New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
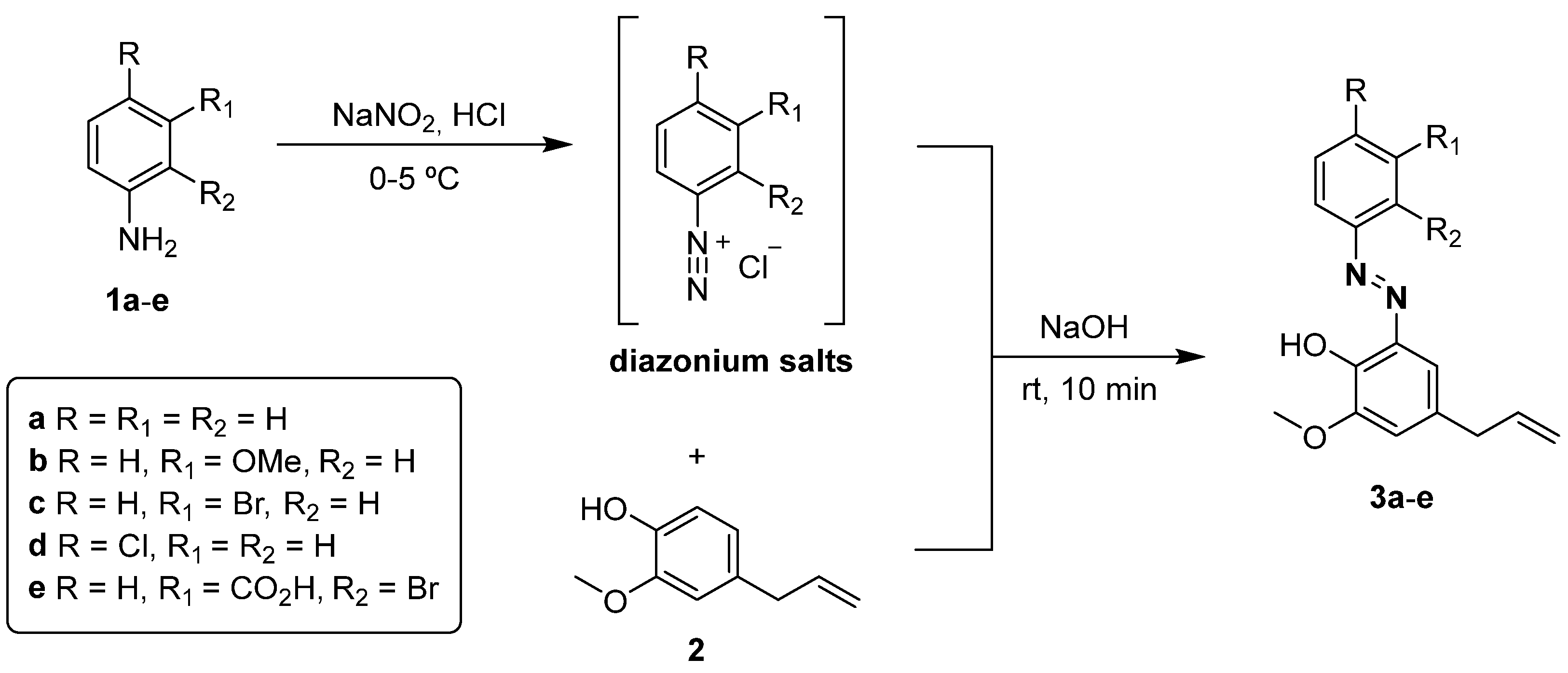
2.1. Synthesis of Eugenol Azo Dyes 3a–e
2.2. UV/Vis Absorption of the Eugenol Azo Dyes 3a–e
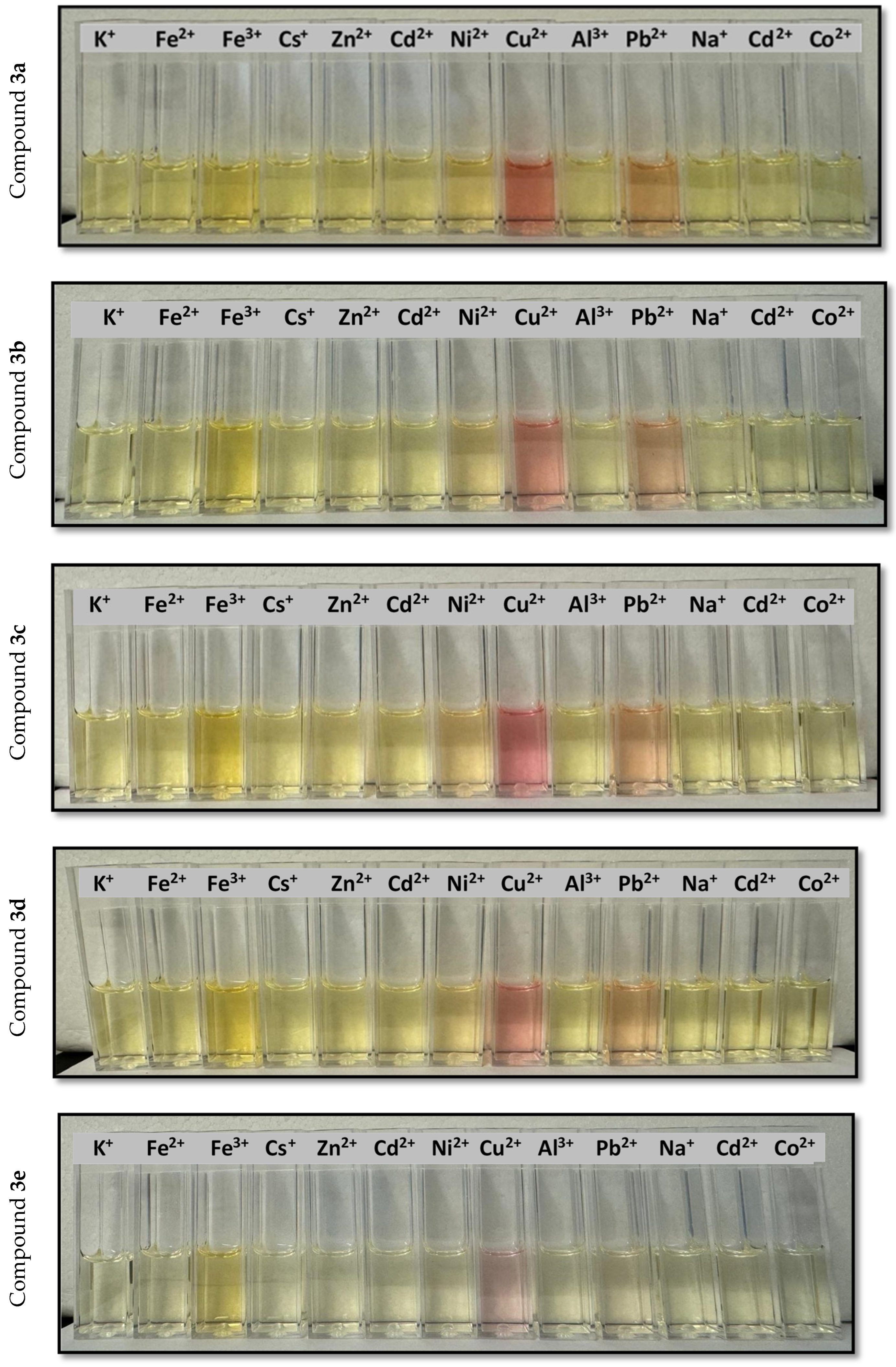
2.3. Colorimetric Assays of Compounds 3a–e as Ion Sensors
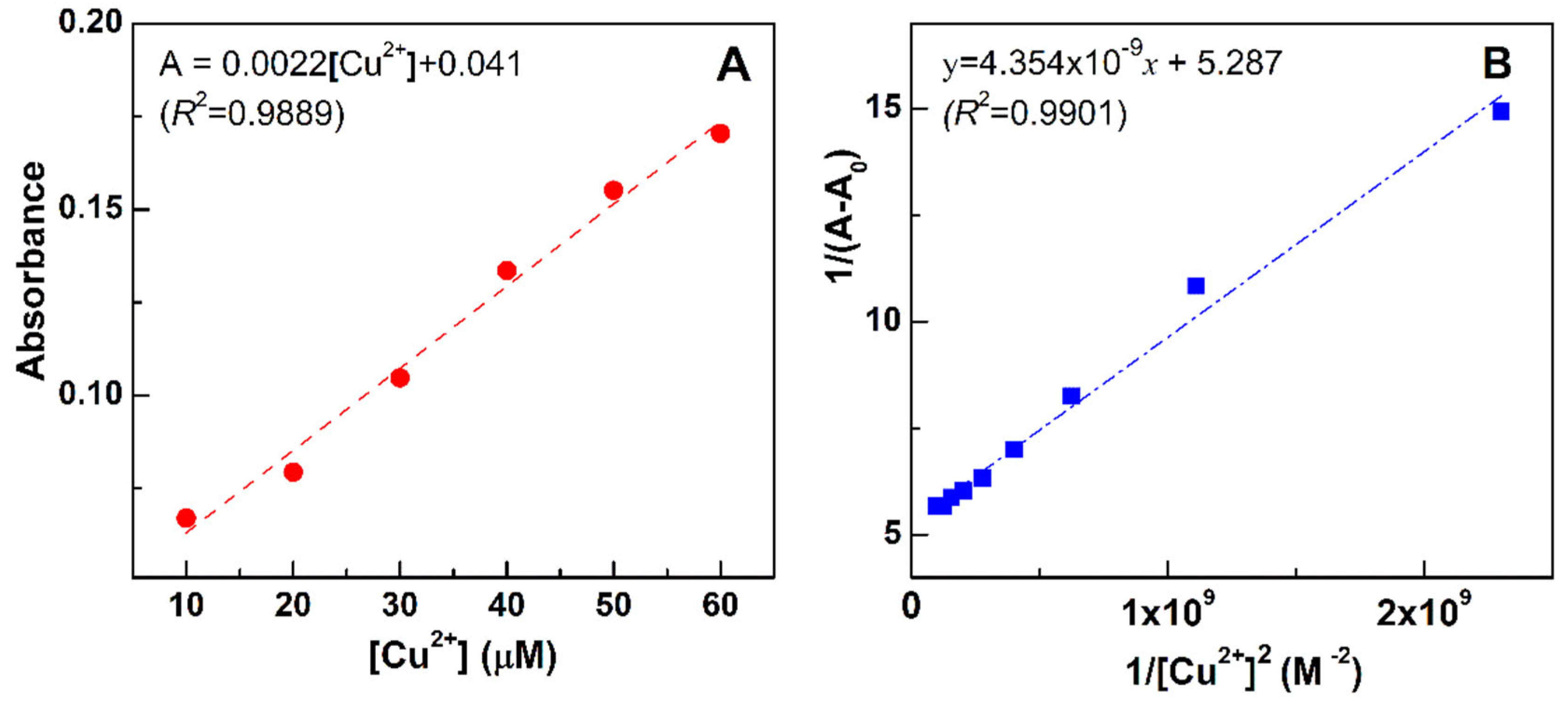
2.4. Titration of Compound 3c with Cu2+
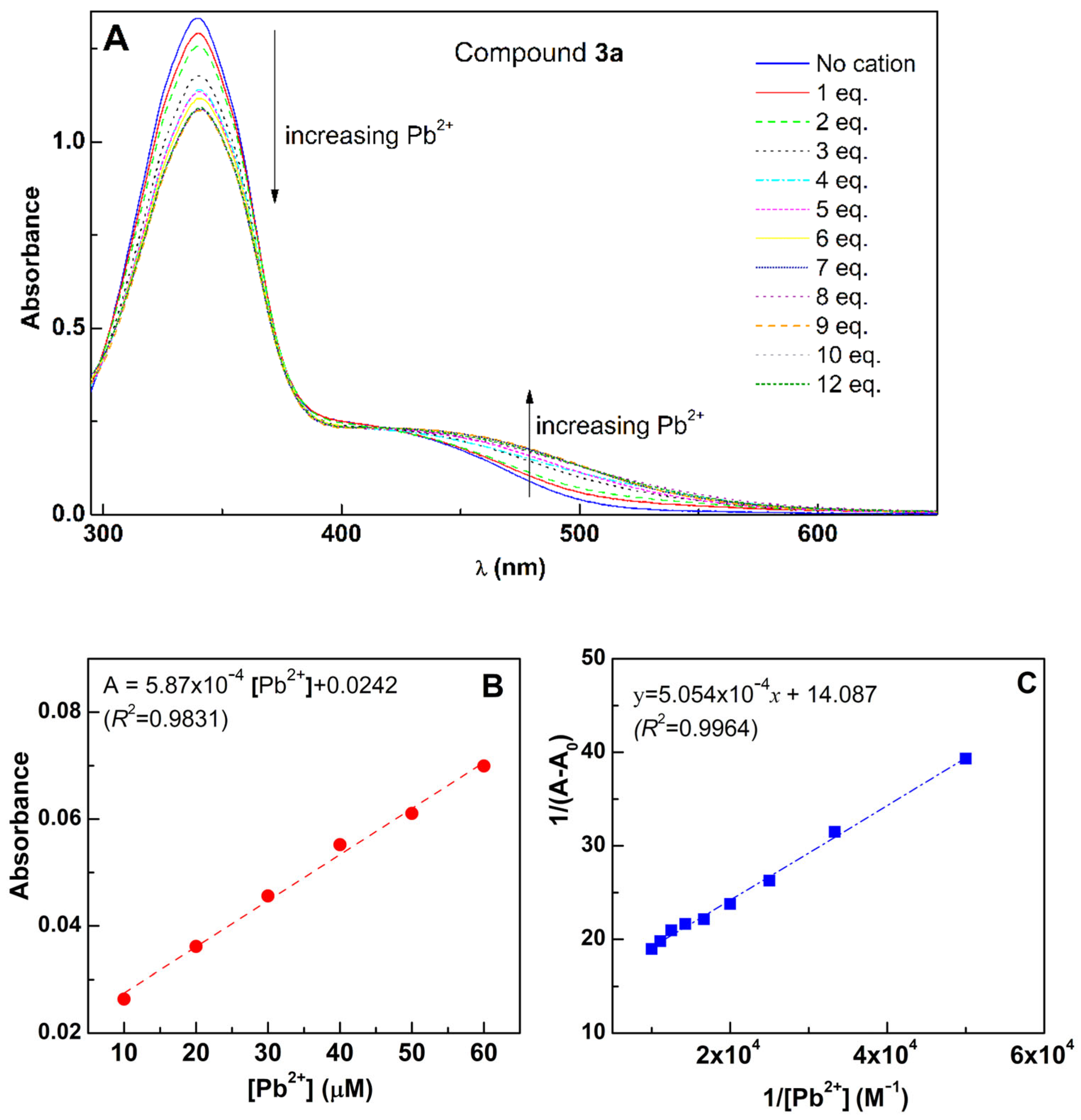
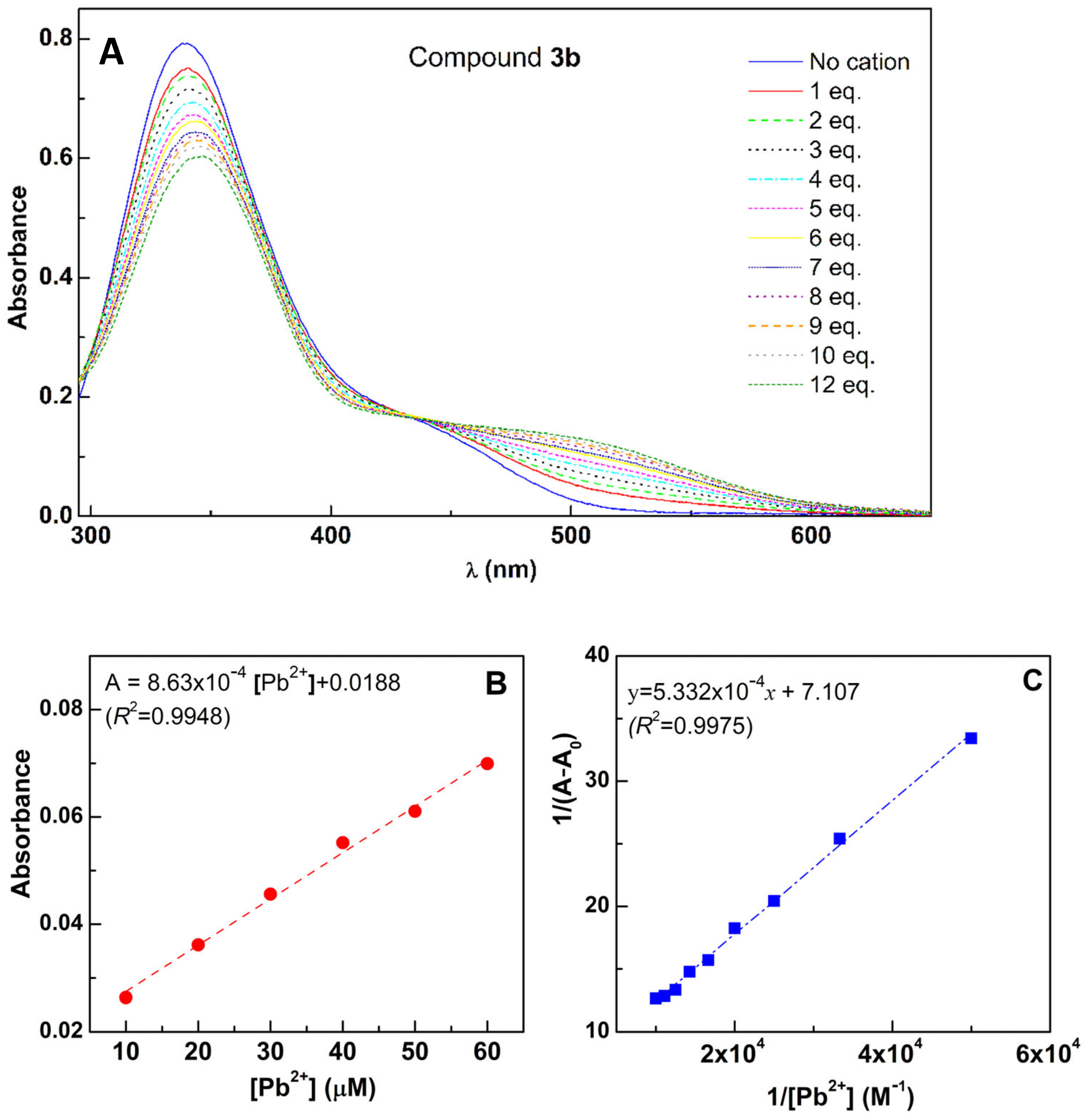
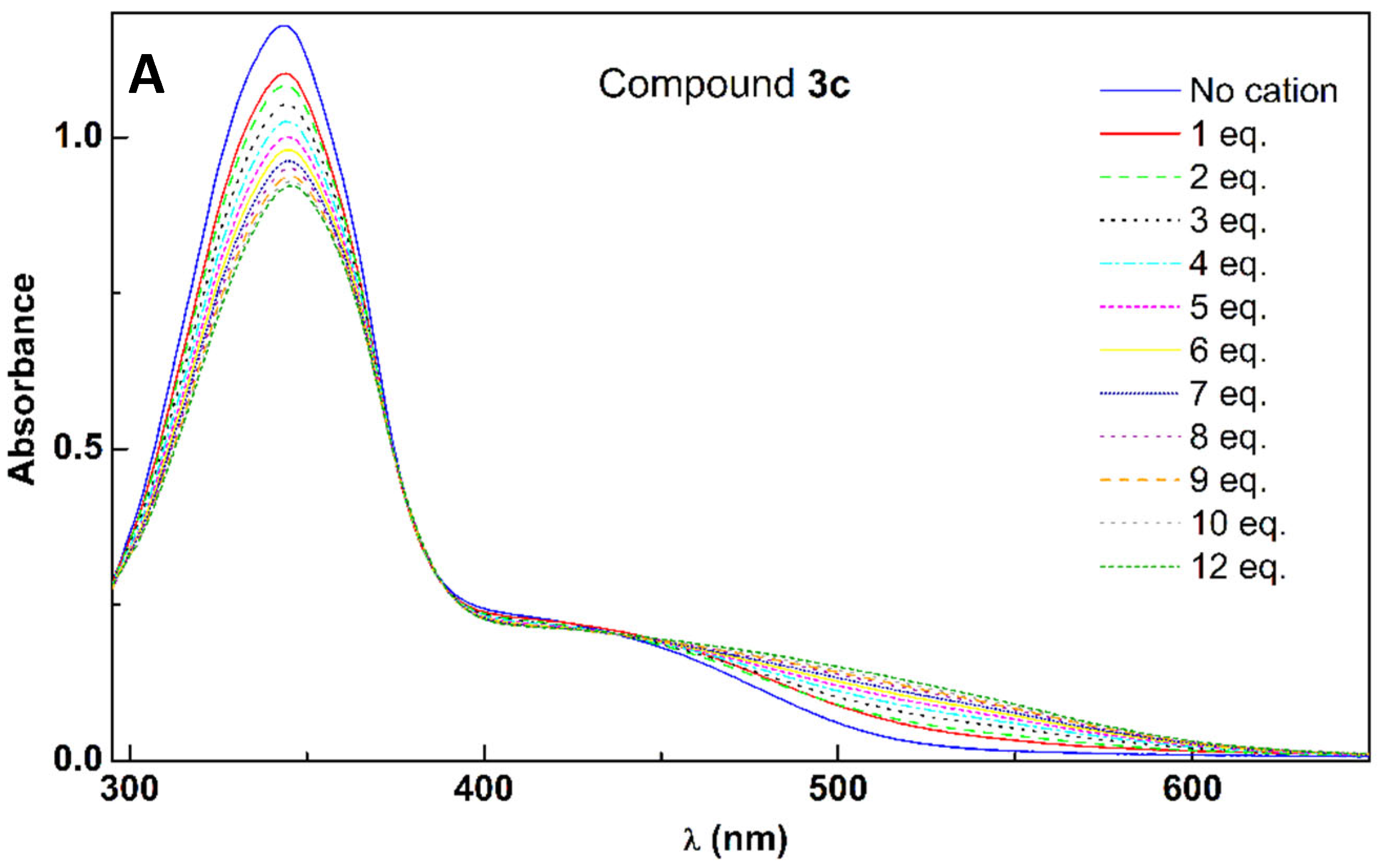
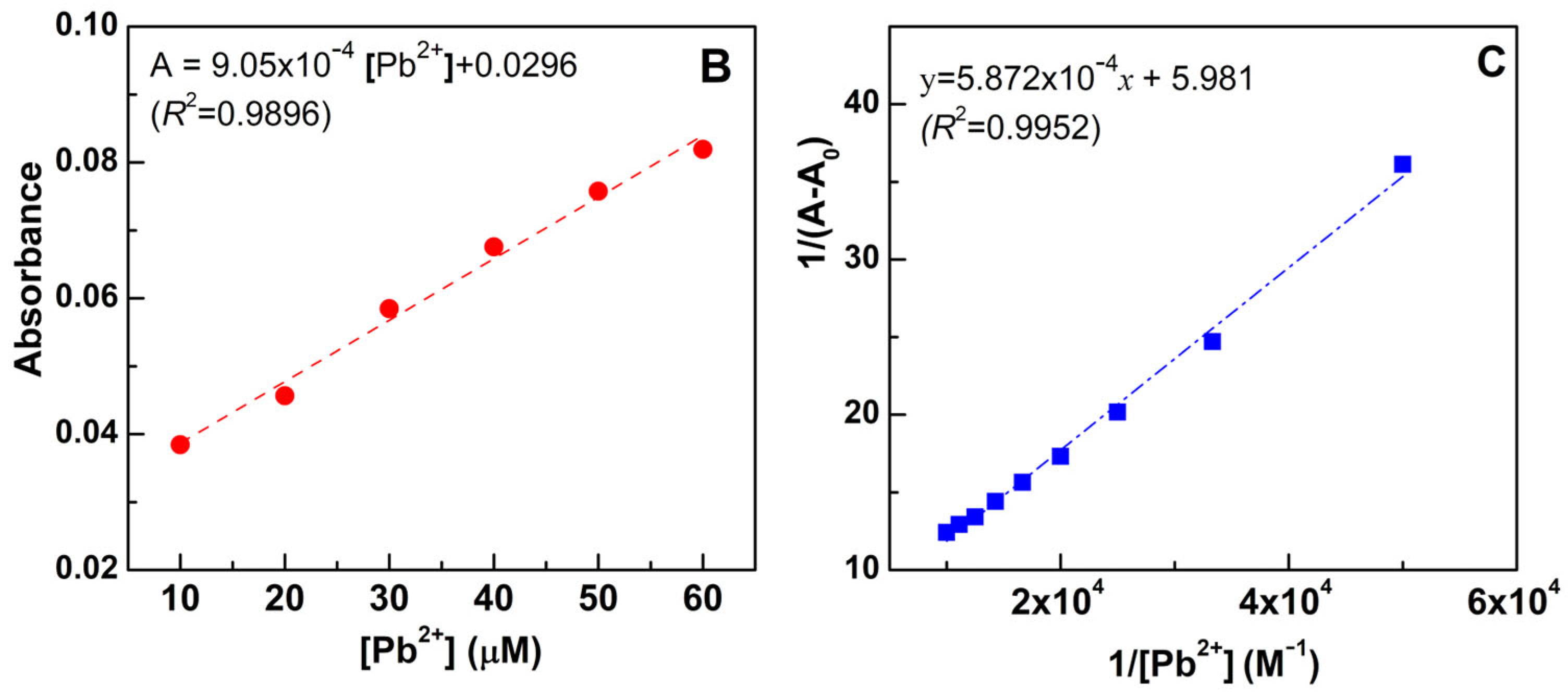
2.5. Titration of Compounds 3a–e with Pb2+
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Analytical Instruments
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Eugenol Azo Dyes 3a–e
3.3.1. 4-Allyl-2-methoxy-6-(phenyldiazenyl)phenol 3a
3.3.2. 4-Allyl-2-methoxy-6-((3-methoxyphenyl)diazenyl)phenol 3b
3.3.3. 4-Allyl-2-((3-bromophenyl)diazenyl)-6-methoxyphenol 3c
3.3.4. 4-Allyl-2-((4-chlorophenyl)diazenyl)-6-methoxyphenol 3d
3.3.5. 3-((5-Allyl-2-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)diazenyl)-2-bromobenzoic Acid 3e
3.4. Photophysical Analysis
3.4.1. Preparation of Solutions
3.4.2. Spectrophotometric Titrations
3.4.3. Ab Initio Molecular Quantum Chemistry Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsantali, R.I.; Raja, Q.A.; Alzahrani, A.Y.A.; Sadiq, A.; Naeem, N.; Mughal, E.U.; Al-Rooqi, M.M.; El Guesmi, N.; Ahmed, S.A. Miscellaneous azo dyes: A comprehensive review on recent advancements in biological and industrial applications. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 199, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespignani, L.; Bonanni, M.; Marradi, M.; Pizzo, B.; Bianchini, R.; Goli, G. Naturalized dyes: A new opportunity for the wood colouring. Polym. J. 2023, 15, 3632–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzicato, B.; Pacifico, S.; Cayuela, D.; Mijas, G.; Riba-Moliner, M. Advancements in sustainable natural dyes for textile applications: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5954–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, J.R.A.; Fernandes, M.J.G.; Gonçalves, M.S.T. New azo carboxylic dyes derived from eugenol: Synthesis and preliminary application to polyamide. Chem. Proc. 2023, 14, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mezgebe, K.; Mulugeta, E. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of azo dye derivatives incorporating heterocyclic scaffolds: A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25932–25946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.I.; Fedor, V.; Drozdov, F.V.; Georgij, V.; Cherkaev, G.V.; Buzin, M.I.; Svidchenko, E.A.; Muzafarov, A.M. Synthesis and properties of new siloxane with terminal azo dyes functions based on eugenol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanavatkar, C.W.; Mishra, V.R.; Sekar, N. Review of NLOphoric azo dyes—Developments in hyperpolarizabilities in last two decades. Dyes Pigment. 2021, 191, 109367–109392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, M.; Popa, C.V.; Tănase, M.A.; Soare, A.C.; Tablet, C.; Bala, D.; Cinteza, L.O.; Diţu, L.M.; Gifu, I.C.; Petcu, C. Synthesis, characterization, DFT study and antifungal activities of some novel 2-(phenyldiazenyl)phenol based azo dyes. Materials 2022, 15, 8162–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanum, R.; Shoukat Ali, R.A.; Rangaswamy, H.R.; Santhosh Kumar, S.R.; Pashantha, A.G.; Jagadisha, A.S. Recent review on synthesis, spectral studies, versatile applications of azo dyes and its metal complexes. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100890–100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deghadi, R.G.; Mahmoud, W.H.; Mohamed, G.G. Metal complexes of tetradentate azo-dye ligand derived from 4,4′-oxydianiline: Preparation, structural investigation, biological evaluation and MOE studies. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaber, M.A.I.; Abd El-Lateef, H.M.; Khalaf, M.M.; Shaaban, S.; Shawky, M.; Mohamed, G.G.; Abdou, A.; Gouda, M.; Abu-Dief, A.M. Design, synthesis, spectroscopic inspection, DFT and molecular docking study of metal chelates incorporating azo dye ligand for biological evaluation. Materials 2023, 16, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L. Simple phenylpropanoids: Recent advances in biological activities, biosynthetic pathways, and microbial production. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 41, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Błajet, M.; Feder-Kubis, J. Monoterpenes and their derivatives–recent development in biological and medical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7078–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandge, S.V.; Nikume, S.R.; Bendre, R.S. An efficient synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and anticancer activities of azo dyes derived from eugenol. Synth. Commun. 2023, 54, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Niccolai, S.; Tanini, D.; D’Agostino, I.; Melfi, F.; Capperucci, A.; Grande, R.; Sisto, F. Nature-inspired compounds: Synthesis and antibacterial susceptibility testing of eugenol derivatives against H. pylori strains. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melfi, F.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Carradori, S.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Mencarelli, N.; Gallorini, M.; Spano, M.; Agamennone, M.; Haji Ali, S.; Al-Samydai, A.; et al. Azo derivatives of monoterpenes as anti-Helicobacter pylori agents: From the synthesis to a structure-based target investigation. RSC Med. Chem. 2025, 16, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.R.F.; Militani, I.A.; de Almeida, K.J.; Lunguinho, A.S.; Saczk, A.A.; Ionta, M.; da Silva, G.A.F.; Felix, F.S.; Nelson, D.L.; Cardoso, M.G. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of essential oils and their principal components: Spectrophotometric, voltammetric, and theoretical investigation of the chelating effect of eugenol and carvacrol. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaphal, Y.R.; Gholap, S.S. Eugenol [2-Methoxy-4-allylphenol (MAP)] a colorimetric sensing probe for selective determination of Iron(III). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2022, 13, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jomova, K.; Valko, M. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 2011, 283, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.M.; Libedinsky, A.; Elorza, A.A. Role of copper on mitochondrial function and metabolism. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 711227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, A.; Mumper, R.J. Elevated copper and oxidative stress in cancer cells as a target for cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardos, J.; Héja, L.; Simon, A.; Jablonkai, I.; Kovács, R.; Jemnitz, K. Copper signalling: Causes and consequences. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ). Lead Poisoning: What Are the Sources? What Are the Risks? TCEQ Publication GI-069. 2004. Available online: https://www.tceq.texas.gov/downloads/toxicology/publications/lead-poisoning-gi-69.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.G.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 7, 100094–100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, M.; Wagner, C.R.; Tamura, E.K.; Garcia, J.; Louie, A.Y. Small molecule sensors for the colorimetric detection of Copper(II): A review of the literature from 2010 to 2022. Dyes Pigment. 2023, 214, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Yu, X.-Q. Small molecular fluorescent probes for the detection of lead, cadmium and mercury ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, H.; Sun, R.; Mao, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. A colorimetric Pb2+ chemosensor: Rapid naked-eye detection, high selectivity, theoretical insights, and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 355, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavalishin, M.N.; Gamov, G.A.; Kiselev, A.N.; Nikitin, G.A. A fluorescein conjugate as colorimetric and red-emissive fluorescence chemosensor for selective recognition Cu2+ ions. Opt. Mater. 2024, 153, 115580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, H.M. Recent advancements in organic chemosensors for the detection of Pb2+: A review. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 4807–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, A.Y. Recent progress in organic fluorescence and colorimetric chemosensors for Cu2+ detection: A comprehensive review (2018–2023). Dyes Pigment. 2023, 220, 111740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.I.; Nassar, S.; Farghaly, T.A. Spectrophotometric method for detecting lead (II) ions using a chemosensor of the thiosemicarbazone-linked phenyl sulphone moiety. Results Chem. 2025, 15, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, R.; Wali, S.; Singh, G.B. The UV and FTIR fingerprint of ocimum kilimandscharicum guerke essential oil: A eugenol-rich chemo type. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2022, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Second Addendum, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, M.C.; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 797S–811S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghule, N.V.; Bhosale, R.S.; Puyad, A.L.; Bhosale, S.V. Naphthalenediimide amphiphile based colorimetric probe for recognition of Cu2+ and Fe3+ ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, T.; Ma, F.; Li, T.; Niu, Q. A novel fluorescent and colorimetric dual-channel sensor for the fast, reversible and simultaneous detection of Fe3+ and Cu2+ based on terthiophene derivative with high sensitivity and selectivity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 383, 111982–111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.C.S.; Gonçalves, R.C.R.; Costa, S.P.G.; Raposo, M.M.M. Colorimetric chemosensor for Cu2+ and Fe3+ based on a meso-triphenylamine-BODIPY derivative. Sensors 2023, 23, 6995–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, A.A.; Ryzhkov, A.I.; Cherkaev, G.V.; Drozdov, F.V.; Muzafarov, A.M. Silicone films with azo dyes moieties based on eugenol with response to Cu2+ metal ions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 318, 129248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Exposure to Lead: A Major Public Health Concern: Preventing Disease Through Healthy Environments, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.who.int/campaigns/international-lead-poisoning-prevention-week (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- World Health Organization. Guideline for Clinical Management of Exposure to Lead; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lead-prevention/about/ (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Wang, L.; Fang, G.; Cao, D. A novel phenol-based BODIPY chemosensor for selective detection of Fe3+ with colorimetric and fluorometric dual-mode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesi, H.A.; Hildebrand, J.H. A spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 2703–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software update: The ORCA program system, version 5.0. WIRES Comput. Molec. Sci. 2022, 12, e1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. An improvement of the resolution of the identity approximation for the formation of the Coulomb matrix. J. Comp. Chem. 2003, 24, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigend, F. Accurate coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeweyher, E.; Ehlert, S.; Hansen, A.; Neugebauer, H.; Spicher, S.; Bannwarth, C.; Grimme, S. A generally applicable atomic-charge dependent London dispersion correction. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 154122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
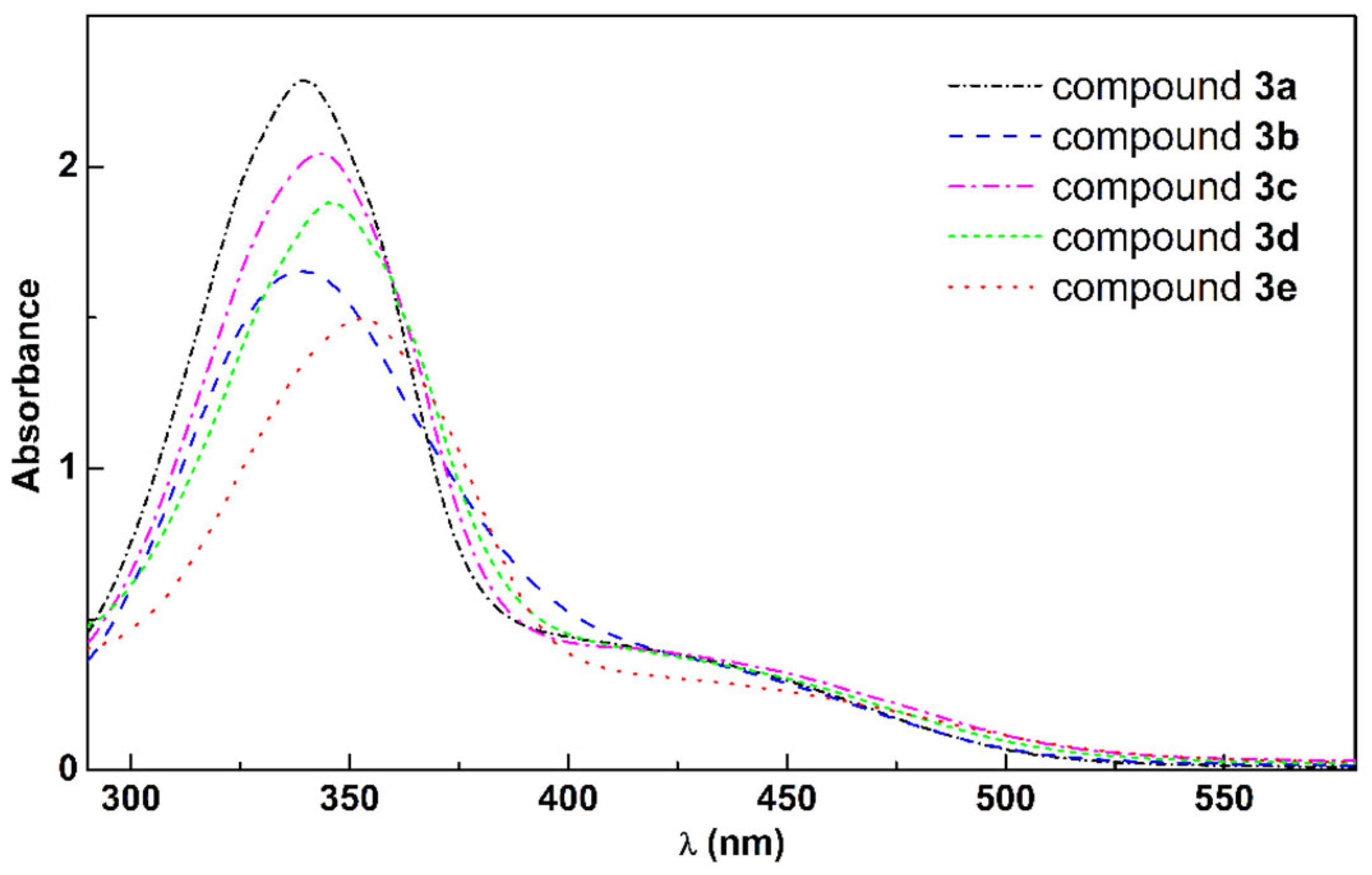




| Compound | λmax (nm) | ε (M−1 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 3a | 340 | 1.14 × 105 |
| 3b | 338 | 8.27 × 104 |
| 3c | 343 | 1.02 × 105 |
| 3d | 345 | 9.40 × 104 |
| 3e | 353 | 7.48 × 104 |
| Transition | Wavelength (nm) | Oscillator Strength (f) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trans | cis | Tautomer | Pb2+ Complex | trans | cis | Tautomer | Pb2+ Complex | |
| S0 → S1 | 448 | 476 | 472 | 537 | 7.40 × 10−4 | 4.02 × 10−2 | 4.94 × 10−2 | 2.51 × 10−3 |
| S0 → S2 | 417 | 395 | 445 | 468 | 8.15 × 10−2 | 6.80 × 10−3 | 1.29 × 10−1 | 1.30 × 10−1 |
| S0 → S3 | 328 | 319 | 348 | 396 | 1.06 | 2.11 × 10−2 | 9.02 × 10−1 | 1.05 × 10−2 |
| S0 → S4 | 302 | 288 | 313 | 347 | 1.76 × 10−2 | 4.96 × 10−3 | 4.05 × 10−3 | 8.59 × 10−2 |
| S0 → S5 | 296 | 280 | 311 | 335 | 3.26 × 10−4 | 1.32 × 10−1 | 1.50 × 10−2 | 7.84 × 10−4 |
| S0 → S6 | 278 | 275 | 287 | 325 | 5.96 × 10−2 | 5.28 × 10−3 | 9.03 × 10−4 | 5.03 × 10−2 |
| S0 → S7 | 256 | 271 | 278 | 324 | 1.97 × 10−3 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 8.14 × 10−3 | 2.99 × 10−1 |
| S0 → S8 | 253 | 258 | 257 | 318 | 1.10 × 10−2 | 7.25 × 10−3 | 8.93 × 10−2 | 2.17 × 10−1 |
| Compound | LOD (µM) | Ka (M−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 3a | 0.19 | 2.80 × 104 |
| 3b | 0.14 | 1.33 × 104 |
| 3c | 0.16 | 1.02 × 104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, J.R.A.; Pacheco, A.R.F.; Domingues, D.C.; Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Temitope, A.A.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Fernandes, M.J.G.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Gonçalves, M.S.T. New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes. Molecules 2025, 30, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132788
Coelho JRA, Pacheco ARF, Domingues DC, Rodrigues ARO, Temitope AA, Coutinho PJG, Fernandes MJG, Castanheira EMS, Gonçalves MST. New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132788
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, José R. A., Ana Rita F. Pacheco, Diogo C. Domingues, Ana Rita O. Rodrigues, Akani A. Temitope, Paulo J. G. Coutinho, Maria José G. Fernandes, Elisabete M. S. Castanheira, and M. Sameiro T. Gonçalves. 2025. "New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132788
APA StyleCoelho, J. R. A., Pacheco, A. R. F., Domingues, D. C., Rodrigues, A. R. O., Temitope, A. A., Coutinho, P. J. G., Fernandes, M. J. G., Castanheira, E. M. S., & Gonçalves, M. S. T. (2025). New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes. Molecules, 30(13), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132788









