Effects of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Leaf Extract on Zebrafish Embryogenesis, Behavior, and Biochemical Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of the Extract on the Survival Rate and Embryonic Development
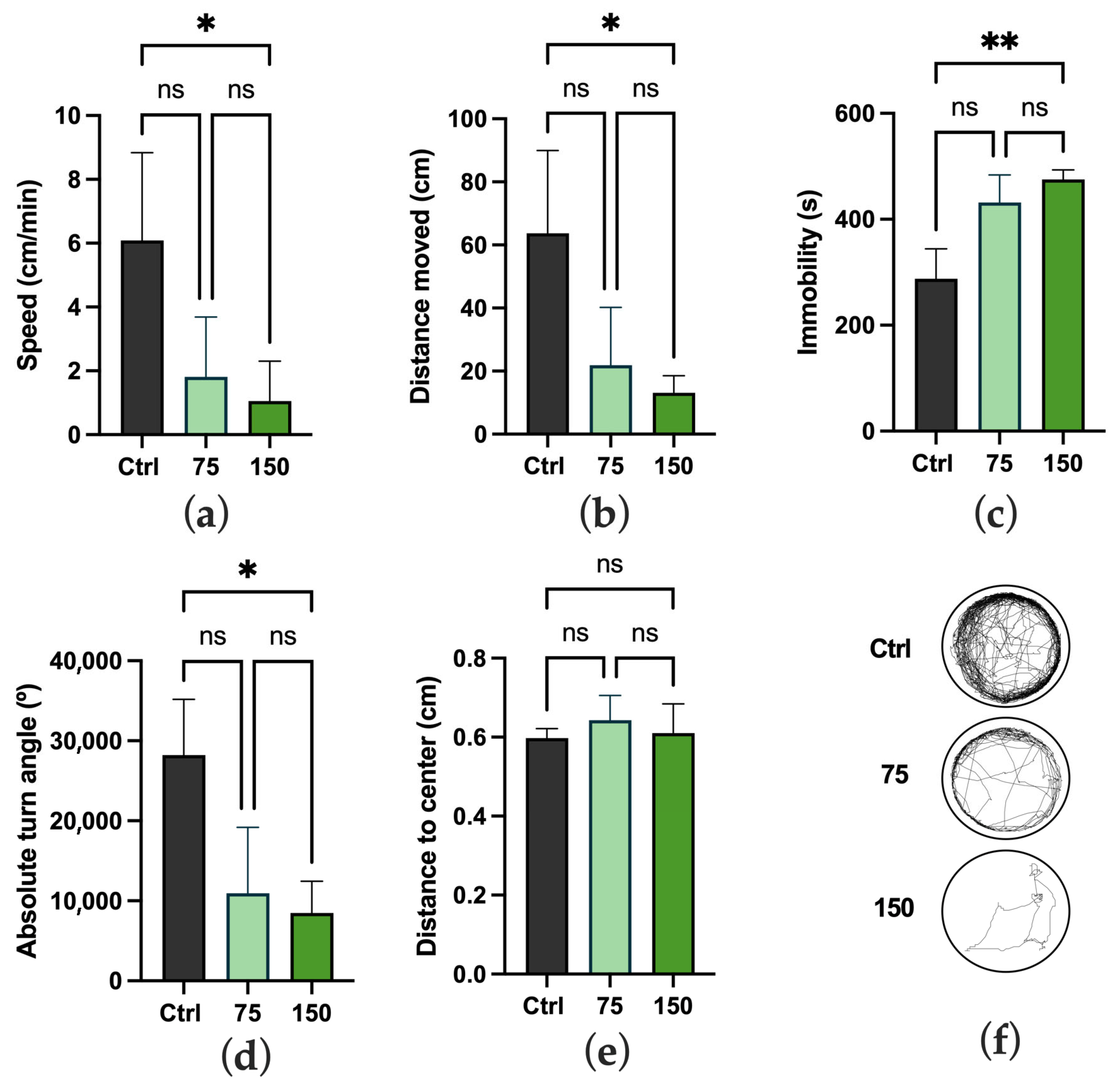
2.2. Impact on Locomotor Activity and Behavioral Responses
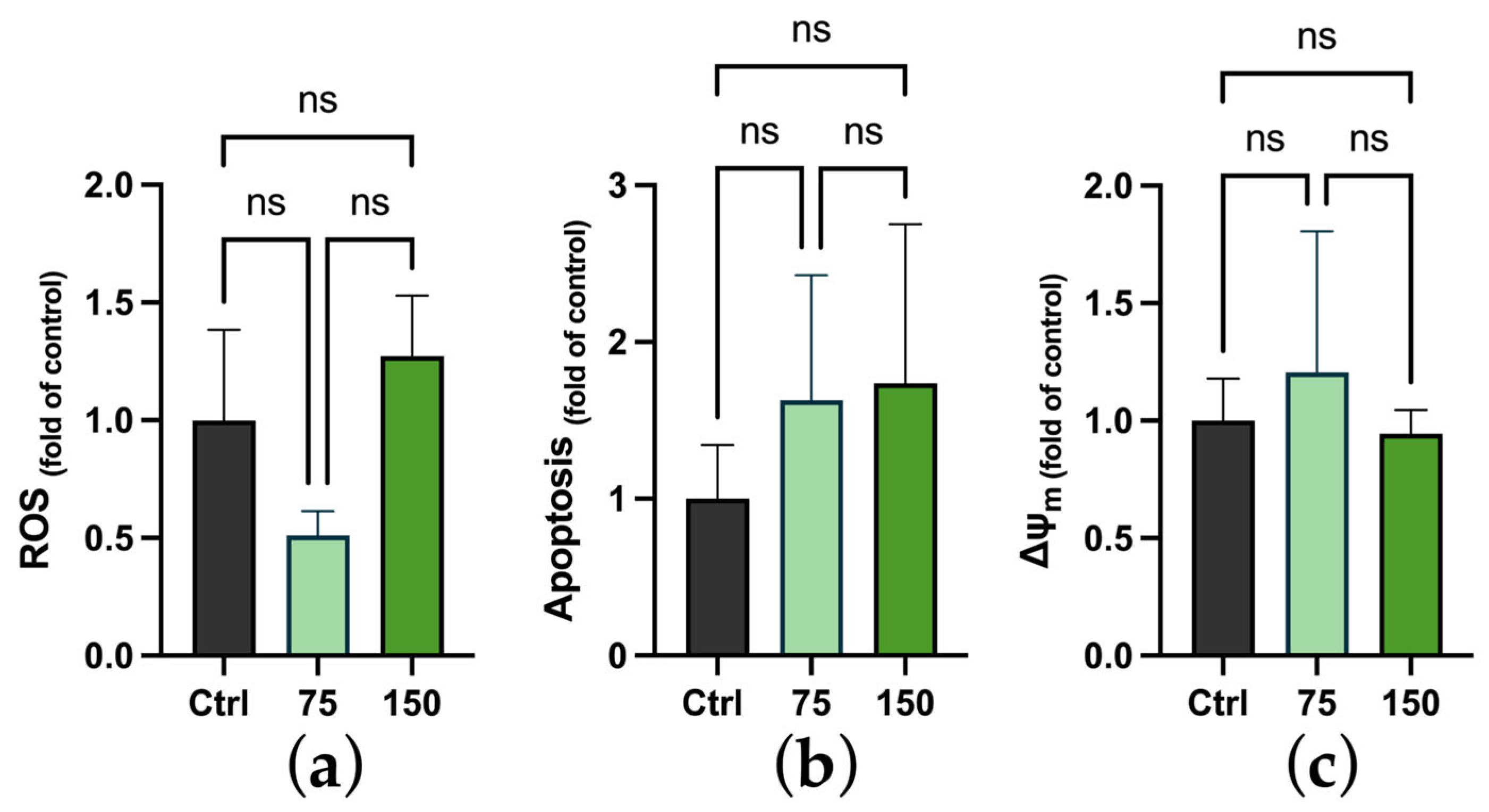
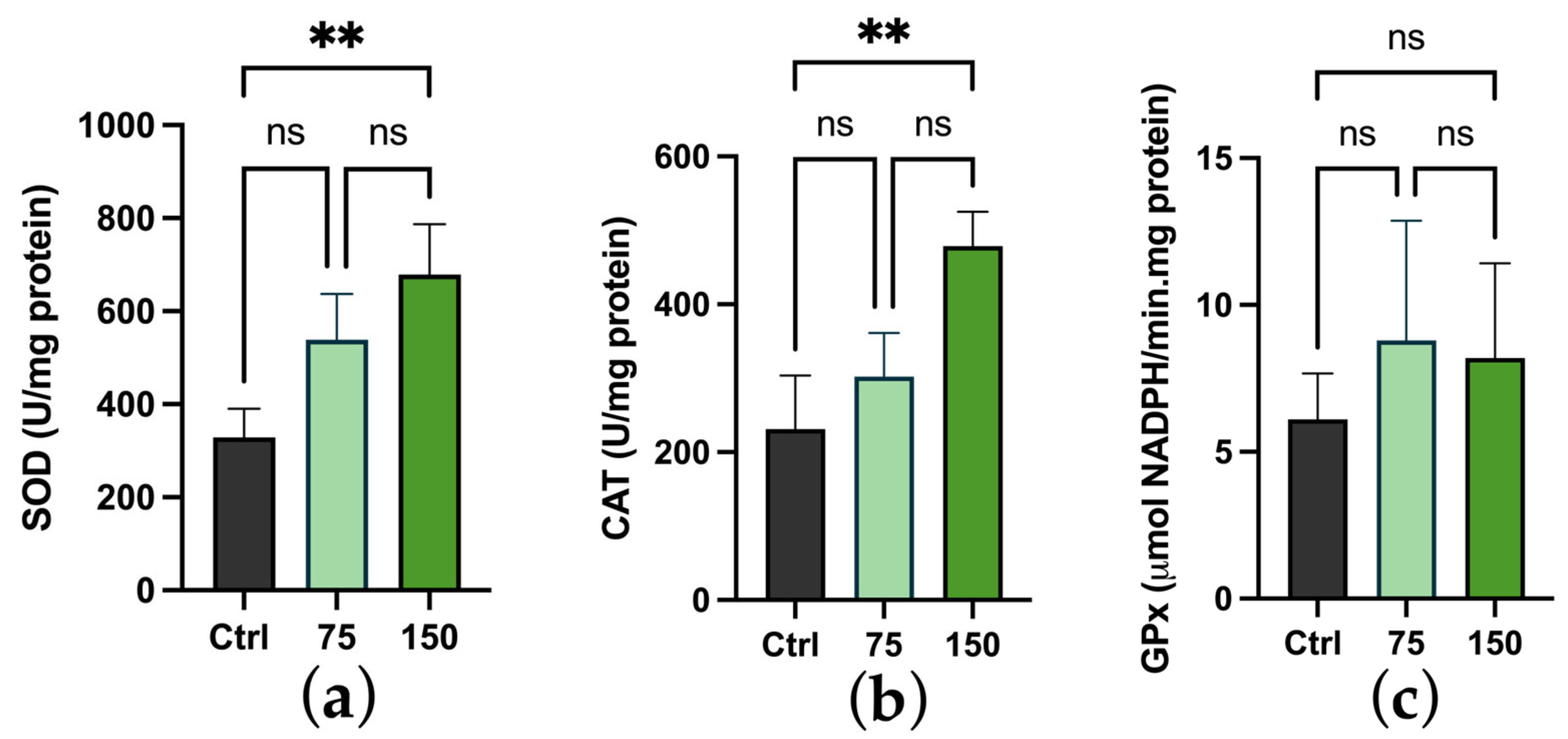
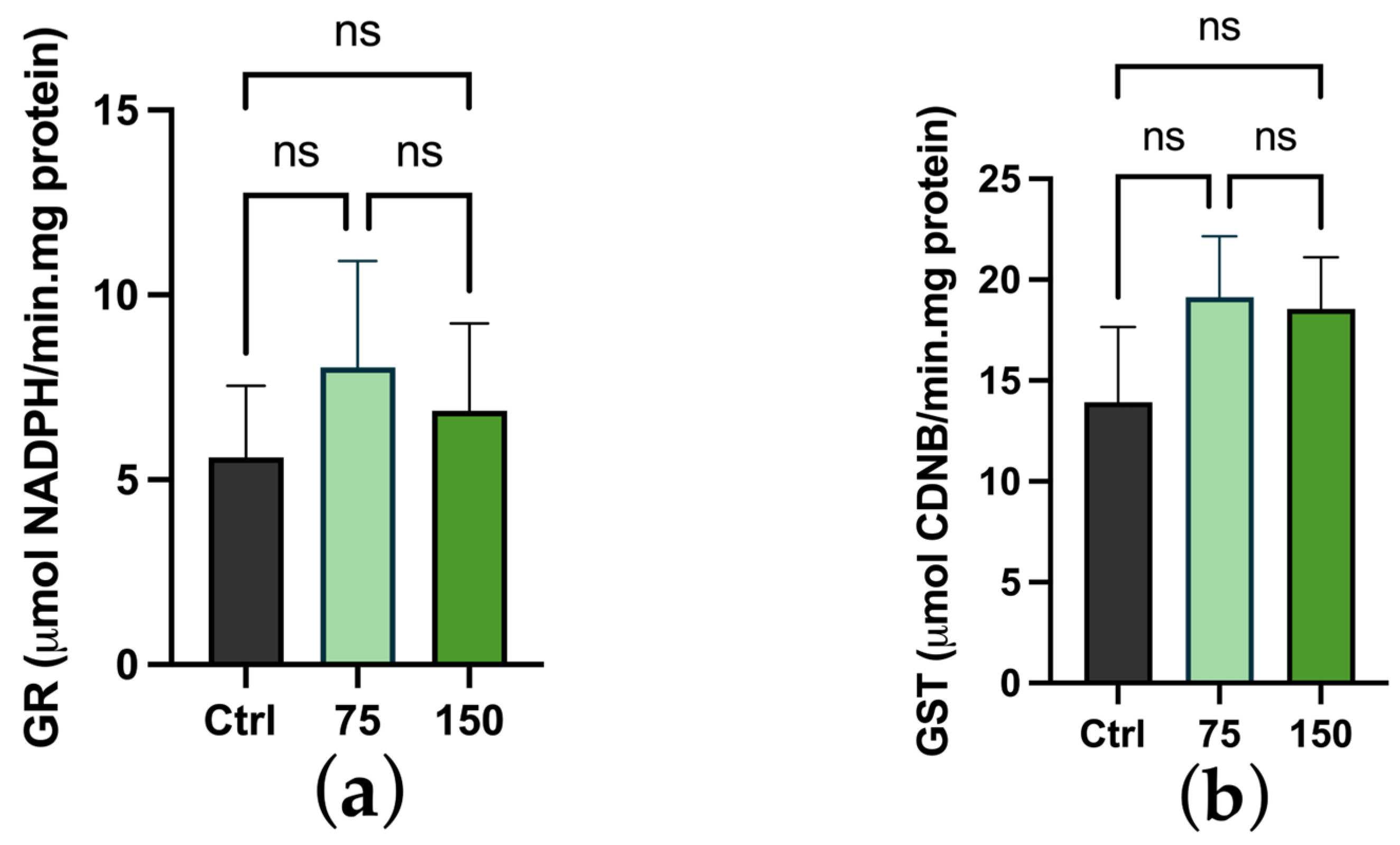
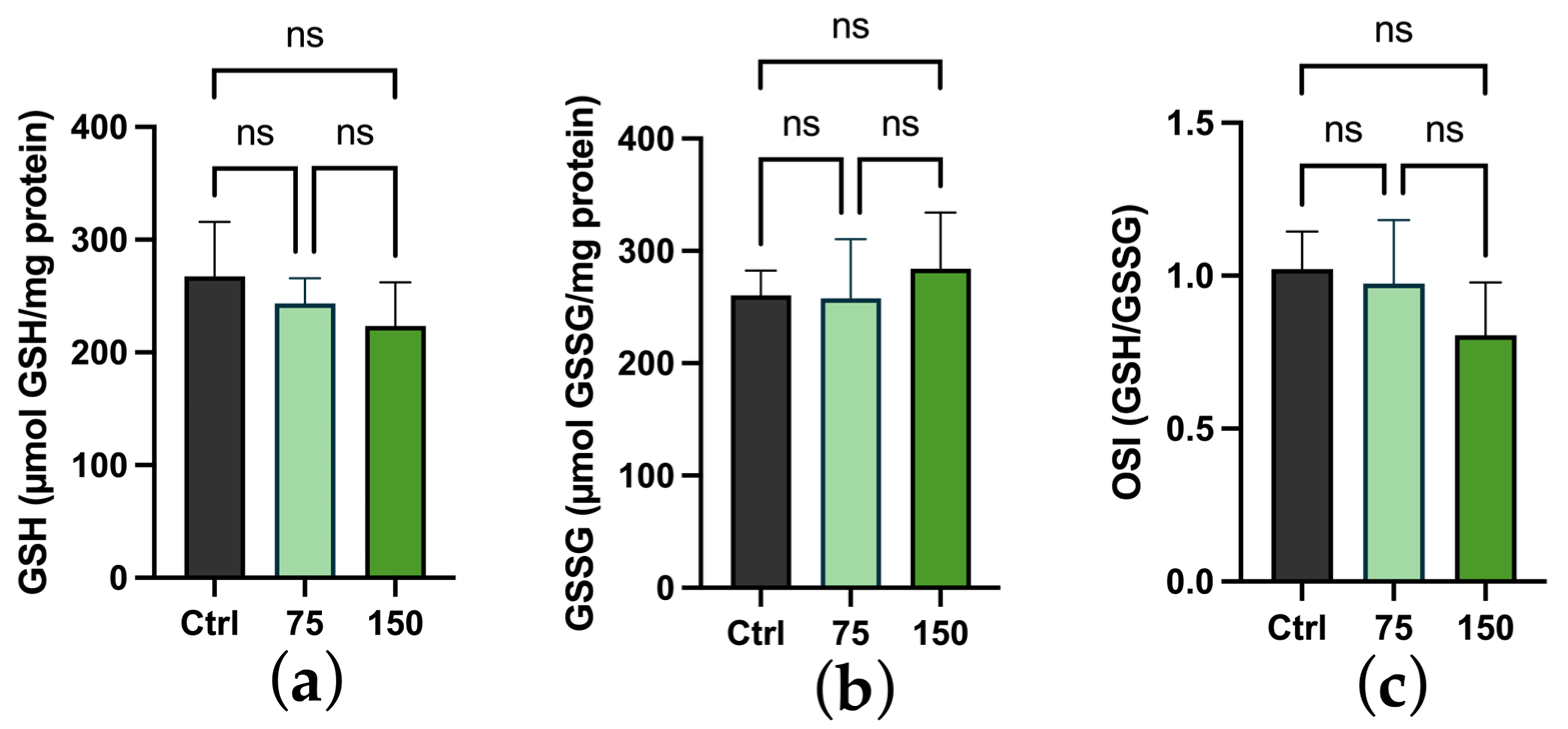
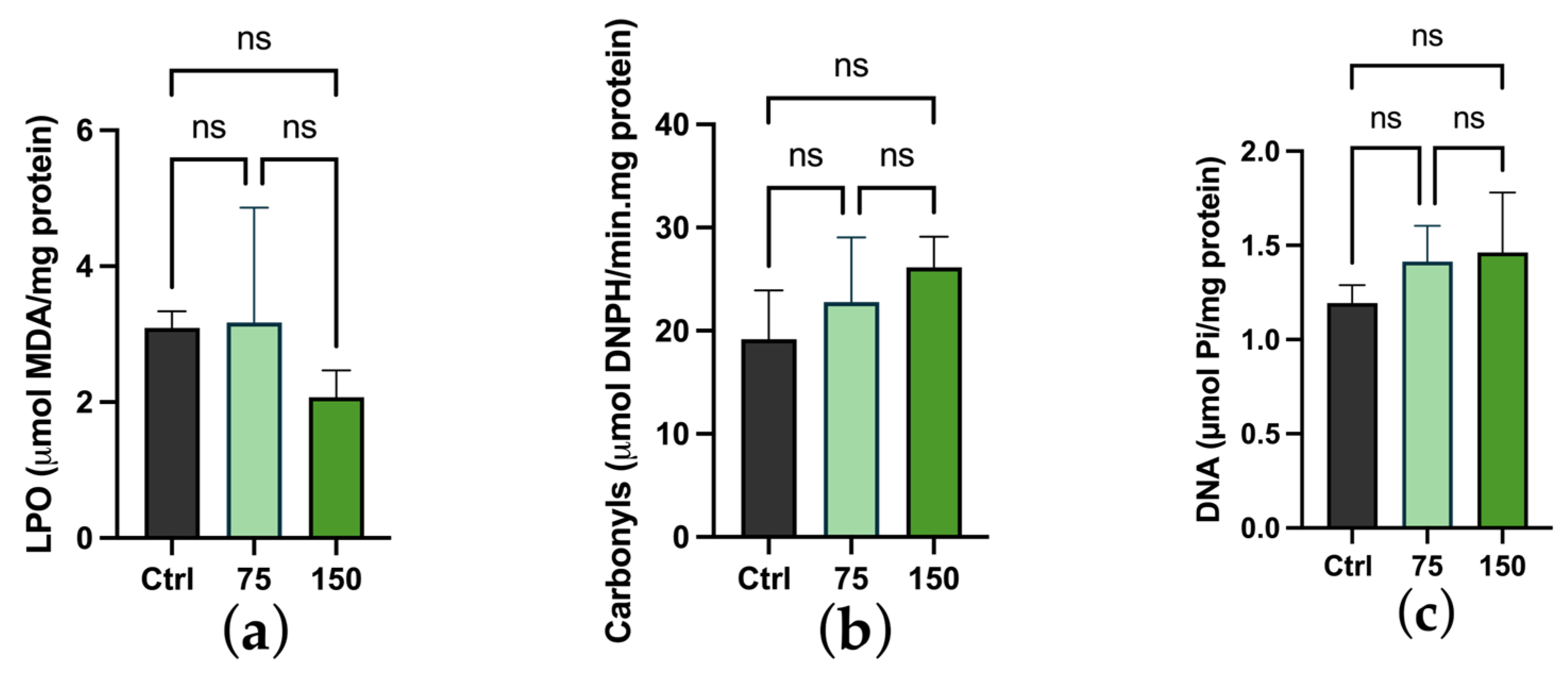
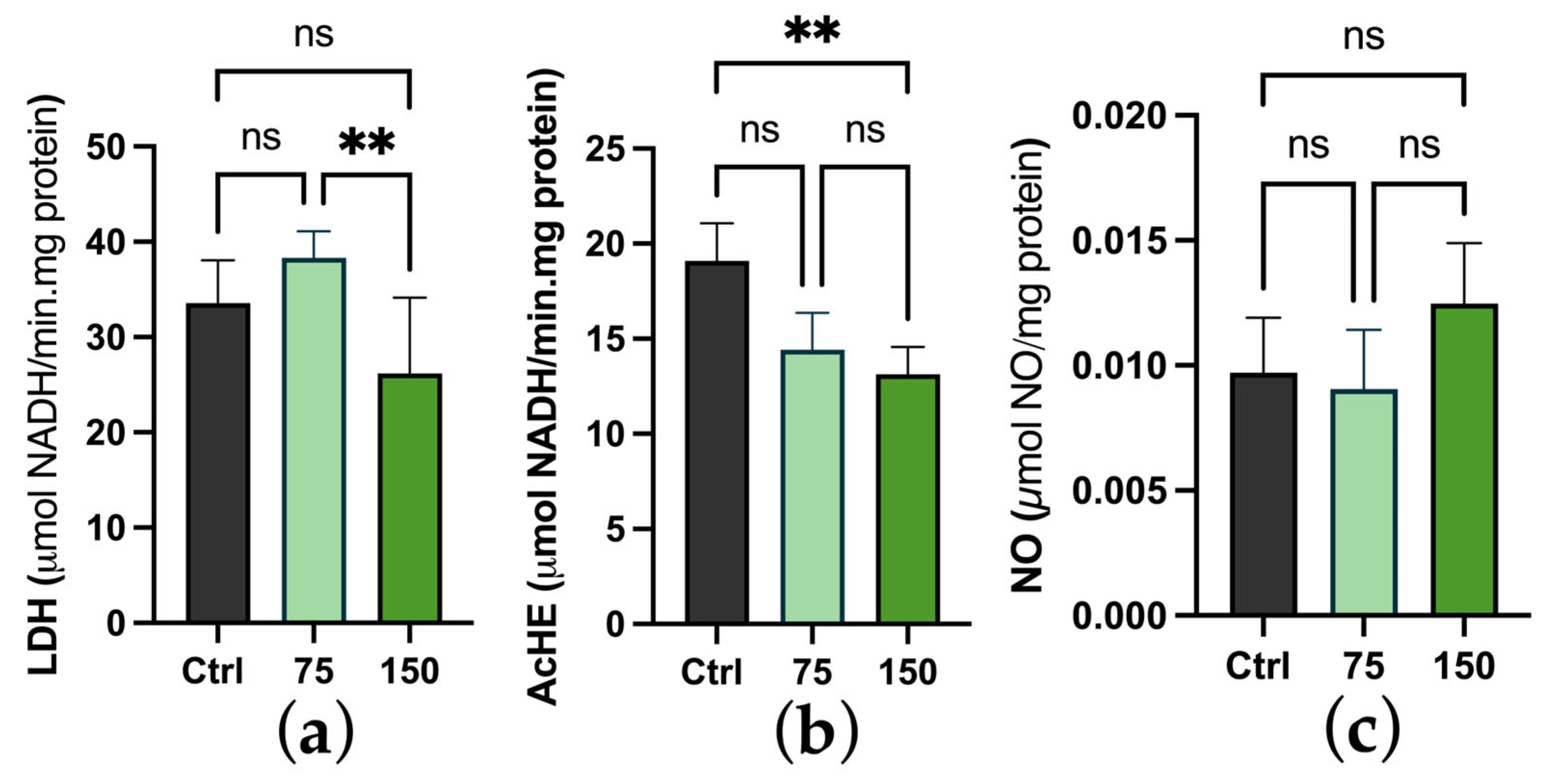
2.3. Biochemical Changes
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Collection of the Leaves of E. japonica and Preparation of the Extract
4.2. Maintenance of Zebrafish
4.3. Exposure to the Extract
4.4. Embryotoxicity
4.5. Behavior
4.6. Multiparameter Detection
4.7. Biochemical Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sarker, S.D.; Latif, Z.; Gray, A.I. Methods in biotechnology 20TM. In Natural Products Isolation, 2nd ed.; Sarker, S.D., Latif, Z., Gray, A.I., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 1-58829-447-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.M.H. (2748) Proposal to Conserve the Name Eriobotrya against Rhaphiolepis (Rosaceae). Taxon 2020, 69, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Li, M.; Pathak, M.L.; Qaiser, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.-F. A Taxonomic Revision of the Genus eriobotrya Lindl. (Rosaceae). Pak. J. Bot. 2022, 54, 958–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.M. A Review on Active Constituents and Pharmacological Effects of Eriobotrya japonica Lindl. (Loquat). Iraqi J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 30, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.P.; Ikeda, M.; de Melo, A.M.; Bambirra Alves, F.E.S.; Carpiné, D.; Ribani, R.H. Eriobotrya Japonica Fruits and Its By-Products: A Promising Fruit with Bioactive Profile and Trends in the Food Application—A Bibliometric Review. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, Q. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicity of Eriobotrya Japonica Leaves: A Summary. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Cheng, F.; Ming, T.; Sun, C.; Ran, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shen, C.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C. Eriobotrya Japonica (Thunb.) Lindl Leaves: Reviewing Their Specialized Metabolites and Pharmacology. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 110, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Biological Activities of Extracts from Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.G.L.; Fernandes, R.; Abraão, A.; Costa, R.D.; Aires, A.; Gouvinhas, I.; Granato, D.; Barros, A.N. Characterization of Azorean Plant Leaves for Sustainable Valorization and Future Advanced Applications in the Food, Cosmetic, and Pharmaceutical Industries. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Abraão, A.; Gouvinhas, I.; Granato, D.; Barros, A.N. Advances in Leaf Plant Bioactive Compounds: Modulation of Chronic Inflammation Related to Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissone, A.; Burgess, S.M. Rare Genetic Blood Disease Modeling in Zebrafish. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, R.; Fronte, B.; Verri, T.; Marchese, M.; Sangiacomo, C.; Santorelli, F.M. Zebrafish Feed Intake: A Systematic Review for Standardizing Feeding Management in Laboratory Conditions. Biology 2024, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.N.; Patnaik, L. Flight for Fish in Drug Discovery: A Review of Zebrafish-Based Screening of Molecules. Biol. Lett. 2023, 19, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, C.D.; Siebel, A.M. Editorial: Zebrafish as a Model for Pharmacological and Toxicological Research. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 976970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, C.; Cooper, A.H.; Ram, P.; Parker, M.O. The Effect of Laboratory Diet and Feeding on Growth Parameters in Zebrafish. Lab Anim. 2024, 53, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, T.P.; Alderton, W.K.; Reynolds, H.M.; Roach, A.G.; Berghmans, S. Zebrafish: An Emerging Technology for in Vivo Pharmacological Assessment to Identify Potential Safety Liabilities in Early Drug Discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Zou, H.K.; Van Doan, H.; Kolangi Miandare, H.; Hoseini, S.M. Evaluation of Some Intestinal Cytokines Genes Expression and Serum Innate Immune Parameters in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Fed Dietary Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) Leaf Extract. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, G.; Peng, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jing, Y.; Gong, Z. Corosolic Acid Isolated from Eriobotrya Japonica Leaves Reduces Glucose Level in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells, Zebrafish and Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/OCDE. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals: Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD/OCDE: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasinghe, C.D.; Jayawardena, U.A. Toxicity Assessment of Herbal Medicine Using Zebrafish Embryos: A Systematic Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 7272808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-S.; Dai, M.-Z.; Zhu, C.-X.; Huang, Y.-F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.-D.; Xie, F.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.-Q.; et al. Validation, Optimization, and Application of the Zebrafish Developmental Toxicity Assay for Pharmaceuticals Under the ICH S5(R3) Guideline. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 721130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winata, C.L.; Korzh, S.; Kondrychyn, I.; Zheng, W.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. Development of Zebrafish Swimbladder: The Requirement of Hedgehog Signaling in Specification and Organization of the Three Tissue Layers. Dev. Biol. 2009, 331, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.N.; McGee, C.A.S.; Dumbarton, T.C.; Croll, R.P.; Smith, F.M. Development of the Swimbladder and Its Innervation in the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. J. Morphol. 2007, 268, 967–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, K.E.; Timme-Laragy, A.R. Zebrafish as a Model for Toxicological Perturbation of Yolk and Nutrition in the Early Embryo. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, F.R.; Mendonça, J.N.; Moraes, L.A.B.; de Oliveira, G.A.R.; Gravato, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Oliveira, D.P. de Toxicological and Behavioral Responses as a Tool to Assess the Effects of Natural and Synthetic Dyes on Zebrafish Early Life. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Jiang, L.; Chu, Y.; Gao, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, S.; Peng, C. The Biological Activity Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Applications in Food Industry: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 943911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, B. Osteogenic Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Application in Clinical Practice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1396354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, P. The Impaired Swim Bladder via ROS-Mediated Inhibition of the Wnt/Hedgehog Pathway in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Eight Toxic Chemicals and Binary Chemical Mixtures. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Cadmium Impairs Zebrafish Swim Bladder Development via ROS Mediated Inhibition of the Wnt/Hedgehog Pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 247, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.; Boix, N.; Teixido, E.; Marizande, F.; Cadena, S.; Bustillos, A. The Zebrafish Embryo as a Model to Test Protective Effects of Food Antioxidant Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First Line Defence Antioxidants-Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT) and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX): Their Fundamental Role in the Entire Antioxidant Defence Grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joibari, F.G.; Bahrekazemi, M.; Keshavarz, M.; Bahram, S.; Javadian, S.R.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. Stimulatory Effects of Dietary Savory (Satureja hortensis L.) Ethanolic Extract on Growth, Digestive Enzymes, Immune Parameters, Antioxidant Defense, and Immune and Antioxidant-Related Genes in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2025, 319, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Fazelan, Z.; El-Haroun, E.; Yousefi, M.; Yazici, M.; Van Doan, H.; Paolucci, M. The Effects of Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Leaf Extract on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Status, and Immunity of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes 2023, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga, C.; Hernandez, C.; Gonzalez, G.; Heredia, J. Effect of Dietary Intake of Phenolic Compounds from Mango Peel Extract on Growth, Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 47, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behra, M.; Cousin, X.; Bertrand, C.; Vonesch, J.-L.; Biellmann, D.; Chatonnet, A.; Strähle, U. Acetylcholinesterase Is Required for Neuronal and Muscular Development in the Zebrafish Embryo. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.A.; Dao, T.L.; Kan, R.K.; Shih, T. Zebrafish as a Model for Acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting Organophosphorus Agent Exposure and Oxime Reactivation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1374, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.S.F.; Venâncio, C.A.S.; Félix, L.M. Behavioral, Metabolic, and Biochemical Alterations Caused by an Acute Stress Event in a Zebrafish Larvae Model. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Faraoni, M.; Castro, M.; Alza, N.; Cavallaro, V. Natural AChE Inhibitors from Plants and Their Contribution to Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 388–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, L.M.; Antunes, L.M.; Coimbra, A.M.; Valentim, A.M. Behavioral Alterations of Zebrafish Larvae after Early Embryonic Exposure to Ketamine. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, P.; Vieira, R.; Venâncio, C.; Félix, L. Oxidative Stress as the Trigger for Menthol-Induced Developmental Alterations in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.R. Zebrafish: Development of a Vertebrate Model Organism. Curr. Protoc. Essent. Lab. Tech. 2018, 16, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Official Journal of the European Union; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Decreto-Lei n.o 113/2013 de 7 de Agosto Medidas Para a Proteção Dos Animais Utilizados Para Fins Científicos Ou; Ministry of Agriculture, Sea, Environment and Spatial Planning: Lisboa, Portugal, 2013. Available online: https://files.dre.pt/1s/2013/08/15100/0470904739.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Xavier, J.; Kripasana, K. Acute Toxicity of Leaf Extracts of Enydra fluctuans Lour in Zebrafish (Danio rerio Hamilton). Scientifica 2020, 2020, 3965376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, D. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.; Venâncio, C.A.S.; Félix, L.M. Toxic Effects of a Mancozeb-Containing Commercial Formulation at Environmental Relevant Concentrations on Zebrafish Embryonic Development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21174–21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, L.; Campos, S.; de Pinho, P.G.; Antunes, L.; Valentim, A.M. Early Developmental Effects of Propofol Exposure in Different Stages of Zebrafish Embryos. Toxicol. Lett. 2025, 403, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time (hpf) | Groups (mg/L) | Statistical Test | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | 75 | 150 | |||
| 8 | Mortality (%) | 4.0 (1.0–6.0) | 2.0 (2.0–5.0) | 2.0 (1.0–5.0) | X2 (2) = 0.63 | 0.756 |
| 24 | Cumulative mortality (%) | 15.2 ± 4.2 | 17.2 ± 2.3 | 13.6 ± 3.3 | F (2, 12) = 1.47 | 0.269 |
| Non-detected tail (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Non-detected head (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Non-detected somites (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Spontaneous movements (mpm) | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 1.6 | 5.7 ± 1.6 | F (2, 12) = 0.19 | 0.829 | |
| 48 | Cumulative mortality (%) | 15.2 ± 4.2 | 18.4 ± 3.8 | 16.4 ± 3.3 | F (2, 12) = 0.92 | 0.426 |
| Eye not developed (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Otolith not developed (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Absent blood circulation (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Non-visible pigmentation (%) 1 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Heartbeat (bpm) | 123.2 ± 9.5 | 116.6 ± 2.2 | 118.2 ± 2.9 | F (2, 12) = 1.72 | 0.220 | |
| 72 | Cumulative mortality (%) | 16.0 (11.0–19.0) a | 32.0 (26.0–32.0) ab | 38.0 (34.0–44.0) b | X2 (2) = 12.64 | <0.0001 |
| Hatching rate (%) | 100 (97.6–100) a | 94.1 (93.0–95.8) b | 93.3 (83.9–96.8) b | X2 (2) = 9.20 | 0.002 | |
| Oedema presence (%) 1,2 | ND | ND | ND | NA | NA | |
| Touch response (%) | 100 (100–100) | 100 (95.0–100) | 100 (95.0–100) | X2 (2) = 1.08 | >0.999 | |
| 96 | Cumulative mortality (%) | 16.0 (11.0–19.0) a | 32.0 (26.0–34.0) ab | 46.0 (43.0–50.0) b | X2 (2) = 12.57 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barros, J.; Gouvinhas, I.; Venâncio, C.; Granato, D.; Barros, A.N.; Félix, L. Effects of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Leaf Extract on Zebrafish Embryogenesis, Behavior, and Biochemical Pathways. Molecules 2025, 30, 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153252
Barros J, Gouvinhas I, Venâncio C, Granato D, Barros AN, Félix L. Effects of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Leaf Extract on Zebrafish Embryogenesis, Behavior, and Biochemical Pathways. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153252
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarros, Jorge, Irene Gouvinhas, Carlos Venâncio, Daniel Granato, Ana Novo Barros, and Luís Félix. 2025. "Effects of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Leaf Extract on Zebrafish Embryogenesis, Behavior, and Biochemical Pathways" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153252
APA StyleBarros, J., Gouvinhas, I., Venâncio, C., Granato, D., Barros, A. N., & Félix, L. (2025). Effects of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. Leaf Extract on Zebrafish Embryogenesis, Behavior, and Biochemical Pathways. Molecules, 30(15), 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153252












