Salivary C-Reactive Protein: A Non-Invasive Alternative to Serum CRP in Pediatric Acute Appendicitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient’s Clinical Data
2.2. Other Clinical Indicators of Acute Appendicitis
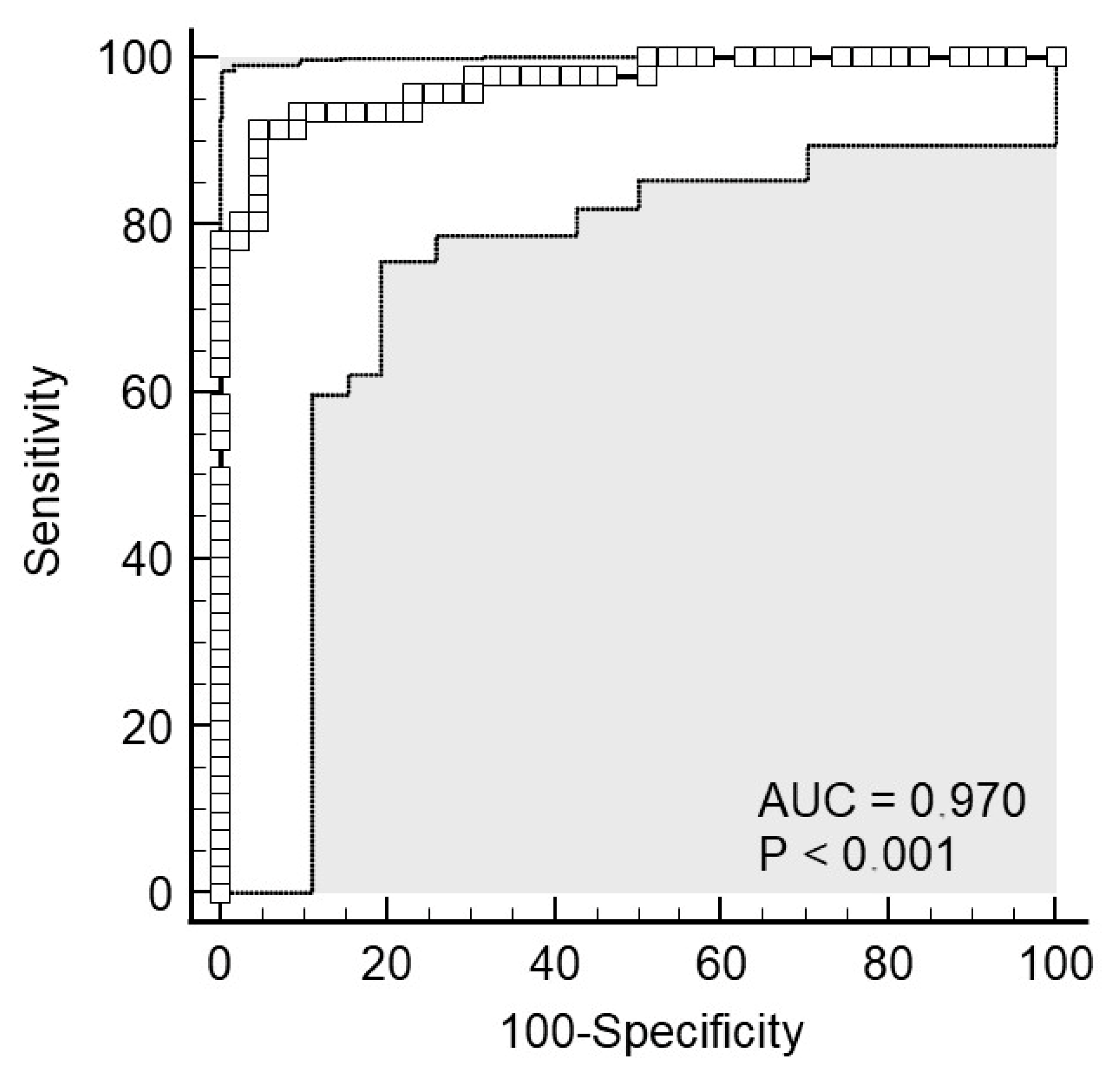
2.3. CRP from Serum as a Biomarker of Acute Appendicitis
2.4. CRP from Saliva as a Biomarker of Acute Appendicitis
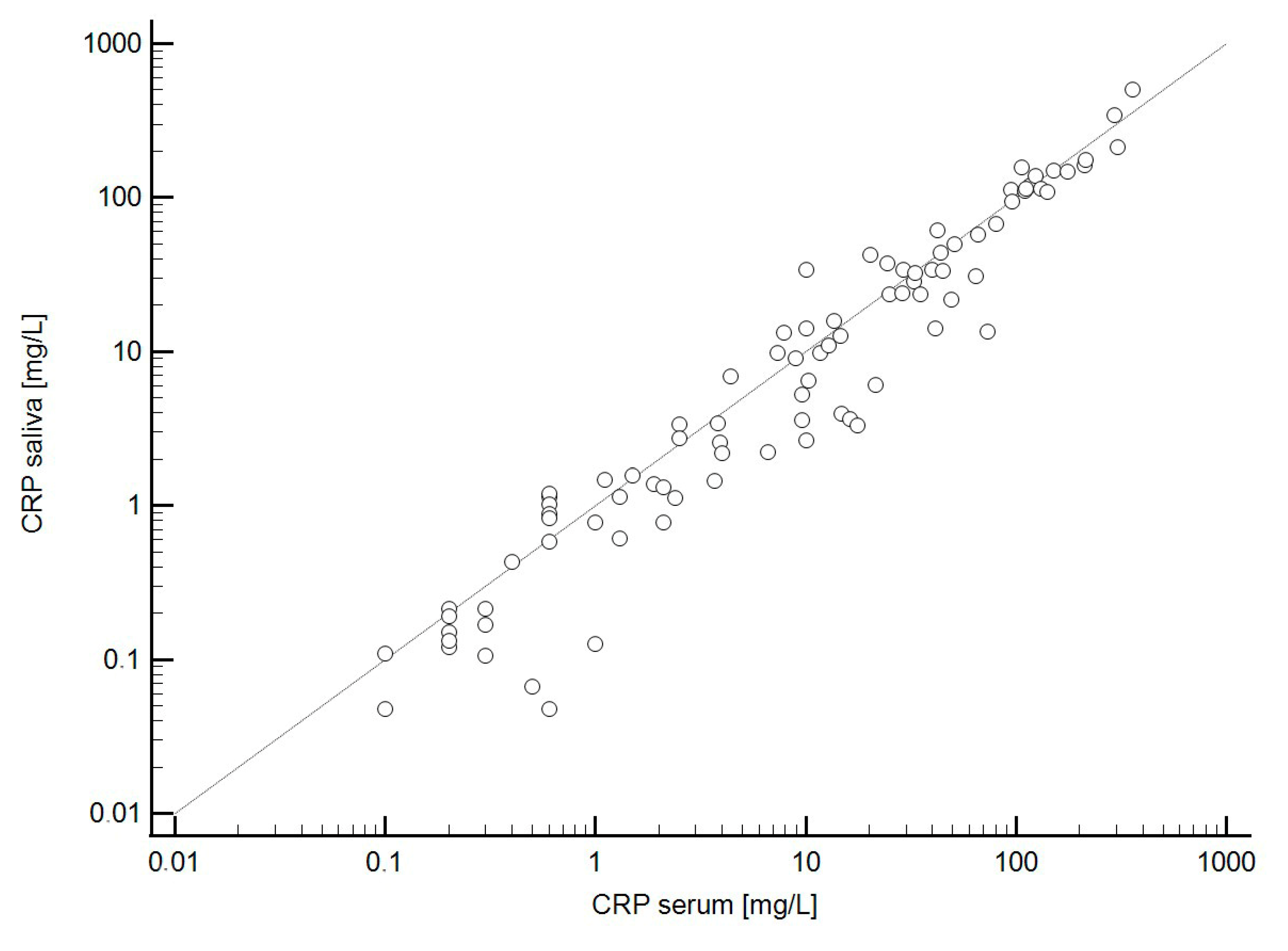
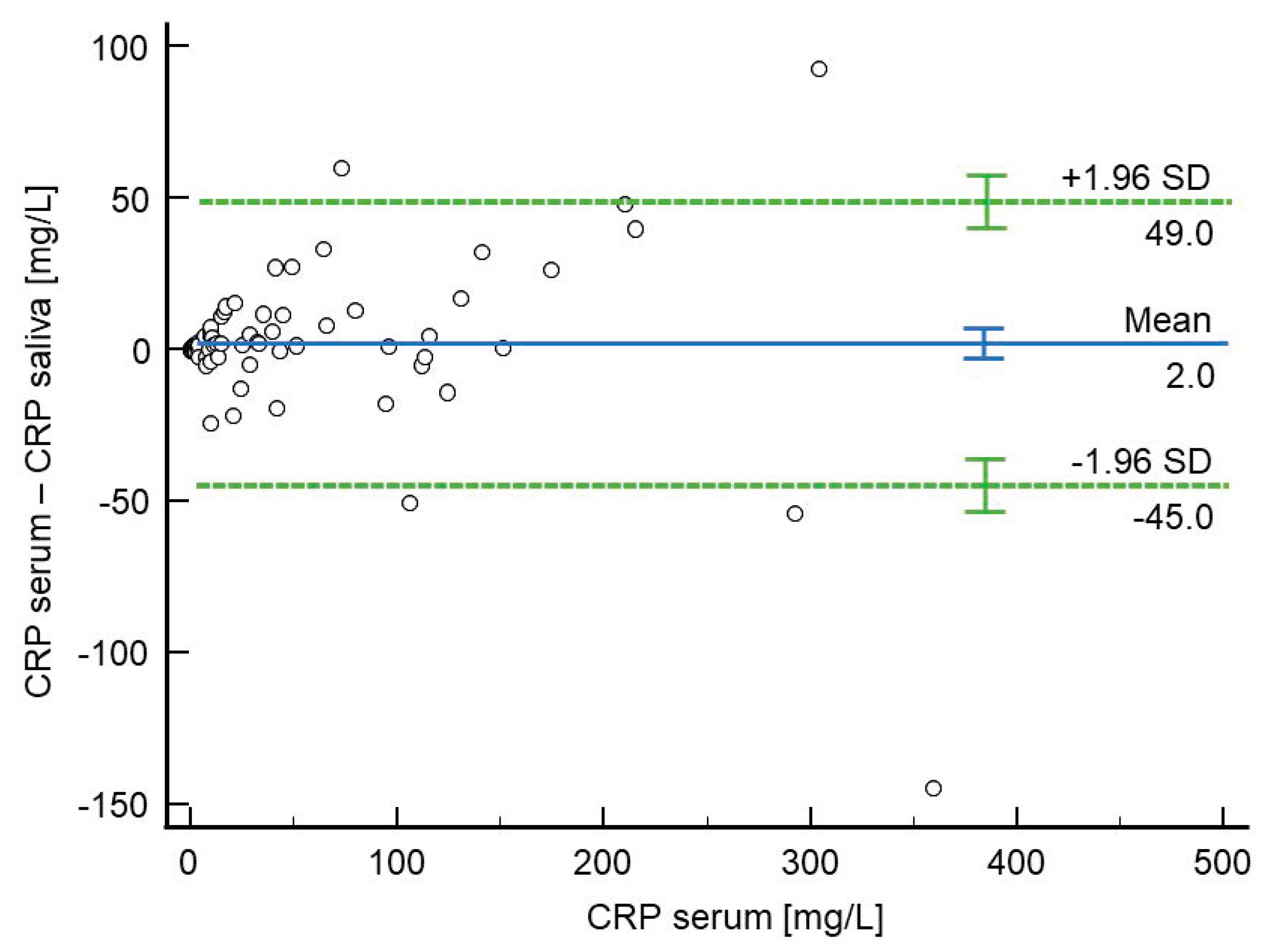
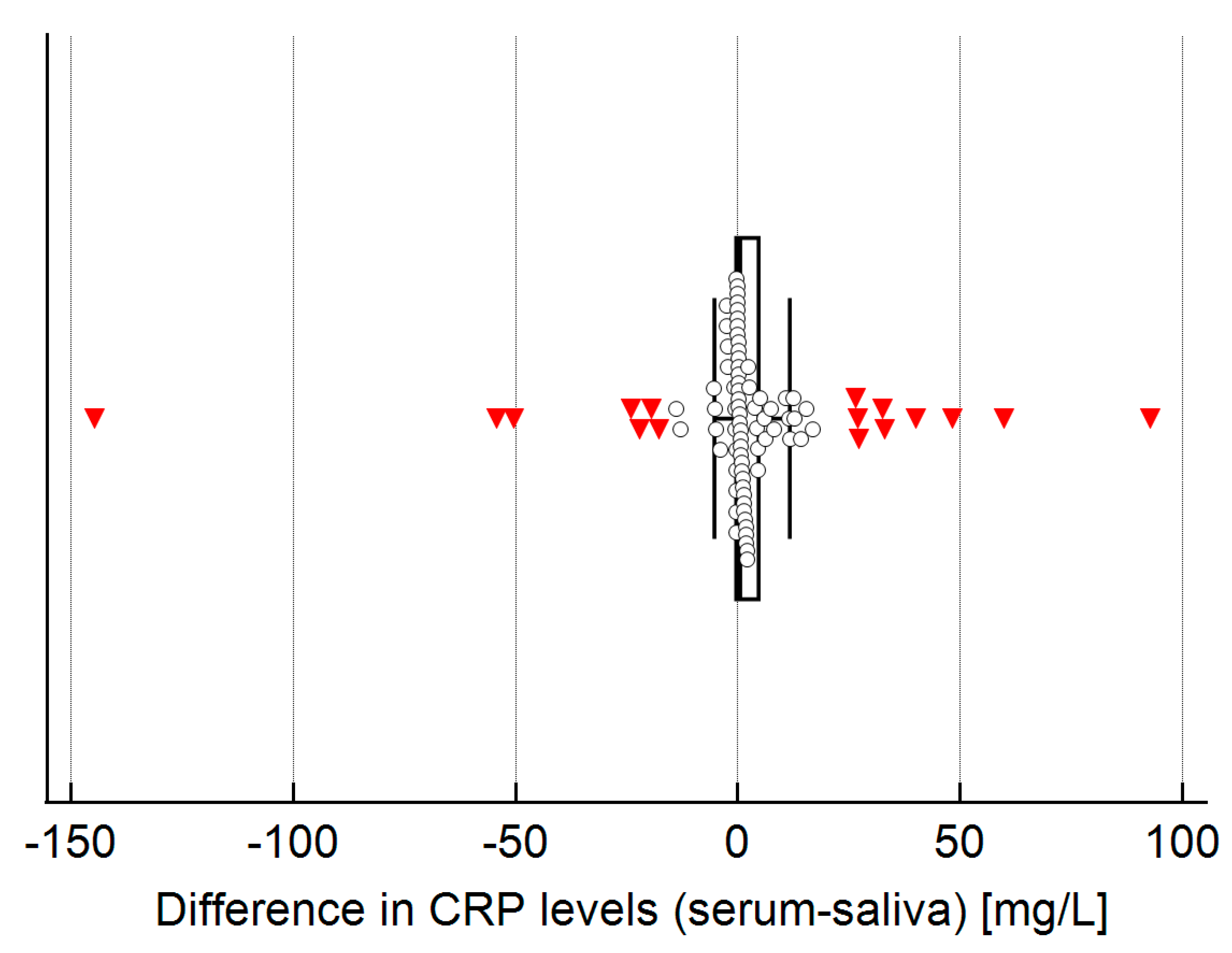
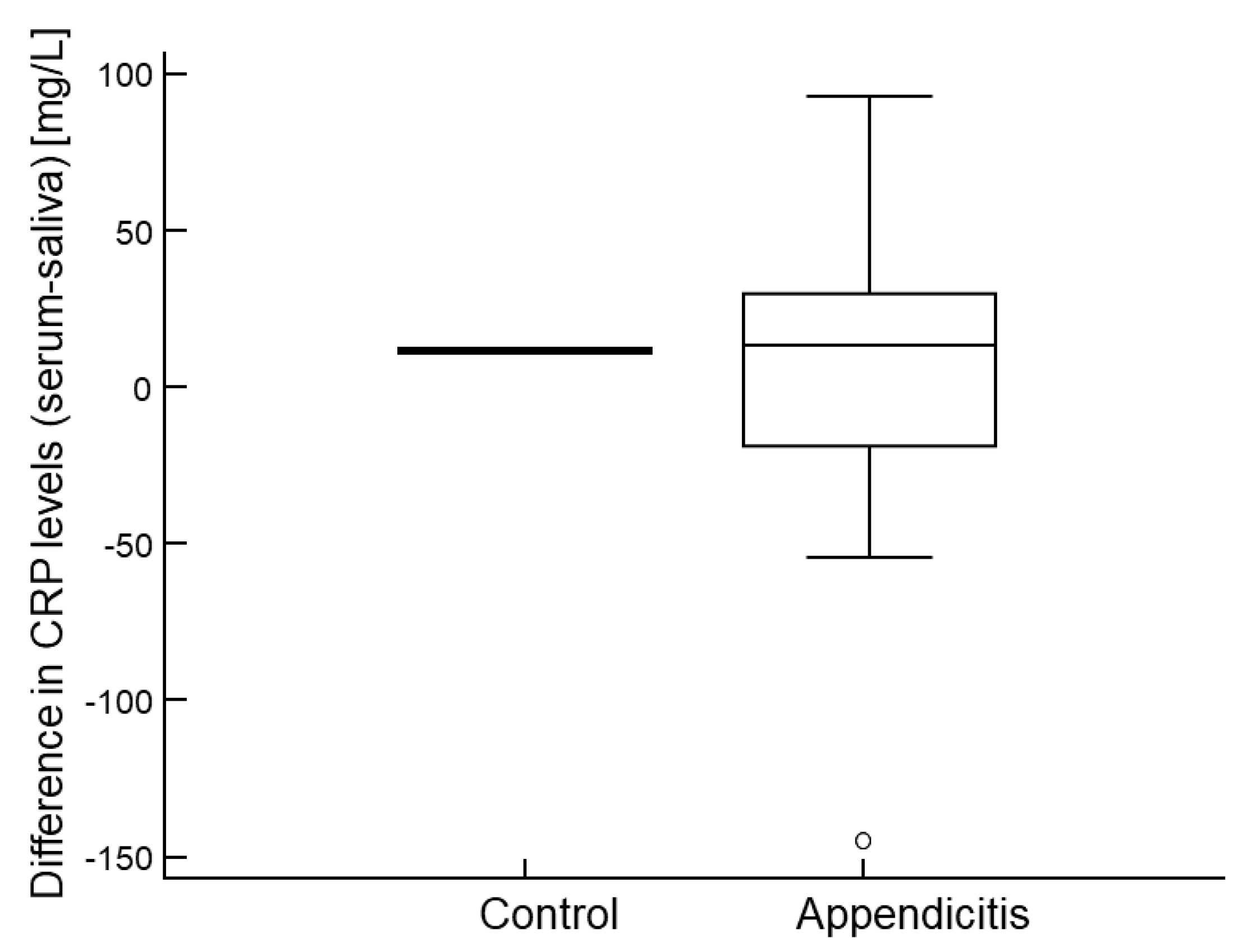
2.5. Agreement Between CRP Levels in Serum and Saliva
2.6. Agreement in Predictive Performance Between Serum and Salivary CRP
3. Discussion
4. Methods
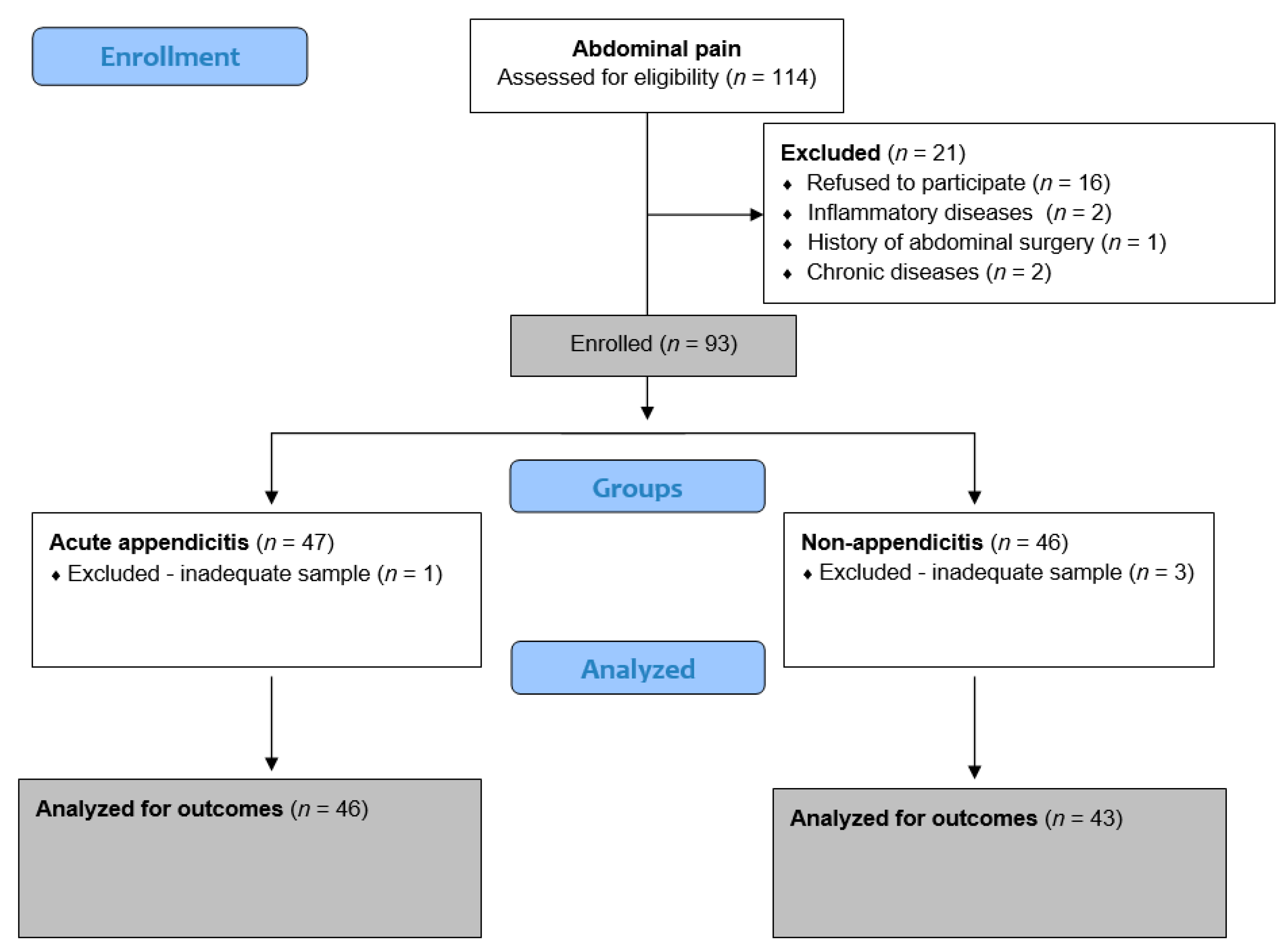
4.1. Study Design and Setting
4.2. Ethical Aspects
4.3. Study Protocol
4.4. Blood Collection and Preparation
4.5. Saliva CRP Collection
4.6. Saliva CRP Analysis
4.7. Final Diagnosis of the Patients
4.8. Sample Size Calculation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glass, C.C.; Rangel, S.J. Overview and diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Semin. Pediatr Surg. 2016, 25, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, M.D. Acute appendicitis. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabbas, R.; Hanna, M.; Shah, J.; Sinert, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of History, Physical Examination, Laboratory Tests, and Point-of-care Ultrasound for Pediatric Acute Appendicitis in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2017, 24, 523–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Janković Marendić, I.; Čohadžić, T.; Jukić, M. Clinical outcomes of daytime versus nighttime laparoscopic appendectomy in children. Children 2023, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukić, M.; Nizeteo, P.; Matas, J.; Pogorelić, Z. Trends and predictors of pediatric negative appendectomy rates: A single-centre retrospective study. Children 2023, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, R.; Muntean, C.; Raio, C.; Borowski, H.; Kalin, C.; Emanuel, J.; Klein, L.R. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis in Pediatrics: A Community Hospital Network Experience. Cureus 2025, 17, e82854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayebi, A.; Olamaeian, F.; Mostafavi, K.; Khosravi, K.; Tizmaghz, A.; Bahardoust, M.; Zakaryaei, A.; Mehr, D.E. Assessment of Alvarado criteria, ultrasound, CRP, and their combination in patients with suspected acute appendicitis: A single centre study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawkner-Corbett, D.; Hayward, G.; Alkhmees, M.; Van Den Bruel, A.; Ordóñez-Mena, J.M.; Holtman, G.A. Diagnostic accuracy of blood tests of inflammation in paediatric appendicitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e056854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Krishnan, N.; Birley, J.R.; Tintor, G.; Bajpai, M.; Pogorelić, Z. Hyponatremia-a new diagnostic marker for complicated acute appendicitis in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Children 2022, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vibhash, C.; Choudhury, S.R.; Maheshwari, A.; Sarin, Y.K.; Sharma, S.; Singh, R. Profile of serum inflammatory biomarkers in children with peritonitis and their role in predicting the severity and outcome. J. Indian Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. 2025, 30, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salö, M.; Roth, B.; Stenström, P.; Arnbjörnsson, E.; Ohlsson, B. Urinary biomarkers in pediatric appendicitis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2016, 32, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.L.; Fan, J.D.; Chen, Y.; Ho, M.F.; Choo, C.S.; Allen, J.; Low, Y.; Jacobsen, A.S.; Nah, S.A. A novel noninvasive appendicitis score with a urine biomarker. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 54, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.L.; Fan, J.D.; Ho, M.F.; Choo, C.S.C.; Ong, L.Y.; Chen, Y. Salivary biomarker for acute appendicitis in children: A pilot study. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2020, 36, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lontra, M.B.; Savaris, R.F.; Cavazzola, L.T.; Maissiat, J. Comparison of leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein-1 (LRG-1) plasma levels between patients with and without appendicitis, a case-controlled study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.; Berezovska, M.M.; Broks, R.; Asare, L.; Delorme, M.; Crouzen, E.; Zviedre, A.; Reinis, A.; Engelis, A.; Kroica, J.; et al. Serum and urine biomarker leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein 1 differentiates pediatric acute complicated and uncomplicated appendicitis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.W.; Juan, L.I.; Wu, M.H.; Shen, C.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Lee, C.C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and white blood cell count for suspected acute appendicitis. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.A.; Mussavira, S.; Bindhu, O.S. Clinical and diagnostic utility of saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic fluid: A systematic review. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y.R.; Ding, Y.J.; Lin, Y.N.; Zhou, J.P.; Li, N.; Li, H.P.; Li, S.Q.; Sun, X.W.; et al. A narrative review of exploring potential salivary biomarkers in respiratory diseases: Still on its way. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 4541–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalane, K.G.; Kriel, M.; Loxton, A.G.; Menezes, A.; Stanley, K.; van der Spuy, G.D.; Walzl, G.; Chegou, N.N. Differential expression of host biomarkers in saliva and serum samples from individuals with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 981984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.A.; Fortunato, C.K.; Beltzer, E.K.; Virag, M.; Bright, M.A.; Out, D. Focus on methodology: Salivary bioscience and research on adolescence: An integrated perspective. J. Adolesc. 2012, 35, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grocholska, P.; Kowalska, M.; Bąchor, R. Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miočević, O.; Cole, C.R.; Laughlin, M.J.; Buck, R.L.; Slowey, P.D.; Shirtcliff, E.A. Quantitative Lateral Flow Assays for Salivary Biomarker Assessment: A Review. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassl, N.; Kulak, N.A.; Pichler, G.; Geyer, P.E.; Jung, J.; Schubert, S.; Sinitcyn, P.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. Ultra-deep and quantitative saliva proteome reveals dynamics of the oral microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintor, G.; Jukić, M.; Šupe-Domić, D.; Jerončić, A.; Pogorelić, Z. Diagnostic accuracy of leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1 as a non-invasive salivary biomarker in pediatric appendicitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakal, U.; Aydin, S.; Sarac, M.; Kuloglu, T.; Kalayci, M.; Artas, G.; Yardim, M.; Kazez, A. Serum, Saliva, and Urine Irisin with and Without Acute Appendicitis and Abdominal Pain. Biochem. Insights 2016, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwali, W.A.; Elmashad, A.M.; Hazzaa, S.M.E.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Hamza, M.B. Salivary C-reactive protein and mean platelet volume as possible diagnostic markers for late-onset neonatal pneumonia. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2024, 13, 88645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, Y.Z.; Slavish, D.C. Measuring salivary markers of inflammation in health research: A review of methodological considerations and best practices. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 124, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, J.; Acedo, Y.; Medrano, L.; Barcena, E.; Garay, R.P.; Arri, E.A. Usefulness of new and traditional serum biomarkers in children with suspected appendicitis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.; Fallon, R.; Riordan, A.; Shaw, B. Markedly raised levels of C-reactive protein are associated with culture-proven sepsis or necrotising enterocolitis in extremely preterm neonates. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, e289–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, S.S.; Wisborg, K.; Hvas, A.M. Diagnostic utility of biomarkers for neonatal sepsis-a systematic review. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, H.; Yousefi-Koma, A.A.; Yousefi-Koma, H. Extensive comparison of salivary collection, transportation, preparation, and storage methods: A systematic review. BMC Oral. Health 2024, 24, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein Kremer, A.; Kuzminsky, E.; Bentur, L.; Nagler, R.M. Salivary and serum analysis in children diagnosed with pneumonia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2014, 49, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, A.; Paulus, J.K.; Gerlanc, D.J.; Maron, J.L. Detection and potential utility of C-reactive protein in saliva of neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, G.S.; Mathews, S.T. Saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic tool for inflammation and insulin-resistance. World J. Diabetes 2014, 5, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marley, G.; Kang, D.; Wilson, E.C.; Huang, T.; Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Tao, X.; Wang, G.; Xun, H.; Ma, W. Introducing rapid oral-fluid HIV testing among high risk populations in Shandong, China: Feasibility and challenges. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, F.M.; Torrance, H.; Anderson, R.A.; Oliver, J.S. Drugs in oral fluid Part, I. Validation of an analytical procedure for licit and illicit drugs in oral fluid. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 150, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagnola, M.; Scarano, E.; Passali, G.C.; Messana, I.; Cabras, T.; Iavarone, F.; Di Cintio, G.; Fiorita, A.; De Corso, E.; Paludetti, G. Salivary biomarkers and proteomics: Future diagnostic and clinical utilities. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, F.M.; Ferreira, R.P.; Vitorino, R. One decade of salivary proteomics: Current approaches and outstanding challenges. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano-Keeler, J.; Wynn, J.L.; Maron, J.L. Great expectorations: The potential of salivary ‘omic’ approaches in neonatal intensive care. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hassaneen, M.; Maron, J.L. Salivary Diagnostics in Pediatrics: Applicability, Translatability, and Limitations. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, E.; Kousvelari, E.; Vastardis, H. Saliva in the “Omics” era: A promising tool in paediatrics. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.M.; Tang, K.S.; Cheng, M.C.; Liu, T.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, C.C.; Yu, H.R. Use of saliva sample to detect C-reactive protein in children with pneumonia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 2457–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramavath, C.; Katam, S.K.; Vardhelli, V.; Deshabhotla, S.; Oleti, T.P. Examining the utility of rapid salivary C-reactive protein as a predictor for neonatal sepsis: An analytical cross-sectional pilot study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabras, T.; Pisano, E.; Mastinu, A.; Denotti, G.; Pusceddu, P.P.; Inzitari, R.; Fanali, C.; Nemolato, S.; Castagnola, M.; Messana, I. Alterations of the salivary secretory peptidome profile in children affected by type 1 diabetes. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2010, 9, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrão, A.L.P.; Falcao, D.P.; de Amorim, R.F.B.; Bezerra, A.C.B.; Pombeiro, G.A.N.; Guimarães, L.J.; Fregni, F.; Silva, L.P.; da Mota, L.M.H. Salivary proteomics: A new adjuvant approach to the early diagnosis of familial juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 89, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, M.; Olianas, A.; Cabras, T.; Manconi, B.; Fanni, D.; Faa, G.; Desiderio, C.; Messana, I.; Castagnola, M. Saliva, a bodily fluid with recognized and potential diagnostic applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3677–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, J.M.; Schafer, C.A.; Schafer, J.J.; Farrell, J.J.; Paster, B.J.; Wong, D.T. Salivary biomarkers: Toward future clinical and diagnostic utilities. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Mihanović, J.; Ninčević, S.; Lukšić, B.; Elezović Baloević, S.; Polašek, O. Validity of Appendicitis Inflammatory Response Score in distinguishing perforated from non-perforated appendicitis in children. Children 2021, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Beara, V.; Jukić, M.; Rashwan, H.; Šušnjar, T. A new approach to laparoscopic appendectomy in children-clipless/sutureless Harmonic scalpel laparoscopic appendectomy. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E.; Bickler, S.W.; Chang, D.C.; Talamini, M.A. Examining a common disease with unknown etiology: Trends in epidemiology and surgical management of appendicitis in California, 1995-2009. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 2787–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Ødeverp, A.; Jukić, M. The safety and feasibility of single-stage versus staged laparoscopic approach for acute appendicitis with inguinal hernia in pediatric patients: A comparative study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Acute Appendicitis (n = 46) | Control Group (n = 43) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 13 (10–15) | 13 (11–14) | 0.859 † | |
| Body weight (kg), mean ± SD | 162.3 ± 16.3 | 161.0 ± 13.7 | 0.603 ‡ | |
| Body height (kg), mean ± SD | 53.3 ± 19.4 | 51.4 ± 13.5 | 0.680 § | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 33 (72) | 25 (58) | 0.181 ¶ |
| Female | 13 (28) | 18 (42) | ||
| Variables | Acute Appendicitis (n = 46) | Control Group (n = 43) | p † |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of symptoms (h) | 28 (24, 48) | 36 (24, 48) | 0.714 |
| AIR score | 9 (7–10) | 3 (2, 3) | <0.001 |
| Body temperature (°C) | 36.9 (36.8, 37.2) | 37.6 (37.2, 38.0) | <0.001 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 15.7 (12, 18.6) | 7.9 (6.7, 10.4) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils | 79.3 (75.5, 84.7) | 56.7 (45.8, 64.5) | <0.001 |
| CRP in serum (mg/L) | 44.3 (21.5, 113.1) | 1.1 (0.4, 3.9) | <0.001 |
| CRP in saliva (mg/L) | 35.7 (15.9, 114.3) | 1.1 (0.2, 2.7) | <0.001 |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 37.5 (28, 60) | - | |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 2 (2, 3) | 4 (3, 6) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milunović, K.P.; Stanišić, L.; Barić, T.; Meštrović, J.; Todorić, D.; Domić, D.Š.; Jerončić, A.; Pogorelić, Z. Salivary C-Reactive Protein: A Non-Invasive Alternative to Serum CRP in Pediatric Acute Appendicitis. Molecules 2025, 30, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163392
Milunović KP, Stanišić L, Barić T, Meštrović J, Todorić D, Domić DŠ, Jerončić A, Pogorelić Z. Salivary C-Reactive Protein: A Non-Invasive Alternative to Serum CRP in Pediatric Acute Appendicitis. Molecules. 2025; 30(16):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163392
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilunović, Klaudio Pjer, Lada Stanišić, Tomislav Barić, Jakov Meštrović, Davor Todorić, Daniela Šupe Domić, Ana Jerončić, and Zenon Pogorelić. 2025. "Salivary C-Reactive Protein: A Non-Invasive Alternative to Serum CRP in Pediatric Acute Appendicitis" Molecules 30, no. 16: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163392
APA StyleMilunović, K. P., Stanišić, L., Barić, T., Meštrović, J., Todorić, D., Domić, D. Š., Jerončić, A., & Pogorelić, Z. (2025). Salivary C-Reactive Protein: A Non-Invasive Alternative to Serum CRP in Pediatric Acute Appendicitis. Molecules, 30(16), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163392







