Cytochrome P450-Induced Backbone Rearrangements in Terpene Biosynthesis of Plants
Abstract
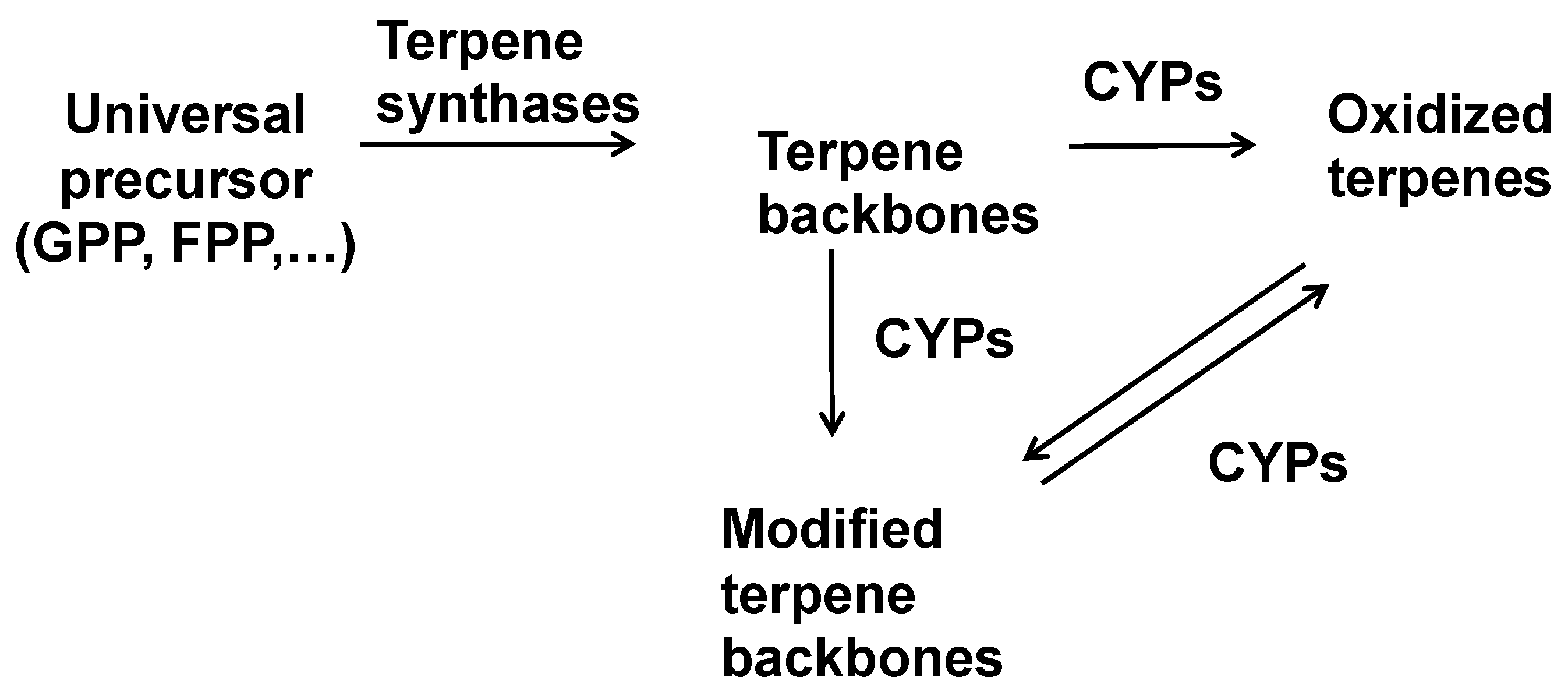
1. Introduction: The Modular Biosynthesis of Terpenes
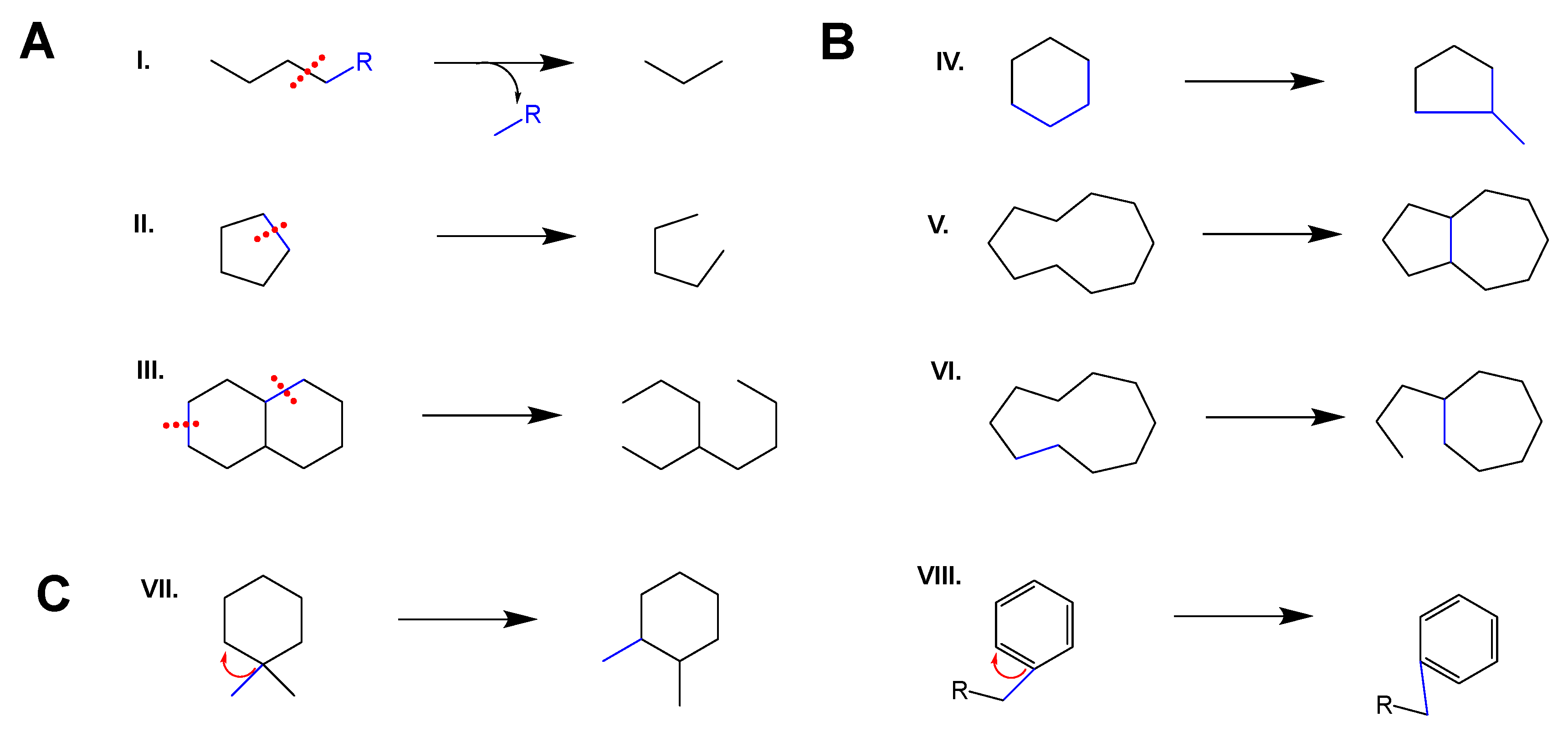
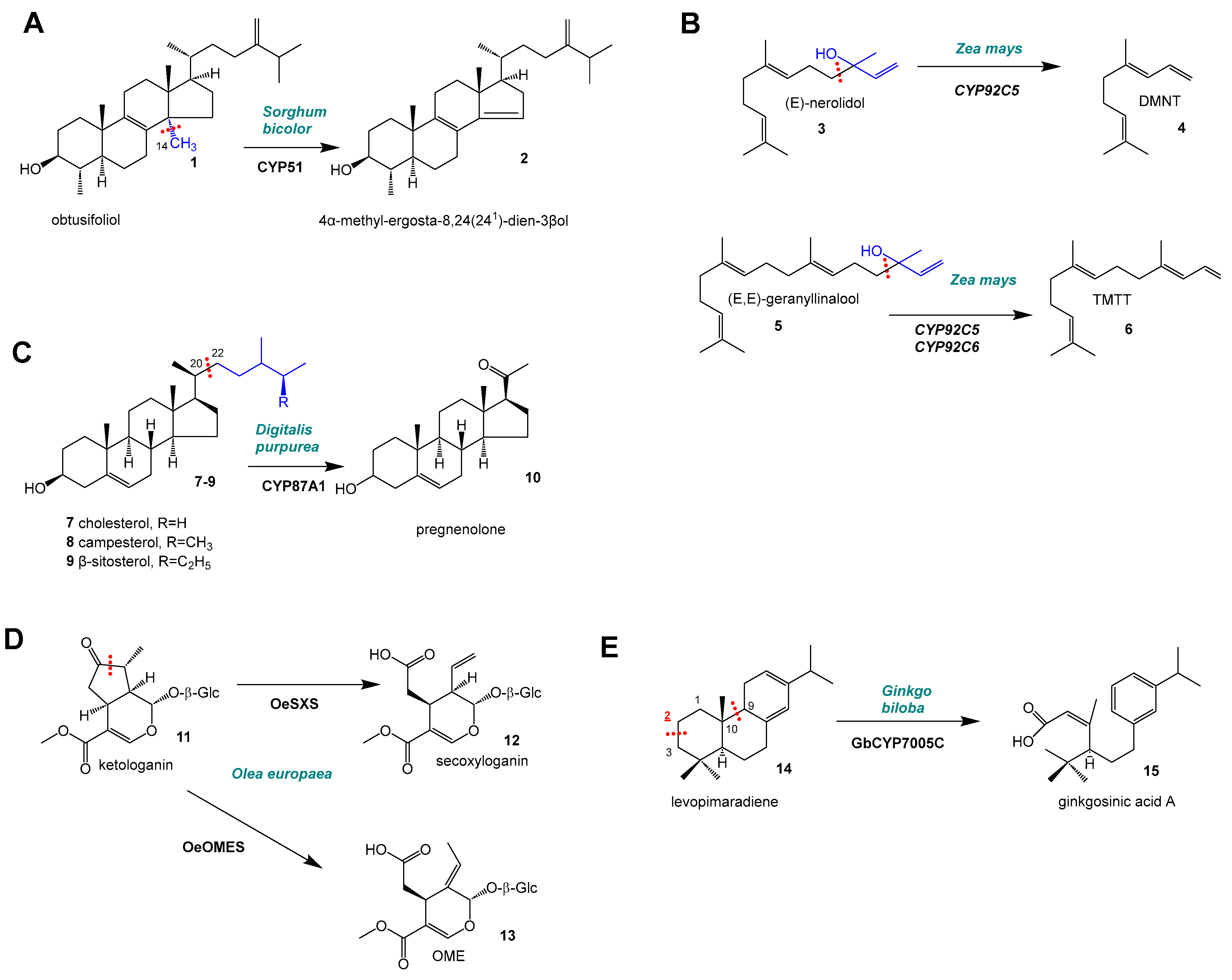
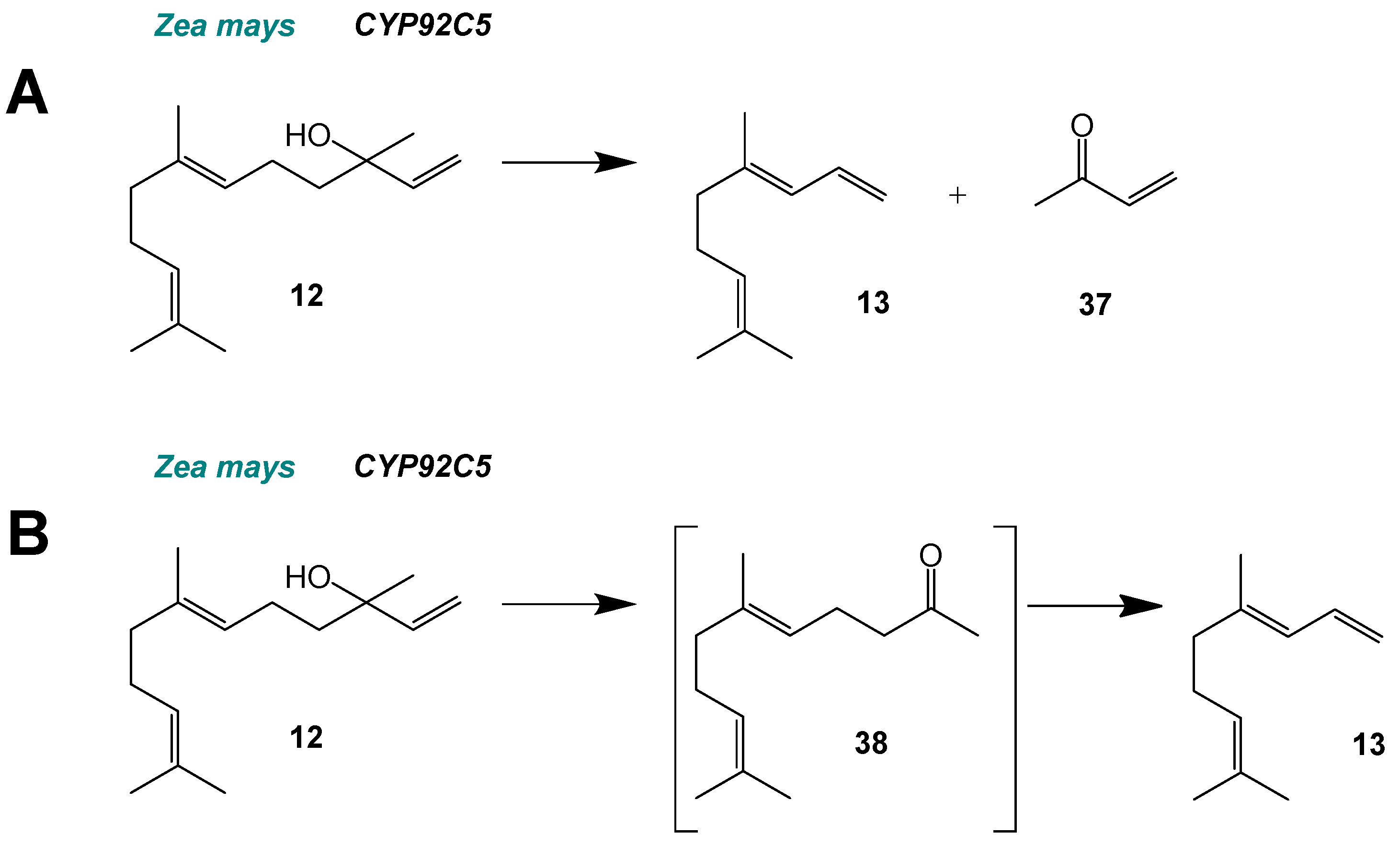
2. C–C Scission and Ring Opening
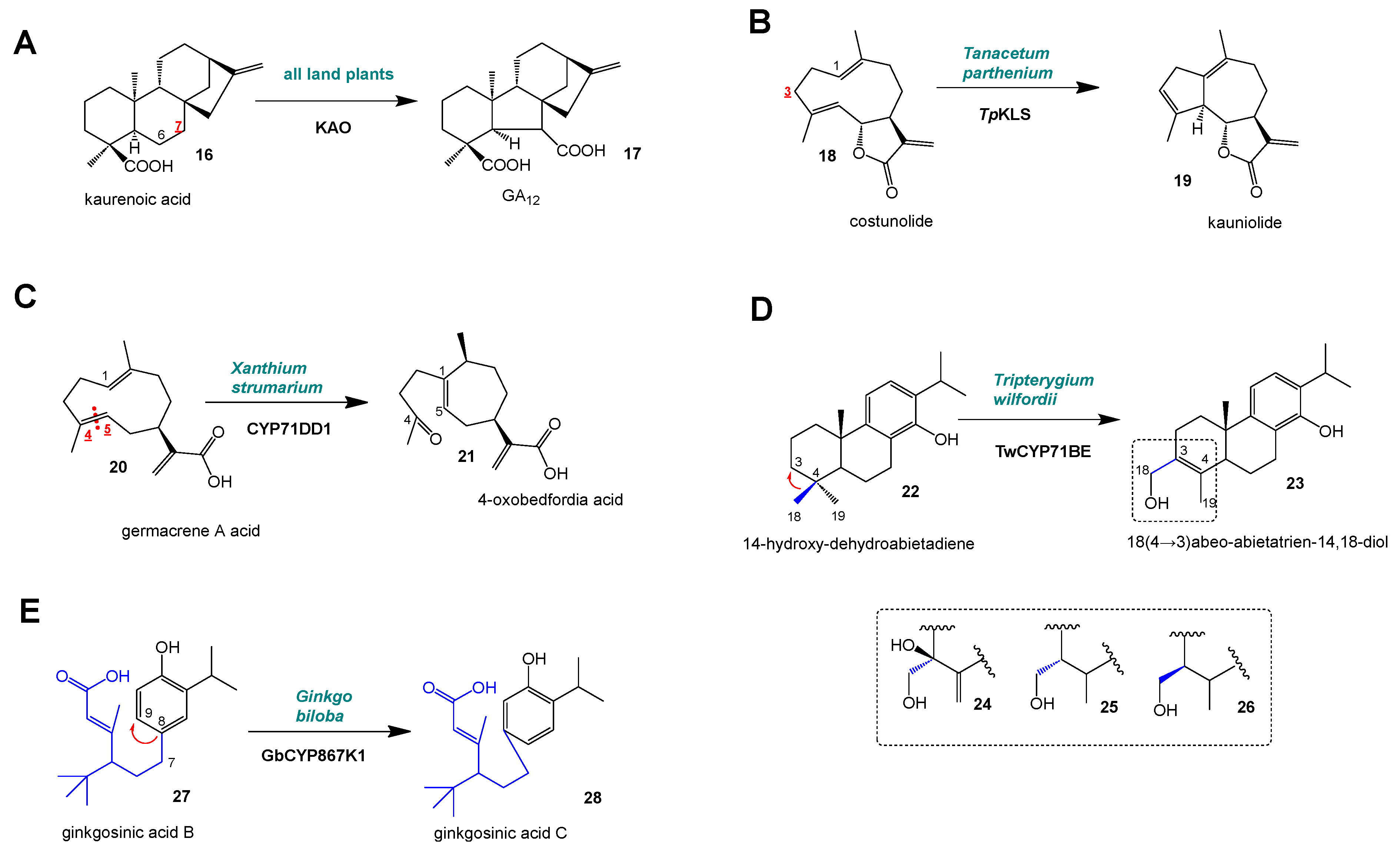
3. Ring Rearrangements of the Backbones (IV)–(VI)
4. Methyl/Alkyl Group Shifts
5. Underlying Mechanisms
5.1. Ring Rearrangement Mechanisms
5.2. Cleavage Mechanisms
5.3. Group Shift Mechanisms
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wink, M. Introduction: Biochemistry, Physiology and Ecological Functions of Secondary Metabolites. In Annual Plant Reviews Volume 40: Biochemistry of Plant Secondary Metabolism; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, M.; Bathe, U.; Meink, L.; Balcke, G.U.; Schmidt, J.; Frolov, A.; Soboleva, A.; Hassanin, A.; Davari, M.D.; Frank, O.; et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis in yeast leads to over 200 diterpenoids. Metab. Eng. 2024, 82, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pateraki, I.; Heskes, A.M.; Hamberger, B. Cytochromes P450 for terpene functionalisation and metabolic engineering. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 148, 107–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, A.; Schaff, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Köllner, T.G.; Schnee, C.; Preiß, S.; Irmisch, S.; Jander, G.; et al. Characterization of Biosynthetic Pathways for the Production of the Volatile Homoterpenes DMNT and TMTT in Zea mays. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, C.E.; Hong, B.; Paetz, C.; Nakamura, Y.; Koudounas, K.; Passeri, V.; Baldoni, L.; Alagna, F.; Calderini, O.; O’Connor, S.E. Two bi-functional cytochrome P450 CYP72 enzymes from olive (Olea europaea) catalyze the oxidative C–C bond cleavage in the biosynthesis of secoxy-iridoids—Flavor and quality determinants in olive oil. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, V.; Luo, D.; Geu-Flores, F.; Lemcke, R.; Nelson, D.R.; Kampranis, S.C.; Staerk, D.; Møller, B.L.; Pateraki, I. A gene cluster in Ginkgo biloba encodes unique multifunctional cytochrome P450s that initiate ginkgolide biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, C.A.; Poole, A.; James Peacock, W.; Dennis, E.S. Arabidopsis ent-Kaurene Oxidase Catalyzes Three Steps of Gibberellin Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, C.A.; Chandler, P.M.; Poole, A.; Dennis, E.S.; Peacock, W.J. The CYP88A cytochrome P450, ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase, catalyzes three steps of the gibberellin biosynthesis pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2065–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Beyraghdar Kashkooli, A.; Manzano, D.; Pateraki, I.; Richard, L.; Kolkman, P.; Lucas, M.F.; Guallar, V.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Franssen, M.C.R.; et al. Kauniolide synthase is a P450 with unusual hydroxylation and cyclization-elimination activity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, F.; Zheng, L.; Yang, L.; Sun, W.; Ro, D.-K.; Qu, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. An independent biosynthetic route to frame a xanthanolide-type sesquiterpene lactone in Asteraceae. Plant J. 2024, 121, e17199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.L.; Kjaerulff, L.; Heck, Q.K.; Forman, V.; Staerk, D.; Møller, B.L.; Andersen-Ranberg, J. Tripterygium wilfordii cytochrome P450s catalyze the methyl shift and epoxidations in the biosynthesis of triptonide. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, S.; Kahn, R.A.; Olsen, C.E.; Halkier, B.A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the obtusifoliol 14α-demethylase of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench, a cytochrome P450 orthologous to the sterol 14α-demethylases (CYP51) from fungi and mammals. Plant J. 1997, 11, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, C.; Rondet, S.; Benveniste, P.; Schaller, H. Virus-induced silencing of sterol biosynthetic genes: Identification of a Nicotiana tabacum L. obtusifoliol-14α-demethylase (CYP51) by genetic manipulation of the sterol biosynthetic pathway in Nicotiana benthamiana L. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Du, W.; Gao, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, M.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Schwab, W.; Wan, X.; et al. Herbivore-induced DMNT catalyzed by CYP82D47 plays an important role in the induction of JA-dependent herbivore resistance of neighboring tea plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Badieyan, S.; Bevan, D.R.; Herde, M.; Gatz, C.; Tholl, D. Herbivore-induced and floral homoterpene volatiles are biosynthesized by a single P450 enzyme (CYP82G1) in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21205–21210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, X.; Jing, W.; An, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. Identification and functional analysis of two P450 enzymes of Gossypium hirsutum involved in DMNT and TMTT biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Yi, G.; Zhang, X. Identification and characterization of two P450 enzymes from Citrus sinensis involved in TMTT and DMNT biosyntheses and Asian citrus psyllid defense. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, M.; Langley, C.; Lucier, R.; Ploss, K.; Rodríguez López, C.E.; Serna Guerrero, D.A.; Rothe, E.; O’Connor, S.E.; Sonawane, P.D. Promiscuous CYP87A enzyme activity initiates cardenolide biosynthesis in plants. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankar, K.; Hakkert, J.C.; Sevenier, R.; Campo, E.; Schipper, B.; Papastolopoulou, C.; Vahabi, K.; Tissier, A.; Bundock, P.; Bosch, D. CRISPR/Cas9 targeted inactivation of the kauniolide synthase in chicory results in accumulation of costunolide and its conjugates in taproots. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 940003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M.; Chantha, S.-C.; Rahier, A.; Matton, D.P. Lipid Signaling in Plants. Cloning and Expression Analysis of the Obtusifoliol 14α-Demethylase from Solanum chacoense Bitt., a Pollination- and Fertilization-Induced Gene with Both Obtusifoliol and Lanosterol Demethylase Activity. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taton, M.; Rahier, A. Properties and structural requirements for substrate specificity of cytochrome P-450-dependent obtusifoliol 14 α-demethylase from maize (Zea mays) seedlings. Biochem. J. 1991, 277, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strushkevich, N.; MacKenzie, F.; Cherkesova, T.; Grabovec, I.; Usanov, S.; Park, H.W. Structural basis for pregnenolone biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10139–10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, H.-P.; Mangold, U.; Schro, G.; Marner, F.-J.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Schro, J. Molecular Analysis and Heterologous Expression of an Inducible Cytochrome P-450 Protein from Periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus L.). Plant Physiol. 1992, 100, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Katano, N.; Ooi, A.; Inoue, K. Secologanin synthase which catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of loganin into secologanin is a cytochrome P450. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmler, S.; Schroder, G.; St-Pierre, B.; Crouch, N.P.; Hotze, M.; Schmidt, J.; Strack, D.; Matern, U.; Schroder, J. Indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus: New enzyme activities and identification of cytochrome P450 CYP72A1 as secologanin synthase. Plant J. 2000, 24, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yu, R.; Zhu, J. Establishment of recombinant Catharanthus roseus stem cells stably overexpressing ORCA4 for terpenoid indole alkaloids biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 196, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, F.C. Sesquiterpene lactones as taxonomic characters in the asteraceae. Bot. Rev. 1982, 48, 121–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Vahabi, K.; Cankar, K.; Lackus, N.D.; Padilla-Gonzalez, F.; Ro, D.-K.; Rieseberg, L.; Spring, O.; Tissier, A. Sesquiterpene Lactones—Insights into Biosynthesis, Regulation and Signalling Roles. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2024, 43, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, C.; Ruttink, T.; Lacchini, E.; Rombauts, S.; Haegeman, A.; De Keyser, E.; Van Poucke, C.; Desmet, S.; Jacobs, T.B.; Eeckhaut, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of CYP71 subclade cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of bitterness compounds in Cichorium intybus. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1200253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedden, P. The Current Status of Research on Gibberellin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1832–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M. Traps and Pitfalls-Unspecific Reactions in Metabolic Engineering of Sesquiterpenoid Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Schmauder, K.; Pateraki, I.; Spring, O. Biosynthesis of Eupatolide-A Metabolic Route for Sesquiterpene Lactone Formation Involving the P450 Enzyme CYP71DD6. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda-Acosta, J.; Fischer, N.H.; Vargas, D. Biomimetic transformations of parthenolide. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankar, K.; Hakkert, J.C.; Sevenier, R.; Papastolopoulou, C.; Schipper, B.; Baixinho, J.P.; Fernández, N.; Matos, M.S.; Serra, A.T.; Santos, C.N.; et al. Lactucin Synthase Inactivation Boosts the Accumulation of Anti-inflammatory 8-Deoxylactucin and Its Derivatives in Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6061–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, W.; Gäbler, A. Biosynthesis of Homoterpenes in Higher Plants. Helv. Chim. Acta 1989, 72, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, A.; Boland, W.; Preiss, U.; Simon, H. Stereochemical Studies on Homoterpene Biosynthesis in Higher Plants; Mechanistic, Phylogenetic, and Ecological Aspects. Helv. Chim. Acta 1991, 74, 1773–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.T.; Eriksson, R.; Gershenzon, J.; Ståhl, B. Diversity and distribution of floral scent. Bot. Rev. 2006, 72, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, W.; Gäbler, A.; Gilbert, M.; Feng, Z. Biosynthesis of C11 and C16 homoterpenes in higher plants; stereochemistry of the C–C-bond cleavage reaction. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 14725–14736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, F.; Li, C.; Ma, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Pickett, J.A.; Zhou, J.-J.; Lin, Y. Overexpression of the homoterpene synthase gene, OsCYP92C21, increases emissions of volatiles mediating tritrophic interactions in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.A.D. Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry; Sir Barton, D., Nakanishi, K., Meth-Cohn, O., Eds.; Pergamon: Berlin, Germany, 1999; pp. 367–400. [Google Scholar]

| Type | Reactions (References) | P450 Subfamily | Enzymes | Number * | Terpene Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | C–C scission, cleaving of C1 unit, demethylation of obtusifoliol ([12,13]) | CYP51G | 3 | Triterpene | |
| I | C–C scission, cleave of a four (-C4) unit from sesquiterpene or diterpene precursors to produce C11- or C16-homoterpenes ([4,14,15,16,17]) | CYP92C | CYP92C5,6 | 2 | Sesqui-/Diterpene |
| CYP82D/G/L | 4 | ||||
| I | C–C scission, cleaving of side chains of various lengths (C6–C8) to produce cardenolides via pregnenolone ([18]) | 3 | Triterpene | ||
| II | C–C scission in the formation of secoiridoids ([5]) | CYP72A | SLAS, SLS, SXS, OMES | 4 | Monoterpene |
| III | C–C scission, ring opening of ring A and ring B in levopimaradiene ([6]) | CYP7005C | CYP7005C1/C3 | 2 | Diterpene |
| IV | Ring contraction of kaurenoic acid B ring in the gibberellin biosynthesis ([8]) | CYP88A | KAO | >10 | Diterpene |
| V | Ring rearrangement, transannular cyclization, formation of 6,7-trans guaianolides ([9,19]) | CYP71BZ | KLS | 4 | Sesquiterpene |
| VI | Ring rearrangement, transannular cyclization, formation of 7,8-trans xanthanolides ([10]) | CYP71DD | CYP72DD1 | 1 | Sesquiterpene |
| VII | Methyl group shift, 18 (4 → 3), via Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement ([11]) | CYP71BE | 2 | Diterpene | |
| VIII | Alkyl group shift along aromatic ring from C8 to C9 of ginkgosinic acid B ([6]) | CYP867K | GbCYP867K1 | 1 | Diterpene |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frey, M.; Jochimsen, C.M.; Degenhardt, J. Cytochrome P450-Induced Backbone Rearrangements in Terpene Biosynthesis of Plants. Molecules 2025, 30, 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173540
Frey M, Jochimsen CM, Degenhardt J. Cytochrome P450-Induced Backbone Rearrangements in Terpene Biosynthesis of Plants. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173540
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrey, Maximilian, Christina Marie Jochimsen, and Jörg Degenhardt. 2025. "Cytochrome P450-Induced Backbone Rearrangements in Terpene Biosynthesis of Plants" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173540
APA StyleFrey, M., Jochimsen, C. M., & Degenhardt, J. (2025). Cytochrome P450-Induced Backbone Rearrangements in Terpene Biosynthesis of Plants. Molecules, 30(17), 3540. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173540






