Protective Effect of a Highly Enriched Nacre-Derived Neutral Polysaccharide Fraction on D-Galactose-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
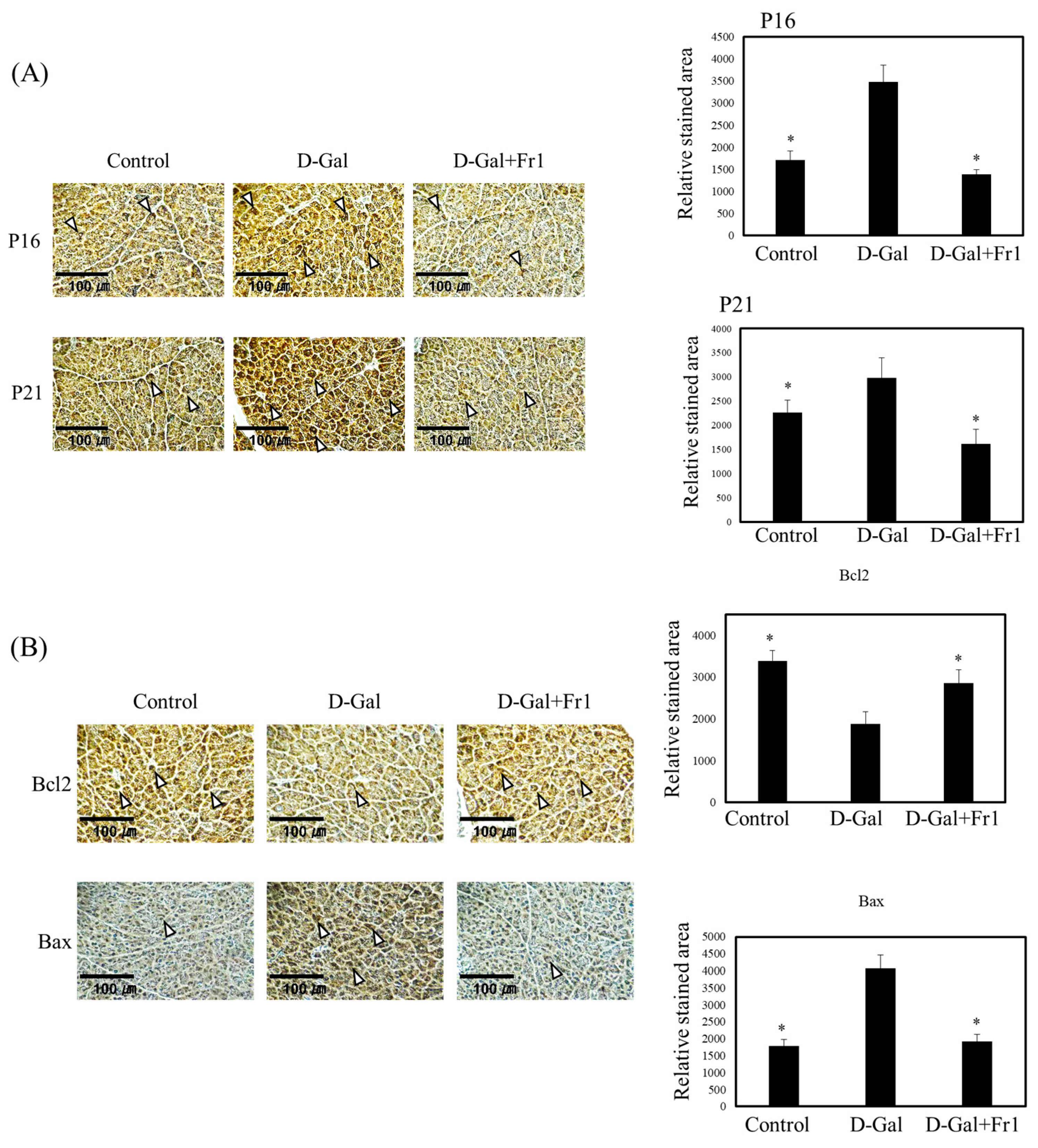
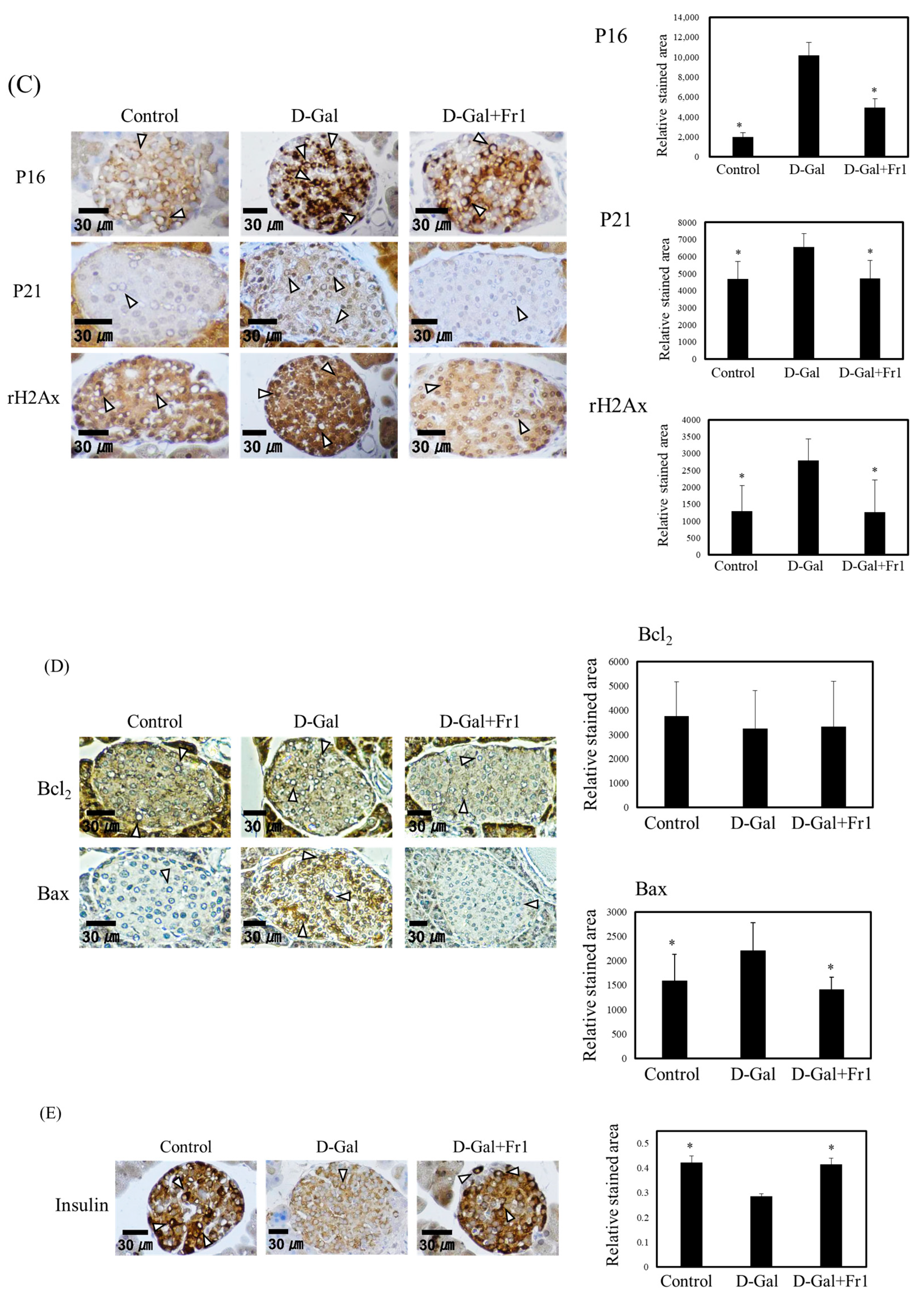
2. Results
Effect of Fraction 1 on Pancreatic Tissue Aging Induced by D-Galactose Administration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Fractionation of Nacre Extract
4.3. Chemical Composition and Structural Characterization of Fraction 1
4.3.1. FT-IR ATR Spectroscopy
4.3.2. MALDI-TOF MS Analysis
4.3.3. Monosaccharide Analysis
4.4. Animals
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Blood Biochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DAB | 3,3’-diaminobenzidine |
| FT-IR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| ATR | Attenuated total reflectance |
| MALDI-TOF-MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| ABEE | 4-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester |
References
- Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, G.; Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Kan, C. Metabolic Diseases and Healthy Aging: Identifying Environmental and Behavioral Risk Factors and Promoting Public Health. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1253506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Lu, Y.; Wei, G.; Yu, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ying, J.; Hua, F. Relieving Cellular Energy Stress in Aging, Neurodegenerative, and Metabolic Diseases, SIRT1 as a Therapeutic and Promising Node. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 738686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Cai, M.; Han, X.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H. The Interaction Between Age and Risk Factors for Diabetes and Prediabetes: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, P.K.; Lee, H.; Steinhauser, M.L. Aging Is a Powerful Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Independent of Body Mass Index. Gerontology 2020, 66, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Inagaki, N.; Kondoh, H. Cellular Senescence in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct Senotherapeutic Strategies for Adipose Tissue and Pancreatic β Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 869414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudurí, E.; Soriano, S.; Almagro, L.; Montanya, E.; Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Nadal, Á.; Quesada, I. The Pancreatic β-Cell in Ageing: Implications in Age-Related Diabetes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 80, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Tata, V. Age-Related Impairment of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function: Pathophysiological and Cellular Mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čater, M.; Križančić Bombek, L. Protective Role of Mitochondrial Uncoupling Proteins against Age-Related Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Breda, E.; Oberg, A.L.; Powell, C.C.; Dalla Man, C.; Basu, A.; Vittone, J.L.; Klee, G.G.; Arora, P.; Jensen, M.D.; et al. Mechanisms of the Age-Associated Deterioration in Glucose Tolerance: Contribution of Alterations in Insulin Secretion, Action, and Clearance. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Azman, K.F.; Safdar, A.; Zakaria, R. D-Galactose-Induced Liver Aging Model: Its Underlying Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Interventions. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-C.; Liu, J.-H.; Wu, R.-Y. Establishment of the Mimetic Aging Effect in Mice Caused by D-Galactose. Biogerontology 2003, 4, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Majdi, A.; McCann, S.K.; Mahmoudi, J.; Vafaee, M.S.; Macleod, M.R. D-Galactose-Induced Brain Ageing Model: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Cognitive Outcomes and Oxidative Stress Indices. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Granato, D. Green Tea Polyphenols Upregulate the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Suppress Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Markers in D-Galactose-Induced Liver Aging in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 836112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.; Chen, X. Dihydromyricetin Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Aging of Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 756, 135963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviciena, A.P.; I’tikafia, F.A.H.; Kharisma, M.; Akhmad, S.A.; Fidianingsih, I. The Effect of Arrowroot Diet on Pancreatic and Kidney Histomorphology of Mice Induced by D-Galactose. AcTion Aceh Nutr. J. 2024, 9, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, M.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Xia, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The Protective Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on Aging Mouse Pancreas Damage Induced by D-Galactose. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, G. The Protective Effect of PL 1-3 on D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1304801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.-H.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Qu, L.; Zeng, H. Effect of Resveratrol on the Repair of Kidney and Brain Injuries and Its Regulation on Klotho Gene in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 40, 127913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumbalová, Z.; Uličná, O.; Kucharská, J.; Rausová, Z.; Vančová, O.; Melicherčík, Ľ.; Tvrdík, T.; Nemec, M.; Kašparová, S. D-Galactose-Induced Aging in Rats—The Effect of Metformin on Bioenergetics of Brain, Skeletal Muscle and Liver. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 163, 111770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Butnariu, M.; Peana, M.; Sarac, I.; Strus, O.; Smetanina, K.; Chirumbolo, S. Natural Compounds and Products from an Anti-Aging Perspective. Molecules 2022, 27, 7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Luo, J.; Bao, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Aging and Anti-Aging Strategies. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, R.L.; El-Gohary, R.M.; Ghalwash, A.A.; Hegab, I.I.; Ghabrial, M.M.; Aboshanady, A.M.; Mostafa, R.A.; El-Azeem, A.H.A.; Farghal, E.E.; Belal, A.A.E.; et al. Luteolin Mitigates D-Galactose-Induced Brain Ageing in Rats: SIRT1-Mediated Neuroprotection. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 2803–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saafan, S.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; El Tedawy, F.A.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Fadly, R.S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; El-Far, A.H.; Alsenosy, A.A. Rutin Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats’ Brain and Liver: Molecular Docking and Experimental Approaches. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5728–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, W.; Fu, K.; Wang, Z. The Application of Pearls in Traditional Medicine of China and Their Chemical Constituents, Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Clinical Research. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 893229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Shimomura, N.; Oura, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Nacre Extract from Pearl Oyster Shell Prevents D-Galactose-Induced Brain and Skin Aging. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, H.; Fuji, T.; Wako, M.; Hasegawa, Y. Sulfated Polysaccharide Isolated from the Nacre of Pearl Oyster Improves Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wako, M.; Ohara, K.; Hasegawa, Y. Sulfated Polysaccharides Isolated from Nacre Extract Suppress Chronic Scopolamine Administration-Induced Amyloid-Beta Deposition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, N.A.; Buslov, D.K.; Sushko, N.I.; Zhbankov, R.G. Investigation of Stretching Vibrations of Glycosidic Linkages in Disaccharides and Polysaccarides with Use of IR Spectra Deconvolution. Biopolymers 2000, 57, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy as a Tool for Polysaccharide Identification in Edible Brown and Red Seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieroba, B.; Kalisz, G.; Krysa, M.; Khalavka, M.; Przekora, A. Application of Vibrational Spectroscopic Techniques in the Study of the Natural Polysaccharides and Their Cross-Linking Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo-Htay, C.; Shwe, T.; Higgins, L.; Palee, S.; Shinlapawittayatorn, K.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Aging Induced by D-Galactose Aggravates Cardiac Dysfunction via Exacerbating Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obese Insulin-Resistant Rats. GeroScience 2020, 42, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Far, A.H.; Lebda, M.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Atta, M.S.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Elfeky, M.; Mousa, S.A. Quercetin Attenuates Pancreatic and Renal D-Galactose-Induced Aging-Related Oxidative Alterations in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Interference Effect of Oral Administration of Mulberry Branch Bark Powder on the Incidence of Type II Diabetes in Mice Induced by Streptozotocin. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 31606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Song, X.; Jia, L. Antihyperglycaemic and Organic Protective Effects on Pancreas, Liver and Kidney by Polysaccharides from Hericium Erinaceus SG-02 in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Yu, W.; Li, P.; Tang, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, L.; Wu, D.; Cheng, S.; Song, Z. Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Enhance Pancreatic β-Cell Function in Diabetic Zebrafish by Mitigating Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage via the AMPK-SIRT1 Pathway. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1601490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xie, H.; Farag, M.A.; Feng, S.; Li, J.; Shao, P. Dendrobium officinale Leaf Polysaccharides Ameliorated Hyperglycemia and Promoted Gut Bacterial Associated SCFAs to Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes in Adult Mice. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Z. Structural Characterization and Hypoglycemic Activity of a Novel Pumpkin Peel Polysaccharide-Chromium(III) Complex. Foods 2022, 11, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedevi, P.; Ramu Ganesan, A.; Moovendhan, M.; Mohan, K.; Sivasankar, P.; Loganathan, S.; Vairamani, S.; Shanmugam, A. Anti-Diabetic Activity of Crude Polysaccharide and Rhamnose-Enriched Polysaccharide from G. Lithophila on Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced in Wistar Rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Yun, J.W. Hypoglycemic Effect of Polysaccharides Produced by Submerged Mycelial Culture of Laetiporus sulphureus on Streptozotocininduced Diabetic Rats. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2010, 15, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.-B.; Cui, Y.-L. Antioxidant Activities of Natural Polysaccharides and Their Derivatives for Biomedical and Medicinal Applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, S.; Song, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y. The Isolation, Structural Characterization and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Neutral Polysaccharides from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fort. Molecules 2024, 29, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Hou, C.; Yan, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill) Fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifsnyder, P.C.; Flurkey, K.; Doty, R.; Calcutt, N.A.; Koza, R.A.; Harrison, D.E. Rapamycin/Metformin Co-Treatment Normalizes Insulin Sensitivity and Reduces Complications of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
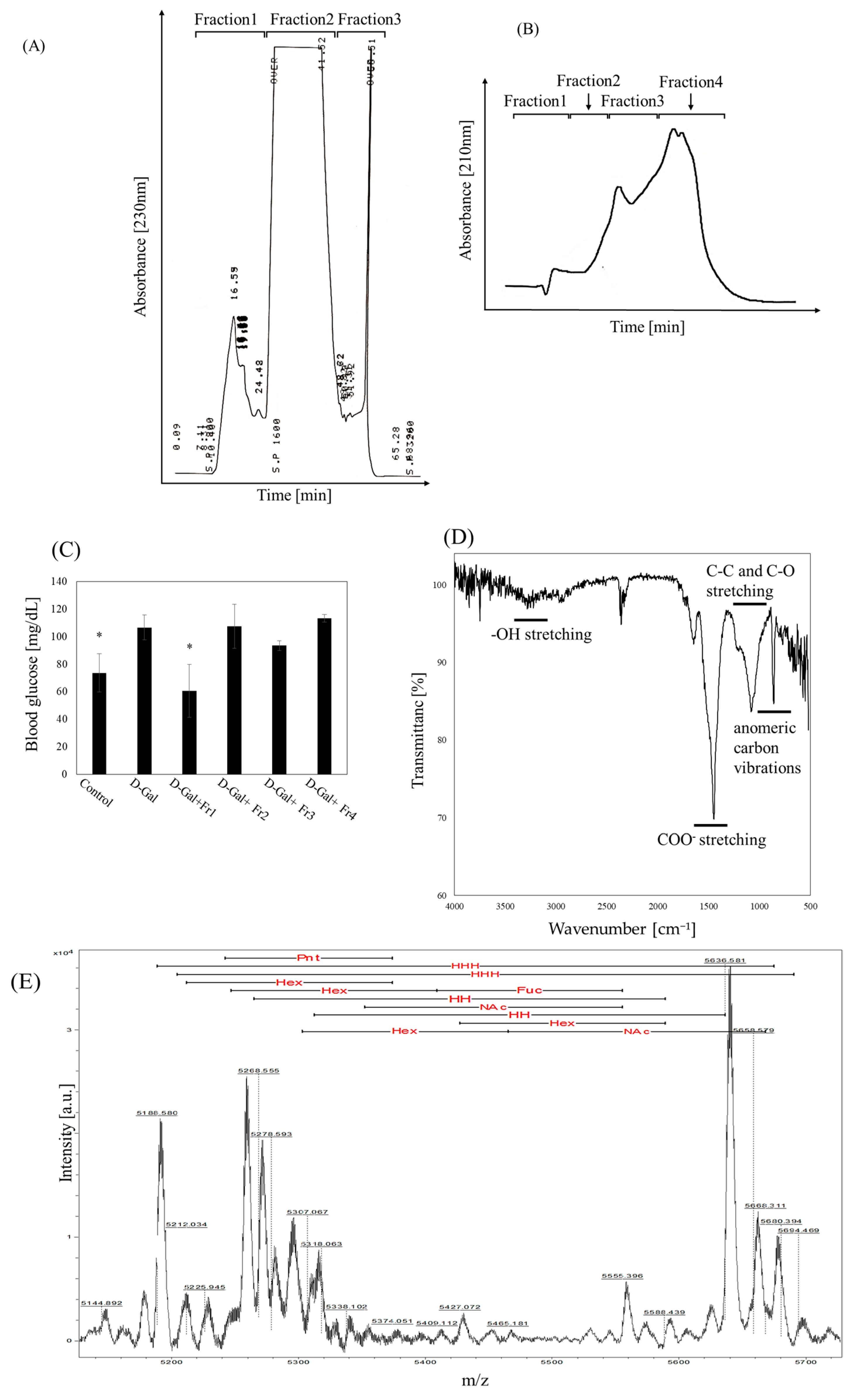


| Monosaccharide | nmol |
|---|---|
| GlcA | 0 |
| GalA | 0 |
| Gal | 5.8 |
| Man | 52.1 |
| Glc | 84.8 |
| Ara | 0 |
| Rib | 0 |
| Xyl | 9.5 |
| ManNAc | 0 |
| GlcNAc | 1.2 |
| Rha | 66.1 |
| Fuc | 2 |
| GalNAc | 11.7 |
| Total | 233.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Hasegawa, Y. Protective Effect of a Highly Enriched Nacre-Derived Neutral Polysaccharide Fraction on D-Galactose-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction. Molecules 2025, 30, 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173555
Zhang H, Hasegawa Y. Protective Effect of a Highly Enriched Nacre-Derived Neutral Polysaccharide Fraction on D-Galactose-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173555
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Heng, and Yasushi Hasegawa. 2025. "Protective Effect of a Highly Enriched Nacre-Derived Neutral Polysaccharide Fraction on D-Galactose-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173555
APA StyleZhang, H., & Hasegawa, Y. (2025). Protective Effect of a Highly Enriched Nacre-Derived Neutral Polysaccharide Fraction on D-Galactose-Induced Pancreatic Dysfunction. Molecules, 30(17), 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173555








