Development of an HPTLC-MS Method for the Differentiation of Celosiae Semen: Celosia argentea Versus C. cristata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Size Assessment via ImageJ
2.2. HPTLC Fingerprints of CAS and CCS
2.3. Advanced Chemical Profiling of HPTLC-Derived Spots by MS-Interface
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Sample Preparation
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
4.3. ImageJ Analysis
4.4. HPTLC-MS Analysis
4.4.1. Equipment
4.4.2. HPTLC Conditions
4.4.3. MS-Interface Conditions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Automatic Developing Chamber |
| CAS | Celosiae Argentea Semen |
| CCS | Celosiae Cristatae Semen |
| ChP 2020 | Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China |
| ESI | Electrospray Ionization |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| HPTLC | High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography |
| HPTLC-MS | High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography coupled with Mass Spectrometry |
| KHP | Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SRAP | Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism |
| SST | System Suitability Test |
| TLC | Thin-Layer Chromatography |
| TOF | Time of Flight |
References
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 207. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, B.I.; Kwon, D.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, M.S.; Bu, Y.M. Medicinal Herbology; Younhlim-Sa: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2012; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.; Sun, Z.-L.; Guo, M.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.-K. Two new compounds from Semen celosiae and their protective effects against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.-L.; Li, Y.-X. Two new hepaprotective saponins from Semen celosiae. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.B.; Wang, Y.; Liang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, M.L.; Zhang, J.J. Novel triterpenoid saponins from the seeds of Celosia argentea L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.-J.; Wang, Y.-M.; Li, H.-J. Dereplication-guided isolation of novel hepatoprotective triterpenoid saponins from Celosiae Semen by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem quadrupole–time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M. Triterpenoid saponins from the seeds of Celosia argentea and their anti-inflammatory and antitumor activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Shen, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Cong, Y.; Shi, B. Chemical compounds with a neuroprotective effect from the seeds of Celosia argentea L. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yan, H.-X.; Wang, Z.-F.; Fan, M.-X.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, X.-T.; Xiong, C.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, B.-P.; Guo, H.-Z. New oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins isolated from the seeds of Celosia argentea. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.I.; Suzuki, H.; Shimbo, K.; Takeya, K.; Morita, H. Celogentins A–C, New Antimitotic Bicyclic Peptides from the Seeds of Celosia a rgentea. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Morita, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Kobayashi, J.I. New antimitotic bicyclic peptides, celogentins D–H, and J, from the seeds of Celosia argentea. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 5307–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-R.; Qi, M.-X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of four Chinese herbs which pass through liver-channel on improving eyesight and protecting oxidative injury of lens and apoptosis of lens epithelial cells. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 9, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Vetrichelvan, T.; Jegadeesan, M.; Devi, B.A.U. Anti-diabetic activity of alcoholic extract of Celosia argentea L INN. seeds in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Wu, Q.-B.; Guo, M.-L. A novel hepatoprotective saponin from Celosia cristata L. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-L.; Gao, G.-L.; Xia, Y.-F.; Feng, J.; Qiao, Z.-Y. A new hepoprotective saponin from Semen Celosia cristatae. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-M.; Wang, X.-F.; Feng, J.; Sun, Z.-L. Chemical constituents of the seeds of Celosia cristata. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, K.; Jia, A.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, L.; Sun, Z. Three new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins from the seeds of Celosia cristata L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Chemical Constituents and Bioactivities of Celosia cristata L. and Penthorum Chinense Pursh; Shanghai Second Military Medical University: Shanghai, China, 2012; pp. 4–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, P.; Ohri, D.; Pal, M. Nuclear DNA content in Celosia (Amaranthaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1992, 182, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Xue, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, R.; Guo, M. Genetic diversity and population structure of Celosia argentea and related species revealed by SRAP. Biochem. Genet. 2009, 47, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.X.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, P.; Li, H.J. Precise identification of Celosia argentea seed and its five adulterants by multiple morphological and chemical means. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 216, 114802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadharaj, V.; Muniyappan, J. Phytochemical and phytotherapeutic properties of Celosia species-a review. Int. J. Pharm. Phytochem. Res. 2017, 9, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, G.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, G.; Ju, Y.S.; Ji, C.Y.; Kim, T.J. Identification of Morphological Appearance of Fine Seed Herbs Using Stereoscope (Report I)-Celosiae Semen, Celoisae Cristatae Semen, Cuscutae Semen, Perillae Semen. J. Korean Med. 2013, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucrose; LC-ESI-QTOF; MS2; CE:Ramp 5-60 V; [M-H]-. MassBank High Quality Mass Spectral Database. 2016. Available online: https://massbank.eu/MassBank/RecordDisplay?id=MSBNK-RIKEN-PR100500&dsn=RIKEN (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.K.T.; Schmid, M.; Phanse, M.; Charegaonkar, A.; Sprecher, H.; Obkircher, M.; Reich, E. Development of the first universal mixture for use in system suitability tests for high-performance thin layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Do, T.K.T.; Trettin, I.; Reich, E. Applicability of the Universal Mixture for describing system suitability and quality of analytical data in routine normal phase High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1666, 462863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: Chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
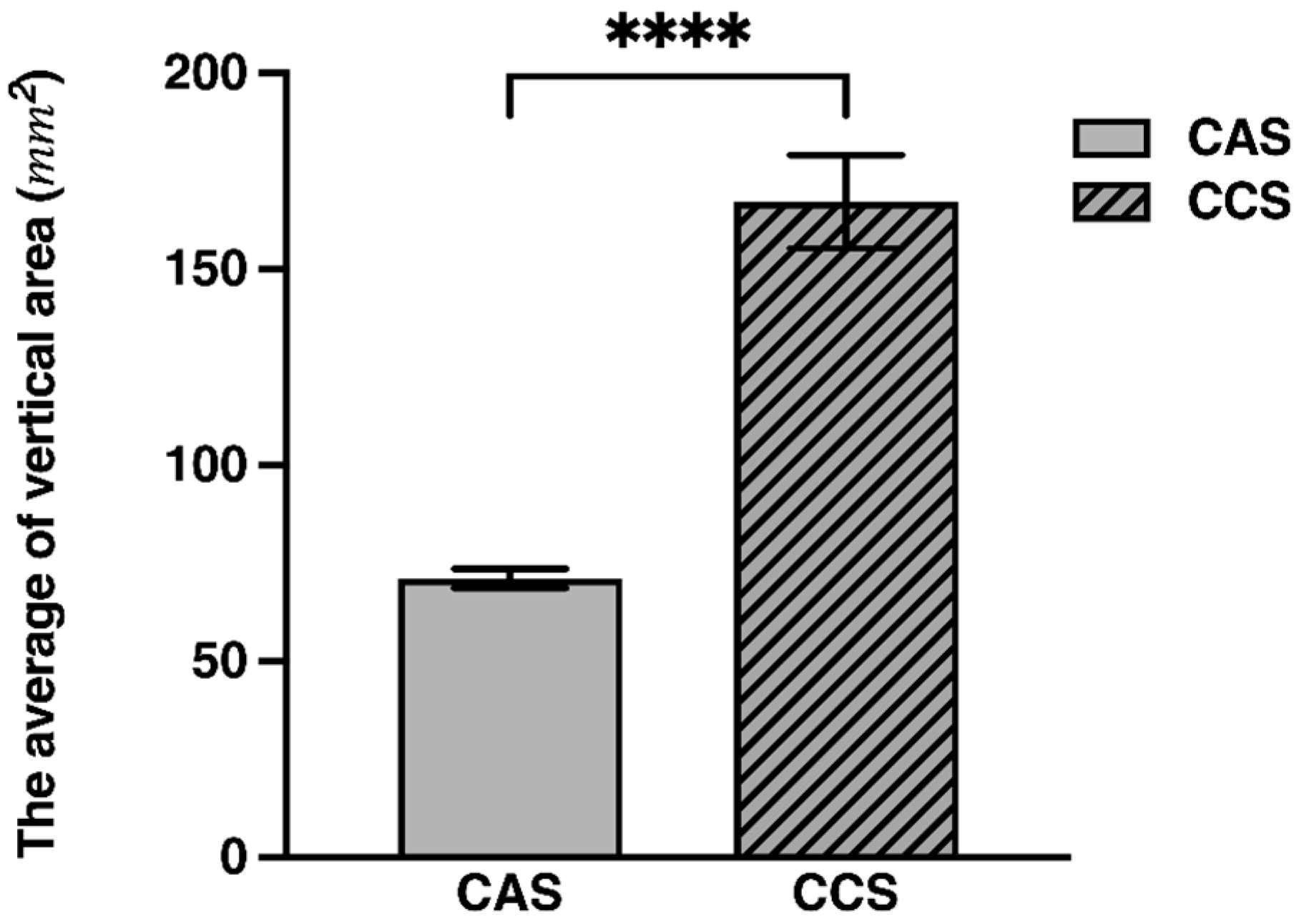
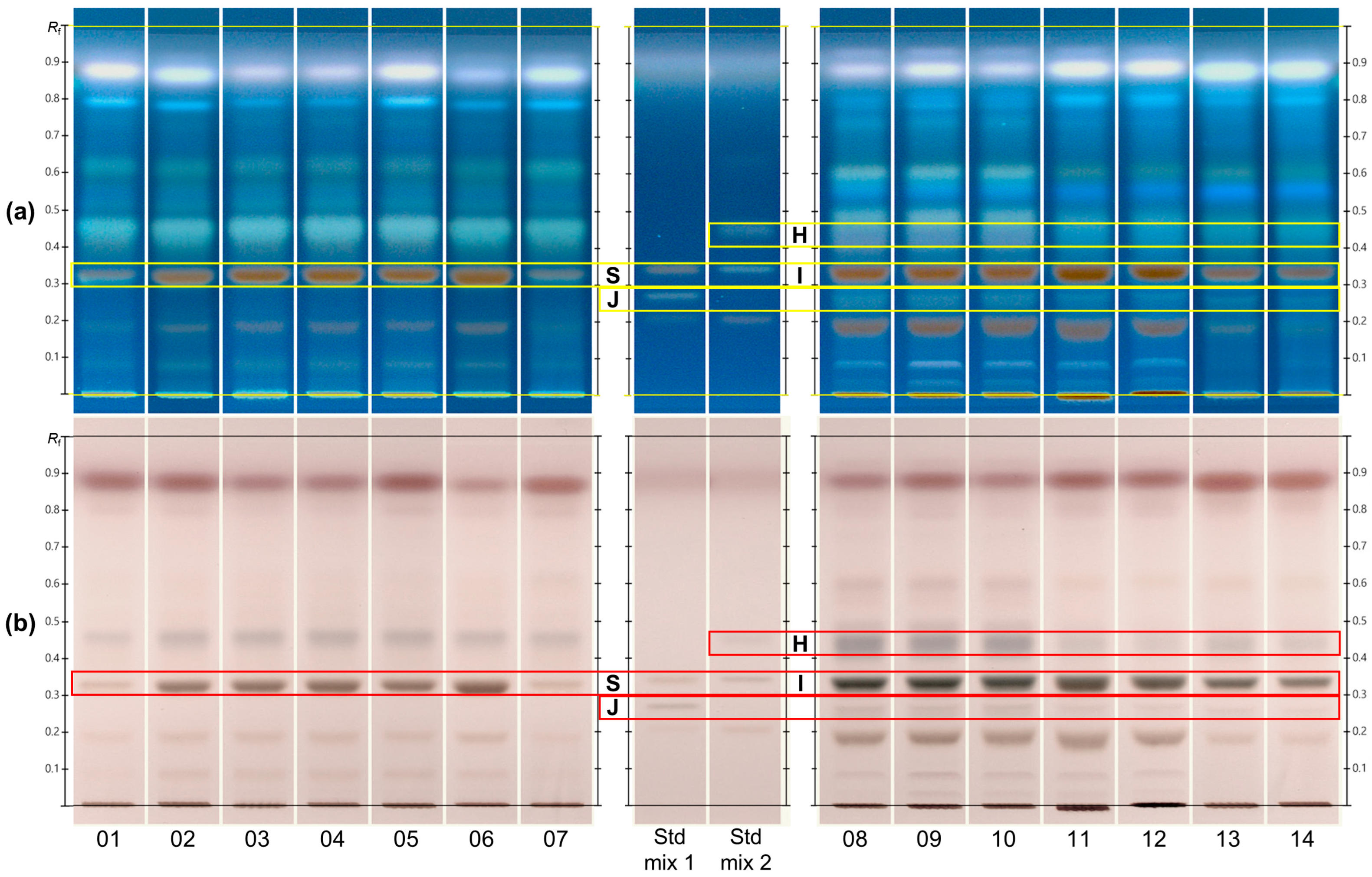
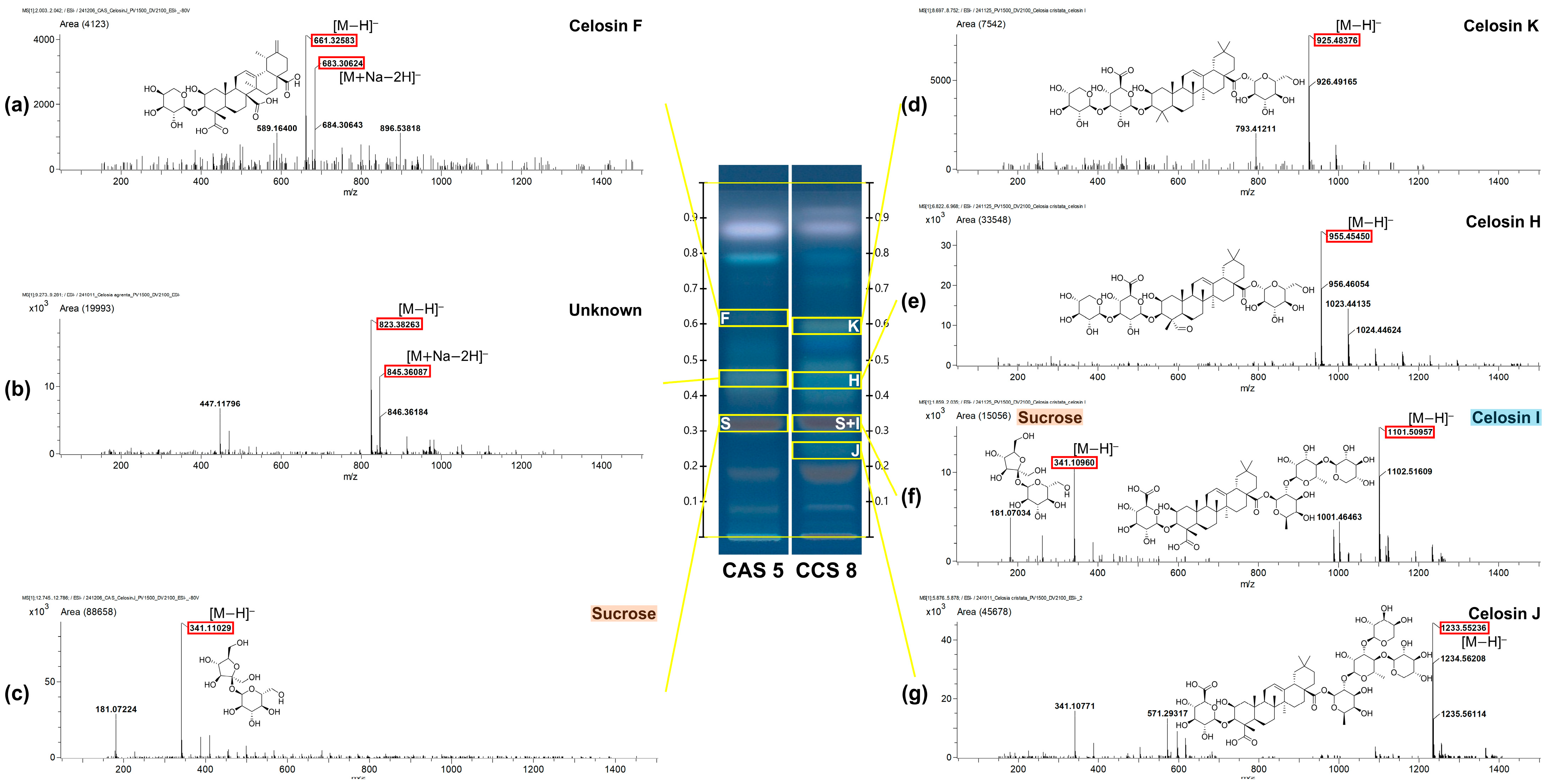
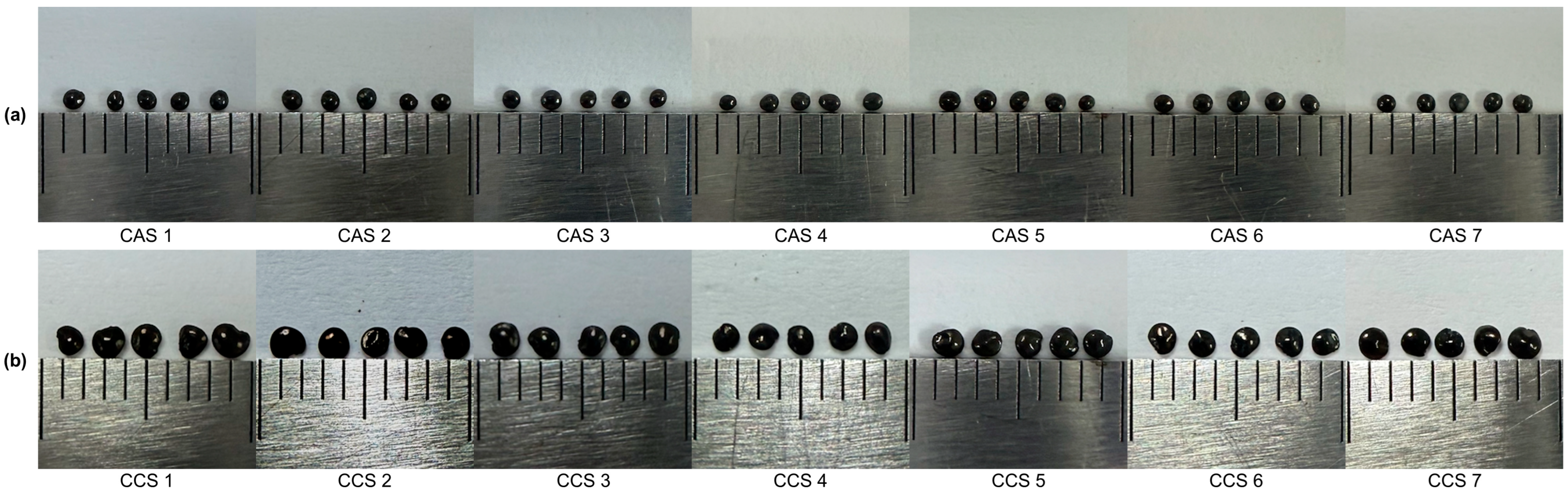
| Rank Sum | U Statistic | Z-Score | p-Value | Z Adjusted | Valid N | 2*1 Sided Exact p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS | CCS | CAS | CCS | |||||
| 2485 | 7385 | 0.0 | 10.2085 | 0.000 | 10.2085 | 70 | 70 | 0.000 |
| No. | RF Value | m/z a | Quasi-Molecular Ion | Mass Difference (mmu) | Molecular Formula | Identification | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 0.62 | 661.32583 | H]− | 3.43 | C35H50O12 | celosin F * | [21] c |
| 683.30624 | 2H]− | 1.89 | |||||
| (b) | 0.46 | 823.38263 | H]− | 1.53 | C34H64O22 | Undefined | - |
| 845.36087 | 2H]− | −2.18 | |||||
| (c) | 0.33 | 341.11029 | H]− | 1.90 | C12H22O11 | sucrose | [24] b,c |
| (d) | 0.6 | 925.48376 | OH]− | 4.07 | C47H74O18 | celosin K | [21] c |
| (e) | 0.44 | 955.45450 | H]− | 0.63 | C47H72O20 | celosin H | [21] b,c |
| (f) | 0.33 | 341.10960 | H]− | 1.22 | C12H22O11 | sucrose | [24] b,c |
| 0.33 | 1101.50957 | H]− | −2.20 | C53H82O24 | celosin I | [21] b,c | |
| (g) | 0.25 | 1233.55236 | H]− | −1.68 | C58H90O28 | celosin J | [21] b,c |
| No. | Sample | Botanical Source | Origin | Supplier | Expiration Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Mageherb | 30 June 2025 |
| 2 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Donguibogam | 18 May 2024 |
| 3 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Hanteut Herbal Medicine | 10 May 2025 |
| 4 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Hanteut Herbal Medicine | 26 February 2025 |
| 5 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Hanteut Herbal Medicine | 9 May 2024 |
| 6 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Dongui Hanjae | 5 July 2024 |
| 7 | Celosiae Semen | C. argentea L. | China | Allborn | 30 June 2025 |
| 8 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | Gyeongshin Seeds | 30 January 2025 |
| 9 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | Danong | 30 March 2025 |
| 10 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | Aram Seeds | 30 January 2025 |
| 11 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | DaeHyo Pharmaceutical | 14 June 2025 |
| 12 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | Gwangmyeongdang Pharmaceutical | 24 May 2024 |
| 13 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | Human Herb | 12 January 2025 |
| 14 | Celosiae Semen | C. cristata L. | China | DaeHyo Pharmaceutical | 22 January 2023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.W.; Park, G.; Ku, S.; Jang, Y.P. Development of an HPTLC-MS Method for the Differentiation of Celosiae Semen: Celosia argentea Versus C. cristata. Molecules 2025, 30, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132786
Kim KW, Park G, Ku S, Jang YP. Development of an HPTLC-MS Method for the Differentiation of Celosiae Semen: Celosia argentea Versus C. cristata. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132786
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyu Won, Geonha Park, Sejin Ku, and Young Pyo Jang. 2025. "Development of an HPTLC-MS Method for the Differentiation of Celosiae Semen: Celosia argentea Versus C. cristata" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132786
APA StyleKim, K. W., Park, G., Ku, S., & Jang, Y. P. (2025). Development of an HPTLC-MS Method for the Differentiation of Celosiae Semen: Celosia argentea Versus C. cristata. Molecules, 30(13), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132786







