The Efficiency and Mechanism of FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed Persulfate for the Degradation of Caffeine Under Visible Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Structure and Properties of FeOCl/Ce
2.2. FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed PS for the Degradation of CAF Under Visible Light
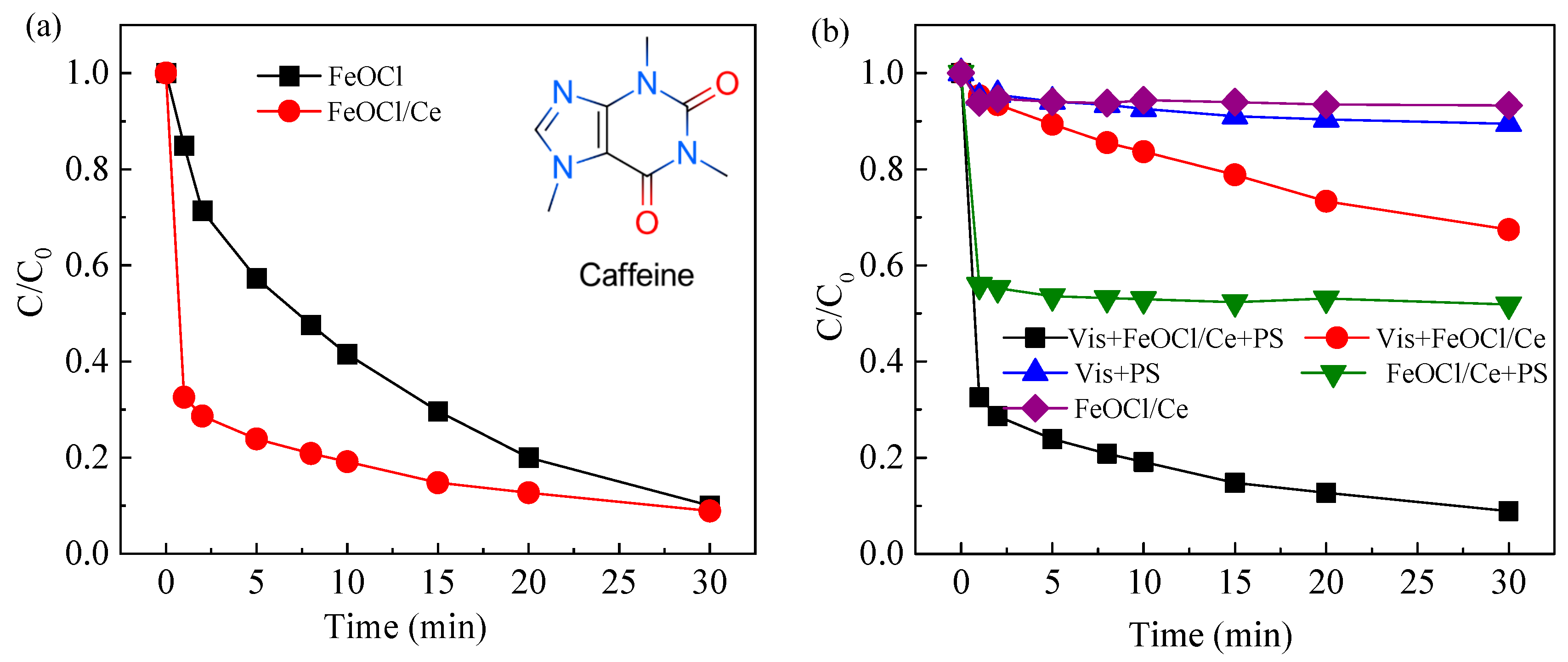
2.2.1. Evaluation of the Catalytic Performance of FeOCl/Ce
2.2.2. Comparison of CAF Degradation in Different Systems
2.3. Effects of Important Parameters on the Degradation Efficiency
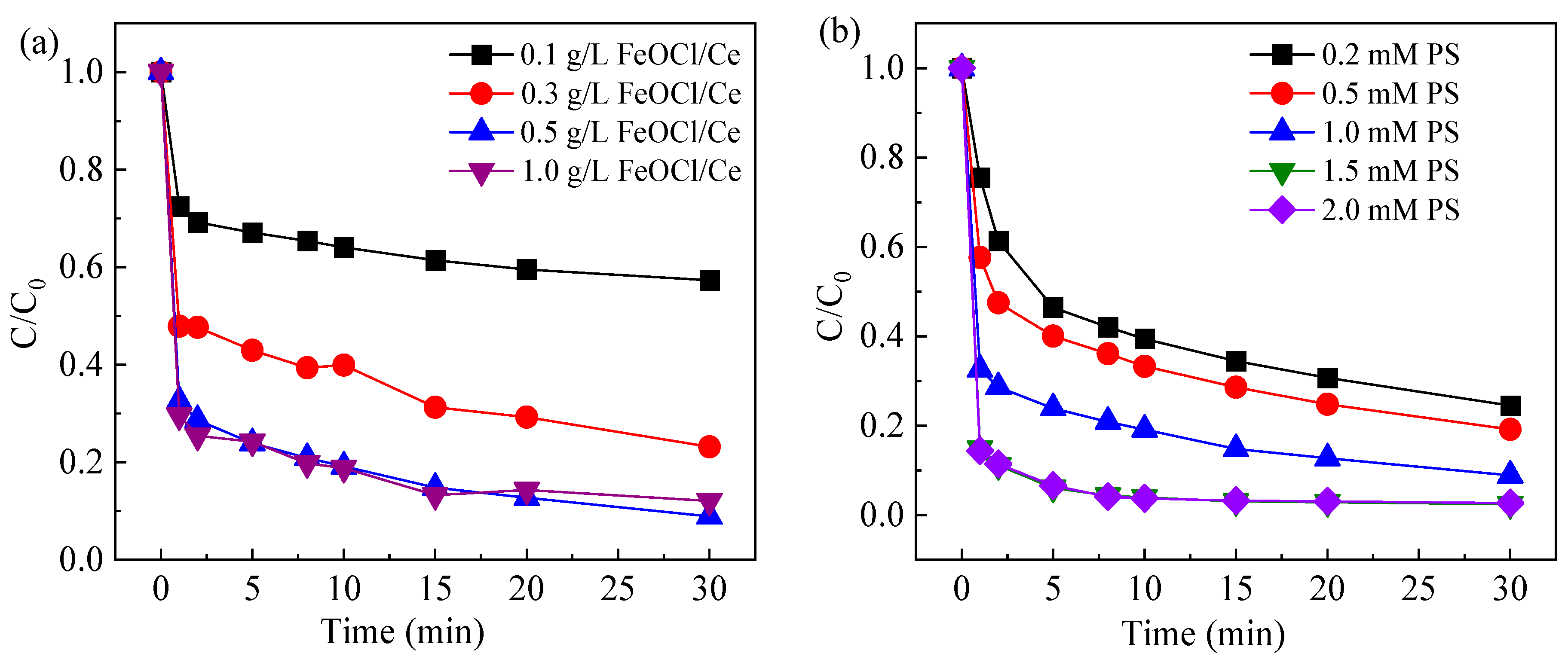
2.3.1. Effect of FeOCl/Ce Dosage
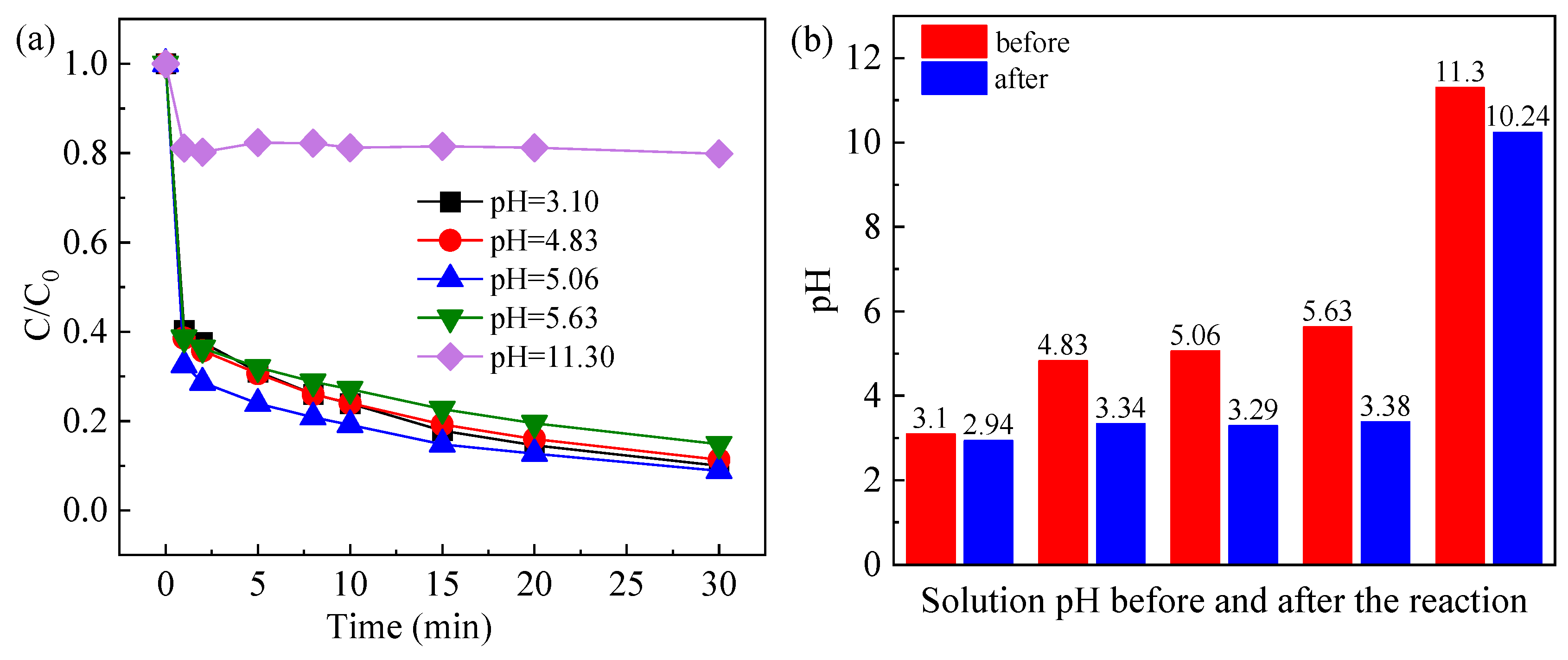
2.3.2. Effect of Initial Solution pH
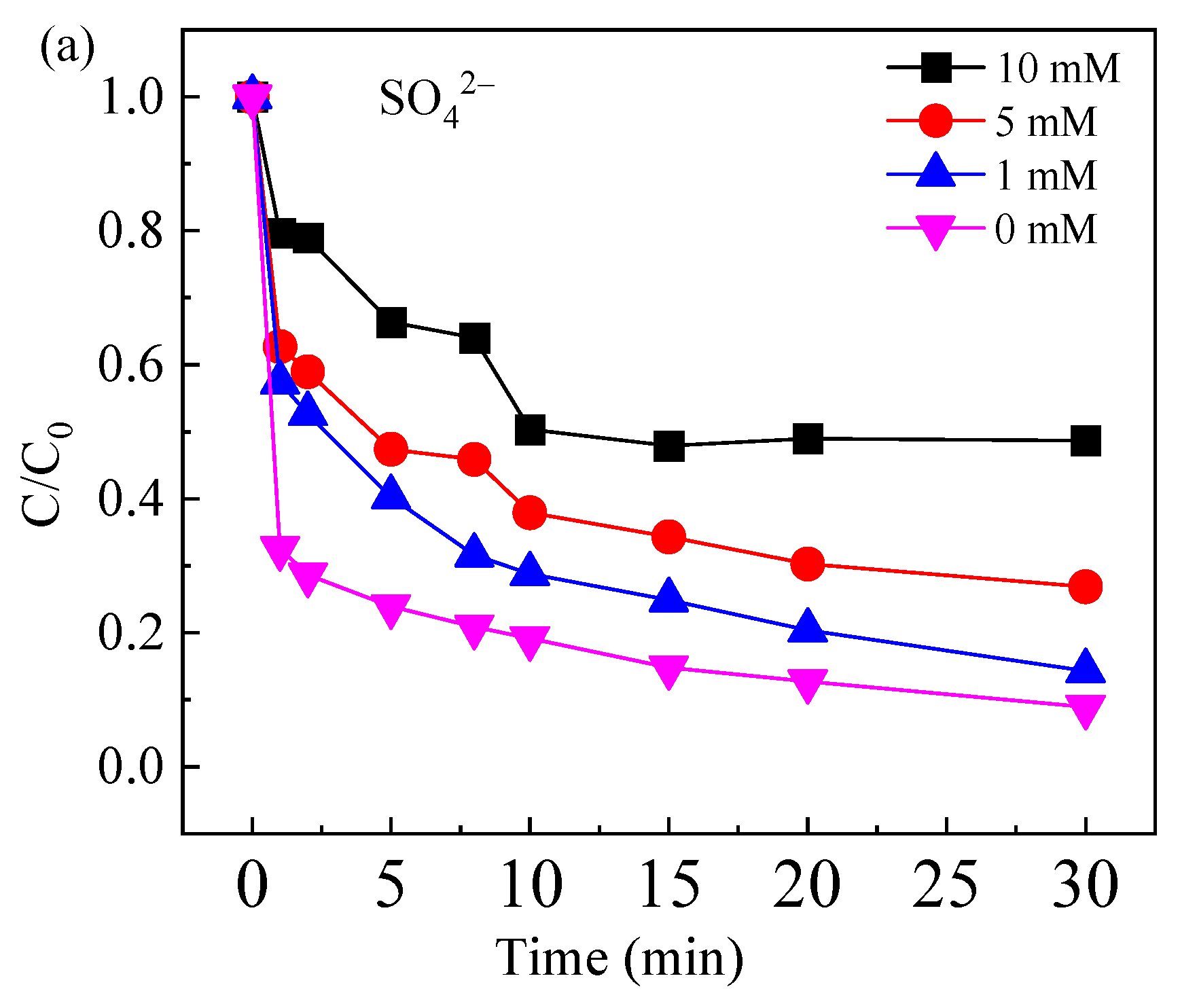
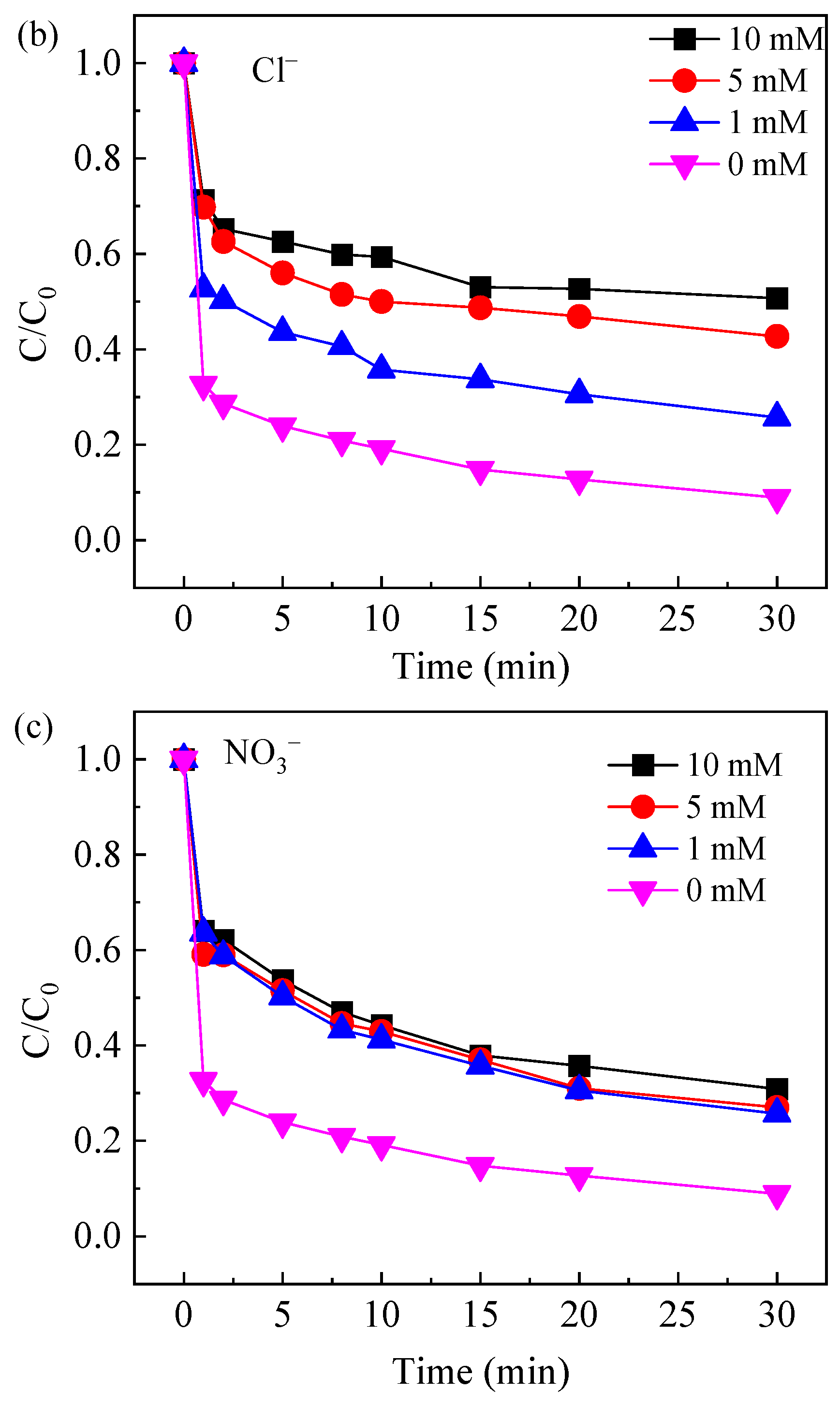
2.3.3. Effect of Common Anions
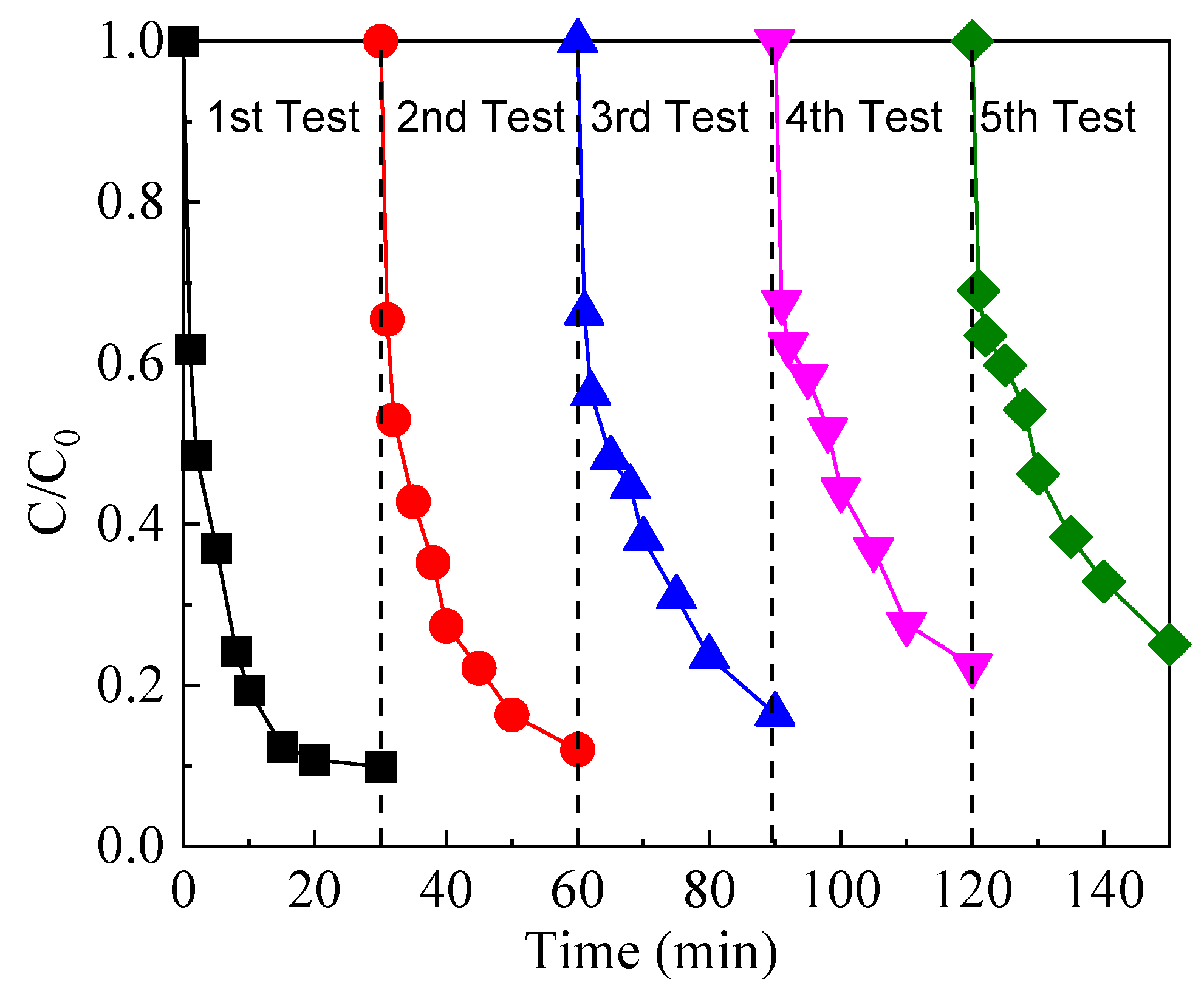
2.4. Evaluation of the Stability of FeOCl/Ce Catalyst
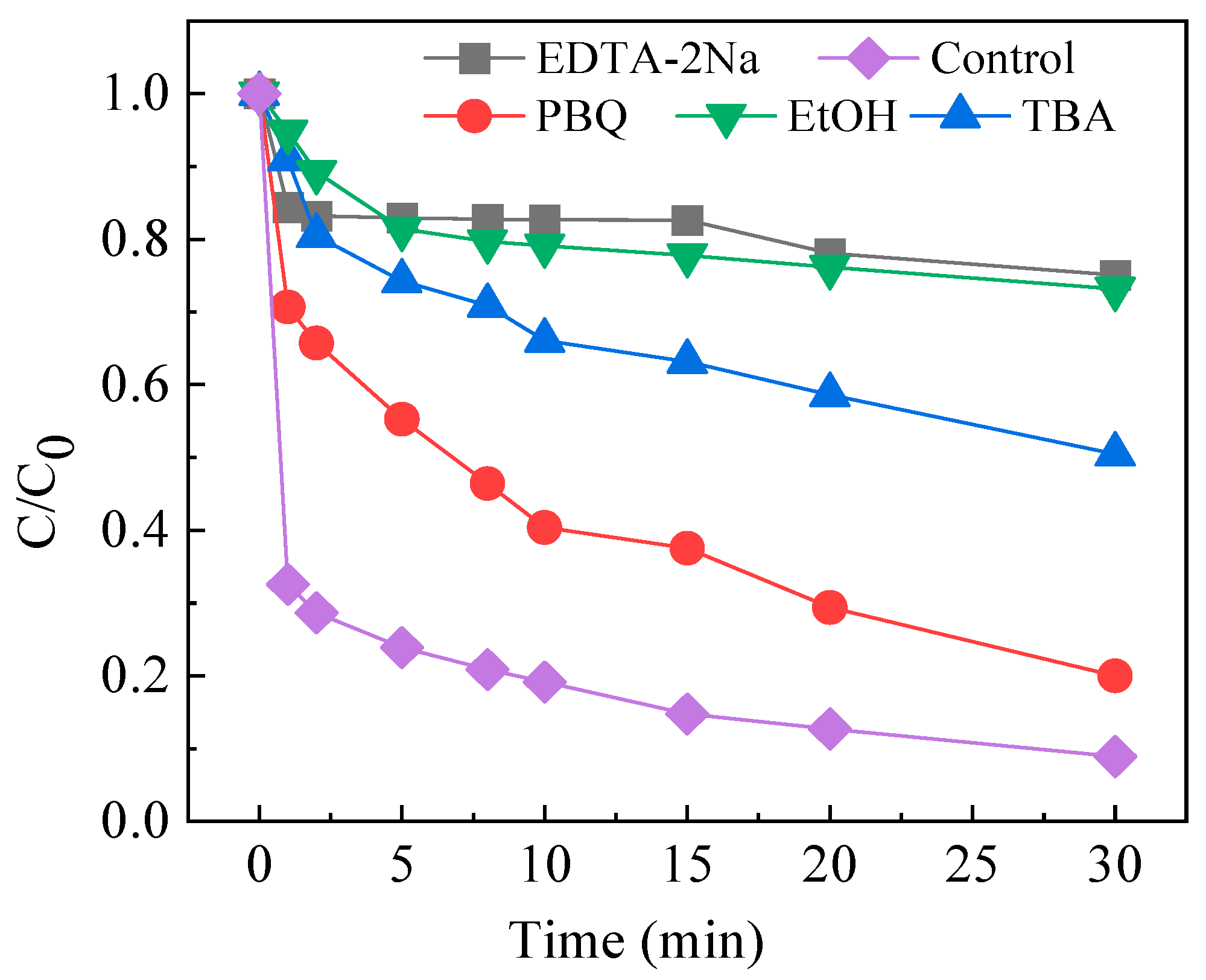
2.5. Degradation Mechanisms
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Characterization
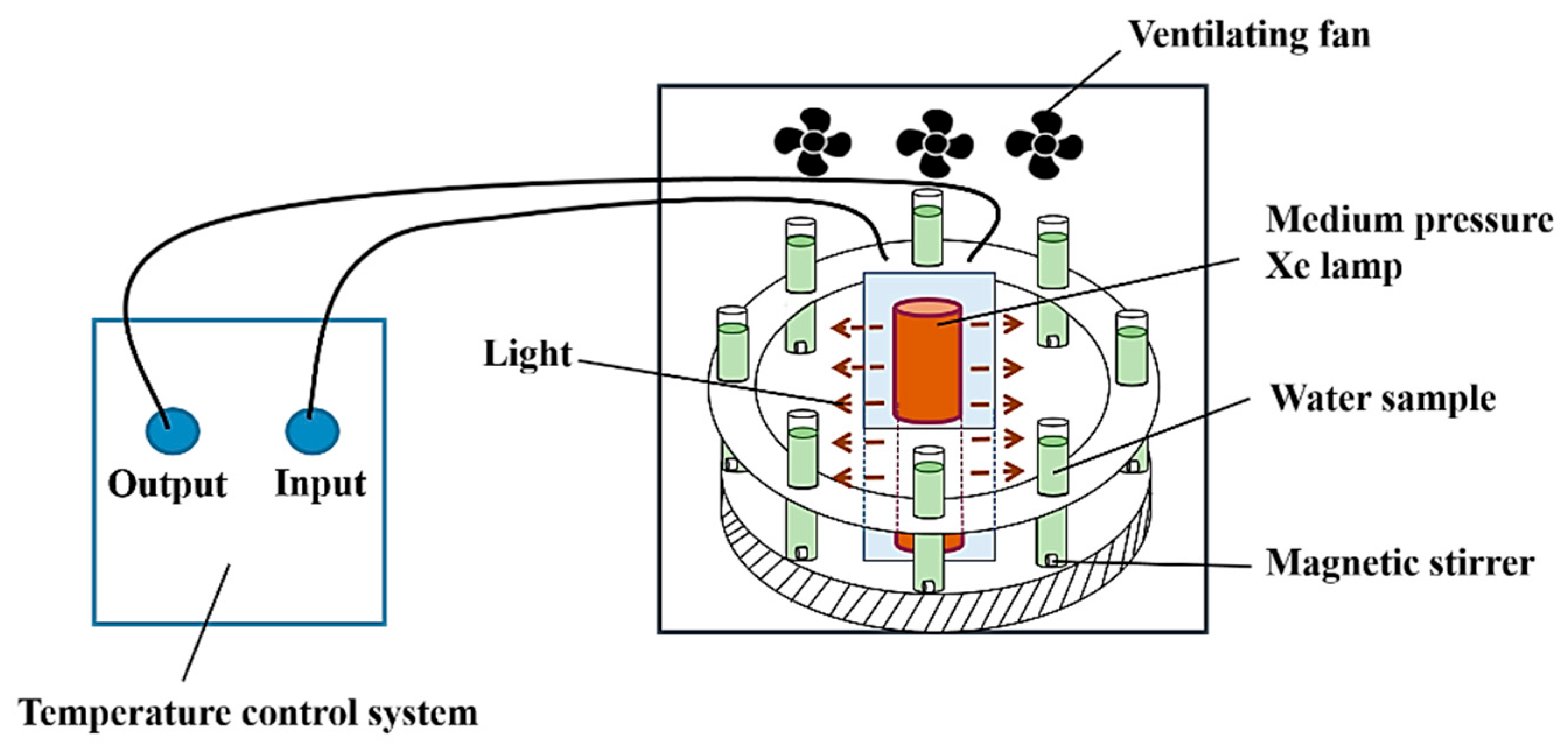
3.4. Photocatalytic Degradation Experiment
3.5. Analytical Testing Methods
3.5.1. Determination of CAF
3.5.2. Determination of PS Concentration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawash, H.B.; Moneer, A.A.; Galhoum, A.A.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Mohamed, W.A.A.; Samy, M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Gaballah, M.S.; Mubarak, M.F.; Attia, N.F. Occurrence and spatial distribution of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the aquatic environment, their characteristics, and adopted legislations. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jin, X.; Johnson, A.C.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Hou, L.; Meng, F.; Wu, F. Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Global Surface Waters: Risk and Drivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 19146–19159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xi, H.; Xu, L.; Jin, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H. Ecotoxicological effects, environmental fate and risks of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the water environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sridharan, S.; Sawarkar, A.D.; Shakeel, A.; Anerao, P.; Mannina, G.; Sharma, P.; Pandey, A. Current research trends on emerging contaminants pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs): A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Snyder, S.A.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Which Micropollutants in Water Environments Deserve More Attention Globally? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y. Occurrence, bioaccumulation, fate, and risk assessment of emerging pollutants in aquatic environments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Han, J.; Shen, G.; Hao, Z.; Han, Y.; Xiong, W.; Liang, B.; Gao, S.; Yang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. The threat of PPCPs from WWTP and solutions of advanced reduction coupled treatment processes with pilot-scale. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 498, 139782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentz, B.; Rauhauser, M.; Krantz, R.T.; Snow, D.D.; Kelly, J.J. Treated wastewater effluent increases pharmaceutical concentrations and alters benthic microbial communities in streams. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1649739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, D.; Bai, B.; Ma, Z.; Zong, S. Insight into antibiotic removal by advanced oxidation processes (AOPs): Performance, mechanism, degradation pathways, and ecotoxicity assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, M.; Cho, D.-W.; Fahad, S.; Jeong, D.-W.; Hwang, J.-H. Photocatalytic innovations in PFAS removal: Emerging trends and advances. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 980, 179567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhapkar, A.R.; Bhame, S. A review on ZnO and its modifications for photocatalytic degradation of prominent textile effluents: Synthesis, mechanisms, and future directions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerdi, A.G.; Bahrami, S.H. Application of heterogeneous nano-semiconductors for photocatalytic advanced oxidation of organic compounds: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-J.; Xu, X.-M.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.-F. Iron Oxychloride (FeOCl): An Efficient Fenton-Like Catalyst for Producing Hydroxyl Radicals in Degradation of Organic Contaminants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16058–16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, S.; Ta, J.; Li, D. Enhancement of peroxymonosulfate activation and utilization efficiency via iron oxychloride nanosheets in visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z. FeOCl in Advanced Oxidization Processes for Water Purification: A Critical Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L. New and highly efficient Ultra-thin g-C3N4/FeOCl nanocomposites as photo-Fenton catalysts for pollutants degradation and antibacterial effect under visible light. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, O.Y.; Dalmis, R.; Birlik, I.; Azem, N.F.A. Comparison of the effect of non-metal and rare-earth element doping on structural and optical properties of CuO/TiO2 one-dimensional photonic crystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 153262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J. Rare earth oxynitrides: Promising visible-light-driven photocatalysts for water splitting. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seles, P.; Vengust, D.; Radosevic, T.; Kocijan, M.; Einfalt, L.; Kurtjak, M.; Shvalya, V.; Knaflic, T.; Bernik, S.; Omerzu, A.; et al. Altering defect population during the solvothermal growth of ZnO nanorods for photocatalytic applications. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 26819–26828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Chand, H.; Krishnan, V. Activation of persulfate by novel TiO2/FeOCl photocatalyst under visible light: Facile synthesis and high photocatalytic performance. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Xia, D. Mechanism of heterogeneous activation of persulfate with FeOCl under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. Enhanced antibiotic mineralization and detoxification through photoregeneration of FeOCl surface active site. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.-Y. Caffeine degradation by methanogenesis: Efficiency in anaerobic membrane bioreactor and analysis of kinetic behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Cui, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. FeOCl/Ln (Ln = La or Y): Efficient photo-Fenton catalysts for ibuprofen degradation. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16273–16280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Xia, D. Activation mechanism of sodium percarbonate by FeOCl under visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 706, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, D.R.; Engelhard, M.H.; Johnson, G.E.; Laskin, J.; Lai, J.; Mueller, K.; Munusamy, P.; Thevuthasan, S.; Wang, H.; Washton, N.; et al. Surface characterization of nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Important needs and challenging opportunities. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2013, 31, 050820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Lian, Y.; Zhong, M.; Sha, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S. Ce3+ self-doped CeOx/FeOCl: An efficient Fenton catalyst for phenol degradation under mild conditions. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 3476–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, M.; Rao, Y. Activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron for degradation of emerging pollutant caffeine. Ind. Water Treat. 2022, 42, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Meng, D.Q.; Guo, Q.B.; Gao, D.; Wang, L. Study on TiO2/g-C3N4 S-Scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for enhanced formaldehyde decomposition. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhan, S.; Li, Y. Understanding the charge separation and transfer in mesoporous carbonate doped phase-junction TiO2 nanotubes for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2018, 225, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Luo, J.C.; Song, T.H.; Yu, X. Research progress on nano-Fe0/PS system for degradation of refractory organics in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of persulfate by nanosized zero-valent iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and transformation products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by Sulfate Radical-based Advanced Oxidation Processes (SR-AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Das, U.; Dalai, A.K. In-situ chemical oxidation: Principle and applications of peroxide and persulfate treatments in wastewater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Wu, M.-S. UV/S2O82− process for degrading polyvinyl alcohol in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2014, 85, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Q.; Gao, N.-Y.; Wang, W.; Kang, S.-F.; Xu, J.-H.; Xiang, H.-M.; Yin, D.-Q. Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A.; Keller, J.; Tait, S.; Radjenovic, J. Assessment of the impact of chloride on the formation of chlorinated by-products in the presence and absence of electrochemically activated sulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-H. Feasibility of using nanoscale zero-valent iron and persulfate to degrade sulfamethazine in aqueous solutions. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenczek-Zajac, A.; Synowiec, M.; Zakrzewska, K.; Zazakowny, K.; Kowalski, K.; Dziedzic, A.; Radecka, M. Scavenger-Supported Photocatalytic Evidence of an Extended Type I Electronic Structure of the TiO2@Fe2O3 Interface. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 38255–38269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Guan, Q.; Chen, C. Identifying the Role of Surface Hydroxyl on FeOCl in Bridging Electron Transfer toward Efficient Persulfate Activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 12922–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Su, H.-W. Identification of Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radicals in Thermally Activated Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhou, D.; Fang, G.; Gao, J. Contribution of alcohol radicals to contaminant degradation in quenching studies of persulfate activation process. Water Res. 2018, 139, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Huang, C.-F.; Mohanty, N.; Kurakalva, R.M. A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
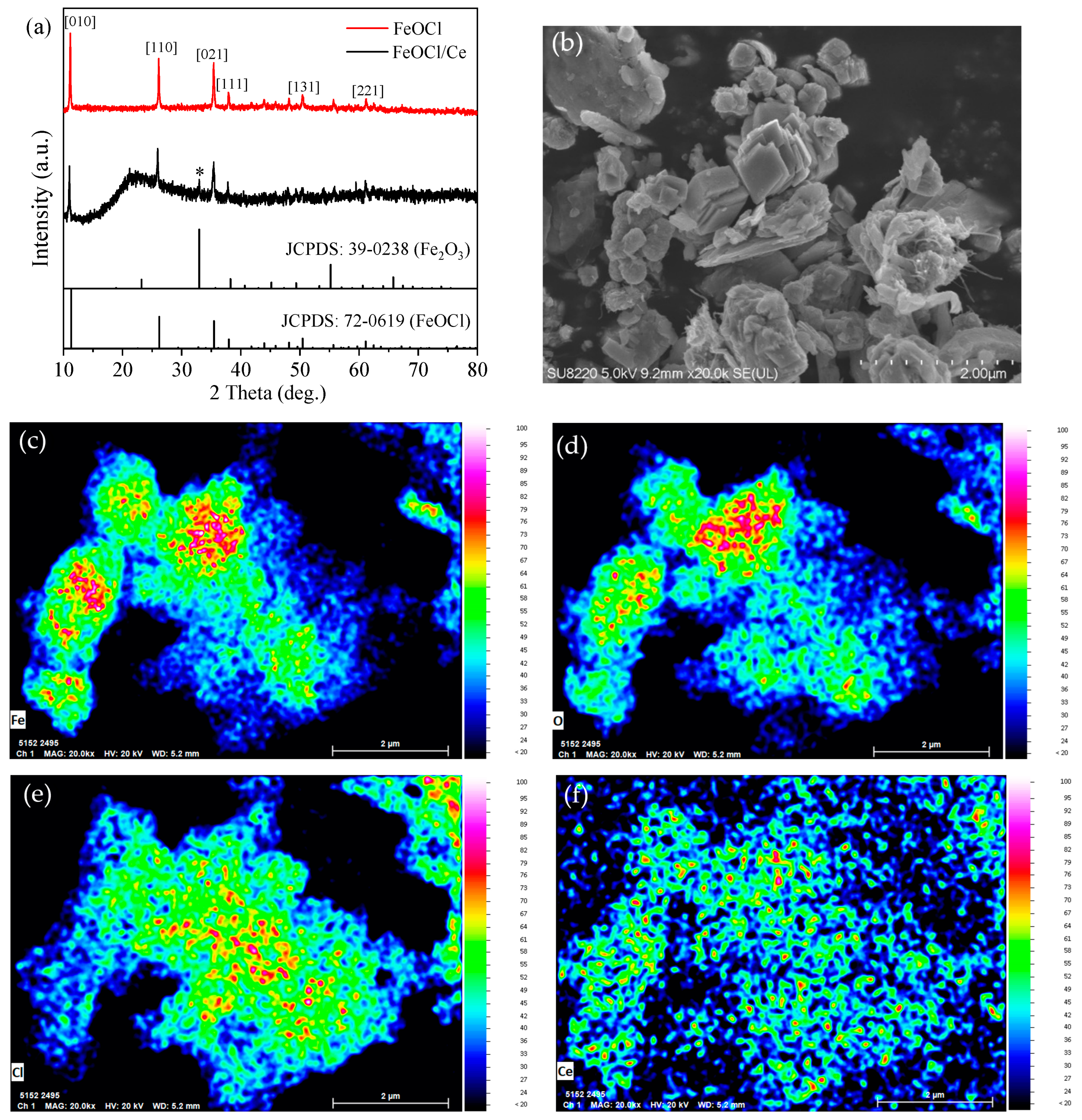
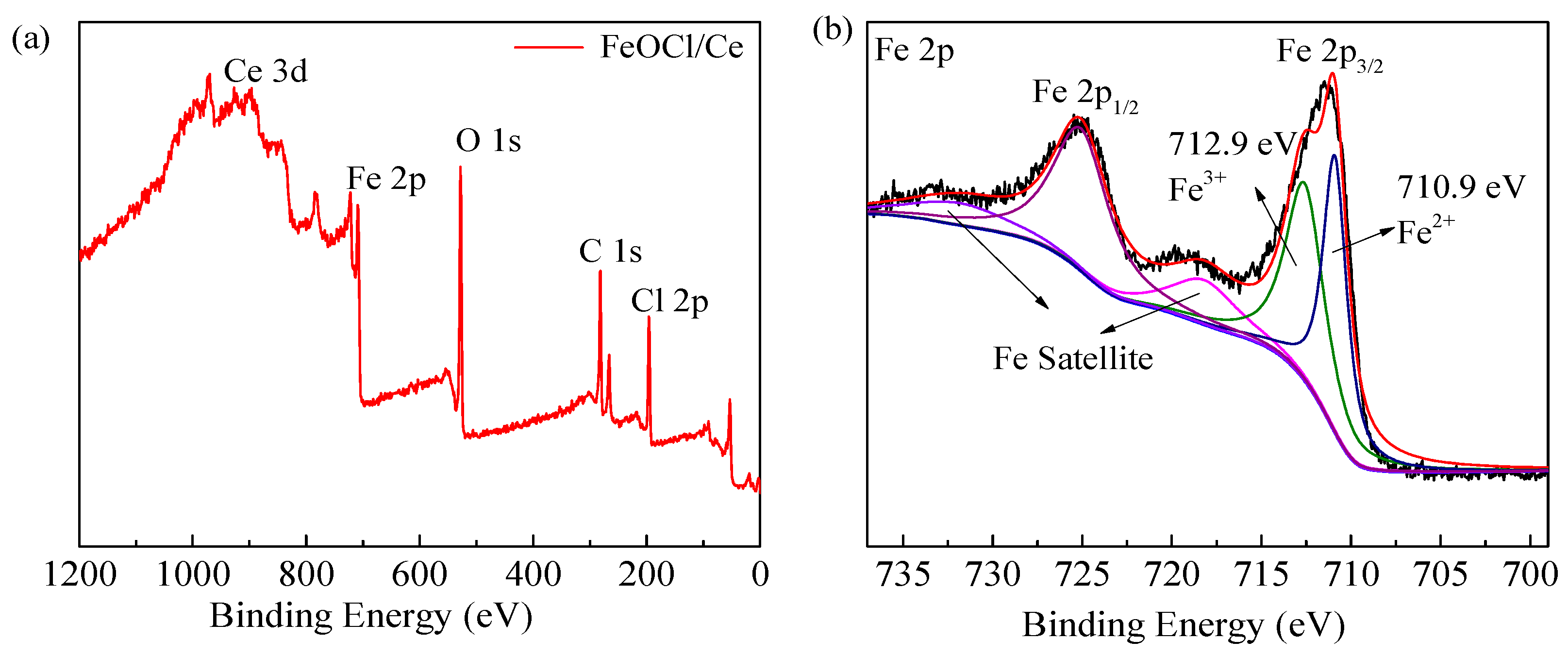
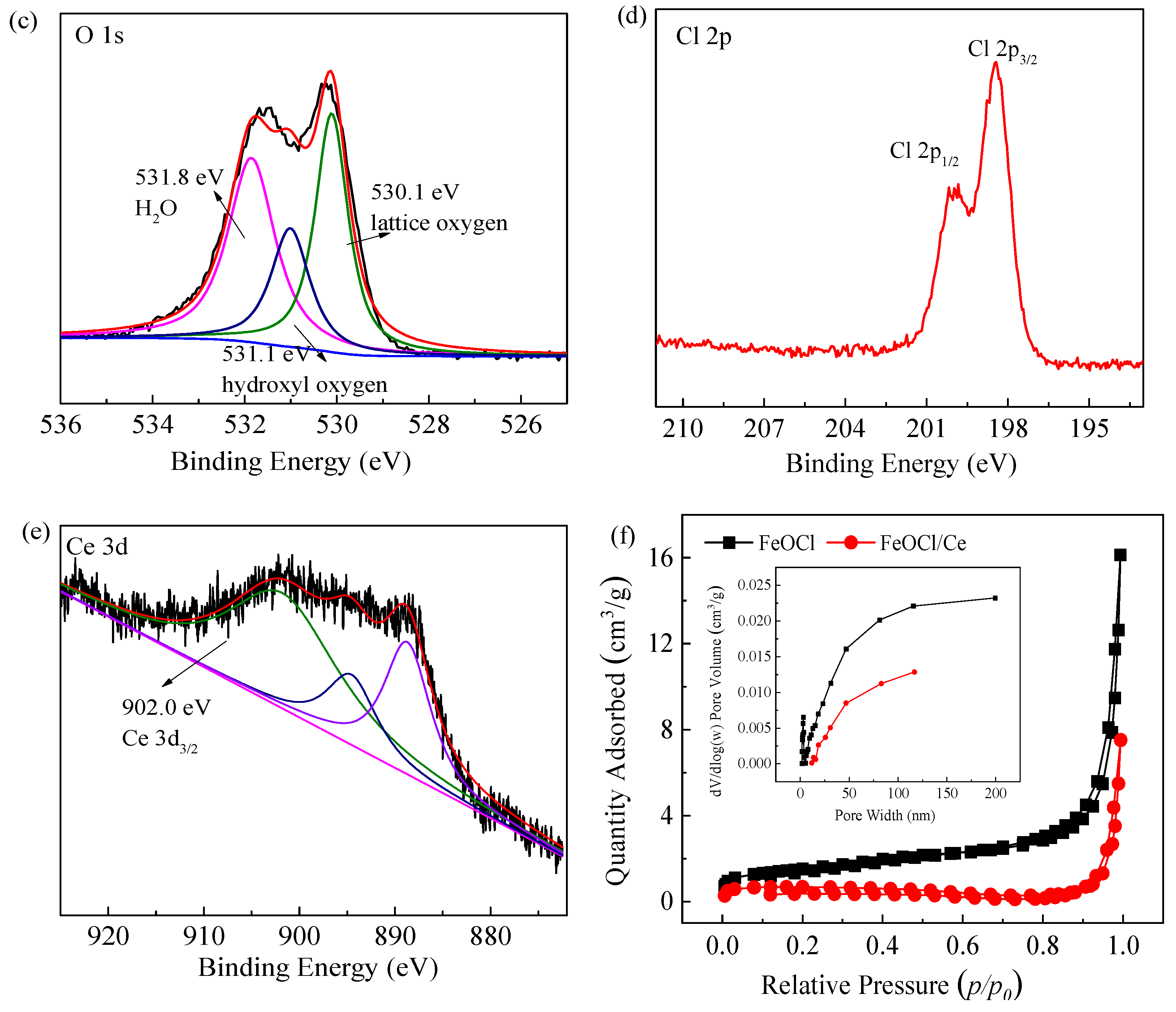
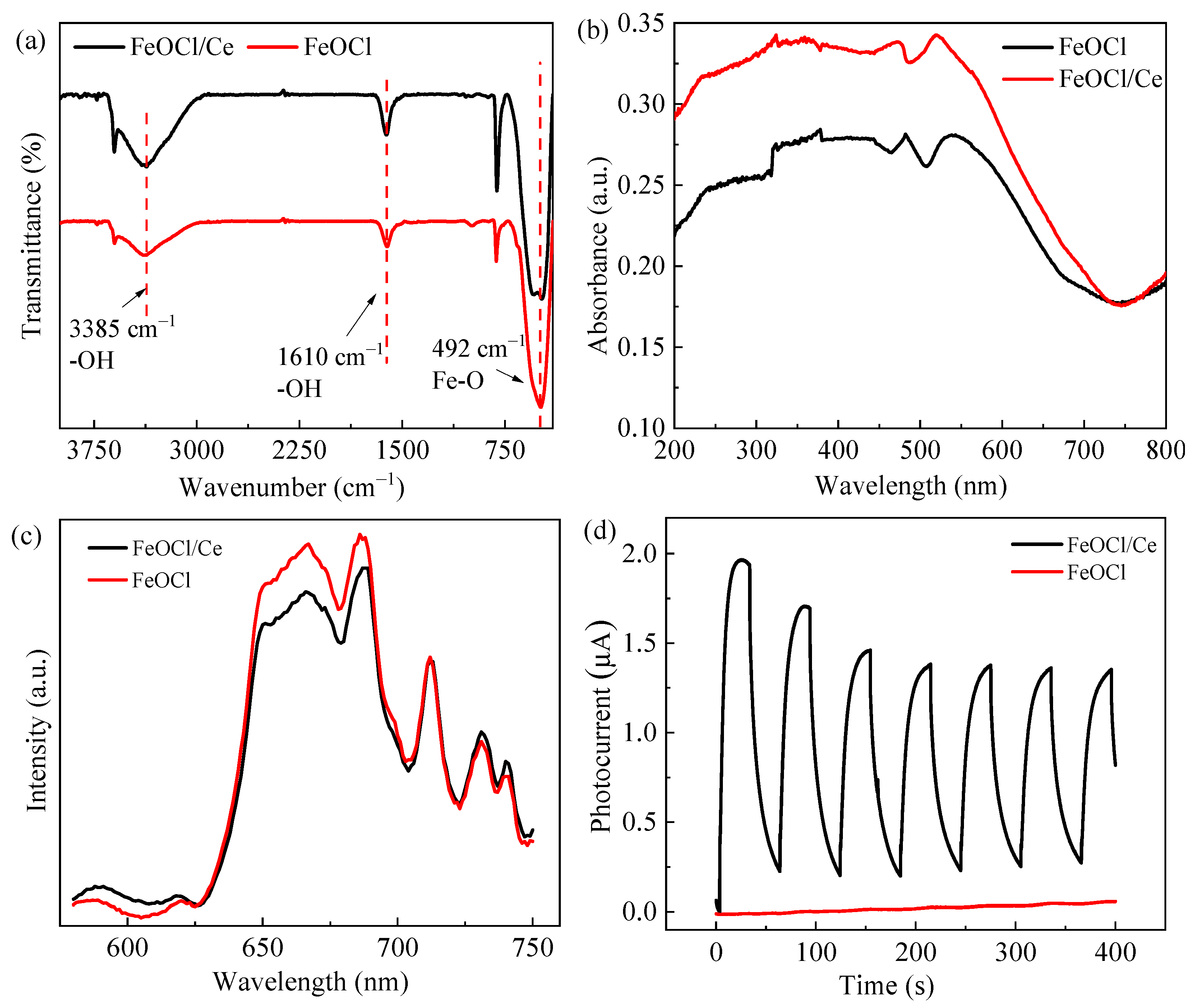


| Element | Mass Norm (%) | Atom (%) | Abs. Error (%)1 Sigma |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 14.88 | 28.48 | 0.98 |
| O | 9.30 | 13.36 | 0.59 |
| Al | 60.22 | 51.29 | 1.58 |
| Cl | 1.95 | 1.26 | 0.06 |
| Fe | 13.60 | 5.60 | 0.22 |
| Ce | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Sum | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Z.; Hu, M.; Li, M.; Wu, W.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y. The Efficiency and Mechanism of FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed Persulfate for the Degradation of Caffeine Under Visible Light. Molecules 2025, 30, 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224381
Bai Z, Hu M, Li M, Wu W, Zhou C, Wang Y. The Efficiency and Mechanism of FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed Persulfate for the Degradation of Caffeine Under Visible Light. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224381
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Zhao, Mingyue Hu, Minrui Li, Weidong Wu, Chi Zhou, and Yuru Wang. 2025. "The Efficiency and Mechanism of FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed Persulfate for the Degradation of Caffeine Under Visible Light" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224381
APA StyleBai, Z., Hu, M., Li, M., Wu, W., Zhou, C., & Wang, Y. (2025). The Efficiency and Mechanism of FeOCl/Ce-Catalyzed Persulfate for the Degradation of Caffeine Under Visible Light. Molecules, 30(22), 4381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224381








