Notoginsenoside R1, a Metabolite from Panax notoginseng, Prevents Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of NGR1 Pretreatment on Paclitaxel-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
2.2. Affinity of NGR1 to MAGL
2.3. Inhibitory Effects of NGR1 on Recombinant Human MAGL Activity
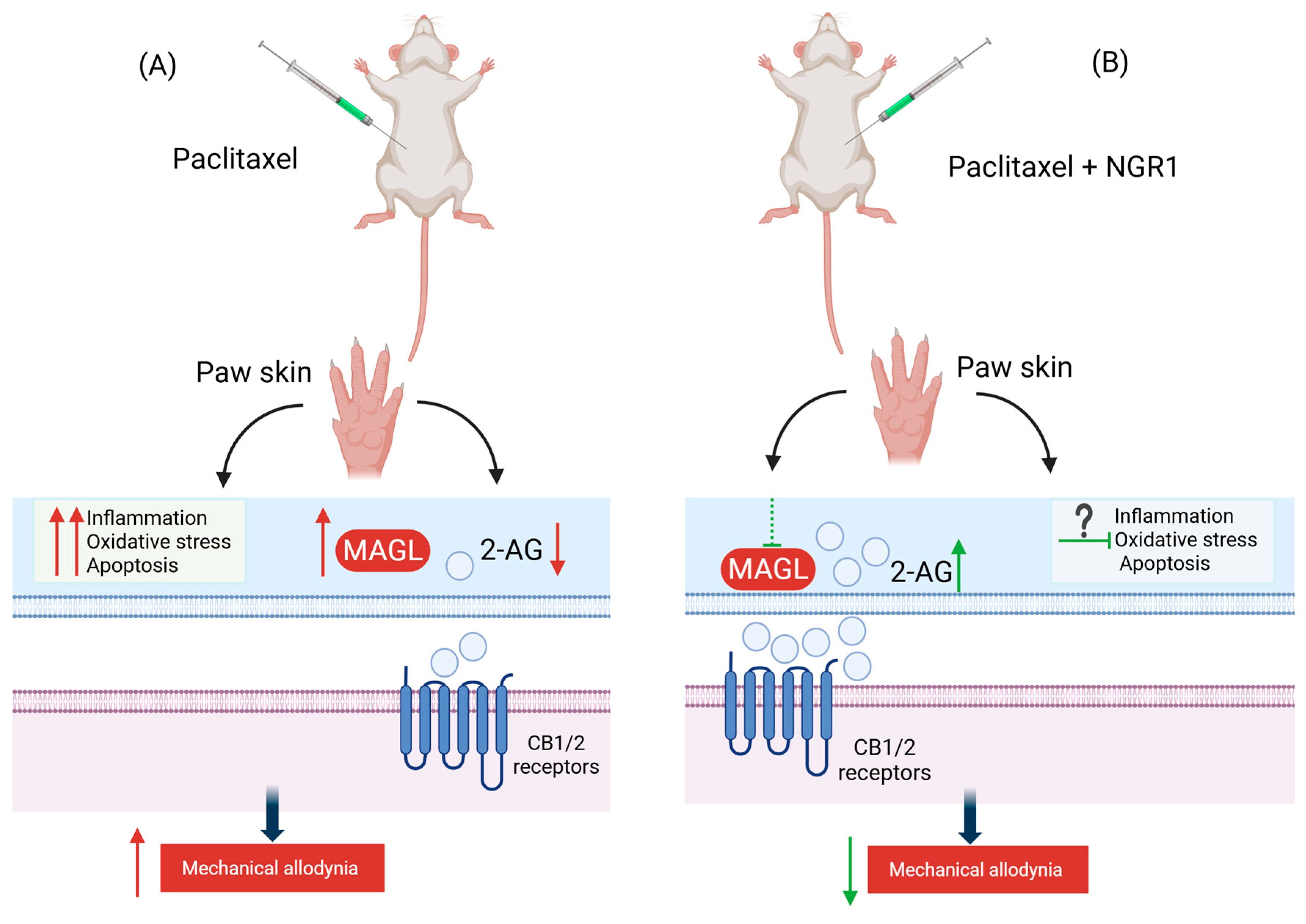
2.4. Effect of NGR1 on Paclitaxel-Induced Monoacylglycerol Lipase Activity in the Paw Skin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. NGR1 Preparation
4.2. Animals
4.3. Induction of PIMA in Mice
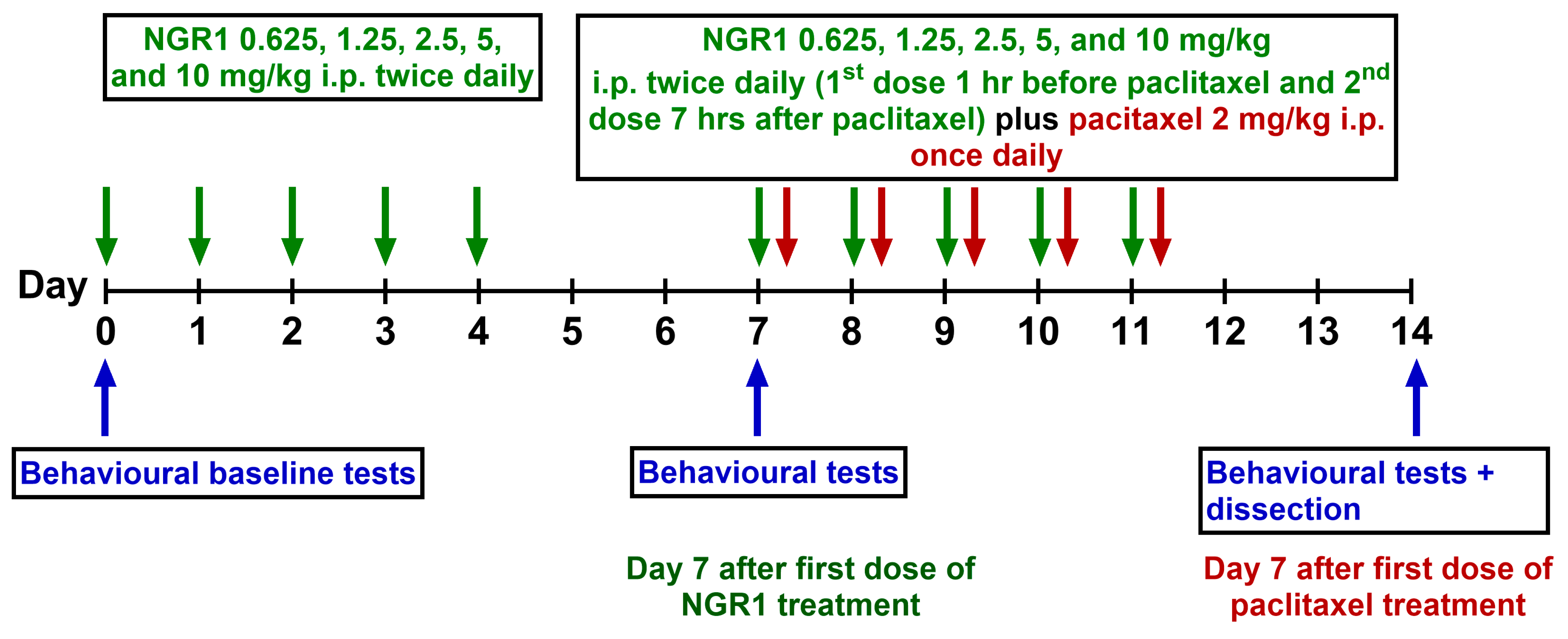
4.4. Drug Administration Protocol
4.5. Assessment of Mechanical Allodynia
4.6. Tissue Dissection
4.7. Molecular Docking
4.8. Assessment of Inhibitory Potential of NGR1 on Human Recombinant Monoacylglycerol Lipase Activity
4.9. Assessment of Inhibitory Potential of NGR1 on Monoacylglycerol Lipase Activity in Mouse Paw Skin Tissue
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonoyl Glycerol |
| 3D | 3-dimensional |
| AEA | Anandamide or N-arachidonoylethanolamide |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ARC | Animal Resources Centre |
| CB1 | Cannabinoid Receptor type 1 |
| CB2 | Cannabinoid Receptor type 2 |
| CIPN | Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy |
| ECS | Endocannabinoid System |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GSH-PX | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| HO1 | Heme Oxygenase 1 |
| HSC | Health Sciences Center |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| IASP | International Association for the Study of Pain |
| IC50 | Inhibitory Concentration |
| IL | Interleukin |
| MAGL | Monoacylglycerol Lipase |
| NGR1 | Notoginsenoside R1 |
| NRF2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 |
| OD | Optical Density |
| PIMA | Paclitaxel-induced Mechanical Allodynia |
| PINP | Paclitaxel-induced Neuropathic Pain |
| SOD2 | Superoxide Dismutase 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
References
- Areti, A.; Yerra, V.G.; Naidu, V.; Kumar, A. Oxidative stress and nerve damage: Role in chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Zhao, F.; Brell, J.; Lewis, M.A.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Weiss, M.; Fisch, M.J. Neuropathic symptoms, quality of life, and clinician perception of patient care in medical oncology outpatients with colorectal, breast, lung, and prostate cancer. J. Cancer Surviv. 2015, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletti, G.; Marmiroli, P.; Renn, C.L.; Dorsey, S.G.; Serra, M.P.; Quartu, M.; Meregalli, C. Cannabinoids: An Effective Treatment for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity? Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 2324–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, E.; Masocha, W. Targeting the endocannabinoid system for management of HIV-associated neuropathic pain: A systematic review. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 10, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasabova, I.A.; Yao, X.; Paz, J.; Lewandowski, C.T.; Lindberg, A.E.; Coicou, L.; Burlakova, N.; Simone, D.A.; Seybold, V.S. JZL184 is anti-hyperalgesic in a murine model of cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 90, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, J.; Lai, Y.; Takacs, S.M.; Bradshaw, H.B.; Hohmann, A.G. Alterations in endocannabinoid tone following chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Effects of endocannabinoid deactivation inhibitors targeting fatty-acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase in comparison to reference analgesics following cisplatin treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 67, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Okine, B.N.; Finn, D.P.; Masocha, W. Peripheral deficiency and antiallodynic effects of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in a mouse model of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Romaiyan, A.; Masocha, W. Pristimerin, a triterpene that inhibits monoacylglycerol lipase activity, prevents the development of paclitaxel-induced allodynia in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 944502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Heydari, M.; Naderinia, K.; Rahimi, R. Plant-derived medicines for neuropathies: A comprehensive review of clinical evidence. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveissi, V.; Ram, M.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Ebrahimi, F.; Rahimi, R.; Naseri, R.; Belwal, T.; Devkota, H.P.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Farzaei, M.H. Medicinal plants and their isolated phytochemicals for the management of chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: Therapeutic targets and clinical perspective. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Bao, Z.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z. Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and inflammation via activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway. Neuroreport 2022, 33, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 441934, Notoginsenoside R1. 2004.
- King, A.R.; Dotsey, E.Y.; Lodola, A.; Jung, K.M.; Ghomian, A.; Qiu, Y.; Fu, J.; Mor, M.; Piomelli, D. Discovery of potent and reversible monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitors. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scripture, C.D.; Figg, W.D.; Sparreboom, A. Peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel: Recent insights and future perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Romaiyan, A.; Barakat, A.; Jose, L.; Masocha, W. An aqueous Commiphora myrrha extract ameliorates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathic pain in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1295096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Nakamichi, N.; Zhang, W.S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kambe, Y.; Fukumori, R.; Takuma, K.; Yamada, K.; Takarada, T.; Taniura, H.; et al. Possible protection by notoginsenoside R1 against glutamate neurotoxicity mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors composed of an NR1/NR2B subunit assembly. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, B.; Yang, T.; Sun, H.; Ran, X.; Lin, W. Protective Effect of NGR1 against Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in HT22 Hippocampal Neuronal Cells by Upregulating the SIRT1/Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 4358163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Sun, G.; Ye, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Notoginsenoside R1-mediated neuroprotection involves estrogen receptor-dependent crosstalk between Akt and ERK1/2 pathways: A novel mechanism of Nrf2/ARE signaling activation. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, S. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates bupivacaine induced neurotoxicity by activating Jak1/Stat3/Mcl1 pathway. Toxicology 2024, 503, 153740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, M. The Protective Effect of Notoginsenoside R1 on Isoflurane-Induced Neurological Impairment in the Rats via Regulating miR-29a Expression and Neuroinflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation 2022, 29, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ran, Y.; Guo, J.; Cui, H.; Liu, S. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. Transl. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.L.; Wang, X.J.; Yang, B.X.; Du, B.; Yun, X.L. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates breast cancer progression by targeting CCND2 and YBX3. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, F.; Dong, Y.; Xu, F. Notoginsenoside R1 (NGR1) regulates the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway by inhibiting RUNX2 expression to accelerate ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Aging 2024, 16, 10446–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Yu, H.; Zhai, H. Suppression of JAK2/STAT3 Pathway by Notoginsenoside R1 Reduces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Liu, R.; Hao, S.; Dou, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Cao, Y.; Huang, H.; Duan, C. Notoginsenoside R1 improves intestinal microvascular functioning in sepsis by targeting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial quality imbalance. Pharm. Biol. 2024, 62, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Toxicological awakenings: The rebirth of hormesis as a central pillar of toxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Staudenmayer, J.W.; Stanek III, E.J.; Hoffmann, G.R. Hormesis outperforms threshold model in National Cancer Institute antitumor drug screening database. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 94, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Liao, X.; Ye, X.; Lai, W. Pharmacokinetics and Biological Activities of Notoginsenoside R1: A Systematical Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2025, 53, 205–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Xi, X.; Li, J. Notoginsenoside R1: A systematic review of its pharmacological properties. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, J.D.; Craft, R.M.; LeResche, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Berkley, K.J.; Fillingim, R.B.; Gold, M.S.; Holdcroft, A.; Lautenbacher, S.; Mayer, E.A. Studying sex and gender differences in pain and analgesia: A consensus report. Pain 2007, 132, S26–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masocha, W.; Thomas, A. Indomethacin plus minocycline coadministration relieves chemotherapy and antiretroviral drug-induced neuropathic pain in a cannabinoid receptors-dependent manner. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 139, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masocha, W.; Aly, E.; Albaloushi, A.; Al-Romaiyan, A. Licofelone, a Dual COX/LOX Inhibitor, Ameliorates Paclitaxel-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats in a Cannabinoid Receptor-Dependent Manner. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
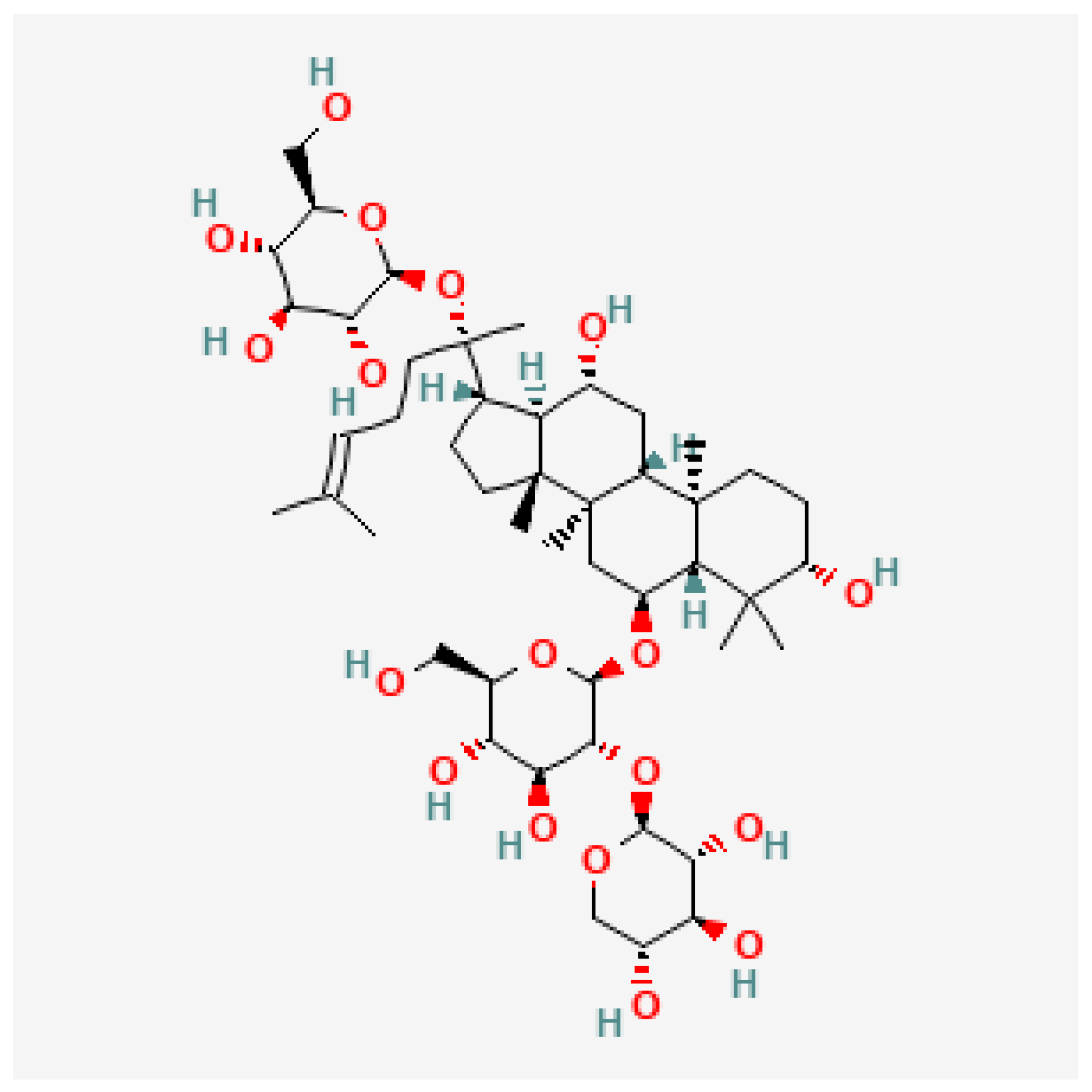


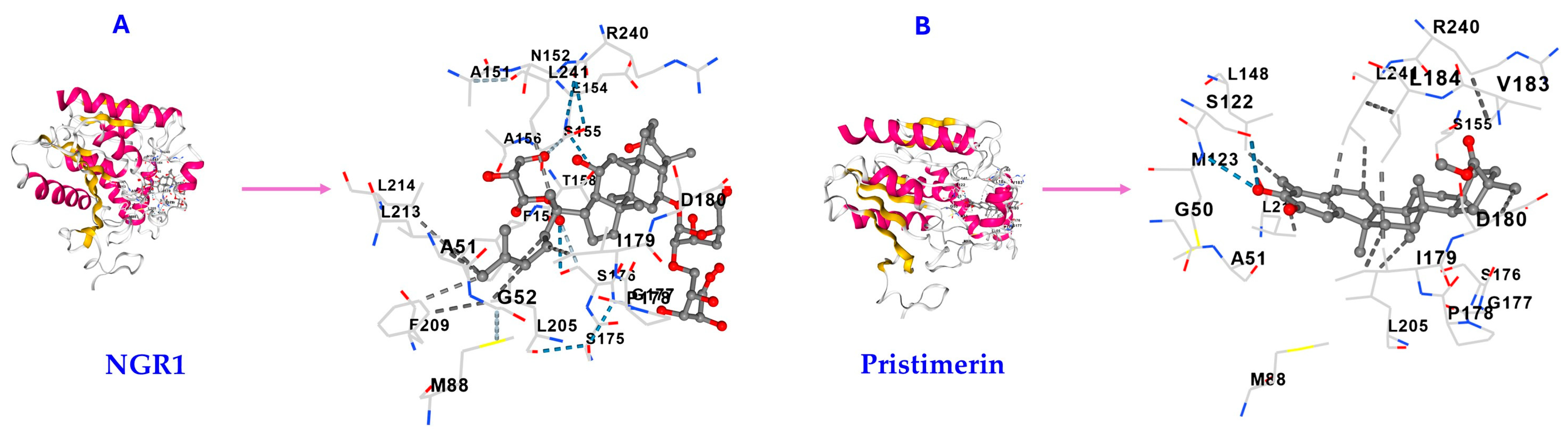



| Triterpene | Vina Score (kcal/mol) | Cavity Volume (Å3) | Center (x, y, z) | Docking Size (x, y, z) | Contact Residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGR1 | −7.8 | 1904 | −10, 17, −6 | 28, 28, 28 | GLY50 ALA51 GLY52 GLU53 MET88 HIS121 SER122 MET123 GLY124 LEU148 ALA151 ASN152 PRO153 GLU154 SER155 ALA156 THR158 PHE159 LEU162 SER175 SER176 GLY177 PRO178 ILE179 ASP180 SER181 VAL183 LEU184 TYR194 ALA203 GLY204 LEU205 LYS206 PHE209 GLY210 ILE211 LEU213 LEU214 VAL217 ALA238 ARG240 LEU241 CYS242 ASP243 HIS269 VAL270 |
| Pristimerin | −10.3 | 1904 | −10, 17, −6 | 23, 23, 23 | GLY50 ALA51 MET88 SER122 MET123 LEU148 ALA151 SER155 ALA156 PHE159 SER176 GLY177 PRO178 ILE179 ASP180 VAL183 LEU184 LEU205 GLY210 LEU213 LEU214 VAL217 ARG240 LEU241 HIS269 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Musailem, M.; Masocha, W.; Al-Romaiyan, A. Notoginsenoside R1, a Metabolite from Panax notoginseng, Prevents Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Molecules 2025, 30, 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173613
Al-Musailem M, Masocha W, Al-Romaiyan A. Notoginsenoside R1, a Metabolite from Panax notoginseng, Prevents Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173613
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Musailem, Muneerah, Willias Masocha, and Altaf Al-Romaiyan. 2025. "Notoginsenoside R1, a Metabolite from Panax notoginseng, Prevents Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Mice" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173613
APA StyleAl-Musailem, M., Masocha, W., & Al-Romaiyan, A. (2025). Notoginsenoside R1, a Metabolite from Panax notoginseng, Prevents Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Molecules, 30(17), 3613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173613






