Composite Material Formation Based on Biochar and Nickel (II)-Copper (II) Ferrites
Abstract
1. Introduction
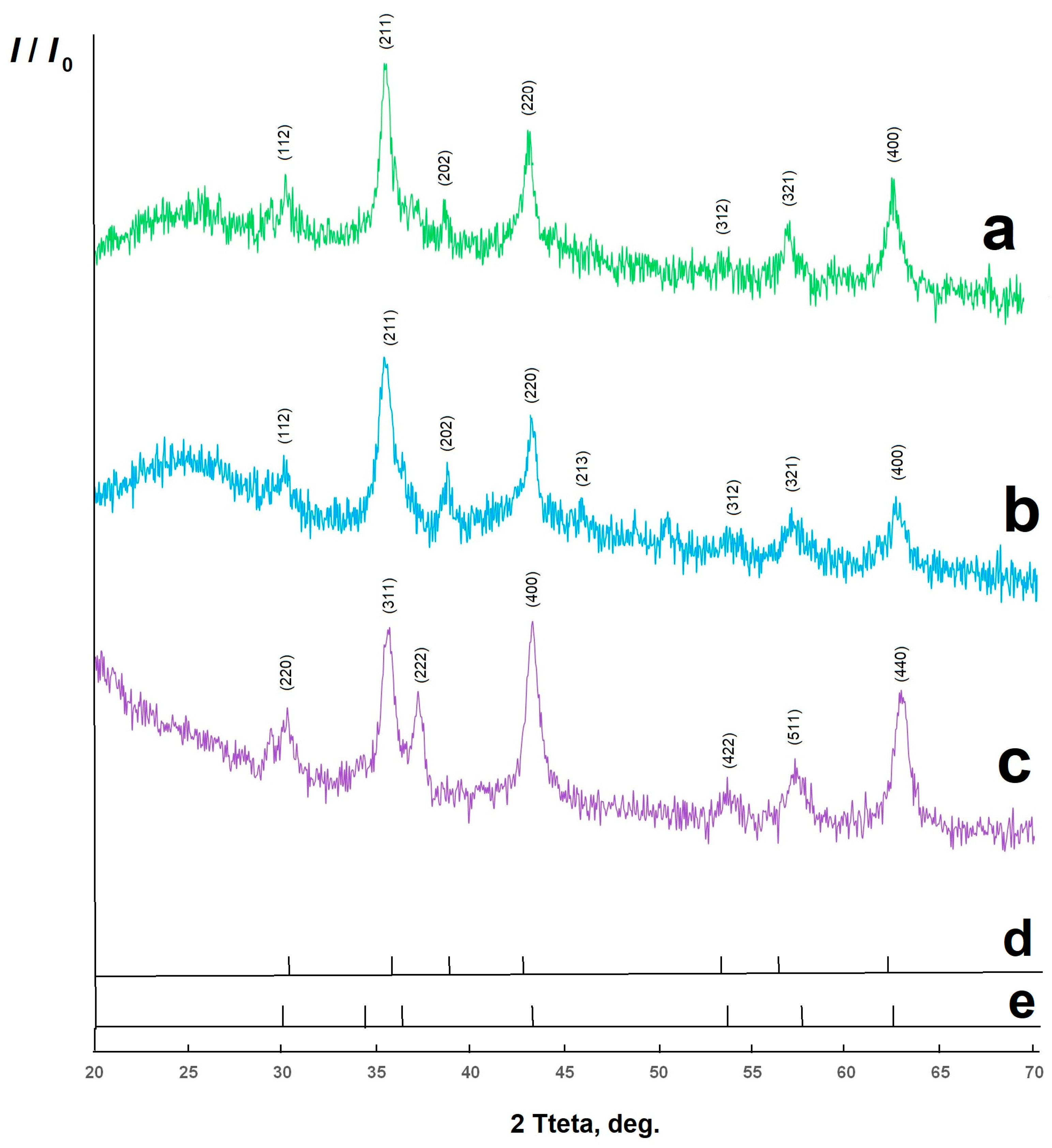
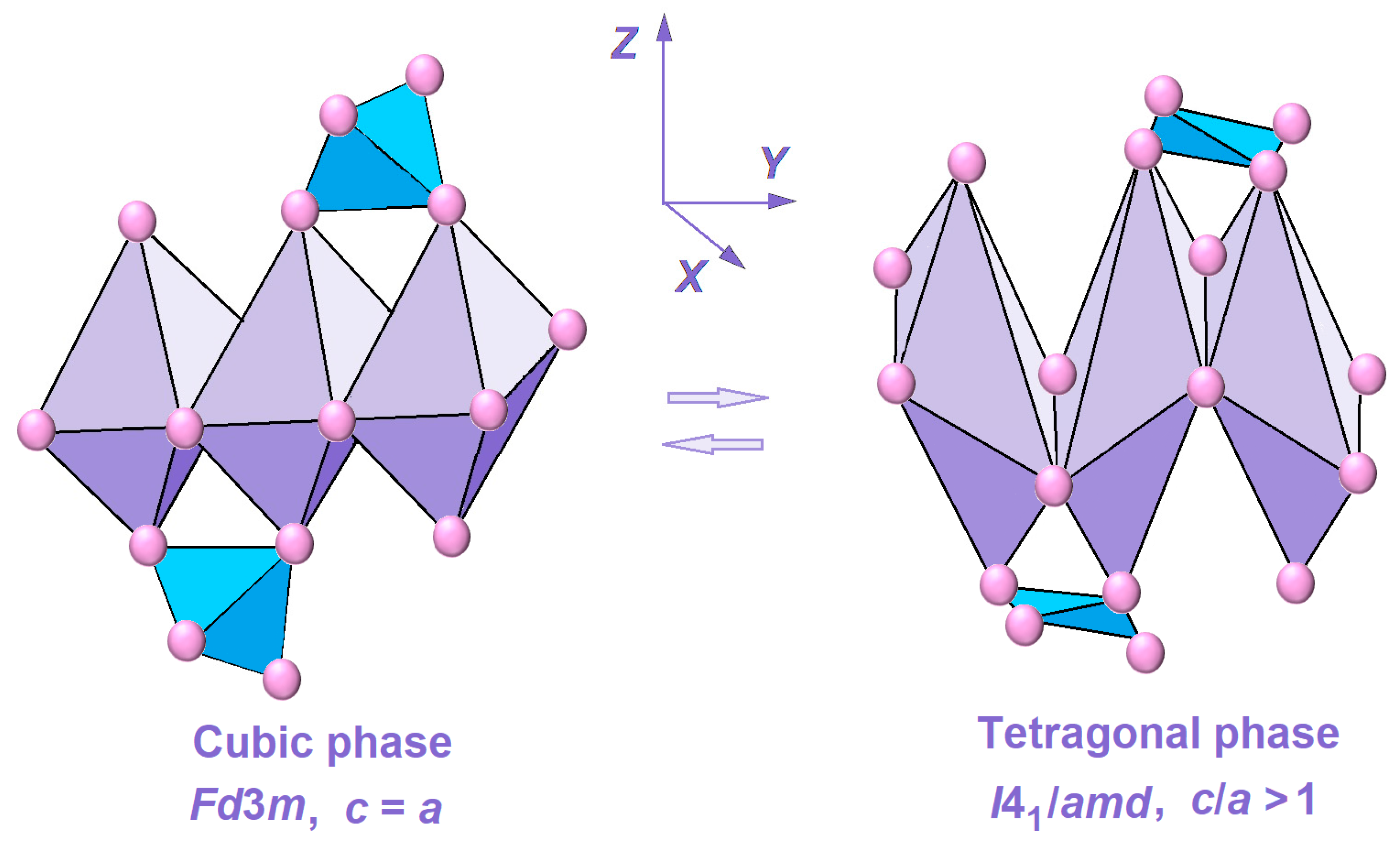
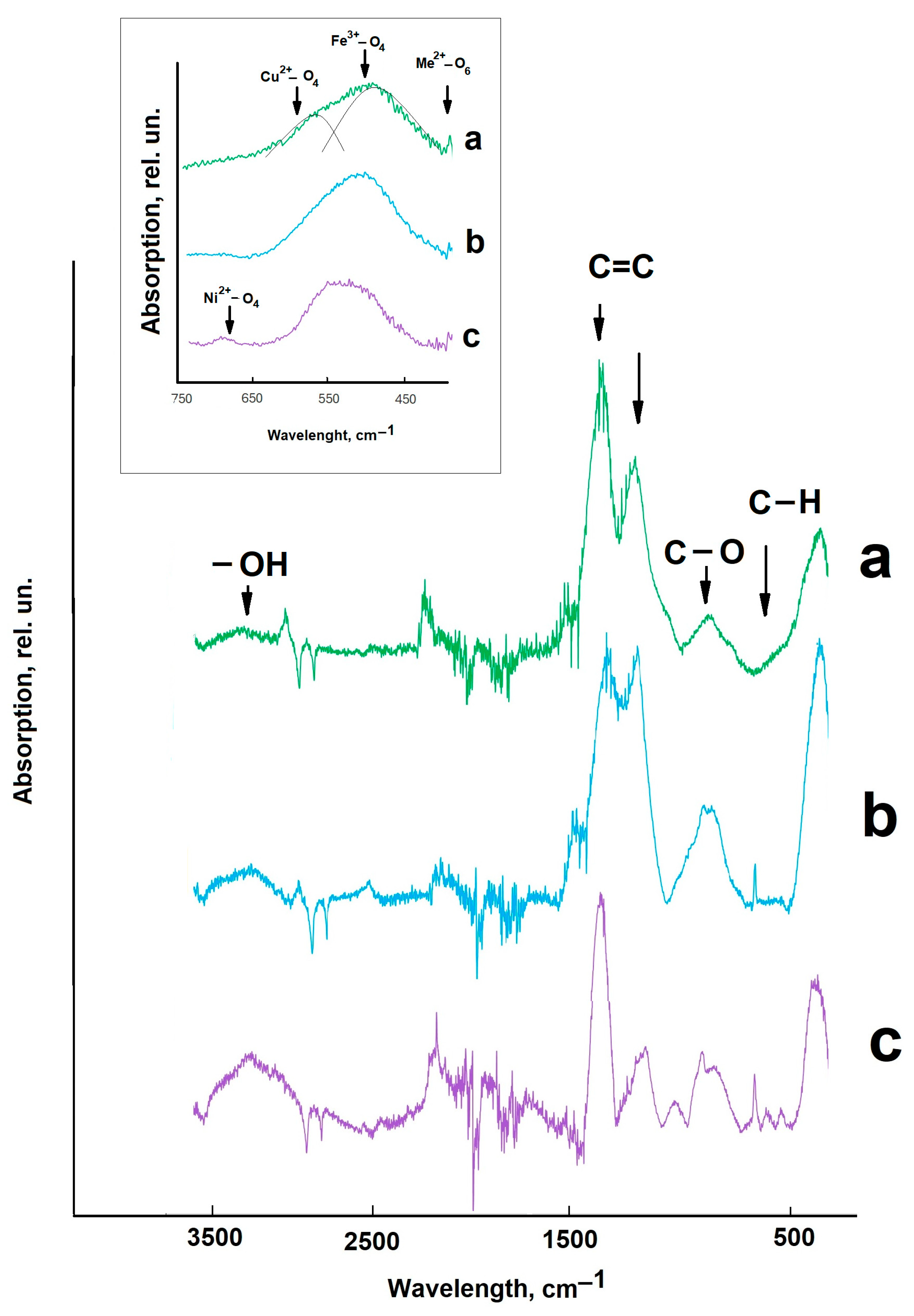
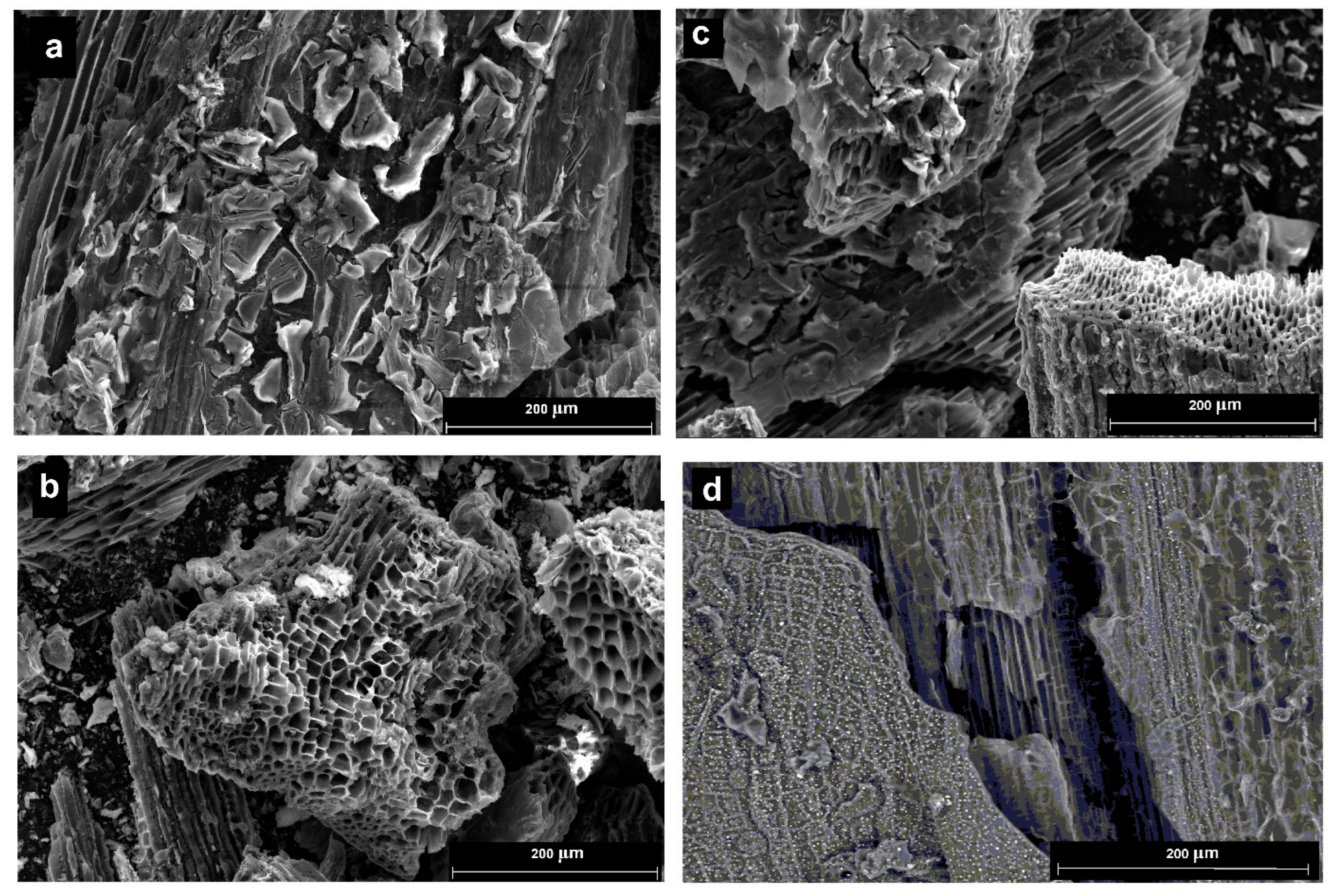
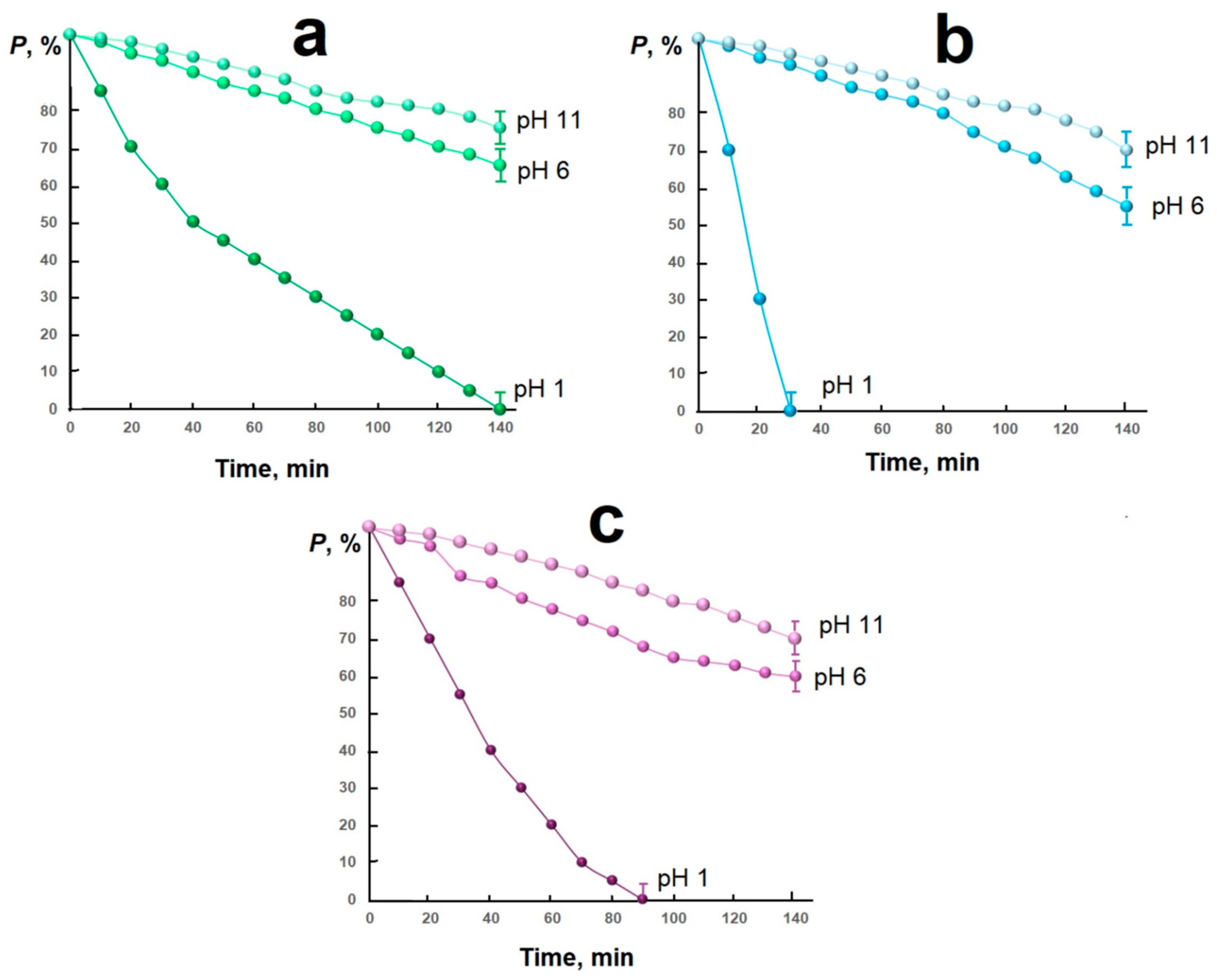
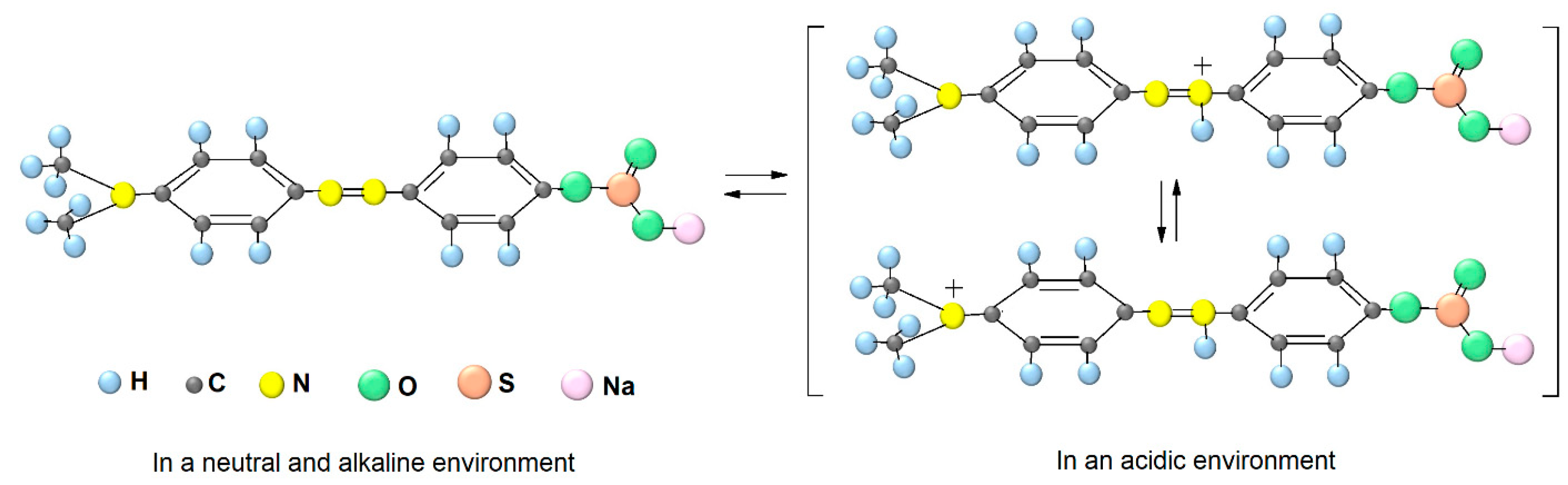
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Biochar
3.3. Synthesis of Composite Material
→ Cu0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 + by-products (NOx, CO2, H2O).
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balachandran, B.; Sabumon, P.C. A comprehensive review on biodegradation of Azo dye mixtures, metabolite profiling with health implications and removal strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 19, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Awady, M.E.; El-Shall, F.N.; Mohamed, G.E.; Abd-Elaziz, A.M.; Abdel-Monem, M.O.; Hassan, M.G. Exploring the decolorization efficiency and biodegradation mechanisms of different functional textile azo dyes by Streptomyces albidoflavus 3MGH. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aounallah, F.; Hkiri, N.; Fouzai, K.; Elaoud, A.; Ayed, L.; Asses, N. Biodegradation pathway of Congo red azo dye by geotrichum candidum and toxicity assessment of metabolites. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 6064–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongal, A.V.; Nandanwar, D.V.; Badwaik, D.S.; Choudhari, Y.D.; Wanjari, S.S. Incorporating effect of rare earths (Sm3+ and Nd3+) and transition metal ions (Al3+ and Cr3+) in modifying the lattice structure, magnetism, and dielectric properties of magnesium copper zinc cubic ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2025, 622, 172950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kanjariya, P.; Roopashree, R.; Ray, S.; Ab Yajid, M.S.; Tantawi, D.; Kumari, M.; Jayabalan, K.; Joshi, K.K.; Pramanik, A. A comprehensive review on the molecular structure of spinel nanomaterials for green hydrogen generation application via photocatalytic water splitting. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1348, 143348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Anju; Kuřitka, I. Spinel ferrite and MXene-based magnetic novel nanocomposites: An innovative high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorber. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2022, 48, 441–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; He, Y.; Xu, P.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. Spinel ferrites (MFe2O4): Synthesis, improvement and catalytic application in environment and energy field. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Wang, J.; Si, R.J.; Rehman, S.; Li, T.; Bi, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.J.; Li, Y.D.; Huang, S.G.; et al. Jahn-Teller assisted polaronic electron hopping in LiCuNb3O9. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalas, C.; Samartzis, A.; Biniskos, N.; Syskakis, E. Effects of Cr-doping on the Jahn-Teller, the orthorhombic to rhombohedral, and the magnetic transitions in LaMn1−xCrxO3 compounds. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 586, 412101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Yao, J.; Li, J.; Gan, Y.; Lv, L.; Tao, L.; et al. Ion-exchange induced Ni doping of α-MnO2 cathode with structural modification for aqueous zinc ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2025, 635, 236518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasamori, T.; Lee, V.; Nagahora, N.; Morisako, S. 1.03—Low-coordinate compounds of heavier group 14–16 elements. In Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry III, 3rd ed.; Reedijk, J., Poeppelmeier, R.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 118–164. ISBN 9780128231531. [Google Scholar]
- Mojahed, M.; Dizaji, H.R.; Gholizadeh, A. Structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of Ni/Zn co-substituted CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 646, 414337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.A.; Baskevich, A.S.; Butyrina, T.E. Influence of plasma synthesis parameters on the magnetic, structural and photocatalytic properties of copper ferrite. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 41461–41471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh, A.; Alizadeh, P.; Yourdkhani, A.; Zarandi, F.M. Synthesis of copper ferrite-decorated bioglass nanoparticles: Investigation of magnetic properties, biocompatibility, and drug release behaviour. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 708, 163713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I.; Solangi, I.B.; Perveen, S.; Kazi, M. Lanthanum doped copper ferrite as efficient Electrocatalyst for simultaneous detection of Bentazone and Diuron in vegetable samples. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 144066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.G.; Parne, S.R.; Nagaraju, P. Room temperature benzene gas sensing with spinal copper ferrite and copper cerium oxide nanocomposite sensors. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, K.; Sivaji, S.P.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, C.-L.; Lin, P.-H.; Sakthinathan, S.; Nehru, S.; Muthusamy, P.; Palanisamy, N.; Mariappan, C. Electrochemical determination of diuron in agricultural products using copper ferrite incorporated with multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 719, 136997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.; Nobrega, G.; Machado, M.; Lima, R.A. Green synthesis of copper ferrite-based nanofluids using Chlorella vulgaris for heat transfer enhancement. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 428, 127498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.; Bibi, I.; Majid, F.; Taj, B.; Aamir, M.; Fatima, G.; Raza, Q.; Elhouichet, H.; Iqbal, M.; Younas, U. Fabrication of a nanocomposite (NiFe2O4/CuO) with varying ratios of nickel ferrite and copper oxide nanoparticles to achieve a synergistic effect toward electrical performance. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 7038–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Verma, R.; Chauhan, A.; Thakur, P.; Wan, F.; Thakur, A. Sustainable high frequency applications of copper ferrite nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 174, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, I.; Mingxia, H.; Anwar, H.; Kashif, M.; Yizhu, Z. Utilization of copper-doped zinc spinel ferrites nano-composites as battery-grade electrode materials for supercapattery device applications. J. Energy Storage 2025, 112, 115498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Appels, L.; Dewil, R.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J.; Mikulcic, H. Producing hydrogen by catalytic steam reforming of methanol using non-noble metal catalysts. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 116019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedi, Á.; Lázár, K.; Solt, H.; Popova, M. Peculiar redox properties of SBA-15 supported copper ferrite catalysts promoting total oxidation of a model volatile organic air pollutant. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsebaii, N.M.; Hegazy, E.Z.; El Maksod, I.H.A.; El-Sayed El-Shafay, S. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of titanium-doped copper ferrite for methyl green dye degradation under commercial visible LED light. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt A, 45479–45487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Alhedrawie, D.; Jain, V.; Kumar, A.; Rekha, M.M.; Kundlas, M.; Sunitha, S.; Ray, S.; Shomurotova, S. Effective removal of auramine O and safranin O from aqueous solutions using nickel copper ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1344, 142933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurenko, J.; Szostak, E.; Gondek, L.; Kaykan, L.; Zywczak, A.; Vyshnevskyi, O. Structural and magnetic studies of Cobalt-Substituted copper ferrites for efficient photocatalytic dye degradation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 171, 113648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, L.; Zha, L.; He, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, O.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Lei, M.; et al. Mild and Effective Decatungstate-Catalyzed Degradation of Methyl Orange Under Visible Light. Catalysts 2025, 15, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beura, R.; Thangadurai, P. Effect of Sn doping in ZnO on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO-Graphene nanocomposite with improved activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5087–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Guan, L.; Li, F.; Yao, M. Visible light active TiO2–ZnO composite films by cerium and fluorine codoping for photocatalytic decontamination. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; Yang, C.; Huang, T.; Situ, Y.; Huang, H. Synthesis of porous ZnO/TiO2 thin films with superhydrophilicity and photocatalytic activity via a template-free sol–gel method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wu, J.; Borjigin, T.; Xing, L. Acid-citrate sequential engineered Hangjin2# clay for photo-fenton degradation of methyl orange: Electron transfer mechanism analysis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 181, 115266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, L.; Robledo, S.; Natera, J.; Massad, W.A. Box-Behnken experimental design to optimize the degradation of methyl orange by β-cyclodextrin-assisted photo-Fenton. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2025, 467, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukwevho, N.; Mafa, P.J.; Kefeni, K.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Mishra, S.B.; Kuvarega, A.T. Photo-Fenton like reaction for the degradation of methyl orange using magnetically retrievable NiFe2O4/CoMoS4 heterojunction photocatalyst. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 65, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Xing, S.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Han, Q. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles supported on carbonized corncob as heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for efficient degradation of methyl orange. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 77, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazril, N.I.H.; Jalil, A.A.; Aziz, F.F.A.; Hassan, N.S.; Fauzi, A.A.; Khusnun, N.F.; Izzudin, N.M.; Jusoh, N.W.C.; Teh, L.P.; Jaafar, N.F.; et al. Selective simultaneous photo-Fenton removal of Cr (VI) and methyl orange dye over critical raw material-free fibrous-silica irons catalyst. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e00994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.Á.; Jiménez, J.A.; Llorente, I.; de la Presa, P.; Hernando, A. Ball milling and annealing effect in structural and magnetic properties of copper ferrite by ceramic synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1006, 176206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbín, A.; Correa, J.R.; Piña, J.J.; Peláez-Abellán, E.; Jiménez, J.; Gordo, Y.; Urones-Garrote, E.; Otero-Díaz, L.C. Synthesis and catalytic study of manganese ferrites obtained by partial oxidation of ferrous hydroxide with permanganate. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2025, 614, 172665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mmelesi, O.K.; Patala, R.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Mamba, B.B.; Kefeni, K.K.; Kuvarega, A.T. Effect of Zn doping on physico-chemical properties of cobalt ferrite for the photodegradation of amoxicillin and deactivation of E. coli. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 649, 129462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mısırlıoğlu, B.S.; Kahya, N.D.; Öztürk, Z. Enhanced dielectric properties of copper substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles for energy storage applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2024, 193, 112195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, B.; Shehzad, K.; Yang, J.; Asif, M.I.; Al-Sulaimi, S.; Asif, M.; Ashraf, G.A.; ul Hassan, R.; Wahab, R.; Xu, Y.; et al. Insight into the structural, magnetic and fluoride (F−1) adsorption properties of copper–manganese ferrite (Cu0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4) and Azadirachta Indica composites synthesized through hydrothermal method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 334, 130415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes Filho, A.L.; Mendes Isidorio, D.K.; Pizarro Borges, L.E.; Vieira, A.C.; Veiga-Junior, V.F.; Pinheiro, W.A. Production and characterizations of silver-doped copper ferrite anchored in RGO surface. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, R.; Nithiyanantham, S.; Mahalakshmi, S.; Kogulakrishnan, K.; Usharani, K.; Gunasekaran, B.; Mohan, R.; Palaniappan, L. Structural, magnetic and electrical studies on nickel doped copper ferrite synthesized using sol-gel method. Results Surf. Interfaces 2024, 17, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Das, T.; Pandey, V.K.; Verma, B. Nanoarchitectonics of GO/PANI/CoFe2O4 (Graphene Oxide/polyaniline/Cobalt Ferrite) based hybrid composite and its use in fabricating symmetric supercapacitor devices. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1266, 133515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabelskaya, N.; Sulima, S.; Sulima, E.; Medennikov, O.; Kulikova, M.; Kolesnikova, T.; Sushkova, S. Study of the Possibility of Using Sol–Gel Technology to Obtain Magnetic Nanoparticles Based on Transition Metal Ferrites. Gels 2023, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogulakrishnan, K.; Nithiyanantham, S.; Koteeshwari, R.S.; Malarkodi, B.; Gobinath, B.; Venkadesh, A.; Mohan, R.; Natarajan, B.; Palaniappan, L. Investigations on the structure, magnetism, electricity, and electrochemistry of copper-doped manganese ferrite: Sol-gel technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2025, 313, 117999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | The Catalyst | Concentration of the Pollutant | Conditions of Catalysis, Degree of Purification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1% Sn-ZnO-graphene | 5 mmol/L | UV, 6 h, 89% Visible, 3 h, 98% | [28] |
| 2 | 5% Sn-ZnO-graphene | 5 mmol/L | UV, 6 h, 80.4% Visible, 3 h, 99% | [28] |
| 3 | ZnO-Zn2TiO4 | 10 mg/L | UV, 3 h, 90% | [29] |
| 4 | ZnO(10%)/TiO | 10.3 mg/L | Visible, 280 min, 78% | [30] |
| 5 | citrate-modified clay | 50 mg/L | UV, 90 min, 100% | [31] |
| 6 | Fe2+, β- Cyclodextrin | 26 mkmol/L | Visible, 30 min, 100% | [32] |
| 7 | NiFe2O4/CoMoS4 | 10 mg/L | Visible, 60 min, 99% | [33] |
| 8 | Fe3O4/biochar made from corn cob | 25 mg/L | Visible, 14 min, 99.7% | [34] |
| 9 | fibrous silica/Fe3O4 | 10 mg/L | Visible, 180 min, 80% | [35] |
| Sample | a | c | c/a | am | V | D | LA | LB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.8371 | 0.8598 | 1.03 | 0.8446 | 0.602 | 109 | 0.3657 | 0.2986 |
| CNF | 0.8340 | 0.8732 | 1.04 | 0.8351 | 0.582 | 130 | 0.3616 | 0.2953 |
| NF | 0.8341 | - | 0.8341 | 0.580 | 107 | 0.3612 | 0.2949 |
| Sample | λ | Formula | ρ, g/sm3 | δ·103 | ε·103 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | 0.24 | Fe0.24Cu0.76[Cu0.24Fe1.76]O4 | 5.29 | 0.138 | 8.47 |
| CNF | 0.87 | Cu0.13Fe0.87[Cu0.37Ni0.5Fe1.13]O4 | 5.42 | 0.144 | 10.42 |
| NF | 0.95 | Fe0.95Ni0.05[Ni0.95Fe1.05]O4 | 5.38 | 0.118 | 7.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabelskaya, N.P.; Vyaltsev, A.V.; Sundukova, N.G.; Baranova, V.A.; Sulima, S.I.; Sulima, E.V.; Gaidukova, Y.A.; Radzhbov, A.M.; Vasileva, E.V.; Yakovenko, E.A. Composite Material Formation Based on Biochar and Nickel (II)-Copper (II) Ferrites. Molecules 2025, 30, 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193900
Shabelskaya NP, Vyaltsev AV, Sundukova NG, Baranova VA, Sulima SI, Sulima EV, Gaidukova YA, Radzhbov AM, Vasileva EV, Yakovenko EA. Composite Material Formation Based on Biochar and Nickel (II)-Copper (II) Ferrites. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193900
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabelskaya, Nina P., Alexandr V. Vyaltsev, Neonilla G. Sundukova, Vera A. Baranova, Sergej I. Sulima, Elena V. Sulima, Yulia A. Gaidukova, Asatullo M. Radzhbov, Elena V. Vasileva, and Elena A. Yakovenko. 2025. "Composite Material Formation Based on Biochar and Nickel (II)-Copper (II) Ferrites" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193900
APA StyleShabelskaya, N. P., Vyaltsev, A. V., Sundukova, N. G., Baranova, V. A., Sulima, S. I., Sulima, E. V., Gaidukova, Y. A., Radzhbov, A. M., Vasileva, E. V., & Yakovenko, E. A. (2025). Composite Material Formation Based on Biochar and Nickel (II)-Copper (II) Ferrites. Molecules, 30(19), 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193900







