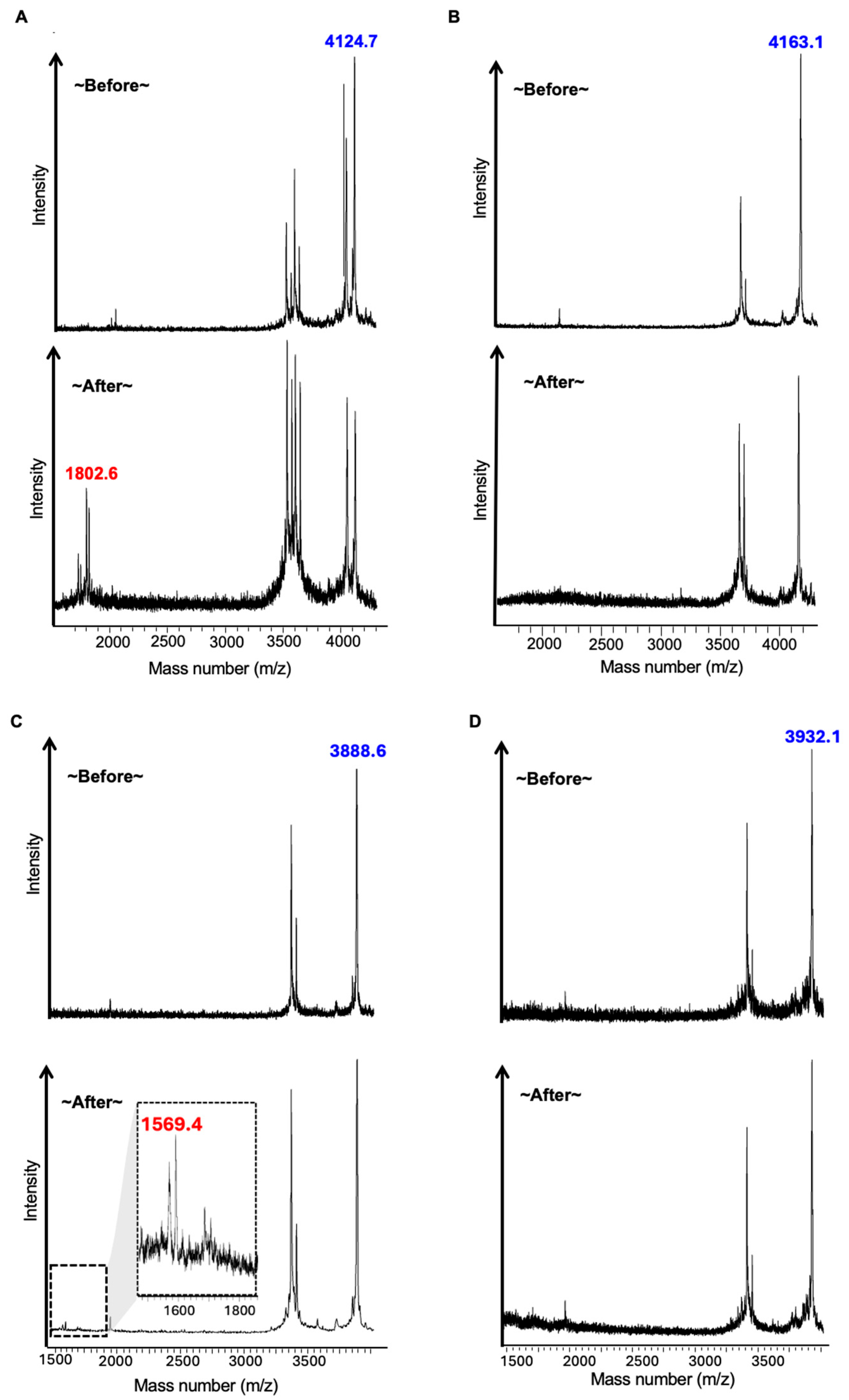
2.2. LGMN Cleavage Test of NOTA-Peptides
2.3. Radiosynthesis of [67Ga]Ga-NOTA-Peptides
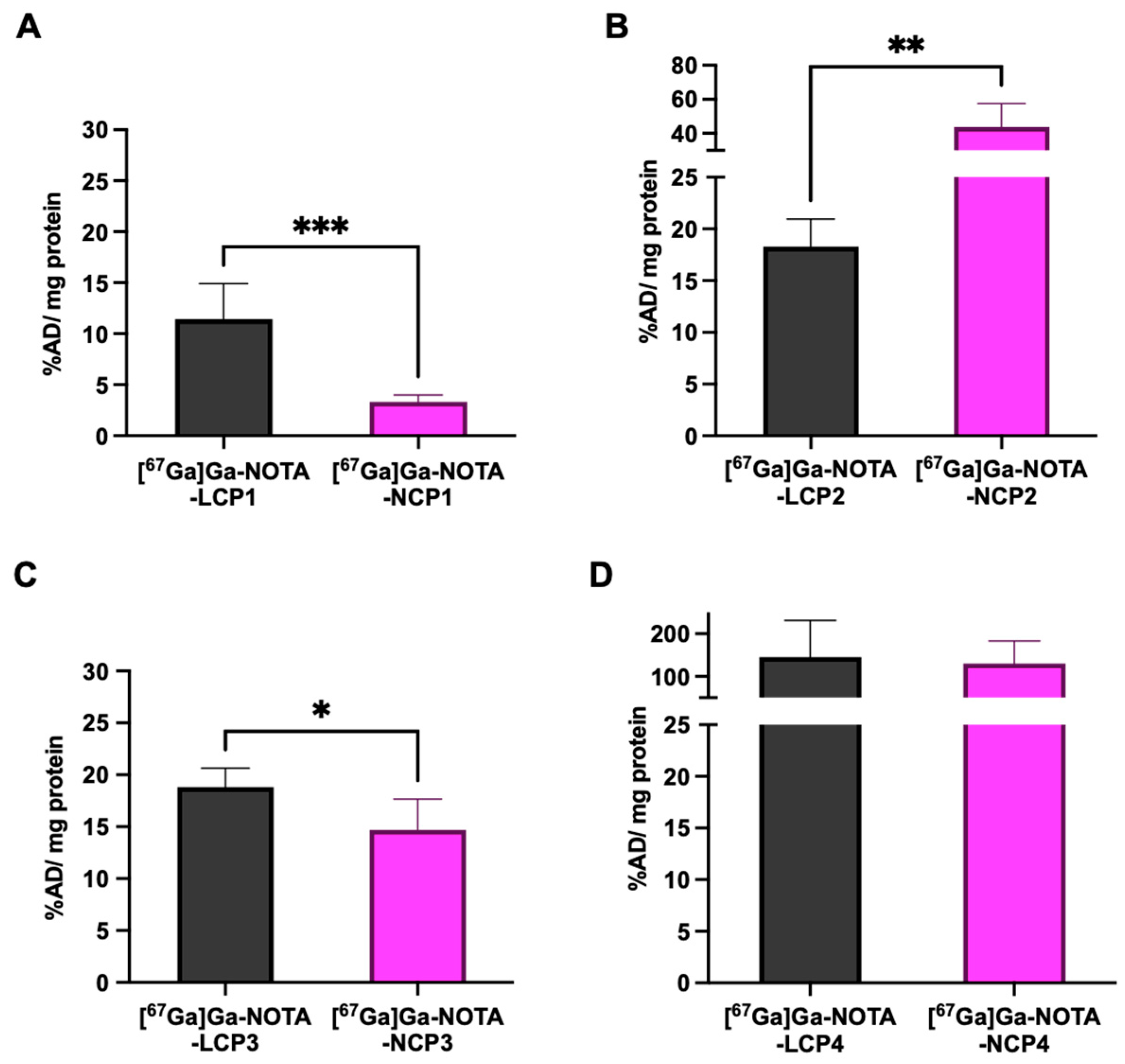
2.4. In Vitro Cellular Uptake of [67Ga]Ga-NOTA-Peptides
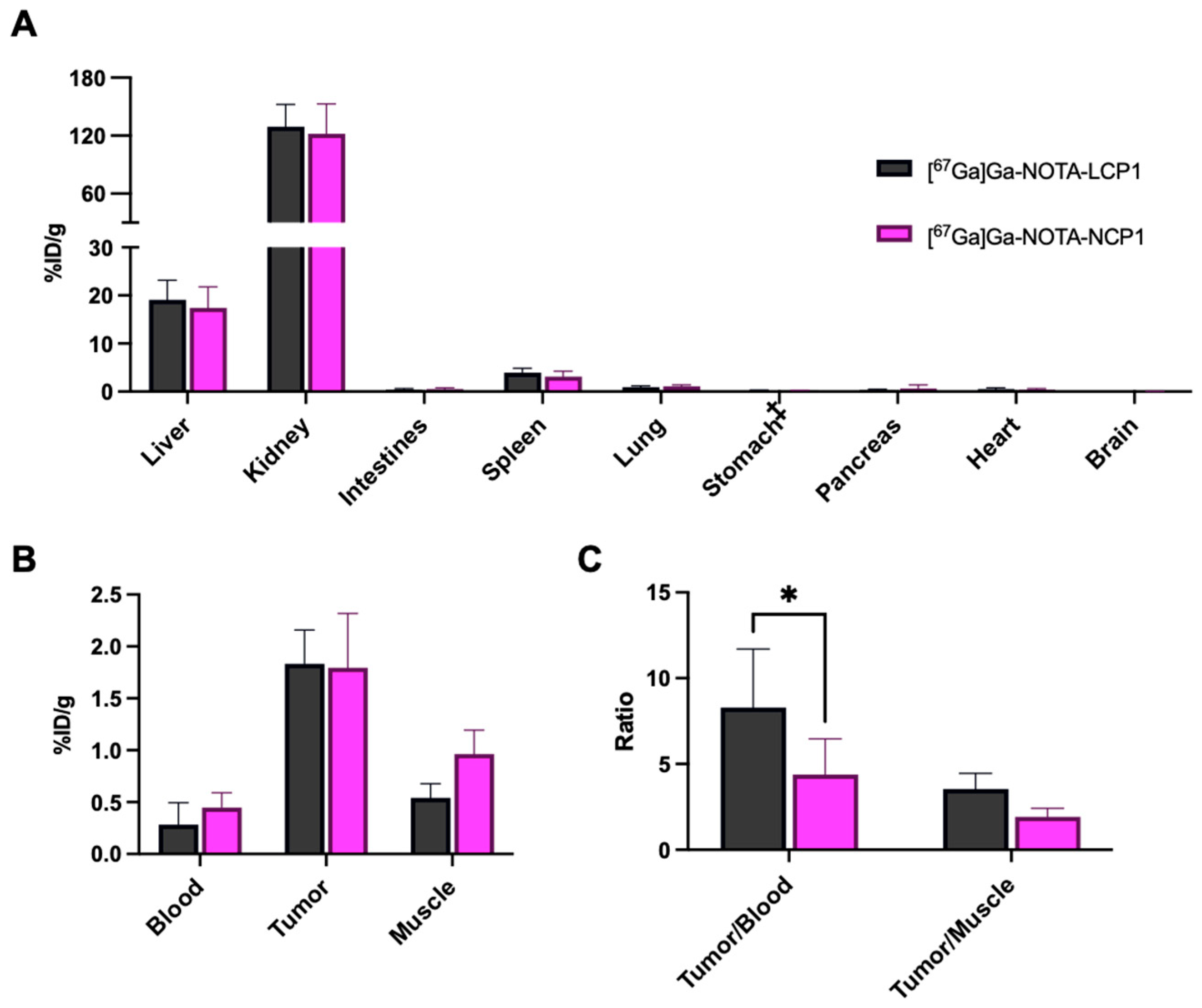
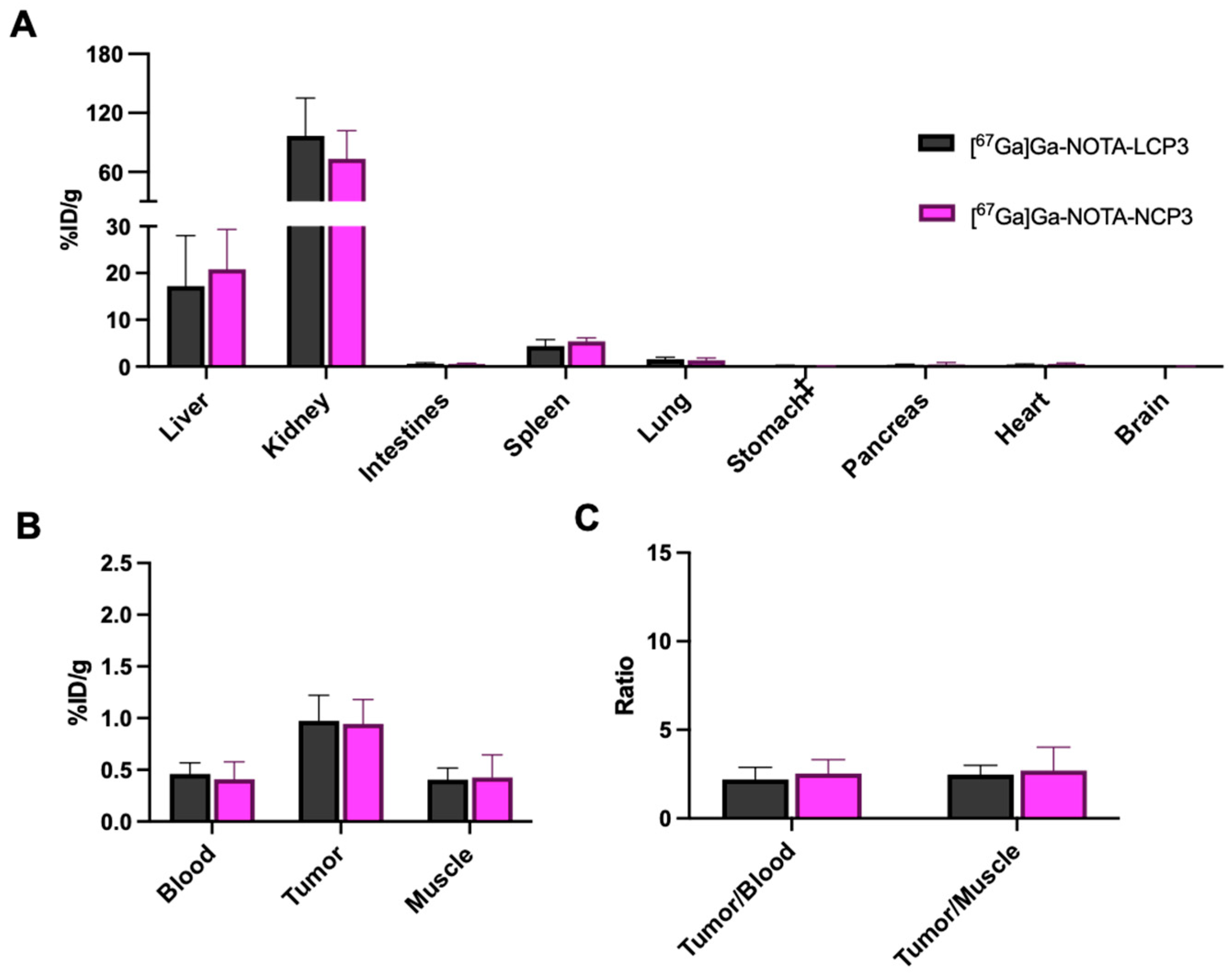
2.5. In Vivo Biodistribution of [67Ga]Ga-NOTA-Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis
3.3. Synthesis of NOTA-Peptides
3.4. Synthesis of Ga-NOTA-Peptides
3.5. Synthesis of [67Ga]Ga-NOTA Peptides
3.6. LGMN Cleavage Assay
3.7. Cellular Uptake Study
3.8. Tumor Xenograft Model
3.9. Biodistribution of [67Ga]Ga-NOTA-Peptides in Tumor-Bearing Mice
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ahx-OH | Aminohexanoic acid |
| CPP | cell-penetrating peptide |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| EDT | 1,2-Ethanedithiol |
| Fmoc | Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl |
| HBTU | 2-(1H-benzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate |
| HOBt | Hydroxybenzotriazole |
| RT-HPLC | Reverse-phase-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| LCP | LGMN-cleavable peptide |
| LGMN | Legumain |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight |
| MES | 2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| NCP | Non-cleavable peptide |
| NOTA | 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| SPECT | Single-photon emission computed tomography |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TIS | Triisopropylsilane |
References
- Dall, E.; Brandstetter, H. Structure and function of legumain in health and disease. Biochimie 2016, 122, 126–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, R.; Lunde, N.N.; Forbord, K.M.; Okla, M.; Kassem, M.; Jafari, A. The Mammalian Cysteine Protease Legumain in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewēn, S.; Zhou, H.; Hu, H.D.; Cheng, T.; Markowitz, D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Xiang, R.; Luo, Y. A Legumain-based minigene vaccine targets the tumor stroma and suppresses breast cancer growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, M.H.; Johansen, H.T.; Pettersen, S.J.; Solberg, R.; Brix, K.; Flatmark, K.; Maelandsmo, G.M. Nuclear legumain activity in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Su, Q.; Wei, C.; Lan, B.; Wang, J.; Bao, G.; Yan, F.; Yu, Y.; Peng, B.; et al. Effects of legumain as a potential prognostic factor on gastric cancers. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Nakashima, J.; Izumi, M.; Ohori, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Tachibana, M. Association of legumain expression pattern with prostate cancer invasiveness and aggressiveness. World J. Urol. 2013, 31, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X. Legumain Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression Through Tumor-associated Macrophages In vitro and In vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Legumain: A biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of human ovarian cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 2679–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, E.; Inoue, M.; Hanahan, D. An amino-bisphosphonate targets MMP-9-expressing macrophages and angiogenesis to impair cervical carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Shao, Y.; Yang, M.; Jia, M.; Peng, Y. Asparaginyl endopeptidase promotes proliferation and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Gene 2016, 594, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, E.; Brandstetter, H. Mechanistic and structural studies on legumain explain its zymogenicity, distinct activation pathways, and regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10940–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Kang, L.; Wang, D.; Xun, J.; Chen, C.a.; Du, L.; Zhang, M.; Gong, J.; Mi, X.; Yue, S.; et al. Legumain-deficient macrophages promote senescence of tumor cells by sustaining JAK1/STAT1 activation. Cancer Lett. 2020, 472, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.C.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Dai, J.; Wen, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, G. Legumain promotes fibrogenesis in chronic pancreatitis via activation of transforming growth factor β1. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, R.V.; Arbman, G.; Gao, J.; Roodman, G.D.; Sun, X.F. Legumain expression in relation to clinicopathologic and biological variables in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Jiang, J.N.; Liu, X.S.; Ji, F.J.; Fang, X.D. MiRNA-3978 regulates peritoneal gastric cancer metastasis by targeting legumain. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83223–83230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, M. New insights into long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, C.; Huang, H.; Janda, K.; Edgington, T. Overexpression of legumain in tumors is significant for invasion/metastasis and a candidate enzymatic target for prodrug therapy. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchigami, T.; Itagaki, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Yoshida, S.; Nakayama, M. Synthesis and evaluation of radioactive/fluorescent peptide probes for imaging of legumain activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, D.; Ge, C.; Wang, J.; Nan, K.; Lin, S. Fabrication of chitosan based nanocomposite with legumain sensitive properties using charge driven self-assembly strategy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ma, W.; Duan, S.; Huang, J.; Jia, R.; Cheng, H.; Chen, B.; He, X.; Wang, K. An endogenous stimulus detonated nanocluster-bomb for contrast-enhanced cancer imaging and combination therapy. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 12118–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiong, M.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, N.; Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Legumain protease-activated TAT-liposome cargo for targeting tumours and their microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Guo, X.; Du, H.; Han, M.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiang, R.; Yue, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Combined legumain- and integrin-targeted nanobubbles for molecular ultrasound imaging of breast cancer. Nanomedicine 2022, 42, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Hu, C.; Tang, X.; Cun, X.; Xiao, W.; Shi, K.; He, Q.; Gao, H. Increased Gold Nanoparticle Retention in Brain Tumors by in Situ Enzyme-Induced Aggregation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10086–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgington, L.E.; Verdoes, M.; Ortega, A.; Withana, N.P.; Lee, J.; Syed, S.; Bachmann, M.H.; Blum, G.; Bogyo, M. Functional imaging of legumain in cancer using a new quenched activity-based probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hai, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, L.; Liang, G. Legumain-Specific Near-Infrared Fluorescence “Turn On” for Tumor-Targeted Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8732–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Ge, S.; Sun, H.; Dong, X.; Zhao, H.; An, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, B.; Liang, G. Intracellular Self-Assembly and Disassembly of (19)F Nanoparticles Confer Respective “Off” and “On” 19F NMR/MRI Signals for Legumain Activity Detection in Zebrafish. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5117–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Aalipour, A.; Vermesh, O.; Yu, J.H.; Gambhir, S.S. Towards clinically translatable in vivo nanodiagnostics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, J.K.; van Bruggen, N.; Dinkelborg, L.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Molecular imaging in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Qiu, L. Development of a Promising (18)F-Radiotracer for PET Imaging Legumain Activity In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Li, X.; Lv, G.; Seimbille, Y.; Li, K.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xie, M.; Lin, J. Radiofluorinated Smart Probes for Noninvasive PET Imaging of Legumain Activity in Living Subjects. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11627–11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustenberger, S.K.; Castro Jaramillo, C.A.; Bärtschi, L.A.; Williams, R.; Schibli, R.; Mu, L.; Krämer, S.D. Towards imaging the immune state of cancer by PET: Targeting legumain with 11C-labeled P1-Asn peptidomimetics carrying a cyano-warhead. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2024, 138–139, 108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duijnhoven, S.M.; Robillard, M.S.; Nicolay, K.; Grüll, H. Tumor targeting of MMP-2/9 activatable cell-penetrating imaging probes is caused by tumor-independent activation. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, T.; Munekane, M.; Ogawa, K. Pharmacokinetics of therapeutic and diagnostic agents conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides. In Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Design, Development and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2022; pp. 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Olson, E.S.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Roy, M.; Jennings, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. Tumor imaging by means of proteolytic activation of cell-penetrating peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17867–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembhavi, A.A.; Buttle, D.J.; Knight, C.G.; Barrett, A.J. The two cysteine endopeptidases of legume seeds: Purification and characterization by use of specific fluorometric assays. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 303, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, P.M.; Fortunato, M.; Smith, L.; Knight, C.G.; McKendrick, J.E.; Barrett, A.J. Pig kidney legumain: An asparaginyl endopeptidase with restricted specificity. Biochem. J. 1999, 339 Pt 3, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarko, D.; Beijer, B.; Garcia Boy, R.; Nothelfer, E.M.; Leotta, K.; Eisenhut, M.; Altmann, A.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W. The pharmacokinetics of cell-penetrating peptides. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.M.; Dando, P.M.; Stevens, R.A.; Fortunato, M.; Barrett, A.J. Cloning and expression of mouse legumain, a lysosomal endopeptidase. Biochem. J. 1998, 335 Pt 1, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, J.; Kothapalli, S.R.; Bohndiek, S.; Yoon, J.K.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Nielsen, C.; Tisma, A.; Bodapati, S.; Gowrishankar, G.; Yan, X.; et al. Molecular photoacoustic imaging of follicular thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, J.; Kothapalli, S.R.; Ma, T.J.; Hartman, K.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T.; Gambhir, S.S. Design, synthesis, and imaging of an activatable photoacoustic probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11264–11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echigo, H.; Mishiro, K.; Munekane, M.; Fuchigami, T.; Washiyama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kinuya, S.; Ogawa, K. Development of probes for radiotheranostics with albumin binding moiety to increase the therapeutic effects of astatine-211 (211At). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, T.; Chiga, T.; Yoshida, S.; Oba, M.; Fukushima, Y.; Inoue, H.; Matsuura, A.; Toriba, A.; Nakayama, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Radiogallium-Labeled Cationic Amphiphilic Peptides as Tumor Imaging Agents. Cancers 2021, 13, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuchigami, T.; Itagaki, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nakayama, M.; Munekane, M.; Ogawa, K. Synthesis and Evaluation of Radiogallium-Labeled Peptide Probes for In Vivo Imaging of Legumain Activity. Molecules 2025, 30, 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234527
Fuchigami T, Itagaki K, Yoshida S, Nakayama M, Munekane M, Ogawa K. Synthesis and Evaluation of Radiogallium-Labeled Peptide Probes for In Vivo Imaging of Legumain Activity. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234527
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuchigami, Takeshi, Kohnosuke Itagaki, Sakura Yoshida, Morio Nakayama, Masayuki Munekane, and Kazuma Ogawa. 2025. "Synthesis and Evaluation of Radiogallium-Labeled Peptide Probes for In Vivo Imaging of Legumain Activity" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234527
APA StyleFuchigami, T., Itagaki, K., Yoshida, S., Nakayama, M., Munekane, M., & Ogawa, K. (2025). Synthesis and Evaluation of Radiogallium-Labeled Peptide Probes for In Vivo Imaging of Legumain Activity. Molecules, 30(23), 4527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234527





