Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): History, Current Concerns, and Future Outlook
Abstract
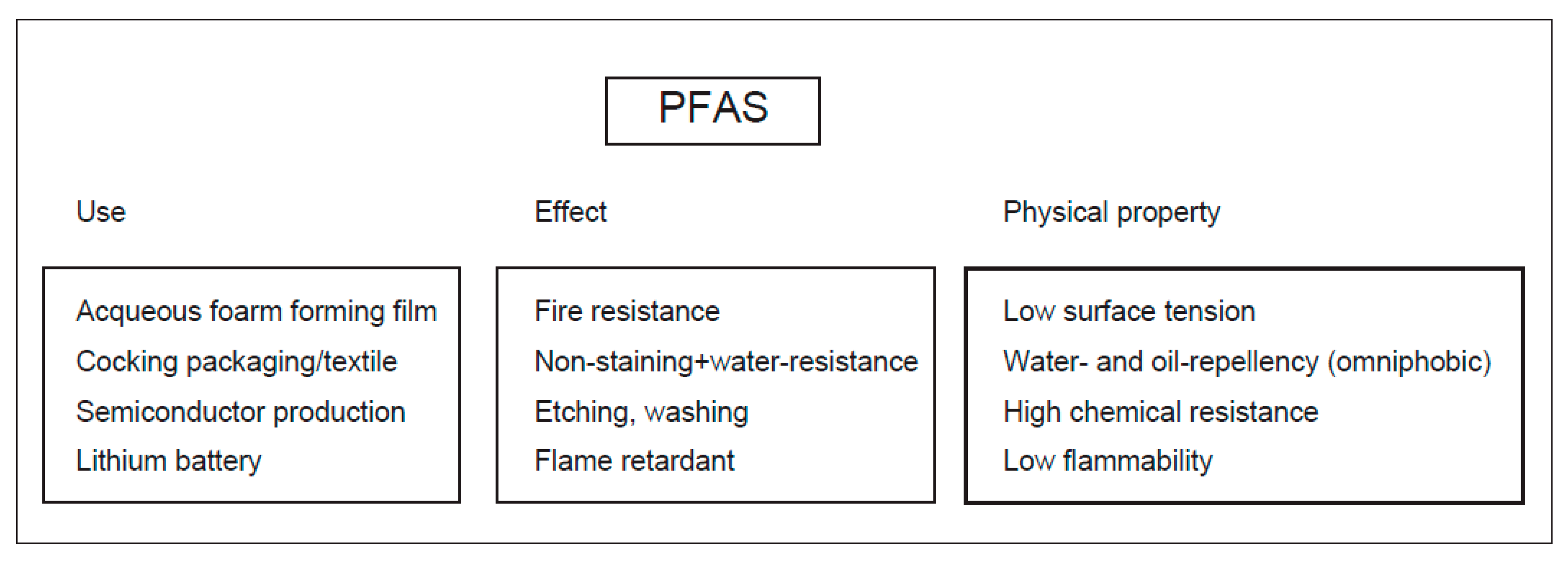
1. Introduction
1.1. History
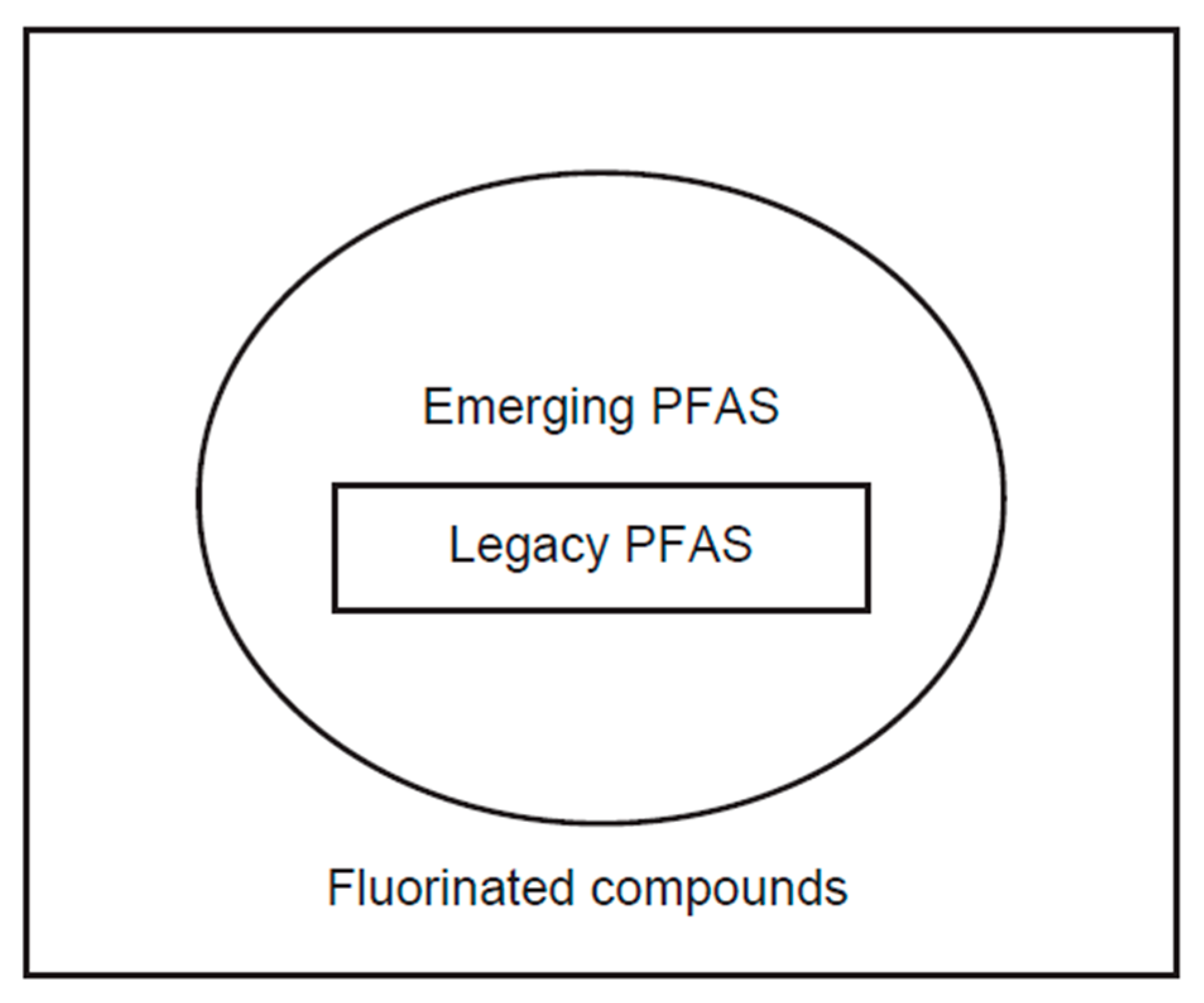
1.2. Nomenclature: Legacy PFAS and Emerging PFAS
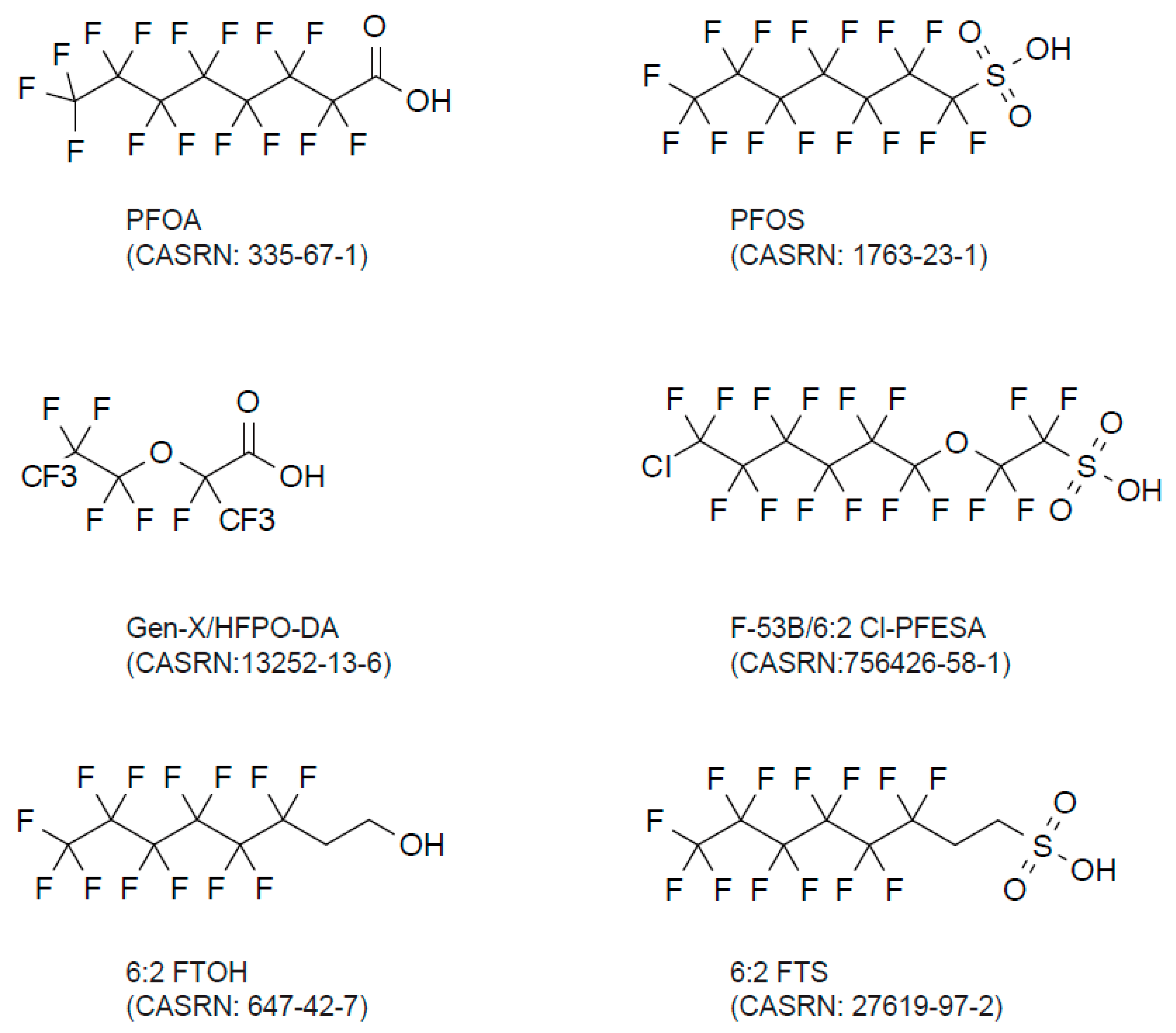
1.2.1. Legacy PFAS
| Method | Target | Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS | Legacy PFAS | Food | [13] |
| Legacy PFAS | Food | [14] | |
| Legacy PFAS | Food | [15] | |
| Legacy PFAS | Drinking water, river water, sea water | [16] | |
| Legacy PFAS | Human serum | [17] | |
| GC-MS | Volatile PFAS | Indoor air | [18] |
| LC-Q-TOF | Non-target | Food | [15] |
| GC-Q-TOF | Volatile PFAS | Water | [19] |
| EOF | Total fluoride | Soil | [20] |
| TOP + EOF | Total fluoride | Honeybees and bee-collected pollen | [21] |
| Total fluoride | Sugarcane pulp, tableware | [22] | |
| Total fluoride | Outdoor textiles, paper packaging, carpeting, and permanent baking sheets | [23] | |
| Total fluoride | Ski wax, snowmelts, and soil from skiing areas | [24] | |
| Total fluoride | Pooled human serum | [25] | |
| Total fluoride | Dust | [26] | |
| Total fluoride | Cosmetics | [27] |
1.2.2. Emerging PFAS
Gen-X and F-53B
Volatile PFAS
1.3. PFAS Synthesis
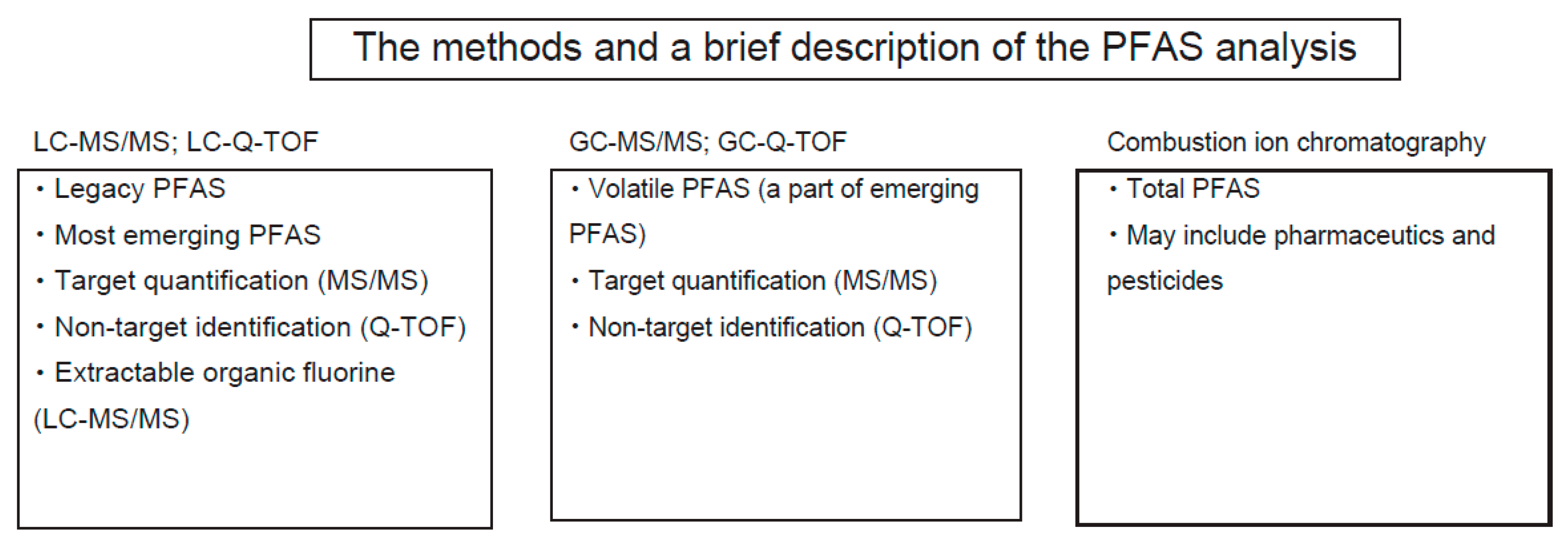
1.4. PFAS Quantification
1.4.1. LC-MS
1.4.2. GC-MS
1.4.3. Quadrupole Time-of-Flight (Q-TOF) Mass Spectrometry
1.4.4. Combustion Ion Chromatography
1.4.5. Comparison of Methodology
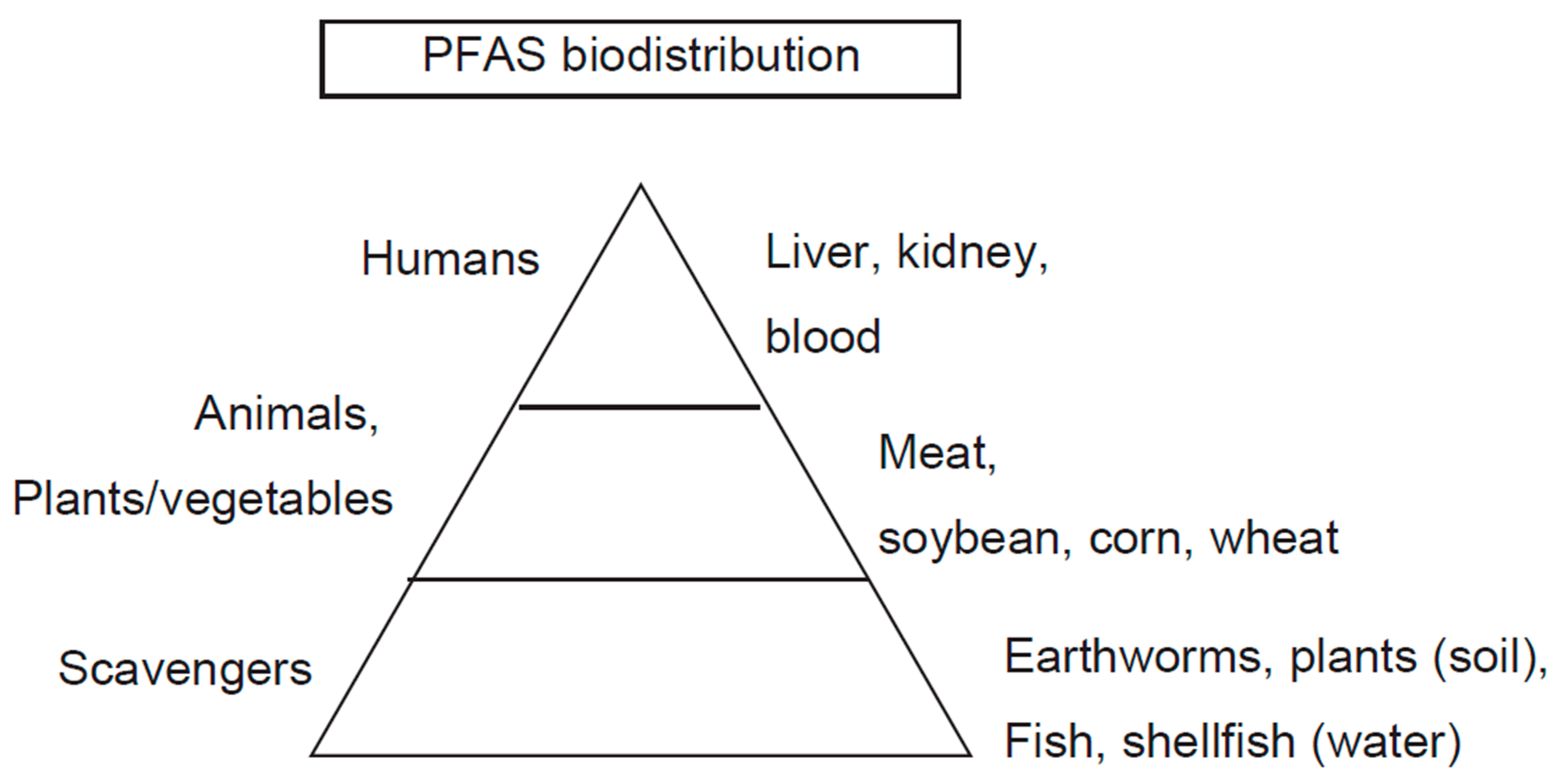
2. Distribution of PFAS
2.1. Soil/Environmental Water
2.2. Drinking Water
2.3. Food
2.4. Biodistribution in Humans
2.4.1. Blood
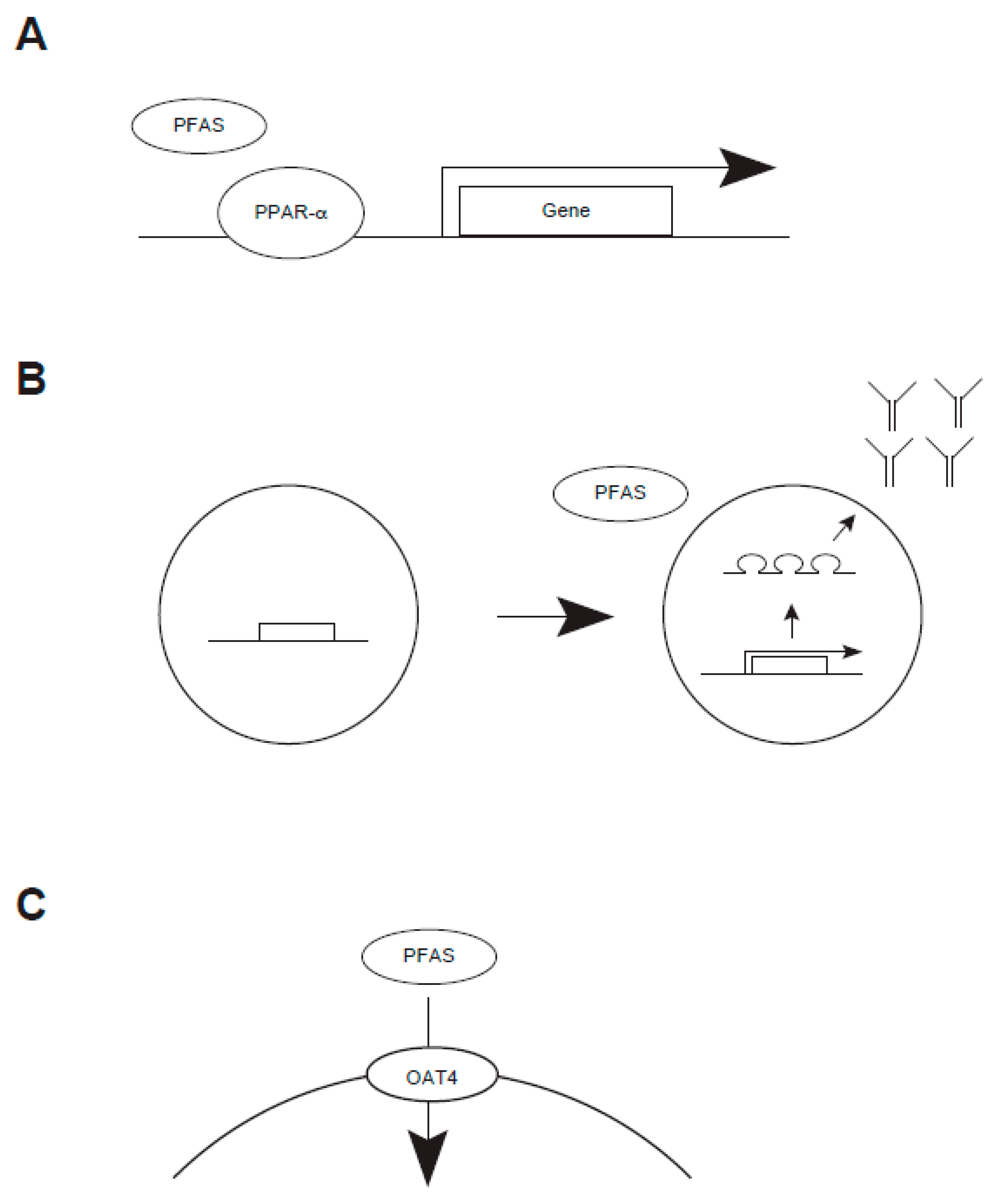
2.4.2. Liver
2.4.3. Kidney
3. Clinical Manifestations
3.1. Dyslipidemia
3.2. Attenuated Immune Response
3.3. Renal Disorder
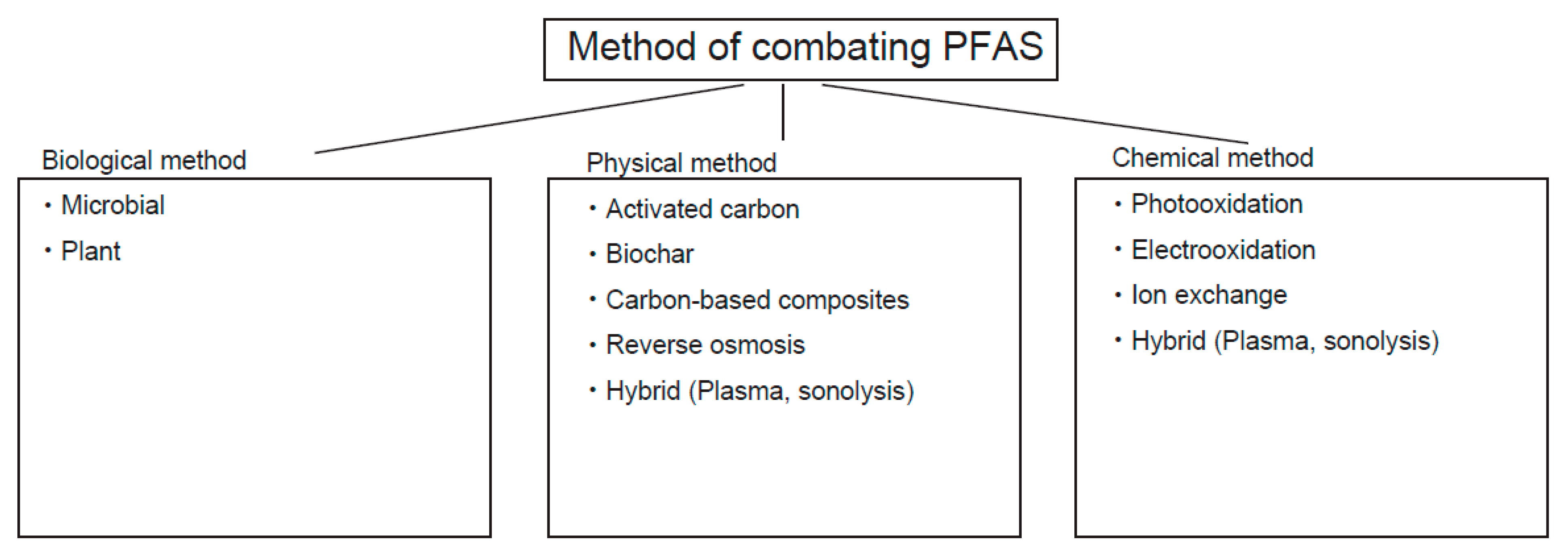
4. PFAS Mitigation
4.1. Removal Technology
Physical Removal of PFAS
4.2. Destruction Technology
4.2.1. Biodegradation
4.2.2. Chemical Degradation
Photocatalysis
Plasma-Mediated Degradation
Sonolysis
4.2.3. Emerging Methods: Hybrid Treatments
4.3. Summary of the Latest Policy Frameworks (EU, US EPA) with Implications for Monitoring
4.3.1. EU
4.3.2. US EPA
5. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
- Global method harmonization;
- Precursor-to-product transformation assessment;
- Development of fluorine-free alternatives.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFFF | aqueous film-forming foam |
| AOF | absorbable organic fluorine |
| CIC | combustion ion chromatography |
| EOF | extractable organic fluoride |
| F-53B | (2-((6-chloro-1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6-dodecafluorohexyl)oxy)-1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethanesulfonic acid) |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| Gen-X | hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid |
| HFPO-DA | hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| PFAS | Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFCA | perfluorocarboxylic acid |
| PFHxS | perfluorohexane sulfonate |
| PFOS | perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| PFOA | perfluorooctanic acid |
| PFSA | perfluorosulfuric acid |
| Q-TOF | quadrupole time-of-flight |
| QuEChERS | Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, Safe |
| TF | total fluorine |
| TOP | total oxidizable precursor |
| WWTP | wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Evich, M.G.; Davis, M.J.B.; McCord, J.P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J.A.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Speth, T.F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M.J.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment. Science 2022, 375, 9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Smaoui, S.; Duffill, J.; Marandi, B.; Varzakas, T. Research Progress in Current and Emerging Issues of PFASs’ Global Impact: Long-Term Health Effects and Governance of Food Systems. Foods 2025, 14, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulcan, R.X.S.; Yarleque, C.M.H.; Lu, X.; Yeerkenbieke, G.; Herrera, V.O.; Gunarathne, V.; Yánez-Jácome, G.S. Characterization of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Chinese River and Lake Sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Legacy Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Alternatives (Short-Chain Analogues, F-53B, GenX and FC-98) in Residential Soils of China: Present Implications of Replacing Legacy PFASs. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghese, M.M.; Feng, J.; Liang, C.L.; Kienapple, N.; Manz, K.E.; Fisher, M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Atlas, E.; Braun, J.M.; Bouchard, M.F.; et al. Legacy, Alternative, and Precursor PFAS and Associations with Lipids and Liver Function Biomarkers: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Adult Females in the MIREC-ENDO Study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2025, 267, 114592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liwara, D.J.; Araújo, A.R.L.; Pavlov, A.; Johansen, J.E.; Liu, H.; Koekkoek, J.; Heinzelmann, M.; de Boer, J.; Leonards, P.E.G.; Brandsma, S. Analysis of Legacy PFAS and Potential Precursors in Curtain, Sofa, and Carpet Fabric Samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 993, 180006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, L.; Espartero, L.; Yamada, M.; Ford, J.; Owens, G.; Prow, T.; Juhasz, A. Health-Related Toxicity of Emerging per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Comparison to Legacy PFOS and PFOA. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; An, X.; Liang, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, C. Shift from Legacy to Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances for Watershed Management along the Coast of China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, W.; Léandri-Breton, D.J.; Corbeau, A.; Herzke, D.; Moe, B.; Nikiforov, V.A.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Chastel, O. A Bad Start in Life? Maternal Transfer of Legacy and Emerging Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances to Eggs in an Arctic Seabird. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6091–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, J.; Guckert, M.; Berger, U.; Fu, Q.; Nödler, K.; Nürenberg, G.; Koschorreck, J.; Schulze, J.; Reemtsma, T. Long Term Trends of Legacy Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Their Substitutes and Precursors in Archived Wildlife Samples from the German Environmental Specimen Bank. Environ. Int. 2025, 201, 109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hong, D.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Yang, B.; Huang, X.; Song, S.; et al. Novel and Legacy Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Indoor Dust from Urban, Industrial, and e-Waste Dismantling Areas: The Emergence of PFAS Alternatives in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, K.H.; Seo, J.I.; Kim, S.M.; Shiea, J.; Yoo, H.H. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): Trends in Mass Spectrometric Analysis for Human Biomonitoring and Exposure Patterns from Recent Global Cohort Studies. Environ. Int. 2024, 194, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroski, K.M.; Sapozhnikova, Y. Method Development and Validation for Analysis of 74 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food of Animal Origin Using QuEChERSER Method and LC-MS/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1364, 344216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genualdi, S.; Beekman, J.; Carlos, K.; Fisher, C.M.; Young, W.; DeJager, L.; Begley, T. Analysis of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Processed Foods from FDA’s Total Diet Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.B.; Sapozhnikova, Y. Comparison and Validation of the QuEChERSER Mega-Method for Determination of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Foods by Liquid Chromatography with High-Resolution and Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1230, 340400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lin, H.; Yamazaki, E.; Eun, H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Quality Assurance and Quality Control of Solid Phase Extraction for PFAS in Water and Novel Analytical Techniques for PFAS Analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Feldmann, J.; Prieler, E.; Brodschneider, R. PFAS in the Buzz: Seasonal Biomonitoring with Honey Bees (Apis Mellifera) and Bee-Collected Pollen. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-McDevitt, M.E.; Becanova, J.; Blum, A.; Bruton, T.A.; Vojta, S.; Woodward, M.; Lohmann, R. The Air That We Breathe: Neutral and Volatile PFAS in Indoor Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corviseri, M.C.; Polidoro, A.; De Poli, M.; Stevanin, C.; Chenet, T.; D’Anna, C.; Cavazzini, A.; Pasti, L.; Franchina, F.A. Targeted Determination of Volatile Fluoroalkyl Pollutants and Non-Targeted Screening for Environmental Monitoring. Talanta 2025, 292, 127944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z. Migration Safety of Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Sugarcane Pulp Tableware: Residue Analysis and Takeout Simulation Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, P.; Schinnen, A.; Riedel, M.; Sommerfeld, T.; Sawal, G.; Bandow, N.; Vogel, C.; Kalbe, U.; Simon, F.G. Investigation of PH-Dependent Extraction Methods for PFAS in (Fluoropolymer-Based) Consumer Products: A Comparative Study between Targeted and Sum Parameter Analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, V.; Andrade Costa, L.C.; Rondan, F.S.; Matic, E.; Mesko, M.F.; Kindness, A.; Feldmann, J. Per and Polyfluoroalkylated Substances (PFAS) Target and EOF Analyses in Ski Wax, Snowmelts, and Soil from Skiing Areas. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2023, 25, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, L.; Plassmann, M.; Benskin, J.P.; Coêlho, A.C.M.F.; Nøst, T.H.; Rylander, C.; Nikiforov, V.; Sandanger, T.M.; Herzke, D. Fluorine Mass Balance, Including Total Fluorine, Extractable Organic Fluorine, Oxidizable Precursors, and Target Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, in Pooled Human Serum from the Tromsø Population in 1986, 2007, and 2015. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14849–14860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.S.; Pickard, H.M.; Sunderland, E.M.; Allen, J.G. Organic Fluorine as an Indicator of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Dust from Buildings with Healthier versus Conventional Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17090–17099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pütz, K.W.; Namazkar, S.; Plassmann, M.; Benskin, J.P. Are Cosmetics a Significant Source of PFAS in Europe? Product Inventories, Chemical Characterization and Emission Estimates. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2022, 24, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, S.; Hkudaigulov, G.; Sharipov, D.; Starikov, S. Probable New Species of Bacteria of the Genus Pseudomonas Accelerates and Enhances the Destruction of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids. Toxics 2024, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.D.; Coon, C.M.; Doherty, M.E.; McHugh, E.A.; Warner, M.C.; Walters, C.L.; Orahood, O.M.; Loesch, A.E.; Hatfield, D.C.; Sitko, J.C.; et al. Engineering and Characterization of Dehalogenase Enzymes from Delftia Acidovorans in Bioremediation of Perfluorinated Compounds. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2022, 7, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, G.; Liu, J.; Duy, S.V.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of F-53B, Gen-X, ADONA, and Emerging Fluoroalkylether Substances in Environmental and Biomonitoring Samples: A Review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 23, e00066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.A.; Cooper, J.; Koh-Fallet, S.E.; Kabadi, S.V. Comparative Analysis of the Physicochemical, Toxicokinetic, and Toxicological Properties of Ether-PFAS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 422, 115531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.A.; Aungst, J.; Cooper, J.; Bandele, O.; Kabadi, S.V. Comparative Analysis of the Toxicological Databases for 6:2 Fluorotelomer Alcohol (6:2 FTOH) and Perfluorohexanoic Acid (PFHxA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 138, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xing, L.; Chu, J. Global Ocean Contamination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Review of Seabird Exposure. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.; Junaid, M.; Sultan, M.; Yoganandham, S.T.; Chuan, O.M. The Untold Story of PFAS Alternatives: Insights into the Occurrence, Ecotoxicological Impacts, and Removal Strategies in the Aquatic Environment. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, R.A.; Mullin, E.J.; Spink, D.C. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Analytical Techniques, Environmental Fate, and Health Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.U.; Hærvig, K.K.; Flachs, E.M.; Bonde, J.P.; Lindh, C.; Hougaard, K.S.; Toft, G.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Tøttenborg, S.S. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Male Reproductive Function in Young Adulthood; a Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, N.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Pan, B.; Yu, H.; Wei, S. Comprehensive Exposure Studies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the General Population: Target, Nontarget Screening, and Toxicity Prediction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14617–14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. On-Line Solid Phase Extraction-Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole/Orbitrap High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Determination of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Human Serum. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1212, 123484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, I.G.; Ekpe, O.D.; Megson, D.; Bruce-Vanderpuije, P.; Sandau, C.D. A Systematic Review of Methods for the Analysis of Total Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 967, 178644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.F.; Isobe, T.; Iwai-Shimada, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishihama, Y.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiyama, M.; Michikawa, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Nitta, H.; et al. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Maternal Serum: Method Development and Application in Pilot Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; van Hees, P.; Karlsson, P.; Jiao, E.; Filipovic, M.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yeung, L.W.Y. What We Learn from Using Mass Balance Approach and Oxidative Conversion—A Case Study on PFAS Contaminated Soil Samples. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 376, 126420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genualdi, S.; Srigley, C.; Young, W.; De Jager, L. Investigation of Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Isomer Profiles in Naturally Contaminated Food Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 16746–16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, Fate and Transport of Perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Mottaghipisheh, J.; Verma, S.; Singh, R.P.; Muthukumaran, S.; Navaratna, D.; Ahrens, L. PFAS Contamination in Key Indian States: A Critical Review of Environmental Impacts, Regulatory Challenges and Predictive Exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Donald, W.A. Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Sydney Drinking Water. Chemosphere 2025, 385, 144611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA); OW. Analysis of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Aqueous, Solid, Biosolids, and Tissue Samples by LC-MS/MS; Ost Method 1633, Revision A; The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bangma, J.; Barry, K.M.; Fisher, C.M.; Genualdi, S.; Guillette, T.C.; Huset, C.A.; McCord, J.; Ng, B.; Place, B.J.; Reiner, J.L.; et al. PFAS Ghosts: How to Identify, Evaluate, and Exorcise New and Existing Analytical Interference. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangma, J.; McCord, J.; Giffard, N.; Buckman, K.; Petali, J.; Chen, C.; Amparo, D.; Turpin, B.; Morrison, G.; Strynar, M. Analytical Method Interferences for Perfluoropentanoic Acid (PFPeA) and Perfluorobutanoic Acid (PFBA) in Biological and Environmental Samples. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateia, M.; Chiang, D.; Cashman, M.; Acheson, C. Total Oxidizable Precursor (TOP) Assay─Best Practices, Capabilities and Limitations for PFAS Site Investigation and Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, K.; de Falco, G.; Fernando, E.; Boufadel, M.C.; Zhang, Z.; Sarkar, D. Assessing PFAS and Their Precursor Transformation in a Landfill Leachate-Impacted Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water Environ. Res. 2025, 97, 70172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pérez-Cejuela, H.; Williams, M.L.; McLeod, C.; Gionfriddo, E. Effective Preconcentration of Volatile Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Gas and Aqueous Phase via Solid Phase Microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1345, 343746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Dada, T.K.; Whelan, A.; Cannon, P.; Sheehan, M.; Reeves, L.; Antunes, E. Microbial and Thermal Treatment Techniques for Degradation of PFAS in Biosolids: A Focus on Degradation Mechanisms and Pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nxumalo, T.; Akhdhar, A.; Mueller, V.; Simon, F.; von der Au, M.; Cossmer, A.; Pfeifer, J.; Krupp, E.M.; Meermann, B.; Kindness, A.; et al. EOF and Target PFAS Analysis in Surface Waters Affected by Sewage Treatment Effluents in Berlin, Germany. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyle, B.J.; Pennoyer, E.H.; Vojta, S.; Becanova, J.; Islam, M.; Webster, T.F.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; Lohmann, R.; Westerhoff, P.; Schaefer, C.E.; et al. High Organofluorine Concentrations in Municipal Wastewater Affect Downstream Drinking Water Supplies for Millions of Americans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2417156122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.G.; Lim, H.J.; Na, S.H.; Choi, B.I.; Shin, D.S.; Chung, S.Y. Biodegradation of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) as an Emerging Contaminant. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, M. Enriching Fluorotelomer Carboxylic Acids-Degrading Consortia from Sludges and Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Lee, M.; O’Carroll, D.; McDonald, J.; Osborne, K.; Khan, S.; Pickford, R.; Coleman, N.; O’Farrell, C.; Richards, S.; et al. Biotransformation of 6:2/4:2 Fluorotelomer Alcohols by Dietzia Aurantiaca J3: Enzymes and Proteomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, V.; Holland, S.; Bhardwaj, S.; McDonald, J.; Khan, S.; O’Carroll, D.; Pickford, R.; Richards, S.; O’Farrell, C.; Coleman, N.; et al. Aerobic Biotransformation of 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonate by Dietzia Aurantiaca J3 under Sulfur-Limiting Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonne, C.; Bank, M.S.; Jenssen, B.M.; Cieseielski, T.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Lam, S.S.; Hansen, M.; Bossi, R.; Gustavson, K.; Dietz, R. PFAS Pollution Threatens Ecosystems Worldwide. Science 2023, 379, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaymat, T.; Robey, N.; Krause, M.; Larson, J.; Weitz, K.; Parvathikar, S.; Phelps, L.; Linak, W.; Burden, S.; Speth, T.; et al. A Critical Review of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Landfill Disposal in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simones, T.L.; Evans, C.; Goossen, C.P.; Kersbergen, R.; Mallory, E.B.; Genualdi, S.; Young, W.; Smith, A.E. Uptake of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Mixed Forages on Biosolid-Amended Farm Fields. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 23108–23117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.H.; Zuverza-Mena, N.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Nason, S.L.; Thomas, S.; White, J.C. PFAS Remediation in Soil: An Evaluation of Carbon-Based Materials for Contaminant Sequestration. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344, 123335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerss, H.; Schramm, T.R.; Sun, L.; Guo, C.; Tang, J.; Ebinghaus, R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Chinese and German River Water—Point Source- and Country-Specific Fingerprints Including Unknown Precursors. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Sivaram, A.K.; Megharaj, M.; Webb, L.; Adhikari, S.; Thomas, M.; Surapaneni, A.; Moon, E.M.; Milne, N.A. Investigation on Removal of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA), Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS), Perfluorohexane Sulfonate (PFHxS) Using Water Treatment Sludge and Biochar. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, N.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Hanari, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Biochar from Paddy Field—A Solution to Reduce PFAS Pollution in the Environment. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.; Patton, H.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Guevara, R.; McCray, J.; Krometis, L.A.; Cohen, A. Microbiological and Chemical Drinking Water Contaminants and Associated Health Outcomes in Rural Appalachia, USA: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahne, H.; Gerstner, D.; Völkel, W.; Schober, W.; Aschenbrenner, B.; Herr, C.; Heinze, S.; Quartucci, C. Human Biomonitoring Follow-up Study on PFOA Contamination and Investigation of Possible Influencing Factors on PFOA Exposure in a German Population Originally Exposed to Emissions from a Fluoropolymer Production Plant. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2024, 259, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukioka, S.; Tanaka, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Echigo, S.; Kärrman, A.; Fujii, S. A Profile Analysis with Suspect Screening of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Firefighting Foam Impacted Waters in Okinawa, Japan. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.; Wiggins, S.; Limm, W.; Fisher, C.M.; Dejager, L.; Genualdi, S. Analysis of Per- and Poly(Fluoroalkyl) Substances (PFASs) in Highly Consumed Seafood Products from U.S. Markets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13545–13553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genualdi, S.; Young, W.; Peprah, E.; Srigley, C.; Fisher, C.M.; Ng, B.; deJager, L. Analyte and Matrix Method Extension of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Food and Feed. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbo, N.; Stoiber, T.; Naidenko, O.V.; Andrews, D.Q. Locally Caught Freshwater Fish across the United States Are Likely a Significant Source of Exposure to PFOS and Other Perfluorinated Compounds. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, H.L.; Blazer, V.S.; Lord, E.; Hurley, S.T.; LeBlanc, D.R. Occurrence and Tissue Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Fishes from Waterbodies with Point and Non-Point Sources in Massachusetts, USA. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 287, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhoff, N.; Bernsmann, T.; Esselen, M.; Stahl, T. A Sensitive Method for the Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Food and Food Contact Material Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, R.; Hagen, T.G.; Champness, D. Accumulation of PFAS by Livestock–Determination of Transfer Factors from Water to Serum for Cattle and Sheep in Australia. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Tuda, H.; Kato, Y.; Kimura, O.; Endo, T.; Harada, K.H.; Koizumi, A.; Haraguchi, K. Levels and Profiles of Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids in Pacific Cod from 14 Sites in the North Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Goodrich, J.A.; Costello, E.; Walker, D.I.; Cardenas-Iniguez, C.; Chen, J.C.; Alderete, T.L.; Valvi, D.; Rock, S.; Eckel, S.P.; et al. Examining Disparities in PFAS Plasma Concentrations: Impact of Drinking Water Contamination, Food Access, Proximity to Industrial Facilities and Superfund Sites. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hron, L.M.C.; Wöckner, M.; Fuchs, V.; Fembacher, L.; Aschenbrenner, B.; Herr, C.; Schober, W.; Heinze, S.; Völkel, W. Monitoring of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Human Blood Samples Collected in Three Regions with Known PFAS Releases in the Environment and Three Control Regions in South Germany. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 3727–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toms, L.M.L.; Bräunig, J.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Phillips, S.; Hobson, P.; Aylward, L.L.; Kirk, M.D.; Mueller, J.F. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Australia: Current Levels and Estimated Population Reference Values for Selected Compounds. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Nakayama, S.F.; Nishihama, Y.; Isobe, T. Determinants of Plasma Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances during Pregnancy: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 294, 118107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Rakovic, J.; Ekdahl, S.; Kallenborn, R. Environmental Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) on Svalbard: Local Sources and Long-Range Transport to the Arctic. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokranov, A.K.; Ransom, K.M.; Bexfield, L.M.; Lindsey, B.D.; Watson, E.; Dupuy, D.I.; Stackelberg, P.E.; Fram, M.S.; Voss, S.A.; Kingsbury, J.A.; et al. Predictions of Groundwater PFAS Occurrence at Drinking Water Supply Depths in the United States. Science 2024, 386, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheringer, M. Innovate beyond PFAS. Science 2023, 381, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Harada, K.H. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Toxicokinetics, Exposure and Health Risks. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2025, 50, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, S.J.; Smith, D.J.; Scholljegerdes, E.; Ivey, S.; Young, W.; Genualdi, S.; Dejager, L.; Snyder, A.; Esteban, E.; Johnston, J.J. Plasma and Skin Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Levels in Dairy Cattle with Lifetime Exposures to PFAS-Contaminated Drinking Water and Feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15945–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Niisoe, T.; Takanaka, K.; Kamiyama, S.; Watanabe, T.; Moon, C.S.; Yang, H.R.; Hung, N.N.; Koizumi, A. Odd-Numbered Perfluorocarboxylates Predominate over Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Serum Samples from Japan, Korea and Vietnam. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleman, S.R.; Li, M.; Fujitani, T.; Harada, K.H. Plasma Eicosapentaenoic Acid, a Biomarker of Fish Consumption, Is Associated with Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acid Exposure in Residents of Kyoto, Japan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2023, 28, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Koizumi, A.; Saito, N.; Inoue, K.; Yoshinaga, T.; Date, C.; Fujii, S.; Hachiya, N.; Hirosawa, I.; Koda, S.; et al. Historical and Geographical Aspects of the Increasing Perfluorooctanoate and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Contamination in Human Serum in Japan. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, I.; Bonato, T.; Fletcher, T.; Batzella, E.; Canova, C. Estimation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Half-Lives in Human Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintern, G.; Scarlett, A.G.; Gagnon, M.M.; Leeder, J.; Amhet, A.; Lettoof, D.C.; Leshyk, V.O.; Bujak, A.; Bujak, J.; Grice, K. Phytoremediation Potential of Azolla Filiculoides: Uptake and Toxicity of Seven Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at Environmentally Relevant Water Concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, A.P.; Engel, S.M.; Whitworth, K.W.; Richardson, D.B.; Stuebe, A.M.; Daniels, J.L.; Haug, L.S.; Eggesbø, M.; Becher, G.; Sabaredzovic, A.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Lipid Concentrations in Plasma during Pregnancy among Women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Environ. Int. 2014, 62, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.M.; Kotlarz, N.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Lea, C.S.; Collier, D.N.; Richardson, D.B.; Hoppin, J.A. Drinking Water–Associated PFAS and Fluoroethers and Lipid Outcomes in the GenX Exposure Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 97002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Ding, N.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.A.; Mukherjee, B.; Calafat, A.M.; Park, S.K. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Lipid Trajectories in Women 45–56 Years of Age: The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 087004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Ding, L. Associations between Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances as Mixtures and Lipid Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study in Jinan. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.W.; Kang, H.; Kim, S.H. Concentrations of Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Lipid Health in Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Korean National Environmental Health Survey 2018–2020. Toxics 2025, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Y.N.; Moustafa, J.S.E.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Tomlinson, M.; Falchi, M.; Menni, C.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Steves, C.J.; Small, K.S. Longitudinal Association of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) Exposure with Lipid Traits, in a Healthy Unselected Population. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 35, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Gade Timmermann, C.A.; Kruse, M.; Nielsen, F.; Vinholt, P.J.; Boding, L.; Heilmann, C.; Mølbak, K. Severity of COVID-19 at Elevated Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkylates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 0244815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coêlho, A.C.M.; Charles, D.; Nøst, T.H.; Cioni, L.; Huber, S.; Herzke, D.; Rylander, C.; Berg, V.; Sandanger, T.M. Temporal and Cross-Sectional Associations of Serum per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Lipids from 1986 to 2016—The Tromsø Study. Environ. Int. 2025, 199, 109508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlezinger, J.J.; Bello, A.; Mangano, K.M.; Biswas, K.; Patel, P.P.; Pennoyer, E.H.; Wolever, T.M.S.; Heiger-Bernays, W.J.; Bello, D. Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Circulation in a Canadian Population: Their Association with Serum-Liver Enzyme Biomarkers and Piloting a Novel Method to Reduce Serum-PFAS. Environ. Health 2025, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembek, Z.F.; Lordo, R.A. Influence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances on Occurrence of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.; Jöud, A. Susceptibility to COVID-19 after High Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Contaminated Drinking Water: An Ecological Study from Ronneby, Sweden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollister, J.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Ellingson, K.D.; Beitel, S.; Fowlkes, A.L.; Lutrick, K.; Tyner, H.L.; Naleway, A.L.; Yoon, S.K.; Gaglani, M.; et al. Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Concentrations and Longitudinal Change in Post-Infection and Post-Vaccination SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catelan, D.; Biggeri, A.; Russo, F.; Gregori, D.; Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Fletcher, T.; Canova, C. Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Mortality for COVID-19: A Spatial Ecological Analysis in the Veneto Region (Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, A.; Johansen, I.S.; Tolstrup, M.; Heilmann, C.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Nielsen, F.; Grandjean, P. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination in Danish Adults Exposed to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): The ENFORCE Study. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.K.; Kleinschmidt, S.E.; Andres, K.L.; Reusch, C.N.; Krisko, R.M.; Taiwo, O.A.; Olsen, G.W.; Longnecker, M.P. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccines among Workers with a Wide Range of Exposure to per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Lesseur, C.; Chen, L.; Andra, S.S.; Narasimhan, S.; Pulivarthi, D.; Midya, V.; Ma, Y.; Ibroci, E.; Gigase, F.; et al. Cross-Sectional Associations of Maternal PFAS Exposure on SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibody Levels during Pregnancy. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Chen, J.; Kaur, K.; Amreen, B.; Lesseur, C.; Dolios, G.; Andra, S.S.; Narasimhan, S.; Pulivarthi, D.; Midya, V.; et al. High-Dimensional Mediation Analysis to Elucidate the Role of Metabolites in the Association between PFAS Exposure and Reduced SARS-CoV-2 IgG in Pregnancy. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 980, 179520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.B.; Ducatman, A. Perfluoroalkyl Acids Serum Concentrations and Their Relationship to Biomarkers of Renal Failure: Serum and Urine Albumin, Creatinine, and Albumin Creatinine Ratios across the Spectrum of Glomerular Function among US Adults. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, H.E.; Li, S.; Walker, D.I.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Rock, S.; Costello, E.; Bjornstad, P.; Pyle, L.; Nelson, J.; et al. The Potential Mediating Role of the Gut Microbiome and Metabolites in the Association between PFAS and Kidney Function in Young Adults: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ouyang, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Yang, A.; Hu, X. Temporal Trend of Serum Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid among U.S. Adults with or without Comorbidities in NHANES 1999–2018. Toxics 2024, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.; Fischer, F.C.; Leth, P.M.; Grandjean, P. Occurrence of Major Perfluorinated Alkylate Substances in Human Blood and Target Organs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.; Nadal, M.; Navarro-Ortega, A.; Fàbrega, F.; Domingo, J.L.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Accumulation of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Human Tissues. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.E.; Hagenbuch, B.; Apte, U.; Corton, J.C.; Fletcher, T.; Lau, C.; Roth, W.L.; Staels, B.; Vega, G.L.; Clewell, H.J.; et al. Why Is Elevation of Serum Cholesterol Associated with Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Humans? A Workshop Report on Potential Mechanisms. Toxicology 2021, 459, 152845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, Q. Associations between Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposures and Blood Lipid Levels among Adults—A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 056001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlezinger, J.J.; Gokce, N. Perfluoroalkyl/Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Links to Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1136–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisse, J.; Dellafiora, L.; van den Heuvel, J.J.M.W.; Rijkers, D.; Leenders, L.; Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Punt, A.; Russel, F.G.M.; Koenderink, J.B. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Are Substrates of the Renal Human Organic Anion Transporter 4 (OAT4). Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinete, N.; Hauser-Davis, R.A. Drinking Water Pollutants May Affect the Immune System: Concerns Regarding COVID-19 Health Effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Cheng, X.; Gunjal, S.J.; Zhang, C. Advancing PFAS Sorbent Design: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Perspectives. ACS Mater. Au 2024, 4, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, V.; Bil, W.; Vandebriel, R.; Granum, B.; Luijten, M.; Lindeman, B.; Grandjean, P.; Kaiser, A.-M.; Hauzenberger, I.; Hartmann, C.; et al. Consideration of Pathways for Immunotoxicity of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Environ. Health 2023, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanvoravongchai, J.; Laochindawat, M.; Kimura, Y.; Mise, N.; Ichihara, S. Clinical, Histological, Molecular, and Toxicokinetic Renal Outcomes of per-/Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, T.; Li, X.; Pan, L. Associations between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Renal Function as Well as Poor Prognosis in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2520903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, L.; Ma, D.; Cao, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. The Occurrence of PFAS in Human Placenta and Their Binding Abilities to Human Serum Albumin and Organic Anion Transporter 4. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Choudhary, A.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, L.; Uline, M.J.; Tagliazucchi, M.; Wang, Q.; Bedrov, D.; Liu, C. Single-Molecule Profiling of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances by Cyclodextrin Mediated Host-Guest Interactions within a Biological Nanopore. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, B.A.; Zhou, J.; Clarke, B.O.; Leung, I.K.H. Enzymatic Degradation of PFAS: Current Status and Ongoing Challenges. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, 202401122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, A.; Taj, T.; Dunder, L.; Lind, P.M.; Lind, L.; Salihovic, S. Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Analysis of Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Kidney Function. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 35, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, J.T.; Anderson, R.H.; Lang, J.R.; Liles, D.; Matteson, K.; Olechiw, T. Field-Scale Demonstration of PFAS Leachability Following In Situ Soil Stabilization. ACS Omega 2021, 7, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biek, S.K.; Khudur, L.S.; Rigby, L.; Singh, N.; Askeland, M.; Ball, A.S. Assessing the Impact of Immobilisation on the Bioavailability of PFAS to Plants in Contaminated Australian Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 20330–20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, T.; Jones, R.; Kastury, F.; Juhasz, A.L. Soil Amendments Reduce PFAS Bioaccumulation in Eisenia Fetida Following Exposure to AFFF-Impacted Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smorada, C.M.; Sima, M.W.; Jaffé, P.R. Bacterial Degradation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 88, 103170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omagamre, E.W.; Custer, G.F. Digging Deep: Microbial PFAS-Degradation in Landfill Sediments. Trends Microbiol. 2025, 33, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackett, L.P. Nothing Lasts Forever: Understanding Microbial Biodegradation of Polyfluorinated Compounds and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; An, Z.; Mei, Y.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Dong, Z.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Guo, H.; et al. Impact of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure on Renal Dysfunction: Integrating Epidemiological Evidence with Mechanistic Insights. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerád, J.; Horká, P.; Filipová, A.; Kukla, J.; Holubová, K.; Musilová, Z.; Jandová, K.; Frouz, J.; Cajthaml, T. The Driving Factors of Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substance (PFAS) Accumulation in Selected Fish Species: The Influence of Position in River Continuum, Fish Feed Composition, and Pollutant Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Xin, X.; Hawkins, G.L.; Huang, Q.; Huang, C.H. Occurrence, Fate, and Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Small- and Large-Scale Municipal Wastewater Treatment Facilities in the United States. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 5428–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazer, V.S.; Walsh, H.L.; Smith, C.R.; Gordon, S.E.; Keplinger, B.J.; Wertz, T.A. Tissue Distribution and Temporal and Spatial Assessment of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Smallmouth Bass (Micropterus Dolomieu) in the Mid-Atlantic United States. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 59302–59319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, W.; Partington, J.M.; Leung, I.K.H.; Clarke, B.O. Premium Ultra-Trace Analytical Method for Part per Quadrillion (Ppq) PFAS Quantification in Drinking Water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1368, 344333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Ekpe, O.D.; Macha, F.J.; Sim, W.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, M.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and Distribution of Brominated and Fluorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants in Surface Sediments Focusing on Industrially Affected Rivers. Chemosphere 2025, 371, 144066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sharkey, M.; Coggins, A.M.; Stubbings, W.; Healy, M.G.; Harrad, S. Concentrations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Sediments and Wastewater Treatment Plant-Derived Biosolids from Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 979, 179380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banayan Esfahani, E.; Asadi Zeidabadi, F.; Jafarikojour, M.; Mohseni, M. Photo-Reductive Decomposition of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Its Common Alternatives by UV/VUV/Sulfite Process: Mechanism, Kinetic Modeling, and Water Matrix Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Leng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Wang, H. A Review of Electrooxidation Systems Treatment of Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): Electrooxidation Degradation Mechanisms and Electrode Materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 42593–42613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Luo, K.; Yao, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, G. Photocatalytic Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Water: A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabaso, N.S.N.; Tshangana, C.S.; Muleja, A.A. Efficient Removal of PFASs Using Photocatalysis, Membrane Separation and Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors. Membranes 2024, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanugo, V.S.; Ojo, B.S.; Lin, T.C.; Huang, Y.W.; Locmelis, M.; Han, D. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Degradation in Water and Soil Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP): A Review. ACS Phys. Chem. Au 2025, 5, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidnell, T.; Wood, R.J.; Hurst, J.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Sonolysis of Per- and Poly Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Meta-Analysis. Ultrason. Sonochem 2022, 87, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ronen, A. A Review on Removal and Destruction of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) by Novel Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grung, M.; Hjermann, D.; Rundberget, T.; Bæk, K.; Thomsen, C.; Knutsen, H.K.; Haug, L.S. Low Levels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Detected in Drinking Water in Norway, but Elevated Concentrations Found near Known Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, J.W.; Rosal, C.G.; McCord, J.P.; Strynar, M.J.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bergman, E.L.; Goodrow, S.M.; Tadesse, H.K.; Pilant, A.N.; Washington, B.J.; et al. Nontargeted Mass-Spectral Detection of Chloroperfluoropolyether Carboxylates in New Jersey Soils. Science 2020, 368, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood-Donelson, K.I.; Dodds, J.N.; Schnetzer, A.; Hall, N.; Baker, E.S. Uncovering Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) with Nontargeted Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry Analyses. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Huang, C.; Zhao, L.; Rappé, A.K.; Kennedy, E.M.; Stockenhuber, M.; Mackie, J.C.; Weber, N.H.; Lucas, J.A.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Direct Measurement of Fluorocarbon Radicals in the Thermal Destruction of Perfluorohexanoic Acid Using Photoionization Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, ADT3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, N.; Jiao, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, H.; Wei, S. Machine Learning-Enhanced Molecular Network Reveals Global Exposure to Hundreds of Unknown PFAS. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, ADN1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Scheringer, M. From “Forever Chemicals” to Fluorine-Free Alternatives. Science 2024, 385, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Compound | Sample | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Gen-X, F-53B, FC-98, and short-chain PFAS | Soil | China | [4] |
| 2022 | 7:3 FTCA | Wildlife birds and eggs | Svalbard/ Norway | [9] |
| 2022 | F-53B, 8:2 Cl-PFESA | Indoor dust | China | [11] |
| 2022 | Gen-X | Freshwater fish | Czech | [34] |
| 2024 | Gen-X | WWTP | U.S. | [35] |
| 2024 | Gen-X, 6:2 FTS | Smallmouth bass | U.S. | [36] |
| 2024 | Gen-X, F-53B, PFBA, and PFBS | Seawater | China | [8] |
| 2025 | Gen-X | Drinking water | Australia | [23] |
| 2025 | F-53B | River water | Korea | [37] |
| 2025 | Gen-X | Biosolid | Ireland | [38] |
| 2025 | Gen-X, PFBA, PFHxA | Serum | Canada | [39] |
| Method | Purpose | Analyte | Sample Work-Up | Detection Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF | Total fluorine | Fluoride | None | CIC | [50] |
| AOF | Absorbable organic fluorine | Fluoride | Activated carbon | CIC | [50] |
| EOF | Extractable organic fluorine | Fluoride | SPE | CIC | [50] |
| TOP | Total oxidizable precursor | Oxidant-reactive PFAS precursors | SPE | LC-MS/MS | [50] |
| Method | Assay | LOD/LOQ (μg/L) | Matrix | Matrix Effect | Effect | Robustness | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS | Target analysis, TOP assay | 0.02–0.2 | Serum | Yes | Ion suppression | Yes | [12,53] |
| GC-MS | Target analysis | 0.05–1.80 | Serum | Yes | Ion suppression | Yes | [12,54] |
| HRMS | Non-target analysis | 0.1–1.0 | Serum | Yes, but relatively small | Ion suppression | Yes | [12,55] |
| CIC | TF, AOF, EOF | 6–9 | Serum | Yes | Overlapping of chloride ion | Yes | [50,56] |
| Specimen | Country | Sample | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | U.S. | Landfill | [58] |
| U.S. | Farm field | [59] | |
| U.S. | Soil | [60] | |
| Germany | River water | [61] | |
| Australia | Soil | [62] | |
| Japan | Soil | [63] | |
| India | Sediment | [42] | |
| China | River water | [61] | |
| Drinking water | U.S. | Surface water + groundwater | [64] |
| EU | Surface water + groundwater | [65] | |
| Australia | Tap water + bottled water | [43] | |
| Japan | Surface water + groundwater | [66] | |
| India | Groundwater | [42] | |
| Food | U.S. | Total diet | [14] |
| U.S. | Seafood | [67] | |
| U.S. | Food | [68] | |
| U.S. | Food | [15] | |
| U.S. | Freshwater fish | [69] | |
| U.S. | Fish | [70] | |
| EU | Egg | [71] | |
| Australia | Livestock | [72] | |
| Japan | Pacific cod | [73] | |
| India | Fish | [42] | |
| Human plasma/serum | U.S. | Plasma | [69,74] |
| U.S. | Blood | [2] | |
| Germany | Blood | [75] | |
| Australia | Human serum | [76] | |
| Japan | Maternal serum | [77] | |
| India | Water, human serum | [42] | |
| Specimen from an uncivilized area | Svalbard/Norway | Meltwater | [78] |
| Germany | Wildlife | [10] |
| Manifestation | Year | Country | Population | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyslipidemia | 2014 | Norway | Pregnant women (n = 891) | [87] |
| 2022 | U.S. | Age range 6–86 years old (n = 326) | [88] | |
| 2023 | U.S. | Women aged 45–56 years old (n = 1130) | [89] | |
| 2024 | China | Non-fasted individuals (n = 575) | [90] | |
| 2025 | Korea | Adolescents aged 12–17 years old (n = 824) | [91] | |
| 2025 | U.K. | A healthy unselected population of twins (n = 2069) | [92] | |
| 2025 | Canada | Pregnant women (n = 282) | [5] | |
| 2025 | Norway | Non-diabetic participants (n = 145) | [93] | |
| 2025 | Canada | Adult males with elevated cholesterol (n = 72) | [39] | |
| Impaired immune response | 2020 | Denmark | SARS-CoV-2-infected subjects aged 30–70 years old (n = 323) | [94] |
| 2021 | Sweden | Age- and sex-standardized adult population (control district n = 898; contaminated district n = 239) | [95] | |
| 2021 | Italy | PFAS-positive area (n = 187,375); control area (n = 4,750,548) | [96] | |
| 2022 | U.S. | Age-matched comparison | [97] | |
| 2022 | U.S. | Aged ≥ 20 years old (n = 415) | [98] | |
| 2023 | U.S. | Unvaccinated (n = 153); vaccinated (n = 860) | [99] | |
| 2023 | U.S. | Pregnant women (n = 72) | [100] | |
| 2024 | Denmark | Aged 50–69 years old (n = 477) | [101] | |
| 2025 | U.S. | Pregnant women (n = 59) | [102] | |
| Exacerbated CKD | 2019 | U.S. | Adults ≥ 20 years old (n = 8220) | [103] |
| 2024 | U.S. | Young adults (n = 78) | [104] | |
| 2024 | U.S. | Adults with CKD (n = 3239); no CKD (n = 10,648) | [105] | |
| 2025 | Sweden | All aged 70 years old at baseline, 50% females (n = 997) | [106] | |
| 2025 | China | Aged ≥ 20 years old (n = 1503) | [20] | |
| 2025 | China | Adults (n = 2801) | [107] |
| Method | Absorption | Cost | Decomposition | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated carbons | ++ | ++ | No | [60] |
| Biochar | +++ | + | No | [60] |
| Carbon nanotubes | + | +++ | No | [60] |
| Carbon-based composites | +++ | + | Yes | [60] |
| Ion exchange | + | +++ | No | [115] |
| Reverse osmosis | + | +++ | No | [121] |
| Phytoremediation | + | ++/+++ | Yes | [122] |
| Method | Substrate | Catalyst/Materials | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial | PFOA | Pseudomonas | [129] |
| PFOA, PFOS | Delftia acidovorans | [130] | |
| PFOA, PFOS | Acidimicrobium sp. strain A6 | [131] | |
| PFOS | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [132] | |
| PFOS | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida 2.4-D | [131] | |
| FTCA | Hyphomicrobium, Methylorubrum, and Achromobacter | [133] | |
| FTS | Dietzia aurantiaca | [134,135] | |
| Photo-oxidation | PFOS | UV | [136] |
| Electro-oxidation | PFOS | Boron-doped diamond and mixed metal oxide | [137] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashima, R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): History, Current Concerns, and Future Outlook. Molecules 2025, 30, 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224415
Mashima R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): History, Current Concerns, and Future Outlook. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224415
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashima, Ryuichi. 2025. "Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): History, Current Concerns, and Future Outlook" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224415
APA StyleMashima, R. (2025). Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): History, Current Concerns, and Future Outlook. Molecules, 30(22), 4415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224415





