Progress and Challenges in the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of eNO3RR to NH3
2.1. Fundamental Principles and Thermodynamic Considerations
2.2. Reaction Pathways of eNO3RR to NH3
2.2.1. The Indirect Reduction Mechanism
2.2.2. The Direct Reduction Mechanism
- (1)
- NO3− adsorption
- (2)
- Reduction of NO3− to NO2−: rate-limiting step
- (3)
- Electrochemical reduction of NO2− to NH3: selectivity determining step


2.3. In Situ/Operando Characterizations
3. Factors Influencing the eNO3RR to NH3
3.1. Electrolyte Microenvironment
3.1.1. Initial NO3− Concentration
3.1.2. Electrolyte pH
3.1.3. Coexisting Ions
3.2. Impact of Applied Potential
3.2.1. Potential-Dependent Product Selectivity
3.2.2. Pulsed Electrolysis: An Advanced Operational Strategy
3.3. Effect of Reactor Structure
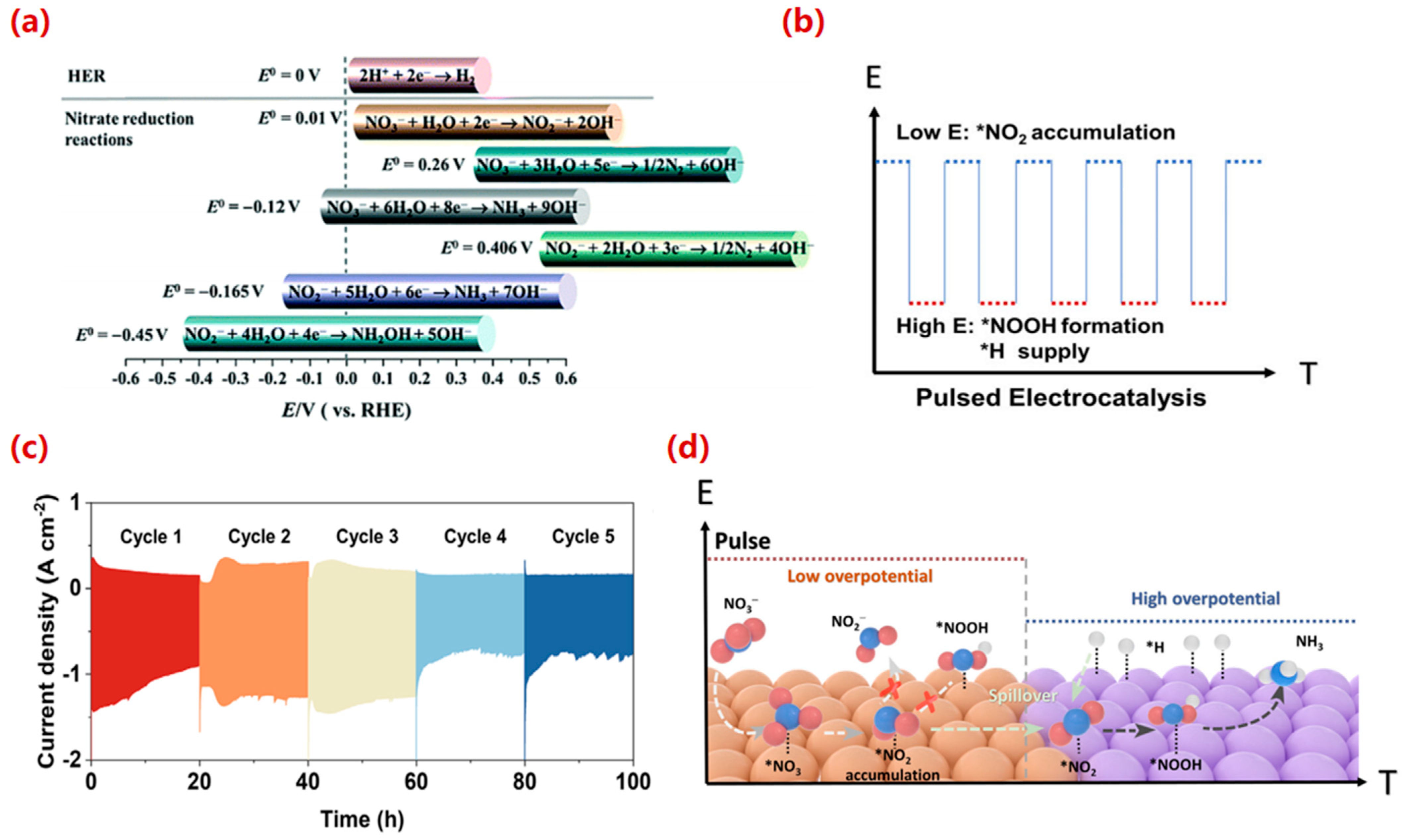
4. Catalysts for eNO3RR to NH3
4.1. Criteria for Selection of Catalysts
4.2. Advances in Different Types of Catalyst Research
4.2.1. Single-Metal Catalysts

4.2.2. Alloy Catalysts
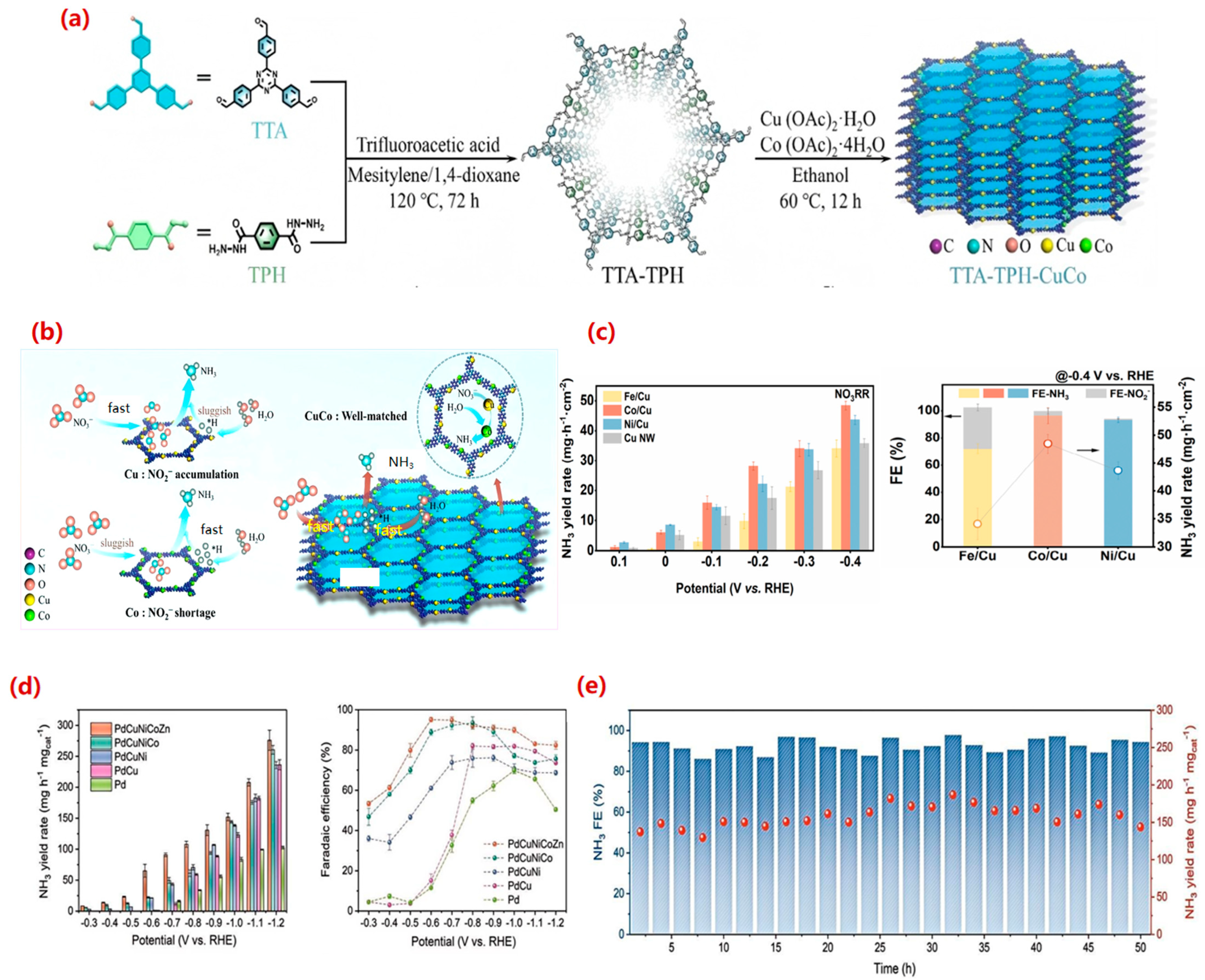
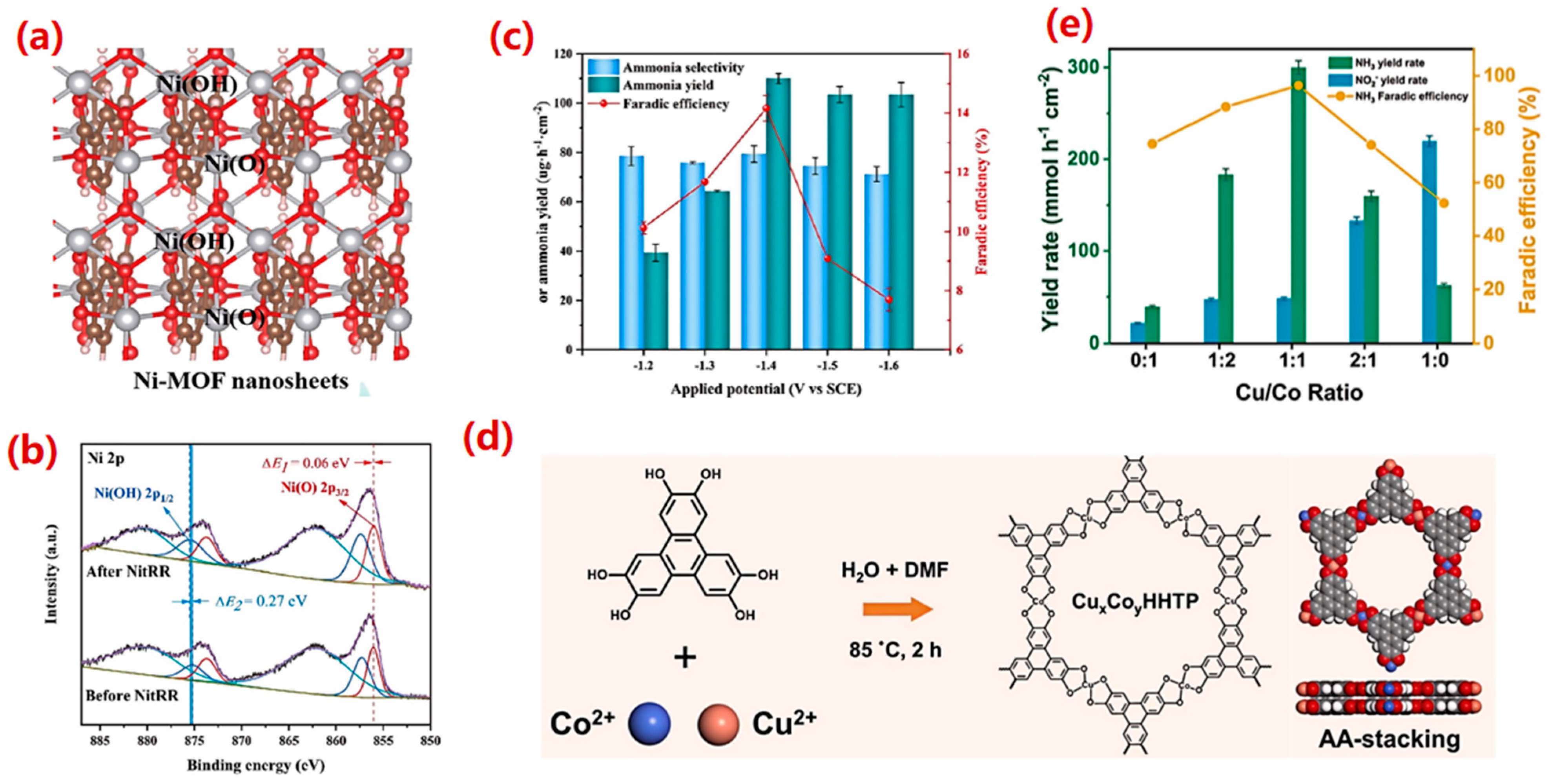
4.2.3. Transition Metal Compound Catalysts
- (1)
- Transition metal oxide catalysts
- (2)
- Other metal compound catalysts
4.2.4. Single-Atom Catalysts
4.2.5. Carbon-Based Non-Metal Catalysts
4.2.6. Composite Catalysts
4.3. Catalyst Design Strategies
4.3.1. Bimetallic or Alloy Strategy
4.3.2. Synergistic Effect of Defect Engineering and Doping
4.3.3. Facet and Morphology Control
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stueken, E.S.; Kipp, M.A.; Koehler, M.C.; Buick, R. The evolution of Earth’s biogeochemical nitrogen cycle. Earth−Sci. Rev. 2016, 160, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Toor, G.S. Sources and mechanisms of nitrate and orthophosphate transport in urban stormwater runoff from residential catchments. Water Res. 2017, 112, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M. Disruption of the global nitrogen cycle: A grand challenge for the twenty-first century. Ambio 2021, 50, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Xue, S.; Liang, Z.; Ren, X.; Liu, A.; Wu, G. Recent Advances in Designing Efficient Electrocatalysts for Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Bian, R.; Wang, N.; Qi, W.; Liu, H. Distribution, Sources, and Potential Health Risks of Fluoride, Total Iodine, and Nitrate in Rural Drinking Water Sources of North and East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Richards, D.; Singh, N. Recent discoveries in the reaction mechanism of heterogeneous electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Nitrate removal from drinking Water-Review. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrabés, N.; Sá, J. Catalytic nitrate removal from water, past, present and future perspectives. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassrullah, H.; Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Energy for desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2020, 491, 114569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarca, F.; Bórquez, R. Comparative study of nanofiltration and ion exchange for nitrate reduction in the presence of chloride and iron in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, A.; Gurreri, L.; Ciofalo, M.; Micale, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A. Electrodialysis for water desalination: A critical assessment of recent developments on process fundamentals, models and applications. Desalination 2018, 434, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Ding, L.; Zhu, J.; Wei, W.; Yan, Y.-M.; Chu, D.; Ni, B.-J. Recent trends and prospects in electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia with an emphasis on cobalt catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 539, 216751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Ortiz, A.; Ortiz, I. State-of-the-art and perspectives of the catalytic and electrocatalytic reduction of aqueous nitrates. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.Z.; Statt, M.J.; Bukas, V.J.; Shapel, S.G.; Pedersen, J.B.; Krempl, K.; Saccoccio, M.; Chakraborty, D.; Kibsgaard, J.; Vesborg, P.C.K.; et al. Increasing stability, efficiency, and fundamental understanding of lithium-mediated electrochemical nitrogen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Nazemi, M.; Gupta, S.; Chismar, A.; Hong, K.; Jacobs, H.; Zhang, W.; Rigby, K.; Hedtke, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Contrasting capability of single atom palladium for thermocatalytic versus electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6804–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Park, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Srivastava, K.; Gu, S.; Shanks, B.H.; Roling, L.T.; Li, W. Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction on Oxide-Derived Silver with Tunable Selectivity to Nitrite and Ammonia. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8431–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Cherepanov, P.V.; Choi, J.; Suryanto, B.H.R.; Hodgetts, R.Y.; Bakker, J.M.; Ferrero Vallana, F.M.; Simonov, A.N. A Roadmap to the Ammonia Economy. Joule 2020, 4, 1186–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, C.; Mittal, M. Utilization of green ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier for decarbonization in spark ignition engines. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 74, 28803–28823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Hill, A.K.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Current and future role of Haber-Bosch ammonia in a carbon-free energy landscape. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; An, Q.; Wang, W.; Meng, Y.; Lai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yip, S.; et al. Synergistic Active Phases of Transition Metal Oxide Heterostructures for Highly Efficient Ammonia Electrosynthesis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Klimpel, M.; Budnyk, S.; Rokicińska, A.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Dronskowski, R.; Mathew, A.; Budnyak, T.; Slabon, A. Combining Electrocatalysts and Biobased Adsorbents for Sustainable Denitrification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Liang, J.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, D.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q.; Hamdy, M.S.; Sun, X.; Ying, B. Recent advances in electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 50, 6–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, B. Mesoporous PdN Alloy Nanocubes for Efficient Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Wang, S.; Ahmad, M.S.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Liu, Q.; Kida, T.; Shafique, A.; Rehman, M.U.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J. Investigating the role of oxygen vacancies in metal oxide for enhanced electrochemical reduction of NO3− to NH3: Mechanistic insights. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 6440–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanto, B.H.R.; Du, H.-L.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Simonov, A.N.; MacFarlane, D.R. Challenges and prospects in the catalysis of electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, H.-M.; Zhu, H.-R.; Huang, C.-J.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Li, G.-R. Recent advances in electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia: Current challenges, resolving strategies, and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 21181–21232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Wicks, J.; Luo, M.; Nam, D.-H.; Tan, C.-S.; et al. Enhanced Nitrate-to-Ammonia Activity on Copper–Nickel Alloys via Tuning of Intermediate Adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5702–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Priest, C.; Wang, G.; Wu, G. Restoring the Nitrogen Cycle by Electrochemical Reduction of Nitrate: Progress and Prospects. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, K.; Liang, Z.; Zou, R.; Xu, Q. Electrochemical nitrogen fixation and utilization: Theories, advanced catalyst materials and system design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5658–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X. Some thoughts about the electrochemical nitrate reduction reaction. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 53, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Tang, C.; Li, G.; Dou, Y.; Liu, H.; Dou, S. Electrocatalytic nitrogen cycle: Mechanism, materials, and momentum. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 9027–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qiao, L.; Peng, S.; Bai, H.; Liu, C.; Fai, W.; Kin, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, K.; Wang, S.; et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for effcient nitrate reduction to ammonial. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-F.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Zhao, M. Electrocatalytic synthesis of ammonia using transition metal-based catalysts under ambient conditions: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2025, 23, 1247–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, M.; Wu, F.; Song, B.; Lu, K.; Zhang, H. Recent Advances in Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction: Strategies To Promote Ammonia Synthesis. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 11475–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B. Nitrate electroreduction: Mechanism insight, in situ characterization, performance evaluation, and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6720–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Xia, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Unveiling Cutting-Edge Developments in Electrocatalytic Nitrate-to-Ammonia Conversion. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2312746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Yang, J. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate—A step towards a sustainable nitrogen cycle. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 2710–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M.T.; Koper, M.T.M. The influence of nitrate concentration and acidity on the electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate on platinum. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 562, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Pillai, H.S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Mu, Q.; Han, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, H.; He, Q.; Xin, H.; et al. Breaking adsorption-energy scaling limitations of electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on intermetallic CuPd nanocubes by machine-learned insights. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, G.E.; de Vooys, A.C.A.; Koper, M.T.M. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate at low concentration on coinage and transition-metal electrodes in acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 554–555, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vooys, A.C.A.; van Santen, R.A.; van Veen, J.A.R. Electrocatalytic reduction of NO3−on palladium/copper electrodes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 154, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in non-noble metal electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, W.; Yang, J. Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction: Selectivity at the Crossroads Between Ammonia and Nitrogen. Chem Catalysis. 2023, 3, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wan, X.; Shao, C.; Guo, Y. Theoretical Insights into the Mechanism of Selective Nitrate-to-Ammonia Electroreduction on Single-Atom Catalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.-F.; Guo, L.; Gan, L.; Zhang, S.; Ajmal, M.; Pan, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Tandem Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia with Industrial-Level Current Density on Hierarchical Cu Nanowires Shelled with NiCo-Layered Double Hydroxide. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 14670–14679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Guo, C. Theoretical Insights into Superior Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia Performance of Copper catalysts. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 14417–14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P.; Reinhard, M.; Schneider, W.F.; Schüth, C.; Shapley, J.R.; Strathmann, T.J.; Werth, C.J. Critical Review of Pd-Based Catalytic Treatment of Priority Contaminants in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3655–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Deng, B.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, R.; Xiang, P.; et al. Critical review in electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia towards a sustainable nitrogen utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 148952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Guo, C.; Fu, X.; Jing, H.; Qin, G.; Li, H.; Xiao, J. Unveiling Potential Dependence in NO Electroreduction to Ammonia. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 6988–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Ooka, H.; Li, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Adachi, K.; Hashizume, D.; Yoshida, N.; Toyoda, S.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Regulation of the electrocatalytic nitrogen cycle based on sequential proton–electron transfer. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, K.; He, M.; Yan, M.; Peng, F.; Gao, F. Modifying Microenvironment in Van der Waals Gap by Cu/N Co-Doping Strategy for Highly Efficient Nitrite Reduction to Ammonia. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2417773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Sheng, T.; Sun, S.-G. In-situ FTIR spectroscopic studies of electrocatalytic reactions and processes. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qian, T.; Wang, M.; Ji, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, C.; Yan, C. Proton-filtering covalent organic frameworks with superior nitrogen penetration flux promote ambient ammonia synthesis. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hegh, D.; Song, D.; Zhang, J.; Usman, K.A.S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, W.; Yang, W.; Qin, S.; et al. Synthesis of nitrogen-sulfur co-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene with enhanced electrochemical properties. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100079. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Luo, R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Tang, C.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. Self-Supported Pd Nanorod Arrays for High-Efficient Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia. Small 2023, 19, 2207743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, H.; Xie, M.; Wang, P.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, P.; Yu, G. Thermally Enhanced Relay Electrocatalysis of Nitrate-to-Ammonia Reduction over Single-Atom-Alloy Oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 7779–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tang, C.; Guo, H.; Wu, H.; Duan, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Cao, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. In Situ Growth of Fe2O3 Nanorod Arrays on Carbon Cloth with Rapid Charge Transfer for Efficient Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49765–49773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, M.; Xu, S.-M.; Zhou, H.; Ji, K.; Chen, F.; Zhou, J.; Duan, H. Selective Electrooxidation of Biomass-Derived Alcohols to Aldehydes in a Neutral Medium: Promoted Water Dissociation over a Nickel-Oxide-Supported Ruthenium Single-Atom Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Hao, F.; Fan, Z. Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction: Ammonia Synthesis and the Beyond. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2304021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, P.; Huang, Y.; Tang, M.; Zou, X.; Pan, Z.; Huo, X.; Wu, J.; Lin, C.; Sun, Z.; et al. Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia on CuCo Nanowires at Practical Level. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tang, C.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. Understanding first electron transfer kinetic process of electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia on Fe2O3 nanorods array. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Latif, A.A.; Bondue, C.J.; Ernst, S.; Hegemann, M.; Kaul, J.K.; Khodayari, M.; Mostafa, E.; Stefanova, A.; Baltruschat, H. Insights into electrochemical reactions by differential electrochemical mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hao, Y.; Chu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, F.; Luo, W. Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia: A perspective on Fe/Cu-containing catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2024, 58, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Jia, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B. Unveiling the Activity Origin of a Copper-based Electrocatalyst for Selective Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5350–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Wu, H.; Zhang, F.; Tang, C.; Chen, G.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. Ruthenium-induced hydrolysis effect on Fe2O3 nanoarrays for high-performance electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 351, 123967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, M.M.; Salvadori, E. Principles and applications of EPR spectroscopy in the chemical sciences. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2534–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gu, X.; Zhu, P.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z. Enhanced electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia via boron-doped copper foam. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 518, 164635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, B. Microenvironment Engineering of Mesoporous Metals for Ammonia Electrosynthesis from Nitrate: Advances, Mechanisms, and Prospects. Acc. Chem. Res. 2025, 58, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, J.; Dieckhöfer, S.; Varhade, S.; Brix, A.C.; Lielpetere, A.; Seisel, S.; Junqueira, J.R.C.; Schuhmann, W. Splicing the active phases of copper/cobalt-based catalysts achieves high-rate tandem electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y. Carbon-Based catalysts for Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia: Design Strategies and Mechanistic Insights. Materials 2025, 18, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Qian, L.; Zhou, D.; Du, P.; Si, N.; Gu, X.; Jiang, D.; Feng, Y. Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia—Recent Progress. ChemElectroChem 2023, 10, e202300419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; Zhou, G. Engineering sulfur vacancies optimization in Ni3Co6S8 nanospheres toward extraordinarily efficient nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 324, 122193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Ling, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S. Recent research progress of electrocatalytic reduction technology for nitrate wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, L.; Silcox, R.; Giammalvo, K.; Brower, E.; Isip, E.; Bala Chandran, R. Combined Effects of Concentration, pH, and Polycrystalline Copper Surfaces on Electrocatalytic Nitrate-to-Ammonia Activity and Selectivity. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 4178–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Y.; Karamad, M.; Yong, X.; Huang, Q.; Cullen, D.A.; Zhu, P.; Xia, C.; Xiao, Q.; Shakouri, M.; Chen, F.-Y.; et al. Electrochemical ammonia synthesis via nitrate reduction on Fe single atom catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, H.; Chang, L.; Lin, A.; Cheng, D. Revealing the pH-dependent mechanism of nitrate electrochemical reduction to ammonia on single-atom catalysts. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 15422–15431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, M.E.; Biset-Peiró, M.; Murcia-López, S.; Morante, J.R. Cu2O–Cu@Titanium Surface with Synergistic Performance for Nitrate-to-Ammonia Electrochemical Reduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3633–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tan, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Selective nitrate removal from aqueous solutions by a hydrotalcite-like absorbent FeMgMn-LDH. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Fang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, X.-Y. Modulating the Electrolyte Microenvironment in Electrical Double Layer for Boosting Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202408382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, T.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J.; Gan, D.; Yuan, S.; Hong, L.; Feng, Y.; Sun, J.; Song, Q.; et al. Sustainable ammonia synthesis: Opportunities for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 105, 630–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhan, G.; Yang, J.; Quan, F.; Mao, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Lei, F.; Li, L.; Chan, A.; et al. Efficient Ammonia Electrosynthesis from Nitrate on Strained Ruthenium Nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-J.; Wu, Z.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-P. Electrochemical nitrate reduction as affected by the crystal morphology and facet of copper nanoparticles supported on nickel foam electrodes (Cu/Ni). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyter, D.; Bélanger, D.; Roué, L. Study of the electroreduction of nitrate on copper in alkaline solution. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5977–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Zheng, Q.-Z.; Lou, Y.-Y.; Zhao, K.-M.; Hu, S.-N.; Li, G.; Akdim, O.; Huang, X.-Y.; Sun, S.-G. Ampere-level current density ammonia electrochemical synthesis using CuCo nanosheets simulating nitrite reductase bifunctional nature. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Zeng, G.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; Li, C. A three-dimensional Cu nanobelt cathode for highly efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9385–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, W.; San Hui, K.; Fang, G. Electrochemical nitrate removal by magnetically immobilized nZVI anode on ammonia-oxidizing plate of RuO2–IrO2/Ti. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, P.; Wang, F. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate via Cu/Ni composite cathode paired with Ir-Ru/Ti anode: High efficiency and N2 selectivity. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 291, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, Z.; Ou, Y.; Zhong, L.; Yan, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Song, P.; et al. Pulsed Electrocatalysis Driven Efficient Ammonia Synthesis by Facilitating *NOOH Formation and Balancing *H Supply. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202510287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, C.; Cheng, C.; Han, S.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Meng, N.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Q.; Yu, Y. Pulsed electroreduction of low-concentration nitrate to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, G.; Tang, K.; Chen, C. Electrochemical nitrate reduction to produce ammonia integrated into wastewater treatment: Investigations and challenges. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Wang, K.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, Y.-Z. Electroreduction of nitrate in water: Role of cathode and cell configuration. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Huo, Q.; Cao, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Hu, Q.; He, C. Achieving Synchronization of Electrochemical Production of Ammonia from Nitrate and Ammonia Capture by Constructing a “Two-In-One” Flow Cell Electrolyzer. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhan, G.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Quan, F.; Fang, C.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jia, F.; et al. Renewable energy driven electroreduction nitrate to ammonia and in-situ ammonia recovery via a flow-through coupled device. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolla, T.H.; Zhang, B.; Matthews, T.; Chabalala, M.P.; Ajayi, S.O.; Sikeyi, L.L.; Liu, X.; Mathe, M.K. Metal/covalent-organic framework-based electrocatalysts for electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 518, 216061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Dong, A.; Shi, M.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Kang, X.; Gao, R.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, T.; et al. Efficient Ammonia Synthesis from Nitrate Catalyzed by Au/Cu with Enhanced Adsorption Ability. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, S.; Han, C.; Kundi, V.; Kumar, P.V.; Thomsen, L.; Johannessen, B.; Peng, L.; Shan, Y.; et al. Surface Engineering on Ag-Decorated Co3O4 Electrocatalysts for Boosting Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 11231–11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cao, R.; Han, Y.; Shang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, G. Electrocatalysts with atomic-level site for nitrate reduction to ammonia. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 96, 642–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Dong, B.; Zhi, C. Pd Doping-Weakened Intermediate Adsorption to Promote Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction on TiO2 Nanoarrays for Ammonia Production and Energy Supply with Zinc-Nitrate Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3938–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Yu, Y. Structurally Disordered RuO2 Nanosheets with Rich Oxygen Vacancies for Enhanced Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Timoshenko, J.; Bai, L.; Li, Q.; Rüscher, M.; Sun, C.; Cuenya, B.R.; Luo, J. Low-coordination rhodium catalysts for an efficient electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Feng, T.; Ma, M.; Li, Z.; Tang, L. Emerging Advances in Cu-based electrocatalysts for electrochemical nitrate reduction (NO3RR). Surf. Interfaces 2024, 48, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Recent Advances of Cu-Based Materials for Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2212089–2212106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Yuan, X.; Ge, M.; Tang, Y. Atomic-Dispersed Cu Catalysts for Electrochemical Nitrate Reduction: Coordination Engineering and Fundamental Insights. Small 2024, 20, 2405158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhao, X.; Hu, X.; He, K.; Yu, Y.; Li, T.; Tu, Q.; Qian, X.; Yue, Q.; Wasielewski, M.R.; et al. Alternative route for electrochemical ammonia synthesis by reduction of nitrate on copper nanosheets. Appl. Mater Today. 2020, 19, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Zheng, H.; Gao, R.; Yang, P.; Zhang, P.; Shao, M.; et al. Reaction Intermediate-Mediated Electrocatalyst Synthesis Favors Specified Facet and Defect Exposure for Efficient Nitrate–ammonia Conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Luo, J. Metallic Co nanoarray catalyzes selective NH3 production from electrochemical nitrate reduction at current densities exceeding 2 A cm−2. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yue, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, N.; Alshehri, A.A.; Hamdy, M.S.; et al. Co–NCNT nanohybrid as a highly active catalyst for the electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 3787–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorlop, K.-D.; Tacke, T. Erste Schritte auf dem Weg zur edelmetallkatalysierten Nitrat-und Nitrit-Entfernung aus Trinkwasser. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1989, 61, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-J.; Wu, Z.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-P. Manipulating the crystalline morphology and facet orientation of copper and copper-palladium nanocatalysts supported on stainless steel mesh with the aid of cationic surfactant to improve the electrochemical reduction of nitrate and N2 selectivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 273, 119053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrón-Calle, G.A.; Fajardo, A.S.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.M.; Garcia-Segura, S. Highly reactive Cu-Pt bimetallic 3D-electrocatalyst for selective nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 302, 120844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Kuan, W.-F.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.P. Mode of electrochemical deposition on the structure and morphology of bimetallic electrodes and its effect on nitrate reduction toward nitrogen selectivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 257, 117909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, F.; Xu, H.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Interfacial Water Structure Modulation on Unconventional Phase Non-Precious Metal Alloy Nanostructures for Efficient Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia in Neutral Media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202508617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Duan, H.; Cai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, W.; Zhang, K.; Han, D.; et al. Cascade Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia Using Bimetallic Covalent Organic Frameworks with Tandem Active Sites. Angew. Chem. 2025, 137, e202507956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, L.; Liu, L.; Xi, J. Revealing the Tandem Behavior of Iron-Group/Copper Binary catalysts in the Electroreduction of Nitrate to Ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 3, 2425084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wei, Y.; Cao, A.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, S.; Zang, S. Electrocatalytic nitrate-to-ammonia conversion with 100% Faradaic efficiency via single-atom alloying. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 316, 121683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Qian, T.; Yan, C.; Lu, J. Maximized atom utilization in a high-entropy 118118metallene via single atom alloying for boosted nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.; et al. Phase Engineering of High-Entropy Alloy for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Bao, D.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, X. Potential-induced synthesis and structural identification of oxide-derived Cu electrocatalysts for selective nitrate reduction to ammonia. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 7529–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Dai, W.; Mou, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Dong, F. Coupling electrocatalytic cathodic nitrate reduction with anodic formaldehyde oxidation at ultra-low potential over Cu2O. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2696–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Q.; Xing, X.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, W.; Li, H. Surface Structure Reformulation from CuO to Cu/Cu(OH)2 for Highly Efficient Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, J.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Z.-F.; Zou, J.-J.; Mu, T.; Gao, J.; Zhu, X.-D.; Zhang, Y.-C. Selenium-Deficient FeSe2/Fe3O4 Electrocatalyst for Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202420903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xie, L.; Liang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Li, N.; Tang, B.; et al. In situ grown Fe3O4 particle on stainless steel: A highly efficient electrocatalyst for nitrate reduction to ammonia. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3050–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B. Promoting selective electroreduction of nitrates to ammonia over electron-deficient Co modulated by rectifying Schottky contacts. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Yang, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, X.; Cao, H.; et al. Elucidating the activity, mechanism and application of selective electrosynthesis of ammonia from nitrate on cobalt phosphide. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Guo, Y.; Ma, D.; Chu, K. Tandem Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia on MBenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; et al. Sulfur vacancy MoS2 for electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia with enhanced selectivity. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 955, 170199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Shuai, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Syntheses and applications of single-atom catalysts for electrochemical energy conversion reactions. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 47, 32–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Dong, F.; Su, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Unraveling the Activity Trends and Design Principles of Single-Atom catalysts for Nitrate Electrocatalytic Reduction. ACS Nano. 2023, 17, 25614–25624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Fan, W.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, F. Modulation of the Second-Beyond Coordination Structure in Single-Atom Electrocatalysts for Confirmed Promotion of Ammonia Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 147, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wang, P.; Li, R.; Liu, K.; Omer, K.M.; Jin, Z.; Li, P. Pyridine-N-rich Cu Single-Atom Catalyst Boosts Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 340, 123228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Deng, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Interfacial polarization in metal-organic framework reconstructed Cu/Pd/CuOx multi-phase heterostructures for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2022, 318, 121805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakakis, G.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Sykes, E.C.H. Single-Atom Alloys as a Reductionist Approach to the Rational Design of Heterogeneous Catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Shen, C.; Peng, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Breaking Local Charge Symmetry of Iron Single Atoms for Efficient Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Mei, B.; Kang, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N. Electron-deficient Cobalt Nanocrystals for Promoted Nitrate Electrocatalytic Reduction to Synthesize Ammonia. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Fan, J.-L.; Liu, S.-B.; Sun, S.-P.; Lou, Y.-Y. Copper-Based Electrocatalysts for Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. Materials 2023, 16, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rong, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Modulating the Local Coordination Environment of Single-Atom Catalysts for Enhanced Catalytic Performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1842–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chen, Q.; Liao, P.; Duan, W.; Liang, S.; Yan, Z.; Feng, C. Single-Atom Cu catalysts for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction with Significant Alleviation of Nitrite Production. Small 2020, 16, 2004526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jin, Z.; Fang, Z.; Yu, G. A single-site iron catalyst with preoccupied active centers that achieves selective ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3522–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xing, X.; Li, J.; Xiong, W.; Li, H. Recent advances in carbon-based catalysts for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Carbon Lett. 2025, 35, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zou, P.; Liu, X.; Ni, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Tao, R. Facile and Tunable Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene with Different Microstructures for High-Performance Supercapacitors. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Fang, J.; Guo, M.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Peng, F. Nitrogen Defective Engineering of a Metal-Free Carbon Catalyst for Ammonia Electrosynthesis from Nitrate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 16320–16328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, S.; Li, X.; Chang, C.; Xie, M.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z. A robust metal-free electrocatalyst for nitrate reduction reaction to synthesize ammonia. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 19, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Sanati, S.; Morsali, A.; García, H. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Niu, J.; Wang, C. Revealing the activity origin of ultrathin nickel metal–organic framework nanosheet catalysts for selective electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia: Experimental and density functional theory investigations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 638, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanad, M.F.; Puente Santiago, A.R.; Tolba, S.A.; Ahsan, M.A.; Fernandez-Delgado, O.; Shawky Adly, M.; Hashem, E.M.; Mahrous Abodouh, M.; El-Shall, M.S.; Sreenivasan, S.T.; et al. Co–Cu Bimetallic Metal Organic Framework Catalyst Outperforms the Pt/C Benchmark for Oxygen Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4064–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yan, J.; Huang, H.; Song, W. Cu/Co bimetallic conductive MOFs: Electronic modulation for enhanced nitrate reduction to ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, S.; Sun, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Chemically Robust Covalent Organic Frameworks: Progress and Perspective. Matter 2020, 3, 1507–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Ji, H.; Huan, Y.; Qian, T.; Yan, C.; Lu, J. Multivariate covalent organic frameworks with tailored electrostatic potential promote nitrate electroreduction to ammonia in acid. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Sun, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, W.; Han, N.; Huang, B.; Li, Y. Near-unity electrochemical conversion of nitrate to ammonia on crystalline nickel porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, Y. Metal–Covalent Organic Frameworks (MCOFs): A Bridge Between Metal–Organic Frameworks and Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13722–13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, K. Conductive metal-covalent organic frameworks as novel catalytic platforms for reduction of nitrate to ammonia. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 9167–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Oh, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Matthews, J.E.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.M.; et al. Homogeneously Mixed Cu–Co Bimetallic Catalyst Derived from Hydroxy Double Salt for Industrial-Level High-Rate Nitrate-to-Ammonia Electrosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 27417–27428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Qian, T.; Xiong, J.; Yang, C.; Yan, C. Interfacial Defect Engineering Triggered by Single Atom Doping for Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huang, K.; Yao, X. Optimization of electronic structure by defect engineering for electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction reaction. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2025, 12, 1743–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yun, S.; Dang, J.; Dang, C.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Deng, Y. Defect engineering via ternary nonmetal doping boosts the catalytic activity of ZIF-derived carbon-based metal-free catalysts for photovoltaics and water splitting. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 27, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, W. Promoting defect formation and inhibiting hydrogen evolution by S-doping NiFe layered double hydroxide for electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Gong, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, N.; Kang, X.; Mao, X.; Chen, Y. Modulating surface oxygen species via facet engineering for efficient conversion of nitrate to ammonia. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 78, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Duan, H.; Gruber, C.G.; Qu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Cheng, D.; et al. Boosting Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction through Enhanced Mass Transfer in Cu-Bipyridine 2D Covalent Organic Framework Films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202421821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, S.; Wang, Y. Progress and Challenges in the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia. Molecules 2025, 30, 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193910
Yin S, Wang Y. Progress and Challenges in the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193910
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Shupeng, and Yinglong Wang. 2025. "Progress and Challenges in the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193910
APA StyleYin, S., & Wang, Y. (2025). Progress and Challenges in the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Nitrate to Ammonia. Molecules, 30(19), 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193910





