Detection of Inosine Monophosphate and the Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with a Surface-Modified Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
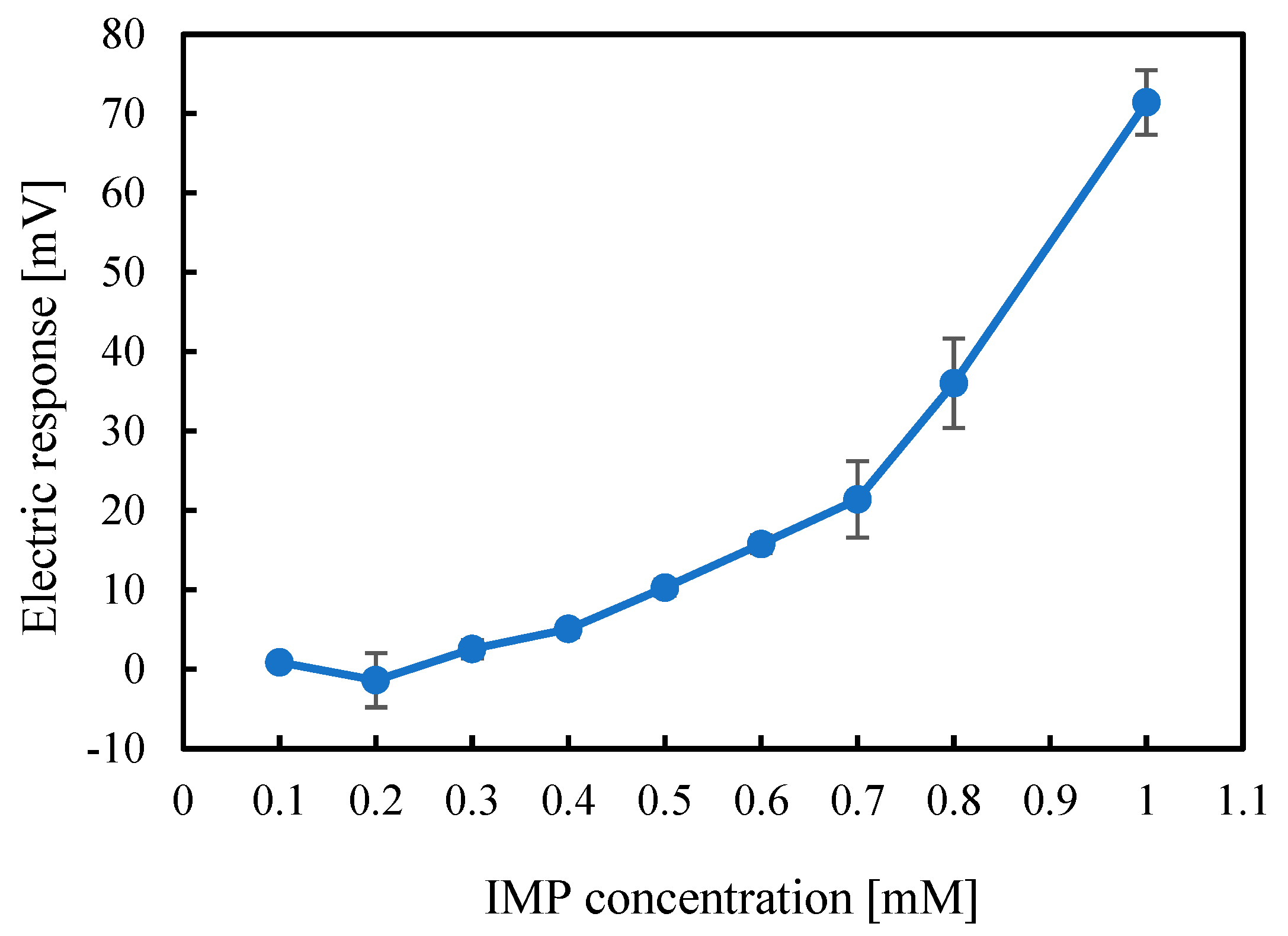
2.1. Measurement of IMP Using a Taste Sensor with a 2,6-DHTPA-Modified Lipid/Polymer Membrane
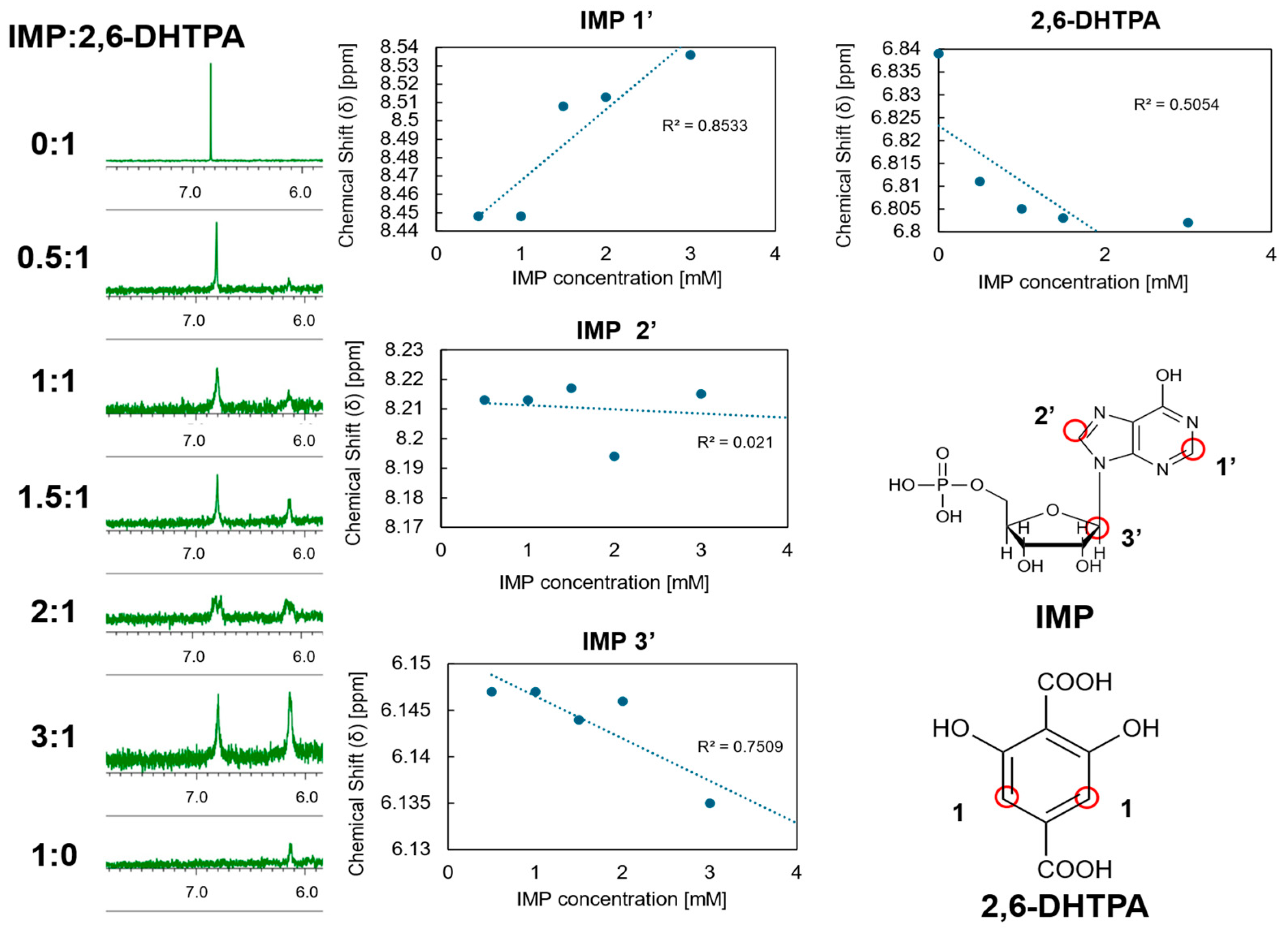
2.2. Mechanistic Consideration of IMP Detection Using 1H-NMR Analysis
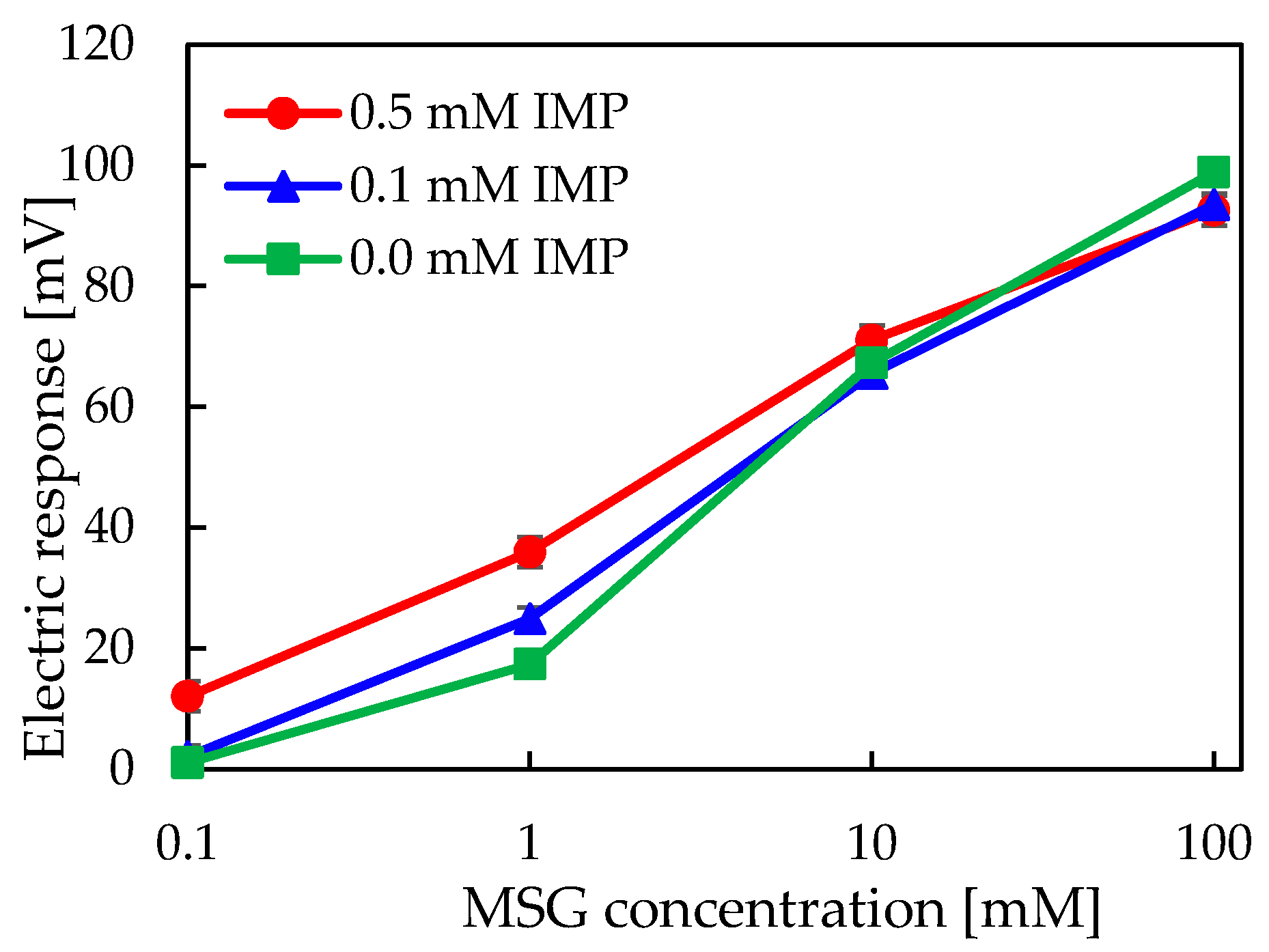
2.3. Measurement of Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with 2,6-DHTPA-Modified Lipid/Polymer Membrane
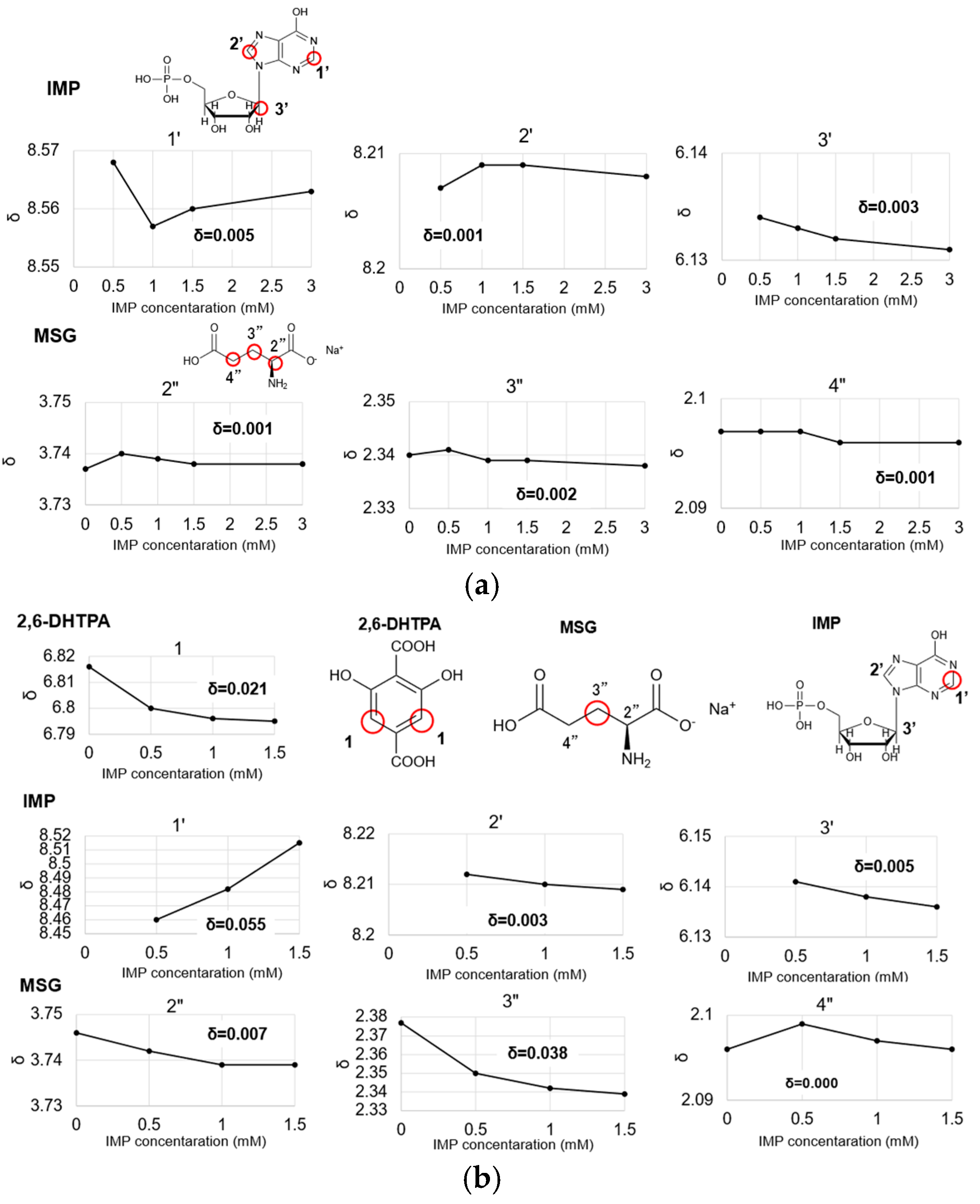
2.4. Consideration of the Mechanism for Measuring Umami Synergistic Effects Using 1H-NMR Analysis
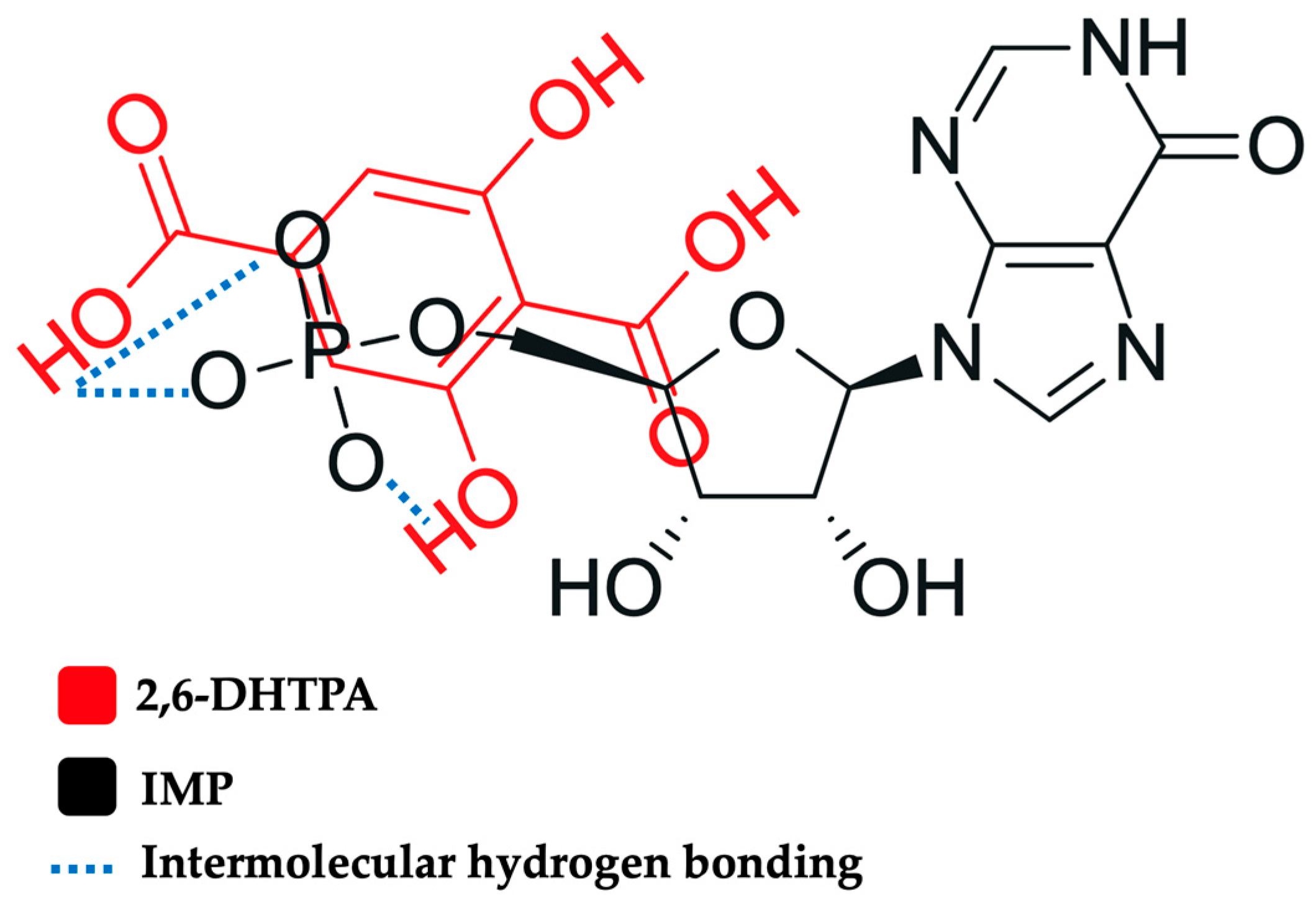
2.5. A Proposed Model of Interaction Between IMP and 2,6-DHTPA
3. Materials and Methods
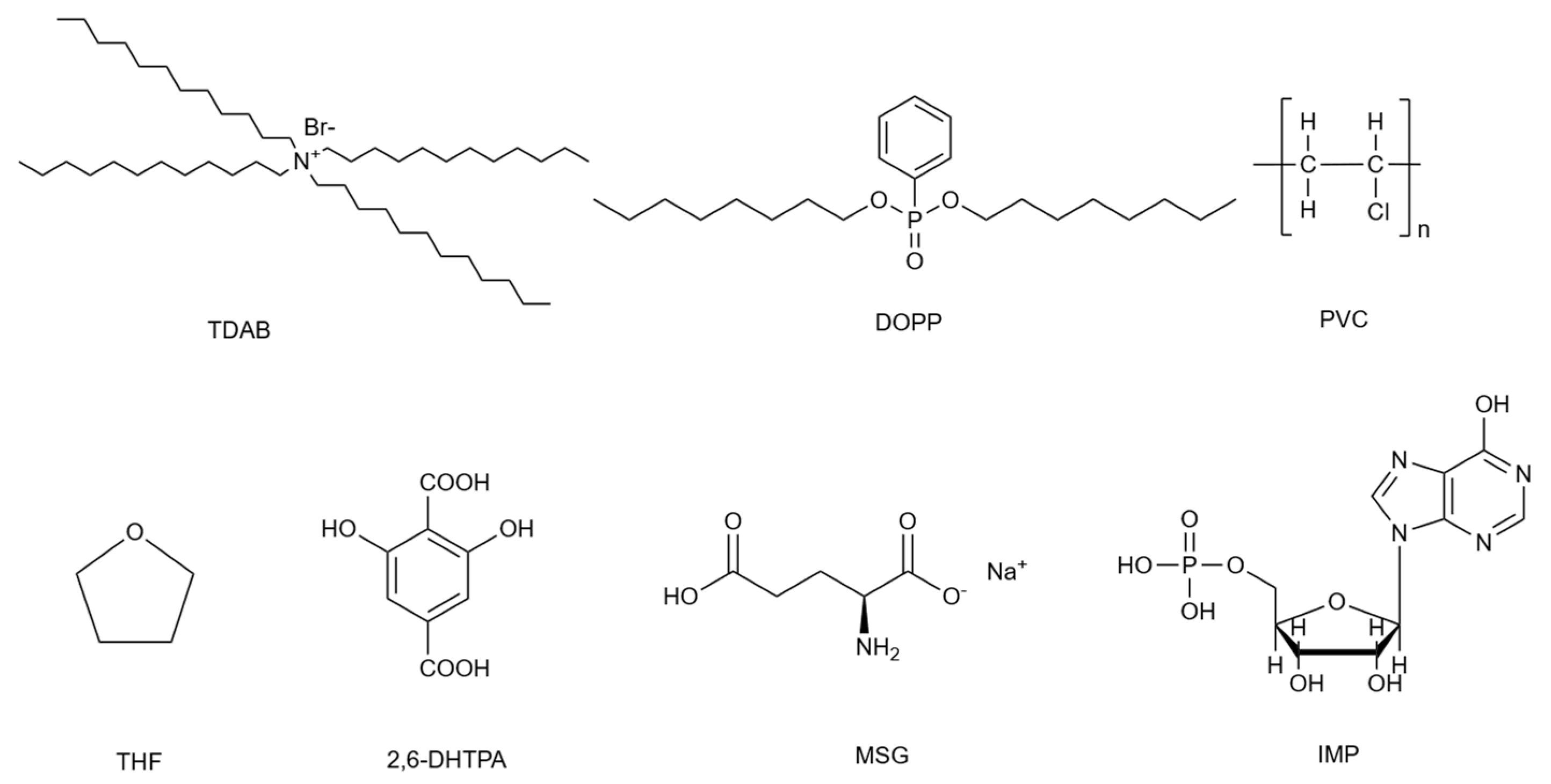
3.1. Reagent
3.2. Solutions
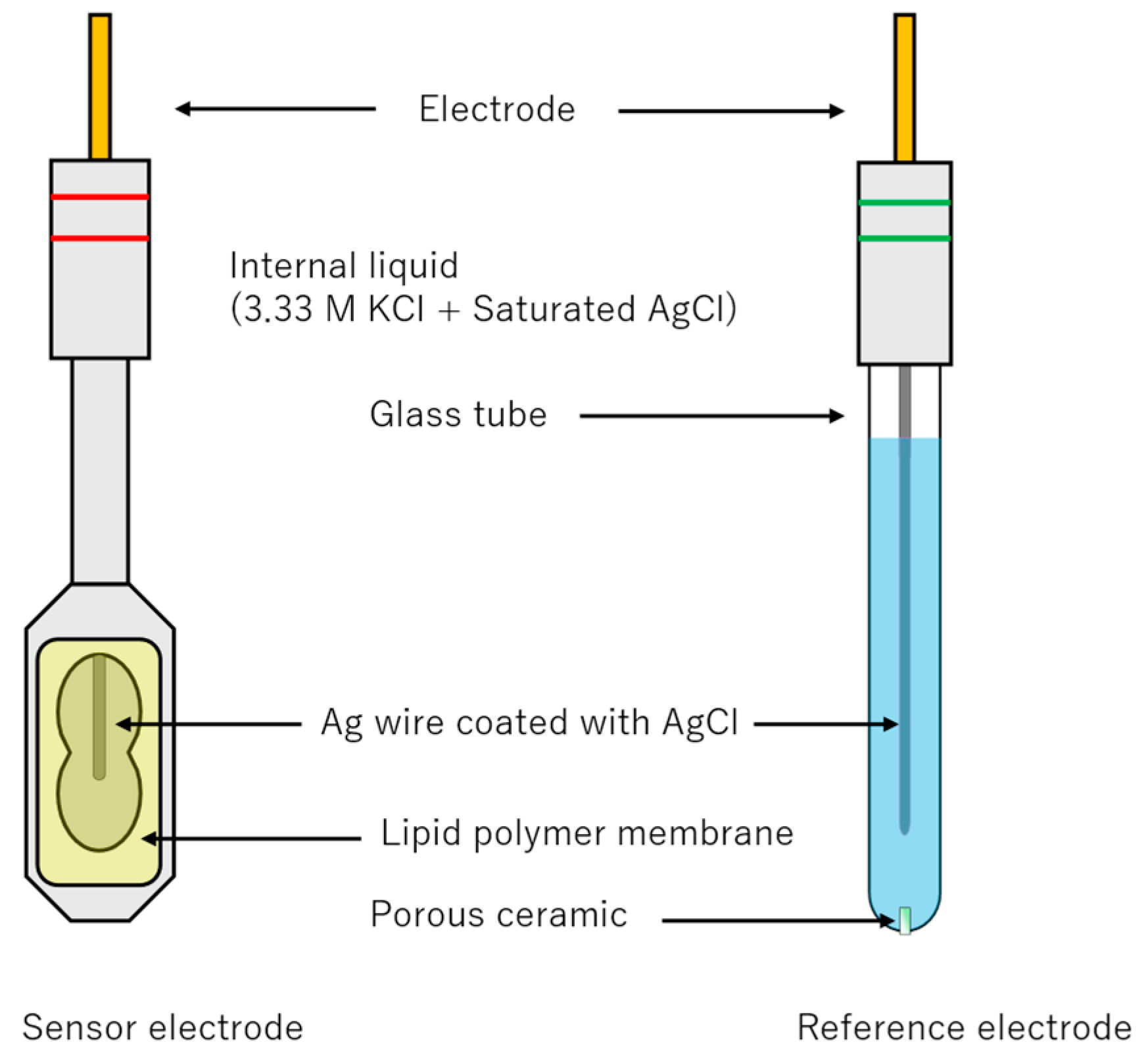
3.3. Preparation of the Lipid/Polymer Membrane
3.4. Assembly of Electrodes and Surface Modification of the Lipid/Polymer Membrane
3.5. Measurement of Umami Substances Using a Taste Sensor
3.6. 1H-NMR Measurement
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shigemura, N.; Ninomiya, Y. Recent Advances in molecular mechanisms of taste signaling and modifying. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 323, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Hoon, M.A.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Zuker, C.S. The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature 2006, 444, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E. One hundred years since the discovery of the “umami” taste from seaweed broth by Kikunae Ikeda, who transcended his time. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Ninomiya, K. Umami and food palatability. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 921S–926S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepeveen, J.; Moerdijk-Poortvliet, T.C.W.; van der Leij, F.R. Molecular insights into human taste perception and umami tastants. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, R.; Ohta, M.; Hayabuchi, H.; Fujitani, S.; Yoshida, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Tsuchihashi, T. Quantitative verification of the effect of using an umami substance (L-glutamate) to reduce salt intake. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uneyama, H.; Kawai, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Torii, K. Contribution of umami taste substances in human salivation during meal. J. Med. Investig. 2009, 56, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, T.; Kurihara, K. Large synergism between monosodium glutamate and 5′-nucleotides in canine taste nerve responses. J. Physiol. 1999, 259, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitanen, M.; Yang, B.; Hopia, A. The effect of cooking on umami compounds in wild and cultivated mushrooms. Food Chem. 2025, 278, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermiki, M.; Phanphensophon, N.; Mottram, D.S.; Methven, L. Contributions of non-volatile and volatile compounds to the umami taste and overall flavour of shiitake mushroom extracts and their application as flavour enhancers in cooked minced meat. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S. Roles and efficacy of sensory evaluation in studies of taste. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1991, 38, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herrmann, K. Taste of food especially more bitter or sweeter, and its relationship to the chemical structure of taste giving substances. Ernahr. Umsch. 1972, 19, 251–256. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Indow, T. A general equi-distance scale of the four qualities of taste. Jap. Psychol. Res. 1966, 8, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fan, M.; Fu, B.; Chang, Z.; Yi, J.; Xie, Y.; Ren, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, S. A novel strategy based on mouse organoid biosensor for detecting umami substances and their synergistic effect. Food Chem. 2025, 491, 145149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuzisawa, F.; Nadamoto, T. Contents of monosodium glutamate in processed foods and their influence on analytical methods of sodium. Jpn. J. Nutr. 1993, 51, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. A taste sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Toko, K. Taste sensor: Electronic tongue with lipid membranes. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, G.; Muszynski, M.; Ruch, P.W. A reconfigurable integrated electronic tongue and its use in accelerated analysis of juices and wines. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ghosh, A. An improved fractional-order circuit model for voltammetric taste sensor system with infused tea as analyte. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7792–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F. Voltammetric electronic tongues—Basic principles and applications. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F.; Lundstrom, I.; Wide, P. The combination of an electronic tongue and an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 58, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Oliveira, O.N. Recent advances in electronic tongues. Analyst 2010, 135, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhondekar, A.P. Development of lipid membrane based taste sensors for electronic tongue. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 70, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetó, X.; Del Valle, M. Electronic tongue applications for wastewater and soil analysis. iScience 2022, 25, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesoty, M.; Przewodowski, W.; Skibinska, P.C. Electronic noses and electronic tongues for the agricultural purposes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164, 117082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Hu, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, D.; Tian, S. Electronic tongue and electronic nose for food quality and safety. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162 Pt B, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Chen, Q. Evaluation of the flavour properties of cooked chicken drumsticks as affected by sugar smoking times using an electronic nose, electronic tongue, and HS-SPME/GC-MS. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 140, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Umami taste evaluation based on a novel mouse taste receptor cell-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y. A novel umami electrochemical biosensor based on AuNPs@ZIF-8/Ti3C2 MXene immobilized T1R1-VFT. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Research on sensing characteristics of three human umami receptors via receptor-based biosensor. Flavour Fragr. J. 2020, 35, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauliukaite, R.; Zhylyak, G.; Citterio, D.; Spichiger-Keller, U.E. L-glutamate biosensor for estimation of the taste of tomato specimens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, L.; Dong, Y.; Shu, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M. Multienzyme-mediated dual-channel magnetic relaxation switching taste biosensor (D-MRSTB) for simultaneous detection of umami compounds and synergistic enhancement in food. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Shu, G.; Wang, R.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, M. Kinetics of a new porcine taste-bud tissue biosensor for the detection of umami substances and their synergistic effect. Biosenseors Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Toko, K. Taste sensor with multiarray lipid/polymer membranes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 158, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toko, K. Research and development of taste sensors as a novel analytical tool. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2023, 99, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Low-temperature and long-time heating regimes on non-volatile compound and taste traits of beef assessed by the electronic tongue system. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ping, C.; Chen, Z. Mining of kokumi peptides in chicken broth with peptidomics. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 32, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikuni, K.; Oe, M.; Sasaki, K.; Shibata, M.; Nakajima, I.; Ojima, K.; Muroya, S. Effects of muscle type on beef taste-traits assessed by an electric sensing system. Anim. Sci. J. 2010, 81, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodake, K.; Numata, M.; Kosai, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Nishiumi, T. Evaluation of changes in the taste of cooked meat products during curing using an artificial taste sensor. Anim. Sci. J. 2013, 84, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Narita, Y.; Iwai, K.; Hanzawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kakiuchi, M.; Ariki, S.; Wu, X.; Miyake, K.; Tahara, Y. Bitterness compounds in coffee brew measured by analytical instruments and taste sensing system. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, G.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Z. Beer taste detection based on electronic tongue. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Miyake, K.; Tahara, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Iwai, K.; Narita, Y.; Hanzawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kakiuchi, M.; Ariki, S. Quantification of bitterness of coffee in the presence of high-potency sweeteners using taste sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; Yamashita, M.; Kato, M.; Suzuki, T.; Omori, M.; Chen, R. Evaluation of the taste of tea with different degrees of fermentation using a taste sensing system. Sens. Mater. 2011, 23, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, L.; Kang, B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Gui, X.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Traditional human taste panel and taste sensors methods for bitter taste masking research on combined bitterness suppressants of berberine hydrochloride. Sens. Mater. 2017, 29, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenblust-Woertz, K.; Pein, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Development and characterization of medicines for children. In Biochemical Sensors: Mimicking Gustatory and Olfactory Senses; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2013; pp. 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hazekawa, M.; Haraguchi, T.; Furuno, H.; Teraoka, M.; Ikezaki, H. Evaluation of palatability of 10 commercial amlodipine orally disintegrating tablets by gustatory sensation testing, OD-mate as a new disintegration apparatus and the artificial taste sensor. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T. Taste sensor assessment of bitterness in medicines: Overview and recent topics. Sensors 2024, 24, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; He, B.; Luo, S.; Tu, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Y. Flavor evaluation of “Hongyang” kiwifruit from different cultivation regions based on electronic tongue sensory assessment and HS-SPME-GCMS analysis. Future Postharvest Food 2025, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, J.; Toko, K.; Tahara, Y.; Ishida, M.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Kojima, H.; Ikegami, S.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T. Development of taste sensor to detect non-charged bitter substances. Sensors 2020, 20, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.E.; Kung, F. Effect of intramolecular hydrogen bonding on ionization constants of substituted salicylic acids. Can. J. Chem. 1965, 44, 1261–1269. Available online: https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/epdf/10.1139/v66-188 (accessed on 28 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.I. Competing intramolecular vs. intermolecular hydrogen bonds in solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19562–19633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Ide, H.; Arima, K.; Zhao, Z.; Matsui, T.; Toko, K. Identification of the principle of taste sensors to detect non-charged bitter substances by 1H-NMR measurement. Sensors 2022, 22, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, R.A. Basic Principles. In In Vivo NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, H. The proton magnetic resonance spectra of organic molecules—Chemical shift and spin-spin coupling. In NMR Spectroscopy: Basic Principles, Concepts and Applications in Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 29–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ujihara, T.; Hayashi, N.; Ikezaki, H. Objective evaluation of astringent and umami taste intensities of matcha using a taste sensor system. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 19, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, W.; Shao, X.; Fu, B.; Qiao, X.; Yuan, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, P.; Du, M.; Tu, M. Identification, screening and taste mechanisms analysis of two novel umami pentapeptides derived from the myosin heavy chain of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Lin, L. Identification and taste characteristics of novel umami and umami-enhancing peptides separated from peanut protein isolate hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Su, L.; Yu, Z. Taste characteristics and umami mechanism of novel umami peptides from hen egg proteins. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 181, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Kuga, H.; Ezaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Toko, K. Peculiar change in membrane potential of taste sensor caused by umami substances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezaki, H.; Chen, R.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced taste sensors based on artificial lipids with global selectivity to basic taste qualities and high correlation to sensory scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Kimura, S.; Toko, K. Development of taste sensor with lipid/polymer membranes for detection of umami substances using surface modification. Biosensors 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Ide, H.; Zhao, Z.; KoFshi, M.; Kimura, S.; Matsui, T.; Toko, K. Investigating the mechanism underlying umami substance detection in taste sensors by using 1H-NMR analysis. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Otsuka, S.; Jin, J.; Onodera, T.; Yatabe, R.; Kimura, S.; Toko, K. Relationship between sensor sensitivity and chemical structure of benzene-carboxylic modifiers for umami substance detection. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Klebansky, B.; Fine, R.M.; Xu, H.; Pronin, A.; Liu, H.; Tachdjian, C.; Li, X. Molecular mechanism for the umami taste synergism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20930–20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Da, L.-T.; Liu, Y. Understanding the molecular mechanism of umami recognition by T1R1-T1R3 using molecular dynamics simulations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otsuka, S.; Koshi, M.; Onodera, T.; Yatabe, R.; Matsui, T.; Toko, K. Detection of Inosine Monophosphate and the Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with a Surface-Modified Membrane. Molecules 2025, 30, 4171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214171
Otsuka S, Koshi M, Onodera T, Yatabe R, Matsui T, Toko K. Detection of Inosine Monophosphate and the Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with a Surface-Modified Membrane. Molecules. 2025; 30(21):4171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214171
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtsuka, Sota, Mariko Koshi, Takeshi Onodera, Rui Yatabe, Toshiro Matsui, and Kiyoshi Toko. 2025. "Detection of Inosine Monophosphate and the Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with a Surface-Modified Membrane" Molecules 30, no. 21: 4171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214171
APA StyleOtsuka, S., Koshi, M., Onodera, T., Yatabe, R., Matsui, T., & Toko, K. (2025). Detection of Inosine Monophosphate and the Umami Synergistic Effect Using a Taste Sensor with a Surface-Modified Membrane. Molecules, 30(21), 4171. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30214171








