Effect of Mg2+ on Enhancing Stabilization and Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Mg2+ on the Formation of MgxFe3−xO4
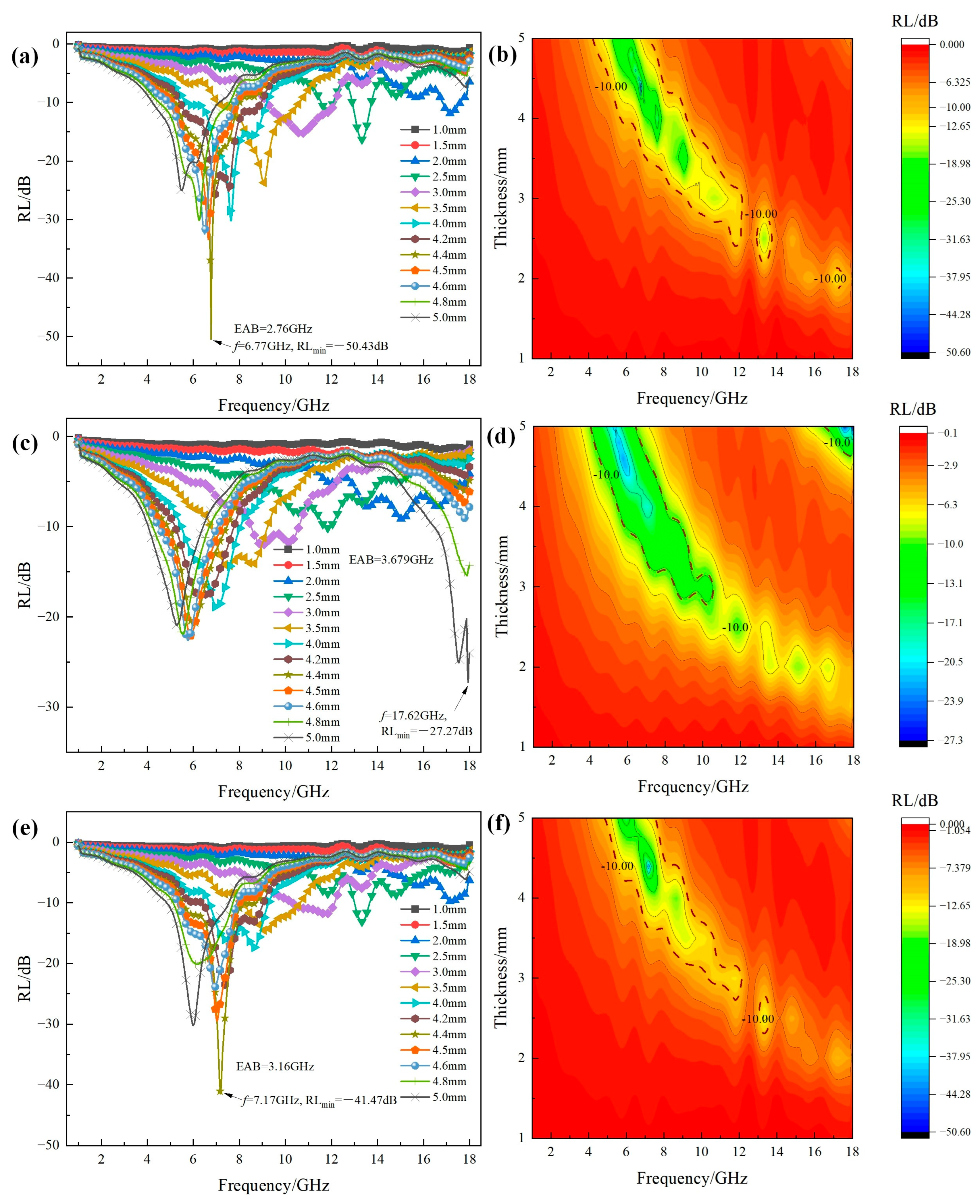
2.2. Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4
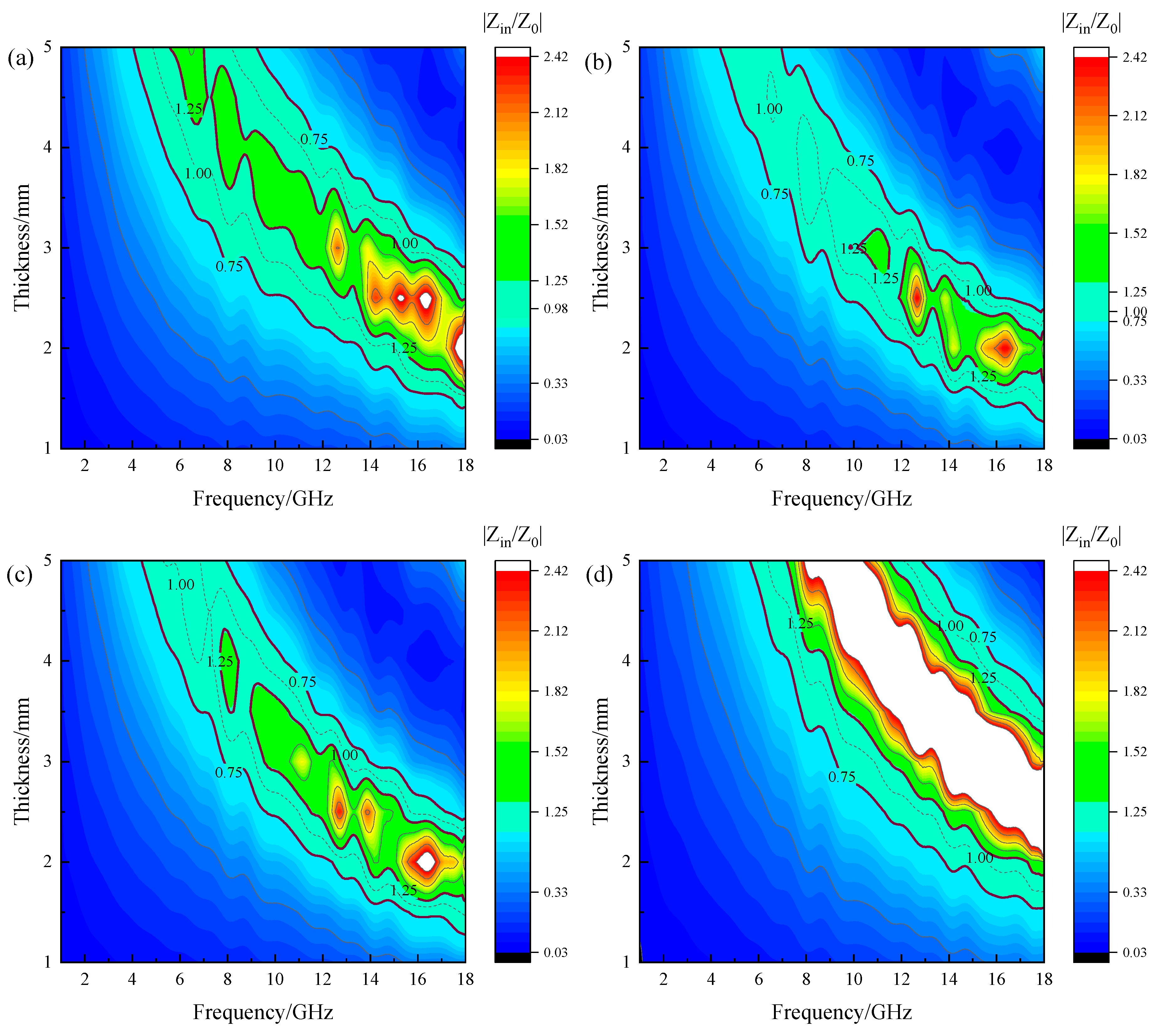
2.3. Microwave Absorption Enhancement Mechanism of Mg2+ for Magnetite
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis Procedure
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Microwave Absorption Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
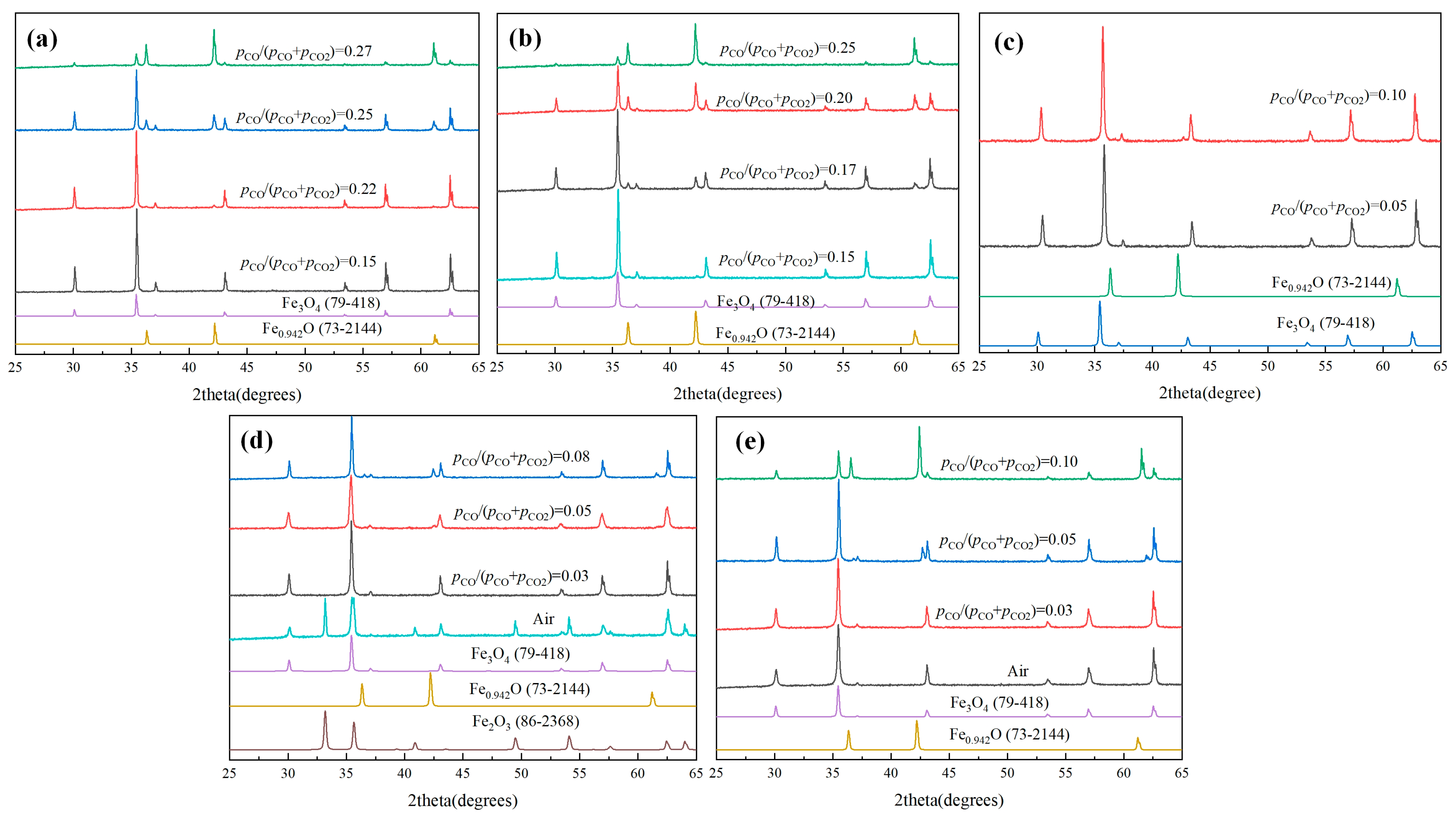
- The reaction behaviors of Fe2O3 and MgO under various pCO/(pCO + pCO2) atmosphere were investigated. It was found that Mg2+ could not only inhibit the re-oxidation of magnetite, but also promote the reduction of MgxFe3−xO4 to MgxFe1−xO, where the pCO/(pCO + pCO2) of reduction beginning for Fe3O4, Mg0.2Fe2.8O4, Mg0.4Fe2.6O4, Mg0.6Fe2.4O4, and MgFe2O4 varied from 0.22, 0.17, 0.10, 0.08, and 0.05, respectively.
- (2)
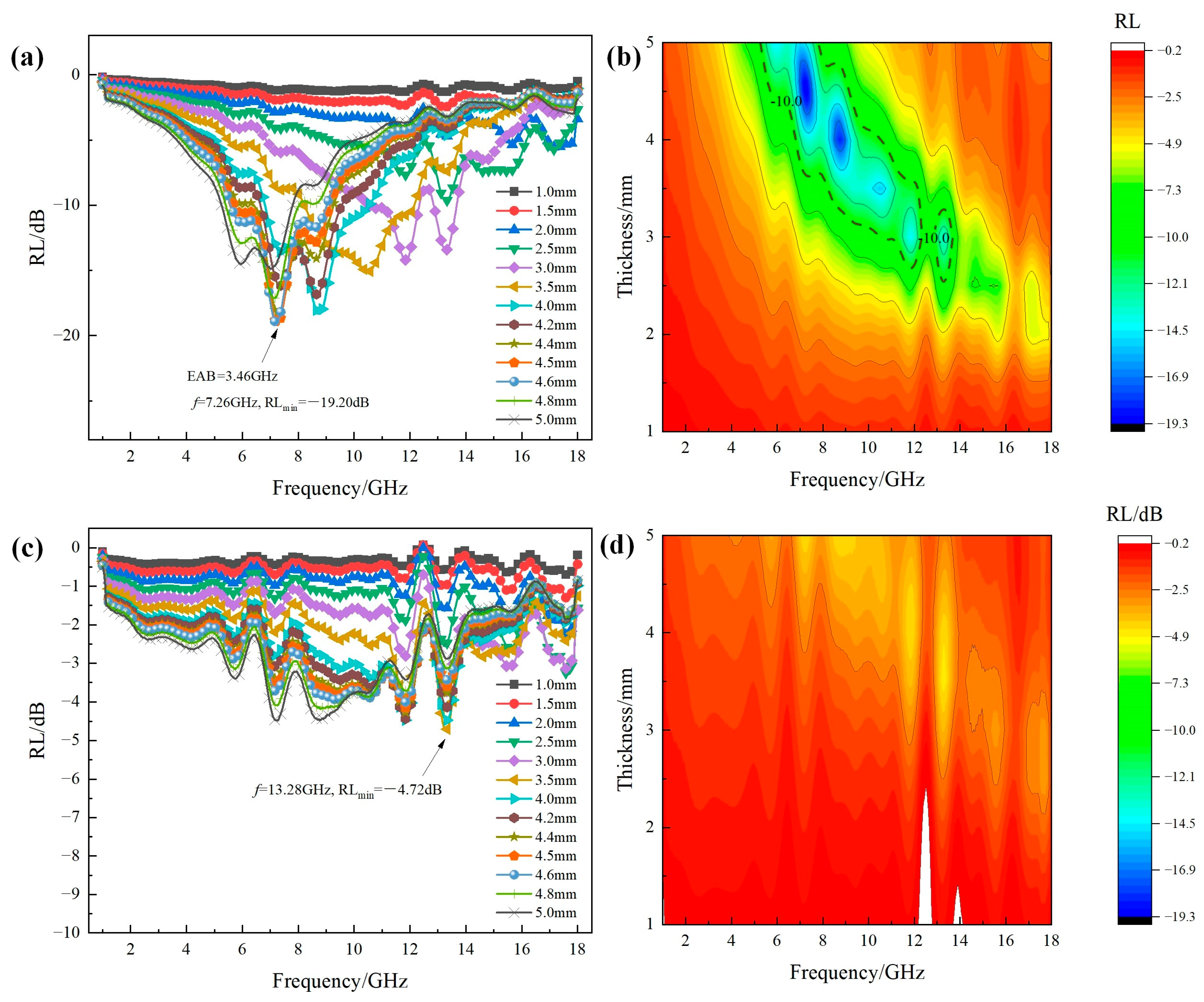
- Microwave absorption performance of MgxFe3−xO4 for the thickness of 1–5 mm was measured and analyzed. It was found that Mg2+ could significantly improve the microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4, where the RLmin value of Mg0.2Fe2.8O4 has decreased to −50.43 dB compared to −19.20 dB for Fe3O4. When the content of Mg2+ in Fe3O4 increased to x = 1 (MgFe2O4), the performance suddenly deteriorated, where the RLmin value decreased to −4.72 dB.
- (3)
- The enhancement mechanism for microwave absorption performance of MgxFe3−xO4 by Mg2+ was revealed through impedance matching, dielectric loss tangent, and magnetic loss and magnetization curves, where the Mg2+ ions could accelerate the hopping of electrons to improve the dielectric loss of magnetite, thus the impedance match could be optimized to a more ideal value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Lin, H. Preparation and research of high electromagnetic wave transmission type concrete in 5G frequency band. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.J.; Choi, J.R.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, H. Frequency tunable Ni–Ti-substituted Ba–M hexaferrite for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption in 8.2–75 GHz range. J. Alloy Compd. 2024, 976, 173019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Yang, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Yu, R.; Shui, J.; et al. Recent advances in carbon composite films for high-performance, multifunctional and intelligent electromagnetic interference shielding and electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2024, 230, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Parne, S.R.; Panda, S.S.S.; Gandi, S. Progress in microwave absorbing materials: A critical review. Adv. Colloid. Interfac. 2024, 327, 103143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lan, D.; Lin, K.; Qin, M.; Kou, K.; Wu, G.; Wu, H. Progress in low-frequency microwave absorbing materials. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 2018, 29, 17122–17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wen, G. Electromagnetic absorption by magnetic oxide nanomaterials: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 22611–22634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Rehman, S.U.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, S.; Chen, C.; Liang, T. In situ synthesis of Fe3O4 coated on iron-based magnetic microwave absorbing materials and the influence of oxide magnetic materials on microwave absorption mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 12972–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Mølhave, K.; Sun, H. Enhanced high-frequency microwave absorption of Fe3O4 architectures based on porous nanoflake. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16013–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, D. Microwave absorption enhancement of asphalt concrete with SiC-Fe3O4 mixtures modifier. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleija, M.; Platnieks, O.; Starkova, O.; Macutkevič, J.; Tsyhanok, D.; Orlova, L.; Gaidukovs, S. Evaluation of thermal conductivity models and dielectric properties in metal oxide-filled poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) composites. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Long, J.; Zheng, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Ren, X.; Lu, S.; Du, X. Preparation of nickel slag derived Fe3O4/conductive carbon black/natural rubber composites and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 35, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Liu, Z.; Sha, A.; Jia, M.; Li, Y. Microwave absorption ability of steel slag and road performance of asphalt mixtures incorporating steel slag. Materials 2020, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on microwave absorption properties of HMA containing copper slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L. Investigation on electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of copper slag-filled cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2016, 74, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Peng, J. Effects of mechanical activation on structural and microwave absorbing characteristics of high titanium slag. Powder Technol. 2015, 286, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, L.; Chen, J.; Peng, J.; Koppala, S.; Omran, M.; Chen, G. Investigations on the microwave absorption properties and thermal behavior of vanadium slag: Improvement in microwave oxidation roasting for recycling vanadium and chromium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.J.; Putnis, A. Magnetic properties of the magnetite-spinel solid solution: Curie temperatures, magnetic susceptibilities, and cation ordering. Am. Mineral. 1996, 81, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Sato, T. Reaction behavior of dolomite accompanied with formation of magnetite solid solution in iron ore sintering process. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Raza, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zou, X.; Ren, Z.; Guo, J.; Zheng, G.; Cheng, J. Dual driving strategy from micro-polarization to macroscopic conductance: Tailoring optimized low-frequency and wide-band microwave absorption in high-entropy oxides. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 235, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, D.; Ye, F.; Lu, F.; Hu, C.; Cheng, L. Effect of Sm doping on structure and microwave absorption properties of brownmillerite oxide Ca2Fe2O5. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 57997–58009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, S.; Lv, C.; Lan, D.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Multi-scale Engineering of N-doped Carbon Nanofibers with Co3O4/CeO2 Heterostructures: Tailoring Heterointerface Polarization for Microwave Absorption. Carbon 2025, 245, 120784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzębska, I.; Przystaś, J.; Pająk, O.; Błachuta, T.; Drożdż, P.; Mandal, S. Corrosion and wettability of Magnesium Orthotitanate (Mg2TiO4) refractory aggregate by copper slags with varying iron/silica ratios. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 46, 117728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Mg doped magnetite nanoparticles by recycling of titanium slag and their application of arsenate adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Cai, Y.; He, H.; Du, Y.; et al. In-situ constructing nanostructured magnesium ferrite on steel slag for Cr (VI) photoreduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; He, D. Low temperature synthesis of Fe3O4 micro-spheres and its microwave absorption properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Lai, Q.; Zeng, G.X.; Li, Y.J.; Xie, H.Z.; Kwan, A.K.H. Combined effects of micro and nano Fe3O4 on workability, strength, packing, microstructure and EM wave absorbing properties of mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, S.; Liu, D.; Bai, Z.; Xie, X.; Tian, X.; Xu, W.; Hou, W.; Meng, X.; Yang, N. Rational design of hollow Fe3O4 microspheres on Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets as highly-efficient and lightweight electromagnetic absorbers. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zeng, X.; Chen, M.; Yu, R. Controllable permittivity in 3D Fe3O4/CNTs network for remarkable microwave absorption performances. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 26801–26808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wang, L.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Pan, F.; Lu, W. Rational construction of MXene/Ferrite@C hybrids with improved impedance matching for high-performance electromagnetic absorption applications. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 129029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazirehpour, M.; Ebrahimi, S.S. Effect of aspect ratio on dielectric, magnetic, percolative and microwave absorption properties of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 638, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Deng, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, L. Natural magnetite/coke composite: A novel promising microwave absorption material. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, Z.; Jiang, T.; Fang, G.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Y. Excellent microwave absorption of Fe3O4/Ag composites attained by synergy of considerable magnetic loss and dielectric loss. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5824–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadav, M.; Bhatnagar, S.P. Particle size controlled magnetic loss in magnetite nanoparticles in RF-microwave region. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 2800208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Gul, I.H.; Khan, M.Z. Enhancement of dielectric, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Co2+-Zr4+ substituted SrFe12O19 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 4768–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qiao, M.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Kang, B.; Quan, B.; Ji, G. Evolution of dielectric loss-dominated electromagnetic patterns in magnetic absorbers for enhanced microwave absorption performances. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4006–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Guo, X.; Xiang, R.; Cheng, L.; Ye, F.; Li, Z.; Yao, Q.; Qi, H.; Long, Q. Balance dielectric and magnetic losses to enhance the microwave absorption performance of CaFe0. 5Mn0. 5O3−δ@ Co3O4@ Fe3O4. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Agarwal, A.; Sanghi, S.; Singh, P. Effect of magnesium substitution on dielectric and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite. Physica. B 2011, 406, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.M.; Dixit, A.K.; Chatterjee, R.; Goel, T.C. Complex permittivity, complex permeability and microwave absorption properties of ferrite–polymer composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 309, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, B. An assessment of the Fe-O system. J. Phase Equilibria 1991, 12, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, X.M. Displacement and Migration Behavior of Al3+ in Ca2Fe2−xAlxO5 Solid Solution During Reduction Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 2601–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
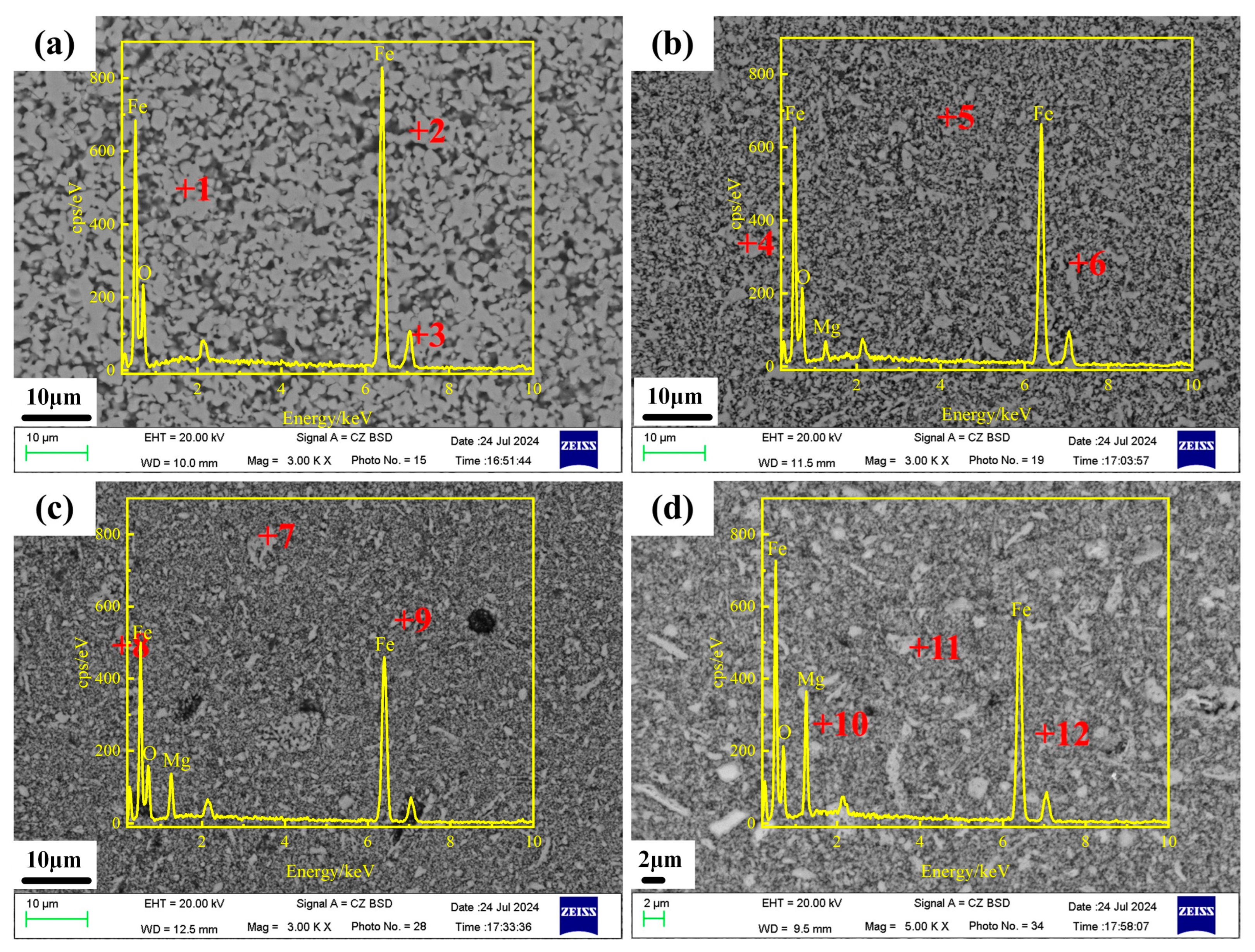





| Position | Fe/at% | Mg/at% | O/at% | Average Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0.0 | Figure 2a +1 | 51.44 | - | 48.56 | Fe: 52.08 ± 1.07 at% O: 47.92 ± 1.07 at% |
| Figure 2a +2 | 51.65 | - | 48.35 | ||
| Figure 2a +3 | 53.15 | - | 46.85 | ||
| x = 0.2 | Figure 2b +4 | 47.76 | 3.56 | 48.68 | Fe: 47.81 ± 0.46 at% O: 48.68 ± 0.52 at% Mg: 3.51 ± 0.05 at% |
| Figure 2b +5 | 48.32 | 3.52 | 48.16 | ||
| Figure 2b +6 | 47.35 | 3.46 | 49.19 | ||
| x = 0.6 | Figure 2c +7 | 43.54 | 10.62 | 45.84 | Fe: 42.61 ± 0.64 at% O: 46.21 ± 0.48 at% Mg: 11.18 ± 0.56 at% |
| Figure 2c +8 | 42.33 | 11.94 | 45.73 | ||
| Figure 2c +9 | 41.97 | 10.98 | 47.06 | ||
| x = 1.0 | Figure 2d +10 | 32.78 | 18.96 | 48.27 | Fe: 33.16 ± 0.38 at% O: 48.41 ± 0.93 at% Mg: 18.43 ± 1.32 at% |
| Figure 2d +11 | 33.41 | 17.11 | 49.48 | ||
| Figure 2d +12 | 33.29 | 19.23 | 47.48 |
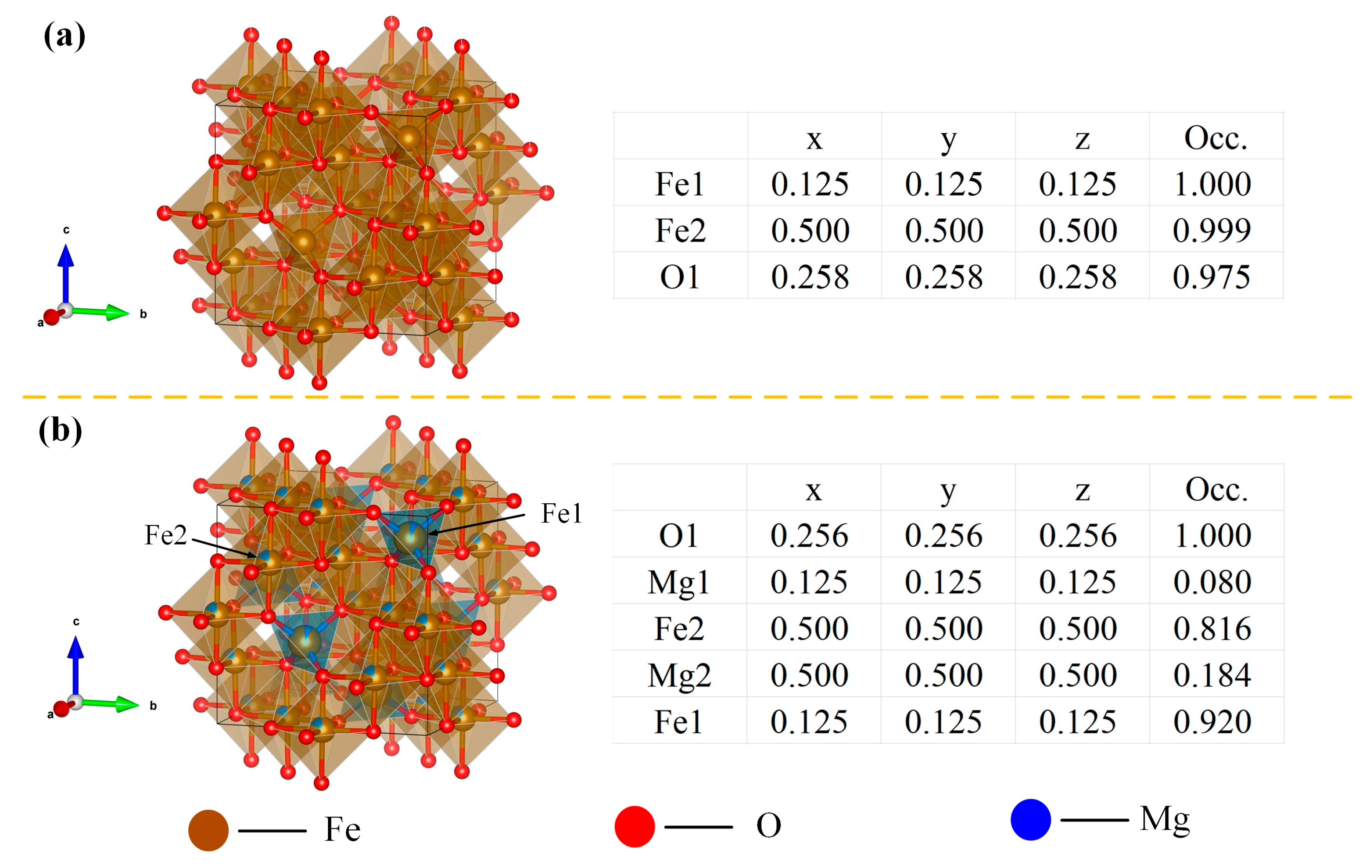
| x | Cell Parameters (Å) | Bond Angle (°) | System | Cell Volume (Å3) | RP (%) | RWP (%) | Rexp (%) | Chi2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | α = β = γ | |||||||
| 0 | 8.398 | 8.398 | 8.398 | 90 | cubic | 592.336 | 2.23 | 3.17 | 2.34 | 1.83 |
| 0.2 | 8.399 | 8.399 | 8.399 | 90 | cubic | 592.445 | 2.02 | 2.57 | 2.33 | 1.21 |
| 0.4 | 8.406 | 8.406 | 8.406 | 90 | cubic | 593.986 | 2.14 | 2.99 | 2.26 | 1.76 |
| 0.6 | 8.396 | 8.396 | 8.396 | 90 | cubic | 591.806 | 2.19 | 2.88 | 2.39 | 1.45 |
| 1.0 | 8.395 | 8.395 | 8.395 | 90 | cubic | 591.649 | 2.16 | 2.82 | 2.31 | 1.49 |
| Materials | Thickness (mm) | RLmin (dB) | EAB (GHz) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 micro-spheres | 4.0 | −20.0 | ~1.9 | [25] |
| FeSiCr@Fe3O4 | 3.7 | −51.4 | 1.7 | [7] |
| Fe3O4 nanoscale spheres | 27.0 | –33.5 | ~3.0 | [26] |
| Fe3O4/MXene | 2.5 | −42.7 | 5.7 GHz | [27] |
| Fe3O4/CNTs | 4.4 | −51 | 3.9 | [28] |
| Ti3C2TX/Fe3O4@C | 1.6 | −45.5 | 3.5 GHz | [29] |
| MgxFe3−xO4 (x=0.2) | 4.5 | −50.43 | 2.8 GHz | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, B.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X. Effect of Mg2+ on Enhancing Stabilization and Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4. Molecules 2025, 30, 4418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224418
Du Y, Sun J, Li B, Du X, Yang Y, Li X, Guo X. Effect of Mg2+ on Enhancing Stabilization and Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224418
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yu, Jianning Sun, Bin Li, Xueyan Du, Yongkun Yang, Xiaoming Li, and Xingmin Guo. 2025. "Effect of Mg2+ on Enhancing Stabilization and Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224418
APA StyleDu, Y., Sun, J., Li, B., Du, X., Yang, Y., Li, X., & Guo, X. (2025). Effect of Mg2+ on Enhancing Stabilization and Microwave Absorption Performance of MgxFe3−xO4. Molecules, 30(22), 4418. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224418







