Evaluation of the Elemental Composition of Dietary Supplements Containing Iron Available on the Polish Market Using ICP-OES, FAAS and CVAAS Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. ICP-OES, AAS and CVAAS Results
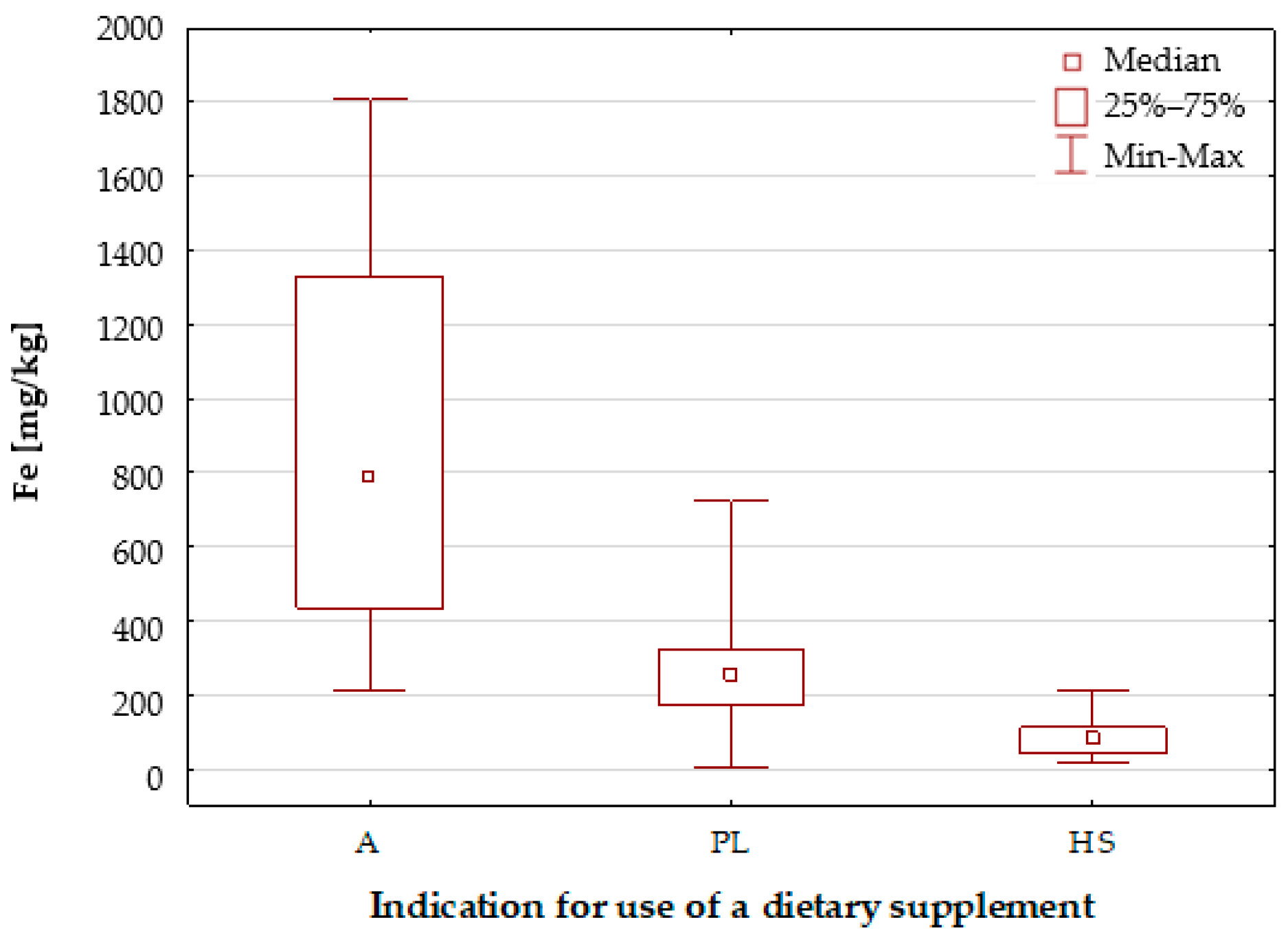
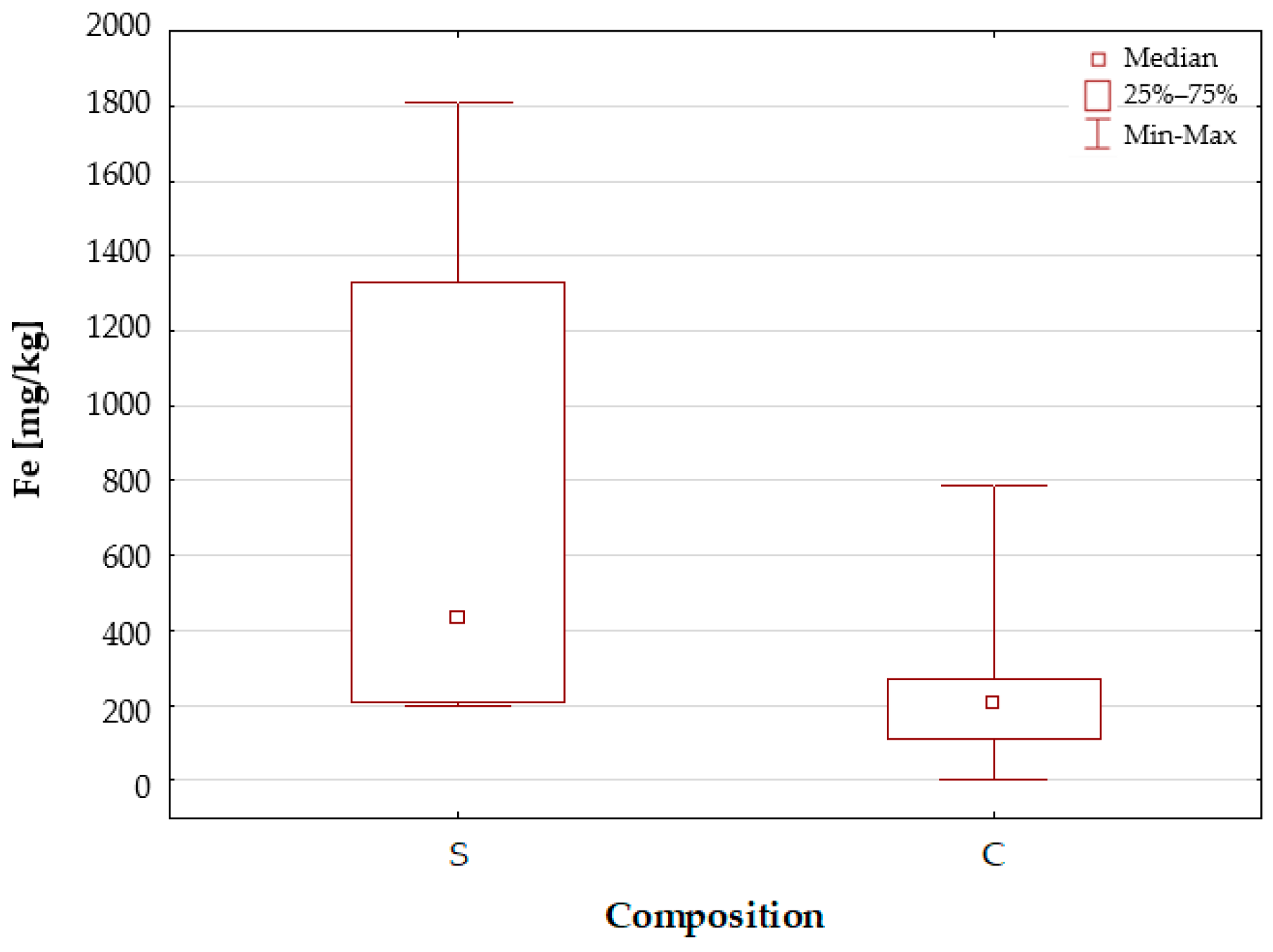
2.1.1. Characteristics of the Elemental Composition of the Studied Dietary Supplements
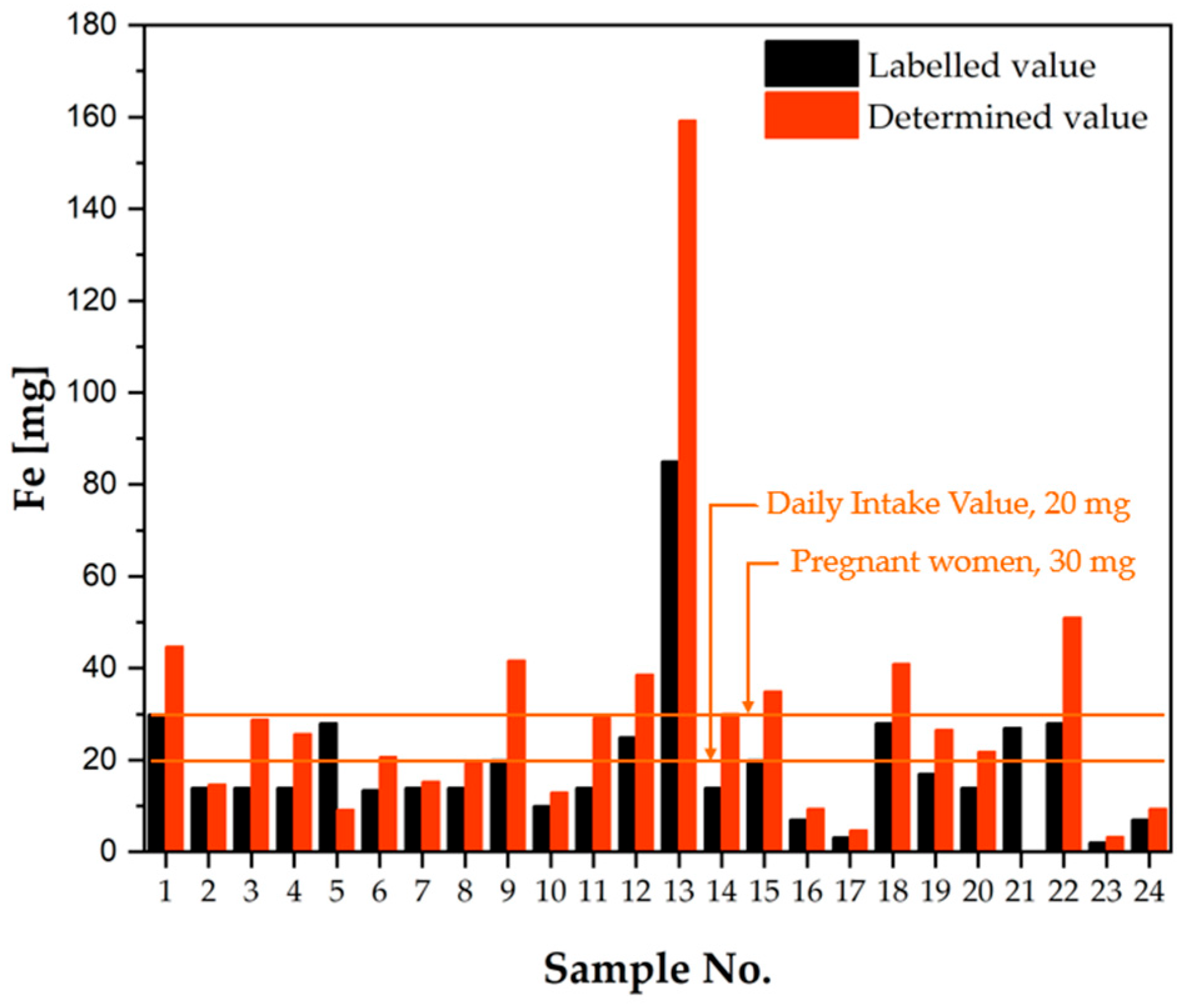
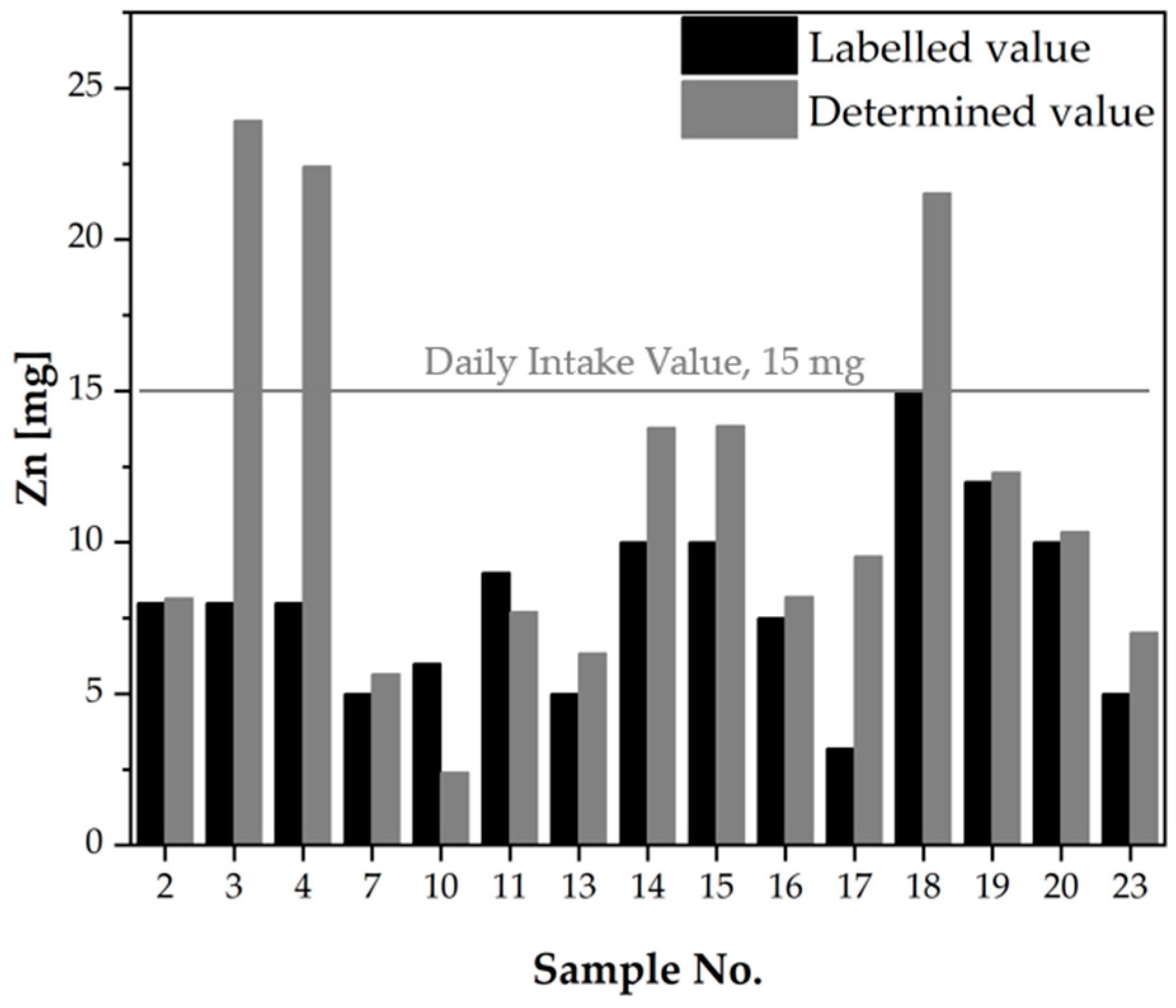
2.1.2. Verification of the Composition of Dietary Supplements According to the Information Provided on the Product Labels
Iron
| Daily Intake Value [mg], [21] | Safe Level of Intake [mg], [23,24] | Composition | Intended Use | Sample No. | Labelled Value [mg] | Determined Value [mg] | Percentage of Determined Value Versus Labelled Value [%] | Iron as an Excipient | Safe Dose [21] |
| *20 **30 | 40 | S | A | 1 | 30.00 | 44.73 | 149.1 | No | No |
| C | PL | 2 | 14.00 | 14.69 | 104.9 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | PL | 3 | 14.00 | 28.83 | 205.9 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | PL | 4 | 14.00 | 25.68 | 183.4 | Yes | Yes | ||
| S | A | 5 | 28.00 | 9.207 | 32.88 | Yes | No | ||
| S | PL | 6 | 13.50 | 20.68 | 153.2 | No | No | ||
| C | PL | 7 | 14.00 | 15.32 | 109.4 | No | Yes | ||
| S | PL | 8 | 14.00 | 19.32 | 138.0 | No | Yes | ||
| S | A | 9 | 20.00 | 41.71 | 208.5 | No | No | ||
| C | PL | 10 | 10.00 | 13.00 | 130.0 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | PL | 11 | 14.00 | 29.24 | 208.9 | No | Yes | ||
| S | A | 12 (U.S.) | 25.00 | 38.61 | 154.4 | No | No | ||
| C | A | 13 (U.S.) | 85.00 | 159.2 | 187.3 | Yes | No | ||
| C | HS | 14 | 14.00 | 30.07 | 214.8 | No | No | ||
| C | PL | 15 | 20.00 | 34.91 | 174.5 | Yes | No | ||
| C | HS | 16 | 7.000 | 9.363 | 133.8 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | HS | 17 | 3.220 | 4.699 | 145.9 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | PL | 18 | 28.00 | 40.95 | 146.2 | No | No | ||
| C | PL | 19 | 17.00 | 26.57 | 156.3 | No | No | ||
| C | PL | 20 | 14.00 | 21.84 | 156.0 | No | Yes | ||
| C | PL | 21 | 27.00 | 0.062 | 0.230 | No | No | ||
| S | PL | 22 | 28.00 | 51.07 | 182.4 | Yes | No | ||
| C | HS | 23 | 2.100 | 3.313 | 157.8 | Yes | Yes | ||
| C | HS | 24 | 7.000 | 9.377 | 134.0 | No | Yes |
Other Minerals
| No. | Ca Daily Intake Value, 1500 mg [21] The Upper Tolerable Intake Level (UL), 2500 mg [24,29] | Cr Daily Intake Value, 0.200 mg [21] | Cu Daily Intake Value, 2 mg [21] The Upper Tolerable Intake Level (UL), 5 mg [24,30] | ||||||||||
| LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | Ca as Other Ingredients | LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | |
| 11 | 150.0 | 223.3 | 148.8 | Yes | Yes | ||||||||
| 13 | 25.00 | 57.72 | 230.9 | Yes | Yes | 2.000 | 2.160 | 108.0 | No | ||||
| 14 | 160.0 | 432.8 | 270.5 | Yes | Yes | 0.025 | 0.027 | 107.3 | Yes | ||||
| 15 | 240.0 | 432.8 | 180.3 | Yes | Yes | 1.000 | 0.963 | 96.26 | Yes | ||||
| 16 | 0.500 | 0.630 | 126.0 | Yes | |||||||||
| 17 | 0.026 | 0.040 | 155.0 | Yes | 0.230 | 0.322 | 140.1 | Yes | |||||
| 18 | 200.0 | 786.5 | 353.3 | Yes | Yes | 1.000 | 1.002 | 100.2 | Yes | ||||
| 19 | 1.000 | 1.239 | 123.9 | Yes | |||||||||
| 20 | 0.500 | 0.672 | 134.4 | Yes | |||||||||
| 23 | 0.040 | 0.048 | 120.5 | Yes | |||||||||
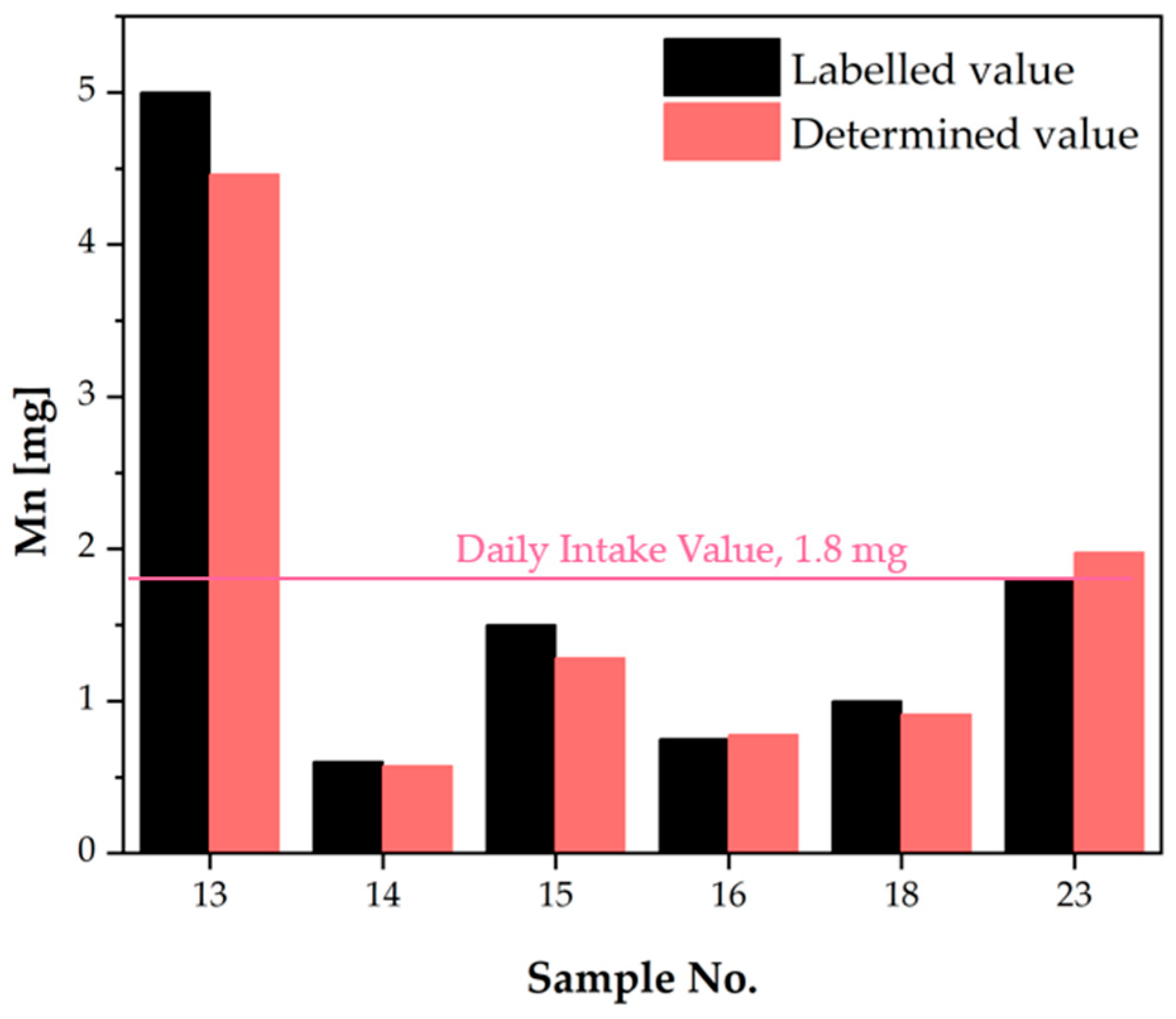
| No. | Mg Daily Intake Value, 400 mg [21] The Upper Tolerable Intake Level (UL), 250 mg [24,31] | Mn Daily Intake Value, 1.8 mg [21] Safe Level of Intake, 8 mg [24,32] | Mo Daily Intake Value, 0.350 mg [21] The Upper Tolerable Intake Level (UL), 0.6 mg [24,31] | Zn Daily Intake Value, 15 mg [21] The Upper Tolerable Intake Level (UL), 25 mg [24,31] | |||||||||||||
| LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | Mg as Other Ingredients | LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | LV [mg] | DV [mg] | DV vs. LV [%] | Safe Dose [21] | |
| 2 | 75.00 | 236.4 | 315.2 | Yes | Yes | 8.000 | 8.150 | 101.9 | Yes | ||||||||
| 3 | 75.00 | 210.8 | 281.0 | Yes | Yes | 8.000 | 23.93 | 299.1 | No | ||||||||
| 4 | 75.00 | 233.7 | 311.7 | Yes | Yes | 8.000 | 22.42 | 280.2 | No | ||||||||
| 7 | 5.000 | 5.649 | 113.0 | Yes | |||||||||||||
| 10 | 6.000 | 2.399 | 29.98 | Yes | |||||||||||||
| 11 | 9.000 | 7.701 | 85.60 | Yes | |||||||||||||
| 13 | 5.000 | 4.463 | 89.26 | No | 5.000 | 6.330 | 126.6 | Yes | |||||||||
| 14 | 112.5 | 287.7 | 255.7 | Yes | Yes | 0.600 | 0.574 | 95.67 | Yes | 0.025 | 0.021 | 83.06 | Yes | 10.00 | 13.78 | 137.8 | Yes |
| 15 | 1.500 | 1.281 | 85.37 | Yes | 0.050 | 0.060 | 120.7 | Yes | 10.00 | 13.85 | 138.5 | Yes | |||||
| 16 | 0.750 | 0.780 | 104.0 | Yes | 0.037 | 0.039 | 106.7 | Yes | 7.500 | 8.205 | 109.4 | Yes | |||||
| 17 | 0.033 | 0.042 | 128.6 | Yes | 3.200 | 9.540 | 298.1 | Yes | |||||||||
| 18 | 58.20 | 144.1 | 247.6 | Yes | Yes | 1.000 | 0.911 | 91.09 | Yes | 15.00 | 21.53 | 143.6 | No | ||||
| 19 | 12.00 | 12.31 | 102.6 | Yes | |||||||||||||
| 20 | 10.00 | 10.35 | 103.5 | Yes | |||||||||||||
| 23 | 57.00 | 205.6 | 360.8 | Yes | Yes | 1.800 | 1.975 | 109.7 | No | 0.050 | 0.058 | 115.7 | Yes | 5.000 | 7.017 | 140.3 | Yes |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Instrumentation
3.3.1. ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectrometry)
3.3.2. F AAS (Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry)
3.3.3. CV AAS
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. 2024. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/COMPS-973/pdf/COMPS-973.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 June 2002 on the Approximation of the Laws of the Member States Relating to Food Supplements. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2002/46/oj/eng (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/1821 of 25 June 2024 Amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Annex II to Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Iron Milk Caseinate Added to Foods and Used in the Manufacture of Food Supplements. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2024/1821/oj/eng (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/248 of 16 January 2024 amending Annex II to Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Iron Hydroxide Adipate Tartrate Used in the Manufacture of Food Supplements. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2024/248/oj/eng (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- WHO Global Report on Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/978924151536 (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Ustawa z Dnia 25 Sierpnia 2006 r. o Bezpieczeństwie Żywności i Żywienia. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20061711225 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Zdrowia z Dnia 9 Października 2007 r. w Sprawie Składu Oraz Oznakowania Suplementów Diety. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20071961425 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Charlebois, E.; Pantopoulos, K. Nutritional Aspects of Iron in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robak, T.; Warzocha, K. Hematologia; Grupa Via Medica: Gdańsk, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Katsarou, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Basics and principles of cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez, A.; Alborzinia, H. Ferroptosis: Mechanism and Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 6, 1301. [Google Scholar]
- Dutt, S.; Hamza, I.; Bartnikas, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Iron and Heme Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domellöf, M.; Sjöberg, A. Iron—A background article for the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 68, 10451. [Google Scholar]
- Geisser, P.; Burckhardt, S. The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Iron Preparations. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczeklik, A.; Gajewski, P. Interna Szczeklika; MP: Warszawa, Poland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, M.; Sieroszewski, P.; Oszukowski, P.; Huras, H.; Fuchs, T.; Pawłosek, A. Rekomendacje Polskiego Towarzystwa Ginekologów i Położników dotyczące suplementacji u kobiet ciężarnych. Ginekol. Perinatol. Prakt. 2020, 5, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Zimnoch, K.M.; Socha, K. Food Supplements Containing Iron—Comparison of Actual Content with Declared Content and Health Consequences. Molecules 2024, 29, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowiecka, J.; Olczyk, P.; Ivanova, D.; Kiselova-Kaneva, Y.; Komosińska-Vassev, K. Analysis of iron content in food supplements in relation to the safety of their use. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2020, 77, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, L. Simple Experiment Assisting Students with Identification of Spectral Interference and Selection Emission Lines for ICP-OES Analysis Using Soil Samples. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvris, C.; Vaughan, T.; Bussan, D.; Bartzas, G.; Thomas, R. How ICP-OES changed the face of trace element analysis: Review of the global application landscape. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summary of Resolutions of the Team for Diet Supplements Operating at the Sanitary and Epidemiological Council. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/gis/zespol-do-spraw-suplementow-diety (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Comission Regulation (EU) 2023/915of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023R0915 (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level for Iron. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8819. [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA). Guidance for establishing and applying tolerable upper intake levels for vitamins and essential minerals. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetley, E.A. Multivitamin and multimineral dietary supplements: Definitions, characterization, bioavailability, and drug interactions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 269S–276S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Tayade, A.; Singh, J.; Walia, S. Bioavailability of Nutrients and Safety Measurements. In Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals; Egbuna, C., Dable Tupas, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielik, V.; Kolisek, M. Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Minerals in Relation to a Healthy Gut Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for chromium. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3845. [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of calcium. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2814. [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA); Re-evaluation of the existing health-based guidance values for copper and exposure assessment from all sources. EFSA J. 2023, 21, 7728. [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for Vitamins and Minerals. European Food Safety Authority. 2006. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/efsa_rep/blobserver_assets/ndatolerableuil.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA); Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level for Manganese. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8413. [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.C.; Riddell, L.J.; Nowson, C.A.; Booth, A.O.; Szymlek-Gay, E.A. Iron and Zinc Nutrition in the Economically-Developed World: A Review. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3184–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Food Additives (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2008/1333/oj/eng (accessed on 14 November 2025).

| Element | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 84.84 | 32.96 | 3.457 | 1205 | 239.6 |
| Ba | 1.456 | 0.853 | 0.180 | 6.006 | 1.359 |
| Ca | 76,080 | 4763 | 27.40 | 655,390 | 163,290 |
| Cd | 0.031 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.375 | 0.083 |
| Co | 4.373 | 1.545 | 0.158 | 39.89 | 8.757 |
| Cr | 12.54 | 3.545 | <LOQ | 118.0 | 26.25 |
| Cu | 365.5 | 0.528 | <LOQ | 2368 | 609.2 |
| Fe | 365.6 | 235.3 | 2.993 | 1810 | 423.0 |
| Hg | 0.003 | 0.002 | <LOQ | 0.013 | 0.003 |
| K | 351.0 | 94.99 | <LOQ | 2513 | 641.7 |
| Mg | 59,310 | 350.3 | 12.36 | 270,720 | 106,940 |
| Mn | 456.5 | 110.3 | 0.697 | 2741 | 762.9 |
| Mo | 13.01 | 0.185 | <LOQ | 122.3 | 30.32 |
| P | 5535 | 307.5 | 13.80 | 38,080 | 10,520 |
| Pb | 0.237 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 2.988 | 0.682 |
| S | 7621 | 1721 | 75.19 | 49,780 | 13,660 |
| Sr | 7.910 | 1.814 | <LOQ | 43.49 | 12.71 |
| Zn | 86.51 | 73.23 | 2.161 | 226.8 | 72.96 |
| Stage | Time [min] | E [W] | T1 [°C] | T2 [°C] | P [bar] |
| 1 | 10 | 1500 | 220 | 70 | 150 |
| 2 | 20 | 1500 | 220 | 70 | 150 |
| Instrument Parameter | Operating Conditions |
|---|---|
| Generator power [W] | 1150 |
| Carrier gas | Argon |
| Plasma gas flow rate [L/min] | 12 |
| Auxiliary gas flow rate [L/min] | 0.5 |
| Nebulizer gas flow rate [L/min] | 0.5 |
| Nebulizer | Concentric quartz |
| Torch | Quartz |
| Analyte | LOQ | INCT-MPH-2 Certified | INCT-MPH-2 Obtained xmean ± SD | 1570a Certified | 1570a Obtained xmean ± SD | 1573a Certified | 1573a Obtained xmean ± SD |
| Al 396.152 a | 0.031 | 670 ± 111 | 681 ± 15 | 310 ± 15 | 300 ± 21 | 598 ± 7.1 | 602 ± 4.9 |
| Ba 493.409 a | 0.020 | 32.5 ± 2.5 | 31.8 ± 0.9 | - | - | 63 | 59 ± 0.9 |
| Ca 393.366 r (%) | 0.042 | 1.08 ± 0.07 | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 1.53 ± 0.07 | 1.50 ± 0.02 | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.04 |
| Cd 228.802 a | 0.005 | - | - | 2.88 ± 0.06 | 2.82 ± 0.04 | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 1.50 ± 0.02 |
| Co 228.616 a | 0.005 | - | - | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.57 ± 0.02 |
| Cr 267.716 a | 0.031 | 1.69 ± 0.13 | 1.61 ± 0.09 | - | - | 1.99 ± 0.03 | 2.01 ± 0.02 |
| Cu 324.754 a | 0.007 | 7.77 ± 0.53 | 7.75 ± 0.40 | 12.2 ± 0.86 | 12.3 ± 0.03 | 4.70 ± 0.14 | 4.80 ± 0.10 |
| K 769.896 r (%) | 0.099 | 1.91 ± 0.12 | 1.92 ± 0.10 | 2.90 ± 0.03 | 2.92 ±0.1 | 2.68 ± 0.5 | 2.72 ± 0.2 |
| Mg 279.553 r (%) | 0.047 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.9 | 0.91 ± 0.1 | 1.20 | 1.22 ± 0.3 |
| Mn 257.610 a | 0.004 | 191 ± 12 | 191 ± 10 | 76.0 ± 1.2 | 76 ± 0.02 | 246 ± 7.1 | 245 ± 1.5 |
| Mo 202.030 a | 0.006 | 0.520 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | - | - | - | - |
| P 177.495 a (%) | 0.044 | 0.25 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.10 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.03 |
| S 180.731 a (%) | 0.088 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 0.96 | 1.00 ± 0.10 |
| Sr 407.771 a | 0.008 | 37.6 ± 2.7 | 38.1 ± 0.9 | 55.5 ± 0.5 | 54.9 ± 0.08 | 85 | 89.1 ± 4.5 |
| Yb * 328.937 a | 0.010 | - | |||||
| Measurement Parameters | Fe 248.814 nm | Zn 213.857 nm | Pb 217.000 nm |
| Gas flow rate [L/h] | 60 | 50 | 65 |
| LOQ [mg/L] | 0.100 | 0.015 | 0.067 |
| Flame type | air–acetylene | air–acetylene | air–acetylene |
| Analyte | INCT-MPH-2 Certified | INCT-MPH-2 Obtained xmean ± SD | 1570a Certified | 1570a Obtained xmean ± SD | 1573a Certified | 1573a Obtained xmean ± SD |
| Fe | 460 | 455 ± 5.5 | - | - | 368 ± 4.3 | 370 ± 2.5 |
| Pb | 2.16 ± 0.23 | 2.15 ± 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | - | - |
| Zn | 33.5 ± 2.1 | 34.2 ± 0.95 | 82.3 ± 3.9 | 83.2 ± 2.5 | 30.9 ± 0.55 | 40.2 ± 0.35 |
| Stage of Decomposition | Heat Temperature [°C] | Heat Time [s] | Flow [L/min] | Slope Time [s] |
| Atomize 1 | 180 | 120 | 0.4 | 120 |
| Atomize 2 | 850 | 120 | 0.4 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maćkiewicz, E.; Klimaszewska, M.; Albińska, J.; Szynkowska-Jóźwik, M.I. Evaluation of the Elemental Composition of Dietary Supplements Containing Iron Available on the Polish Market Using ICP-OES, FAAS and CVAAS Techniques. Molecules 2025, 30, 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234511
Maćkiewicz E, Klimaszewska M, Albińska J, Szynkowska-Jóźwik MI. Evaluation of the Elemental Composition of Dietary Supplements Containing Iron Available on the Polish Market Using ICP-OES, FAAS and CVAAS Techniques. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234511
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaćkiewicz, Elżbieta, Martyna Klimaszewska, Jadwiga Albińska, and Małgorzata Iwona Szynkowska-Jóźwik. 2025. "Evaluation of the Elemental Composition of Dietary Supplements Containing Iron Available on the Polish Market Using ICP-OES, FAAS and CVAAS Techniques" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234511
APA StyleMaćkiewicz, E., Klimaszewska, M., Albińska, J., & Szynkowska-Jóźwik, M. I. (2025). Evaluation of the Elemental Composition of Dietary Supplements Containing Iron Available on the Polish Market Using ICP-OES, FAAS and CVAAS Techniques. Molecules, 30(23), 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234511







