Determination of Selected Hydroxylated PAHs in Urine Samples of Individuals Consuming Grilled Marshmallows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Hydroxy-PAHs Standards
3.3. Apparatus
3.4. Grilled Marshmallows
3.5. Characteristics of Participants Consuming Grilled Marshmallows
3.6. Urine Sampling
3.7. Analysis of Hydroxy-PAHs in Urine
3.7.1. Hydrolysis
3.7.2. Solid-Phase Extraction of the Hydroxy-PAHs-Containing Fraction
3.7.3. Determination of Hydroxy-PAHs by HPLC-FLD
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maciejczyk, M.; Janoszka, B.; Szumska, M.; Pastuszka, B.; Waligóra, S.; Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A.; Nowak, A.; Tyrpień-Golder, K. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Grilled Marshmallows. Molecules 2024, 29, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–139. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/agents-classified-by-the-iarc/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Nsonwu-Anyanwu, A.C.; Helal, M.; Khaled, A.; Elnemr, A.; Ejemot-Nwadiaro, R.I.; Usoro, C.A.O.; EL-Sikaily, A. Urinary Biomonitoring and Cancer Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Exposure in Relation to Water Intake in Calabar, Nigeria. Expo. Health 2025, 17, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, M.; Song, G.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K.; Shin, M.-Y.; Kim, S. Toxicokinetic Analyses of Naphthalene, Fluorene, Phenanthrene, and Pyrene in Humans after Single Oral Administration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, V.; Dias da Silva, D.; Martins, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Pinto, J. Metabolomics Perspectives of the Ecotoxicological Risks of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Scoping Review. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T. Xenobiotic-Metabolizing Enzymes Involved in Activation and Detoxification of Carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 21, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, J.; Gomółka, E.; Szot, W. Urinary 1-Hydroxypyrene in Occupationally-Exposed and Non-Exposed Individuals in Silesia, Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styszko, K.; Pamuła, J.; Pac, A.; Sochacka-Tatara, E. Biomarkers for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Human Excreta: Recent Advances in Analytical Techniques—A Review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 7099–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motorykin, O.; Santiago-Delgado, L.; Rohlman, D.; Schrlau, J.E.; Harper, B.; Harris, S.; Harding, A.; Kile, M.L.; Massey Simonich, S.L. Metabolism and Excretion Rates of Parent and Hydroxy-PAHs in Urine Collected after Consumption of Traditionally Smoked Salmon for Native American Volunteers. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, X.; Huang, D.; Ge, M.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Oxidation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Triggered by a Photochemical Synergistic Effect between High- and Low-Molecular-Weight PAHs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 17807–17816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.; Arey, J. Atmospheric Chemistry of Gas-Phase Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Formation of Atmospheric Mutagens. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakin, A.; George Dixon, D.; Greenberg, B.M. Pathway of Anthracene Modification under Simulated Solar Radiation. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrado, A.I.; Garcia, S.; Castrillejo, Y.; Perez, R.M. Hydroxy–PAH Levels in Atmospheric PM10 Aerosol Samples Correlated with Season, Physical Factors and Chemical Indicators of Pollution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratelle, M.; Khoury, C.; Adlard, B.; Laird, B. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Levels in Urine Samples Collected in a Subarctic Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Jiang, S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Z.; Xiang, P.; Chang, Z.; Duan, W.; Shen, G.; Qin, Y.; et al. Occurrence, Formation Mechanism, and Health Risk of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Barbecued Food. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 293, 118046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Wu, P.-R.; Guo, Y. Urinary Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Pregnant Women and Their Association with a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27281–27290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Romanoff, L.; Bartell, S.; Pittman, E.N.; Trinidad, D.A.; McClean, M.; Webster, T.F.; Sjödin, A. Excretion Profiles and Half-Lives of Ten Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolites after Dietary Exposure. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Maldonado, I.N.; Ochoa-Martínez, Á.C.; López-Ramírez, M.L.; Varela-Silva, J.A. Urinary Levels of 1-Hydroxypyrene and Health Risk Assessment in Children Living in Mexican Communities with a High Risk of Contamination by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, L.; Baldini, G.M.; Piscopo, M.; Liguori, G.; Lombardi, R.; Ricciardi, M.; Esposito, G.; Pinto, G.; Fontanarosa, C.; Spinelli, M.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Environment: Occupational Exposure, Health Risks and Fertility Implications. Toxics 2025, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trask, M.; Rahman, S.M.; Kampouri, M.; Raqib, R.; Ekström, E.-C.; Kajantie, E.; Islam, M.R.; Krais, A.M.; Lindh, C.; Rahman, A.; et al. Childhood Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Cardiometabolic Indicators in Childhood and Adolescence: Findings from a Cohort Study in Rural Bangladesh. Environ. Res. 2025, 278, 121653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, X.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, Q. Internal Exposure Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursafa, P.; Amin, M.M.; Hajizadeh, Y.; Mansourian, M.; Pourzamani, H.; Ebrahim, K.; Sadeghian, B.; Kelishadi, R. Association of Atmospheric Concentrations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons with Their Urinary Metabolites in Children and Adolescents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17136–17144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakken, C.L.; Sørhus, E.; Holmelid, B.; Meier, S.; Mjøs, S.A.; Donald, C.E. Transformative Knowledge of Polar Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons via High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 960, 178349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Du, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhi, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, Z.; Ku, T.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Metastatic Effects of Hydroxy-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Liver Cancer Cells Mediated by Estrogen Receptor α. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qigang, N.; Afra, A.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Turki Jalil, A.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Gatea, M.A.; Efriza; Asban, P.; Mousavi, S.K.; Kanani, P.; et al. The Effect of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biomarkers on Cardiovascular Diseases. Rev. Environ. Health 2024, 39, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, A.; Xu, Q. The Association between Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Metabolites and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Su, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, B.; Gao, R. Preliminary Evidence for an Influence of Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota and Neurodevelopment in Three-Year-Old Healthy Children. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Song, S.; Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Cong, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, P. The Association between Internal Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Exposure and Risk of Obesity—A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Kalantary, R.; Jaffarzadeh, N.; Rezapour, M.; Hesami Arani, M. Association between Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11531–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wallace, E.R.; Ni, Y.; Loftus, C.T.; Szpiro, A.; Day, D.; Barrett, E.S.; Nguyen, R.H.N.; Kannan, K.; Robinson, M.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Cognition in Early Childhood. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, X.; Xiong, W.; Cui, T.; Xi, W.; Jin, S.; Zhang, X. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Exposure in Early Pregnancy on Child Neurodevelopment. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrám, R.J.; Solanský, I.; Pastorková, A.; Velemínský, M.; Velemínský, M.; Hoňková, K.; Barošová, H.; Schmuczerová, J.; Urbancová, K.; Dvořáková, D.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Growth Parameters. J. Appl. Biomed. 2024, 22, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Yu, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Deng, S.; Hu, J.; Deng, Q.; et al. Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Accelerated DNA Methylation Aging. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grova, N.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B.; Feidt, C.; Andre, F.; Rychen, G. Determination of Phenanthrene and Hydroxyphenanthrenes in Various Biological Matrices at Trace Levels Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Campo, L.; Rosella, F.; Fustinoni, S. Development of a Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantify Several Urinary Monohydroxy Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Occupationally Exposed Subjects. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 875, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugheri, S.; Bonari, A.; Gentili, M.; Cappelli, G.; Pompilio, I.; Bossi, C.; Arcangeli, G.; Campagna, M.; Mucci, N. High-Throughput Analysis of Selected Urinary Hydroxy Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by an Innovative Automated Solid-Phase Microextraction. Molecules 2018, 23, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, M.; Rykowska, I.; Wolski, R.; Andrzejewski, P. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Their Derivatives (O-PAHs, N-PAHs, OH-PAHs): Determination in Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)—A Review. Environ. Process. 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Martinez-Moral, M.-P.; Kannan, K. Variability in Urinary Biomarkers of Human Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Its Association with Oxidative Stress. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-Y.; Song, G.; Lee, K.; Kho, Y. Levels of OH-PAHs and Markers of Oxidative Stress in Urine of Taxi Drivers and Controls. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2024, 39, e2024027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Duarte, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pena, A.; Morais, S. Exposure of Nursing Mothers to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Levels of Un-Metabolized and Metabolized Compounds in Breast Milk, Major Sources of Exposure and Infants’ Health Risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongeneelen, F.J.; Anzion, R.B.M.; Henderson, P.T. Determination of Hydroxylated Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urine. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1987, 413, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishikawa, N.; Morita, S.; Wada, M.; Ohba, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Kuroda, N. Determination of Hydroxylated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Airborne Particulates by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Slezakova, K.; Alves, M.J.; Fernandes, A.; Teixeira, J.P.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pereira, M.d.C.; Morais, S. Firefighters’ Exposure Biomonitoring: Impact of Firefighting Activities on Levels of Urinary Monohydroxyl Metabolites. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger-Brito, I.; Machour, N.; Morin, C.; Portet-Koltalo, F. Experimental Designs for Optimizing Multi-Residual Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Chromatographic Analysis of Oxygenated (Hydroxylated, Quinones) Metabolites of PAHs in Sediments. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoff, L.C.; Li, Z.; Young, K.J.; Blakely, N.C.; Patterson, D.G.; Sandau, C.D. Automated Solid-Phase Extraction Method for Measuring Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolites in Human Biomonitoring Using Isotope-Dilution Gas Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 835, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, G.R.; Guizellini, G.M.; da Silva, S.A.; de Almeida, A.P.; Pinaffi-Langley, A.C.C.; Rogero, M.M.; de Camargo, A.C.; Torres, E.A.F.S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Foods: Biological Effects, Legislation, Occurrence, Analytical Methods, and Strategies to Reduce Their Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, S.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Alemdar, S.; Erdogan, S.; Agaoglu, S. The Presence of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Grilled Beef, Chicken and Fish by Considering Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsonwu-Anyanwu, A.C.; Helal, M.; Khaked, A.; Eworo, R.; Usoro, C.A.O.; EL-Sikaily, A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Content of Food, Water and Vegetables and Associated Cancer Risk Assessment in Southern Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cai, K.; Xu, B. A Review of Hazards in Meat Products: Multiple Pathways, Hazards and Mitigation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingenbleek, L.; Veyrand, B.; Adegboye, A.; Hossou, S.E.; Koné, A.Z.; Oyedele, A.D.; Kisito, C.S.K.J.; Dembélé, Y.K.; Eyangoh, S.; Verger, P.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Foods from the First Regional Total Diet Study in Sub-Saharan Africa: Contamination Profile and Occurrence Data. Food Control. 2019, 103, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, E.N.; Hajeb, P.; Selamat, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Bioaccessibility of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Grilled Meat: The Effects of Meat Doneness and Fat Content. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Slezakova, K.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pereira, M.C.; Morais, S. Children Environmental Exposure to Particulate Matter and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Biomonitoring in School Environments: A Review on Indoor and Outdoor Exposure Levels, Major Sources and Health Impacts. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsawansong, P.; Prapamontol, T.; Singkaew, J.; Li, G.; Pan, X. Significantly Elevated Urinary OH-PAHs and Oxidative Damage Concentrations Attributable to PM2.5 Exposure: A Panel Study of Preaging Females in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Nat. Life Sci. Commun. 2024, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Commission of the European Communities. 2002/657/EC: Commission Decision of 12 August 2002 Implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC Concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results (Text with EEA Relevance) (Notified Under Document Number C(2002) 3044). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dec/2002/657/oj/eng (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Konieczko, P.; Namieśnik, J. Ocena i Kontrola Jakości Wyników Pomiarów Analitycznych; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinkova, Z.; Wenzl, T. The Occurrence of 16 EPA PAHs in Food—A Review. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 248–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Food—Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, H.A.; Pan, C.-H. 1-Hydroxypyrene as a Biomarker for Environmental Health. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and Their Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Craig, E.; Liu, X.; Ge, Y.; Brunner, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Hopke, P.K.; Miller, R.K.; Barrett, E.S.; et al. Urinary 1-Hydroxypyrene in Pregnant Women in a Northeastern U.S. City: Socioeconomic Disparity and Contributions from Air Pollution Sources. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 34, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, S.F.; Pardo, O.; Hernández, C.S.; Garlito, B.; Yusà, V. Children’s Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Valencian Region (Spain): Urinary Levels, Predictors of Exposure and Risk Assessment. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, A.; Roth, A.; Schwedler, G.; Schmied-Tobies, M.I.H.; Rucic, E.; Pluym, N.; Scherer, M.; Scherer, G.; Conrad, A.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in Urine of Children and Adolescents in Germany—Human Biomonitoring Results of the German Environmental Survey 2014–2017 (GerES V). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 226, 113491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapole, D.; Rychen, G.; Grova, N.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B.; Feidt, C. Milk and Urine Excretion of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Hydroxylated Metabolites after a Single Oral Administration in Ruminants. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2624–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.-Y.; Xie, S.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Bao, L.-J.; Tao, S.; Zeng, E.Y. Importance of Dermal Absorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Derived from Barbecue Fumes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8330–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Capelas, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S. Grill Workers Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Levels and Excretion Profiles of the Urinary Biomarkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, K.; Dobbe, L.; Rahman, R.; Elmassry, M.; Paz, P. Lung Morphology and Surfactant Function in Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: A Narrative Review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4031–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, N.P.; Hickey, A.J. Targeting Inhaled Therapy beyond the Lungs. Respiration 2014, 88, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhuang, X. Insights into Inhalation Drug Disposition: The Roles of Pulmonary Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Minko, T. Nanotherapeutics for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery: An Approach to Bypass the Blood Brain Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, L.R.; Frey, W.H. Intranasal Delivery Bypasses the Blood-Brain Barrier to Target Therapeutic Agents to the Central Nervous System and Treat Neurodegenerative Disease. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Mao, H.; Wang, T. Influence of Exposure Pathways on Tissue Distribution and Health Impact of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Derivatives. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyda, A.J.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Majewski, G.; Bralewska, K.; Widziewicz-Rzońca, K.; Piekarska, B.; Rogulski, M.; Bihałowicz, J.S. Inhalation Risk to PAHs and BTEX during Barbecuing: The Role of Fuel/Food Type and Route of Exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozielska, B.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W. Wielopierścieniowe Węglowodory Aromatyczne w Pyle Zawieszonym w Miastach Górnego Śląska. Arch. Gospod. Odpad. I Ochr. Sr. 2014, 16, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, B.A.; Broten, T.; Stranieri, M.T.; Holahan, M.A.; Cook, J.J. Simple High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method to Analyze Serum Creatinine Has Several Advantages over the Jaffé Picric Acid Reaction as Demonstrated with a Cimetidine Dose Response in Rhesus Monkeys. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 759, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnroe, R.J. Evaluation of Precision of Quantitative Measurement Procedures: Approved Guideline; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014; ISBN 1562389688. [Google Scholar]


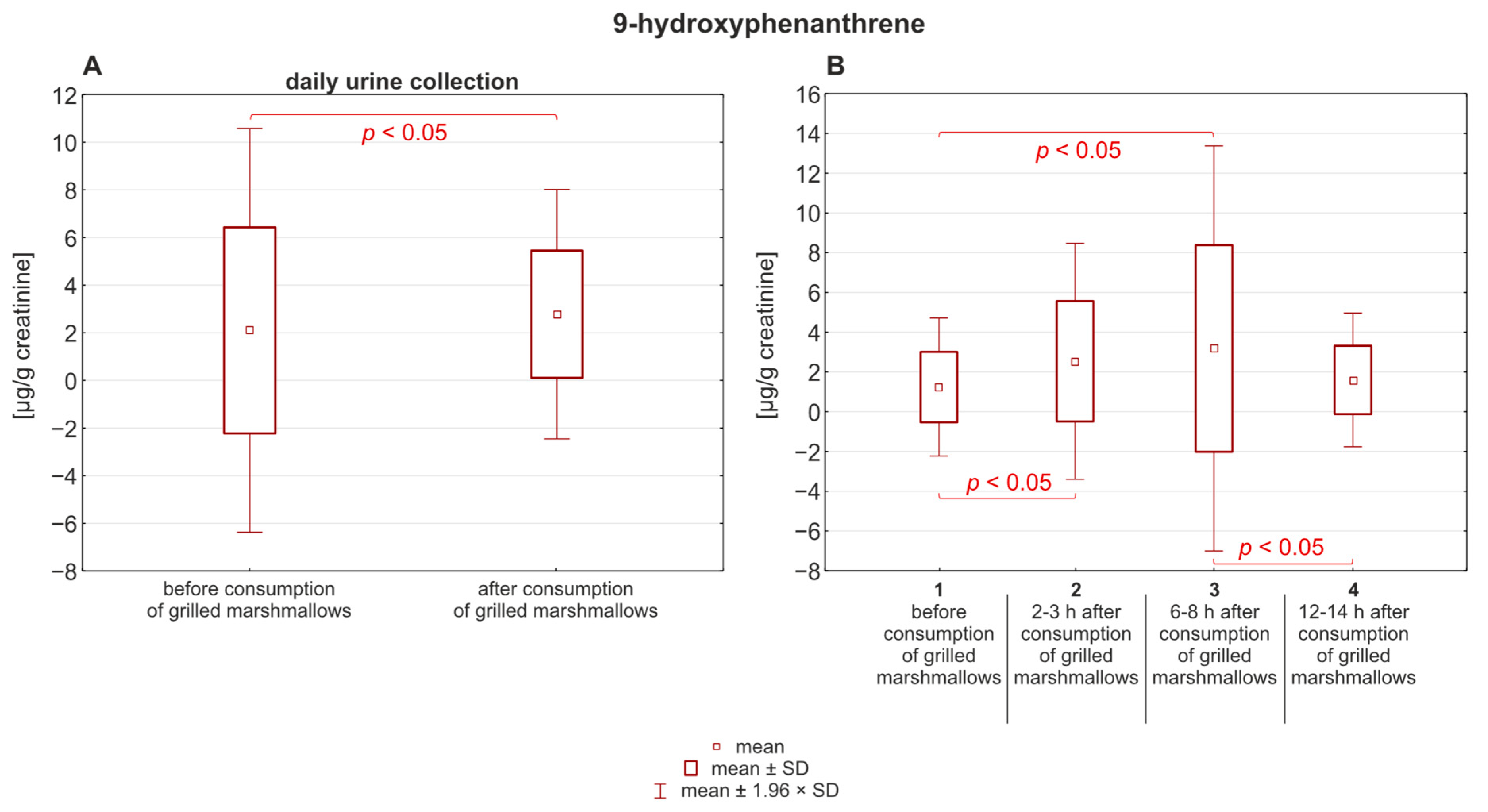
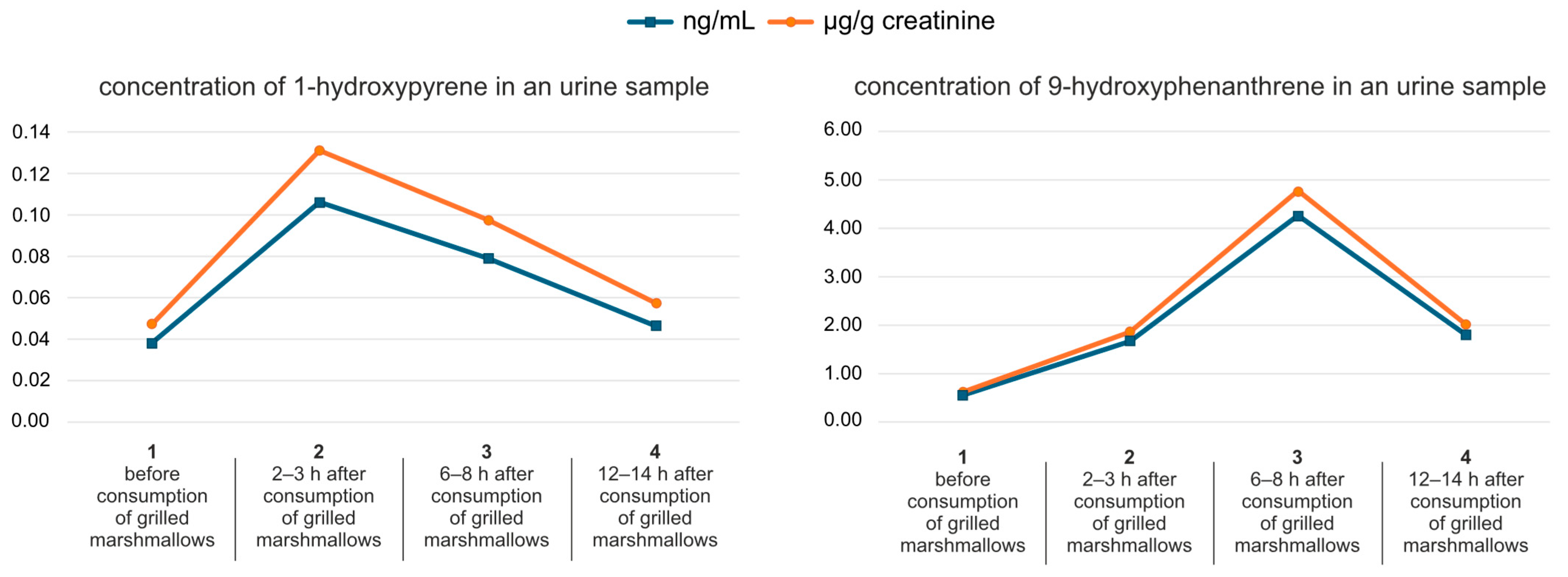
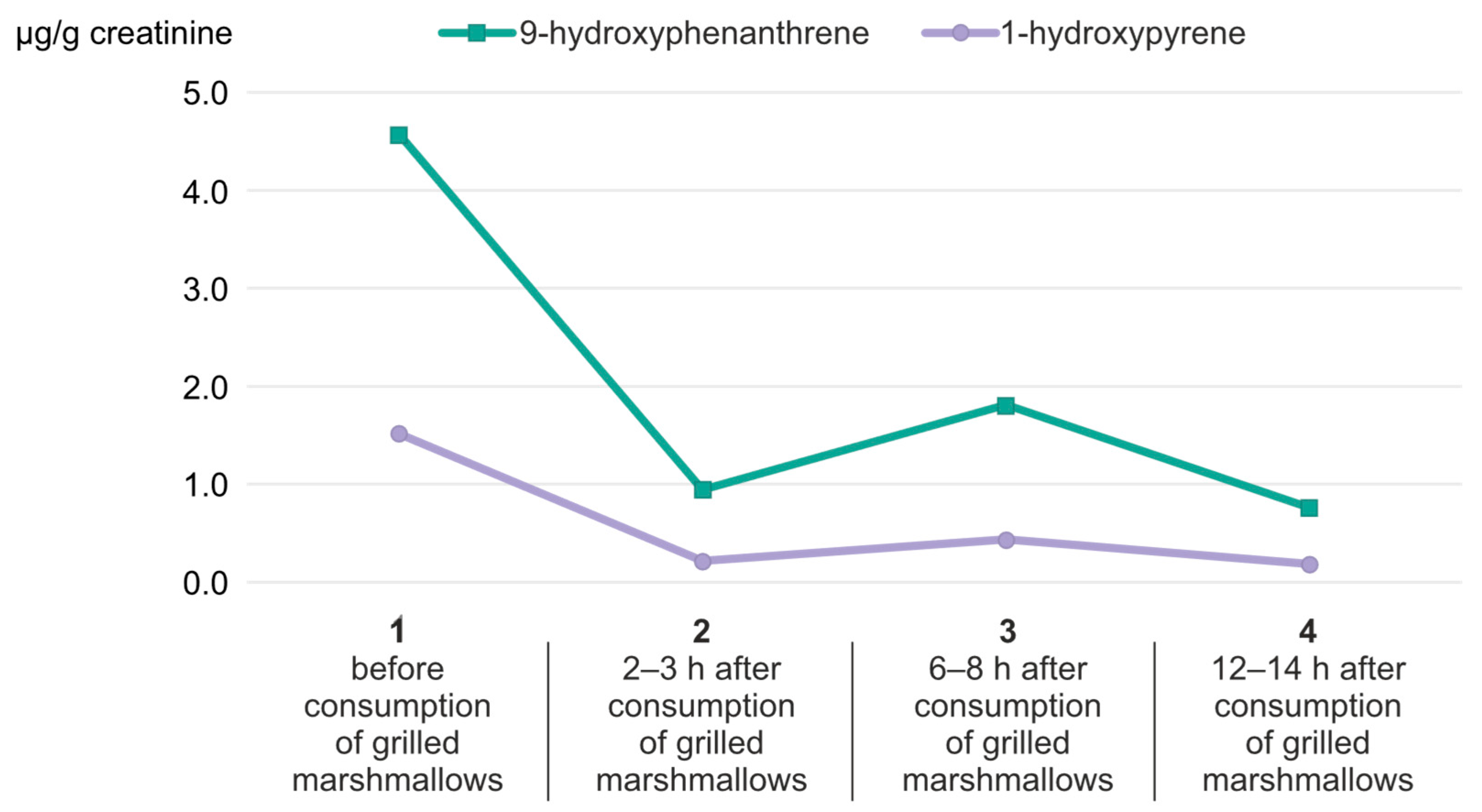

| Parameter | 9-Hydroxyphenanthrene | 1-Hydroxypyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Calibration curve equation 1 | y = 70.729x − 0.8354 | y = 261.03x − 0.6396 |
| Correlation coefficient [r] | 0.9999 | 0.9996 |
| LOD and LOQ [ng/mL] 2 | 0.15 and 0.50 | 0.15 and 0.50 |
| LOQ [ng/mL urine] | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| Recovery % and (RSD%) 3 for the spiking levels: | ||
| 10 ng/mL urine | n.d. 4 | 80.0 (5.1) |
| 30 ng/mL urine | 72.1 (4.1) | 73.2 (3.7) |
| 60 ng/mL urine | 69.9 (2.5) | 62.1 (1.0) |
| 100 ng/mL urine | 61.3 (2.5) | n.d. 4 |
| Intra-day and inter-day precision expressed as RSD% 3 for the concentration levels: | ||
| 10 ng/mL | 1.3 and 0.9 | 3.0 and 5.6 |
| 25 ng/mL | 1.0 and 1.3 | 0.3 and 4.3 |
| 50 ng/mL | 0.5 and 1.2 | 1.1 and 4.1 |
| 100 ng/mL | 0.6 and 1.2 | 0.4 and 1.8 |
| Consumption of Grilled Marshmallows | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Overall Consumption White and Colored (n = 24) | Only Colored (n = 8) | Only White (n = 16) |
| 1-hydroxypyrene mean ± SD [µg/g creatinine] | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 0.24 ± 0.20 | 0.19 ± 0.09 |
| 9-hydroxyphenanthrene mean ± SD [µg/g creatinine] | 2.78 ± 2.55 | 3.07 ± 2.40 1 | 2.65 ± 2.30 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szumska, M.; Maciejczyk, M.; Janoszka, B.; Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A.; Nowak, A.; Tyrpień-Golder, K. Determination of Selected Hydroxylated PAHs in Urine Samples of Individuals Consuming Grilled Marshmallows. Molecules 2025, 30, 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183787
Szumska M, Maciejczyk M, Janoszka B, Damasiewicz-Bodzek A, Nowak A, Tyrpień-Golder K. Determination of Selected Hydroxylated PAHs in Urine Samples of Individuals Consuming Grilled Marshmallows. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183787
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzumska, Magdalena, Maciej Maciejczyk, Beata Janoszka, Aleksandra Damasiewicz-Bodzek, Agnieszka Nowak, and Krystyna Tyrpień-Golder. 2025. "Determination of Selected Hydroxylated PAHs in Urine Samples of Individuals Consuming Grilled Marshmallows" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183787
APA StyleSzumska, M., Maciejczyk, M., Janoszka, B., Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A., Nowak, A., & Tyrpień-Golder, K. (2025). Determination of Selected Hydroxylated PAHs in Urine Samples of Individuals Consuming Grilled Marshmallows. Molecules, 30(18), 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183787






