Development of Certified Reference Material of L-Thyroxine by Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Qualitative Characterization
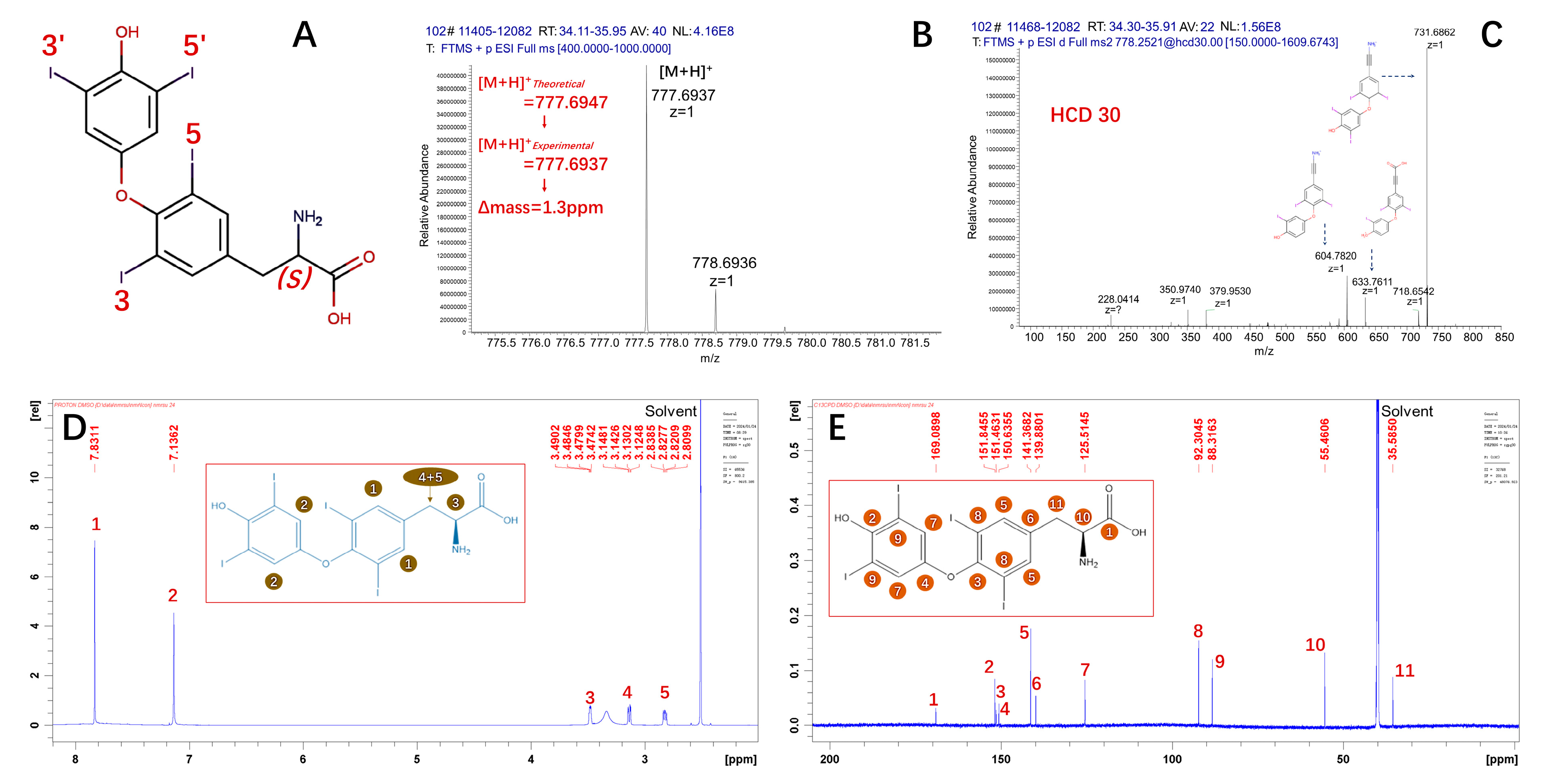
2.1.1. The Measurand
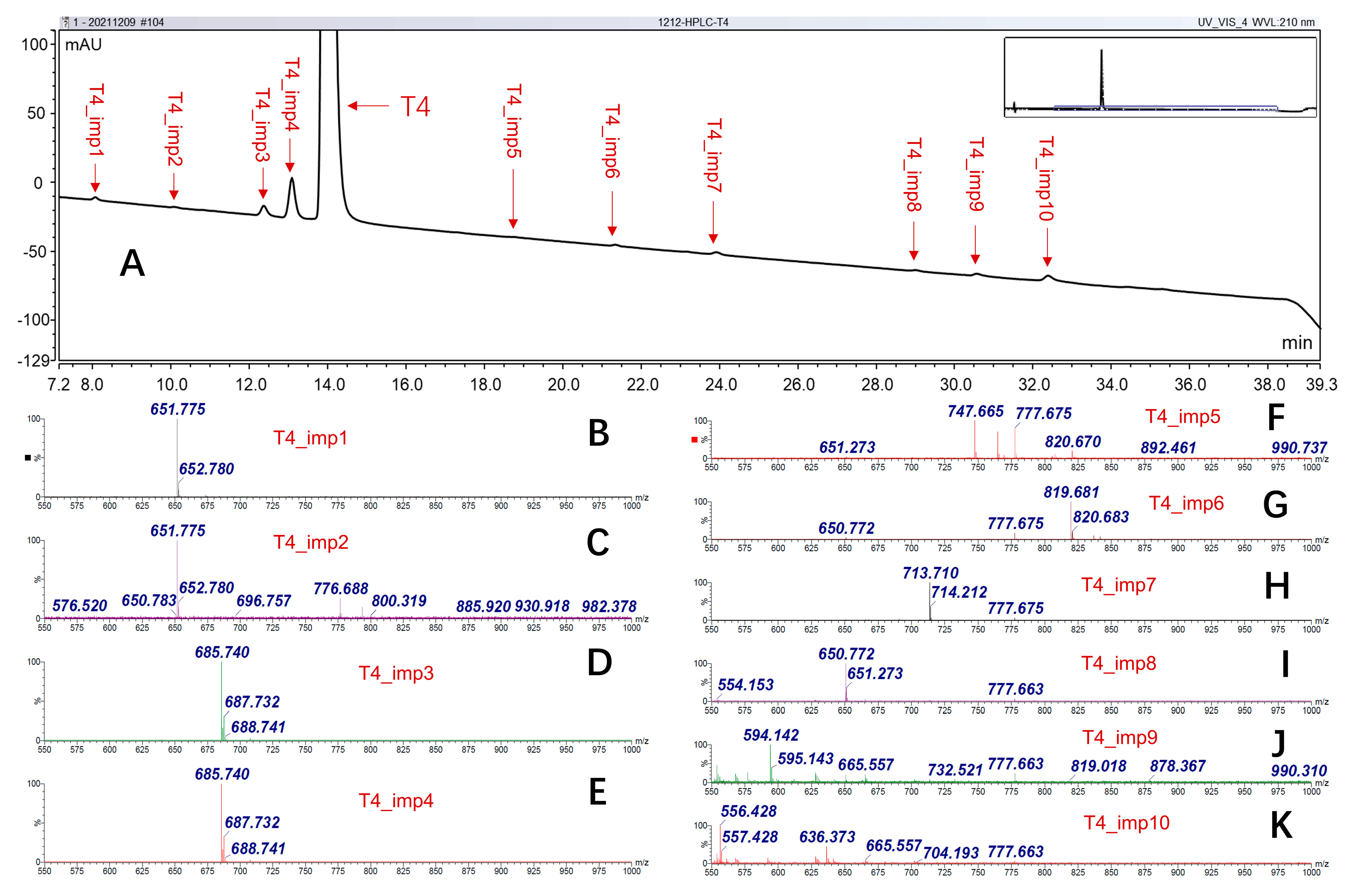
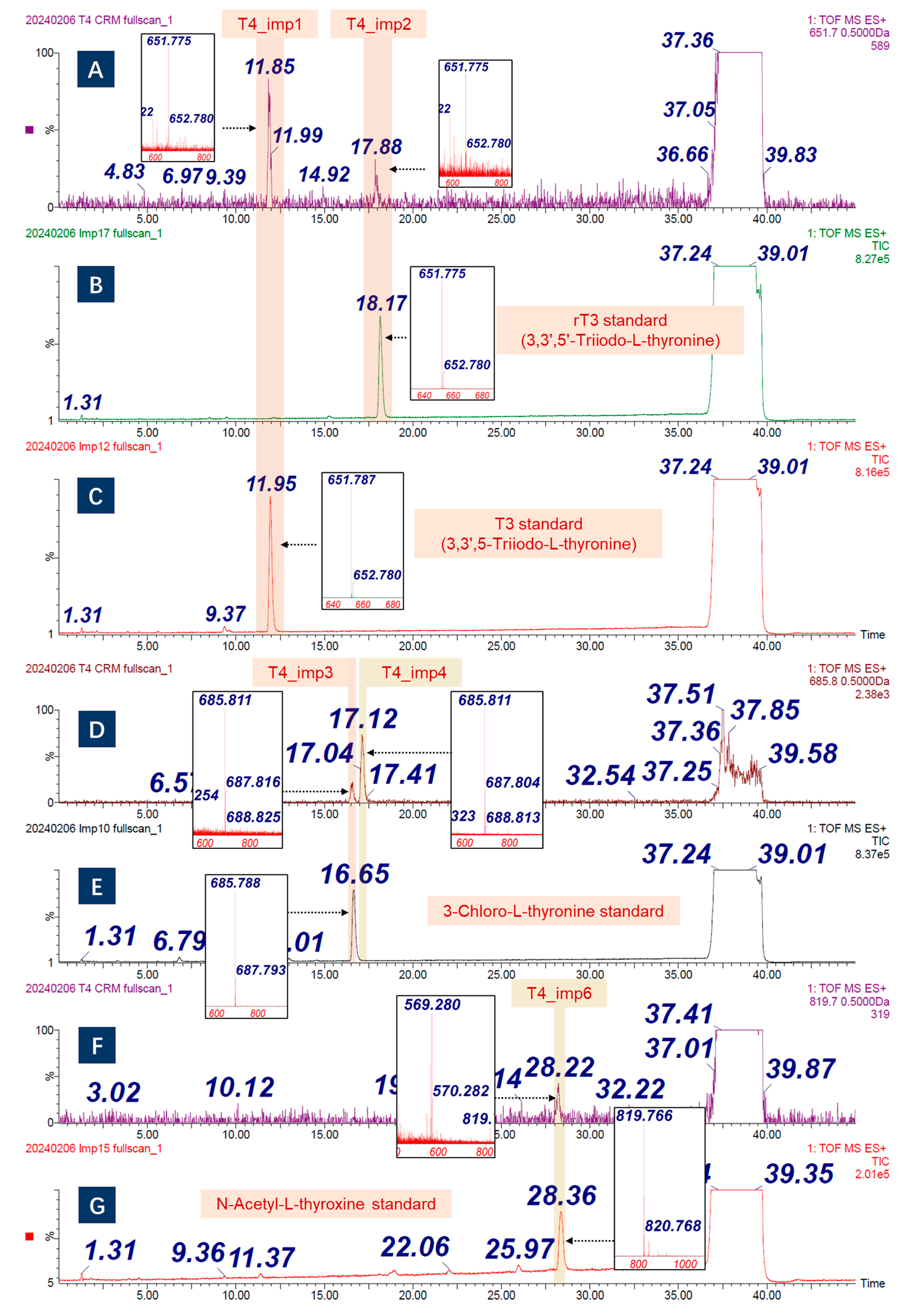
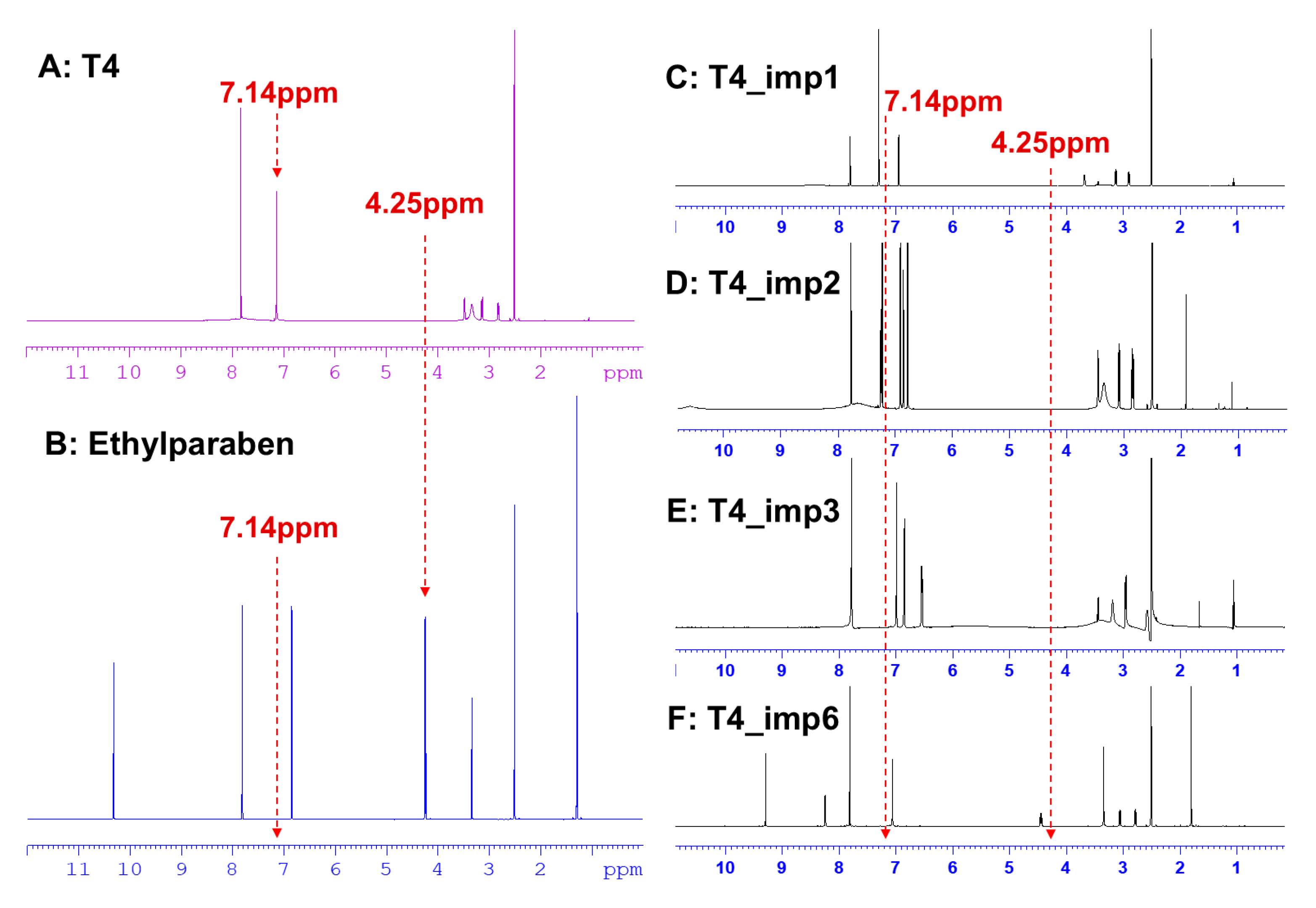
2.1.2. Structural-Related Impurities
2.1.3. Enantiomer in CRM Candidate
| Code | Mono. M.W. (Da) | Compound | CAS | High-Pure Material | Validated by | Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC | MS | Ref. | ||||||
| T4_imp1 | 650.7 | 3,3′,5-Triiodo-L-thyronine | 6893-02-3 | √ | √ | √ | [23] | 0.057% |
| T4_imp2 | 650.7 | 3,3′,5′-Triiodo-L-thyronine | 5817-39-0 | √ | √ | √ | [23] | 0.019% |
| T4_imp3 | 684.8 | 3-chloro-L-thyronine | 1628720-66-0 | √ | √ | √ | / | 0.187% |
| T4_imp4 | 684.8 | X-chloro-L-thyronine | / | √ | / | √ | / | 0.702% |
| T4_imp5 | 746.6 | Acetamide | 176258-88-1 | / | / | √ | / | / |
| T4_imp6 | 818.7 | N-acetyl-L-thyroxine | 26041-51-0 | √ | √ | √ | / | 0.041% |
| T4_imp7 | 1425.4 | T3−T4 dimer (biphenyl-bridged) | / | / | / | √ | [13] | / |
| T4_imp8 | 1299.5 | T3−T3 dimer (biphenyl-bridged) | / | / | / | √ | [13] | / |
| T4_imp9 | 593.1 | / | / | / | / | √ | / | / |
| T4_imp10 | 555.4 | / | / | / | / | √ | / | / |
2.2. Homogeneity and Stability
2.3. Quantitative Analysis by MB
2.3.1. Structurally Related Impurity Determination
2.3.2. Water Determination
2.3.3. Inorganic Impurity Determination
2.3.4. Residual Organic Solvent Determination
2.3.5. Mass Fraction by MB
2.4. Quantitative Analysis by 1H qNMR
2.5. Uncertainty Evaluation
2.5.1. Uncertainty of Homogeneity
2.5.2. Uncertainty of Stability
2.5.3. Uncertainty of the MB Method
2.5.4. Uncertainty of the qNMR Method
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Qualitative Characterization
3.3.1. IR Analysis
3.3.2. UV Analysis
3.3.3. Mass Spectrum Analysis
3.3.4. 1H NMR Spectrum
3.3.5. Enantiomer Characterization
3.4. Test of Homogeneity and Stability
3.5. MB Quantitative Experiments
3.5.1. Analysis of the Structurally Related Impurity
3.5.2. Analysis of the Water Impurity
3.5.3. Analysis of the Inorganic Impurity
3.5.4. Analysis of the Residual Organic Solvent Impurity
3.6. 1H qNMR Quantitative Experiments
3.7. Uncertainties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goemann, I.M.; Romitti, M.; Meyer, E.L.S.; Wajner, S.M.; Maia, A.L. Role of thyroid hormones in the neoplastic process: An overview. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R367–R385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.R.; Bassett, J.H.D. Thyroid diseases and bone health. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Song, D.; Ju, H.; Xing, W.; Ma, J.; Xiao, P. Mass spectrometry in measurement of thyroid biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 562, 119872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Ba, J.; Chen, B.; Du, J.; He, L.; Lai, X.; Teng, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Universal Salt Iodization on Thyroid Disorders: Epidemiological Evidence from 31 Provinces of Mainland China. Thyroid 2020, 30, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17511:2020; In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices—Requirements for Establishing Metrological Traceability of Values Assigned to Calibrators, Trueness Control Materials and Human Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Bièvre, P.D.; Dybkær, R.; Fajgelj, A.; Hibbert, D.B. Metrological traceability of measurement results in chemistry: Concepts and implementation (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1873–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houcke, S.K.; Van Uytfanghe, K.; Shimizu, E.; Tani, W.; Umemoto, M.; Thienpont, L.M. IFCC international conventional reference procedure for the measurement of free thyroxine in serum: International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) Working Group for Standardization of Thyroid Function Tests (WG-STFT)(1). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, H.I.; van der Steen, R.; Brandt, A.; Olthaar, A.J.; Vesper, H.W.; Shimizu, E.; Heijboer, A.C.; Van Uytfanghe, K.; van Herwaarden, A.E. Description and validation of an equilibrium dialysis ID-LC-MS/MS candidate reference measurement procedure for free thyroxine in human serum. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, S.; Choteau, T.; Daireaux, A.; Josephs, R.D.; Wielgosz, R.I. Mass balance method for the SI value assignment of the purity of organic compounds. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, G.F.; Chen, S.N.; Simmler, C.; Lankin, D.C.; Gödecke, T.; Jaki, B.U.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Napolitano, J.G. Importance of purity evaluation and the potential of quantitative 1H NMR as a purity assay. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9220–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, A.; Ruiz, M.E.; Volonté, M.G. A derivative UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of levothyroxine sodium in tablets. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, B.M.; Craik, D.J. 1H and 13C NMR relaxation studies of molecular dynamics of the thyroid hormones thyroxine, 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine, and 3,5-diiodothyronine. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggenthaler, M.; Grass, J.; Schuh, W.; Huber, C.G.; Reischl, R.J. Impurity profiling of liothyronine sodium by means of reversed phase HPLC, high resolution mass spectrometry, on-line H/D exchange and UV/Vis absorption. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2017, 143, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopley, C.J.; Stokes, P.; Webb, K.S.; Baynham, M. The analysis of thyroxine in human serum by an ‘exact matching’ isotope dilution method with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, J.R.; Dickson, G.T.; Elks, J.; Hems, B.A. 715. The synthesis of thyroxine and related substances. Part V. A synthesis of L-thyroxine from L-tyrosine. J. Chem. Soc. 1949, 3424–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.V.; Bowman, W.R.; Coe, P.F.; Turner, A.T.; Whybrow, D. Synthesis of thyroxine: Biomimetic studies. Can. J. Chem. 1997, 75, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemburkar, S.R.; Deming, K.C.; Reddy, R.E. Chemistry of thyroxine: An historical perspective and recent progress on its synthesis. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, D.; Feng, M.; Yang, Q.; Hu, W.; Han, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, M.; Yu, L. “Ghost peak” of clofazimine: A solution degradation product of clofazimine via nucleophilic substitution by nitrite leaching from certain glass HPLC vials. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2018, 150, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Adhikari, S.; Lee, W.; Yoon, H.-R. Development of Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Enantiomer Resolution of Thyroxine on a Chiral Crown Ether Derived Chiral Stationary Phase. Chromatographia 2023, 86, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Adhikari, S.; Ji, M.G.; Paik, M.J.; Lee, G.; Lee, W. Chiral LC–MS/MS method for the discrimination of triiodothyronine enantiomers on a crown ether-based chiral stationary phase. Chirality 2023, 35, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.A.; Stavrou, I.J.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C. Comparison of cyclofructan-, cyclodextrin-, and polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases for the separation of pharmaceuticals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, M.J.; Heckelman, P.E.; Koch, C.B.; Roman, K.J. The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 1743. [Google Scholar]
- Piehl, S.; Heberer, T.; Balizs, G.; Scanlan, T.S.; Köhrle, J. Development of a validated liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the distinction of thyronine and thyronamine constitutional isomers and for the identification of new deiodinase substrates. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3286–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 33405:2024; Reference Materials—Approaches for Characterization and Assessment of Homogeneity and Stability. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Tu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H. Purity Assessment of Dinotefuran Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Molecules 2023, 28, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y. Separation and characterization of the impurities in 3,3-diamino-4,4-azoxyfurazan by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography combined with Q-orbitrap mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Han, Z. Preparation and characterization of the aflatoxin B1 purity certified reference material (GBW (E) 100599). Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 109919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M.; Yang, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Development of purity certified reference materials to establish metrological traceability for the measurement of nitroimidazoles in agricultural products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 6437–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JJF 1343–2022; Characterization, Homogeneity and Stability Assessment of Reference Materials. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- JJF 1855–2020; Metrological Technical Specification for Purity Assessment of Certified Reference Materials-Organic Purity Certified Reference Materials. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- ISO 15194:2009; In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices—Measurement of Quantities in Samples of Biological Origin—Requirements for Certified Reference Materials and the Content of Supporting Documentation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
| (n = 6) | Purity | SD | F Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 99.61% | 1.006% | 3.563% | 0.0001% | 0.132% | 94.92% | 0.095% | 3.76 | 94.90% |
| qNMR | / | / | / | / | / | 94.88% | 0.049% |
| 0.186 | 0.281 | 0.168 | 0.0047 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.168 | 0.336 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Song, D.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Yao, H.; Xing, W.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Xiao, P. Development of Certified Reference Material of L-Thyroxine by Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Molecules 2025, 30, 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132840
Zhao Q, Zhang W, Song D, Zhou X, Li X, Yao H, Xing W, Li H, Ma J, Xiao P. Development of Certified Reference Material of L-Thyroxine by Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132840
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qiang, Weifei Zhang, Dan Song, Xirui Zhou, Xianjiang Li, Huan Yao, Wenjing Xing, Hongmei Li, Jian Ma, and Peng Xiao. 2025. "Development of Certified Reference Material of L-Thyroxine by Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132840
APA StyleZhao, Q., Zhang, W., Song, D., Zhou, X., Li, X., Yao, H., Xing, W., Li, H., Ma, J., & Xiao, P. (2025). Development of Certified Reference Material of L-Thyroxine by Using Mass Balance and Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Molecules, 30(13), 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132840








