Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Early-Stage Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Rats: A Comparative Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Behavioral Phenotyping
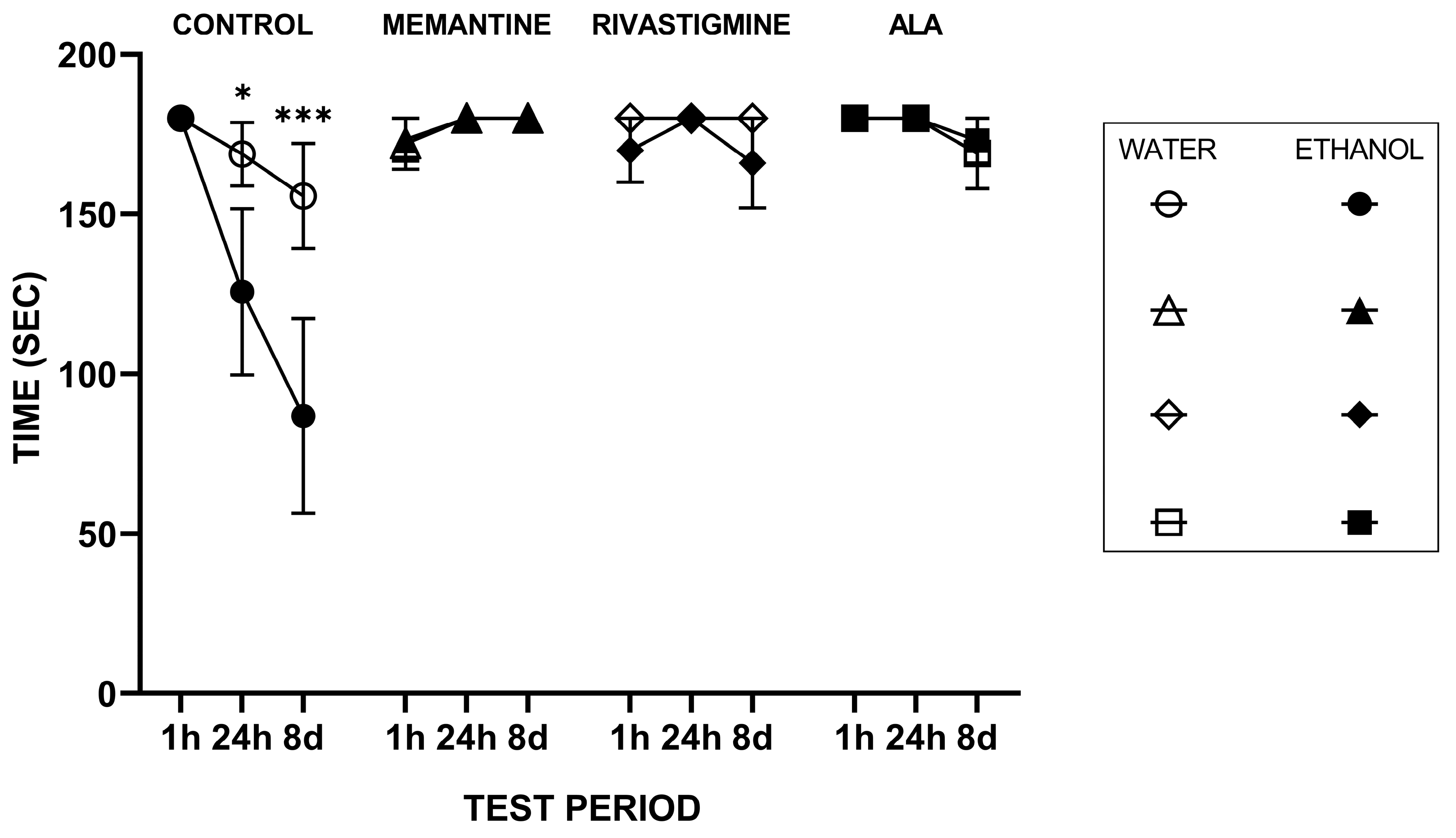
2.1.1. Step-Through Passive Avoidance Test
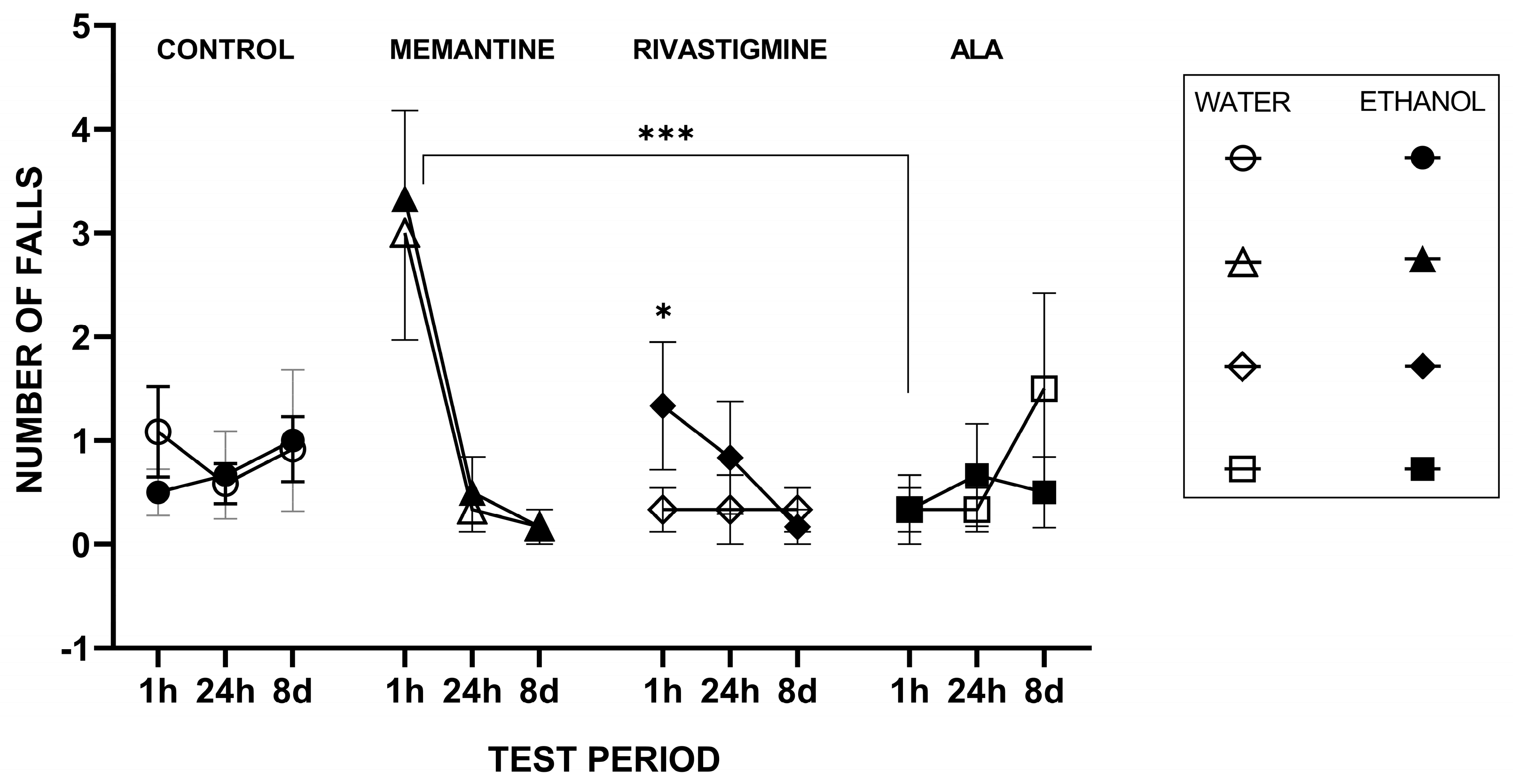
2.1.2. Rotarod Performance Test
2.2. Body Weight and Relative Brain Weight Measurement
2.2.1. Body Weight Measurement
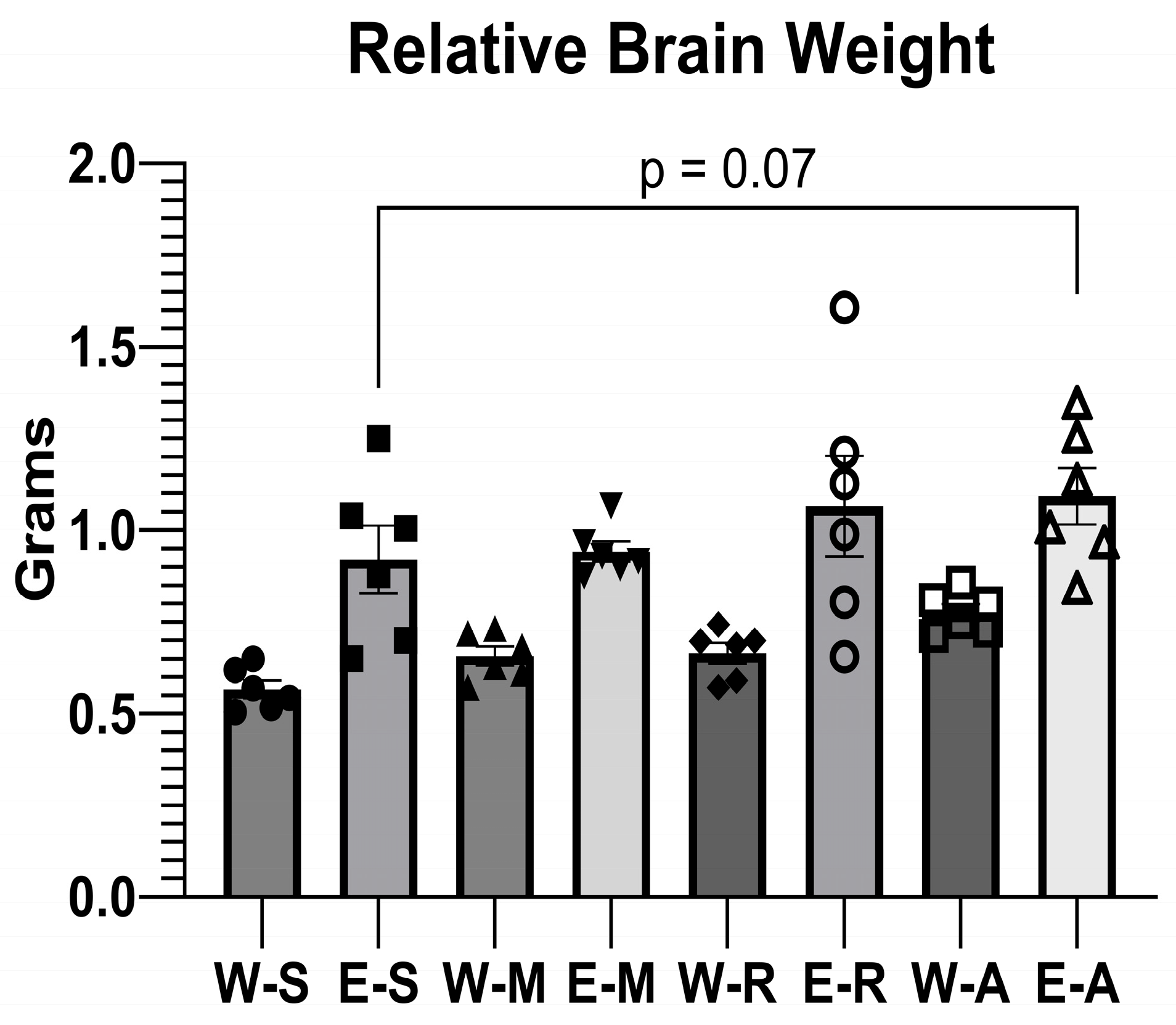
2.2.2. Relative Brain Weight Measurement
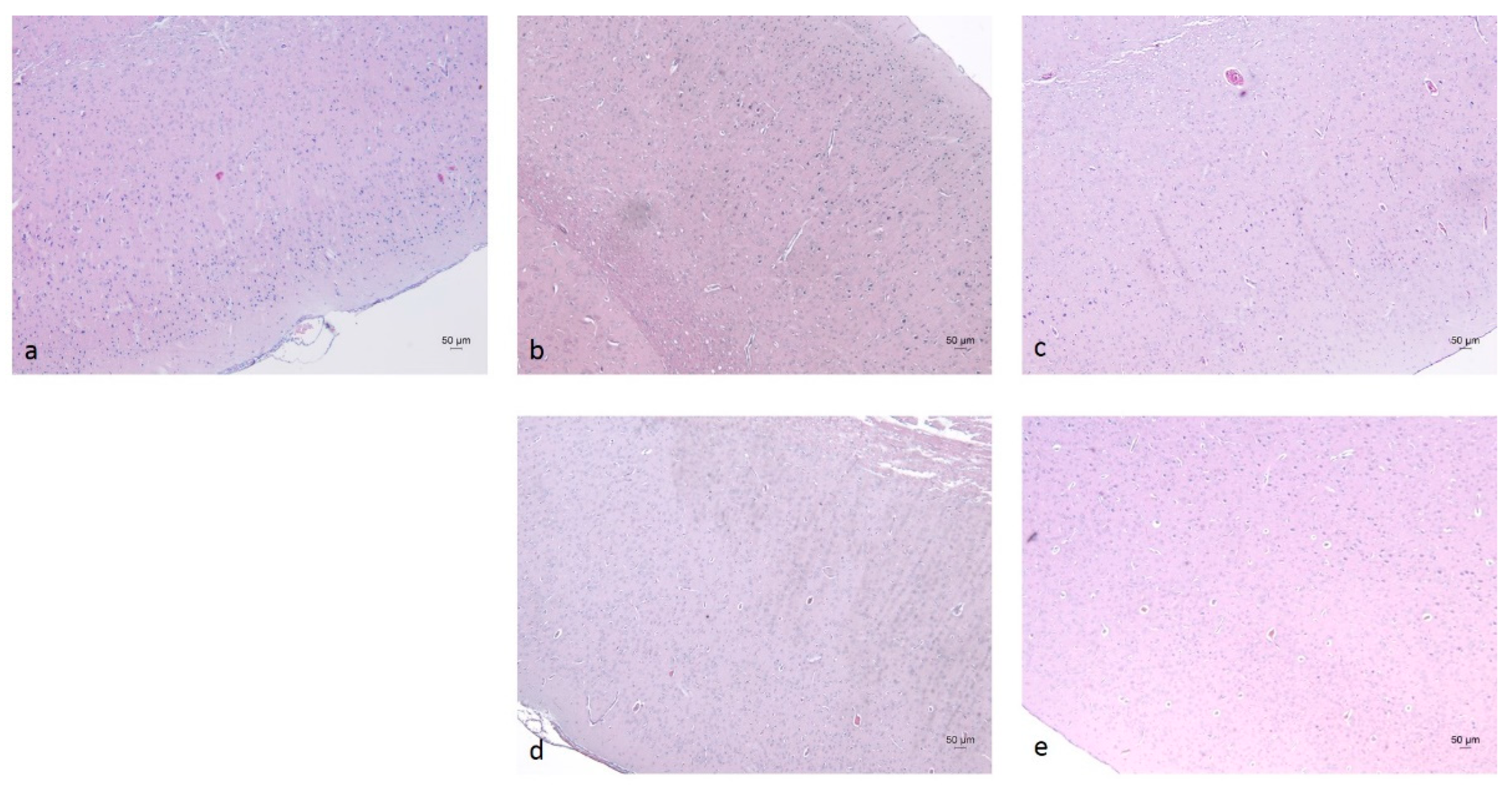
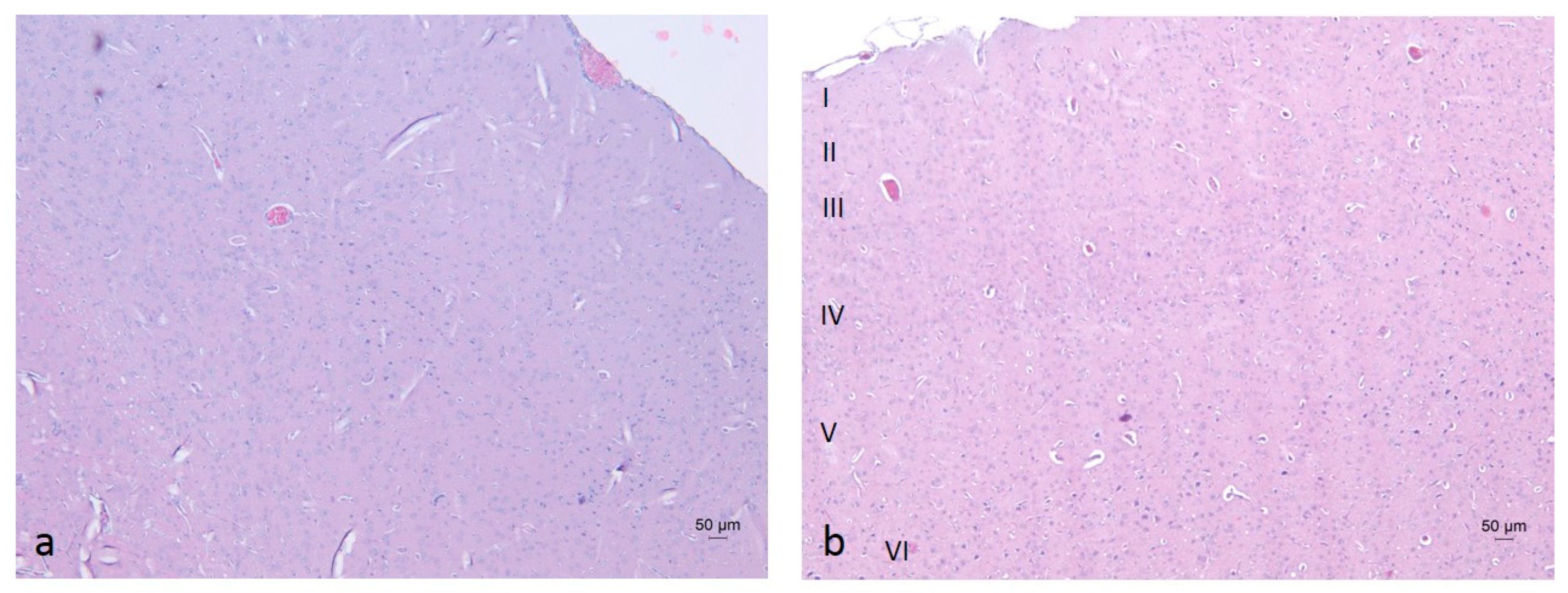
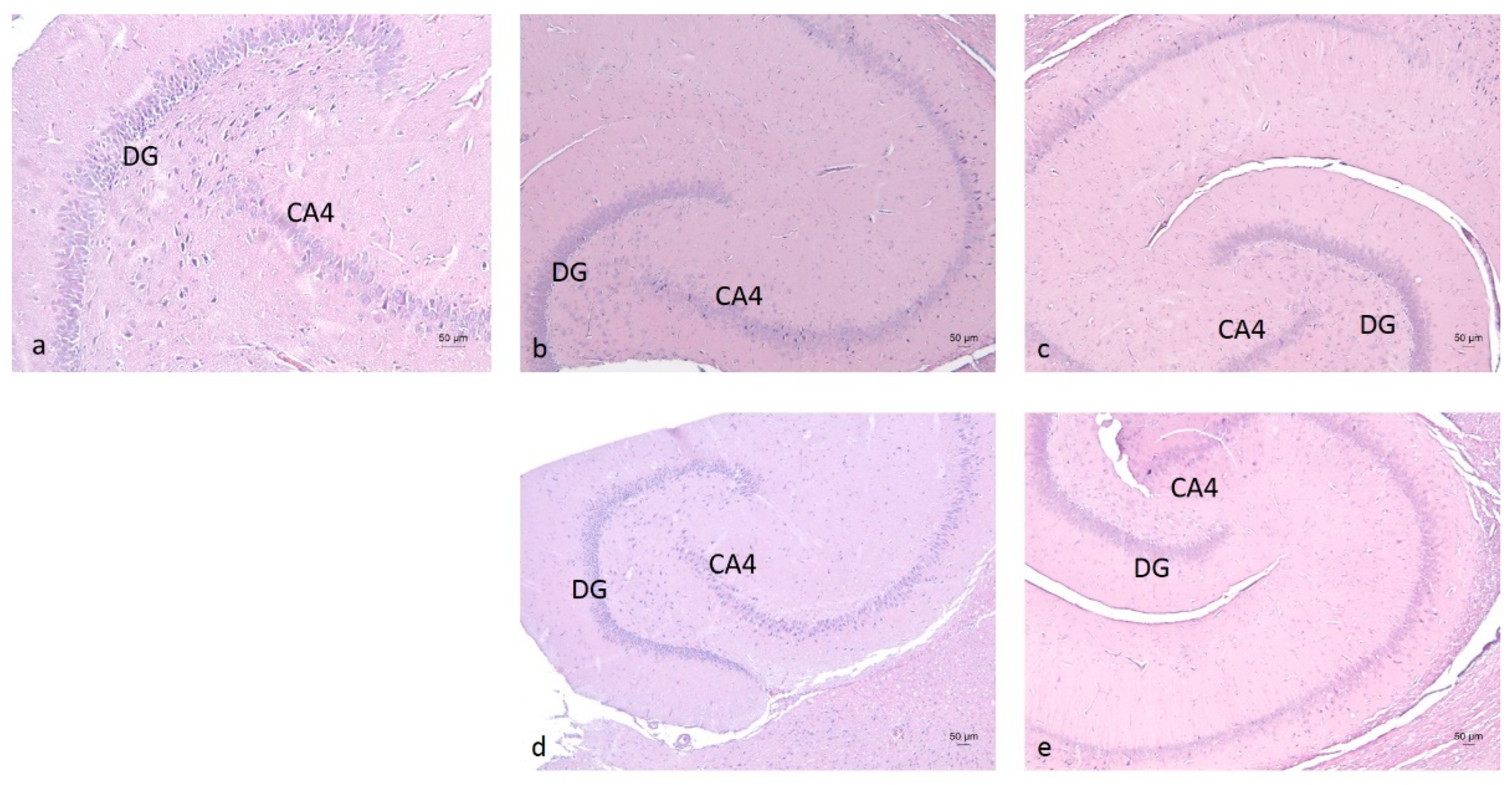
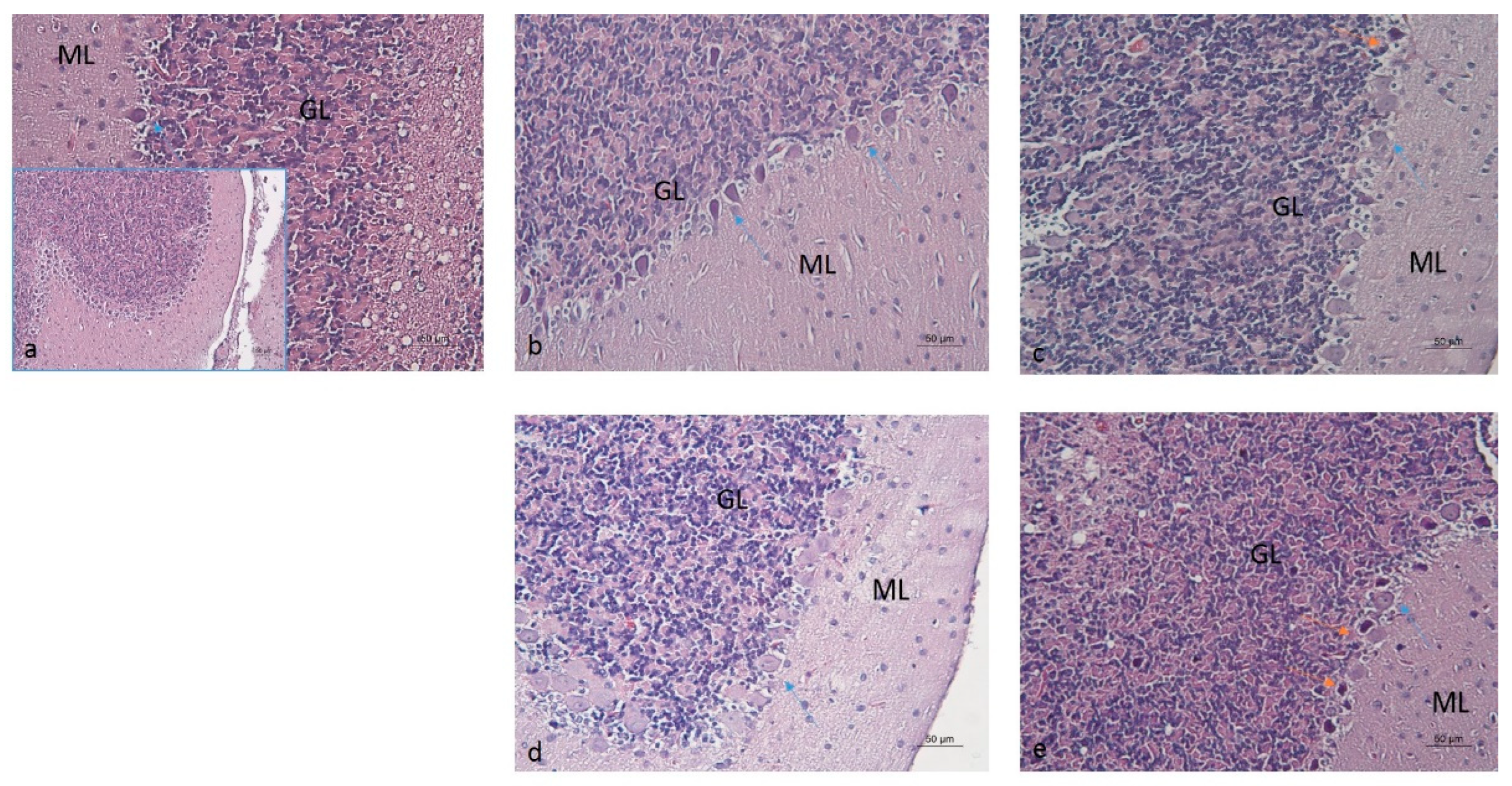
2.3. Histopathological Analysis of Brain Tissues
2.4. Biochemical Analysis of Brain Tissues
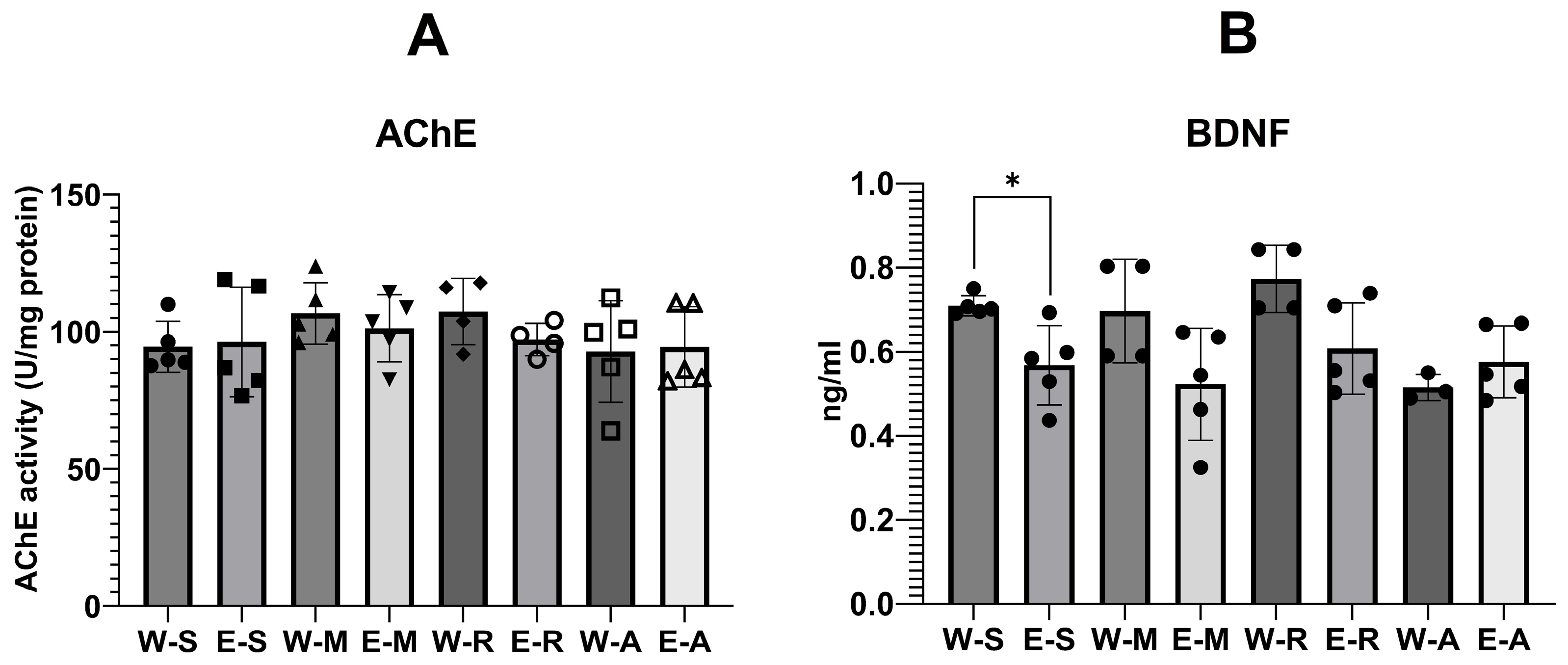
2.4.1. AChE Activity and BDNF Levels
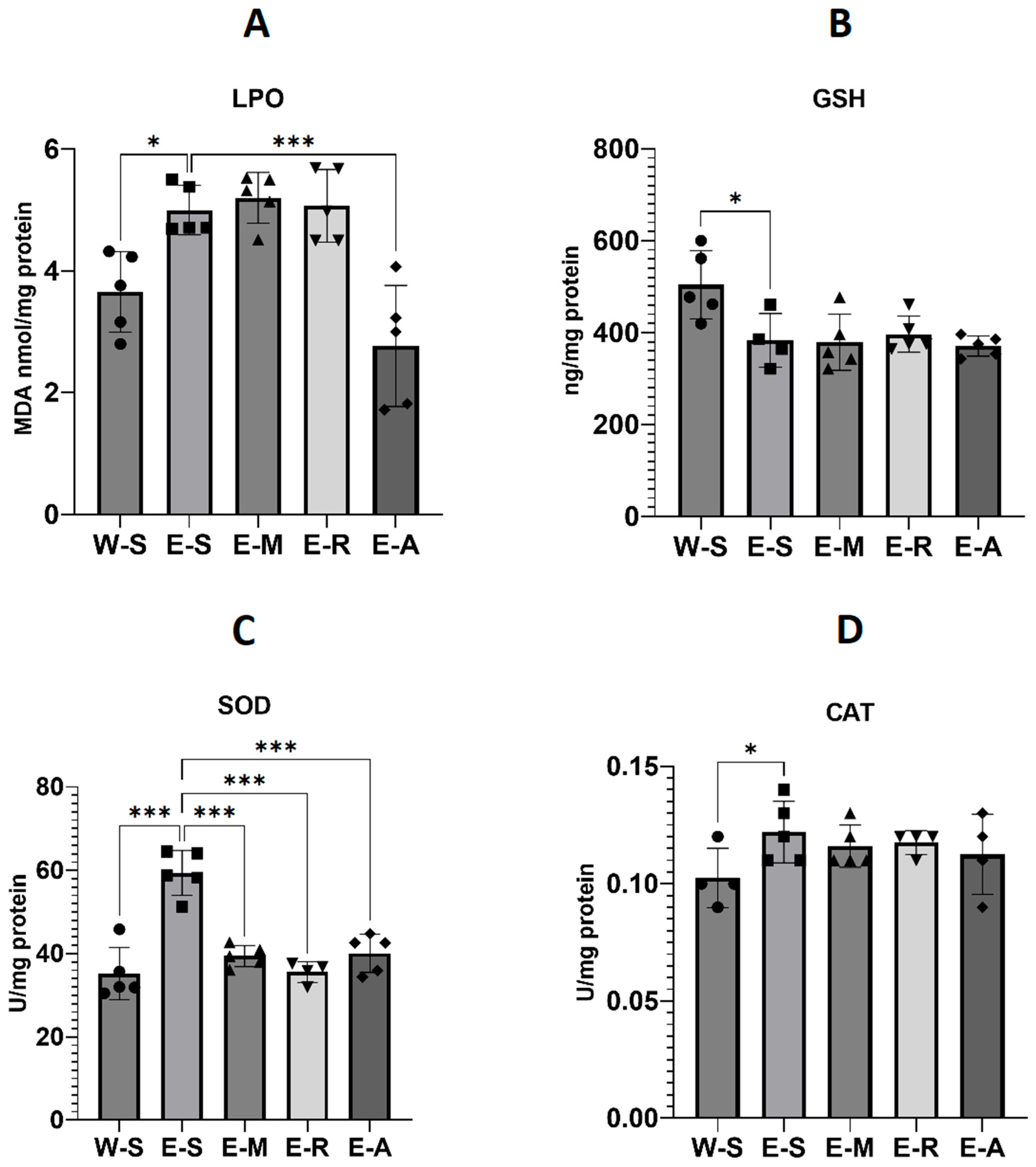
2.4.2. Oxidative Stress Levels
3. Discussion
3.1. Step-Through Passive Avoidance Test
3.2. AChE Activity
3.3. BDNF Levels
3.4. Oxidative Stress Parameters
3.5. Body Weight, Brain Weight and Relative Brain Weight
3.6. Histopathological Analysis
3.7. Rotarod Test
3.8. Summary and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Substances
4.2. Experimental Animals
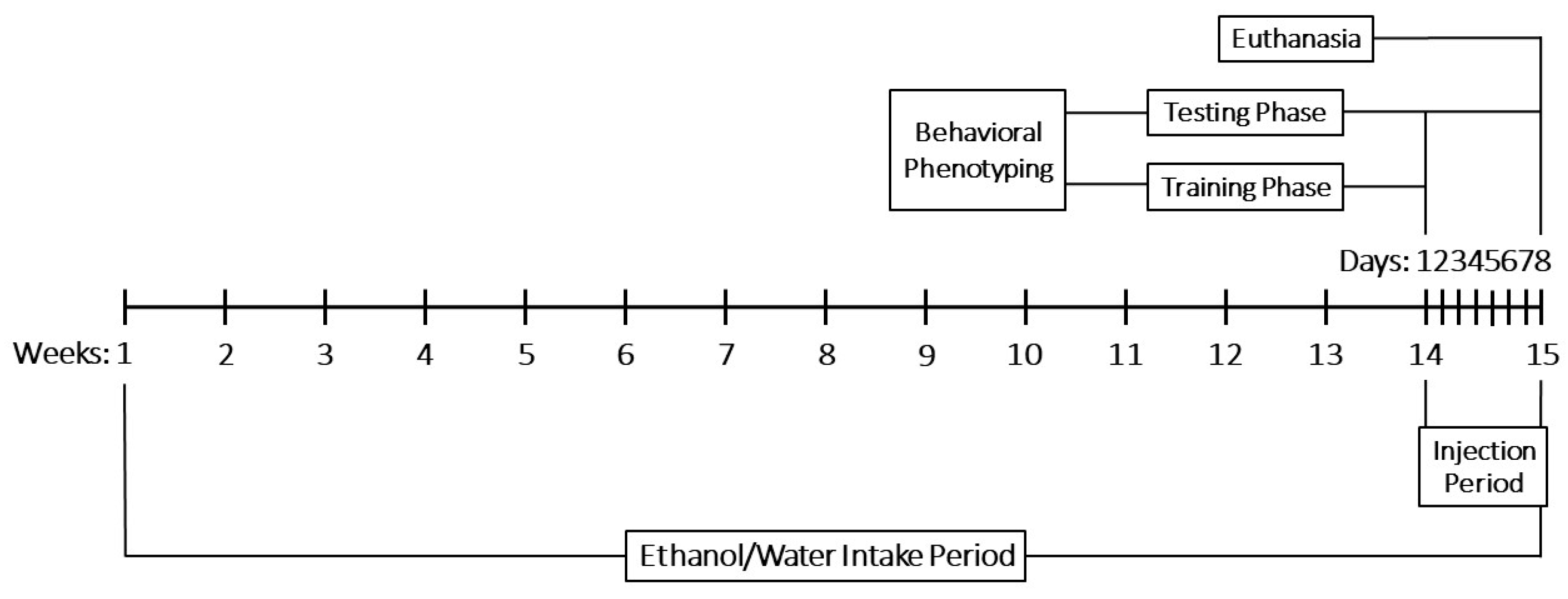
4.3. Experimental Design
- Water–Saline group (W-S), injected with 0.9% NaCl (0.5 mL/100 g i.p.).
- Water–ALA group (W-A) injected with ALA (30 mg/kg i.p.).
- Water–Rivastigmine group (W-R), injected with rivastigmine (1.5 mg/kg i.p.).
- Water–Memantine group (W-M), injected with memantine (5 mg/kg i.p.).
- Ethanol–Saline group (E-S), injected with 0.9% NaCl (0.5 mL/100 g i.p.).
- Ethanol–ALA group (E-A), injected with ALA (30 mg/kg i.p.).
- Ethanol–Rivastigmine group (E-R), injected with rivastigmine (1.5 mg/kg i.p.).
- Ethanol–Memantine group (E-M), injected with memantine (5 mg/kg i.p.).
4.3.1. Behavioral Phenotyping
- Step-through Passive Avoidance Test [167]
- Rotarod Performance Test [168]
4.3.2. Body Weight, Brain Weight and Relative Brain Weight Measurement
4.3.3. Histopathological Analysis of Brain Tissues
4.3.4. Biochemical Analysis of Brain Tissues
- AChE Levels [169]
- BDNF Levels
- Oxidative Stress Levels
4.3.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| ALA | Alpha-lipoic acid |
| ARBD | Alcohol-related brain damage |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CAT | Catalase |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DHLA | Dihydrolipoic acid |
| E-A | Ethanol–ALA group |
| EGs | Ethanol-drinking groups |
| E-M | Ethanol–Memantine group |
| E-R | Ethanol–Rivastigmine group |
| E-S | Ethanol–Saline group |
| GSH | Total glutathione |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IL | Initial latency |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LPO | Lipid peroxidation |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NOX | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase |
| pCREB | cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| STL | Step-through latency |
| TLR2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| W-A | Water–ALA group |
| WGs | Water-drinking groups |
| W-M | Water–Memantine group |
| W-R | Water–Rivastigmine group |
References
- Castro, F.G.; Manuel Barrera, J.; Mena, L.A.; Aguirre, K.M. Culture and Alcohol Use: Historical and Sociocultural Themes From 75 Years of Alcohol Research. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs Supplement. 2014, 75 (Suppl. S17), 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, E.; Fiore, A.; Yurasek, A.M.; Cook, R.L.; Boissoneault, J. Association of therapeutic and recreational reasons for alcohol use with alcohol demand. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 31, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, F.; Goyal, A. Ethanol. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556147/ (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Zhao, J.; Stockwell, T.; Naimi, T.; Churchill, S.; Clay, J.; Sherk, A. Association Between Daily Alcohol Intake and Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analyses. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e236185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators G 2016 A. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcohol. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Health (US) NI of Study BSC. Information about Alcohol. In NIH Curriculum Supplement Series; National Institutes of Health (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK20360/ (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Quelch, D.; Roderique-Davies, G.; John, B. Alcohol-related brain damage: An umbrella (term) for the approaching post-COVID monsoon. Future Healthc. J. 2023, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/docs/default-source/improving-care/better-mh-policy/college-reports/college-report-cr185.pdf?sfvrsn=66534d91_2 (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Available online: https://alcoholforum.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Alcohol-Related-Brain-Injury-A-guide-for-Professionals.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Torvik, A.; Lindboe, C.F.; Rogde, S. Brain lesions in alcoholics. A neuropathological study with clinical correlations. J. Neurol. Sci. 1982, 56, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.T.; Kipp, B.T.; Reitz, N.L.; Savage, L.M. Aging with Alcohol-Related Brain Damage: Critical Brain Circuits Associated with Cognitive Dysfunction. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 148, 101–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.A.; Neafsey, E.J. Ethanol and adult CNS neurodamage: Oxidative stress, but possibly not excitotoxicity. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2012, 4, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistarz, N.; Andersen, K.; Nielsen, A.S.; Goudriaan, A.E.; Michel, T.M.; Skøt, L.; Nielsen, D.G.; Mellentin, A.I. Pharmacological enhancing agents targeting cognition in patients with alcohol-induced neurocognitive disorders: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 125, 608–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem. Lipoic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6112 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Smith, A.R.; Shenvi, S.V.; Widlansky, M.; Suh, J.H.; Hagen, T.M. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Dihydrolipoic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/421 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Muresan, A.; Vergely, C. Alpha-lipoic acid: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential in diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billgren, E.S.; Cicchillo, R.M.; Nesbitt, N.M.; Booker, S.J. Lipoic acid biosynthesis and enzymology. In Comprehensive Natural Products II; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 181–212. Available online: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?scp=84904626958&partnerID=8YFLogxK (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Wang, J.Q.; Ling, X.; Wang, H.J.; Chen, F.E. α-Lipoic acid chemistry: The past 70 years. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 36346–36363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipoic Acid|Linus Pauling Institute|Oregon State University. 2014. Available online: https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/lipoic-acid (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Ledesma, J.C.; Aragon, C.M.G. Alpha-lipoic acid, a scavenging agent for H2O2, reduces ethanol-stimulated locomotion in mice. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, J.C.; Baliño, P.; Aragon, C.M.G. Reduction in central H2O2 levels prevents voluntary ethanol intake in mice: A role for the brain catalase-H2O2 system in alcohol binge drinking. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirlich, M.; Kiok, K.; Sandig, G.; Lochs, H.; Grune, T. Alpha-lipoic acid prevents ethanol-induced protein oxidation in mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 328, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.H.; Min, A.K.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, I.K.; Park, K.G. Alpha lipoic acid induces hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 expression via up-regulation of CREBH. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y. α-Lipoic acid up-regulates gene expression but reduces protein levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in HepG2 cells. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 131, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Schneeberger, M.; Fan, W.; Bugde, A.; Gautron, L.; Vale, K.; Hammer, R.E.; Zhang, Y.; Friedman, J.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. FGF21 counteracts alcohol intoxication by activating the noradrenergic nervous system. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 429–437.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staykov, H.; Kalfin, R.; Tancheva, L. Review on the Synthesis of Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Its Therapeutic Potential in Experimental Model of Dementia. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2024, 59, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoliu, C.; Vallés, S.; Renau-Piqueras, J.; Guerri, C. Ethanol-Induced Oxygen Radical Formation and Lipid Peroxidation in Rat Brain: Effect of Chronic Alcohol Consumption. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Nixon, K. Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration and Regeneration in Alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008, 44, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in brain during acute and chronic ethanol treatment and ethanol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, F.T.; Collins, M.A.; Dlugos, C.; Littleton, J.; Wilkins, L.; Neafsey, E.J.; Pentney, R.; Snell, L.D.; Tabakoff, B.; Zou, J.; et al. Alcohol-Induced Neurodegeneration: When, Where and Why? Alcohol Clin Amp Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.; Achille, N.; Neafsey, E.J.; Collins, M.A. Binge ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in rat organotypic brain slice cultures: Effects of PLA2 inhibitor mepacrine and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shafiee, A.; Jafarabady, K.; Rafiei, M.A.; Beiky, M.; Seighali, N.; Golpayegani, G.; Jalali, M.; Abhari, F.S.; Bahri, R.A.; Safari, O.; et al. Effect of alcohol on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) blood levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, K.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure decreases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Zonooz, S.; Hasani, M.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Beatriz Pizarro, A.; Heydari, H.; Yosaee, S.; Rezamand, G.; Heshmati, J. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baziar, N.; Nasli-Esfahani, E.; Djafarian, K.; Qorbani, M.; Hedayati, M.; Mishani, M.A.; Faghfoori, Z.; Ahmaripour, N.; Hosseini, S. The Beneficial Effects of Alpha Lipoic Acid Supplementation on Lp-PLA2 Mass and Its Distribution between HDL and apoB-Containing Lipoproteins in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 5850865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, N.M.; Shekhar, M.A.; Vishwanath, B.S. α-lipoic acid: An inhibitor of secretory phospholipase A2 with anti-inflammatory activity. Life Sci. 2006, 80, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Han, Y.; Ji, Y.; Sun, K.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K. The effect of a-Lipoic acid (ALA) on oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in high glucose–induced human corneal epithelial cells. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yan, X.Z.; Xu, S.F.; Pang, Z.Q.; Li, L.B.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.G.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Guo, C.; et al. α-Lipoic Acid Maintains Brain Glucose Metabolism via BDNF/TrkB/HIF-1α Signaling Pathway in P301S Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 262. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/aging-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00262/full (accessed on 31 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Liggett, A. Adding an orange to the banana bag: Vitamin C deficiency is common in alcohol use disorders. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Reimers, E.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.M.; Candelaria Martín-González, M.; Hernández-Betancor, I.; Abreu-González, P.; de la Vega-Prieto, M.J.; Elvira-Cabrera, O.; Santolaria-Fernández, F. Antioxidant Vitamins and Brain Dysfunction in Alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014, 49, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sachdeva, A.; Chandra, M.; Choudhary, M.; Dayal, P.; Anand, K.S. Alcohol-related dementia and neurocognitive impairment: A review study. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2016, 5(3), e27976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamenti, F.; Scali, C.; Vannucchi, M.G.; Bartolini, L.; Pepeu, G. Long-term ethanol consumption by rats: Effect on acetylcholine release in vivo, choline acetyltransferase activity, and behavior. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.R.; Xu, F.; Xu, X.C.; Tan, G.J.; Liu, L.M.; Wu, N.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Liu, J.-X. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on spatial learning and memory, oxidative stress, and central cholinergic system in a rat model of vascular dementia. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, A.; Farhat, S.M.; Iqbal, G.; Babar, M.M.; Zaidi Nus, S.S.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ahmed, T. Alpha-lipoic acid-mediated activation of muscarinic receptors improves hippocampus- and amygdala-dependent memory. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 122, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staykov, H.; Lazarova, M.; Hassanova, Y.; Stefanova, M.; Tancheva, L.; Nikolov, R. Neuromodulatory Mechanisms of a Memory Loss-Preventive Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in an Experimental Rat Model of Dementia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, S.M.; Romeiro, C.F.R.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Cerqueira, A.R.L.; Monteiro, M.C. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Beneficial or Harmful in Alzheimer’s Disease? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8409329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermpini, E.E.; Plemenitaš Ilješ, A.; Dolžan, V. Alcohol-Induced Oxidative Stress and the Role of Antioxidants in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.A.Q.; Santos, S.M.d.; Gato, L.d.S.; Espíndola, K.M.M.; Silva, R.K.M.d.; Davis, K.; Navegantes-Lima, K.C.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Romao, P.R.T.; Coleman, M.D.; et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, I.T.; Doran, E.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Tournay, A.; Head, E.; Gillen, D.L. Down Syndrome and Dementia: A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Antioxidant Supplementation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2011, 155, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, M.; de la Monte, S.M. Early-Stage Moderate Alcohol Feeding Dysregulates Insulin-Related Metabolic Hormone Expression in the Brain: Potential Links to Neurodegeneration Including Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Rep. 2024, 8, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airapetov, M.I.; Eresko, S.O.; Shamaeva, S.A.; Bychkov, E.R.; Lebedev, A.A.; Shabanov, P.D. Study of Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus during Ethanol Exposure and Pharmacological Correction with Azithromycin: New Data and Future Perspectives. Biochemistry 2024, 89, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, F.; Radanovic, M.; PR, C.; VJR, P.; OV, F. Anti-dementia medications: Current prescriptions in clinical practice and new agents in progress. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2015, 6, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.; Park, J.; Joe, K.H.; Kim, D.J. The effect of 12-week open-label memantine treatment on cognitive function improvement in patients with alcohol-related dementia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustembegović, A.; Kundurović, Z.; Sapcanin, A.; Sofic, E. A placebo-controlled study of memantine (Ebixa) in dementia of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Med. Arh. 2003, 57, 149–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, U.; Taazimi, B.; Borda, T.; Grabbe, H.D. Improvement of a woman’s alcohol-related dementia via off-label memantine treatment: A 16-month clinical observation. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; You, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, R.; Xu, S.; Zhao, R.; et al. Memantine can improve chronic ethanol exposure-induced spatial memory impairment in male C57BL/6 mice by reducing hippocampal apoptosis. Toxicology 2018, 406–407, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Pirritano, D.; Plastino, M.; Cristiano, D.; Puccio, G.; Colica, C.; Ermio, C.; De Bartolo, M.; Mauro, G.; Bosco, D. The Effect of Lipoic Acid Therapy on Cognitive Functioning in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 454253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stazi, M.; Wirths, O. Chronic Memantine Treatment Ameliorates Behavioral Deficits, Neuron Loss, and Impaired Neurogenesis in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi Tari, P.; Parsons, C.G.; Collingridge, G.L.; Rammes, G. Memantine: Updating a rare success story in pro-cognitive therapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2024, 244, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, K.; Labuz, K.; Gibula-Bruzda, E.; Jenda, M.; Marszalek-Grabska, M.; Filarowska, J.; Silberring, J.; Kotlinska, J.H. Cholinesterase inhibitors, donepezil and rivastigmine, attenuate spatial memory and cognitive flexibility impairment induced by acute ethanol in the Barnes maze task in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, K.; Labuz, K.; Gibula-Bruzda, E.; Jenda, M.; Marszalek-Grabska, M.; Silberring, J.; Kotlinska, J.H. Acquisition and reinstatement of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in rats: Effects of the cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil and rivastigmine. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, G.; Zivkovic, N. Rivastigmine in Treatment of Alcohol-Induced Persisting Dementia. Eur. Psychiatry 2009, 24 (Suppl. S1), 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angunawela, I.I.; Barker, A. Anticholinesterase drugs for alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2001, 16, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, K.; Marahrens, A.; Kenklies, M.; Riederer, P.; Münch, G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer [corrected] type dementia. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2001, 32, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, K.; Kenklies, M.; McAfoose, J.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease--a 48 months follow-up analysis. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 2007, 72, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yanev, P.G.; Dimitrova, D.S.; Getova-Spassova, D.P. Effects of rivastigmine and memantine alone and in combination on learning and memory in rats with scopolamine-induced amnesia. Open Med. 2015, 10, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulas, A.; Zilles, K.; Hilgetag, C.C. Cortical Gradients and Laminar Projections in Mammals. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cabezas, M.Á.; Zikopoulos, B.; Barbas, H. The Structural Model: A theory linking connections, plasticity, pathology, development and evolution of the cerebral cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 985–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanein, P.; Seifi, R.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Emamjomeh, A. Rosmarinic acid protects against chronic ethanol-induced learning and memory deficits in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, F.; Stancampiano, R.; Imperato, A.; Carta, G.; Fadda, F. Chronic ethanol consumption in rats: Correlation between memory performance and hippocampal acetylcholine release in vivo. Neuroscience 1996, 74, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauton, P.; Deschamps, C.; Jeanblanc, V.; Pierrefiche, O.; Jeanblanc, J.; Naassila, M. Interstrain differences in voluntary binge-like drinking behavior and in two acute ethanol injections-induced synaptic plasticity deficits in rats. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portal de Periódicos da CAPES. Effect of Ethanol and Acetaldehyde on Membrane-Bound Enzymes in Rat Brain. Available online: https://www.periodicos.capes.gov.br/index.php/acervo/buscador.html?task=detalhes&id=W2412076819 (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Arendt, T.; Allen, Y.; Marchbanks, R.M.; Schugens, M.M.; Sinden, J.; Lantos, P.L.; Gray, J. Cholinergic system and memory in the rat: Effects of chronic ethanol, embryonic basal forebrain brain transplants and excitotoxic lesions of cholinergic basal forebrain projection system. Neuroscience 1989, 33, 435–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.W.; Rieck, R.W. Effects of chronic ethanol administration on acetylcholinesterase activity in the somatosensory cortex and basal forebrain of the rat. Brain Res. 1993, 627, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, K.; Somani, S.M. Effect of exercise training and chronic ethanol ingestion on cholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation in blood and brain regions of rat. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 22, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, T.; Henning, D.; Gray, J.A.; Marchbanks, R. Loss of neurons in the rat basal forebrain cholinergic projection system after prolonged intake of ethanol. Brain Res. Bull. 1988, 21, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, R.G.; Pereira, S.R.; Pittella, J.E.; Franco, G.C.; Ferreira, C.L.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ribeiro, A.M. The contribution of mild thiamine deficiency and ethanol consumption to central cholinergic parameter dysfunction and rats’ open-field performance impairment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 70, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, T.; Schugens, M.M.; Bigl, V. The cholinergic system and memory: Amelioration of ethanol-induced memory deficiency by physostigmine in rat. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1990, 50, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Geiss, J.M.T.; Sagae, S.C.; Paz, E.D.R.; de Freitas, M.L.; Souto, N.S.; Furian, A.F.; Oliveira, M.S.; Guerra, G.P. Oral administration of lutein attenuates ethanol-induced memory deficit in rats by restoration of acetylcholinesterase activity. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 204, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerri, C.; Grisolía, S. Chronic ethanol treatment affects synaptosomal membrane-bound enzymes. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1983, 18 (Suppl. S1), 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phunchago, N.; Wattanathorn, J.; Chaisiwamongkol, K. Tiliacora triandra, an Anti-Intoxication Plant, Improves Memory Impairment, Neurodegeneration, Cholinergic Function, and Oxidative Stress in Hippocampus of Ethanol Dependence Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 918426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon, A.D.C.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Correa, M.M.; Morsch, V.M.; da Silva, J.E.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Zanatta, N. Effects per se of organic solvents in the cerebral acetylcholinesterase of rats. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ameno, K.; Ameno, S.; Morishita, J.; Wang, W.; Kumihashi, M.; Ikuo, U.; Miki, T.; Ijiri, I. Changes in cholinergic function in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of rat exposed to ethanol and acetaldehyde. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.R.; Menezes, G.A.; Franco, G.C.; Costa, A.E.; Ribeiro, A.M. Chronic ethanol consumption impairs spatial remote memory in rats but does not affect cortical cholinergic parameters. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1998, 60, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, M.J.; Sánchez-Martín, M.M.; Alonso, J.M.; Hueso, P. Changes of acetylcholinesterase activity in brain areas and liver of sucrose- and ethanol-fed rats. Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancheva, L.; Kalfin, R.; Minchev, B.; Uzunova, D.; Tasheva, K.; Tsvetanova, E.; Georgieva, A.; Alexandrova, A.; Stefanova, M.; Solak, A.; et al. Memory Recovery Effect of a New Bioactive Innovative Combination in Rats with Experimental Dementia. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivazhagan, P.; Ayusawa, D.; Panneerselvam, C. Protective efficacy of alpha-lipoic acid on acetylcholinesterase activity in aged rat brain regions. Rejuvenation Res. 2006, 9, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadrawy, Y.A.; Khoder, N.M.; Sawie, H.G.; Sharada, H.M.; Hosny, E.N.; Abdulla, M.S. The Neuroprotective Effect of α-Lipoic Acid and/or Metformin against the Behavioral and Neurochemical Changes Induced by Hypothyroidism in Rat. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 112, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, R.M. Lipoic Acid increases hippocampal choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities and improvement memory in epileptic rats. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, E.N.; Sawie, H.G.; El-Gizawy, M.M.; Mohammed, H.S.; Faraag, A.R.; Khadrawy, Y.A. Therapeutic effects of alpha lipoic acid and/or caffeine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles on memory impairment and neurochemical changes in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Physiol. Behav. 2024, 287, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, C.N.S.; Meneses, L.N.; Vasconcelos, G.S.; da Silva Medeiros, I.; Silva, M.C.C.; Mouaffak, F.; Kebir, O.; Leite, C.M.G.d.S.; Patrocinio, M.C.A.; Macedo, D.; et al. Neuroprotective evidence of alpha-lipoic acid and desvenlafaxine on memory deficit in a neuroendocrine model of depression. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Yu, R.; Deochand, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential Contributions of Alcohol and the Nicotine-Derived Nitrosamine Ketone (NNK) to Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Resistance in the Adolescent Rat Brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.A.; de Andrade, K.Q.; dos Santos, J.C.F.; Goulart, M.O.F. Lipoic Acid: Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 458–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, A.; Gentsch, C. Co-administration of memantine has no effect on the in vitro or ex vivo determined acetylcholinesterase inhibition of rivastigmine in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.M.; Taylor, J.R.; De Vries, T.J.; Peters, J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and addiction: Pathological versus therapeutic effects on drug seeking. Brain Res. 2015, 1628, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.I. Ethanol-BDNF interactions: Still More Questions than Answers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglianti, S.; Alotaibi, A.; Wong, W.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Childers, W.; Sari, Y. Effects of novel GLT-1 modulator, MC-100093, on neuroinflammatory and neurotrophic biomarkers in mesocorticolimbic brain regions of male alcohol preferring rats exposed chronically to ethanol. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 211, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Peña, D.; García-Marchena, N.; Alén, F.; Araos, P.; Rivera, P.; Vargas, A.; García-Fernández, M.I.; Martín-Velasco, A.I.; Villanúa, M.Á.; Castilla-Ortega, E.; et al. Alcohol-induced cognitive deficits are associated with decreased circulating levels of the neurotrophin BDNF in humans and rats. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.M.; Stewart, W.N.; Savage, L.M. Chronic Drinking During Adolescence Predisposes the Adult Rat for Continued Heavy Drinking: Neurotrophin and Behavioral Adaptation after Long-Term, Continuous Ethanol Exposure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logrip, M.L.; Janak, P.H.; Ron, D. Escalating ethanol intake is associated with altered corticostriatal BDNF expression. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.A.; McClain, J.A.; Wooden, J.I.; Nixon, K. Microglia Dystrophy Following Binge-Like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescent and Adult Male Rats. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X. α-Lipoic acid attenuates obesity-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation and increases the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in ovariectomized rats fed a high-fat diet. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Ji, A. A-lipoic acid protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, G.S.; Ximenes, N.C.; de Sousa, C.N.S.; Oliveira Tde, Q.; Lima, L.L.L.; de Lucena, D.F.; Gama, C.S.; Macêdo, D.; Vasconcelos, S.M. Alpha-lipoic acid alone and combined with clozapine reverses schizophrenia-like symptoms induced by ketamine in mice: Participation of antioxidant, nitrergic and neurotrophic mechanisms. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 165, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Fu, L.C.; Nurrahma, H.A.; Lai, J.H.; Shirakawa, H.; Yang, S.-C. Protective Effects of Fish Oil Against Brain Impairment in Rats with Chronic Ethanol-Induced Liver Damage Involving the NRF2 Pathway and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.; Charehsaz, M.; Sipahi, H.; Ekici, A.I.D.; Macit, Ç.; Akkaya, H.; Aydın, A. Energy Drink Induced Lipid Peroxidation and Oxidative Damage in Rat Liver and Brain When Used Alone or Combined with Alcohol. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, S.M.; Husain, K.; Diaz-Phillips, L.; Lanzotti, D.J.; Kareti, K.R.; Trammell, G.L. Interaction of exercise and ethanol on antioxidant enzymes in brain regions of the rat. Alcohol 1996, 13, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliño, P.; Romero-Cano, R.; Sánchez-Andrés, J.V.; Valls, V.; Aragón, C.G.; Muriach, M. Effects of Acute Ethanol Administration on Brain Oxidative Status: The Role of Acetaldehyde. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, R.; Khabbazi, T.; Safa, J. Alpha lipoic acid supplementation improved antioxidant enzyme activities in hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monette, J.S.; Gómez, L.A.; Moreau, R.F.; Dunn, K.C.; Butler, J.A.; Finlay, L.A.; Michels, A.J.; Shay, K.P.; Smith, E.J.; Hagen, T.M. (R)-α-Lipoic Acid Treatment Restores Ceramide Balance in Aging Rat Cardiac Mitochondria. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homans, C.; Yalcin, E.B.; Tong, M.; Gallucci, G.; Bautista, D.; Moriel, N.; de la Monte, S. Therapeutic Effects of Myriocin in Experimental Alcohol-Related Neurobehavioral Dysfunction and Frontal Lobe White Matter Biochemical Pathology. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Ziplow, J.L.; Mark, P.; de la Monte, S.M. Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Homans, C.; Pelit, W.; Delikkaya, B.; de la Monte, S.M. Progressive Alcohol-Related Brain Atrophy and White Matter Pathology Are Linked to Long-Term Inhibitory Effects on mTOR Signaling. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, F.B.R.; Cunha, P.A.; Ribera, P.C.; Barros, M.A.; Cartágenes, S.C.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; Teixeira, F.B.; Fontes-Júnior, E.A.; Prediger, R.D.; Lima, R.R.; et al. Heavy Chronic Ethanol Exposure From Adolescence to Adulthood Induces Cerebellar Neuronal Loss and Motor Function Damage in Female Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.B.; McLean, T.; Tong, M.; de la Monte, S.M. Progressive white matter atrophy with altered lipid profiles is partially reversed by short-term abstinence in an experimental model of alcohol-related neurodegeneration. Alcohol 2017, 65, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, B.; Yano, B.; Sellers, R.S.; Perry, R.; Morton, D.; Roome, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Schafer, K. Evaluation of organ weights for rodent and non-rodent toxicity studies: A review of regulatory guidelines and a survey of current practices. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.H.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, E.H.; Cho, E.H.; Jeong, E.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Park, K.-G.; et al. Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Body Weight in Obese Subjects. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, e1–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.Y.; Ha, A.W.; Kim, W.K. α-Lipoic acid reduced weight gain and improved the lipid profile in rats fed with high fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2012, 6, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Hontoria, P.L.; Pérez-Matute, P.; Fernández-Galilea, M.; Barber, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Lipoic acid prevents body weight gain induced by a high fat diet in rats: Effects on intestinal sugar transport. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 65, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukgoncu, S.; Zhou, E.; Lucas Kb Tek, C. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) as a supplementation for weight loss: Results from a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta Atmaca, H.; Akbas, F. The Effect of Short Term Alpha Lipoic Acid Administration on Adiponectin and Body Weight in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Acta Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, Z. Rivastigmine. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080552323625449 (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Polinsky, R.J. Clinical pharmacology of rivastigmine: A new-generation acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Ther. 1998, 20, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbimbo, B.P. Pharmacodynamic-tolerability relationships of cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 2001, 15, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathirathan, K.; Brown, J.; Neafsey, E.J.; Collins, M.A. Linking binge alcohol-induced neurodamage to brain edema and potential aquaporin-4 upregulation: Evidence in rat organotypic brain slice cultures and in vivo. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajuddin, N.; Moon, K.H.; Marshall, S.A.; Nixon, K.; Neafsey, E.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Collins, M.A. Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in adult rat brain from binge ethanol exposure: Abrogation by docosahexaenoic acid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuddin, N.F.; Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Pak, T.R.; Neafsey, E.J.; Collins, M.A. Effect of repetitive daily ethanol intoxication on adult rat brain: Significant changes in phospholipase A2 enzyme levels in association with increased PARP-1 indicate neuroinflammatory pathway activation. Alcohol 2013, 47, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Collins, M.A.; Zou, J.Y.; Neafsey, E.J. Brain damage due to episodic alcohol exposure in vivo and in vitro: Furosemide neuroprotection implicates edema-based mechanism. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.A.; Neafsey, E.J. Neuroinflammatory pathways in binge alcohol-induced neuronal degeneration: Oxidative stress cascade involving aquaporin, brain edema, and phospholipase A2 activation. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P. The Laboratory Rat: Relating Its Age With Human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andreollo, N.A.; Santos EFdos Araújo, M.R.; Lopes, L.R. Rat’s age versus human’s age: What is the relationship? Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2012, 25, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agabio, R.; Colombo, G. GABAB receptor ligands for the treatment of alcohol use disorder: Preclinical and clinical evidence. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S.; DeCarli, L.M. The feeding of alcohol in liquid diets: Two decades of applications and 1982 update. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1982, 6, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Wheaton, M.; Murphy, D.L. What’s wrong with my mouse model? Advances and strategies in animal modeling of anxiety and depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, B.B. Reduction of Purkinje cell volume in cerebellum of alcoholics. Brain Res. 2004, 1007, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugos, C.A. Ethanol-related Increases in Degenerating Bodies in the Purkinje Neuron Dendrites of Aging Rats. Brain Res. 2008, 1221, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.C.; Tong, M.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor resistance with neurodegeneration in an adult chronic ethanol exposure model. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.A.; Chuffa, L.G.A.; Fioruci-Fontanelli, B.A.; Lizarte Neto, F.S.; Novais, P.C.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Oishi, J.C.; Stefanini, M.A.; Martinez, M.; Martinez, F.E. Apoptosis of Purkinje and granular cells of the cerebellum following chronic ethanol intake. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, I.G.; Queiroz, L.Y.; da Silva, C.C.S.; Cartágenes, S.C.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; de Souza-Junior, F.J.C.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Lima, R.R.; Martins, M.D.; Schmidt, T.R.; et al. Ethanol binge drinking exposure during adolescence displays long-lasting motor dysfunction related to cerebellar neurostructural damage even after long-term withdrawal in female Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.R.; Williams, D.K.; Light, K.E. Purkinje cell vulnerability to developmental ethanol exposure in the rat cerebellum. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.R.; Hayar, A.; Williams, D.K.; Light, K.E. Olivary climbing fiber alterations in PN40 rat cerebellum following postnatal ethanol exposure. Brain Res. 2011, 1378, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaatinen, P.; Rintala, J. Mechanisms of ethanol-induced degeneration in the developing, mature, and aging cerebellum. Cerebellum 2008, 7, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajgopal, Y.; Chetty, C.S.; Vemuri, M.C. Differential modulation of apoptosis-associated proteins by ethanol in rat cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 470, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.M.P.; Lopes, K.S.; Santana, L.N.S.; Fontes-Júnior, E.A.; Ribeiro, C.H.M.A.; Silva, M.C.F.; Paraense, R.S.D.O.; Crespo-López, M.E.; Gomes, A.R.Q.; Lima, R.R.; et al. Repeated Cycles of Binge-Like Ethanol Intake in Adolescent Female Rats Induce Motor Function Impairment and Oxidative Damage in Motor Cortex and Liver, but Not in Blood. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 3467531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wu, C. Protective effect of apple polyphenols on chronic ethanol exposure-induced neural injury in rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2020, 326, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, M.; Blanco, A.M.; Cauli, O.; Miñarro, J.; Guerri, C. Intermittent ethanol exposure induces inflammatory brain damage and causes long-term behavioural alterations in adolescent rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.B.; Santana LNda, S.; Bezerra, F.R.; De Carvalho, S.; Fontes-Júnior, E.A.; Prediger, R.D.; Crespo-López, M.E.; Maia, C.S.F.; Lima, R.R. Chronic ethanol exposure during adolescence in rats induces motor impairments and cerebral cortex damage associated with oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Thomas, J.D.; West, J.R. Long-term deficits in cerebellar growth and rotarod performance of rats following ‘binge-like’ alcohol exposure during the neonatal brain growth spurt. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1991, 13, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulman, R.S.; Auta, J.; Wandling, G.M.; Patwell, R.; Zhang, H.; Pandey, S.C. Persistence of cerebellar ataxia during chronic ethanol exposure is associated with epigenetic upregulation of Fmr1 gene expression in rat cerebellum. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadwater, M.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Different chronic ethanol exposure regimens in adolescent and adult male rats: Effects on tolerance to ethanol-induced motor impairment. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 225, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzbay, I.T.; Kayaalp, S.O. Heterogeneity of tolerance developed to effects of ethanol on rotarod and accelerod performances in rats. Alcohol 1995, 12, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R.A.; Assi, A.A.A.; Kostandy, B.B. Rivastigmine reverses aluminum-induced behavioral changes in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 659, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réus, G.Z.; Valvassori, S.S.; Machado, R.A.; Martins, M.R.; Gavioli, E.C.; Quevedo, J. Acute treatment with low doses of memantine does not impair aversive, non-associative and recognition memory in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 376, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festing, M.F.W.; Altman, D.G. Guidelines for the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory animals. ILAR J. 2002, 43, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festing, M.; Overend, P.; Das, R.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Berdoy, M. The Design of Animal Experiments: Reducing the Use of Animals in Research Through Better Experimental Design; Laboratory Animal Handbooks: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Magnard, R.; Langdon, A.J.; Lee, D.; Janak, P.H. Chronic ethanol exposure produces sex-dependent impairments in value computations in the striatum. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadt0200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom-Rocha, C.; Bis-Humbert, C.; García-Fuster, M.J. Evaluating signs of hippocampal neurotoxicity induced by a revisited paradigm of voluntary ethanol consumption in adult male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, A.; Traykov, V.; Prodanov, D.; Mantchev, G.; Yakimova, K.; Krushkov, I.; Boyadjieva, N. Effect of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor galanthamine on learning and memory in prolonged alcohol intake rat model of acetylcholine deficit. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 21, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Bejar, C.; Weinstock, M. Gender differences in the effect of rivastigmine on brain cholinesterase activity and cognitive function in rats. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvanová, M.; Lakso, M.; Wong, G. Identification of genes regulated by memantine and MK-801 in adult rat brain by cDNA microarray analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesierska, M.; Svoboda, J.; Stuchlik, A. A therapeutic dose of memantine improves the performance of rats in an active place avoidance task under the continuous dissociation of distal room and proximal arena cues. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2019, 162, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvik, M.E.; Kopp, R. An improved one-trial passive avoidance learning situation. Psychol. Rep. 1967, 21, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.J.; Roberts, D.J. The quantiative measurement of motor inco-ordination in naive mice using an acelerating rotarod. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1968, 20, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Feather-Stone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
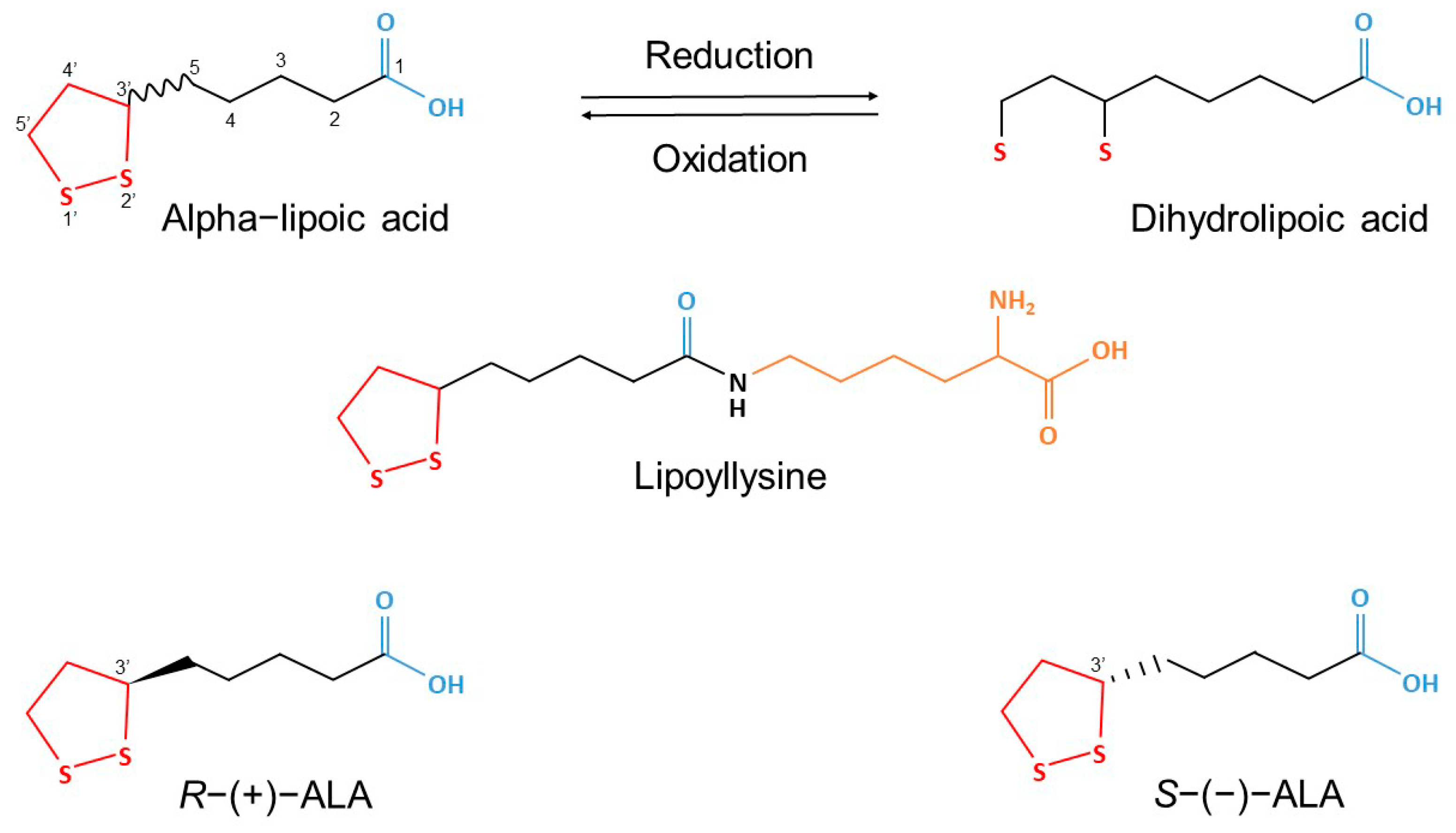

| MECHANISM | ETHANOL | ALPHA LIPOIC ACID |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) transcription → oxidative stress-inducing enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines synthesis | ↑ NF-κB transcription → ↑ the activity of oxidative stress-inducing enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines | ↓ NF-κB transcription → ↓ the activity of oxidative stress-inducing enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines |
| Phosphorylated cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (pCREB) transcription | ↓ pCREB transcription → neurons are more vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced damage | ↑ pCREB transcription → neurons are less vulnerable to oxidative stress-induced damage |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) levels | ↑ | ↓ |
| Lipid peroxidation (LPO), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) activities → ↑ formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) | ↑ | ↓ |
| Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activities → ↑ formation of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins | ↑ | ↓ |
| Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity | ↑ → ↑ levels of nitric oxide (NO) free radicals | ↓ → ↓ levels of NO free radicals |
| Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 (TLR2/TLR4) neuromodulation pathways | ↑ cytokine induction by TLR2 and TLR4 ligands | ↓ TLR2 and TLR4 expression |
| Total glutathione (GSH) levels | ↓ the glutathione/glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG) ratio → ↓ antioxidant protection | ↑ GSH levels → ↑antioxidant protection |
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels | ↓ → ↓ neural progenitor cell proliferation and survival | ↑ |
| Vitamins C and E levels | ↓ | regenerates the endogenous antioxidants, vitamins C and E → ↑ their antioxidant activity |
| Cholinergic activity | ↓ | ↑ |
| Mitochondrial function | ↓ | ↑ |
| GROUP | PURKINJE CELL LOSS | NUCLEAR PYKNOSIS | MORPHOLOGICAL ALTERATIONS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water–Saline (W-S) | - | - | - |
| Ethanol–Saline (E-S) | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Ethanol–Memantine (E-M) | + | + | + |
| Ethanol–Rivastigmine (E-R) | ++ | ++ | + |
| Ethanol–ALA (E-A) | ++ | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staykov, H.; Dragomanova, S.; Hodzhev, Y.; Grigorova, V.; Minchev, B.; Uzunova, D.; Georgieva, A.; Sulikovska, I.; Todorova, K.; Tsvetanova, E.; et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Early-Stage Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Rats: A Comparative Pilot Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194007
Staykov H, Dragomanova S, Hodzhev Y, Grigorova V, Minchev B, Uzunova D, Georgieva A, Sulikovska I, Todorova K, Tsvetanova E, et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Early-Stage Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Rats: A Comparative Pilot Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194007
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaykov, Hristian, Stela Dragomanova, Yordan Hodzhev, Valya Grigorova, Borislav Minchev, Diamara Uzunova, Ani Georgieva, Inna Sulikovska, Katerina Todorova, Elina Tsvetanova, and et al. 2025. "Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Early-Stage Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Rats: A Comparative Pilot Study" Molecules 30, no. 19: 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194007
APA StyleStaykov, H., Dragomanova, S., Hodzhev, Y., Grigorova, V., Minchev, B., Uzunova, D., Georgieva, A., Sulikovska, I., Todorova, K., Tsvetanova, E., Georgieva, A., Stefanova, M., Valadbeigi, P., Kalfin, R., Nikolov, R., & Tancheva, L. (2025). Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Early-Stage Alcohol-Related Brain Damage in Rats: A Comparative Pilot Study. Molecules, 30(19), 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30194007








