The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer: Recent Advances
Abstract
1. Introduction
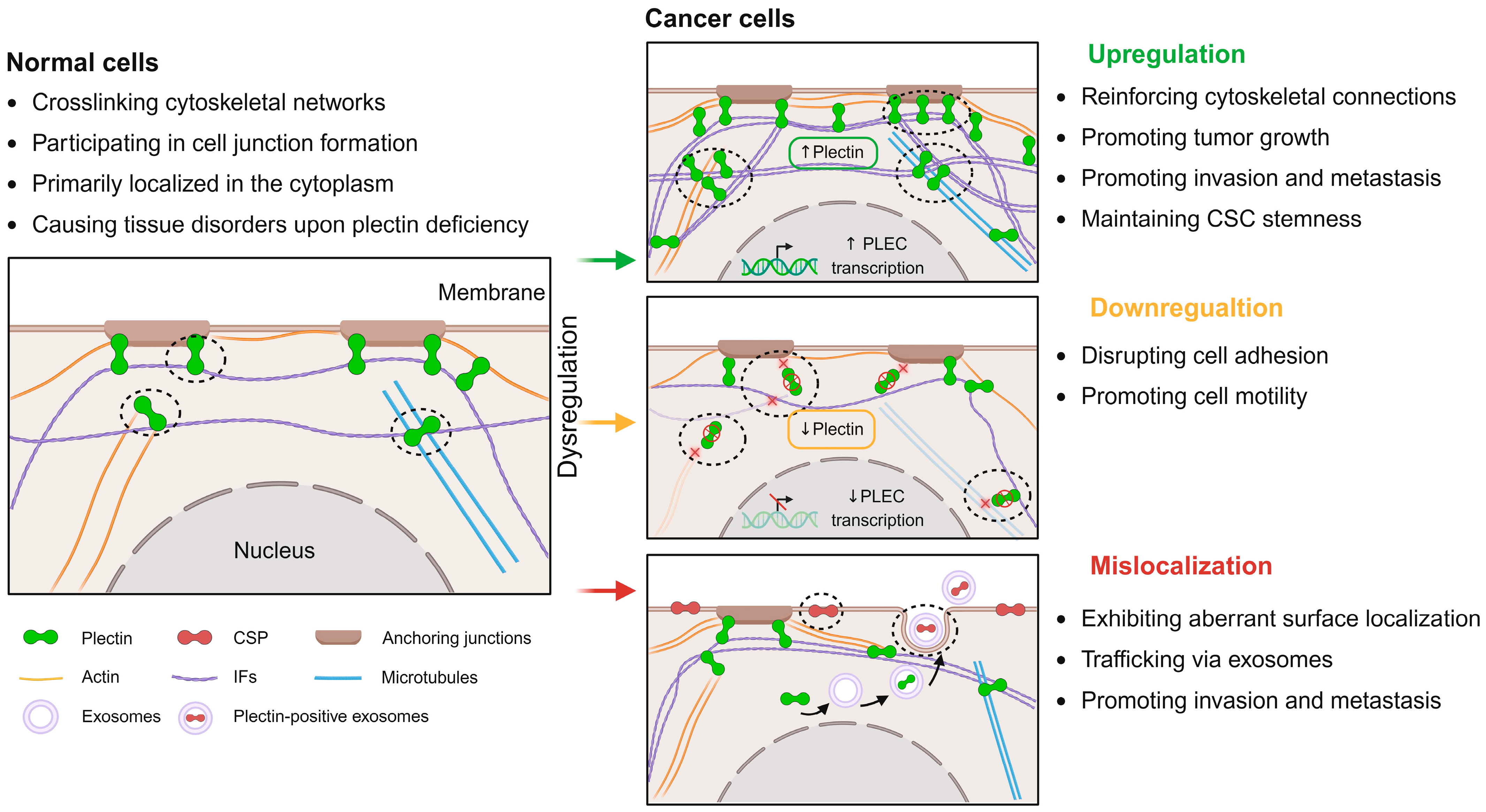
2. Dysregulation of Plectin in Cancer
2.1. Upregulation of Plectin in Cancer
2.2. Downregulation of Plectin in Cancer
2.3. Mislocalization of Plectin in Cancer
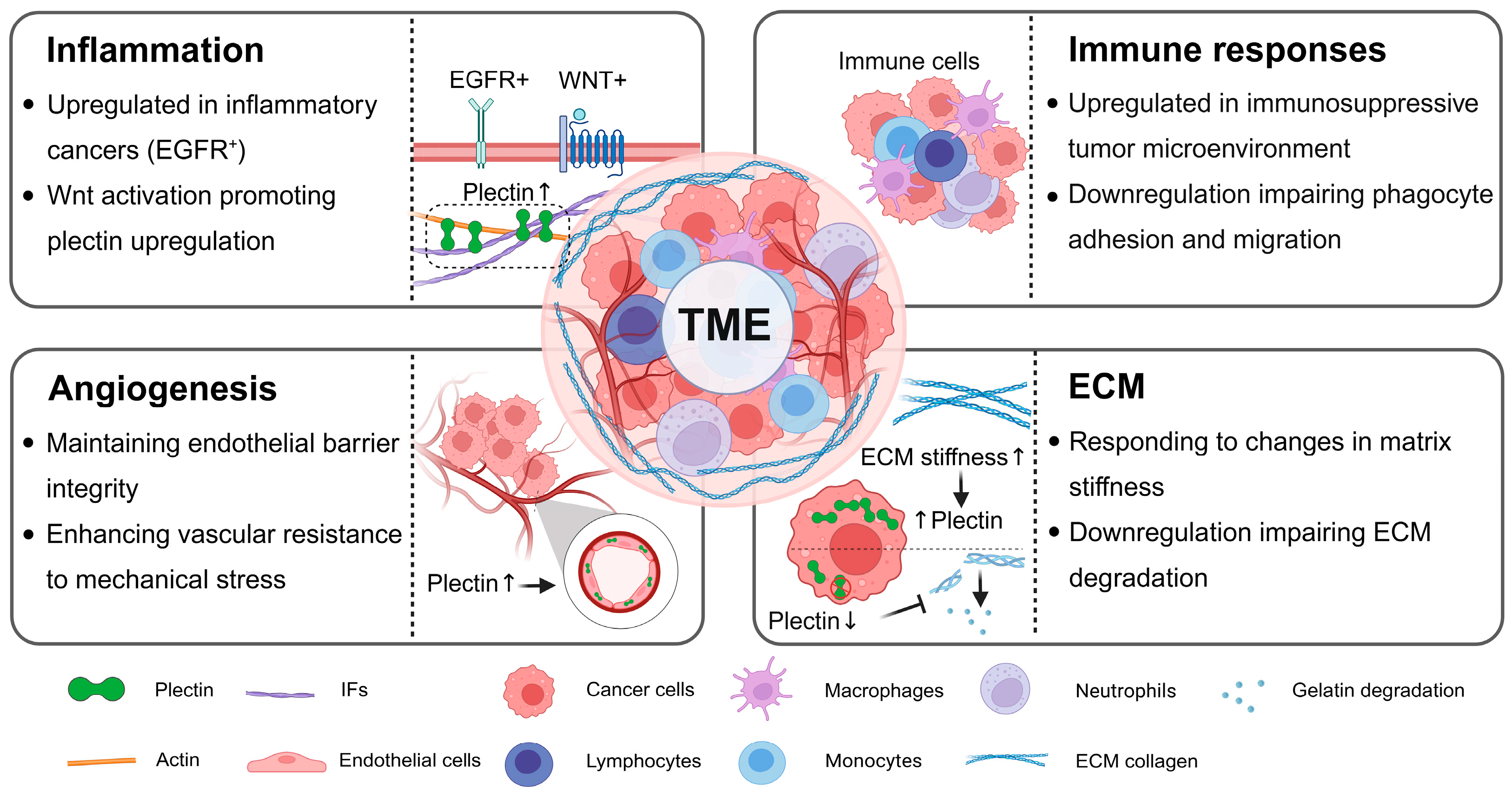
3. The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer
3.1. Sustaining Tumor Growth
3.2. Promoting Invasion and Metastasis
3.3. Sustaining Tumor Stemness
3.4. Bidirectional Regulation Between Plectin and TME
4. Targeting Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer Therapy
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFs | Actin filaments |
| ABD | Actin-binding domain |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| ALDH | Aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| BCC | Basal cell carcinomas |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| CSP | Cancer-specific plectin |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| Erk 1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| FAs | Focal adhesions |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HDs | Hemidesmosomes |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| IFs | Intermediate filaments |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PanINs | Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms |
| PST | Plecstatin-1 |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinomas |
| Src | Rous sarcoma |
| SSE | Stratified squamous epithelium |
| Rac1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
References
- Bausch, D.; Thomas, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernández-del, C.C.; Bauer, T.W.; Williams, M.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Kelly, K.A. Plectin-1 as a Novel Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zeng, S.; Yang, J.; Zhuo, J.; Wang, P.; Wen, S.; Fang, C. Plectin-1-Targeted Recognition for Enhancing Comprehensive Therapy in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 18584–18596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proby, C.; Fujii, Y.; Owaribe, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Amagai, M. Human Autoantibodies against HD1/Plectin in Paraneoplastic Pemphigus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaapveld, R.Q.J.; Borradori, L.; Geerts, D.; van Leusden, M.R.; Kuikman, I.; Nievers, M.G.; Niessen, C.M.; Steenbergen, R.D.M.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Sonnenberg, A. Hemidesmosome Formation Is Initiated by the B4 Integrin Subunit, Requires Complex Formation of B4 and HD1/Plectin, and Involves a Direct Interaction between B4 and the Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 180. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outla, Z.; Prechova, M.; Korelova, K.; Gemperle, J.; Gregor, M. Mechanics of Cell Sheets: Plectin as an Integrator of Cytoskeletal Networks. Open Biol. 2025, 15, 240208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiche, G.; Winter, L. Plectin Isoforms as Organizers of Intermediate Filament Cytoarchitecture. Bioarchitecture 2011, 1, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrä, K.; Kornacker, I.; Jörgl, A.; Zörer, M.; Spazierer, D.; Fuchs, P.; Fischer, I.; Wiche, G. Plectin-Isoform-Specific Rescue of Hemidesmosomal Defects in Plectin (–/–) Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, P.R.; Charles, S.E.; D’Souza, Z.C.; Vaidya, M.M. Hemidesmosomal Linker Proteins Regulate Cell Motility, Invasion and Tumorigenicity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Derived Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, A.; Stockinger, A.; Wiche, G.; Foisner, R. Polarisation-Dependent Association of Plectin with Desmoplakin and the Lateral Submembrane Skeleton in MDCK Cells. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieperhoff, S.; Rickelt, S.; Heid, H.; Claycomb, W.C.; Zimbelmann, R.; Kuhn, C.; Winter-Simanowski, S.; Kuhn, C.; Frey, N.; Franke, W.W. The Plaque Protein Myozap Identified as a Novel Major Component of Adhering Junctions in Endothelia of the Blood and the Lymph Vascular Systems. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.; Osmanagic-Myers, S.; Burgstaller, G.; Wolfram, M.; Fischer, I.; Walko, G.; Resch, G.P.; Jörgl, A.; Herrmann, H.; Wiche, G. Mechanosensing through Focal Adhesion-anchored Intermediate Filaments. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.G.; Maercker, C.; Castañon, M.J.; Hauptmann, R.; Wiche, G. Human Plectin: Organization of the Gene, Sequence Analysis, and Chromosome Localization (8q24). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4278–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.M.; Brinton, L.T.; Kelly, K.A. Plectin in Cancer: From Biomarker to Therapeutic Target. Cells 2021, 10, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezniczek, G.A.; Abrahamsberg, C.; Fuchs, P.; Spazierer, D.; Wiche, G. Plectin 5’-Transcript Diversity: Short Alternative Sequences Determine Stability of Gene Products, Initiation of Translation and Subcellular Localization of Isoforms. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 3181–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszewska, I.; Fischer, I.; Wiche, G. Plectin Isoform 1-Dependent Nuclear Docking of Desmin Networks Affects Myonuclear Architecture and Expression of Mechanotransducers. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 7373–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, L.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Grimm, M.; Zeöld, A.; Fischer, I.; Wiche, G. Plectin Isoform P1b and P1d Deficiencies Differentially Affect Mitochondrial Morphology and Function in Skeletal Muscle. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4530–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, P.; Fuchs, P.; Reipert, S.; Kunz, W.S.; Zeöld, A.; Fischer, I.; Paulin, D.; Schröder, R.; Wiche, G. Myofiber Integrity Depends on Desmin Network Targeting to Z-Disks and Costameres via Distinct Plectin Isoforms. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInroy, L.; Määttä, A. Plectin Regulates Invasiveness of SW480 Colon Carcinoma Cells and Is Targeted to Podosome-like Adhesions in an Isoform-Specific Manner. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2468–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañón, M.J.; Walko, G.; Winter, L.; Wiche, G. Plectin–Intermediate Filament Partnership in Skin, Skeletal Muscle, and Peripheral Nerve. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 140, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiche, G. Role of Plectin in Cytoskeleton Organization and Dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, L.; Wiche, G. The Many Faces of Plectin and Plectinopathies: Pathology and Mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuga, K. Plectin-Related Skin Diseases. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 77, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.A.; Bardeesy, N.; Anbazhagan, R.; Gurumurthy, S.; Berger, J.; Alencar, H.; DePinho, R.A.; Mahmood, U.; Weissleder, R. Targeted Nanoparticles for Imaging Incipient Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Smith, J.A.; Rezniczek, G.A.; Pan, S.; Chen, R.; Brentnall, T.A.; Wiche, G.; Kelly, K.A. Unexpected Gain of Function for the Scaffolding Protein Plectin Due to Mislocalization in Pancreatic Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19414–19419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, S.M.; Dimastromatteo, J.; Landen, C.N.; Kelly, K.A. A Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Cancer-Specific Plectin Has Potent Antitumor Activity in Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outla, Z.; Oyman-Eyrilmez, G.; Korelova, K.; Prechova, M.; Frick, L.; Sarnova, L.; Bisht, P.; Novotna, P.; Kosla, J.; Bortel, P.; et al. Plectin-Mediated Cytoskeletal Crosstalk as a Target for Inhibition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis. eLife 2025, 13, RP102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, A.C.; Gao, B.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Gomika Udugamasooriya, D. Unbiased Peptoid Combinatorial Cell Screen Identifies Plectin Protein as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Cancer Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikardsen, O.G.; Magnussen, S.N.; Svineng, G.; Hadler-Olsen, E.; Uhlin-Hansen, L.; Steigen, S.E. Plectin as a Prognostic Marker in Non-Metastatic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuta, K.; Matsubara, T.; Goto, A.; Addison, W.N.; Nakatomi, M.; Matsuo, K.; Tada-Shigeyama, Y.; Yaginuma, T.; Honda, H.; Yoshioka, I.; et al. Plectin Promotes Tumor Formation by B16 Mouse Melanoma Cells via Regulation of Rous Sarcoma Oncogene Activity. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckup, M.; Rice, M.A.; Hsu, E.-C.; Garcia-Marques, F.; Liu, S.; Aslan, M.; Bermudez, A.; Huang, J.; Pitteri, S.J.; Stoyanova, T. Plectin Is a Regulator of Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Oncogene 2021, 40, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; He, S.; Ma, D.; Liang, R.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. Plectin Downregulation Inhibits Migration and Suppresses Epithelial Mesenchymal Transformation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via ERK1/2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. High Matrix Stiffness Accelerates Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through the Integrin Β1-Plectin-F-Actin Axis. BMC Biol. 2025, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, L.; Zou, D.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Fu, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. The Expression Pattern of Hypoxia-Related Genes Predicts the Prognosis and Mediates Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 814621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Ge, J.; Tang, G.; Xiong, D.; Zhu, D.; Ding, X.; Zhou, X.; Sang, M. Machine Learning-Based Identification of Biomarkers and Drugs in Immunologically Cold and Hot Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.Y.; Cristofanilli, M.; Robertson, F.; Reuben, J.M.; Mu, Z.; Beavis, R.C.; Im, H.; Snyder, M.; Hofree, M.; Ideker, T.; et al. Genome Wide Proteomics of ERBB2 and EGFR and Other Oncogenic Pathways in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2805–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Sengupta, A.; Heo, L.; Pethö, L.; Michler, J.; Geiser, T.; De Jesus Perez, V.A.; Kuebler, W.M.; Zeinali, S.; Guenat, O.T. Effects of Biomechanical and Biochemical Stimuli on Angio- and Vasculogenesis in a Complex Microvasculature-on-Chip. iScience 2023, 26, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Der Heide, E.K.; Neumann, M.; Vosberg, S.; James, A.R.; Schroeder, M.P.; Ortiz-Tanchez, J.; Isaakidis, K.; Schlee, C.; Luther, M.; Jöhrens, K.; et al. Molecular Alterations in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.-D.; Fu, X.; Luo, Y.; He, X.; Yin, H.-H.; Mo, D.-P.; Wu, J.-X.; Wu, M.-J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.-N.; et al. Epoxy Metabolites of Linoleic Acid Promote the Development of Breast Cancer via Orchestrating PLEC/NFκB1/CXCL9-Mediated Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.M.V.; Likith, M.; Kavya, R.; Hariprasad, T.P.N. Plectin as a Putative Novel Biomarker for Breast Cancer: An in Silico Study. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinforma. 2022, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.C.; Araujo, C.B.; Iwai, L.K.; Ferro, E.S.; Forti, F.L. A Cyclin D2-Derived Peptide Acts on Specific Cell Cycle Phases by Activating ERK1/2 to Cause the Death of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Proteom. 2017, 151, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegh, A.H.; Herrmann, H.; Lampel, S.; Weisenberger, D.; Andrä, K.; Seper, M.; Wiche, G.; Krammer, P.H.; Peter, M.E. Identification of the Cytolinker Plectin as a Major Early In Vivo Substrate for Caspase 8 during CD95- and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Mediated Apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 5665–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, L.; Khoroshkin, M.; Navickas, A.; Garcia, K.; Culbertson, B.; Hänisch, B.; Zhang, S.; Nguyen, H.C.B.; Soto, L.M.; Dermit, M.; et al. A Prometastatic Splicing Program Regulated by SNRPA1 Interactions with Structured RNA Elements. Science 2021, 372, eabc7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harryman, W.L.; Pond, E.; Singh, P.; Little, A.S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Cress, A.E. Laminin-Binding Integrin Gene Copy Number Alterations in Distinct Epithelial-Type Cancers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sutoh Yoneyama, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Habuchi, T.; Inoue, T.; Nakamura, T.; Funyu, T.; Wiche, G.; Ohyama, C.; Tsuboi, S. Vimentin Intermediate Filament and Plectin Provide a Scaffold for Invadopodia, Facilitating Cancer Cell Invasion and Extravasation for Metastasis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Deng, G.; Yu, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, W.; Yu, X. Unraveling the Oncogenic Characteristics of the Cytolinker, Plectin, in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Guan, X.; Liang, Y.; Yao, X.; Tan, D.; Bai, Y.; Xiong, G.; Yang, K. Germline Copy Number Loss of UGT2B28 and Gain of PLEC Contribute to Increased Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in Southwest China. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3056–3071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pawar, H.; Kashyap, M.K.; Sahasrabuddhe, N.A.; Renuse, S.; Harsha, H.C.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, J.; Kandasamy, K.; Marimuthu, A.; Nair, B.; et al. Quantitative Tissue Proteomics of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma for Novel Biomarker Discovery. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žugec, M.; Furlani, B.; Castañon, M.J.; Rituper, B.; Fischer, I.; Broggi, G.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Di Rosa, M.; Tibullo, D.; et al. Plectin Plays a Role in the Migration and Volume Regulation of Astrocytes: A Potential Biomarker of Glioblastoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Yu, J.; Lou, Y.; He, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Lv, P.; Lin, J.; et al. Deletion of TMEM268 Inhibits Growth of Gastric Cancer Cells by Downregulating the ITGB4 Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katada, K.; Tomonaga, T.; Satoh, M.; Matsushita, K.; Tonoike, Y.; Kodera, Y.; Hanazawa, T.; Nomura, F.; Okamoto, Y. Plectin Promotes Migration and Invasion of Cancer Cells and Is a Novel Prognostic Marker for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-I.; Wang, C.-L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Feng, H.-P.; Liu, P.-J.; Chang, Y.-S.; Yu, J.-S.; Yu, C.-J. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals a Novel Role of Karyopherin Alpha 2 in Cell Migration through the Regulation of Vimentin–pErk Protein Complex Levels in Lung Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.P.; Raymond, A.; Rustagi, V.; Kedika, S.R.; Tran, O.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Udugamasooriya, D.G. A Novel Peptidomimetic Therapeutic for Selective Suppression of Lung Cancer Stem Cells over Non-Stem Cancer Cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 116, 105340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroknai, V.; Ecsedi, S.; Vízkeleti, L.; Kiss, T.; Szász, I.; Lukács, A.; Papp, O.; Ádány, R.; Balázs, M. Genomic Profiling of Invasive Melanoma Cell Lines by Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, B.L.; Grahovac, J.; Flint, M.S.; Sun, M.; Charro, N.; Becker, D.; Wells, A.; Conrads, T.P. Proteomic Analysis of Laser Microdissected Melanoma Cells from Skin Organ Cultures. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Militaru, I.V.; Rus, A.A.; Munteanu, C.V.A.; Manica, G.; Petrescu, S.M. New Panel of Biomarkers to Discriminate between Amelanotic and Melanotic Metastatic Melanoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1061832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, T.; Escalona, R.M.; Kannourakis, G.; Ahmed, N. Plakin Expression in Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Has the Potential to Impede Metastatic Spread and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition: A Comparative Expression Analysis of Immunohistochemical and In Silico Datasets. Cancers 2024, 16, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Qian, X.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Cui, X.; Cheng, M.; Han, Y. Plectin, a Novel Regulator in Migration, Invasion and Adhesion of Ovarian Cancer. Cell Biosci. 2025, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. Emerging Targeted Drug Delivery Strategies toward Ovarian Cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Cheng, M.; Han, Y. RNA-Seq Reveals the Diverse Effects of Substrate Stiffness on Epidermal Ovarian Cancer Cells. Aging 2020, 12, 20493–20511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Castillo, C.F.; Warshaw, A.L.; Kelly, K.A.; Thayer, S.P. Plectin-1 Is a Biomarker of Malignant Pancreatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. J. Gastrointest. Surg. Off. J. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract. 2009, 13, 1948–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenta, T.; Schmidt, A.; Zhang, Q.; Devarajan, R.; Singh, P.; Yang, X.; Ahtikoski, A.; Vaarala, M.; Wei, G.-H.; Manninen, A. Disassembly of α6β4-Mediated Hemidesmosomal Adhesions Promotes Tumorigenesis in PTEN-Negative Prostate Cancer by Targeting Plectin to Focal Adhesions. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3804–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Tao, H.; Liang, N.; Wu, S.; Yu, T.; Cui, X.; Xie, Y.; Zuo, H.; et al. Joint Analysis of WES and RNA-SEQ Identify Signature Genes Related to Metastasis in Prostate Cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumard-Hernández, B.; Calvete, O.; Inglada Pérez, L.; Tejero, H.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Pita, G.; Barroso, A.; Carlos Triviño, J.; Urioste, M.; Valverde, C.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies PLEC, EXO5 and DNAH7 as Novel Susceptibility Genes in Testicular Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, V.; Kanitakis, J.; Charvat, S.; Euvrard, S.; Faure, M.; Claudy, A. Expression of Basement Membrane Antigens and Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in Cutaneous Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.-C.; Lai, Y.-C.C.; Lai, Y.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chao, W.-T.; Sia, K.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-H. Transient Knockdown-Mediated Deficiency in Plectin Alters Hepatocellular Motility in Association with Activated FAK and Rac1-GTPase. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-S.; Cheng, C.-C.; Lee, M.-T.; Chao, W.-T.; Lai, Y.-C.C.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-H. The Prognostic Value of Cytokeratin and Sal-Like Protein 4 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intra-Hepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in Taiwan. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1746–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-C.; Chao, W.-T.; Liao, C.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Lai, Y.-C.C.; Lai, Y.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-H. Plectin Deficiency in Liver Cancer Cells Promotes Cell Migration and Sensitivity to Sorafenib Treatment. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2018, 12, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ai, L.; et al. Revealing Biomarkers Associated with PARP Inhibitors Based on Genetic Interactions in Cancer Genome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4435–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, M.V.; Kane, T.Q.; Chiong, E.; Rahmat, J.N.; Mahendran, R. Loss of Glutathione-S-Transferase Theta 2 (GSTT2) Modulates the Tumor Microenvironment and Response to BCG Immunotherapy in a Murine Orthotopic Model of Bladder Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Ho, C.-C.; Chao, W.-T.; Pei, R.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Yeh, K.-T.; Ho, L.-C.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lai, Y.-S. The Influence of Plectin Deficiency on Stability of Cytokeratin18 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Ho, C.-C.; Cheng, C.-C.; Chao, W.-T.; Pei, R.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Lai, Y.-S. Cytokeratin 18-Mediated Disorganization of Intermediate Filaments Is Induced by Degradation of Plectin in Human Liver Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, M.; Gao, K.; Chai, K.; Zhu, B.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y. Rap2B Drives Tumorigenesis and Progression of Colorectal Cancer through Intestinal Cytoskeleton Remodeling. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gibson, S.B. Three Dimensions of Autophagy in Regulating Tumor Growth: Cell Survival/Death, Cell Proliferation, and Tumor Dormancy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, N.; German, R.; Podicheti, R.; Rockey, P.; Sandusky, G.E.; Temm, C.J.; Nakshatri, H.; Addison, R.J.; Selman, B.; Althouse, S.K.; et al. FAM83A Is a Potential Biomarker for Breast Cancer Initiation. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aho, S. Plakin Proteins Are Coordinately Cleaved during Apoptosis but Preferentially through the Action of Different Caspases. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaltriti, M.; Santamaria, A.; Paciucci, R.; Bettuzzi, S. Intracellular Clusterin Induces G2-M Phase Arrest and Cell Death in prostate cancer-3 Prostate Cancer Cells1. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6174–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstberger, S.; Jiang, Q.; Ganesh, K. Metastasis. Cell 2023, 186, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Lu, M.; Mu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhan, X. TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics Revealed Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)-Related Molecular Characterizations for Potentially Prognostic Assessment and Personalized Treatment of FSH-Positive Non-Functional Pituitary Adenomas. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strouhalova, K.; Přechová, M.; Gandalovičová, A.; Brábek, J.; Gregor, M.; Rosel, D. Vimentin Intermediate Filaments as Potential Target for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borradori, L.; Sonnenberg, A. Structure and Function of Hemidesmosomes: More Than Simple Adhesion Complexes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivusalo, S.; Schmidt, A.; Manninen, A.; Wenta, T. Regulation of Kinase Signaling Pathways by α6β4-Integrins and Plectin in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, S.H.M.; de Pereda, J.M.; Sonnenberg, A. Current Insights into the Formation and Breakdown of Hemidesmosomes. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmello, C.; Sawant, S.; Alam, H.; Gangadaran, P.; Tiwari, R.; Dongre, H.; Rana, N.; Barve, S.; Costea, D.E.; Chaukar, D.; et al. Vimentin-Mediated Regulation of Cell Motility through Modulation of Beta4 Integrin Protein Levels in Oral Tumor Derived Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 70, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.T.; Babicky, M.; Jaquish, D.; French, R.; Marayuma, K.; Mose, E.; Niessen, S.; Hoover, H.; Shields, D.; Cheresh, D.; et al. The RON-Receptor Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration through Phosphorylation-Dependent Breakdown of the Hemidesmosome. Int. J. Cancer. 2012, 131, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.-J.; Ma, S. Hallmarks of Cancer Stemness. Cell Stem Cell 2024, 31, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Liang, R.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. Pressure Loading Regulates the Stemness of Liver Cancer Stem Cells via YAP/BMF Signaling Axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2025, 240, e31451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardzija, C.; Greening, D.W.; Escalona, R.; Chen, M.; Bilandzic, M.; Luwor, R.; Kannourakis, G.; Findlay, J.K.; Ahmed, N. Knockdown of Stem Cell Regulator Oct4A in Ovarian Cancer Reveals Cellular Reprogramming Associated with Key Regulators of Cytoskeleton-Extracellular Matrix Remodelling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Que, H.; Li, Q.; Wei, X. Wnt/β-Catenin Mediated Signaling Pathways in Cancer: Recent Advances, and Applications in Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Han, S.; Cui, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, Q. Plectin Regulates Wnt Signaling Mediated-Skeletal Muscle Development by Interacting with Dishevelled-2 and Antagonizing Autophagy. Gene 2021, 783, 145562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nii, T.; Konno, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Bhukhai, K.; Borwornpinyo, S.; Sakai, K.; Hongeng, S.; Sugiyama, D. The Bioactive Peptide SL-13R Expands Human Umbilical Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells In Vitro. Molecules 2021, 26, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, J.C.; Salvucci, M.; Carberry, S.; Barat, A.; Segura, M.F.; Fenn, J.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Stallings, R.L.; Piskareva, O. A Context-Dependent Role for MiR-124-3p on Cell Phenotype, Viability and Chemosensitivity in Neuroblastoma in Vitro. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 559553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradžik, M.; Humphries, J.D.; Stojanović, N.; Nestić, D.; Majhen, D.; Dekanić, A.; Samaržija, I.; Sedda, D.; Weber, I.; Humphries, M.J.; et al. KANK2 Links αVβ5 Focal Adhesions to Microtubules and Regulates Sensitivity to Microtubule Poisons and Cell Migration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Semba, T.; Manyam, G.C.; Wang, J.; Shao, S.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Phi, L.T.H.; Pearson, T.; et al. EGFR Is a Master Switch between Immunosuppressive and Immunoactive Tumor Microenvironment in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Cui, Z.-Y.; Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, D.-D.; Guo, R.-J.; Han, M. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muok, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Esmonde, C.; Arthur, P.; Wang, X.; Singh, M.; Driscoll, T.; Li, Y. Inflammatory Response and Exosome Biogenesis of Choroid Plexus Organoids Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-G.; Liang, R.; Wang, H.-T.; Jin, S.-H.; Hu, W.; Frey, B.; Fietkau, R.; Hecht, M.; Ma, H.; Gaipl, U.S. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs as Novel Putative Biomarkers to Predict Anti-PD-1 Monotherapy Response in Metastatic Melanoma Patients—Knowledge from Two Independent International Studies. Neoplasia 2023, 37, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, S.M.; Martinez, R.; Benware, A.; LaFlamme, S.E. Regulation of the Association of α6β4 with Vimentin Intermediate Filaments in Endothelial Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 281, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmanagic-Myers, S.; Rus, S.; Wolfram, M.; Brunner, D.; Goldmann, W.H.; Bonakdar, N.; Fischer, I.; Reipert, S.; Zuzuarregui, A.; Walko, G.; et al. Plectin Reinforces Vascular Integrity by Mediating Crosstalk between the Vimentin and the Actin Networks. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 4138–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.M.; Turner, J.E.; Harrington, A.; Davis-Knowlton, J.; Lindner, V.; Gridley, T.; Vary, C.P.H.; Liaw, L. Notch2 and Proteomic Signatures in Mouse Neointimal Lesion Formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Song, G. Matrix Stiffness-Driven Cancer Progression and the Targeted Therapeutic Strategy. Mechanobiol. Med. 2023, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechova, M.; Adamova, Z.; Schweizer, A.-L.; Maninova, M.; Bauer, A.; Kah, D.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Wiche, G.; Fabry, B.; Gregor, M. Plectin-Mediated Cytoskeletal Crosstalk Controls Cell Tension and Cohesion in Epithelial Sheets. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 221, e202105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borutzki, Y.; Skos, L.; Gerner, C.; Meier-Menches, S.M. Exploring the Potential of Metal-Based Candidate Drugs as Modulators of the Cytoskeleton. ChemBioChem 2023, 24, e202300178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremlett, W.D.J.; Goodman, D.M.; Steel, T.R.; Kumar, S.; Wieczorek-Błauż, A.; Walsh, F.P.; Sullivan, M.P.; Hanif, M.; Hartinger, C.G. Design Concepts of Half-Sandwich Organoruthenium Anticancer Agents Based on Bidentate Bioactive Ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 213950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, S.M.; Kreutz, D.; Winter, L.; Klose, M.H.M.; Cseh, K.; Weiss, T.; Bileck, A.; Alte, B.; Mader, J.C.; Jana, S.; et al. An Organoruthenium Anticancer Agent Shows Unexpected Target Selectivity For Plectin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8267–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafinger, O.R.; Hayward, J.J.; Meng, Y.; Geddes-McAlister, J.; Li, Y.; Mar, S.; Sheng, M.; Su, B.; Thillainadesan, G.; Lipsman, N.; et al. Cancer Cell Extravasation Requires Iplectin-Mediated Delivery of MT1-MMP at Invadopodia. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedge, M.-E.; Jennings, V.A.; Crupi, M.J.F.; Poutou, J.; Jamieson, T.; Pelin, A.; Pugliese, G.; De Souza, C.T.; Petryk, J.; Laight, B.J.; et al. Virally Programmed Extracellular Vesicles Sensitize Cancer Cells to Oncolytic Virus and Small Molecule Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerhalder, D.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Pelster, M.; Borad, M.J.; Vandross, A.L.; Spira, A.I.; Perez, S.; Brinton, L.; Kelly, K.; Ramanathan, R.K.; et al. A Phase 1/2, First-in-Human Trial of ZB131, a Novel Antibody Targeting Cancer-Specific Plectin (CSP) in Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimastromatteo, J.; He, J.; Adams, R.B.; Kelly, K.A. Imaging Cell Surface Plectin in PDAC Patients—A First-In-Human Phase 0 Study Report. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2025, 27, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dysregulation | Cancer Types | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulation | AML | PLEC gene mutation | [37] |
| Breast cancer | Promoting growth and metastasis; substrate for caspases; orchestrating PLEC/NFκB1/CXCL9 axis; SNRPA1-mediated PLEC alternative splicing | [38,39,40,41,42] | |
| Bladder cancer | Promoting invasion and metastasis; promoting invadopodia formation | [43,44] | |
| CRC | Promoting invasion; targeting podosome-like adhesions; contributing to drug resistance | [18,33] | |
| ESCC | Maintaining anchorage and proliferation; increasing ESCC risk | [45,46,47] | |
| GBM | Enhancing migration; regulating morphological changes | [48] | |
| Gastric cancer | Promoting growth; integrin β4–plectin complex forming | [49] | |
| HCC | Promoting migration and invasion; promoting EMT; involving the Integrin β1/Plectin/F-actin axis; upregulating in high matrix stiffness | [26,31,32] | |
| HNSCC | Promoting migration and invasion; upregulating Erk 1/2 kinase | [50] | |
| Lung cancer | Enhancing invasion and migration; maintaining stemness | [27,51,52] | |
| Melanoma | Metastasis biomarker; promoting growth; activating Src signaling | [29,53,54,55] | |
| OSCC | Prognostic marker; enhancing cell motility, invasion, and tumorigenicity | [8,28] | |
| Ovarian cancer | Promoting migration, invasion, and adhesion; upregulating in high substrate stiffness | [56,57,58,59] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Malignant biomarker; promoting proliferation, migration, and invasion; participating in integrin β4-dependent exosomal transport | [23,24,60] | |
| Prostate cancer | Promoting growth and metastasis; targeting focal adhesions | [30,61,62] | |
| Testicular cancer | Novel susceptibility genes | [63] | |
| Downregulation | BCC and SCC | Promoting invasion | [64] |
| ESCC | Disrupting stratified squamous epithelium homeostasis | [45] | |
| HCC | Promoting cell motility; activating FAK and Rac1-GTPase | [65,66,67] | |
| Ovarian cancer | Downregulating during tumor progression; promoting EMT | [56] | |
| Mislocalization | CRC | Plectin 1k targeting podosome-like adhesions | [18] |
| ESCC | Localizing in the cell membrane | [47] | |
| GBM | Co-localization with membrane-related-aquaporin 4 aggregates | [48] | |
| HCC | Perimembranous enrichment | [26] | |
| HNSCC | Uniform in the cytoplasm and the cell membrane | [50] | |
| Lung cancer | Biomarker of ALDH+ lung cancer stem cells | [27] | |
| OSCC | Mainly at the plasma membrane | [28] | |
| Ovarian cancer | Monoclonal antibodies targeting CSP; a target for drug delivery | [56,57,58] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Participating in exosome formation and enhancing tumor growth | [23,24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Lyu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer: Recent Advances. Molecules 2025, 30, 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183675
Wang W, Lyu C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Luo Q, Song G. The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer: Recent Advances. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183675
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenbin, Chang Lyu, Zhihui Wang, Xu Zhang, Qing Luo, and Guanbin Song. 2025. "The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer: Recent Advances" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183675
APA StyleWang, W., Lyu, C., Wang, Z., Zhang, X., Luo, Q., & Song, G. (2025). The Role of Plectin Dysregulation in Cancer: Recent Advances. Molecules, 30(18), 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183675






