DFT Study of Functionalized Benzoxazole-Based D–π–A Architectures: Influence of Ionic Fragments on Optical Properties and Their Potential in OLED and Solar Cell Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Electrostatic Potential Maps
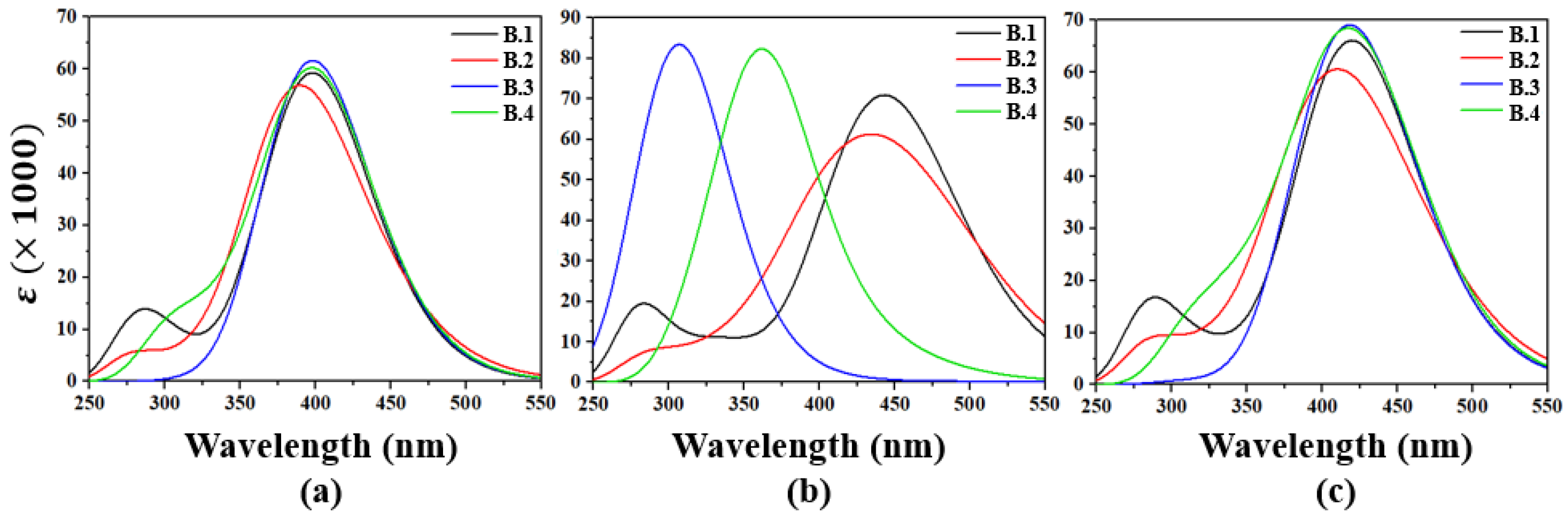
2.2. Calculation of Molar Absorptivity
2.3. Calculation of Emission
2.4. Light-Harvesting Efficiency and High Absorption–Emission Conversion Efficiency
2.5. Calculation of Dipole Moment, Polarizability, and First Hyperpolarizability
2.6. Calculation of Two-Photon Absorption (TPA)
2.7. Discussion
3. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| TPA | Two-photon absorption |
| b3lyp | Becke, 3-parameter, Lee–Yang–Parr functional |
References
- Abbas, Z.; Fatima, K.; Parveen, A.; Aslam, M.; Zetspin, A.; Nassani, A.A. A comparative study on the impact of cation replacements on the structural, optoelectronic and thermodynamic characteristics of hexafluorides red phosphors Cs2MF6 (M = C, Ge, Pb, Si) using first-principles calculations: A prospect for warm-white LEDs (w-LEDs) applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, A.; Yeong, K.Y. Targeting disease with benzoxazoles: A comprehensive review of recent developments. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 406–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramczyk, H.; Brozek-Pluska, B.; Jarota, A.; Surmacki, J.; Imiela, A.; Kopec, M. A look into the use of Raman spectroscopy for brain and breast cancer diagnostics: Linear and non-linear optics in cancer research as a gateway to tumor cell identity. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Althobiti, R.A.; Al Naim, A.F.; Alzahrani, E.; Tarabiah, A.E. Tailoring the optical properties of dye–polymer composite films based on polyvinyl alcohol doped with phenol red toward flexible optoelectronic applications. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 065932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, S.; Madi, F.; Nouar, L.; Gheid, A. Effect of cyclodextrins inclusion complexes into absorption and emission spectra of p-methylaminobenzoate derivatives: A DFT and TD-DFT investigation. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.W.; Gaeta, A.L.; Giese, E. Nonlinear Optics. In Springer Handbook of Lasers and Optics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2023; pp. 1097–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Castillejo, M.; Oujja, M.; Agua, F.; Sanz, M.; Morales-Martin, D.; García-Heras, M.; Villegas, M.Á. Study of historical glass grisailles by nonlinear optical microscopy. Proc. SPIE 2021, 11784, 1178412. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, T.M.; Corrêa, D.S. Síntese e caracterização de novos derivados benzoxazol e naftoxazol. Rev. Inic. Cient. ULBRA 2021, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Datar, M.; Dhanwad, R.; Javeed, M.; Yernale, N.G.; Mathada, B.S. Synthesis, structural investigations, DFT calculations, and molecular docking studies of novel 2-(substituted-aryloxymethyl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazoles. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. in press. 2024.
- Finger, V.; Kucera, T.; Kafkova, R.; Muckova, L.; Dolezal, R.; Kubes, J.; Novak, M.; Prchal, L.; Lakatos, L.; Andrs, M.; et al. 2,6-Disubstituted 7-(naphthalen-2-ylmethyl)-7H-purines as a new class of potent antitubercular agents inhibiting DprE1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 258, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.; Ans, M.; Iqbal, J. DFT insight of methoxy diphenylamine-substituted carbazole derivatives as hole transport material for efficient perovskite and organic solar cell. Phys. Scr. 2023, 99, 015904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanna, N.D.; Vagdevi, H.M.; Dharshan, J.C.; Prashith Kekuda, T.R. Antioxidant Evaluation of Novel 1-(5,7-Dichloro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]quinoline Derivatives. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 234074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, K.; Breunig, H.G.; Batista, A.; Schindele, A.; Zieger, M.; Kaatz, M. Translation of two-photon microscopy to the clinic: Multimodal multiphoton CARS tomography of in vivo human skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 014515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnok, A.; Tymchenko, M.; Alù, A. Nonlinear metasurfaces: A paradigm shift in nonlinear optics. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, P.; Kodisundaram, P.; Sundararajan, M.L.; Jeyakumar, T. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and theoretical study of a compound with benzodiazole ring: Antimicrobial activity and DNA binding. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 129, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, F.; Altuzarra, C.; Classen, A.; Agarwal, G.S. Squeezed light induced two-photon absorption fluorescence of fluorescein biomarkers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 254001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.C. Quinoline derivatives as potential anti-tubercular agents: Synthesis, molecular docking and mechanism of action. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, C.; Chouk, R.; Baatout, K.; Jaballah, N.S.; Khalfaoui, M.; Majdoub, M. Synthesis, characterization and DFT study of new anthracene-based semiconducting polyethers for OLED application. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 131993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, Y.S.; Armaković, S.; Armaković, S.J.; Yadav, R.; Celik, I.; Mane, P.; Chakraborty, B. Stability and reactivity study of bio-molecules brucine and colchicine towards electrophile and nucleophile attacks: Insight from DFT and MD simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Jacobs, R. Opportunities and Challenges for Machine Learning in Materials Science. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2020, 50, 71–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, R.; Goushi, K.; Nakanotani, H.; Adachi, C. Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs): Materials, Photophysics, and Device Physics. In Organic Electronics Materials and Devices; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2024; pp. 73–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepici, G.; Silvestro, S.; Trubiani, O.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Salivary biomarkers: Future approaches for early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.; Rubio, V.; Puerto, G.; Vasquez, L.; Bernal, A.; Mora, J.R.; Cuesta, S.A.; Paz, J.L.; Insuasty, B.; Abonia, R.; et al. QSAR Studies, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Quinolinone-Based Thiosemicarbazones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, M.; Albarracin, A.; Angel, L.; Izquierdo, R.; Ramírez, M.; Migliore, B.; Cáceres, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Charris, J.; Israel, A.; et al. La teoría del funcional de la densidad para el estudio de análogos novedosos del N-dicloroaralquil-2-aminoindano con actividad dopaminérgica central. Rev. Fac. Farm. 2023, 86, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, N.; Espinosa, D.; Ball, A.; Ballato, J.; Boucaud, P.; Boudebs, G.; Campos, C.L.A.V.; Dragic, P.; Gomes, A.S.L.; Huttunen, M.J.; et al. Post-2000 nonlinear optical materials and measurements: Data tables and best practices. J. Phys. Photonics 2023, 5, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Gu, Z.G.; Li, Q.H.; Zhang, J. Predict the Polarizability and Order of Magnitude of Second Hyperpolarizability of Molecules by Machine Learning. J. Phys. Chem. A 2023, 127, 6109–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Zemmouche, M.; Carmona-García, J.; Francés-Monerris, A.; Mulet, P.; Navizet, I.; Roca-Sanjuán, D. Multiconfigurational Quantum Chemistry Determinations of Absorption Cross Sections (σ) in the Gas Phase and Molar Extinction Coefficients (ε) in Aqueous Solution and Air–Water Interface. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 3571–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, Z.; Li, Z. Ultrafast Third-Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Benzothiazole-Based Push–Pull D–π–A Molecules for Two-Photon Absorption Applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Gros, C.P.; Bolze, F.; Xu, H.J. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties and Two-Photon Absorption of Benzothiazole/Benzoxazole π-Expanded Carbazole Dyes. Dyes Pigments 2022, 204, 110447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Sameena; Fatima, T.; Bibi, S.; ur Rehman, S.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Chaudhry, A.R. Study of Optical and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Symmetric/Asymmetric Benzo[d]oxazole Derivatives under Gas and Solvent Solute Interaction Models. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2025, 1251, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakshe, B.U.; Li, Y.; Corbin, B.; Wijesinghe, K.J.; Pang, Y.; Abeywickrama, C.S. Copper-Induced Fluorescence Quenching in a Bis[2-(2′-Hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole]pyridinium Derivative for Quantification of Cu2+ in Solution. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Wang, D.; Li, M.; Cai, H.; Kong, L.; Tian, Y.; Gan, X.; Zhou, H. Small Molecules Based Benzoxazole-Pyridinium Salts with Different Anions: Two-Photon Fluorescence Regulation and Difference in Cell Imaging Application. Dyes Pigments 2021, 194, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.M. GaussView, version 5.0; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An Advanced Semantic Chemical Editor, Visualization, and Analysis Platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Spitznagel, G.W.; Schleyer, P.v.R. Efficient Diffuse Function–Augmented Basis Sets for Anion Calculations. III. The 6-311+G(d,p) Basis Set for Atoms Li to Cl. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidas, K.; Bast, R.; Christensen, O.; Dalskov, E.K.; Ekström, U.; Ettenhuber, P.; Fernández, B.; Ferrighi, L.; Frenssen, J.; Hald, K.; et al. The DALTON Quantum Chemistry Program System. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, P.; Ruud, K.; Ågren, H. Calculations of Molecular Two-Photon Absorption Cross Sections Using Density-Functional Response Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 10461–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Abbr. | Structure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B.1 |  | 4,4’-bis(benzoxazol-2-yl)terphenyl |
| B.2 |  | 4-((2-(benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzylidene)benzoxazole |
| B.3 |  | (E)-4-[2-(benzoxazol-2-yl)vinyl]-N-(4-nitrophenyl)aniline |
| B.4 | 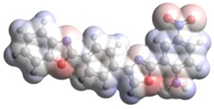 | 2-((4-((5-nitro-2-oxo-1,3-benzoxazol-3(2H)-yl)amino)phenyl)methyl)-1,3-benzoxazole |
| Compound | Medium/Phase | Band-to-Band Overlap (%) |
|---|---|---|
| B.1 | Gas phase | <35 |
| B.1 | Methanol | — |
| B.1 | Toluene | — |
| B.2 | Gas phase | 53 |
| B.2 | Methanol | 50 |
| B.2 | Toluene | 40–50 |
| B.3 | Gas phase | <35 |
| B.3 | Methanol | 70 |
| B.3 | Toluene | 34 |
| B.4 | Gas phase | <35 |
| B.4 | Methanol | 95 |
| B.4 | Toluene | 40–50 |
| Organic Compound | Dipole Moment (Debye) | esu | esu | esu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Phase | ||||
| B.1 | 2.29 | 348.39 | 7.10 | 5.08 |
| B.2 | 3.82 | 362.61 | 13.37 | 8.19 |
| B.3 | 6.75 | 367.77 | 8.34 | 6.65 |
| B.4 | 9.09 | 384.65 | 12.48 | 8.17 |
| Methanol | ||||
| B.1 | 3.52 | 464.39 | 21.22 | 10.89 |
| B.2 | 5.73 | 476.85 | 31.56 | 14.74 |
| B.3 | 9.52 | 497.33 | 22.33 | 9.80 |
| B.4 | 13.26 | 515.74 | 56.90 | 21.84 |
| Toluene | ||||
| B.1 | 2.80 | 406.47 | 13.29 | 9.92 |
| B.2 | 4.59 | 412.12 | 20.86 | 14.93 |
| B.3 | 7.98 | 429.88 | 13.56 | 10.15 |
| B.4 | 10.88 | 440.36 | 26.21 | 17.95 |
| Abbr. | Structure | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B.1 | 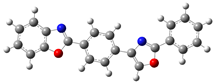 | 4,4’-bis(benzoxazol-2-yl)terphenyl |
| B.2 | 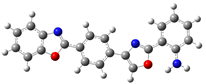 | 4-((2-(benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzylidene)benzoxazole |
| B.3 | 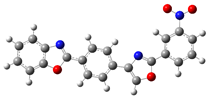 | (E)-4-[2-(benzoxazol-2-yl)vinyl]-N-(4-nitrophenyl)aniline |
| B.4 | 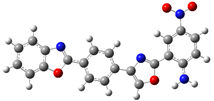 | 2-((4-((5-nitro-2-oxo-1,3-benzoxazol-3(2H)-yl)amino)phenyl)methyl)-1,3-benzoxazole |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera, E.; Ceballo, R.; Neira, O.; Avila, O.; Fonseca, R. DFT Study of Functionalized Benzoxazole-Based D–π–A Architectures: Influence of Ionic Fragments on Optical Properties and Their Potential in OLED and Solar Cell Devices. Molecules 2025, 30, 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183737
Rivera E, Ceballo R, Neira O, Avila O, Fonseca R. DFT Study of Functionalized Benzoxazole-Based D–π–A Architectures: Influence of Ionic Fragments on Optical Properties and Their Potential in OLED and Solar Cell Devices. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183737
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera, Edwin, Ronal Ceballo, Oscar Neira, Oriana Avila, and Ruben Fonseca. 2025. "DFT Study of Functionalized Benzoxazole-Based D–π–A Architectures: Influence of Ionic Fragments on Optical Properties and Their Potential in OLED and Solar Cell Devices" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183737
APA StyleRivera, E., Ceballo, R., Neira, O., Avila, O., & Fonseca, R. (2025). DFT Study of Functionalized Benzoxazole-Based D–π–A Architectures: Influence of Ionic Fragments on Optical Properties and Their Potential in OLED and Solar Cell Devices. Molecules, 30(18), 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183737






