Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid: Two Hydroxycinnamic Acids Modulate the Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activities in Pancreatic INS1 Beta-Cells—Novel Data in Favor of Two Putative Conformations of the G6Pase Within the ER Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Glucose Release Under Glucagon Stimulation and Microsomal G6Pase Activity in Hepatic Cells in Presence of CGA and CGA
2.2. Microsomal G6Pase Activities from INS1 Beta-Cells Cultivated in RPMI with Different Glucose Concentrations
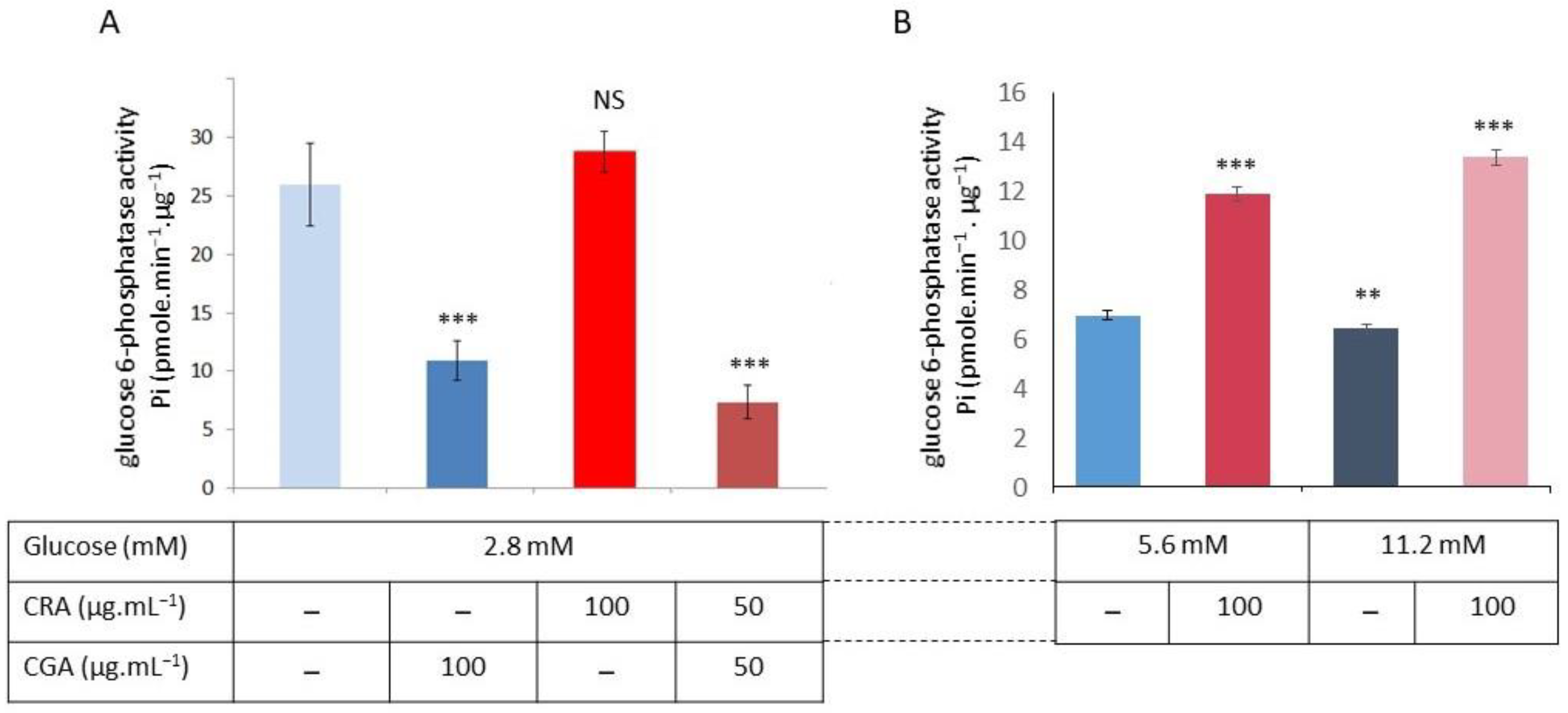
2.3. CGA and CRA Effects on the Microsomal G6Pase Activities from INS1 Beta-Cells Cultivated in RPMI Medium (11.2 mM Glucose)
2.4. CGA and CRA Effects on the G6Pase Activities in INS1 Beta-Cells Cultivated in the 2.8, 5.6, and 11.2 mM Glucose in RPMI Medium
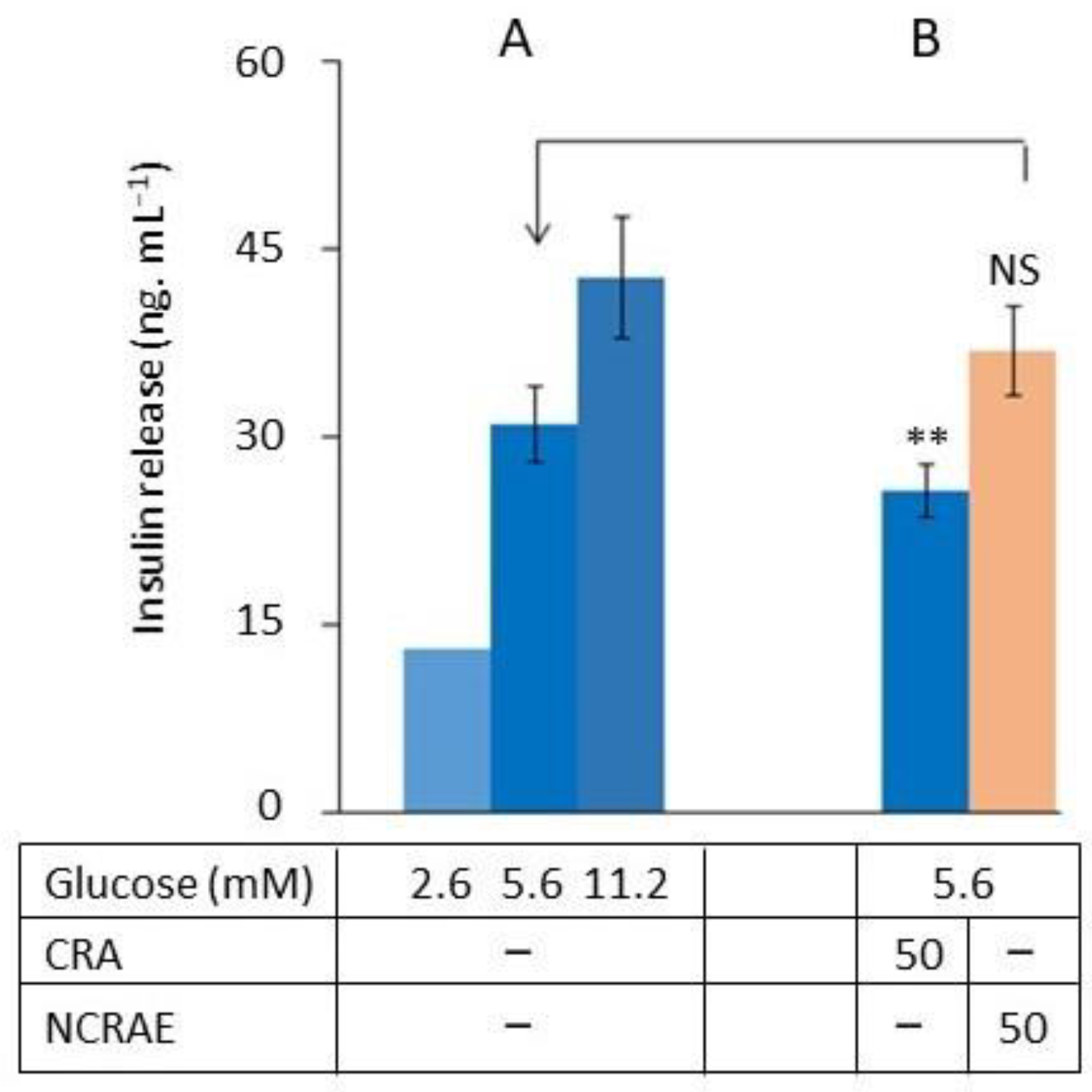
2.5. CRA’s Effect on Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
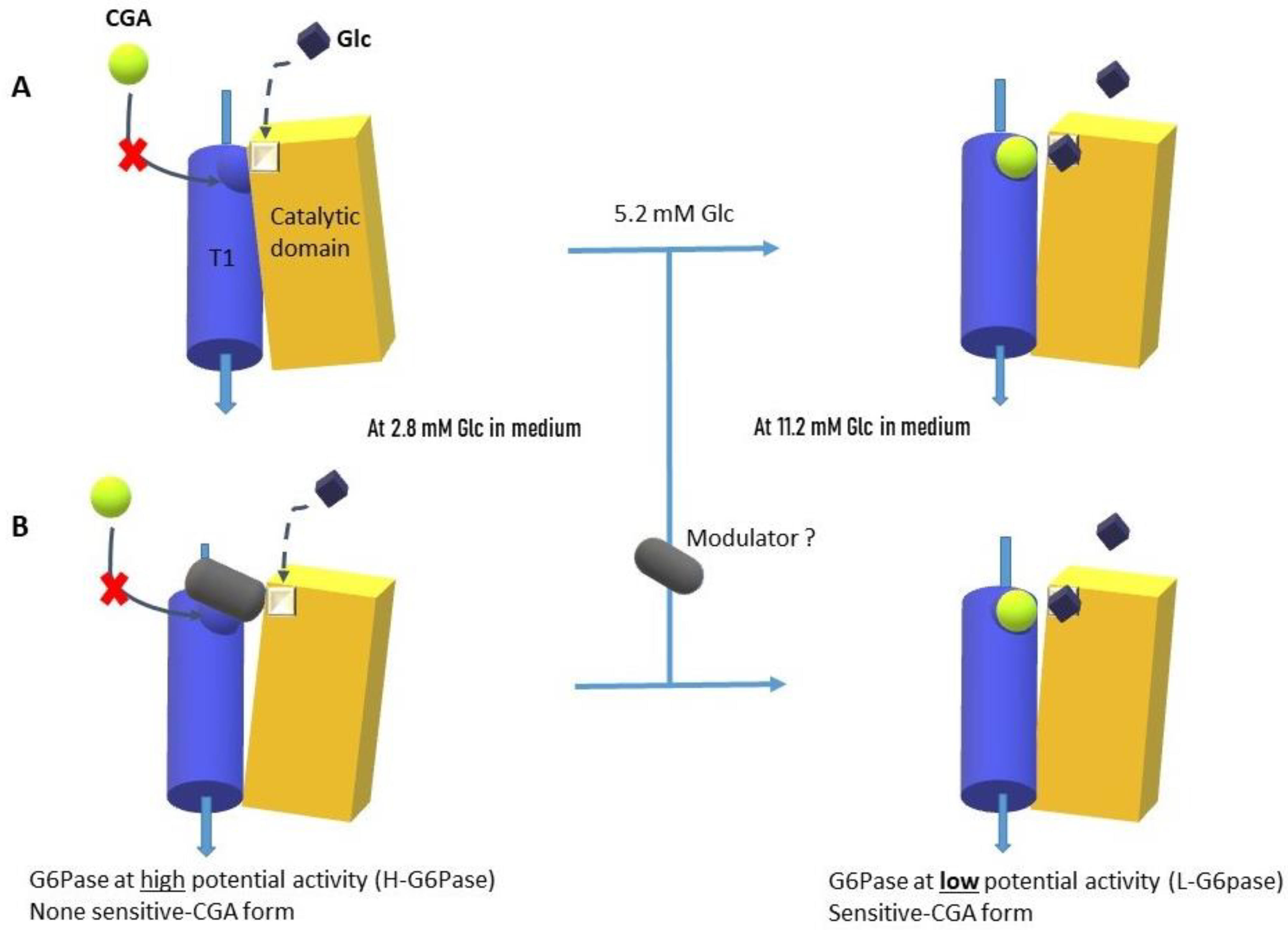
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. INS-1 Beta-Cell Cultures
4.3. Insulin Secretion Measurements
4.4. The Evaluation of the Glycogenolysis of Hepatocyte Cell Cultures
4.5. The Isolation of the INS1 Beta-Cells’ Microsomal Fraction
4.6. Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activity Test
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRA | Chicoric Acid |
| CGA | Chlorogenic Acid |
| G6Pase | Glucose-6-Phosphatase |
| NCRAE | Natural Chicoric Acid Extract |
| IGRP | Islet-Specific G6PC-Related Protein |
| GSIS | Glucose-Sensitive Insulin Secretion |
References
- Fraisse, D.; Felgines, C.; Texier, O.; Lamaison, J.-L. Caffeoyl Derivatives: Major Antioxidant Compounds of Some Wild Herbs of the Asteraceae Family. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.; Poucheret, P.; Idres, A.Y.; Bidel, L.; Tousch, D. The Bitter Asteraceae: An Interesting Approach to Delay the Metabolic Syndrome Progression. NFS J. 2020, 18, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.E.; Olthof, M.R.; Meeuse, J.C.; Seebus, E.; Heine, R.J.; Van Dam, R.M. Acute Effects of Decaffeinated Coffee and the Major Coffee Components Chlorogenic Acid and Trigonelline on Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Scagel, C.F. Chicoric Acid: Chemistry, Distribution, and Production. Front. Chem. 2013, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, T.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Lv, X.; Jing, F.; Qin, L.; Zhao, T.; et al. Chicoric Acid: Natural Occurrence, Chemical Synthesis, Biosynthesis, and Their Bioactive Effects. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 888673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Cao, J.; Feng, Q.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y. Roles of Chlorogenic Acid on Regulating Glucose and Lipids Metabolism: A Review. eCAM 2013, 2013, 801457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinholes, J.; Silva, M.; Silva, L.R. Hydroxycinnamic acids (HCAS): Structure, biological properties and health effects. In Advances in Medicine and Biology; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 88, Chapter 8; 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, K.L.; Kao, C.L.; Hung, C.H.; Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, H.C.; Chu, P.M. Chicoric acid is a potent anti-atherosclerotic ingredient by antioxidant action and anti-inflammation capacity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29600–29612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, B.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Yeni, Y.; Danisman, B.; Ozkaraca, M.; Mokhtare, B.; Kantarci, M.; Spanakis, M.; Nikitovic, D.; Lazopoulos, G.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Markers of Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Nrf2/HO-1 and Dityrosine Signaling. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrare, K.; Bidel, L.P.R.; Awwad, A.; Poucheret, P.; Cazals, G.; Lazennec, F.; Azay-Milhau, J.; Tournier, M.; Lajoix, A.-D.; Tousch, D. Increase in Insulin Sensitivity by the Association of Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid Contained in a Natural Chicoric Acid Extract (NCRAE) of Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) for an Antidiabetic Effect. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 215, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Sozio, C.; Pipicelli, L.; Raia, M.; Palmiero, A.; Santillo, M.; Damiano, S. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Differentiative Effects of Chlorogenic Acid on M03-13 Human Oligodendrocyte-like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, G.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, W.-T.; Hsu, C.-L. Effects of Polyphenolic Compounds on Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α)-Induced Changes of Adipokines and Oxidative Stress in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassoli, B.K.; Cassolla, P.; Borba-Murad, G.R.; Constantin, J.; Salgueiro-Pagadigorria, C.L.; Bazotte, R.B.; Da Silva, R.S.D.S.F.; De Souza, H.M. Chlorogenic Acid Reduces the Plasma Glucose Peak in the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Effects on Hepatic Glucose Release and Glycaemia. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2008, 26, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, L.M.; Da Silva, D.; Sola-Penna, M.; De Magalhães Camargo, L.M.; De Moura Celestrini, D.; Tinoco, L.W.; Costa, S.S. Identification of Chicoric Acid as a Hypoglycemic Agent from Ocimum Gratissimum Leaf Extract in a Biomonitoring in Vivo Study. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Huang, T.; Bai, Y.; Chen, K. Antidiabetic Effect of Burdock (Arctium lappa L.) Root Ethanolic Extract on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousch, D.; Lajoix, A.-D.; Hosy, E.; Azay-Milhau, J.; Ferrare, K.; Jahannault, C.; Cros, G.; Petit, P. Chicoric Acid, a New Compound Able to Enhance Insulin Release and Glucose Uptake. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 2008, 377, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azay-Milhau, J.; Ferrare, K.; Leroy, J.; Aubaterre, J.; Tournier, M.; Lajoix, A.-D.; Tousch, D. Antihyperglycemic Effect of a Natural Chicoric Acid Extract of Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.): A Comparative in Vitro Study with the Effects of Caffeic and Ferulic Acids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousch, D.; Bidel, L.P.; Cazals, G.; Ferrare, K.; Leroy, J.; Faucanie, M.; Chevassus, H.; Tournier, M.; Lajoix, A.D.; Azay-Milhau, J. Chemical Analysis and Antihyperglycemic Activity of an Original Extract from Burdock Root (Arctium lappa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7738–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaou, N.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Tsakris, Z.; Rozos, G.; Tsigalou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Interactions between Medical Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds: Focus on Antimicrobial Combination Effects. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanankutty, A.; Famurewa, A.C.; Oprea, E. Natural Bioactive Compounds and Human Health. Molecules 2024, 29, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Sit, N. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Materials Using Combination of Various Novel Methods: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerle, H.; Burger, H.-J.; Below, P.; Schubert, G.; Rippel, R.; Schindler, P.W.; Paulus, E.; Herling, A.W. Chlorogenic Acid and Synthetic Chlorogenic Acid Derivatives: Novel Inhibitors of Hepatic Glucose-6-Phosphate Translocase. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaftingen, E.; Gerin, I. The Glucose-6-Phosphatase System. Biochem. J. 2002, 362, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, F.; Pégorier, J.P.; Minassian, C.; Bruni, N.; Tarpin, S.; Girard, J.; Mithieux, G. Development and Regulation of Glucose-6-Phosphatase Gene Expression in Rat Liver, Intestine, and Kidney: In Vivo and in Vitro Studies in Cultured Fetal Hepatocytes. Diabetes 1998, 47, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaud, D.; Kirby, T.L.; Newgard, C.B.; Lange, A.J. Stimulation of Glucose-6-Phosphatase Gene Expression by Glucose and Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12854–12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Flemming, B.P.; Martin, C.C.; Allen, S.R.; Walters, J.; Oeser, J.K.; Hutton, J.C.; O’Brien, R.M. Long-Range Enhancers Are Required to Maintain Expression of the Autoantigen Islet-Specific Glucose-6-Phosphatase Catalytic Subunit–Related Protein in Adult Mouse Islets In Vivo. Diabetes 2008, 57, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.Y.; Mansfield, B.C. Mutations in the Glucose-6-Phosphatase-α (G6PC) Gene That Cause Type Ia Glycogen Storage Disease. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, T.H.; Van Der Sluijs, F.H.; Wiegman, C.H.; Baller, J.F.W.; Gustafson, L.A.; Burger, H.-J.; Herling, A.W.; Kuipers, F.; Meijer, A.J.; Reijngoud, D.-J. Acute Inhibition of Hepatic Glucose-6-Phosphatase Does Not Affect Gluconeogenesis but Directs Gluconeogenic Flux toward Glycogen in Fasted Rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25727–25735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Chandramouli, V.; Östenson, C.-G.; Löw, H.; Landau, B.R.; Efendić, S. Glucose Cycling in Islets From Healthy and Diabetic Rats. Diabetes 1990, 39, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, I.R.; Najafi, H.; Li, G.; Grodberg, J.; Matschinsky, F.M. Measurement and Modeling of Glucose-6-Phosphatase in Pancreatic Islets. Am. J. Physiol. Endoc Metabol. 1997, 272, E696–E711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, J.C.; O’Brien, R.M. Glucose-6-Phosphatase Catalytic Subunit Gene Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29241–29245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, S.J.H.; Randle, P.J. Glucose-6-Phosphatase Activity of Mouse Pancreatic Islets. Nature 1968, 219, 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrolonis, A.J.; Yang, Q.; Tummino, P.J.; Fish, S.M.; Prack, A.E.; Jain, S.; Parsons, T.F.; Li, P.; Dales, N.A.; Ge, L.; et al. Enzymatic Characterization of the Pancreatic Islet-Specific Glucose-6-Phosphatase-Related Protein (IGRP). J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13976–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, L.D.; Oeser, J.K.; O’Brien, T.P.; Wang, Y.; Faulman, C.J.; Dadi, P.K.; Jacobson, D.A.; Hutton, J.C.; McGuinness, O.P.; Shiota, M.; et al. G6PC2: A Negative Regulator of Basal Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Khandelwal, R.; Wolfrum, C. Futile Cycles: Emerging Utility from Apparent Futility. Cell Metabol. 2024, 36, 1184–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Nakhe, A.Y.; Banerjee, D.R.; Overway, E.M.; Bosma, K.J.; Rosch, J.C.; Oeser, J.K.; Wang, B.; Lippmann, E.S.; Jacobson, D.A.; et al. Glucose-6-Phosphatase Catalytic Subunit 2 Negatively Regulates Glucose Oxidation and Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic beta-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overway, E.M.; Bosma, K.J.; Claxton, D.P.; Oeser, J.K.; Singh, K.; Breidenbach, L.B.; Mchaourab, H.S.; Davis, L.K.; O’Brien, R.M. Nonsynonymous Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the G6PC2 Gene Affect Protein Expression, Enzyme Activity, and Fasting Blood Glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Chandramouli, V.; Ostenson, C.G.; Ahrén, B.; Schumann, W.C.; Löw, H.; Landau, B.R.; Efendić, S. Evidence for the Presence of Glucose Cycling in Pancreatic Islets of the Ob/Ob Mouse. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 9732–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, K.; Nakajima, H.; Ono, A.; Okita, K.; Miyazaki, J.; Miyagawa, J.; Namba, M.; Hanafusa, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Stable Overexpression of the Glucose-6-Phosphatase Catalytic Subunit Attenuates Glucose Sensitivity of Insulin Secretion from a Mouse Pancreatic Beta-Cell Line. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 164, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulceri, R.; Kardon, T.; Bánhegyi, G.; Pralong, W.-F.; Gamberucci, A.; Marcolongo, P.; Benedetti, A. Glucose-6-Phosphatase in the Insulin Secreting Cell Line INS-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arion, W.J.; Canfield, W.K.; Callaway, E.S.; Burger, H.-J.; Hemmerle, H.; Schubert, G.; Herling, A.W.; Oekonomopulos, R. Direct Evidence for the Involvement of Two Glucose 6-Phosphate-Binding Sites in the Glucose-6-Phosphatase Activity of Intact Liver Microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6223–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfari, M.; Janjic, D.; Meda, P.; Li, G.; Halban, P.A.; Wollheim, C.B. Establishment of 2-Mercaptoethanol-Dependent Differentiated Insulin-Secreting Cell Lines. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; Ponsoda, X.; Castell, J.V. A Microassay for Measuring Glycogen in 96-Well-Cultured Cells. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 236, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalpando, S.; Cazevieille, C.; Fernandez, A.; Lamb, N.J.; Hani, E.-H. Type II PKAs Are Anchored to Mature Insulin Secretory Granules in INS-1 beta-Cells and Required for cAMP-Dependent Potentiation of Exocytosis. Biochimie 2016, 125, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murataliev, M.B.; Vulfson, E.N. The Effect of 1-cyclohexyl-3-(2-morpholinoethyl)Carbodiimide on the Rat Liver Microsomal Glucose-6-phosphatase System. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 160, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, N.; Rajas, F.; Payrastre, B.; Mauco, G.; Zitoun, C.; Mithieux, G. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Translocates onto Liver Endoplasmic Reticulum and May Account for the Inhibition of Glucose-6-Phosphatase during Refeeding. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3597–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tousch, D.; Thomasset, M.; Ferrare, K.; Lajoix, A.-D.; Azay-Milhau, J.; Poucheret, P. Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid: Two Hydroxycinnamic Acids Modulate the Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activities in Pancreatic INS1 Beta-Cells—Novel Data in Favor of Two Putative Conformations of the G6Pase Within the ER Membrane. Molecules 2025, 30, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193949
Tousch D, Thomasset M, Ferrare K, Lajoix A-D, Azay-Milhau J, Poucheret P. Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid: Two Hydroxycinnamic Acids Modulate the Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activities in Pancreatic INS1 Beta-Cells—Novel Data in Favor of Two Putative Conformations of the G6Pase Within the ER Membrane. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193949
Chicago/Turabian StyleTousch, Didier, Melodie Thomasset, Karine Ferrare, Anne-Dominique Lajoix, Jacqueline Azay-Milhau, and Patrick Poucheret. 2025. "Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid: Two Hydroxycinnamic Acids Modulate the Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activities in Pancreatic INS1 Beta-Cells—Novel Data in Favor of Two Putative Conformations of the G6Pase Within the ER Membrane" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193949
APA StyleTousch, D., Thomasset, M., Ferrare, K., Lajoix, A.-D., Azay-Milhau, J., & Poucheret, P. (2025). Chicoric Acid and Chlorogenic Acid: Two Hydroxycinnamic Acids Modulate the Glucose 6-Phosphatase Activities in Pancreatic INS1 Beta-Cells—Novel Data in Favor of Two Putative Conformations of the G6Pase Within the ER Membrane. Molecules, 30(19), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193949







