Novel ST-Specific Molecular Target-Based Method for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus ST7, ST188 and ST398
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of S. aureus Isolates

2.2. Identification of ST-Specific Genes of S. aureus
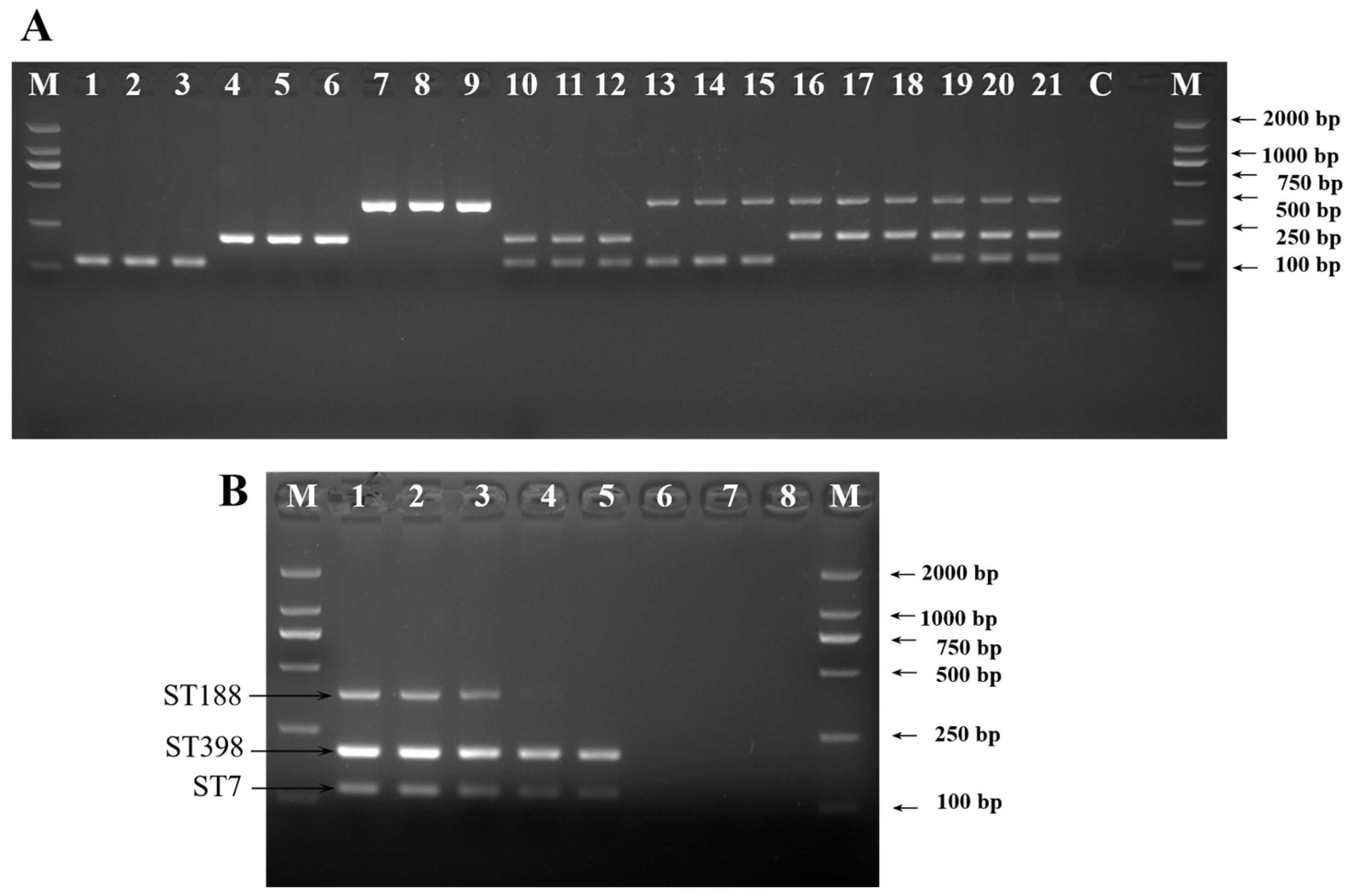
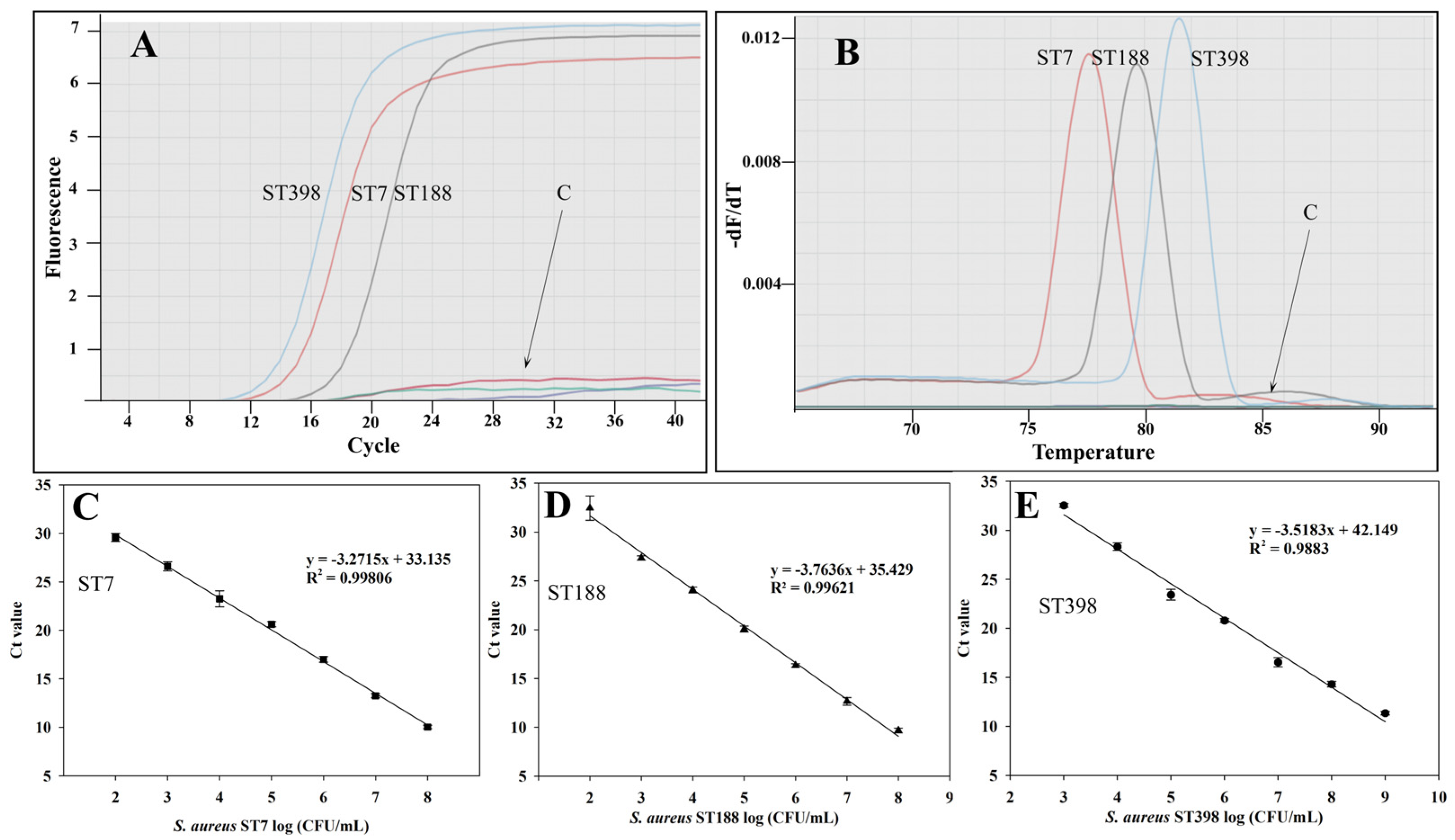
2.3. Evaluating Specificity and Sensitivity of ST-Specific Genes Using PCR Assay
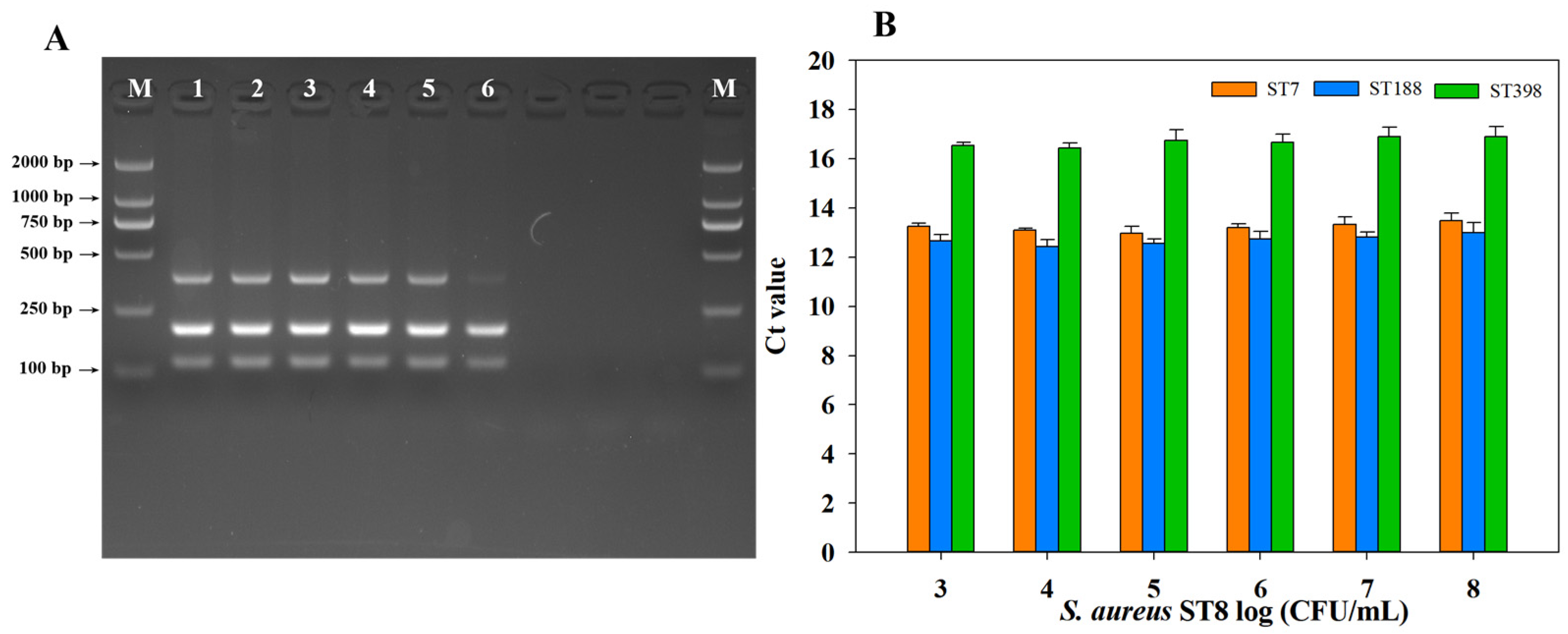
2.4. Detection of Predominant S. aureus STs in Artificially Contaminated Milk
2.5. Anti-Interference Test for mPCR and qPCR
2.6. Application of mPCR and qPCR in Natural Milk to Detect Three S. aureus STs
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Genomic DNA Extraction
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Screening of S. aureus ST-Specific Targets
4.4. Primer-Based Evaluation of Novel ST-Specific Targets
4.5. Multiplex PCR and Quantitative PCR Conditions
4.6. Sensitivity of the mPCR/qPCR Assays in Artificially Contaminated Milk Samples
4.7. Evaluation of Specificity and Anti-Interference Capability of mPCR/qPCR Assays
4.8. Application of the mPCR and qPCR Assays for the Analysis of Food Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Xie, R.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yodsanit, N.; Zhu, M.; Burger, J.C.; Ye, M.; Tong, Y.; Gong, S. Multimodal nanoimmunotherapy engages neutrophils to eliminate Staphylococcus aureus infections. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, F.; Xiang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Novel species-specific targets for real-time PCR detection of four common pathogenic Staphylococcus spp. Food Control 2022, 131, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Predominant pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Xi, M.; Meng, J. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in retail foods in Shaanxi, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, N.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Teng, D.; Wang, J. An amphipathic peptide combats multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and biofilms. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Guan, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, H.; Cui, Z.; Wu, S. Biomimetic bacteriophage-like particles formed from probiotic extracts and NO donors for eradicating multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2206134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cripe, J.; Conway, W.; Meng, J.; Hall, G.; Bhagwat, A.A. Isolation and characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from ready-to-eat foods in Florida. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2006, 72, 5073–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, F.P.; Suaya, J.A.; Ray, G.T.; Baxter, R.; Brown, M.L.; Mera, R.M.; Close, N.M.; Thomas, E.; Amrine-Madsen, H. spa typing and multilocus sequence typing show comparable performance in a macroepidemiologic study of Staphylococcus aureus in the United States. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akineden, Ö.; Murata, K.J.; Gross, M.; Usleber, E. Microbiological quality of raw dried pasta from the German market with special emphasis on Cronobacter species. J. Food Sci. 2021, 80, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H. The changing pattern of population structure of Staphylococcus aureus from bacteremia in China from 2013 to 2016: ST239-030-MRSA replaced by ST59-t437. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Chang, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y. Prevalence and characteristics of enterotoxin B-producing Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food sources: A particular cluster of ST188 strains was identified. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Ge, Q.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, M.; Xiao, Y. Reshaping the battlefield: A decade of clonal wars among Staphylococcus aureus in China. Drug Resist. Updates 2025, 78, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Q.; Lu, H.; Meng, H.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis and virulence determinant of the host-adapted Staphylococcus aureus lineage ST188 in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shen, S.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, J.; Tian, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y. ST7 becomes one of the most common Staphylococcus aureus clones after the COVID-19 epidemic in the city of Wuhan, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Zhong, Q.; Cao, X.; Gu, S.; Peng, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hang, Y.; Fang, X.; et al. Comparison of molecular characteristics between methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates by whole-genome sequencing. Infect. Drug Resist. Updates 2022, 15, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kong, L.; Diao, L.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, W.; Zeng, Z. Relationship between biofilm formation and molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus from animal origin. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 602–612. [Google Scholar]
- Petinaki, E.; Spiliopoulou, I. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among companion and food-chain animals: Impact of human contacts. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.Z.; Siegel, J.; Lowy, F.D.; Zychowski, D.; Taylor, A.; Lee, C.J.; Boyle-Vavra, S.; Daum, R.S. Asymptomatic carriage of sequence type 398, spa type t571 methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in an urban jail: A newly emerging, transmissible pathogenic strain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Meng, J. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus ST398 isolates from retail foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 196, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Boto, D.; D’Arrigo, M.; García-Lafuente, A.; Bravo, D.; Pérez-Baltar, A.; Gaya, P.; Medina, M.; Arqués, J.L. Staphylococcus aureus in the processing environment of cured meat products. Foods 2023, 12, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J.; Carter, M.Q.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Genetic diversity and virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw and processed food commodities in Shanghai. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Dai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus isolated from rice and flour products in Guangdong, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 406, 110348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitt, A.; Lienen, T.; Wichmann-Schauer, H.; Cuny, C.; Tenhagen, B.A. The occurrence and distribution of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 on German dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11806–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Whole-genome analysis of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398 strains isolated from patients with bacteremia in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belkum, A.; Melles, D.C.; Peeters, J.K.; Van Leeuwen, W.B.; Van Duijkeren, E.; Huijsdens, X.W.; Spalburg, E.; De Neeling, A.J.; Verbrugh, H.A. Methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398 in pigs and humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wamel, W.J.; Hansenová Manásková, S.; Fluit, A.C.; Verbrugh, H.; de Neeling, A.J.; Van Duijkeren, E.; Van Belkum, A. Short term micro-evolution and PCR-detection of methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feil, E.J.; Nickerson, E.K.; Chantratita, N.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Srisomang, P.; Cousins, R.; Pan, W.; Zhang, G.; Xu, B.; Day, N.P.; et al. Rapid detection of the pandemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone ST 239, a dominant strain in Asian hospitals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegger, M.; Lindsay, J.A.; Moodley, A.; Skov, R.; Broens, E.M.; Guardabassi, L. Rapid PCR detection of Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex 398 by targeting the restriction-modification system carrying sau1-hsdS1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, R.; Xie, T.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Lei, T.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Chen, M.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals the potential risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from ready-to-eat foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Charlesworth, J.; Achtman, M. HierCC: A multi-level clustering scheme for population assignments based on core genome MLST. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3645–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, S.; Inoue, O.; Yamagami, T.; Yanagimoto, K.; Uematsu, K.; Hisada, Y.; Uchida, T.; Ohta, M.; Suzuki-Inoue, K. Clinical characteristics and molecular analysis of USA300 and ST 764 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from outpatients in Japan by PCR-based open reading frame typing. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Shang, Y.; Chen, M.; Pang, R.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. Identification of new serovar-specific detection targets against Salmonella B serogroup using large-scale comparative genomics. Food Control 2021, 124, 107862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiebel, J.; Böhm, A.; Nitschke, J.; Burdukiewicz, M.; Weinreich, J.; Ali, A.; Roggenbuck, D.; Rödiger, S.; Schierack, P. Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics associated with biofilm formation by human clinical Escherichia coli isolates of different pathotypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01660-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardyn, S.E.; Smith, T.C. False positives and negatives obtained with PCR-based identification of Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex 398. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McInerney, J.O.; McNally, A.; O’Connell, M.J. Why prokaryotes have pangenomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.J.; Webb, A.L.; Mutschall, S.K.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Barker, D.; Hetman, B.M.; Gannon, V.; Abbott, D.W.; Thomas, J.E.; Inglis, G.D.; et al. A genome-wide association study to identify diagnostic markers for human pathogenic Campylobacter jejuni strains. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Won, J.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.Y. Real-time PCR method for the rapid detection and quantification of pathogenic Staphylococcus species based on novel molecular target genes. Foods 2021, 10, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H. Dual recombinase polymerase amplification system combined with lateral flow immunoassay for simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 255, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, S.; Kılıç, Y.; Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Altintas, Z. A novel smartphone-based nanozyme-enhanced electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive direct detection of Staphylococcus aureus in milk and blood serum. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 49, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, P.A.; McCulloch, J.A.; Oliveira, G.A.; Mamizuka, E.M. Molecular techniques for MRSA typing: Current issues and perspectives. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
| Target | Target Genes | Presence Profile in | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Strain | Non-Target Strain | |||
| S. aureus ST7 | group_10498 | 10 (100%) | 0 (0%) | This study |
| group_10499 | 10 (100%) | 0 (0%) | This study | |
| S. aureus ST188 | group_9419 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | This study |
| group_9415 | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | This study | |
| S. aureus ST398 | group_9911 | 34 (100%) | 0 (0%) | This study |
| A07 | 34 (100%) | 2 (0.4%) | [26] | |
| C01 | 34 (100%) | 21 (4.2%) | [26] | |
| sau1-hsdS1 | 34 (100%) | 18 (3.6%) | [28] | |
| Target | Name of Target Gene | Encoded Protein | * Gene Location | Primer Set Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | LOD in Pure Culture (cfu/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ST7 | group_10498 | hypothetical protein | 2366410~2366754 | ST-1 (F) | GTTACATCAGATCAAGCAGAG | 119 | 8.6 × 103 |
| ST-1 (R) | GCATTTAGAAAAGCAGTGG | ||||||
| group_10499 | hypothetical protein | 2366764~2367651 | ST-2 (F) | CGACTATCAGTTTTACAATCC | 369 | 8.6 × 104 | |
| ST-2 (R) | CGTATAGACCTAACCCAGC | ||||||
| S. aureus ST188 | group_9419 | hypothetical protein | 2475310~2475726 | ST-3 (F) | GATGTTATTCCTATCGCAACG | 238 | 1.2 × 104 |
| ST-3 (R) | GAACGCCACTACTTTCACTTT | ||||||
| group_9415 | hypothetical protein | 2445882~2446304 | ST-4 (F) | GCCCTATAACTTTACGACGCAG | 388 | 1.2 × 103 | |
| ST-4 (R) | CCAACTATTGATTTGATTTACCACG | ||||||
| S. aureus ST398 | group_9911 | hypothetical protein | 2275068~2275370 | ST-5 (F) | CTTCTACGATGCCTTAGC | 231 | 6.4 × 104 |
| ST-5 (R) | TGTTCAATGACGGTTTCT |
| No. | Bacterial Species | Strains | ST Type | Number of Strains | Source * | Special Target for PCR Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST7 | ST188 | ST398 | ||||||
| 1–23 | S. aureus | 7-1, 22-0, 22-1, 42-0, 42-1, 42-2, 44-1, 151-0, 151-1, 173-0, 177-0, 178-1, 178-2, 192-0, 192-1, 201-0, 201-1, 201-2, 202-1, 203-0, 203-2, 306-1, 322-1 | 7 | 23 | a | + | − | − |
| 1–23 | 65-1, 65-2, 126-0, 126-1, 153-0, 1475-1, 1863-1, 510A-1, 545-1, 636-1, 663-1, 742-1, 3055-1, 3151-1, 3151C1, 3153-1, 3153A1, 3153A2, 3153B3, 3185-1, 3188-1, 3231-1, 3260-1 | 188 | 23 | a | − | + | − | |
| 1–81 | 9-0, 67-0, 229-0, 436, 489, 531, 548, 549, 646, 706, 976, 1003, 1023, 1142, 1198, 1255, 1272, 1352B, 1387-1C, 1492, 1494, 1723, 1772, 1823-0, 1879, 1929-0, 1973-0, 1973-1, 2011-1, 2092-0, 2094-0, 2094-1, 2152-0, 2155-0, 2180-0, 2183-0, 2194-1, 2197-0, 2429-1, 2517-0, 2517-1, 2553-0, 2553-2, 2566-1, 2566-2, 2651-0, 2651-1, 2680-0, 2831, 3026, 3122, 3152, 3224, 3373, 3375, 3677, 3678, 3728A1, 3755, 3755A1, 3838B1, 3838C2, 3981, 3988, 3993, 3993A1, 4022C2, 4051, 4051A3, 4076A1, 4123, 4173, 4174, 4260A1, 4266C1, 4275, 4291A1, 697A, 2816-5, 2816-8, 2831-3 | 398 | 81 | a | − | − | + | |
| 1 | 16-0 | 1 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 2 | 396 | 10 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 3 | 922-0 | 1085 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 4 | 1393 | 12 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 5 | 2753-2 | 1301 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 6 | 3895 | 133 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 7 | 17 | 15 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 8 | 41421 | 1635 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 9 | 3456B1 | 1659 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 10 | 2874B1 | 1920 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 11 | 1843 | 20 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 12 | 3098 | 22 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 13 | 486 | 25 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 14 | 260 | 2592 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 15 | 1025 | 2990 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 16 | 353 | 30 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 17 | 1148 | 3055 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 18 | 421 | 333 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 19 | 3652C1 | 3355 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 20 | 2194-2 | 3685 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 21 | 3043 | 403 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 22 | 157-0 | 4062 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 23 | 3929 | 4691 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 24 | 2630-1 | 4692 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 25 | 3704 | 4693 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 26 | 3929 | 4694 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 27 | 4029C2 | 5 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 28 | 29-0 | 504 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 29 | 52-0 | 522 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 30 | 1022 | 537 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 31 | 1831-0 | 573 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 32 | 368 | 59 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 33 | 24-0 | 630 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 34 | 1813-0 | 672 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 35 | 2039-0 | 692 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 36 | 24-2 | 72 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 37 | 1-1 | 8 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 38 | 631 | 88 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 39 | 1-0 | 9 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 40 | 223-2 | 906 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 41 | 3251B1 | 943 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 42 | 73-1 | 944 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 43 | 3675C1 | 950 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 44 | 1190 | 965 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 45 | 707 | 97 | 1 | a | − | − | − | |
| 46 | S. epidermidis | 612-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 47 | S. hominis | 0651-3 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 48 | S. haemolyticus | 0770-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 49 | S. capitis | 0640-3 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 50 | S. warneri | 0629-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 51 | S. saprophyticus | 1045-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 52 | S. sciuri | 0729-7 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 53 | S. lugdunensis | 0791-2 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 54 | S. cohnii | 0616-5 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 55 | S. pasteuri | 0821-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 56 | S. gallinarum | 2483-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 57 | S. hyicus | 0747-6 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 58 | S. equorum | 1217-4 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 59 | S. schleiferi | 2926B2-2 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 60 | S. succinus | 1580-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 61 | S. lentus | 1091-2 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 62 | Shigella sonnei | 0639-1 | / | 1 | a | − | − | − |
| 63 | L. monocytogenes | ATCC19114 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| 64 | V. parahemolyticus | ATCC33847 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| 65 | P. aeruginosa | ATCC15442 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| 66 | Escherichia coli | CMCC44103 | / | 1 | c | − | − | − |
| 67 | P. mirabilis | CMCC49005 | / | 1 | c | − | − | − |
| 68 | S. enteritidis | CMCC50335 | / | 1 | c | − | − | − |
| 69 | C. sakazakii | ATCC29544 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| 70 | B. cereus | ATCC14579 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| 71 | C. jejuni | ATCC6633 | / | 1 | b | − | − | − |
| No. | Sample | Test Results for | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST7 | ST188 | ST398 | ||||||||
| Conventional MLST | mPCR | qPCR | Conventional MLST | mPCR | qPCR | Conventional MLST | mPCR | qPCR | ||
| 1 | Milk (n = 10) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 3 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 4 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 5 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 6 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 7 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 8 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 10 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 11 | pork meat (n = 10) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 12 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 13 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 14 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 15 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 16 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 17 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 18 | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | |
| 19 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 20 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 21 | wet rice noodle (n = 10) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 22 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 23 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 24 | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | |
| 25 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 26 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 27 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 28 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 29 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 30 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Species Strain | Number of Samples | Standard MLST Method | mPCR Method | qPCR Method | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | − | + | − | + | − | |||||
| S. aureus ST7 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| S. aureus ST188 | 30 | 2 | 28 | 2 | 28 | 2 | 28 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| S. aureus ST398 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 30 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, B.; Nie, X.; Mao, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, B.; Wu, X. Novel ST-Specific Molecular Target-Based Method for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus ST7, ST188 and ST398. Molecules 2025, 30, 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193889
Zhou B, Nie X, Mao X, Chen J, Chen J, Ma B, Wu X. Novel ST-Specific Molecular Target-Based Method for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus ST7, ST188 and ST398. Molecules. 2025; 30(19):3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193889
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Baoqing, Xiang Nie, Xudong Mao, Jiaxin Chen, Jiawen Chen, Bingfeng Ma, and Xin Wu. 2025. "Novel ST-Specific Molecular Target-Based Method for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus ST7, ST188 and ST398" Molecules 30, no. 19: 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193889
APA StyleZhou, B., Nie, X., Mao, X., Chen, J., Chen, J., Ma, B., & Wu, X. (2025). Novel ST-Specific Molecular Target-Based Method for Simultaneous and Quantitative Detection of Staphylococcus aureus ST7, ST188 and ST398. Molecules, 30(19), 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30193889







