Fast-Disintegrating Oral Films Containing Nisin-Loaded Niosomes
Abstract
1. Introductions
2. Application of Nisin Loaded Niosomes
3. Aim and Objectives
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Niosomes Formulation
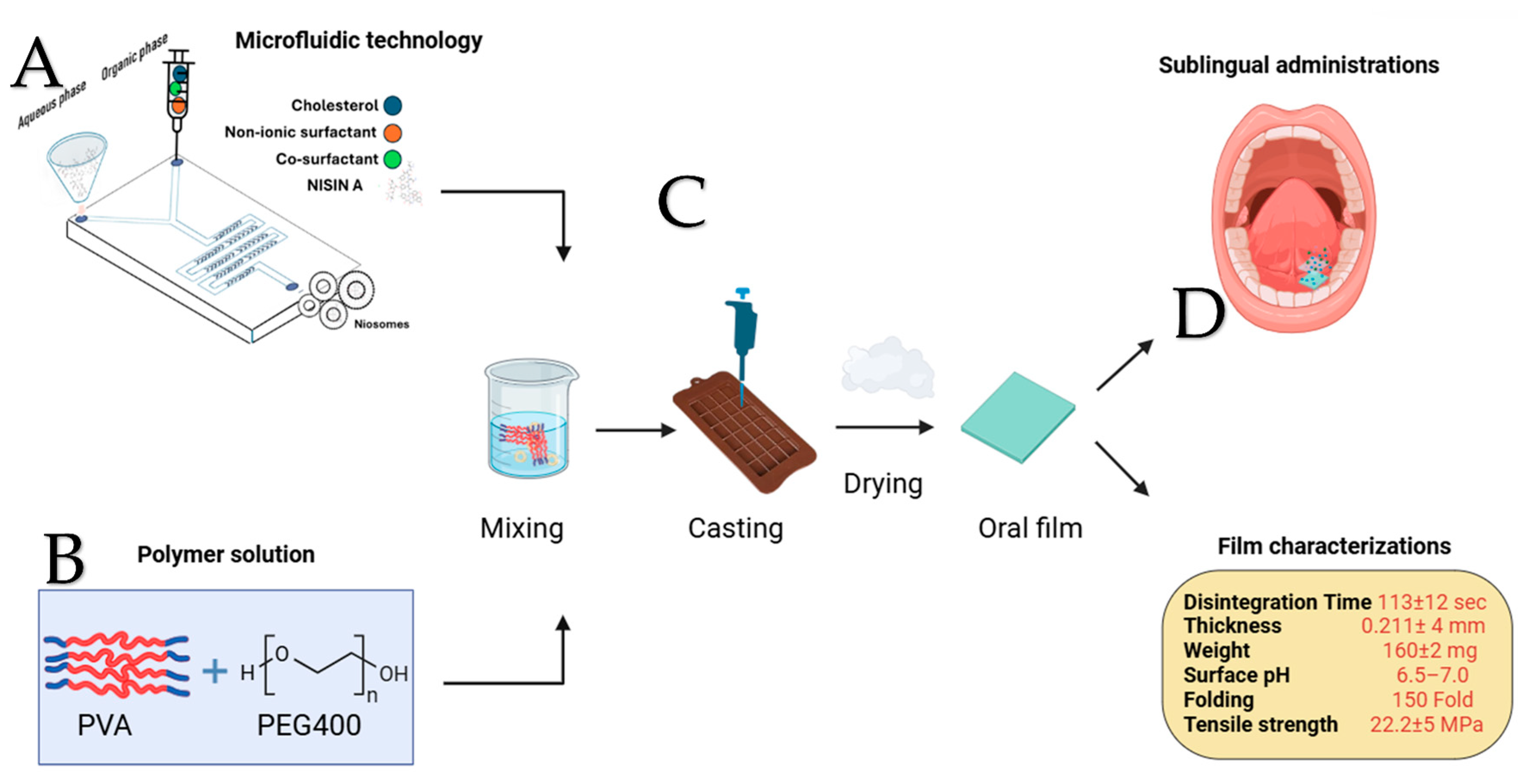
4.2.2. Microfluidic Niosome Synthesis
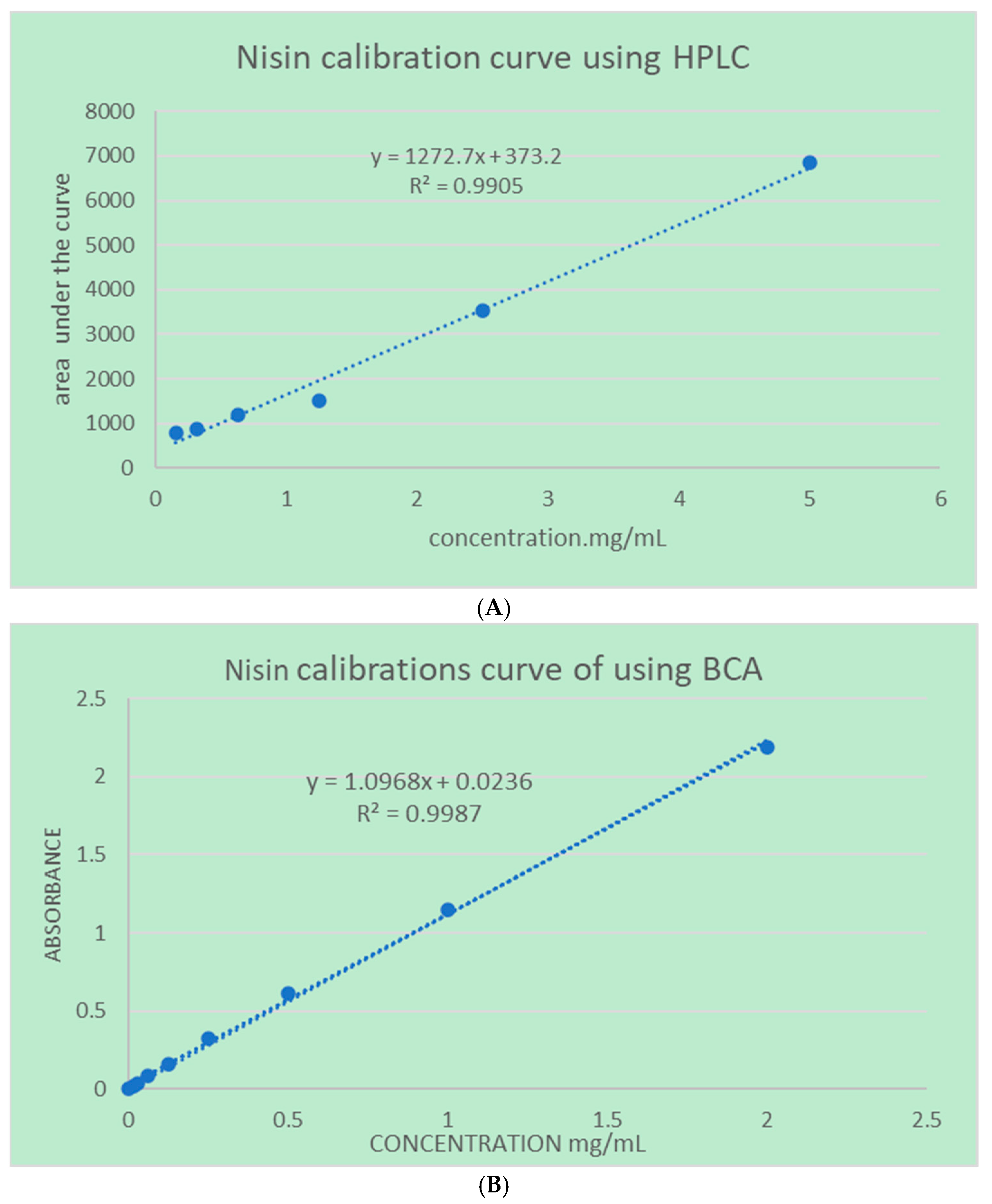
4.2.3. Quantifications Methods
4.3. Niosome Characterization
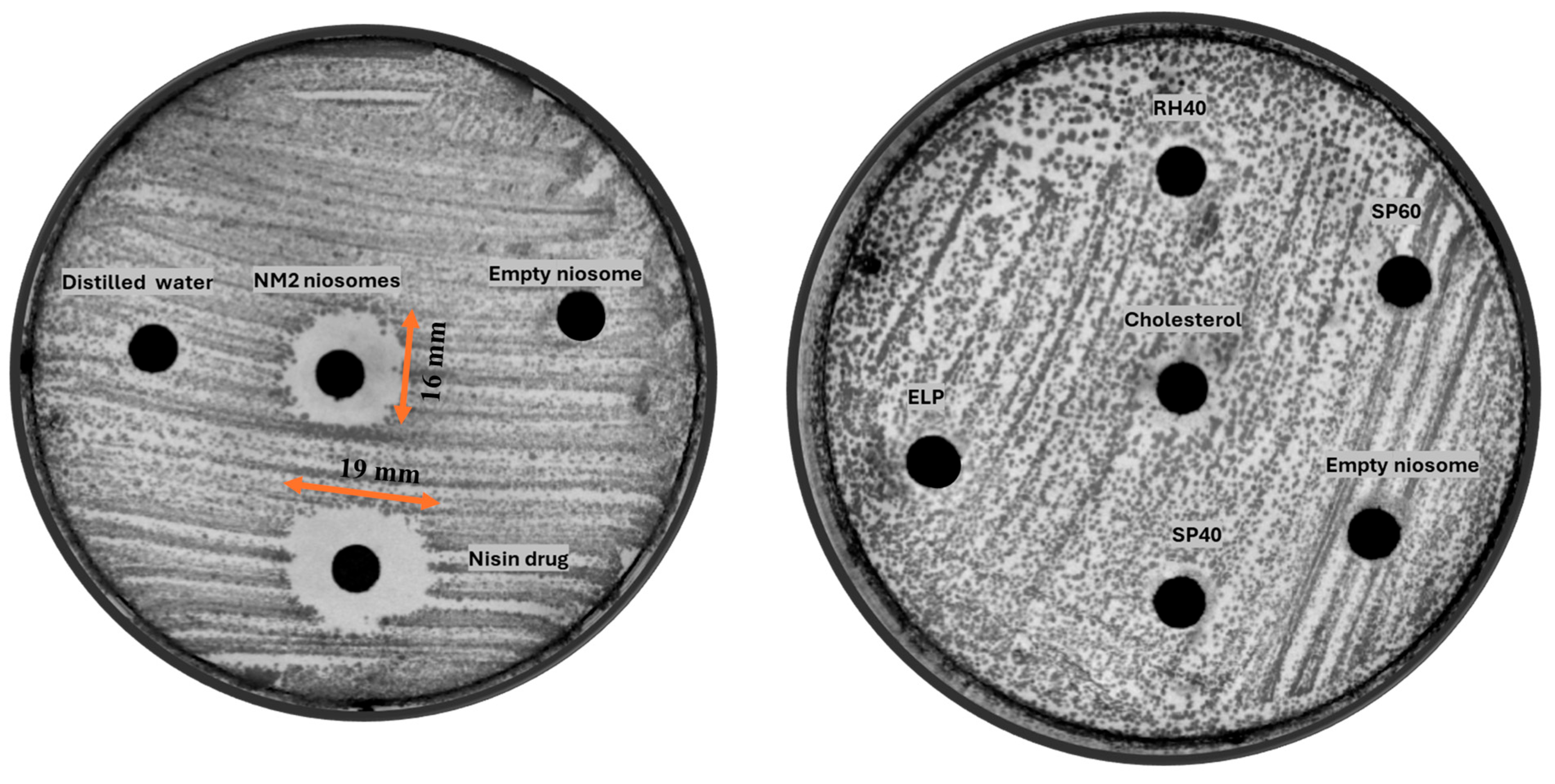
4.4. Antibiotic Assay Using an Agar Diffusion Method
4.5. Film Optimization, Preparation, and Characterization Method
4.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.7. Thermal Analysis
4.7.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA/DTG)
4.7.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.8. Nisin Release Study
4.9. Kinetic Model Fitting
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Microfluidic Technology
5.2. Antimicrobial Activity
5.3. Film Characterization
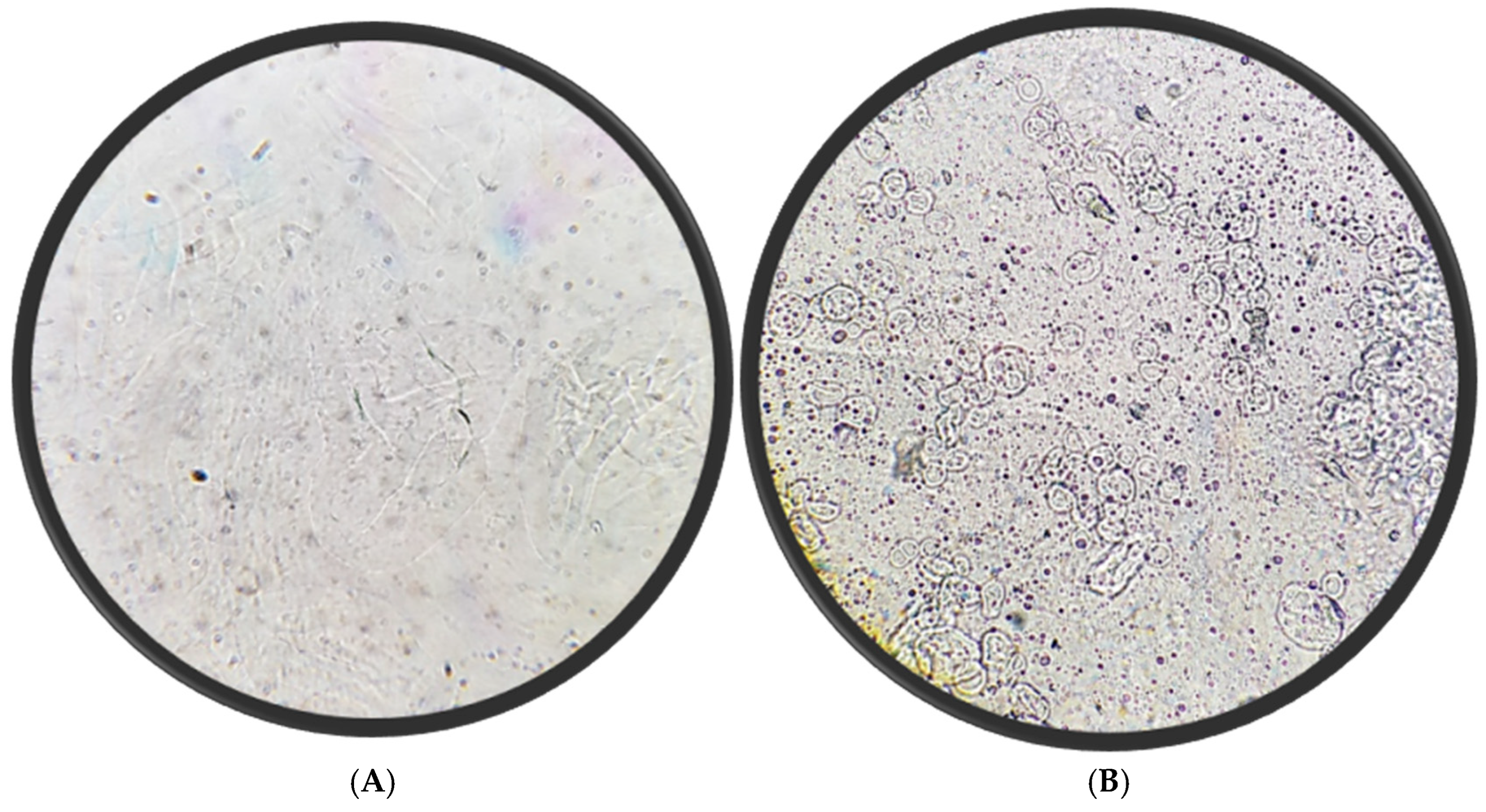
5.4. Microscopic Appearance
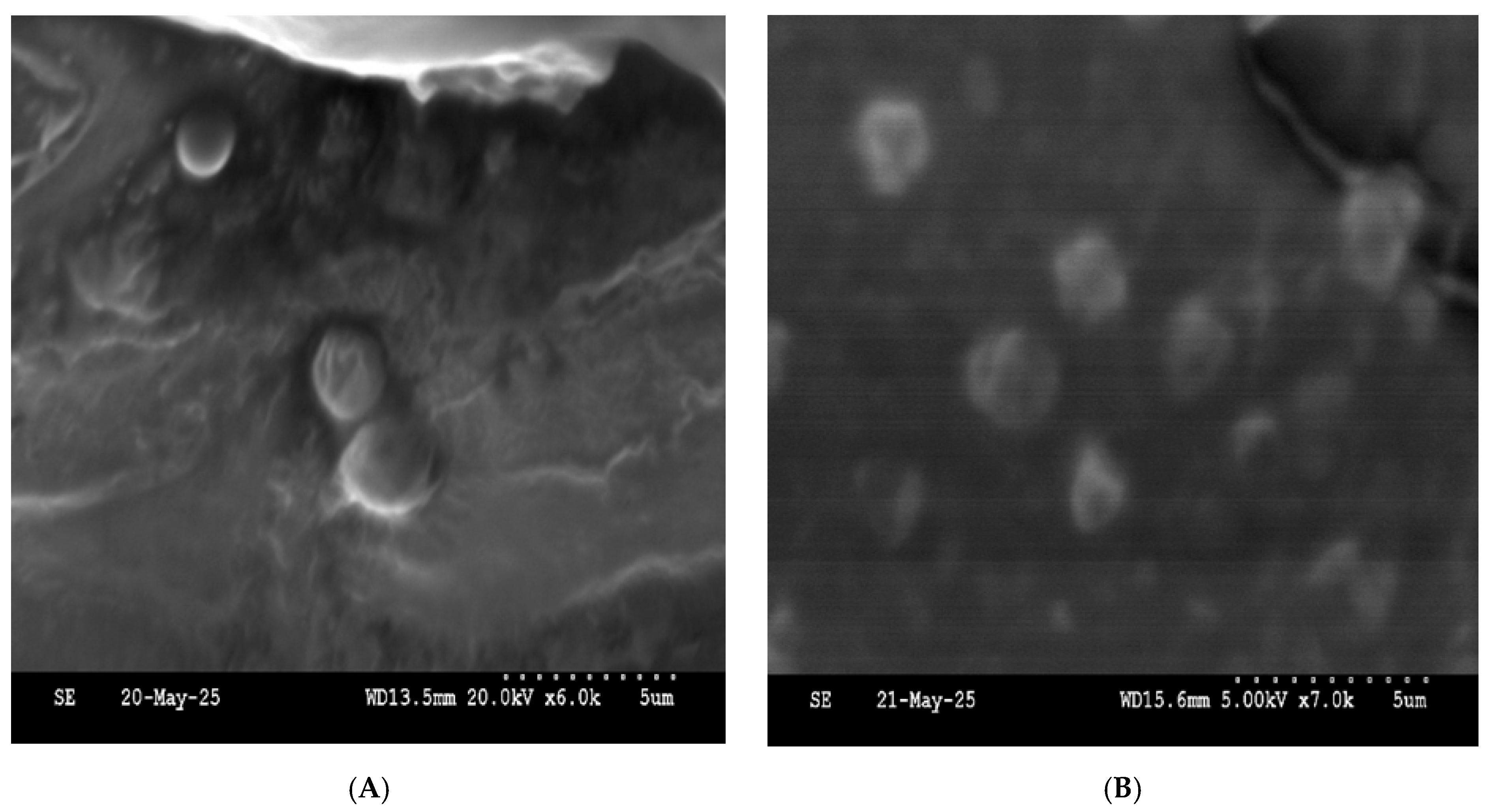
5.5. Scanning Electron Microscope
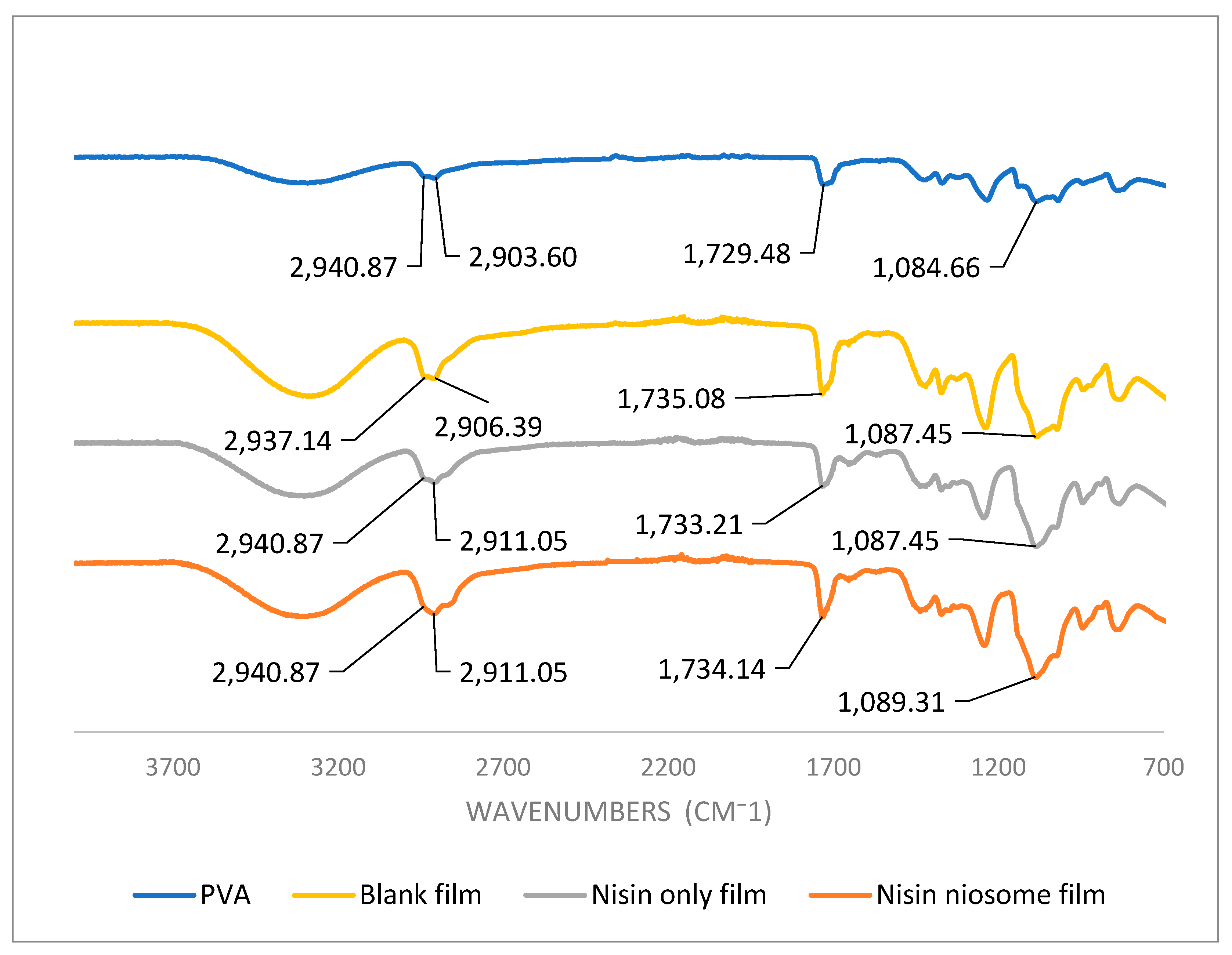
5.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
5.7. Thermal Analysis Results
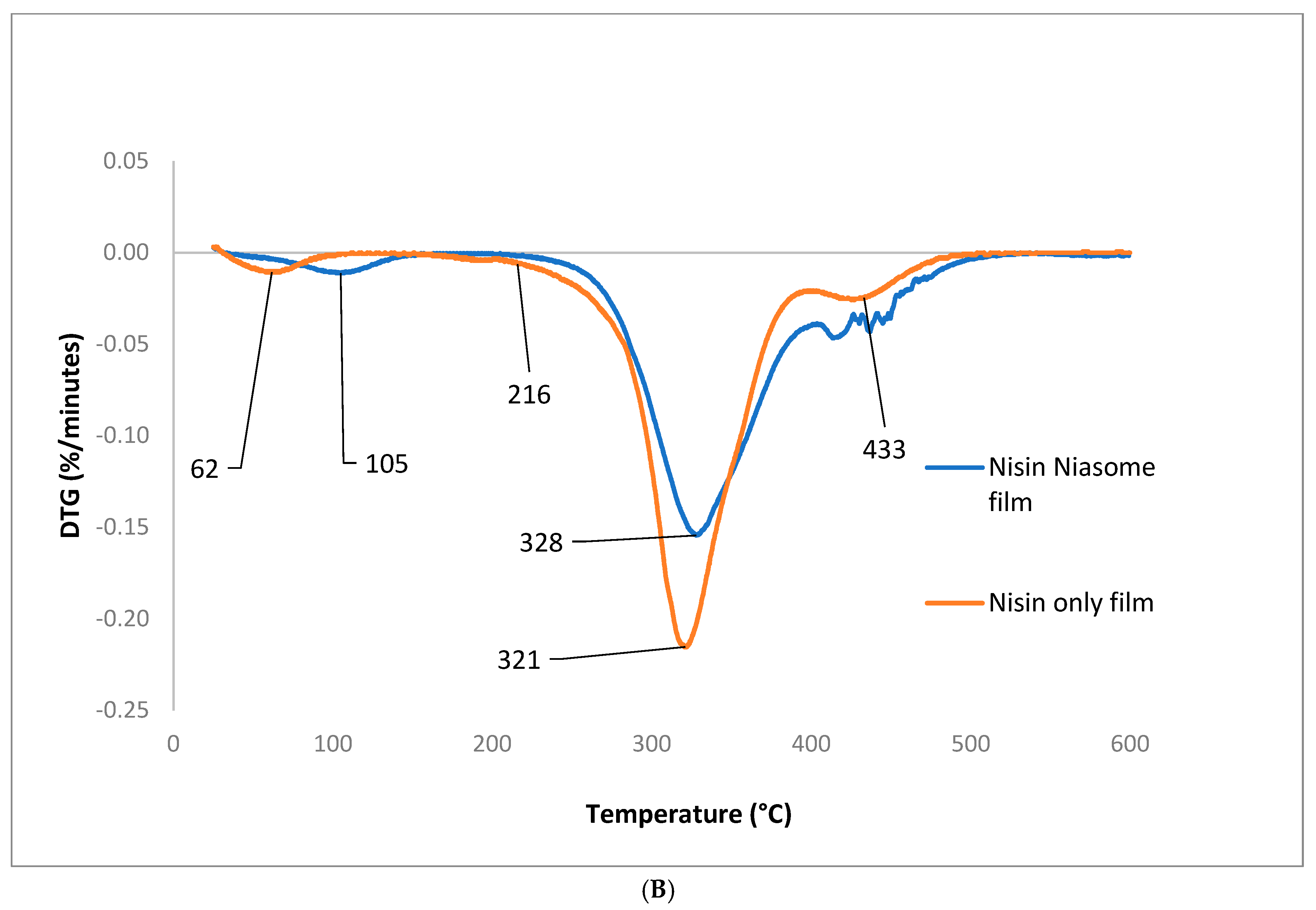
5.7.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
5.7.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
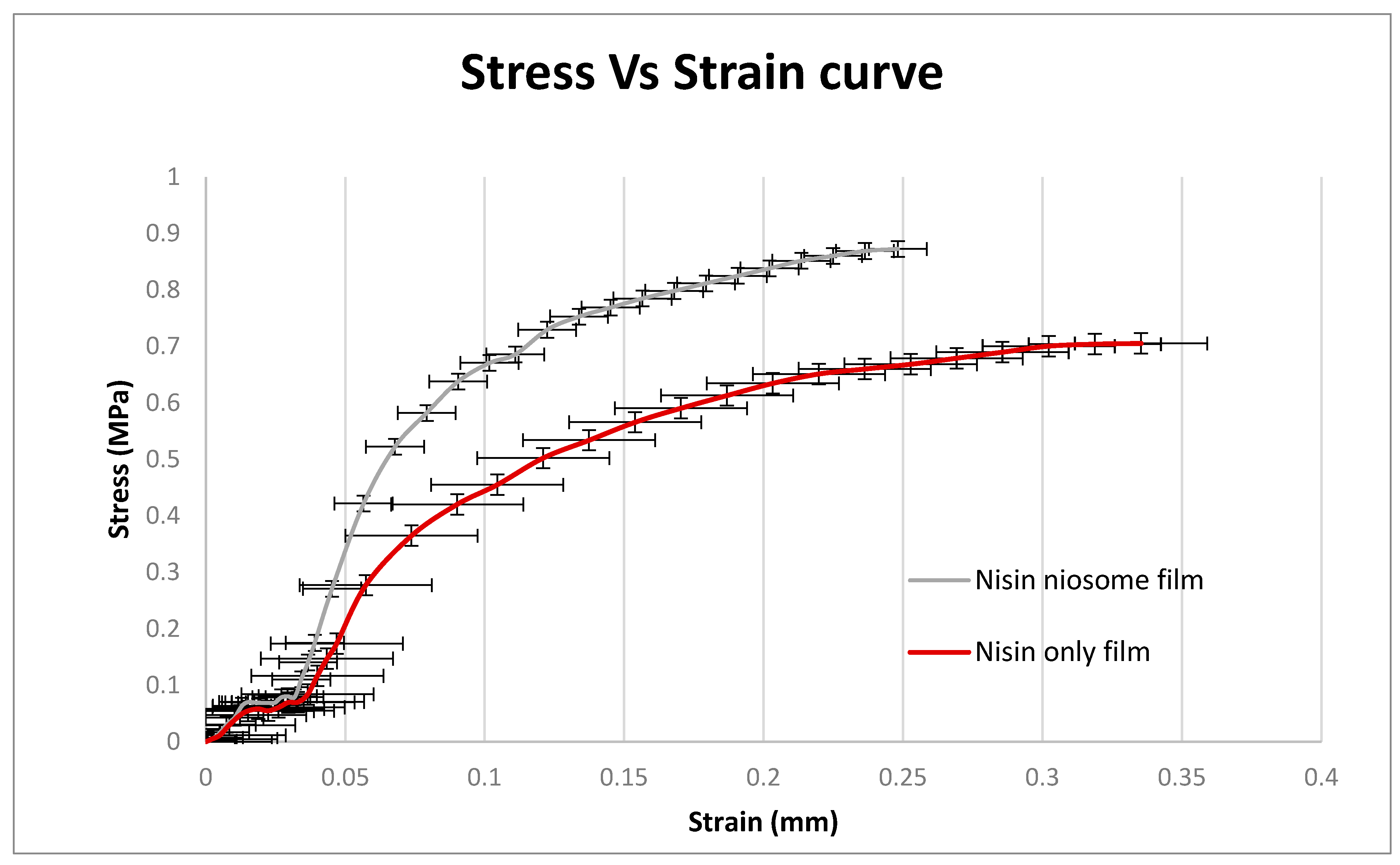
5.8. Film Tensile Strength
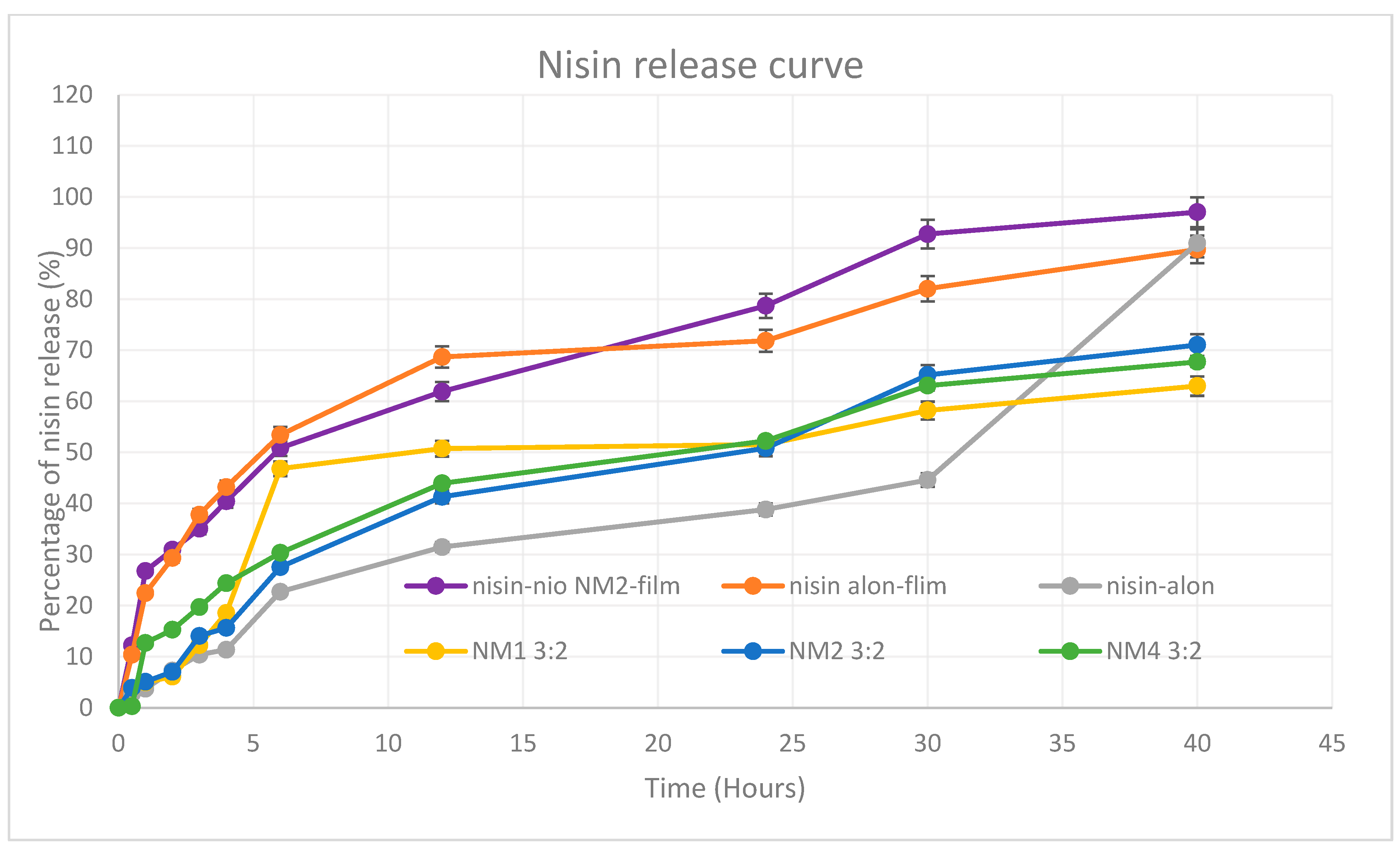
5.9. In Vitro Release Profile
5.10. Kinetic Modelling of Drug Release
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Momekova, D.B.; Gugleva, V.E.; Petrov, P.D. Nanoarchitectonics of Multifunctional Niosomes for Advanced Drug De-livery. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33265–33273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
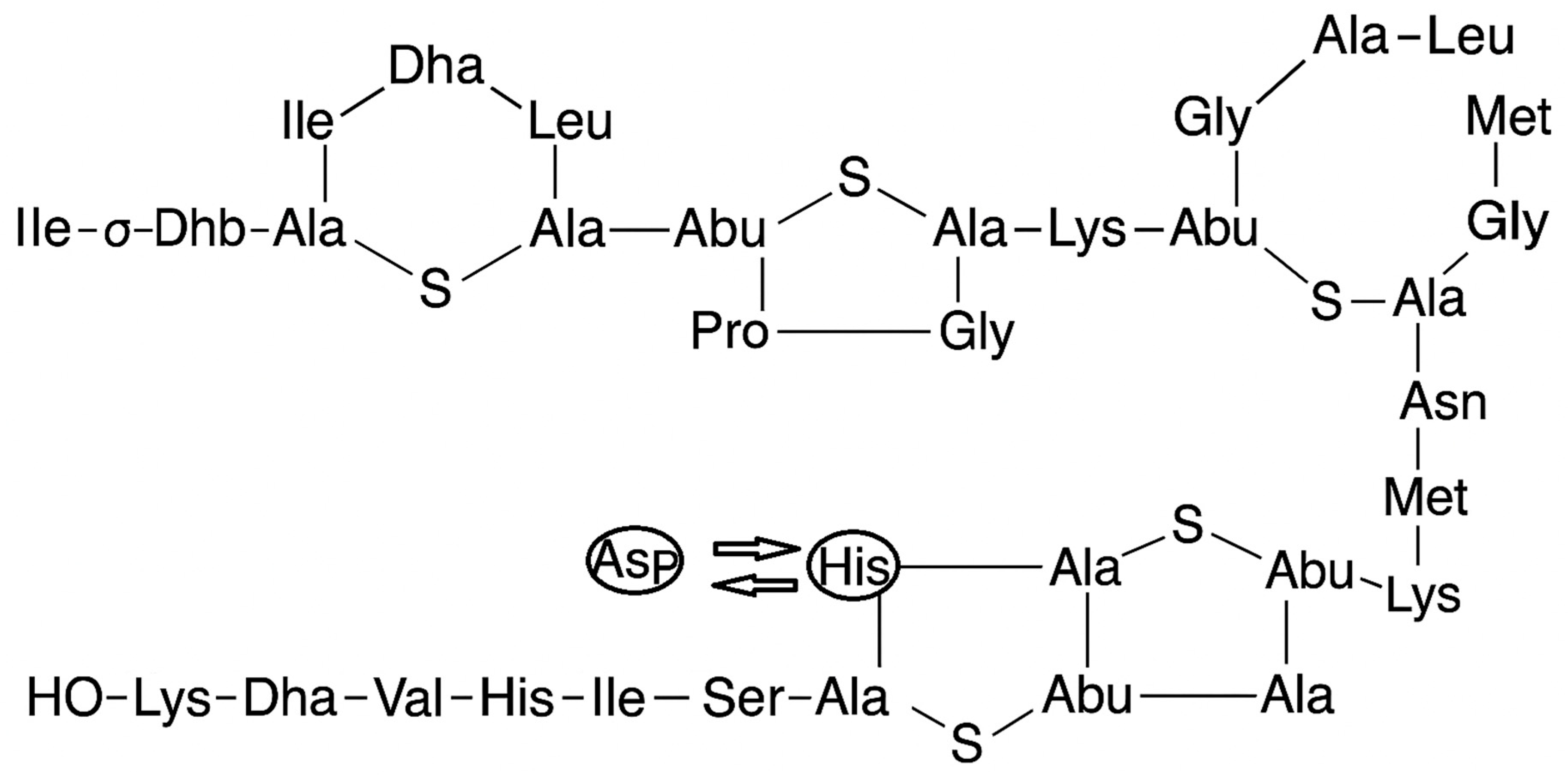
- Gross, E.; Morell, J.L. Structure of nisin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 4634–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fael, H.; Demirel, A.L. Nisin/polyanion layer-by-layer films exhibiting different mechanisms in antimicrobial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10329–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hansen, J.N. Some chemical and physical properties of nisin, a small-protein antibiotic produced by Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delves-Broughton, J.; Blackburn, P.; Evans, R.J.; Hugenholtz, J. Applications of the bacteriocin, nisin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1996, 69, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, J.W.M.; Boerrigter, I.J.; Rollema, H.S.; Siezen, R.J.; de Vos, W.M. Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-T.D.; Breukink, E.; Tischenko, E.; Lutters, M.A.G.; De Kruijff, B.; Kaptein, R.; Bonvin, A.M.; Van Nuland, N.A. The nisin–lipid II complex reveals a pyrophosphate cage that provides a blueprint for novel antibiotics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punyauppa-path, S.; Phumkhachorn, P.; Rattanachaikunsopon, P. Nisin: Production and mechanism of antimicrobial action. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2015, 7, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Benmechernene, Z.; Fernandez-No, I.; Kihal, M.; Bohme, K.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velazquez, J. Recent Patents on Bacteriocins: Food and Biomedical Applications. Recent Pat. DNA Gene Seq. 2013, 7, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, C.; Draper, L.A.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. A comparison of the activities of lacticin 3147 and nisin against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, J.-C.; Shi, W.; Rao, V.M.; Omri, A.; Mozafari, M.R.; Singh, H. Microscopical investigations of nisin-loaded nanoliposomes prepared by Mozafari method and their bacterial targeting. Micron 2007, 38, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Gwak, J.; Kamarajan, P.; Fenno, J.; Rickard, A.; Kapila, Y. Biomedical applications of nisin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 120, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K.-I.; Zendo, T.; Sugimoto, S.; Iwase, T.; Tajima, A.; Yamada, S.; Sonomoto, K.; Mizunoe, Y. Effects of Bacteriocins on Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5572–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.H.; Hayday, H.; Colman, G. The Effects of Nisin on the Microbial Flora of the Dental Plaque of Monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1978, 45, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.H.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Blackburn, P.; Projan, S.J.; de la Harpe, J.; Williams, R.C. The effect of a mouthrinse based on nisin, a bacteriocin, on developing plaque and gingivitis in beagle dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1993, 20, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, E.; Verma, V.; Lowry, D.; Perrie, Y. Microfluidic-controlled manufacture of liposomes for the solubilisation of a poorly water soluble drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.F.; Silva, C.; Coelho, J.F.; Simões, S. Oral films: Current status and future perspectives. J. Control. Release 2015, 206, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, A.A.; Bingle, L.; Chaw, C.S.; Elkordy, A.A. Development of Vancomycin, a Glycopeptide Antibiotic, in a Suitable Nanoform for Oral Delivery. Molecules 2025, 30, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulence, A.; Perreault, V.; Thibodeau, J.; Firdaous, L.; Fliss, I.; Bazinet, L. Nisin Purification from a Cell-Free Supernatant by Electrodialysis in a Circular Economy Framework. Membranes 2023, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bioengineering Lantibiotics for Therapeutic Success. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, C.A.; Dos Santos, G.R.; Soeiro, V.S.; Dos Santos, J.R.; Rebelo, M.D.A.; Chaud, M.V.; Gerenutti, M.; Grotto, D.; Pandit, R.; Rai, M.; et al. Bacterial nanocellulose membranes combined with nisin: A strategy to prevent microbial growth. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6681–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-S.; Lee, M. Different Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Methods to Determine Vancomycin Susceptibility and MIC for Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Vancomycin Susceptibility. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-P.; Yoon, I.; Kim, K.; Jung, S. Structural and Physiochemical Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol–Succinoglycan Biodegradable Films. Polymers 2024, 16, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, D.; Danzer, A.; Sadowski, G. Water Sorption in Glassy Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Based Polymers. Membranes 2022, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repka, M.A.; McGinity, J.W. Physical–mechanical, moisture absorption and bioadhesive properties of hydroxypropylcellulose hot-melt extruded films. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panraksa, P.; Tipduangta, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Jantrawut, P. Formulation of Orally Disintegrating Films as an Amorphous Solid Solution of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Membranes 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, M.T.; Joorabloo, A.; Adeli, H.; Mansoori-Moghadam, Z.; Moghaddam, A. Design and optimization of process parameters of polyvinyl (alcohol)/chitosan/nano zinc oxide hydrogels as wound healing materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthfianti, H.R.; Waresindo, W.X.; Edikresnha, D.; Chahyadi, A.; Suciati, T.; Noor, F.A.; Khairurrijal, K. Physicochemical Characteristics and Antibacterial Activities of Freeze-Thawed Polyvinyl Alcohol/Andrographolide Hydrogels. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2915–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Fardis, D.; Ntampou, X.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Panayiotou, C. Thermal Behavior of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in the Form of Physically Crosslinked Film. Polymers 2023, 15, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhou, B.-Y.; Wu, X.-H.; Liu, X.-A.; Huo, M.-W.; Huang, X.-X.; Shi, L.-Z.; Shi, L.-L.; Cao, Q.-R. Development of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyethylene Glycol Copolymer-based Orodispersible Films Loaded with Entecavir: Formulation and In vitro Characterization. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkar, Y.; Anis, T.; Elkordy, A.A.; Faheem, A. Flexipill: A novel 3D printed flexible dose combination for hypertension with a floating element. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2025, 212, 114736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Formulation | Niosomes Composition | Cholesterol | Span 60 | Span 40 | Kolliphor RH40 | Kolliphor ELP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM1 | Ch-SP60-RH40 | 35% | 45% | 20% | ||
| NM2 | Ch-SP60-RH40 | 50% | 40% | 10% | ||
| NM3 | Ch-SP40-ELP | 35% | 45% | 20% | ||
| NM4 | Ch-SP60-ELP | 35% | 45% | 20% | ||
| NM5 | Ch-SP40-RH40 | 35% | 45% | 20% |
| Formulation | Niosome Composition | Aqueous to Organic Phase Ratio | Size (nm) | PDI | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM1 | Ch-SP60-RH40 | 3:1 | 140.9 ± 1.6 | 0.227 ± 0.005 | 23.41 |
| 3:2 | 203.3 ± 1.3 | 0.198 ± 0.024 | 36.90 | ||
| NM2 | Ch-SP60-RH40 | 3:1 | 145.1 ± 1.2 | 0.145 ± 0.009 | 25.74 |
| 3:2 | 165.3 ± 0.2 | 0.044 ± 0.020 | 58.32 | ||
| NM3 | Ch-SP40-ELP | 3:1 | 219.0 ± 1.5 | 0.269 ± 0.014 | 21.78 |
| 3:2 | 236.1 ± 3.4 | 0.316 ± 0.019 | 40.47 | ||
| NM4 | Ch-SP60-ELP | 3:1 | 260.9 ± 2.7 | 0.313 ± 0.063 | 40.21 |
| 3:2 | 230.1 ± 14.3 | 0.358 ± 0.010 | 47.43 | ||
| NM5 | Ch-SP40-RH40 | 3:1 | 109.1 ± 1.2 | 0.231 ± 0.013 | 25.87 |
| 3:2 | 354.2 ± 3.0 | 0.149 ± 0.035 | 36.57 |
| Polymer | Film-Forming Ability | Visual Appearance | Flexibility | Peelability | Brittleness | Selected for Further Optimization | Film Shape and Surface Uniformity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPMC | Poor | Clear, smooth | Low | Poor | High | No |  |
| PVA | Excellent | Transparent, slightly tacky | High | Good | Slight | Yes |  |
| PVP | Moderate | Brittle, shrinks on drying | Low | Good | High | No |  |
| HPC | Poor | Sticky on drying | Low | Poor | None | No |  |
| Formulation Code | Disintegrant | Disintegration Time (s) | Thickness (mm) | Weight Variation (mg) | Surface pH | Folding | Surface Uniformity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) | 59 ± 4 | 0.211 ± 4 | 188 ± 30 | 6.5–7.0 | 44 ± 6 |  |
| F2 | Sodium Starch Glycolate (SSG) | 27 ± 6 | 0.211 ± 4 | 173 ± 8 | 6.5–7.0 | 77 ± 10 |  |
| F3 | Croscarmellose Sodium (COS) | 104 ± 2 | 0.201 ± 4 | 165 ± 20 | 6.5–7.0 | 20 ± 8 |  |
| F4 | None | 113 ± 12 | 0.211 ± 4 | 160 ± 2 | 6.5–7.0 | 150 |  |
| Kinetic Model | Nisin-Loaded Niosome NM2-Film | Nisin-Only Film | Nisin Only | NM1 3:2 | NM2 3:2 | NM4 3:2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero order | R2 | 0.954 | 0.905 | 0.955 | 0.857 | 0.968 | 0.946 |
| AIC | 47.510 | 51.462 | 44.553 | 53.604 | 39.995 | 42.975 | |
| First order | R2 | 0.971 | 0.983 | 0.838 | 0.964 | 0.992 | 0.986 |
| AIC | 45.253 | 36.636 | 71.497 | 41.106 | 26.045 | 30.475 | |
| Higuchi | R2 | 0.991 | 0.966 | 0.932 | 0.923 | 0.991 | 0.987 |
| AIC | 42.523 | 47.018 | 64.706 | 45.890 | 33.530 | 26.758 | |
| Hopfenberg | R2 | 0.967 | 0.984 | 0.836 | 0.966 | 0.965 | 0.980 |
| AIC | 49.257 | 47.316 | 71.179 | 42.812 | 45.306 | 35.582 | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas model | R2 | 0.994 | 0.981 | 0.952 | 0.925 | 0.990 | 0.988 |
| AIC | 25.389 | 36.128 | 45.498 | 47.826 | 28.966 | 46.130 | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas model release exponent (n) | 0.390 | 0.352 | 0.881 | 0.480 | 0.611 | 0.481 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amer, A.A.; Karkar, Y.; Bingle, L.; Elkordy, A.A.; Chaw, C.S. Fast-Disintegrating Oral Films Containing Nisin-Loaded Niosomes. Molecules 2025, 30, 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183715
Amer AA, Karkar Y, Bingle L, Elkordy AA, Chaw CS. Fast-Disintegrating Oral Films Containing Nisin-Loaded Niosomes. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183715
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmer, Ali A., Yasir Karkar, Lewis Bingle, Amal Ali Elkordy, and Cheng Shu Chaw. 2025. "Fast-Disintegrating Oral Films Containing Nisin-Loaded Niosomes" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183715
APA StyleAmer, A. A., Karkar, Y., Bingle, L., Elkordy, A. A., & Chaw, C. S. (2025). Fast-Disintegrating Oral Films Containing Nisin-Loaded Niosomes. Molecules, 30(18), 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183715






