Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-CCR8 Full-Sized IgG and Its Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Cancer Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
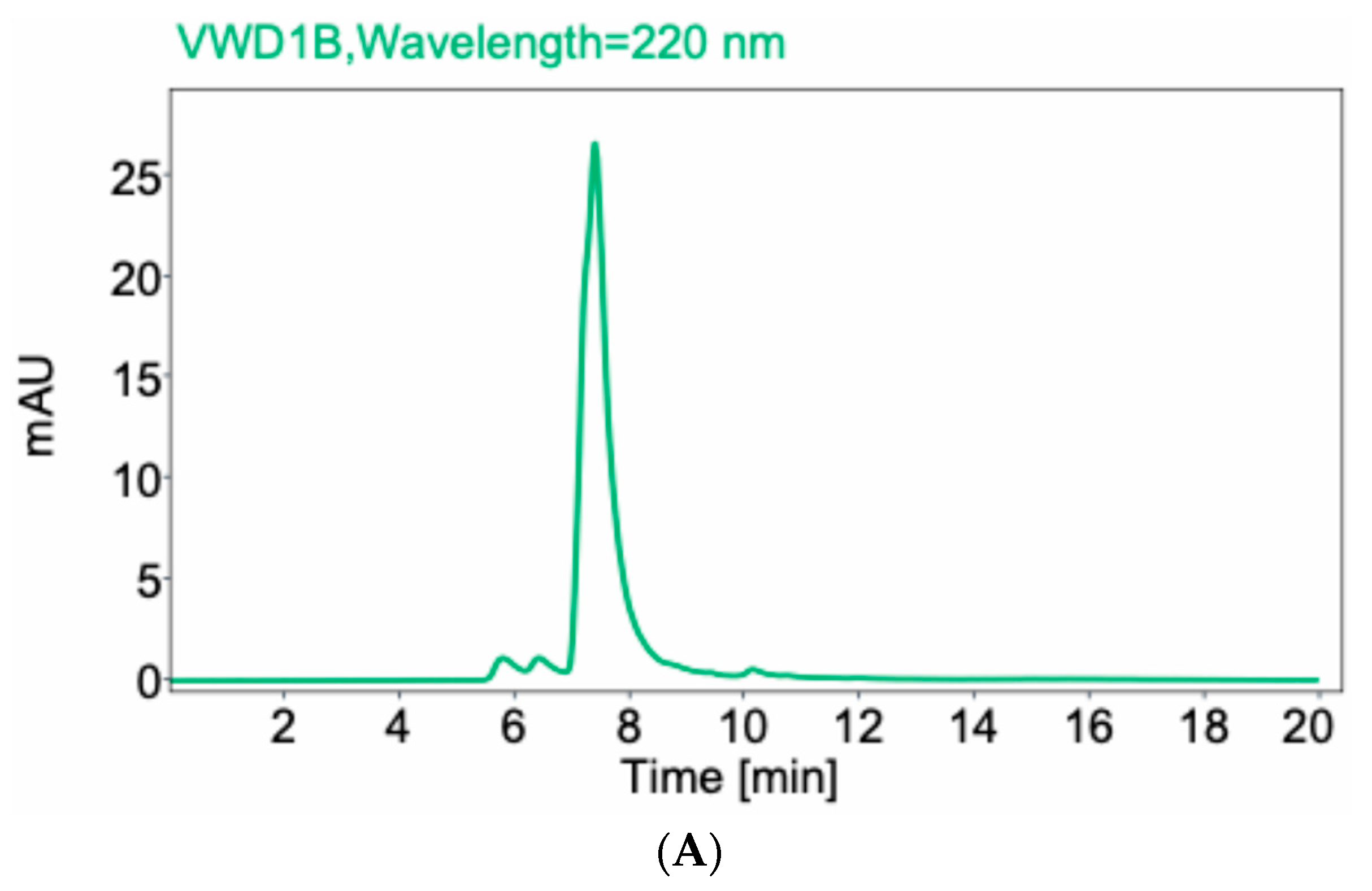
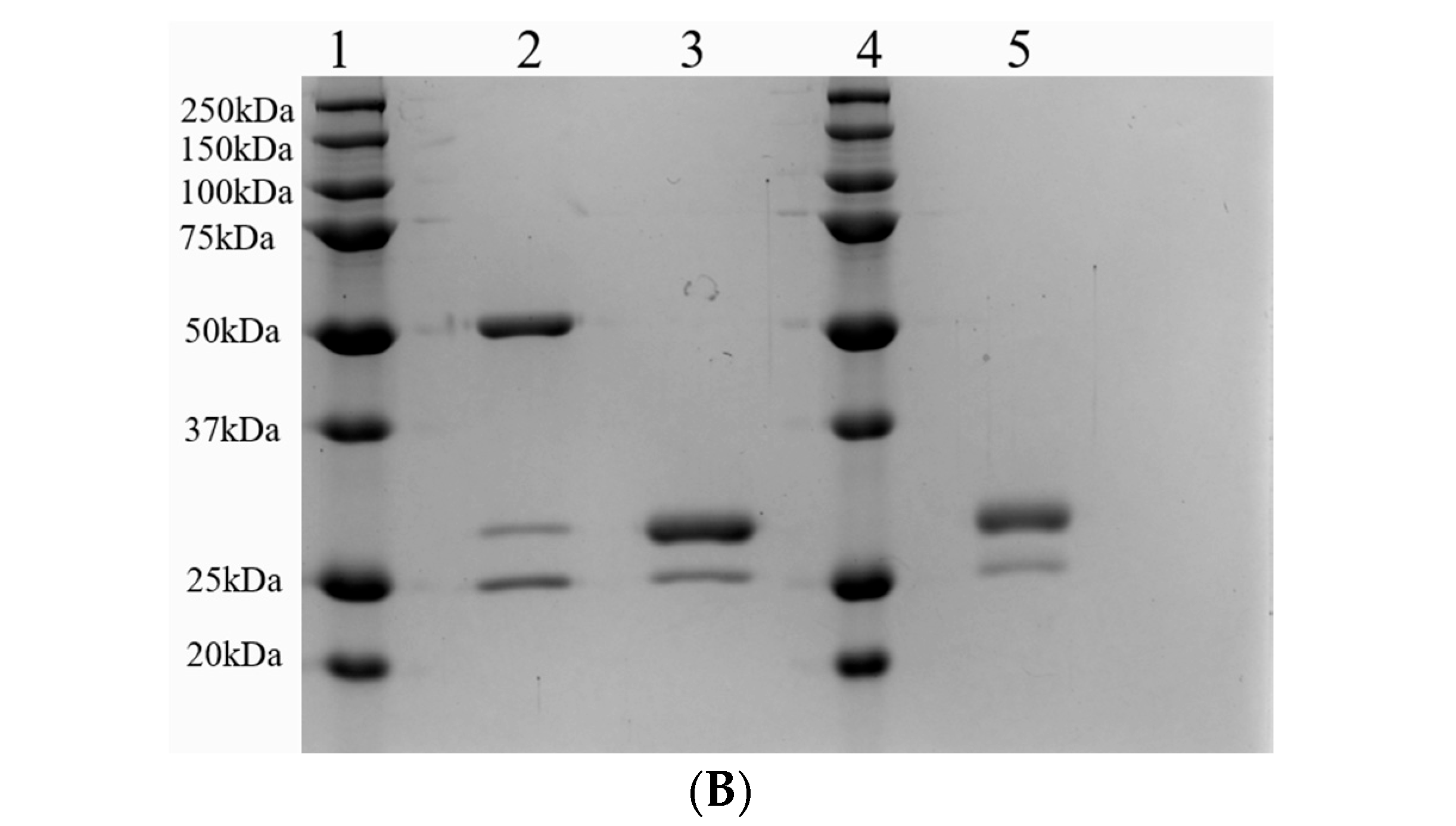
2.1. Structural Analyses of Anti-CCR8 Whole IgG and Its Fab Fragments
2.2. Conjugation of Whole Anti-CCR8 IgG and Fab Fragments to DOTA and Their Immunoreactivity
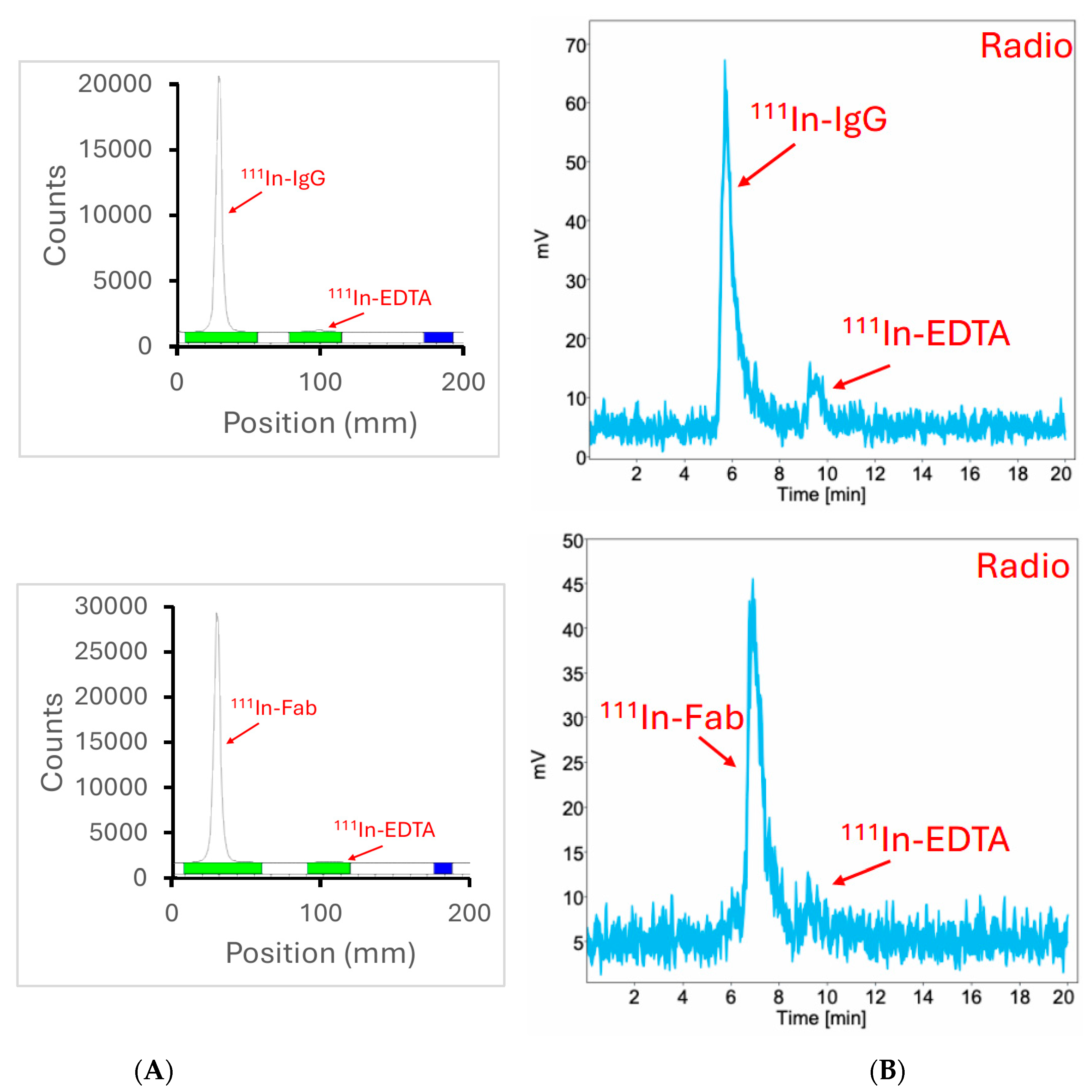
2.3. Immunoreactivity of Whole Anti-CCR8 IgG and Fab Fragments Towards CCR8 Before and After Conjugation to DOTA
2.4. Both DOTA-Conjugated Anti-CCR8 Whole IgG and Its Fab Fragment Radiolabeled Quantitively with 111In
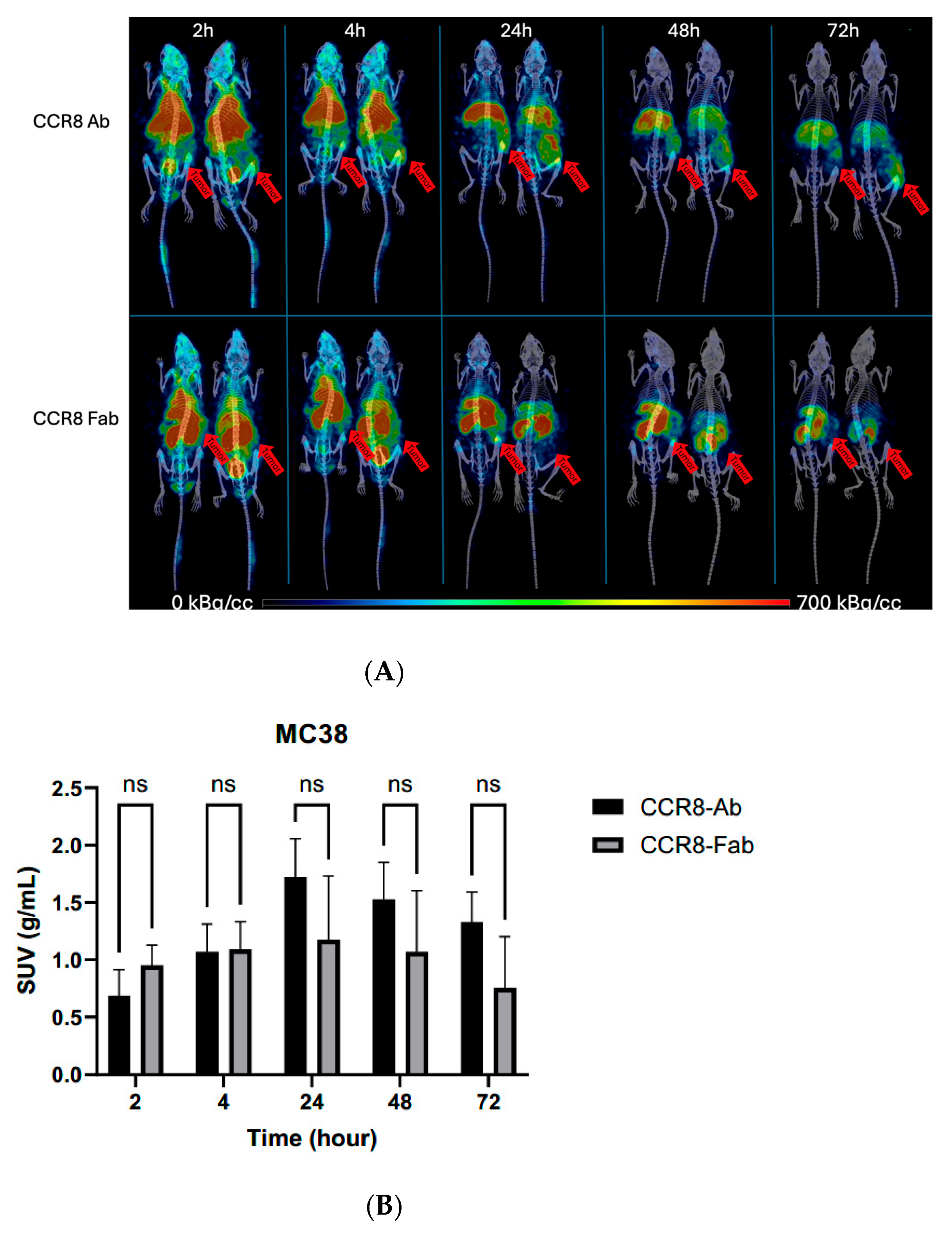
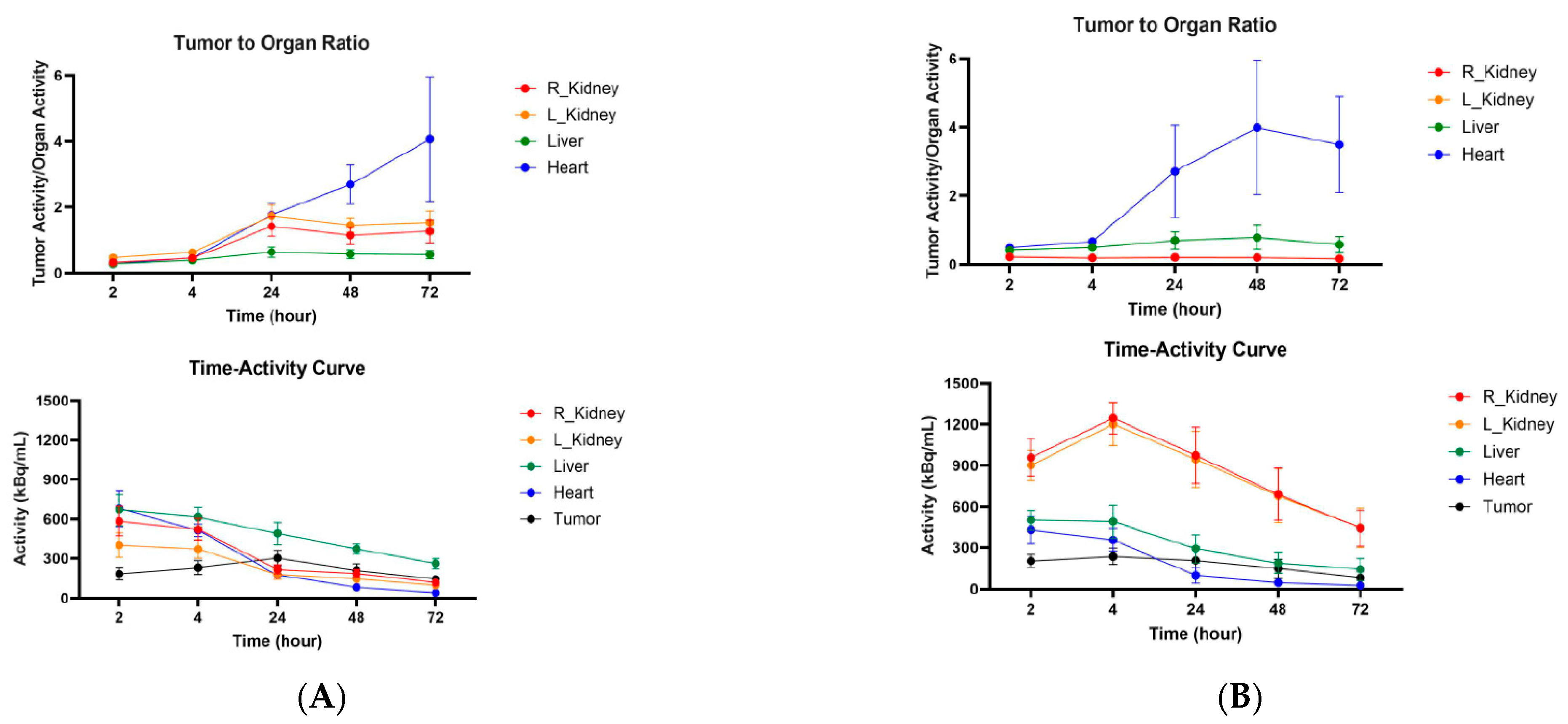
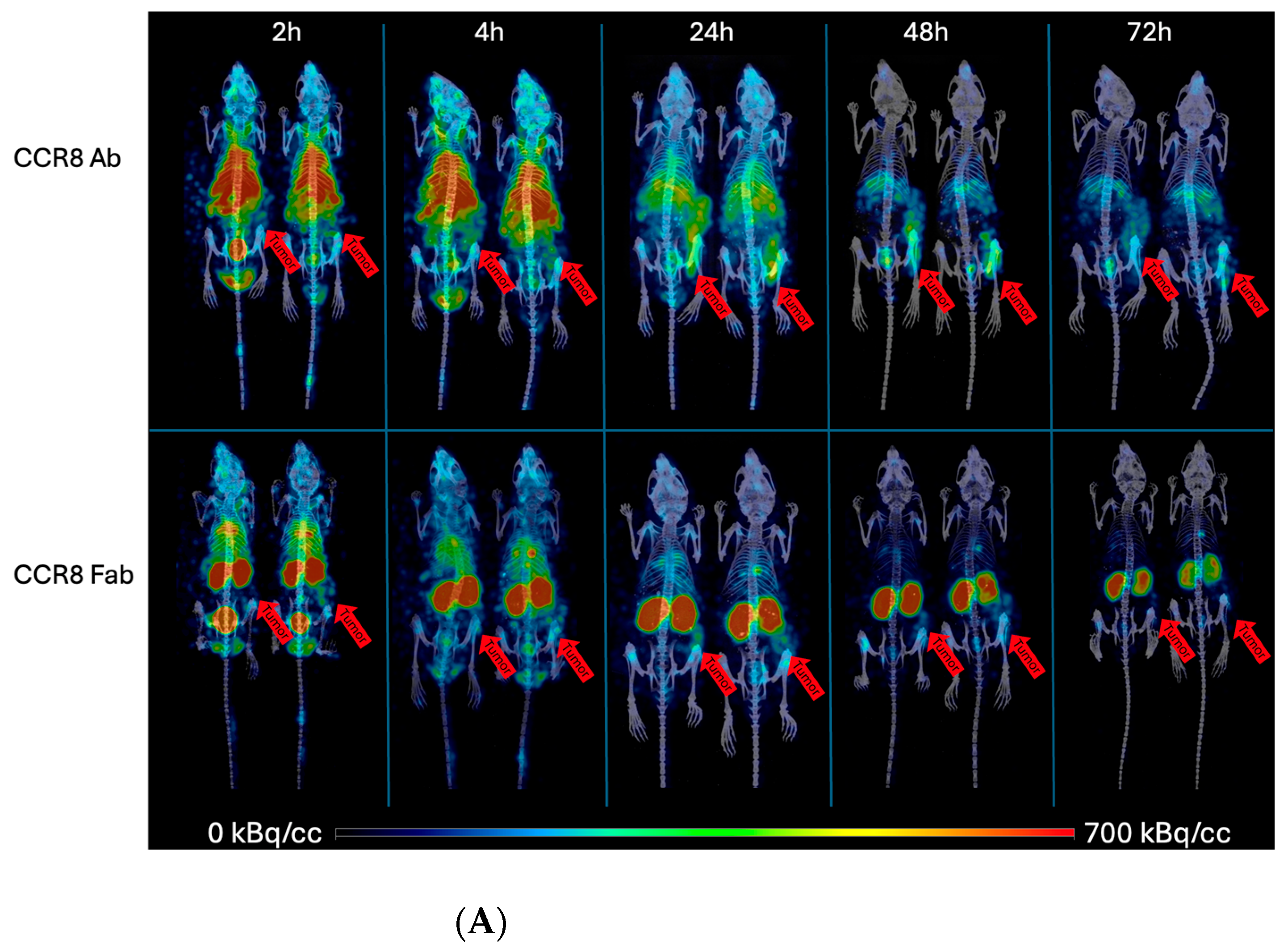
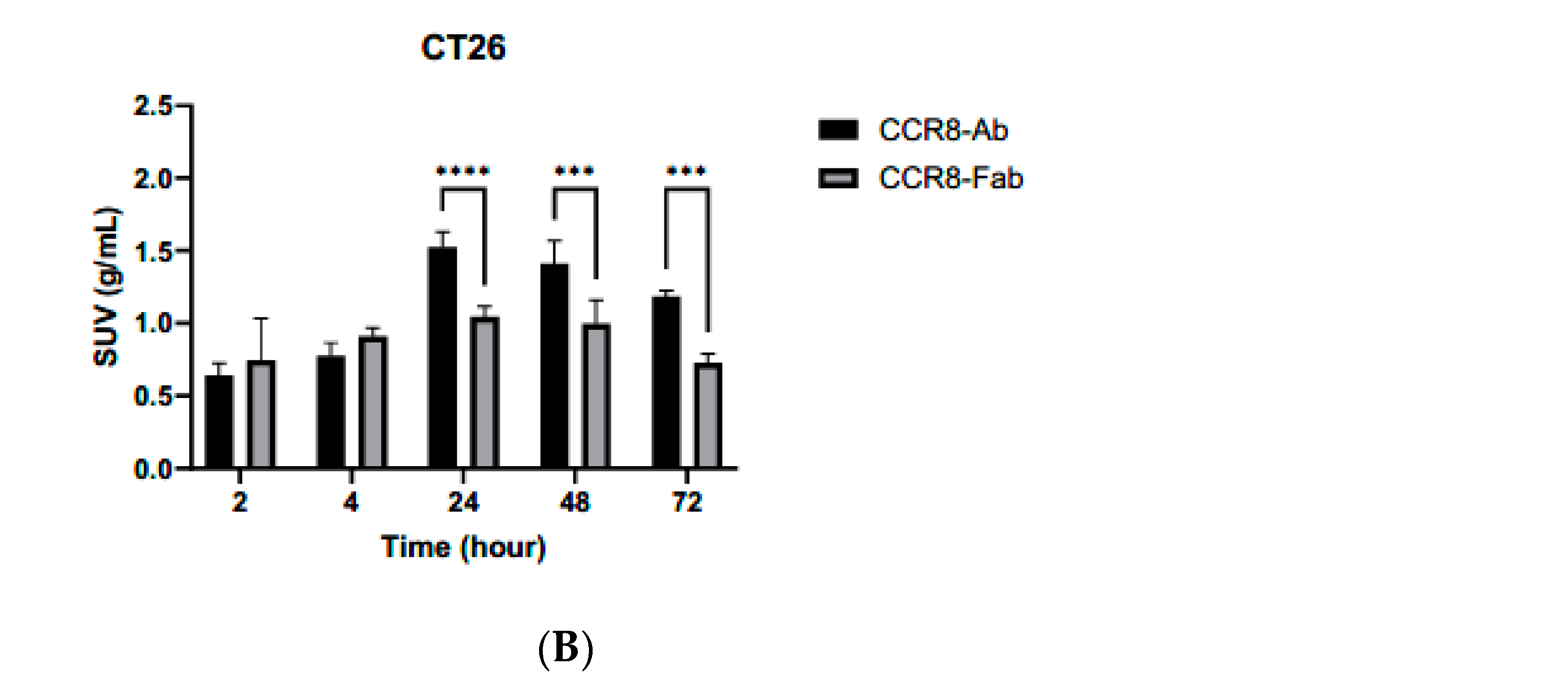
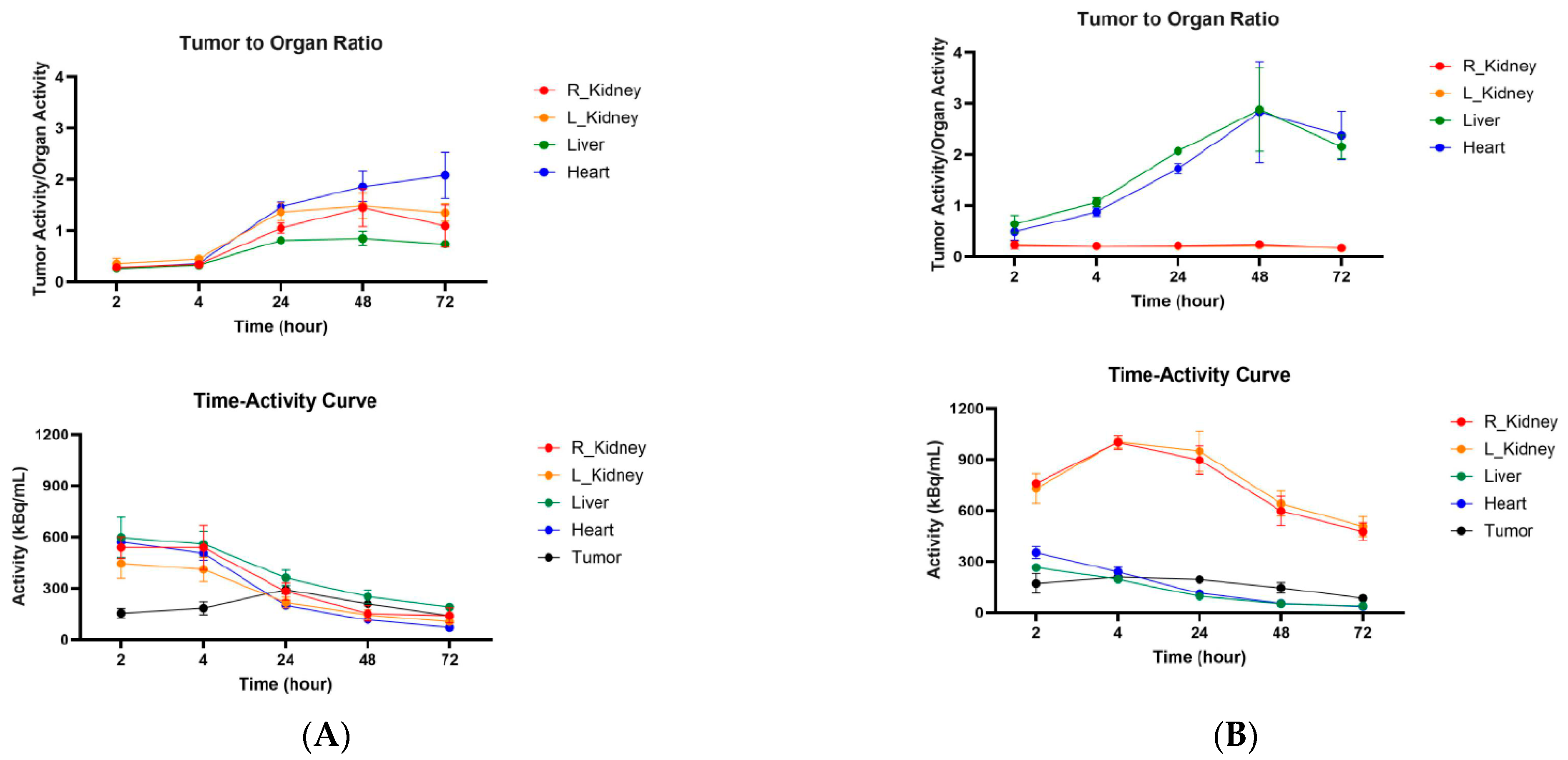
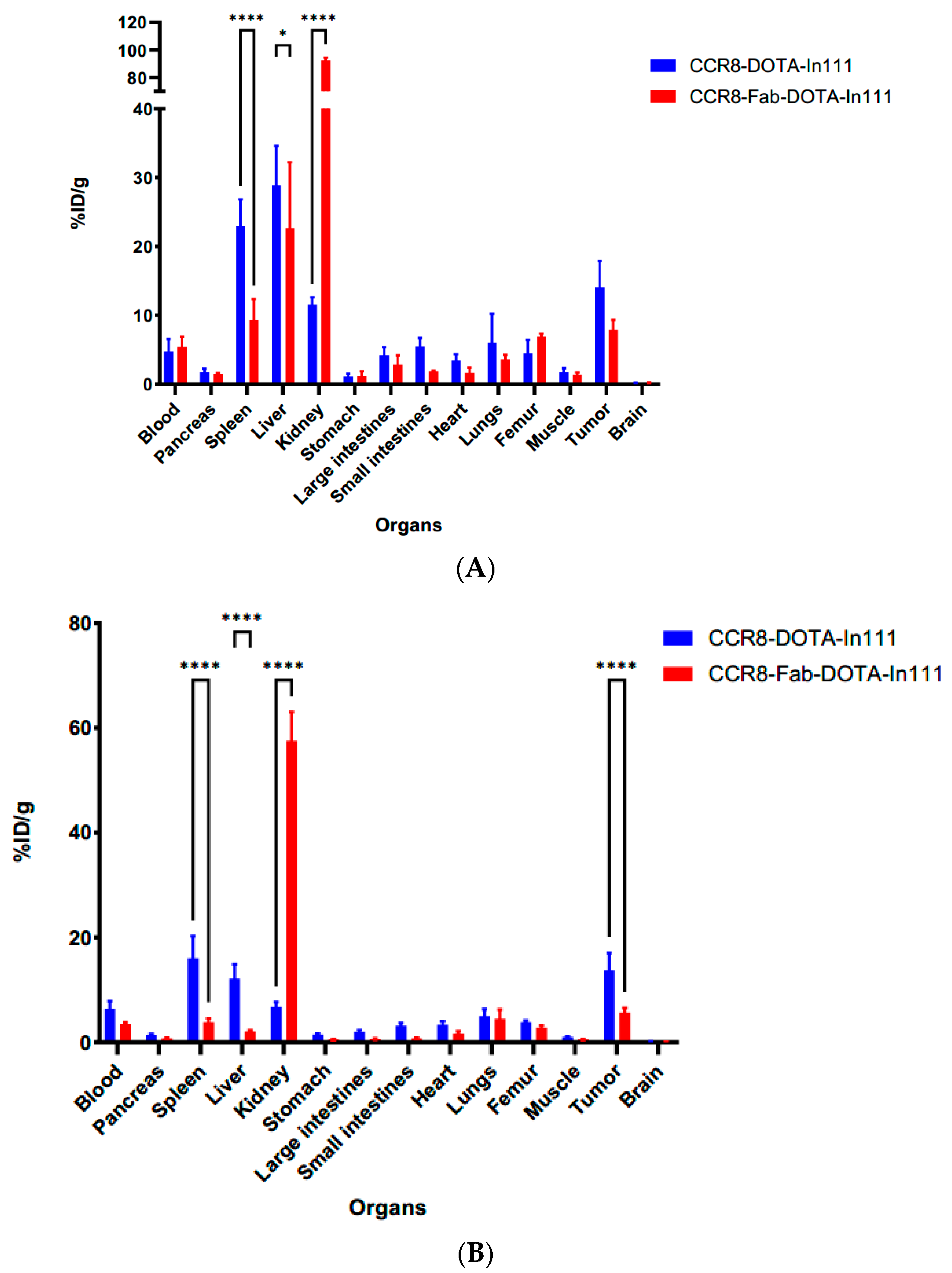
2.5. Microspect/CT Imaging and Biodistribution of 111In-Labeled Anti-CCR8 IgG and Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Tumor Models CT26 and MC38
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Fab Fragments
4.2. Conjugation of Whole IgG and Fab Fragments to DOTA, CAR Determination by MALDI MS and Radiolabeling of DOTA-Conjugated Whole IgG and Fab Fragments with 111In
4.3. Flow Cytometry of Whole IgG and Fab Fragments Binding to CCR8+ T Cells
4.4. SPECT/CT Imaging of CT26 and MC38 Tumor-Bearing Mice with 111In-Labeled Anti-CCR8 IgG and Its Fab Fragments
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ti-Tregs | Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells |
| microSPECT/CT | Micro single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| iTLC | Instant thin layer chromatography |
| CAR | Chelator-to-antibody ratio |
| MALDI MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry |
| DOTA | S-2-(4-Isothiocyanatobenzyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane tetraacetic acid |
| RIT | Radioimmunotherapy |
References
- Sakaguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ono, M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008, 133, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel, T.J.; Coukos, G.; Zou, L.; Alvarez, X.; Cheng, P.; Mottram, P.; Evdemon-Hogan, M.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Burow, M.; et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohue, Y.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: Can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, A.M.; Kiner, E.; Ergun, A.; Park, J.S.; Asinovski, N.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Kilcoyne, A.; Paoluzzi-Tomada, E.; Weissleder, R.; Mathis, D.; et al. Identification and validation of a tumor-infiltrating Treg transcriptional signature conserved across species and tumor types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10672–E10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.A.; Ling, M.F.; Leung, J.; Shreffler, W.G.; Luster, A.D. Identification of human CCR8 as a CCL18 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, H.; Dombrecht, B.; Kiss, M.; Roose, H.; Allen, E.; Van Overmeire, E.; Kancheva, D.; Martens, L.; Murgaski, A.; Bardet, P.M.; et al. Therapeutic depletion of CCR8+ tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells elicits antitumor immunity and synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Xiao, Z.; Allen, K.J.H.; Jiao, R.; Malo, M.E.; Dadachova, E. 225Actinium-armed antibody targeting CCR8+ regulatory T cells synergizes with immunotherapy to promote tumor rejection in syngeneic colorectal cancer models. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1662216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Cheung, N.K.; Press, O.W. Radioimmunotherapy of human tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegt, E.; de Jong, M.; Wetzels, J.F.; Masereeuw, R.; Melis, M.; Oyen, W.J.; Gotthardt, M.; Boerman, O.C. Renal toxicity of radiolabeled peptides and antibody fragments: Mechanisms, impact on radionuclide therapy, and strategies for prevention. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkett, B.J.; Bartlett, D.J.; McGarrah, P.W.; Lewis, A.R.; Johnson, D.R.; Berberoglu, K.; Pandey, M.K.; Packard, A.T.; Halfdanarson, T.R.; Hruska, C.B.; et al. A review of theranostics: Perspectives on emerging approaches and clinical advancements. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2023, 5, e220157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Cai, Z.; Chan, C.; Brown, M.K.; Reilly, R.M. Preclinical Comparison of [111In]In- and [225Ac]Ac-DOTA-Trastuzumab IgG, F(ab’)2 and Fab for Theranostic SPECT/CT Imaging and α-Particle Radioimmunotherapy of HER2-Positive Human Breast Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, P. On the fragmentation of monoclonal IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b from BALB/c mice. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 2895–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinman, A.W.L.; Pompano, R.R. Optimization of Enzymatic Antibody Fragmentation for Yield, Efficiency, and Binding Affinity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Gebler, J.C.; Wu, J. Papain digestion of different mouse IgG subclasses as studied by electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2000, 237, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.B.; Allen, K.J.H.; Malo, M.E.; Frank, C.; Dadachova, E. Comparison of radiobiological effects induced by radiolabeled antibodies in human cancer cells and fungal cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2025, 101, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Salapa, H.E.; Allen, K.J.H.; Levin, M.C.; Dawicki, W.; Dadachova, E. Antibody-Mediated Depletion of Autoreactive T Lymphocytes through PD-1 Improves Disease Outcomes and Visualizes T Cell Activation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2024, 212, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, R.A.; Weiner, L.M.; Davis, H.M. Antibody constructs in cancer therapy: Protein engineering strategies to improve exposure in solid tumors. Cancer 2007, 109, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, T.M.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Becker, W. Reducing the renal uptake of radiolabeled antibody fragments and peptides for diagnosis and therapy: Present status, future prospects and limitations. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 25, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Araki, M.; Tatsugi, K.; Ichinohe, K.; Uehara, T.; Arano, Y. Reduction of the Renal Radioactivity of 111In-DOTA-Labeled Antibody Fragments with a Linkage Cleaved by the Renal Brush Border Membrane Enzymes. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8600–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckel, M.; Ehrenberg, S.; Schmidt, T.; Ritt, P.; Moré, M.I.; Bergmann, R.; Mathe, D.; Zhernosekov, K. Reduced Renal Uptake of Various Radiopharmaceuticals with Sodium Paraaminohippurate Coadministration in a Rat Model. J. Nucl. Med. 2025, 66, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Dadachova, E. Combination of Radioligand Therapy and Immunotherapy: How to Make It Work in Clinic? Immunotargets Ther. 2025, 14, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.J.H.; Frank, C.; Jiao, R.; Malo, M.E.; Bello, M.; De Nardo, L.; Meléndez-Alafort, L.; Dadachova, E. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Random versus Site-Specific Conjugation of Bifunctional Chelating Agents to the CD33-Binding Antibody for Use in Alpha- and Beta-Radioimmunotherapy. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 50000–50011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Jiao, R.; Allen, K.J.H.; Frank, C.; Malo, M.E.; Dadachova, E. Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-CCR8 Full-Sized IgG and Its Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Cancer Models. Molecules 2025, 30, 4445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224445
Hu T, Jiao R, Allen KJH, Frank C, Malo ME, Dadachova E. Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-CCR8 Full-Sized IgG and Its Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Cancer Models. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224445
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Tongshuo, Rubin Jiao, Kevin J. H. Allen, Connor Frank, Mackenzie E. Malo, and Ekaterina Dadachova. 2025. "Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-CCR8 Full-Sized IgG and Its Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Cancer Models" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224445
APA StyleHu, T., Jiao, R., Allen, K. J. H., Frank, C., Malo, M. E., & Dadachova, E. (2025). Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Anti-CCR8 Full-Sized IgG and Its Fab Fragments in Murine Colorectal Cancer Models. Molecules, 30(22), 4445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224445





