Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Gastrodiae Rhizoma Peel and Core and Their Lifespan-Extending Potential in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HPLC Analysis
2.2. GC–IMS Analysis
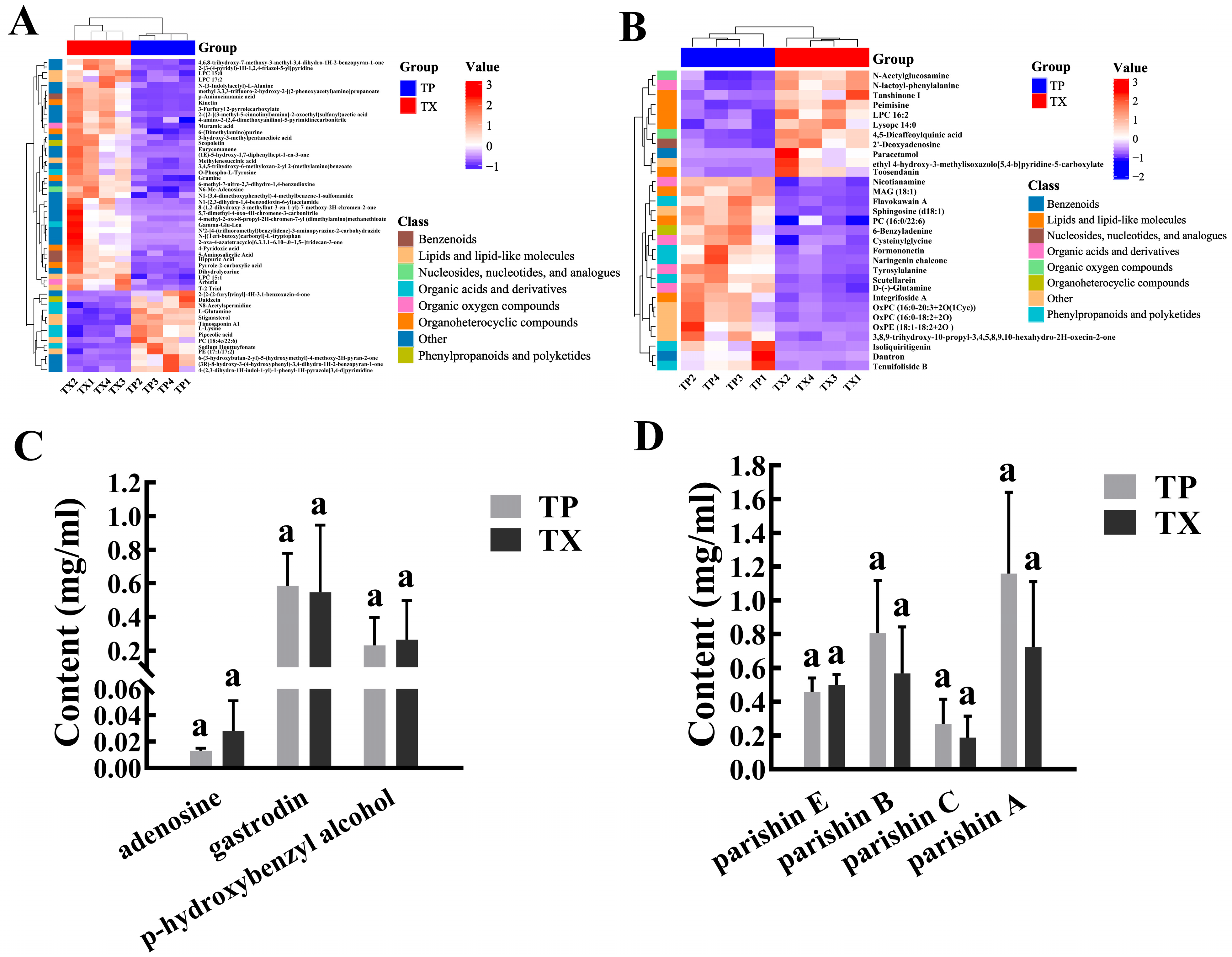
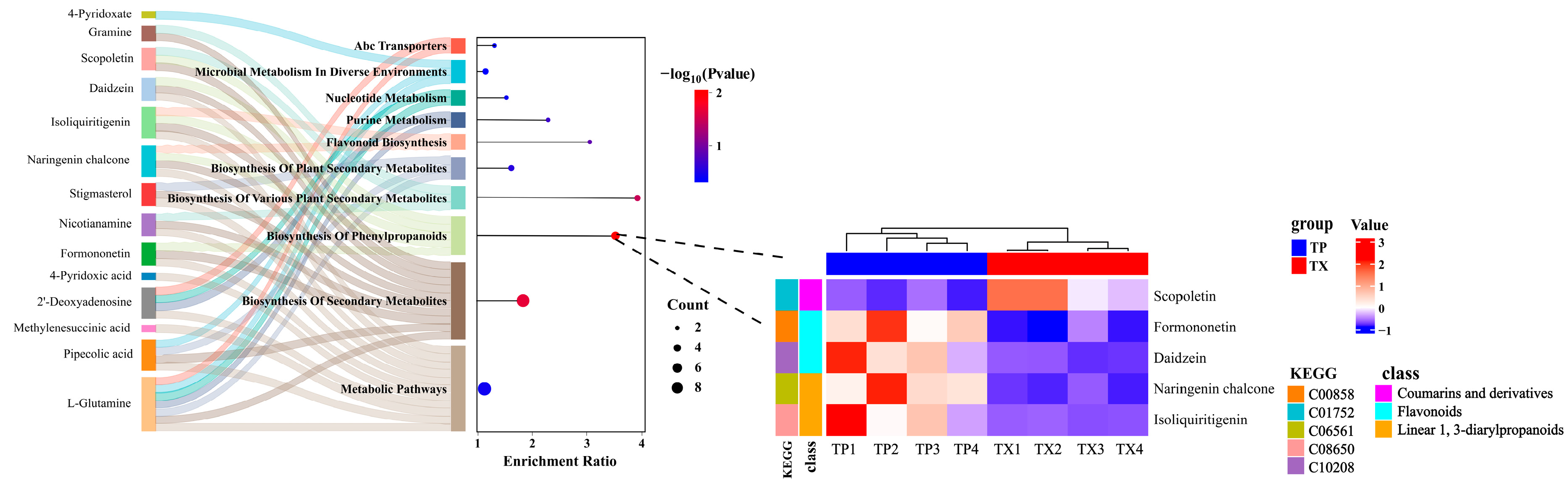
2.3. Metabolomics Analysis
2.4. Lifespan-Extending Potential Analysis
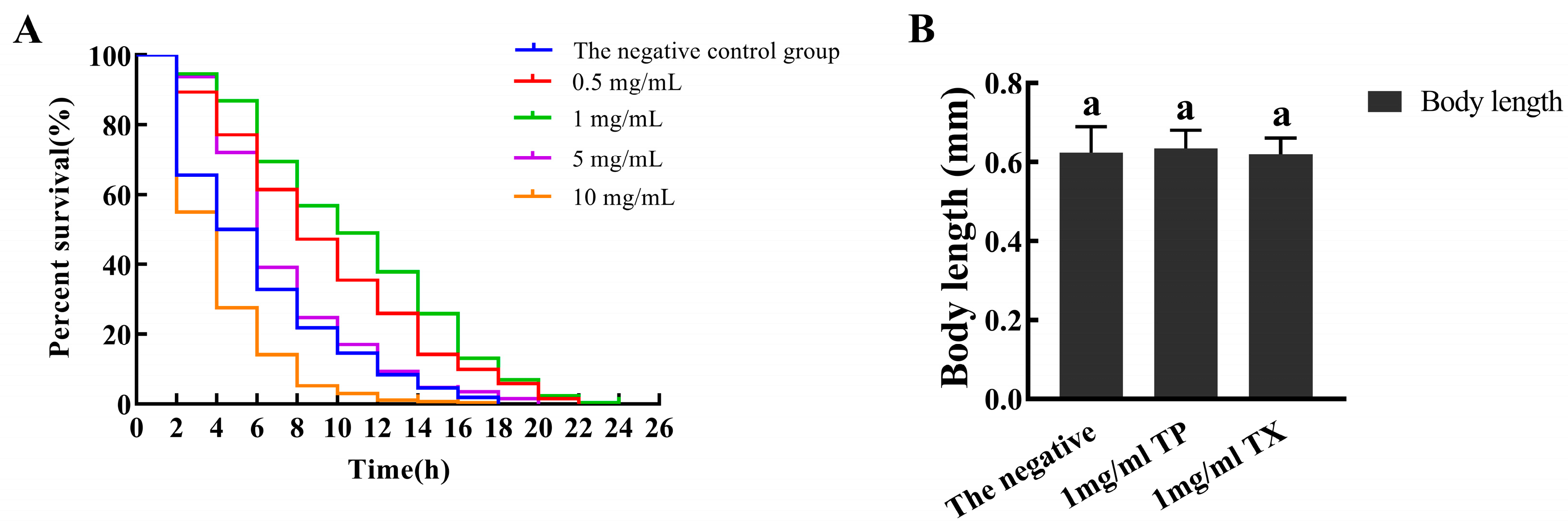
2.4.1. Multiple-Concentration Screening of Test Concentration of the TP
2.4.2. Effects of the TP and TX on the Lifespan of C. elegans
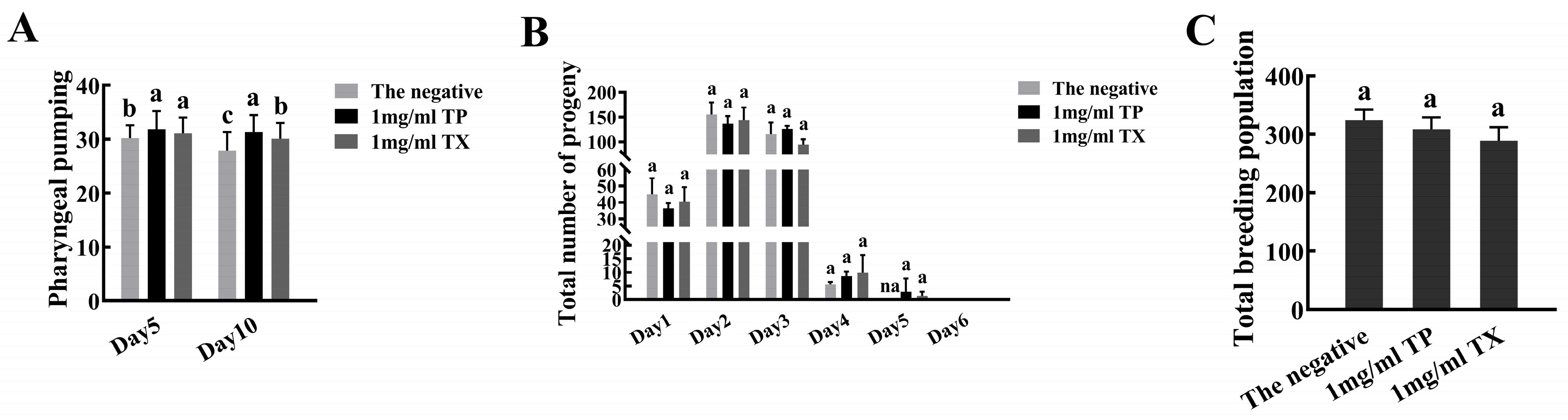
2.4.3. Effects of the TP and TX on the Healthspan of C. elegans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of the Whole TM, TP and TX
4.3. HPLC Analysis
4.3.1. Chromatographic Conditions
4.3.2. Fingerprints Similarity Evaluation
4.3.3. Standard Solution Preparation
4.3.4. Sample Preparation
4.3.5. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses
4.4. GC–IMS Analysis
4.5. LC-MS Analysis
4.6. Lifespan-Extending Potential of Different Parts of TM in C. elegans
4.6.1. Preparation of Different Parts of TM Water Extract Administration Extract Solution
4.6.2. Culture of E. coli OP50 and C. elegans
4.6.3. Multiple-Concentration Screening of the Drug Group and Design of Experimental Groups
4.6.4. Measurements of Body Length
4.6.5. Lifespan Assay
4.6.6. Reproduction Assays
4.6.7. Pharyngeal Pumping
4.6.8. Heat Stress and Oxidative Stress Tests
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, F.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, C.; Liu, L. History of consumption of Gastrodia elata Bl and proposals for its development. China Food Drug Adm. 2021, 3, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. The traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Gastrodia elata Blume: A comprehensive review. Arab. J. Chem. 2025, 18, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, F.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, M.; Yan, Y.; et al. Anti-depressant-like effect of fermented Gastrodia elata Bl. by regulating monoamine levels and BDNF/NMDAR pathways in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, N.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, L.; Su, J.; et al. Gastrodin Improves the Activity of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway to Degrade Mutant Huntingtin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, M.Z.; Liu, X.M. Protective effect of Gastrodia elata Blume ameliorates simulated weightlessness-induced cognitive impairment in mice. Life Sci. Space Res. 2023, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Cui, Y.; Xu, T.; Lu, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Zhao, P.; et al. Bioactivities and chemical profiling comparison and metabolomic variations of polyphenolics and steroidal glycoalkaloids in different parts of Solanum nigrum L. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 35, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, R.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; Song, N.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.; et al. Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin Improve Energy Metabolism Disorders and Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Antagonize Vascular Dementia. Molecules 2023, 28, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Qiu, D.; Hu, G. In situ analysis of volatile oil in Angelica sinensis roots by fluorescence imaging combined with mass spectrometry imaging. Talanta 2023, 255, 124253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Ma, C.; Irge, D.D.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Gastrodia elata and parishin ameliorate aging induced ‘leaky gut’ in mice: Correlation with gut microbiota. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Lei, M.; Li, F.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Long, H.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, C.; Wu, W. Structural Characterization of a Polysaccharide from Gastrodia elata and Its Bioactivity on Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Zhang, W.; Dou, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Dou, H. Towards a better understanding of the relationships between the structure and antitumor activity of Gastrodia elata polysaccharides by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Huang, N.-K.; Shiao, Y.-J.; Lu, C.-K.; Chao, Y.-M.; Huang, Y.-J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-L. Gastrodiae rhizoma attenuates brain aging via promoting neuritogenesis and neurodifferentiation. Phytomedicine 2021, 87, 153576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Osada, H.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Structure Characterization and Action Mechanism of an Antiaging New Compound from Gastrodia elata Blume. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5459862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Health Commission and the State Administration for Market Regulation. Announcement on 9 New Substances Including Codonopsis pilosula That are Traditionally Used as Both Food and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Available online: https://www.samr.gov.cn/xw/sj/art/2023/art_8d005589c2914083a4aa9442102babf8.html (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Gong, W.; Zhan, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Huang, B.; Liu, D. Literature Researching Again on Gastrodia elata. Mod. Chin. Med. 2018, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Zhai, X.; Wu, h.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, J. Materia medica research on the correlation of “processing in producing area-processing-quality evaluation” of Gastrodia elata. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2020, 43, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, X.; Zhang, X.; Kong, K.W.; Xie, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Integration of volatile and non-volatile metabolite profile, and in vitro digestion reveals the differences between different preparation methods on physico-chemical and biological properties of Gastrodia elata. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopoeia, C.N. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 1st ed.; Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dossou, S.S.K.; Xu, F.; Cui, X.; Sheng, C.; Zhou, R.; You, J.; Tozo, K.; Wang, L. Comparative metabolomics analysis of different sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) tissues reveals a tissue-specific accumulation of metabolites. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhan, C.; Yang, C.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. Metabolomics-centered mining of plant metabolic diversity and function: Past decade and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J. Study on Quality Assessment and Processing of Tianma Decoction Pieces. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M. Study on Quality Assessment and Processing of Gastrodia elata from ShanXi Hanzhong. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kotta, L.R.; Vijayalakshmi, A. Metabolic profiling of plant constituents through LC-MS. Ann. Phytomedicine Int. J. 2024, 13, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, N.S. Plants Metabolome Study: Emerging Tools and Techniques. Plants 2021, 10, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Huang, H.; Fang, Y.; Qin, X.; Ma, Y.; Rao, C.; Gao, J. Analysis of aroma components in Gastrodia elata based on HS-SPME-GC-MS. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2023, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Yao, B.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, H. The qualitative identification mechanism of different grades of Gastrodiae Rhizoma based on odor and the construction of its qualitative identification model. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2025, 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1546.R.20250121.1140.006 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Recent progress in food flavor analysis using gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry (GC–IMS). Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Dual Challenges in the Context of Healthy Aging: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Association Between Malnutrition and Cognitive Decline in Disabled Elderly. Aging Dis. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Xiu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Gastrodin extends the lifespan and protects against neurodegeneration in the Drosophila PINK1 model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7816–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Yan, R.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, C.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Parishin treatment alleviates cardiac aging in naturally aged mice. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Shiao, Y.-J.; Chao, Y.-M.; Huang, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-L. T1-11, an adenosine derivative, ameliorates aging-related behavioral. Aging 2020, 12, 10556–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Yue, Y.; Park, Y. A living model for obesity and aging research: Caenorhabditis elegans. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bahramimehr, F.; Shahhamzehei, N.; Fu, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Efferth, T.; Hong, C. Anti-aging effects of medicinal plants and their rapid screening using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeayeng, S.; Thongsroy, J.; Chuaijit, S. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model to Study Aging and Photoaging. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slade, L.; Etheridge, T.; Szewczyk, N.J. Consolidating multiple evolutionary theories of ageing suggests a need for new approaches to study genetic contributions to ageing decline. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lin, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Caenorhabditis elegans as an in vivo model for the identification of natural antioxidants with anti-aging actions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, L.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characteristic fingerprints and volatile flavor compound variations in Liuyang Douchi during fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, J. Characteristic flavor compounds in Guizhou green tea and the environmental factors influencing their formation: Investigation using stable isotopes, electronic nose, and headspace-gas chromatography ion migration spectrometry. LWT 2024, 196, 115887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Shen, Y. Characterization and metabolism pathway of volatile compounds in walnut oil obtained from various ripening stages via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC–MS. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Li, P.; Yao, J.; Xiong, J. Determination of potential off-flavour in yeast extract. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimaa Awadain, E.; Buettner, A. Influence of the chemical structure on the odor characters of β-citronellol and its oxygenated derivatives. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, Z. Volatile compounds, affecting factors and evaluation methods for rice aroma: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Geng, C. Chemical and biological comparison of different parts of Paeonia suffruticosa (Mudan) based on LCMS-IT-TOF and multi-evaluation in vitro. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 144, 112028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, P.; Hu, X.; Li, J. Comprehensive evaluation of aroma and taste properties of different parts from the wampee fruit. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Liao, S.; Xing, D.; Chen, R.; Pang, D.; Zou, Y. Comparative study of intelligent sensory technologies combined multiple metabolomics in evaluating sensory attributes and health profiles across different grades and varieties of green tea-processed mulberry leaf tea. Food Chem. X 2025, 28, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Arellano, I.; Flores, M.; Toldrá, F. The ability of peptide extracts obtained at different dry cured ham ripening stages to bind aroma compounds. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, S. Geraniol and β-citronellol participate in the vasorelaxant effects of Rosa damascena Miller essential oil on the rat thoracic aorta. Fitoterapia 2022, 161, 105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder Veras, R.-F.; Camila Meirelles, d.S.S.; de Siqueira, R.J.; Saad, L.; Armênio Aguiar, d.S.; Pedro Jorge Caldas, M. Biphasic cardiovascular and respiratory effects induced by β-citronellol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 775, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, J.M.; Espitia, P.J.P.; Batista, R.A. Formononetin: Biological effects and uses—A review. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddha, A.P.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Daidzein ameliorates peripheral neuropathy in Sprague Dawley rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1385419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddha, A.P.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicity, and formulations of daidzein: An important isoflavone. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 2578–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerra, V.G.; Kalvala, A.K.; Kumar, A. Isoliquiritigenin reduces oxidative damage and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by SIRT1 activation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 47, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Ke, L.; Nie, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, C.; Liu, X. Sake lees extract obtained using a novel continuous phase-transition extraction method: Evaluation of its bioactive composition, anti-aging efficacy and mechanism. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 3862–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchweger, B.; Zwirchmayr, J.; Grienke, U.; Rollinger, J.M. The role of Caenorhabditis elegans in the discovery of natural products for healthy aging. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1849–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Sun, X. Quality assessment of Panax notoginseng flowers based on fingerprinting using high-performance liquid chromatography–PDA. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 40, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Feng, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S.; Geng, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; et al. Application of HPLC Fingerprint Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Multi-Component Determination in Quality Evaluation of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench. Molecules 2022, 27, 6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Lei, W.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Tu, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. Metabolomics and volatilomics unravel the signature of pivotal bioactive metabolites in sea buckthorn juice and pomace under hydrolysis of cellulase and pectinase. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendy, H.; Insanu, M.; Fidrianny, I. Extracts, Fractions, and Subfractions from Purple-Orange Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.): Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Potential and Antioxidant Properties. Molecules 2025, 30, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Xie, D.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Lv, H.; Yang, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characterization of white tea metabolome: Comparison against green and black tea by a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; Du, B. Anti-aging Effect of Polysaccharide from Dendrobium officinale Leaves in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-de-la-Riva, M.; Fontrodona, L.; Villanueva, A.; Cerón, J. Basic Caenorhabditis elegans Methods: Synchronization and Observation. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 64, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yu, G.; Zuo, Y.; Pei, S. The Normalize Harvest Process and Classification of the Gastrodia elata. For. By-Prod. Spec. China 2015, 4, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhan, Y. The differentiation of total polyphenols and total flavonoids contents in Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. Chow extracts using different solvents and their antioxidant capacities. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

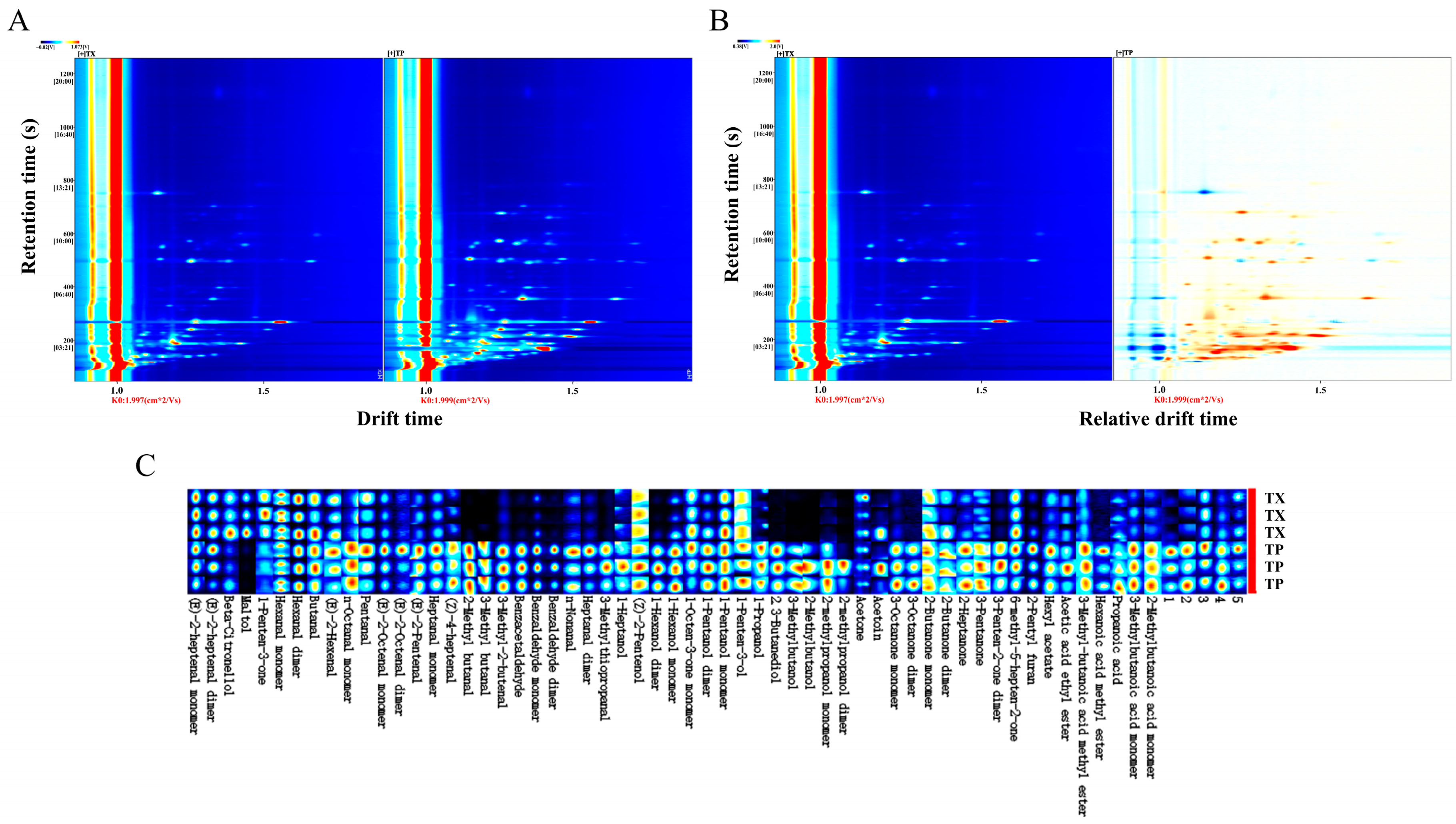
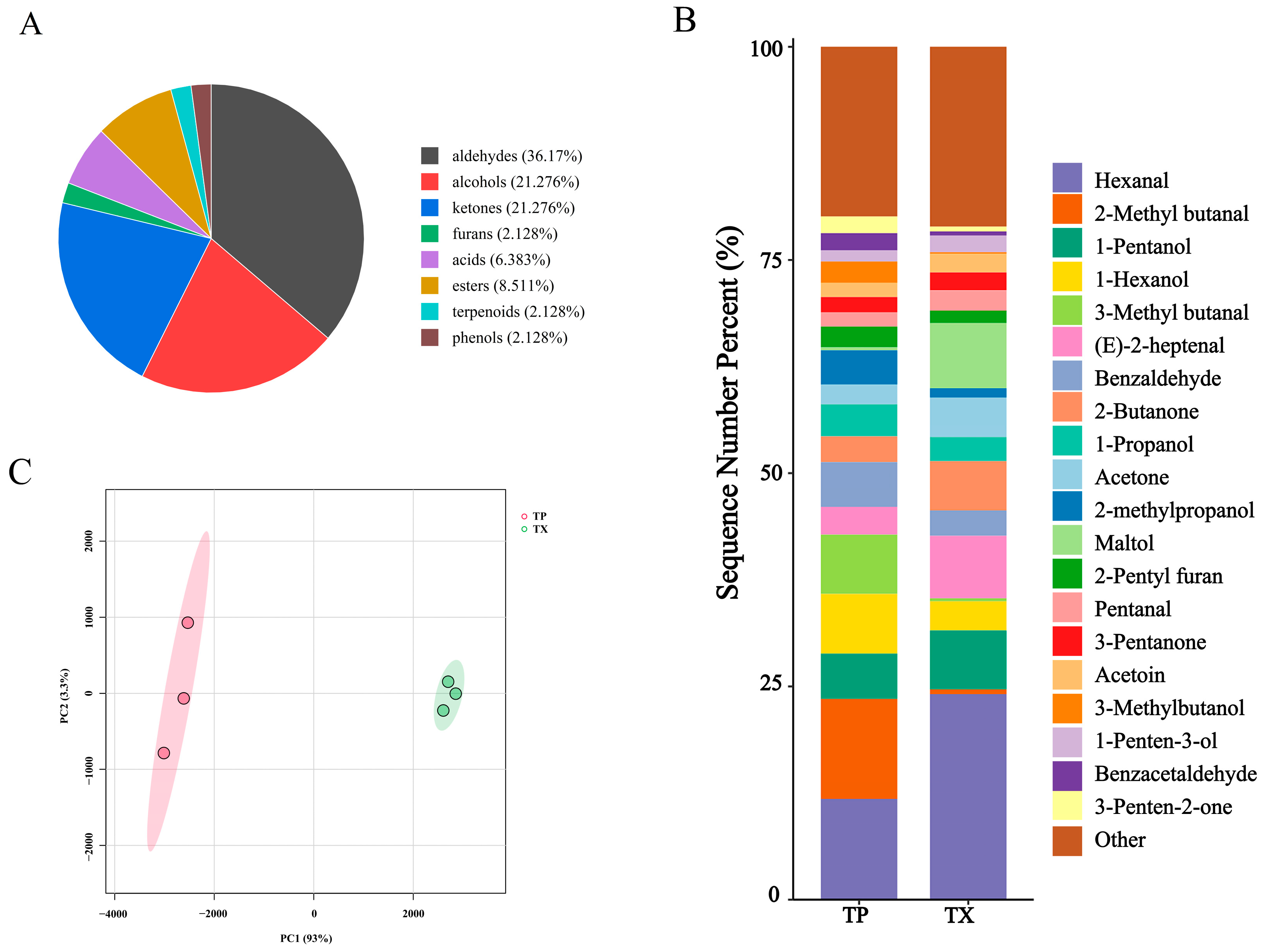
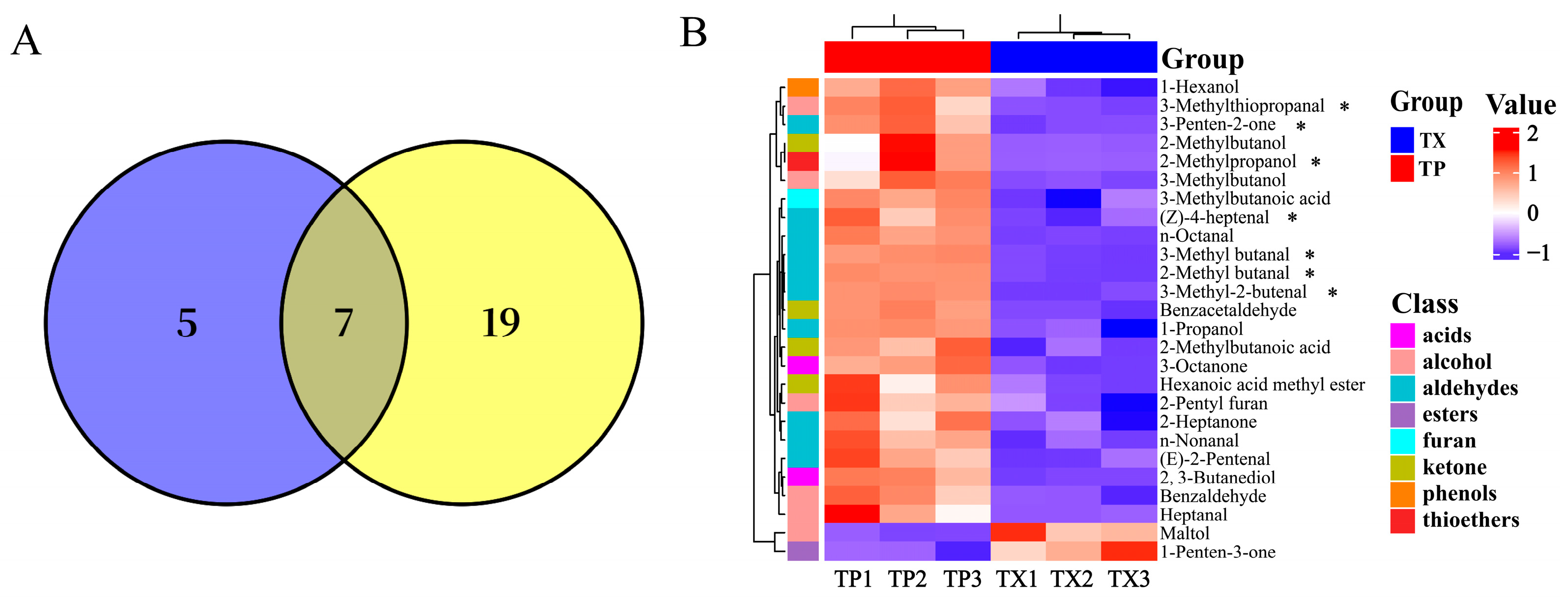
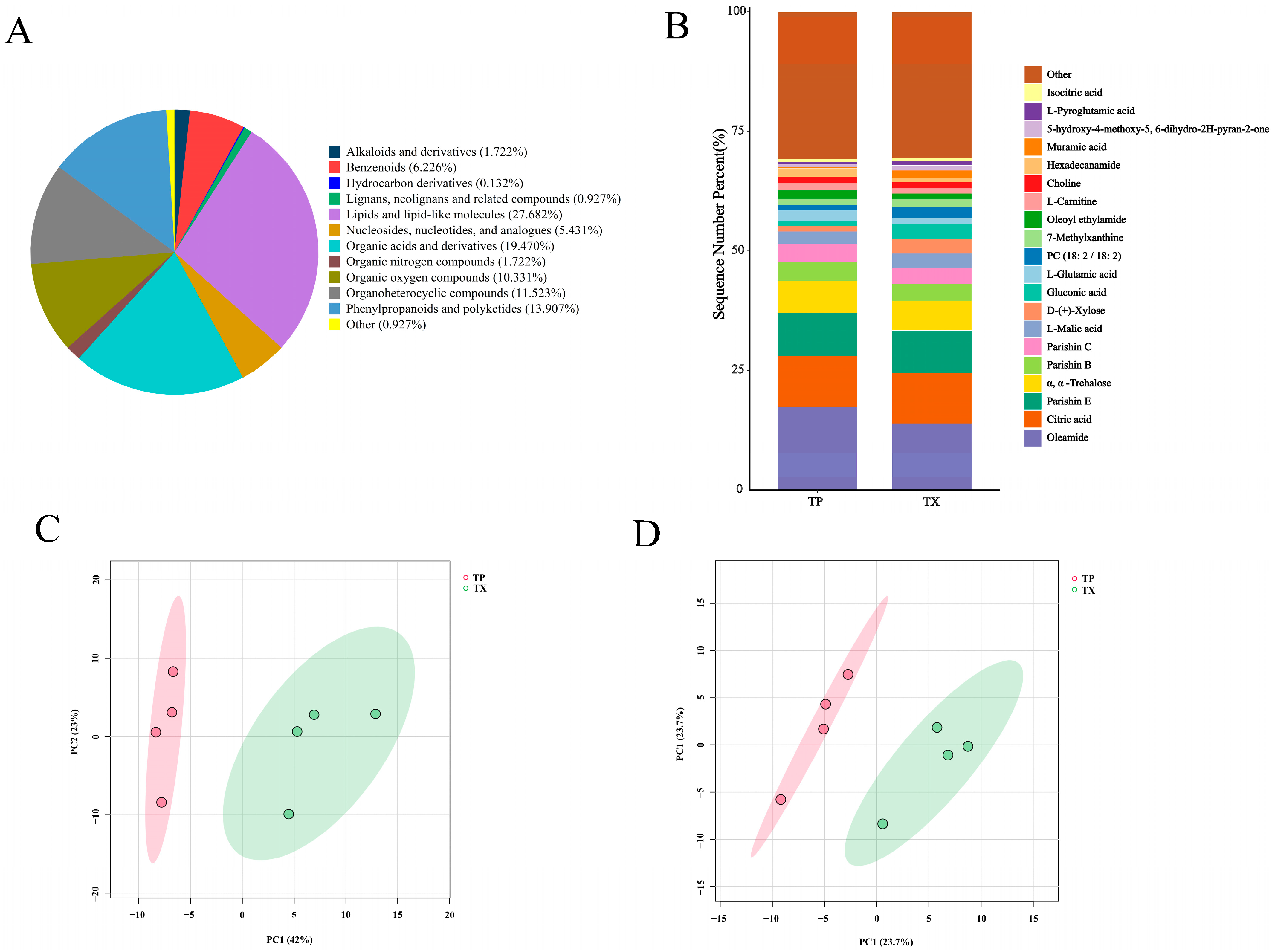


| Number | Similarity | Number | Similarity | Number | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM1 | 0.967 | TP1 | 0.972 | TX1 | 0.959 |
| TM2 | 0.971 | TP2 | 0.971 | TX2 | 0.967 |
| TM3 | 0.98 | TP3 | 0.969 | TX3 | 0.889 |
| TM4 | 0.984 | TP4 | 0.867 | TX4 | 0.974 |
| Compound | Threshold Odor (μg/L) | ROAV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TX | TP | ||
| (Z)-4-heptenal | 0.0034 | 43.622 | 100 |
| Beta-Citronellol | 0.01 | 100 | 53.939 |
| Hexanal | 0.23 | 46.259 | 42.304 |
| 1-Pentanol | 0.153 | 19.722 | 28.57 |
| 1-Octen-3-one | 0.016 | 14.838 | 11.881 |
| 2-methylpropanol | 0.33 | 1.495 | 9.959 |
| 3-Methyl-2-butenal | 0.5 | <1 | 1.916 |
| 2-Butanone | 1.3 | 1.926 | 1.915 |
| 2-Methyl butanal | 5.2 | <1 | 1.861 |
| 3-Methylthiopropanal | 0.43 | <1 | 1.359 |
| 3-Penten-2-one | 1.2 | <1 | 1.339 |
| 3-Methyl butanal | 5.4 | <1 | 1.061 |
| Group | Average Life/h | Median Life/h | Longest Life/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| The negative control group | 6.066 ± 0.261 D | 6 | 16.667 ± 2.309 A |
| 0.5 mg/mL | 9.523 ± 0.323 B | 8 | 20.667 ± 1.155 A |
| 1 mg/mL | 10.950 ± 0.328 A | 10 | 22.000 ± 2.000 A |
| 5 mg/mL | 8.344 ± 0.289 C | 6 | 18.667 ± 4.163 A |
| 10 mg/mL | 4.148 ± 0.166 E | 4 | 14.667 ± 4.163 A |
| Group | Average Life/h | Median Life/h | Longest Life/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| The negative control group | 18.317 ± 0.934 B | 18 | 25.333 ± 1.155 Bc |
| 1 mg/mL the TP group | 20.878 ± 0.201 A | 20 | 33.333 ± 1.155 Aa |
| 1 mg/mL the TX group | 20.472 ± 0.347 A | 20 | 28.667 ± 1.155 Bb |
| Group | Average Life/h | Median Life/h | Longest Life/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| The negative control group | 6.451 ± 0.415 B | 4 | 36.670 ± 1.155 A |
| 1 mg/mL the TP group | 11.674 ± 0.602 A | 8 | 36.670 ± 2.309 A |
| 1 mg/mL the TX group | 10.388 ± 0.659 A | 6 | 37.330 ± 1.155 A |
| Group | Average Life/h | Median Life/h | Longest Life/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| The negative control group | 6.378 ± 0.098 B | 6 | 10.000 ± 0.000 b |
| 1 mg/mL the TP group | 7.267 ± 0.099 A | 6 | 11.333 ± 1.1547 ab |
| 1 mg/mL the TX group | 7.356 ± 0.109 A | 6 | 12.667 ± 1.1547 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Mo, K.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Z. Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Gastrodiae Rhizoma Peel and Core and Their Lifespan-Extending Potential in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2025, 30, 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173474
Li B, Mo K, Zhou L, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang W, Zhu C, Sun Z. Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Gastrodiae Rhizoma Peel and Core and Their Lifespan-Extending Potential in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173474
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Baoshan, Ke Mo, Lipeng Zhou, Yanjun Wang, Yaping Li, Wei Zhang, Chenghao Zhu, and Zhirong Sun. 2025. "Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Gastrodiae Rhizoma Peel and Core and Their Lifespan-Extending Potential in Caenorhabditis elegans" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173474
APA StyleLi, B., Mo, K., Zhou, L., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, C., & Sun, Z. (2025). Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Gastrodiae Rhizoma Peel and Core and Their Lifespan-Extending Potential in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules, 30(17), 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173474






