A Novel and Validated GC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Four Opioids and Seven Fentanoids in Oral Fluid for Forensic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
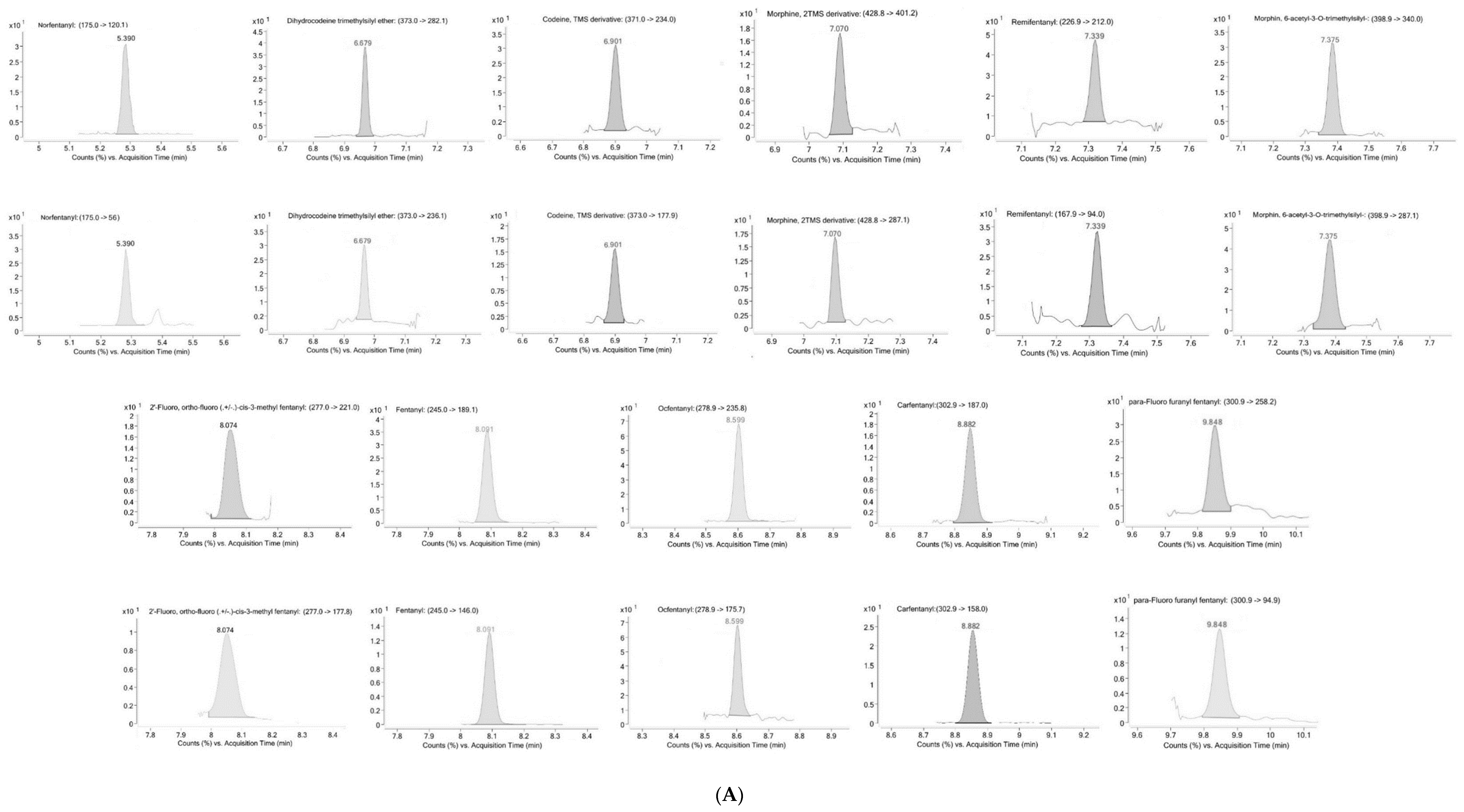
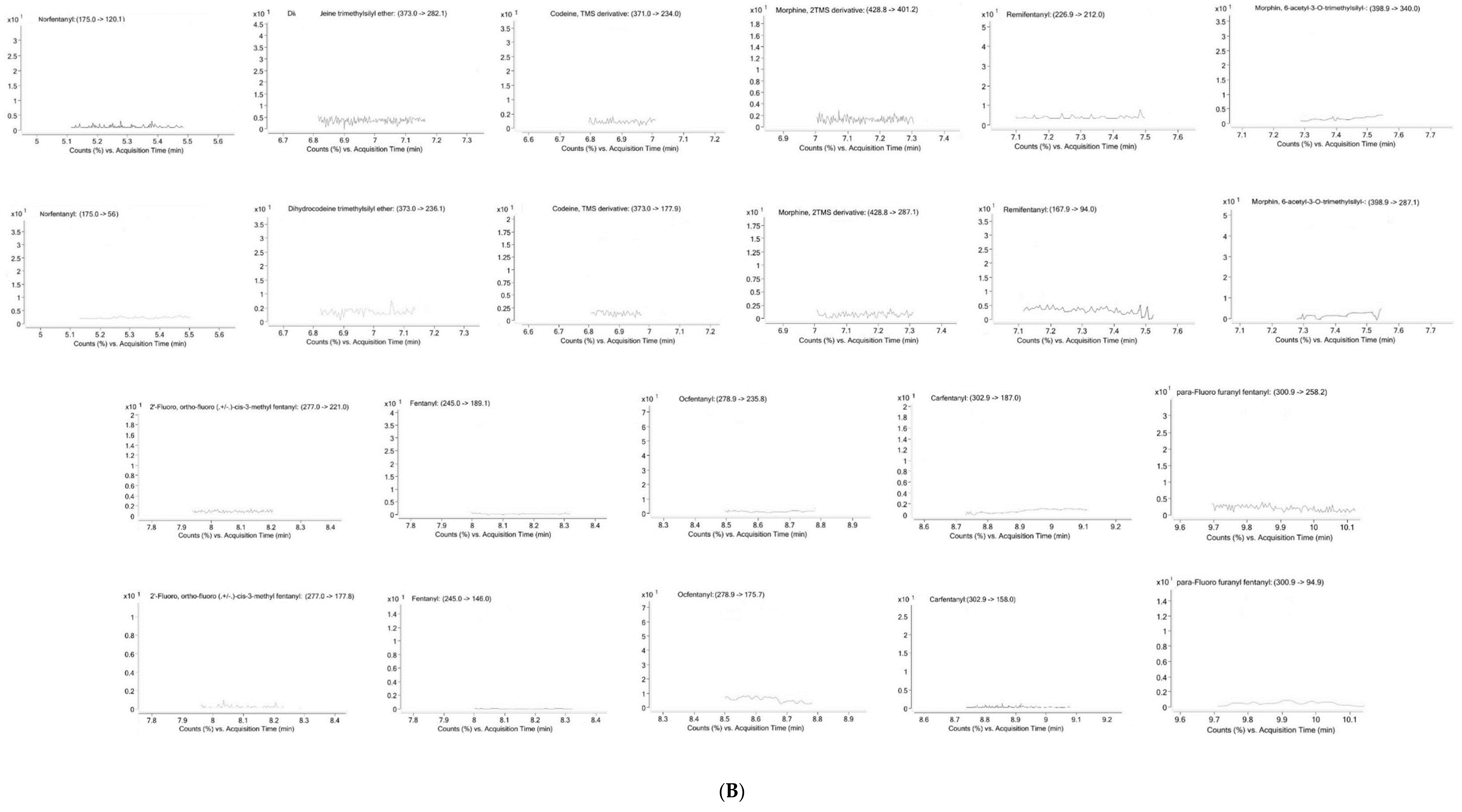
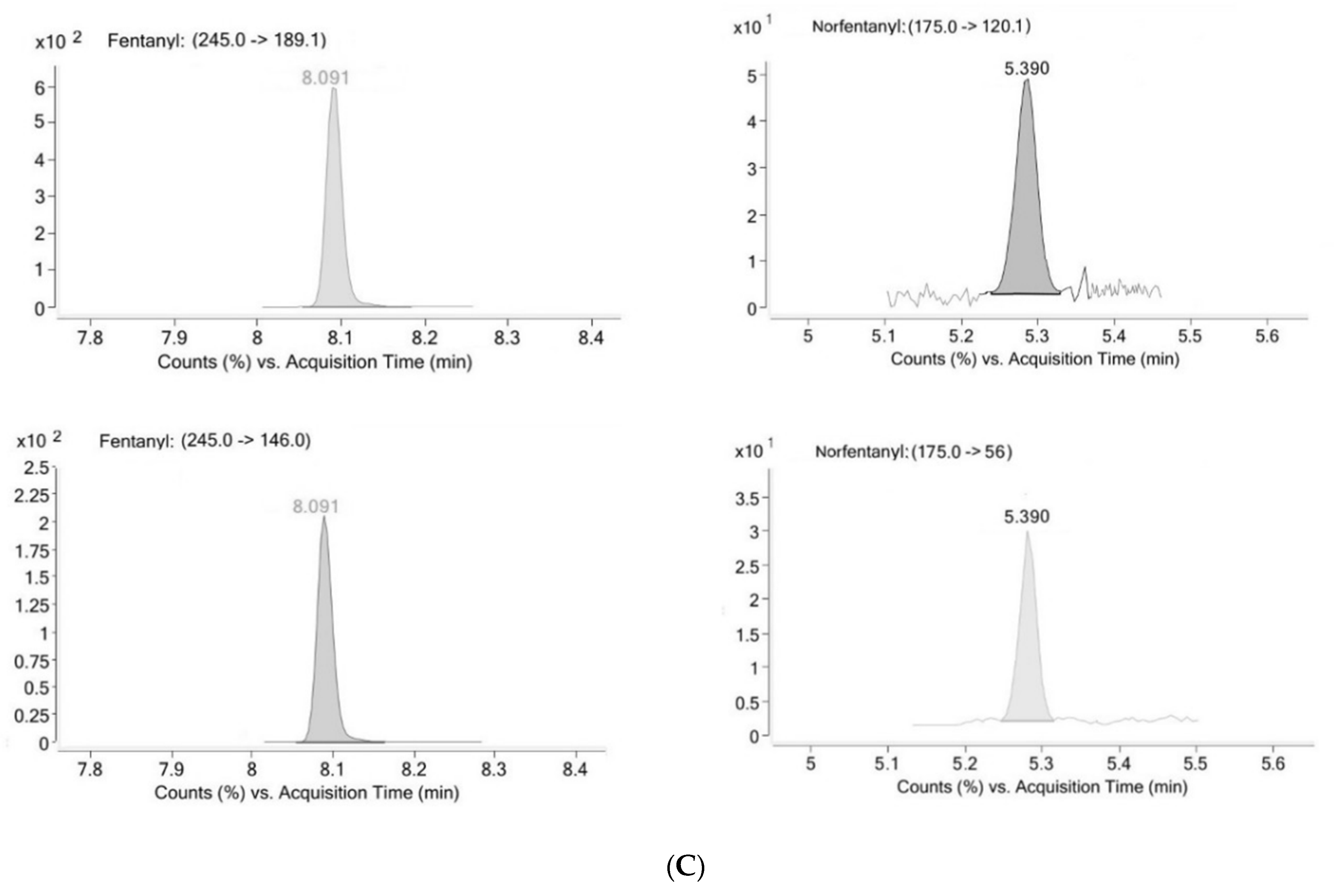
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
2.2. Real Samples Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Calibration and Quality Control Samples
4.3. Oral Fluid Samples
4.4. Oral Fluid Preparation
4.5. Instrumentation
4.6. Method Validation
4.6.1. Selectivity
4.6.2. Linearity
4.6.3. Accuracy, Precision, Limit of Detection (LOD), and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
4.6.4. Carryover and Recovery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| US | United States |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| OF | Oral fluid |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| GC-MS/MS | Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| 6-MAM | 6-monoacetylmorphine |
| EI | Electron impact ionization |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantification |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| QC | Quality control |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| RT | Retention Time |
| IS | Internal standard |
References
- Tittarelli, R.; Gismondi, A.; Di Marco, G.; Mineo, F.; Vernich, F.; Russo, C.; Marsella, L.T.; Canini, A. Forensic Application of Genetic and Toxicological Analyses for the Identification and Characterization of the Opium Poppy (Papaver somniferum L.). Biology 2022, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Yuan, K.; Lu, L. The Rising Crisis of Illicit Fentanyl Use, Overdose, and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salani, D.; McKay, M.; Zdanowicz, M. The Deadly Trio: Heroin, Fentanyl, and Carfentanil. J. Emerg. Nurs. 2020, 46, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.P. Fentanyl for Breakthrough Pain: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1197–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenian, P.; Vo, K.T.; Barr-Walker, J.; Lynch, K.L. Fentanyl, Fentanyl Analogs and Novel Synthetic Opioids: A Comprehensive Review. Neuropharmacology 2018, 134, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillas, S.M.; Pickens, C.M.; Tanz, L.J.; Vivolo-Kantor, A.M. Estimating the Ratio of Fatal to Non-Fatal Overdoses Involving All Drugs, All Opioids, Synthetic Opioids, Heroin or Stimulants, USA, 2010–2020. Inj. Prev. 2024, 30, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). Overdose Deaths Decline, Fentanyl Threat Looms. DEA Press Release. 2024. Available online: https://www.dea.gov/press-releases/2024/12/16/overdose-deaths-decline-fentanyl-threat-looms (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC Reports Nearly 24% Decline in U.S. Drug Overdose Deaths. CDC Newsroom. 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2025/2025-cdc-reports-decline-in-us-drug-overdose-deaths.html (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). European Drug Report 2024: Trends and Developments. EMCDDA Publications. 2024. Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2024_en (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Saloner, B.; McGinty, E.E.; Beletsky, L.; Bluthenthal, R.; Beyrer, C.; Botticelli, M.; Sherman, S.G. A Public Health Strategy for the Opioid Crisis. Public Health Rep. 2018, 133 (Suppl. S1), 24S–34S. [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers, N.A.; Huestis, M.A. Oral Fluid Drug Testing: Analytical Approaches, Issues and Interpretation of Results. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 415–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummer, O.H. Drug Testing in Oral Fluid. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2006, 27, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Truver, M.T.; Swortwood, M.J. Quantitative Analysis of Novel Synthetic Opioids, Morphine and Buprenorphine in Oral Fluid by LC–MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Carlier, J.; Giorgetti, R.; Tagliabracci, A.; Pacifici, R.; Gottardi, M.; Pichini, S. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Quantifying Fentanyl and 22 Analogs and Metabolites in Whole Blood, Urine, and Hair. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mannocchi, G.; Pirani, F.; Gottardi, M.; Sirignano, A.; Busardò, F.P.; Ricci, G. Determination of Nine New Fentanyl Analogues and Metabolites in Consumers’ Urine by Ul-Tra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 4394–4399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almeida, E.; Soares, S.; Gonçalves, J.; Rosado, T.; Fernández, N.; Rodilla, J.M.; Passarinha, L.A.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E. Stability of Cocaine, Opiates, and Metabolites in Dried Saliva Spots. Molecules 2022, 27, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares-Fuentes, A.M.; Lorenzo, R.A.; Fernández, P.; Fernández, A.M.; Furton, K.G.; Kabir, A.; Carro, A.M. Determination of Synthetic Opioids in Oral Fluid Samples Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1663, 462768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camedda, N.; Dagoli, S.; Anzillotti, L.; Cecchi, R. Development and Validation of a Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Fentanyl and Butyryl Fentanyl in Oral Fluid. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2024, 6, e202400038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, J.R.; McIntire, G.L. A Dilute-and-Shoot LC–MS Method for Quantitating Opioids in Oral Fluid. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, A.C.F.; Da Cunha, K.F.; Cardoso, M.S.; Oliveira, K.D.; Costa, J.L. Development and Validation of Quantitative Analytical Method for 50 Drugs of Antidepressants, Benzodiazepines and Opioids in Oral Fluid Samples by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol. 2021, 39, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, K.B.; Swortwood, M.J. Data-Independent Screening Method for 14 Fentanyl Analogs in Whole Blood and Oral Fluid Using LC-QTOF-MS. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 297, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, F.; Montesano, C.; Pirau, S.; Gregori, A.; Di Rosa, F.; Curini, R.; Sergi, M. Simultaneous Quantification of 25 Fentanyl Derivatives and Metabolites in Oral Fluid by Means of Microextraction on Packed Sorbent and LC–HRMS/MS Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 5870. [Google Scholar]
- Degreef, M.; Blanckaert, P.; Berry, E.M.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; Maudens, K.E. Determination of Ocfentanil and W-18 in a Suspicious Heroin-like Powder in Belgium. Forensic Toxicol. 2019, 37, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.Y.; Dong, H.; Stringfellow, E.; Hasgul, Z.; Park, J.; Glos, L.; Kazemi, R.; Jalali, M.S. Temporal and Spatial Trends of Fentanyl Co-Occurrence in the Illicit Drug Supply in the United States: A Serial Cross-Sectional Analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2024, 39, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. CY 2023 Annual Heroin Report; DEA: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.dea.gov/resources/documents (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Wille, S.M.; Coucke, W.; De Baere, T.; Peters, F.T. Update of Standard Practices for New Method Validation in Forensic Toxicology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5442–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, F.T.; Drummer, O.H.; Musshoff, F. Validation of New Methods. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 165, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAFS Standards Board. Standard Practices for Method Validation in Forensic Toxicology; American Academy of Forensic Sciences: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.aafs.org/sites/default/files/media/documents/036_Std_e1.pdf (accessed on 16 November 2025).
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC−MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analyte | LOD (ng/mL) | LLOQ (ng/mL) | Linearity | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope a | Intercept a | ||||
| Norfentanyl | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0480 ± 0.0013 | 0.0401 ± 0.0042 | 0.993 ± 0.002 |
| Dihydrocodeine | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0371 ± 0.0024 | 0.0050 ± 0.0023 | 0.996 ± 0.001 |
| Codeine | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0360 ± 0.0016 | −0.0022 ± 0.0031 | 0.995 ± 0.003 |
| Morphine, 2TMS | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0402 ± 0.0018 | 0.0040 ± 0.0010 | 0.996 ± 0.001 |
| Remifentanyl | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0032 ± 0.0026 | 0.0002 ± 0.0003 | 0.993 ± 0.002 |
| 6-MAM TMS | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0351 ± 0.0017 | 0.0210 ± 0.0010 | 0.996 ± 0.002 |
| 2′-fluoro, ortho-fluoro (+/−)-cis-3-methyl fentanyl | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0071 ± 0.0032 | 0.0001 ± 0.0002 | 0.994 ± 0.002 |
| Fentanyl | 0.050 | 0.200 | 0.1476 ± 0.0013 | −0.0340 ± 0.0010 | 0.995 ± 0.003 |
| Ocfentanyl | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0043 ± 0.0014 | −0.0001 ± 0.0013 | 0.996 ± 0.002 |
| Carfentanyl | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0024 ± 0.0010 | −0.0011 ± 0.0034 | 0.995 ± 0.003 |
| p-fluoro Fu-F | 0.100 | 0.500 | 0.0022 ± 0.0013 | −0.0010 ± 0.0022 | 0.993 ± 0.001 |
| Analyte | Inter-Assay Precision (%CV) | Intra-Assay Precision (%CV) | Accuracy (Bias%) | R (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low QC | Mid QC | High QC | Low QC | Mid QC | High QC | Low QC | Mid QC | High QC | ||
| Norfentanyl | 6.8 | 9.8 | 12.1 | 2.9 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 8.3 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 78 |
| Dihydrocodeine | 11.7 | 6.6 | 11.4 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 2.3 | −15.6 | 114 |
| Codeine | 1.8 | 4.6 | 15.2 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 4.0 | -4.1 | 120 |
| Morphine, 2TMS | 8.5 | 6.5 | 15.5 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 15.4 | 4.8 | 3.4 | −6.8 | 89 |
| Remifentanyl | 11.7 | 7.9 | 6.0 | 11.9 | 5.1 | 6.5 | −10.0 | −1.4 | −19.6 | 60 |
| 6-MAM TMS | 2.5 | 7.2 | 18.8 | 1.1 | 6.4 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 4.2 | 2.2 | 86 |
| 2′-fluoro, ortho-fluoro (+/−)-cis-3-methyl fentanyl | 8.9 | 4.0 | 7.1 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 6.1 | 3.9 | 0.2 | −3.1 | 57 |
| Fentanyl | 3.6 | 2.9 | 16.0 | 3.5 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 4.6 | 3.0 | −2.6 | 78 |
| Ocfentanyl | 10.6 | 5.8 | 17.7 | 4.0 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 3.0 | −2.7 | 117 |
| Carfentanyl | 8.3 | 6.0 | 14.9 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 4.5 | 3.8 | −0.1 | −0.7 | 70 |
| p-fluoro Fu-F | 9.9 | 8.1 | 11.3 | 10.6 | 8.6 | 10.5 | −11.5 | −11.8 | −12.4 | 96 |
| Analyte | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norfentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 2.1 | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Dihydrocodeine | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Codeine | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 12.2 | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 9.2 |
| Morphine, 2TMS | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 4.0 | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 5.4 |
| Remifentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| 6-MAM TMS | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| 2′-fluoro, ortho-fluoro (+/−)-cis-3-methyl fentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Fentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | 11.2 | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Ocfentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Carfentanyl | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| p-fluoro Fu-F | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ | <LLOQ |
| Analyte | RT (min) | MRM Transitions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE (eV) | Qualifier (m/z) | CE (eV) | Quantifier (m/z) | ||
| Norfentanyl | 5.23 | 20 | 175 → 56 | 10 | 175 → 120.1 |
| Dihydrocodeine | 6.70 | 15 | 373 → 236.1 | 15 | 373 → 282.1 |
| Codeine | 6.92 | 10 | 373 → 177.9 | 10 | 371 → 234.1 |
| Codeine-D3 | 6.91 | - | - | 10 | 374 → 237.1 |
| Morphine, 2TMS | 7.10 | 15 | 428.8 → 287.1 | 15 | 428.8 → 401.2 |
| Morphine, 2TMS-D3 | 7.08 | - | - | 15 | 402 → 343.1 |
| Remifentanyl | 7.30 | 15 | 167.9 → 94 | 5 | 226.9 → 212 |
| 6-MAM TMS | 7.38 | 15 | 398.9 → 287.1 | 15 | 398.9 → 340 |
| 6-MAM TMS-D3 | 7.37 | - | - | 15 | 402 → 343.1 |
| 2′-fluoro, ortho-fluoro (+/−)-cis-3-methyl fentanyl | 8.08 | 15 | 277 → 177.8 | 5 | 277 → 221 |
| Fentanyl | 8.10 | 15 | 277 → 146 | 5 | 245 → 189.1 |
| Fentanyl-D5 | 8.09 | - | - | 5 | 250 → 151.1 |
| Ocfentanyl | 8.58 | 10 | 278.1 → 175.7 | 10 | 278.1 → 235.8 |
| Carfentanyl | 8.91 | 25 | 302.9 → 158 | 15 | 302.9 → 187 |
| p-fluoro Fu-F | 9.89 | 25 | 300.9 → 94.9 | 15 | 300.9 → 258.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tittarelli, R.; Filardi, D.; Mineo, F.; Mannocchi, G. A Novel and Validated GC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Four Opioids and Seven Fentanoids in Oral Fluid for Forensic Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224478
Tittarelli R, Filardi D, Mineo F, Mannocchi G. A Novel and Validated GC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Four Opioids and Seven Fentanoids in Oral Fluid for Forensic Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224478
Chicago/Turabian StyleTittarelli, Roberta, Davide Filardi, Federico Mineo, and Giulio Mannocchi. 2025. "A Novel and Validated GC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Four Opioids and Seven Fentanoids in Oral Fluid for Forensic Applications" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224478
APA StyleTittarelli, R., Filardi, D., Mineo, F., & Mannocchi, G. (2025). A Novel and Validated GC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Four Opioids and Seven Fentanoids in Oral Fluid for Forensic Applications. Molecules, 30(22), 4478. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224478






