High-Resolution Electrospray and Ion Mobility Sequential Mass Spectrometry for Structural Characterisation of Anticancer Stem Cell Agent Salinomycin and Its Isomers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Overview
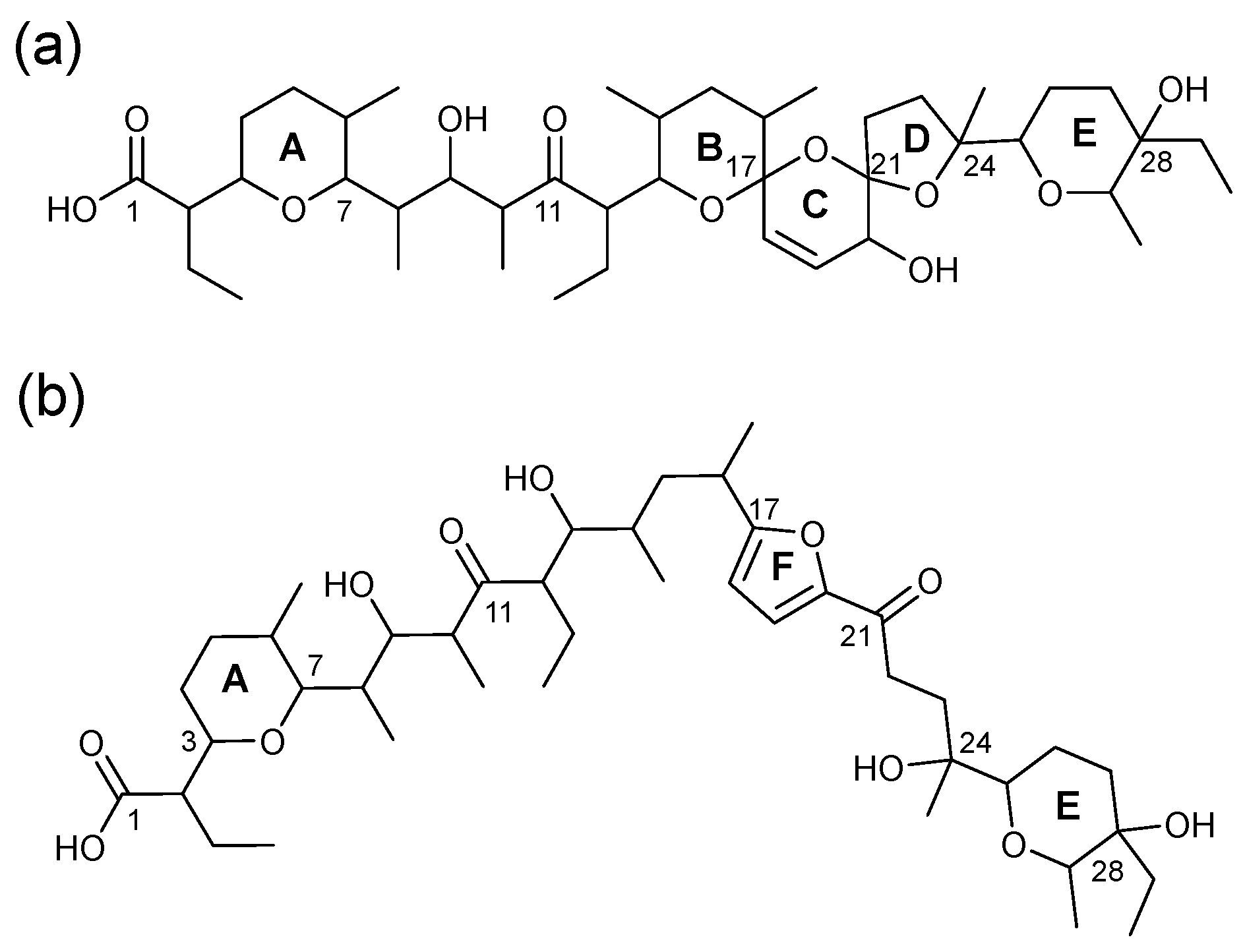
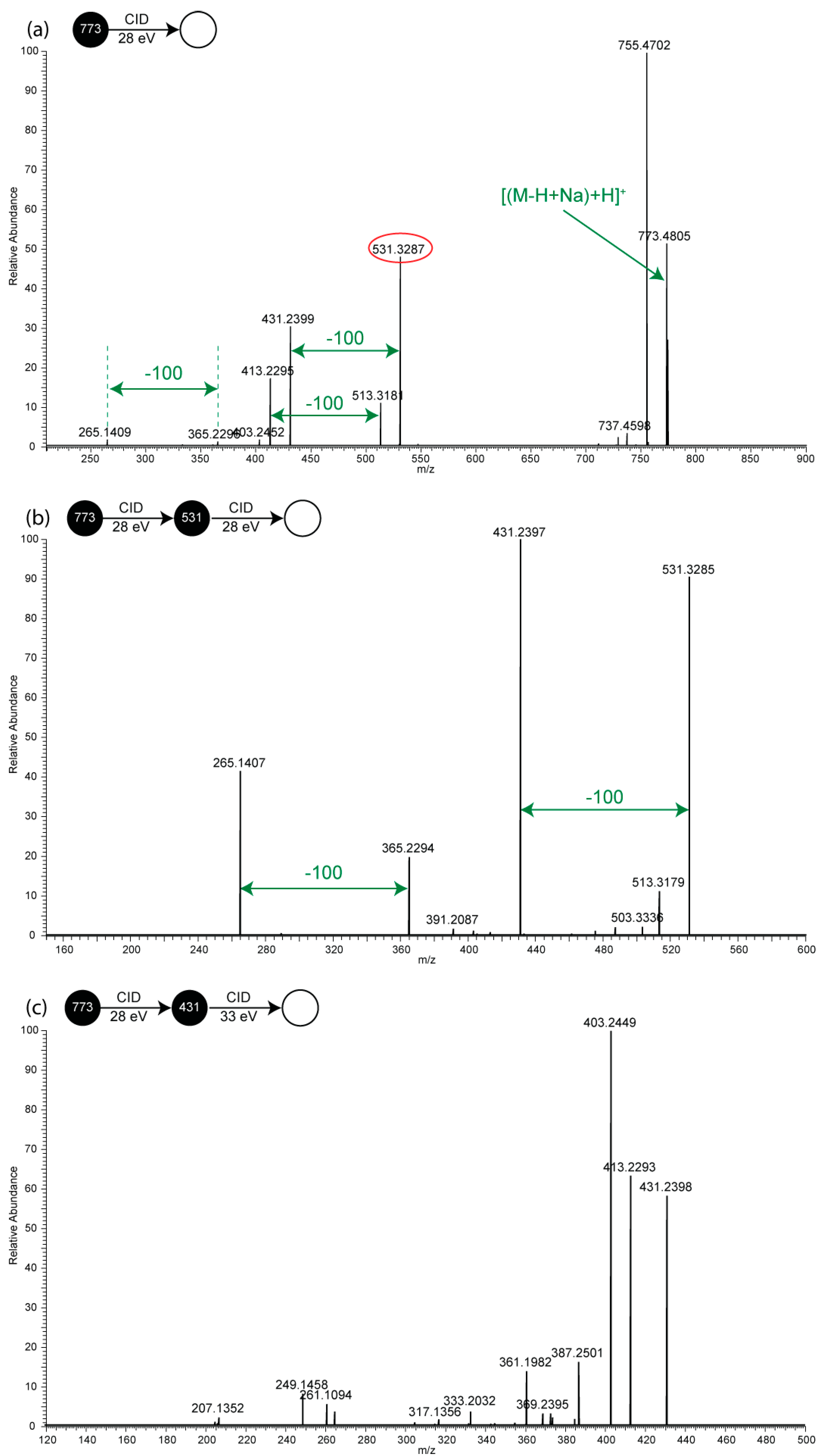
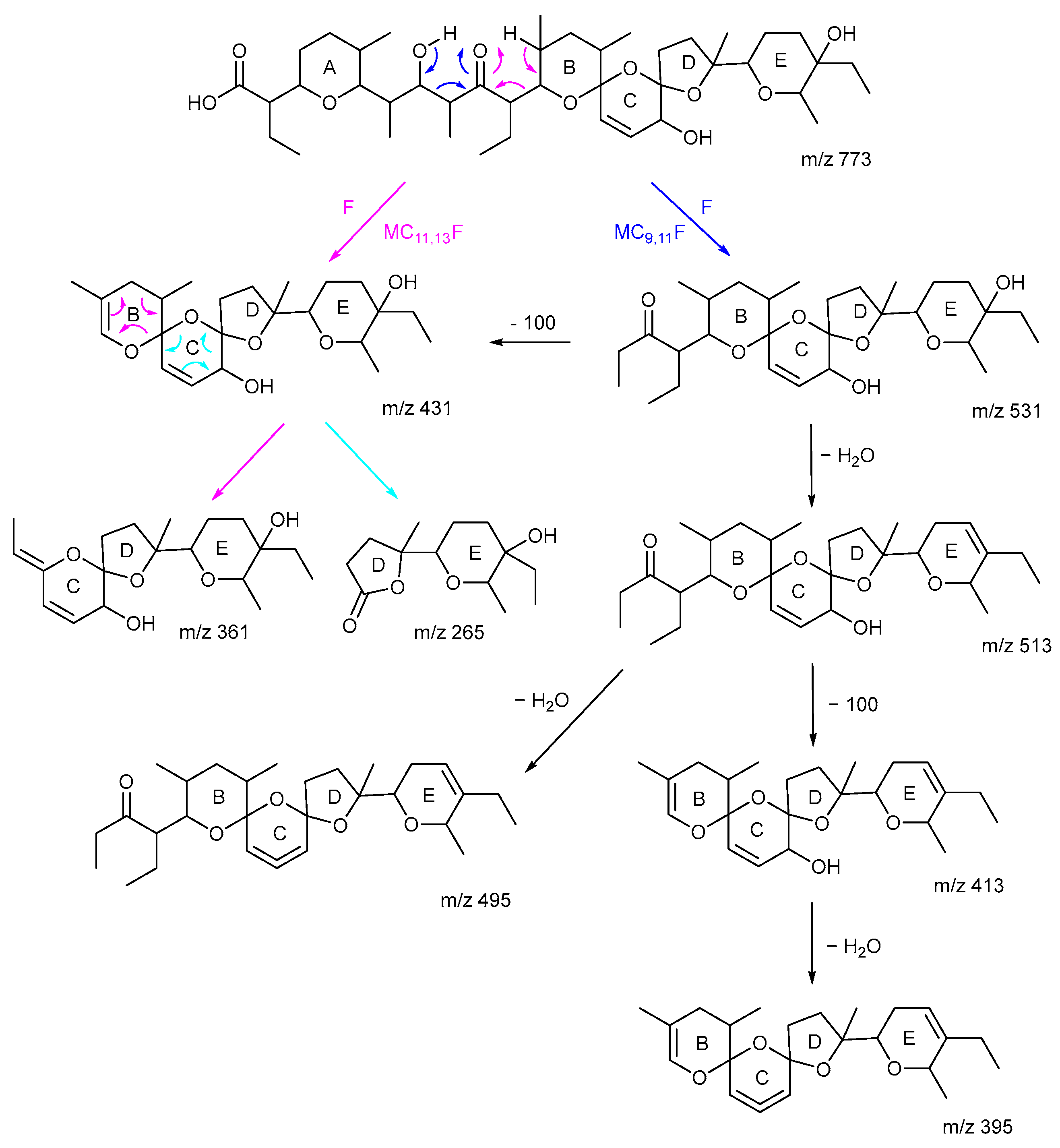
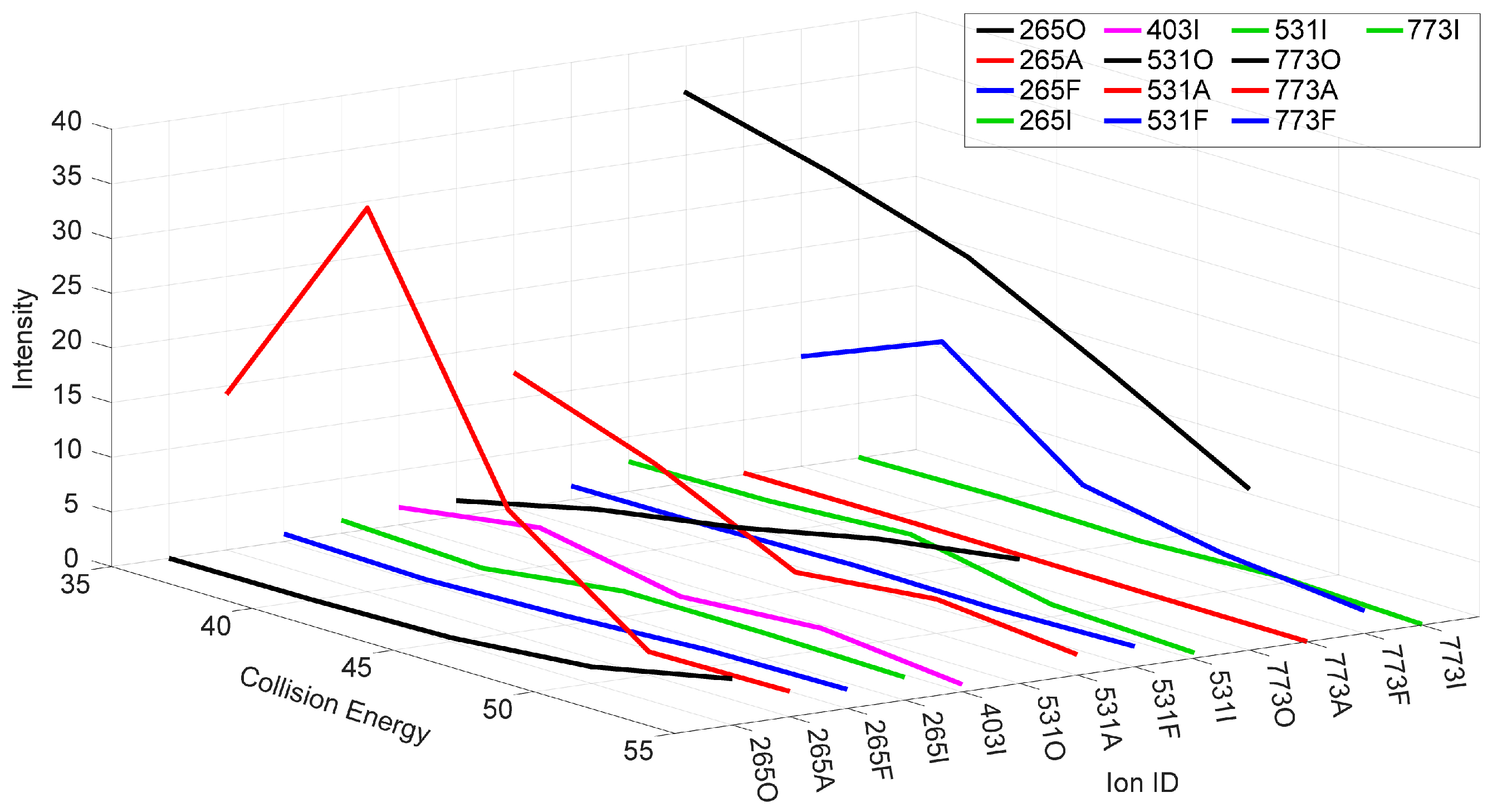
2.2. MSn of Salinomycin, m/z 773
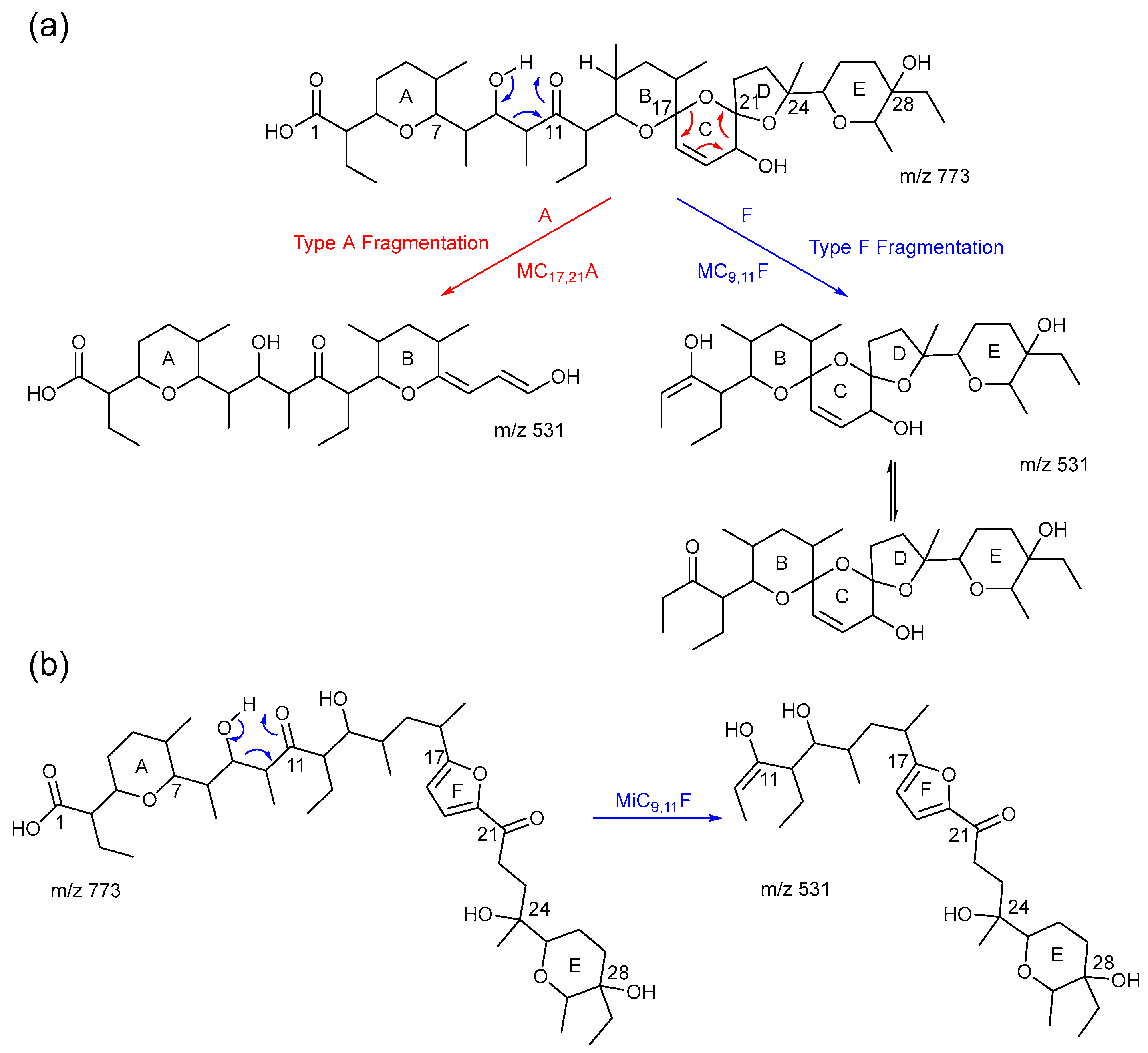
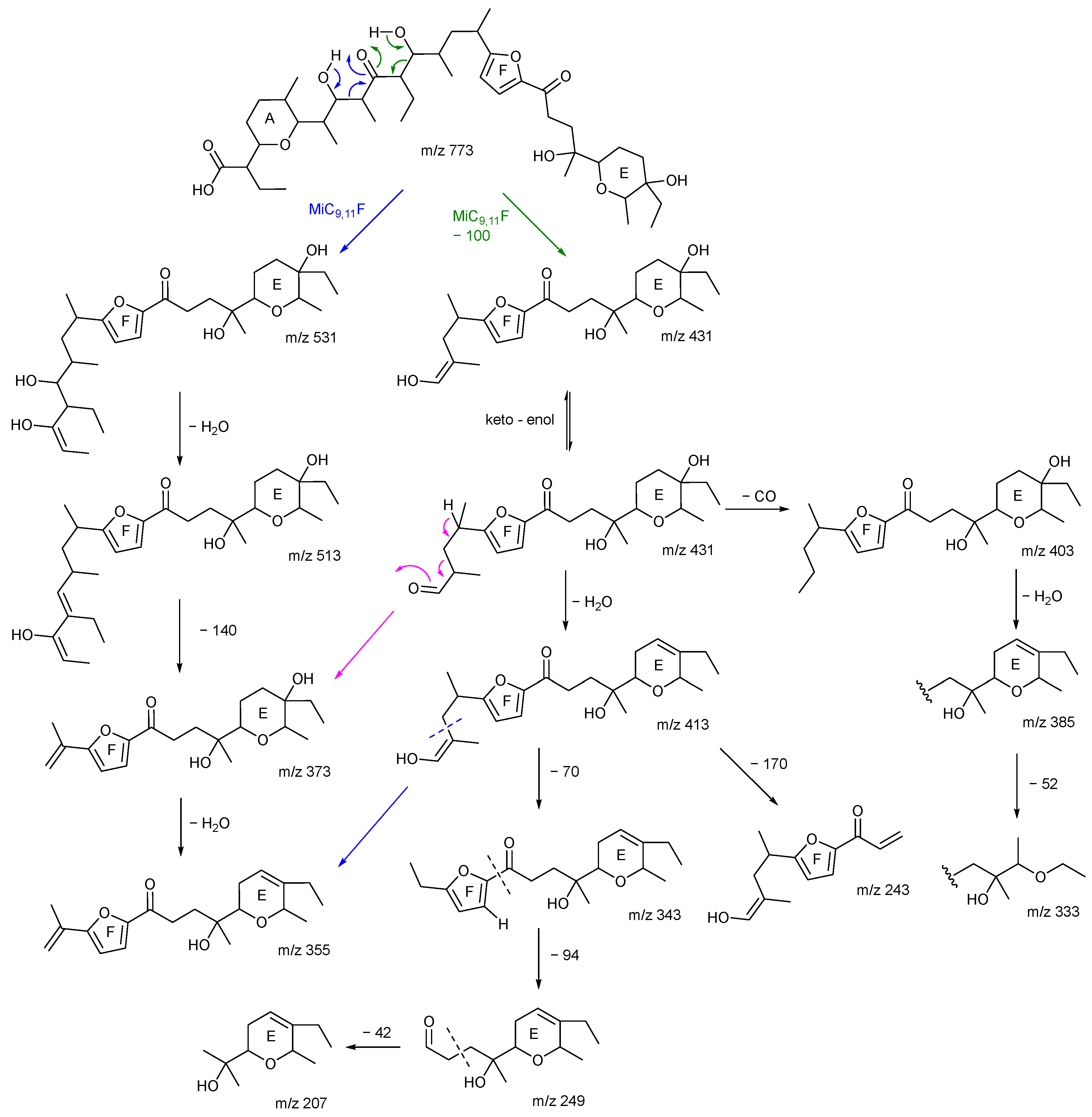
2.3. Consideration of Product Ion m/z 531
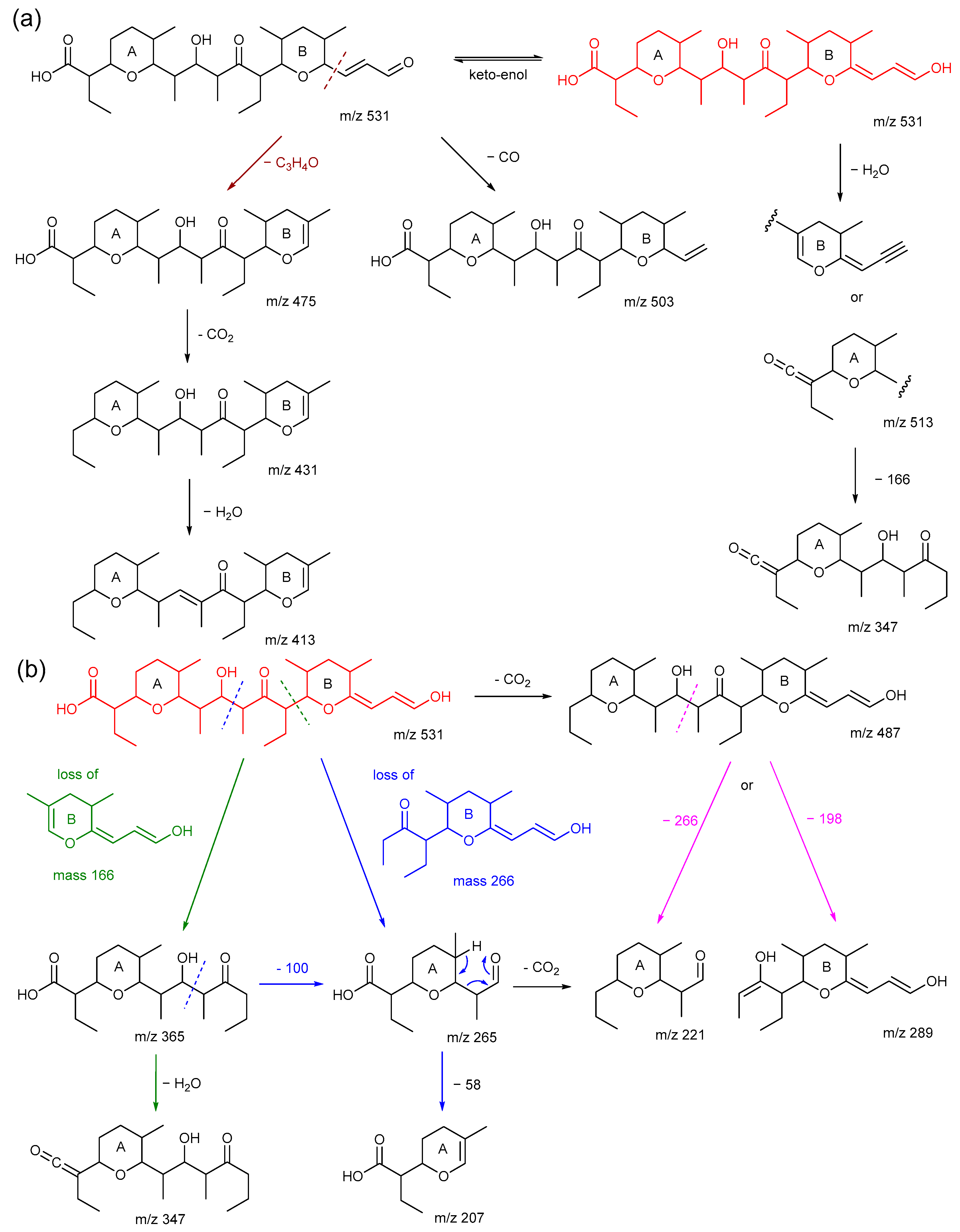
2.4. The Product Ions of m/z 531
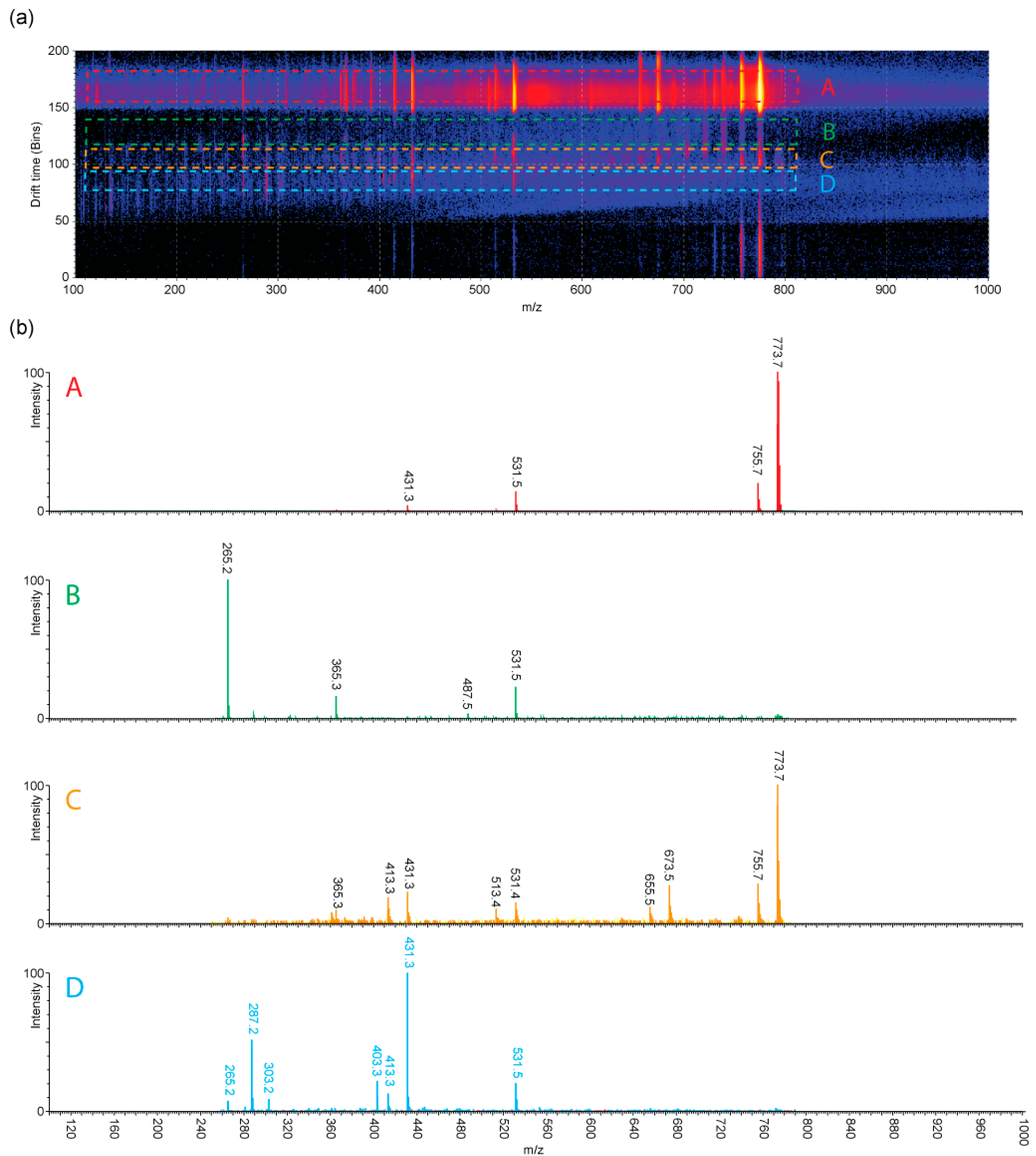
2.5. IMS-MS/MS of Salinomycin
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CID | Collision Induced Dissociation |
| CCS | Collision Cross-Section |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| EBG | Energy Breakdown Graph |
| ESI | Electrospray Ionisation |
| HESI | Heated Electrospray Ionisation |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| HRAM | High Resolution Accurate Mass |
| IMS | Ion Mobility Spectrometry |
| iSAL | Isomeric Salinomycin |
| M | Neutral Salinomycin Molecule |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MS/MS | Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MSn | Sequential Mass Spectrometry |
| SAL | Salinomycin |
References
- Miyazaki, Y.; Shibata, A.; Yahagi, T.; Hara, M.; Hara, K.; Yoneda, S.; Kasahara, H.; Nakamura, Y. Method of Producing Salinomycin Antibiotics. U.S. Patent US4212942A, 15 July 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Anadón, A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R. Veterinary drugs residues: Coccidiostats. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, R.R.; Silva, L.F.G.; Pereira, A.M.P.T.; Esteves, A.; Duarte, S.C.; Pena, A. Coccidiostats and poultry: A comprehensive review and current legislation. Foods 2022, 11, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakara Reddy, B.; Sivajothi, S.; Rayulu, V.C. Clinical coccidiosis in adult cattle. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, W.R.; Bardsley, K.D. Ruminant coccidiosis. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2006, 22, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockrell, R.S.; Harris, E.J.; Pressman, B.C. Energetics of potassium transport in mitochondria induced by valinomycin. Biochemistry 1966, 5, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cui, C.; Cai, F. Anticancer mechanisms of salinomycin in breast cancer and its clinical applications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, T.; Reshkin, S.J.; Harguindey, S. (Eds.) An Innovative Approach to Understanding and Treating Cancer: Targeting pH; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 335–359. [Google Scholar]
- Naujokat, C.; Steinhart, R. Salinomycin as a drug for targeting human cancer stem cells. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 950658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressman, B.C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1976, 45, 501–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzabal, L.; El-Nikhely, N.; Redrado, M.; Seeger, W.; Savai, R.; Calvo, A. Differential effects of drugs targeting cancer stem cell (CSC) and non-CSC populations on lung primary tumors and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 9, e79798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Wong, E.T.; Fonkem, E.; Hsieh, T.C.; Wu, J.M.; Wu, E. Salinomycin: A novel anti-cancer agent with known anti-coccidial activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4095–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeberdytė, A.; Sarapinienė, I.; Aleksander-Krasko, J.; Stankevičius, V.; Sužiedėlis, K.; Jarmalaitė, S. Dichloroacetate and salinomycin exert a synergistic cytotoxic effect in colorectal cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokka, M.; Jestoi, M.; Peltonen, K. Trace level determination of polyether ionophores in feed. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 151363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fang, J.; Wu, S.; Ma, K.; Li, H.; Yan, X.; Dong, F. Identification and quantification of salinomycin in intoxicated human plasma by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchflower, W.J.; Kennedy, D.G. Determination of monensin, salinomycin and narasin in muscle, liver and eggs from domestic fowl using liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 675, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, L.; Daeseleire, E.; Peteghem, C.V. Determination of the ionophoric coccidiostats narasin, monensin, lasalocid and salinomycin in eggs by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisso, B.F.; Ferreira, R.G.; Pereira, M.U.; Monteiro, M.A.; Cruz, T.A.; Costa, R.P.; Lima, A.M.B.; Nóbrega, A.W. Simultaneous determination of polyether ionophores, macrolides and lincosamides in hen eggs by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry using a simple solvent extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 682, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinashi, H.; Ōtake, N. An interpretation of the mass spectra of salinomycin and its derivatives. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1976, 40, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.-S.; March, R.E.; Metcalfe, C.D. Fragmentation study of salinomycin and monensin A antibiotics using electrospray quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.L.; Harris, J.A.; Russell, C.A.; Wilkins, J.P.G. Investigations by HPLC-electrospray mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy into the isomerisation of salinomycin. Analyst 1999, 124, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLafferty, F.W. Mass spectrometric analysis. Molecular rearrangements. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, C.H.; Goo, Y.M.; Kim, M.S. Application of fast atom bombardment combined with tandem mass spectrometry to the structural elucidation of O-demethylabierixin and related polyether antibiotics. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masike, K.; Stander, M.A.; de Villiers, A. Recent applications of ion mobility spectrometry in natural product research. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale Neto, F.; Clark, T.N.; Lopes, N.P.; Linington, R.G. Evaluation of ion mobility spectrometry for improving constitutional assignment in natural product mixtures. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, S.M.; Lareau, N.M.; Hines, K.M.; McNees, C.R.; Goodwin, C.R.; Bachmann, B.O.; Mclean, J.A. Natural Products Analysis: Instrumentation, Methods, and Applications; Havlíček, V., Spížek, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 397–431. [Google Scholar]
- Warnke, S.; Seo, J.; Boschmans, J.; Sobott, F.; Scrivens, J.H.; Bleiholder, C.; Bowers, M.T.; Gewinner, S.; Schöllkopf, W.; Pagel, K.; et al. Protomers of benzocaine: Solvent and permittivity dependence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4236–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, N.P.; Stark, C.B.W.; Hong, H.; Gates, P.J.; Staunton, J. Fragmentation studies on monensin A and B by accurate-mass electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, C.P.G.; Dyson, P.J.; Johnson, B.F.G.; Langridge-Smith, P.R.R.; McIndoe, J.S.; Whyte, C. On the use of breakdown graphs combined with energy-dependent mass spectrometry to provide a complete picture of fragmentation processes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörlein, S.; Schuster, C.; Paal, M.; Vogeser, M. Collision energy-breakdown curves—An additional tool to characterize MS/MS methods. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 18, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Iwamuro, Y.; Ishimaru, R.; Chinaka, S.; Kato, N.; Sakamoto, Y.; Sugimura, N.; Hasegawa, H. Energy-resolved mass spectrometry for differentiation of the fluorine substitution position on the phenyl ring of fluoromethcathinones. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 54, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Gates, P.J. Systematic characterisation of the fragmentation of flavonoids using high-resolution accurate mass electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Larriba-Andaluz, C.; Hogan, C.J. Collision cross section calculations for polyatomic ions considering rotating diatomic/linear gas molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 194107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
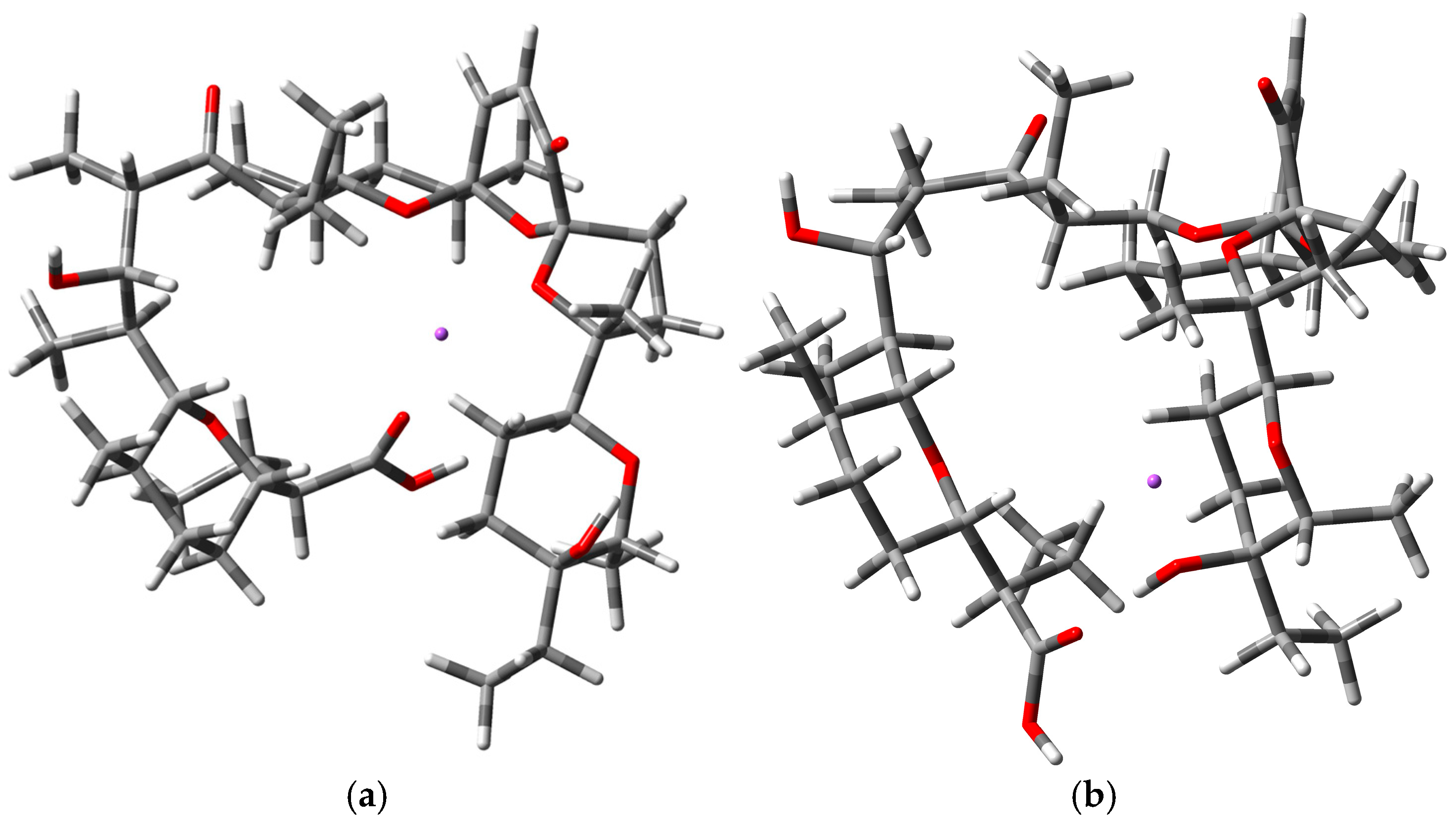
| Name | Position of Na Cation | Calculated CCS (A2) |
|---|---|---|
| [(SAL−H+Na)+H]+ | Middle | 283.58 |
| [(SAL−H+Na)+H]+ | Ring End | 277.28 |
| [(iSAL-H+Na]+H]+ | Middle | 285.54 |
| 531 Na iF | - | 261.25 |
| 531 Na A | - | 241.59 |
| 531 Na F | - | 225.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Gates, P.J. High-Resolution Electrospray and Ion Mobility Sequential Mass Spectrometry for Structural Characterisation of Anticancer Stem Cell Agent Salinomycin and Its Isomers. Molecules 2025, 30, 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234512
Jiang C, Gates PJ. High-Resolution Electrospray and Ion Mobility Sequential Mass Spectrometry for Structural Characterisation of Anticancer Stem Cell Agent Salinomycin and Its Isomers. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234512
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Candy, and Paul J. Gates. 2025. "High-Resolution Electrospray and Ion Mobility Sequential Mass Spectrometry for Structural Characterisation of Anticancer Stem Cell Agent Salinomycin and Its Isomers" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234512
APA StyleJiang, C., & Gates, P. J. (2025). High-Resolution Electrospray and Ion Mobility Sequential Mass Spectrometry for Structural Characterisation of Anticancer Stem Cell Agent Salinomycin and Its Isomers. Molecules, 30(23), 4512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234512






