Heterojunction-Engineered g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites with Superior Bilirubin Removal Efficiency for Enhanced Hemoperfusion Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
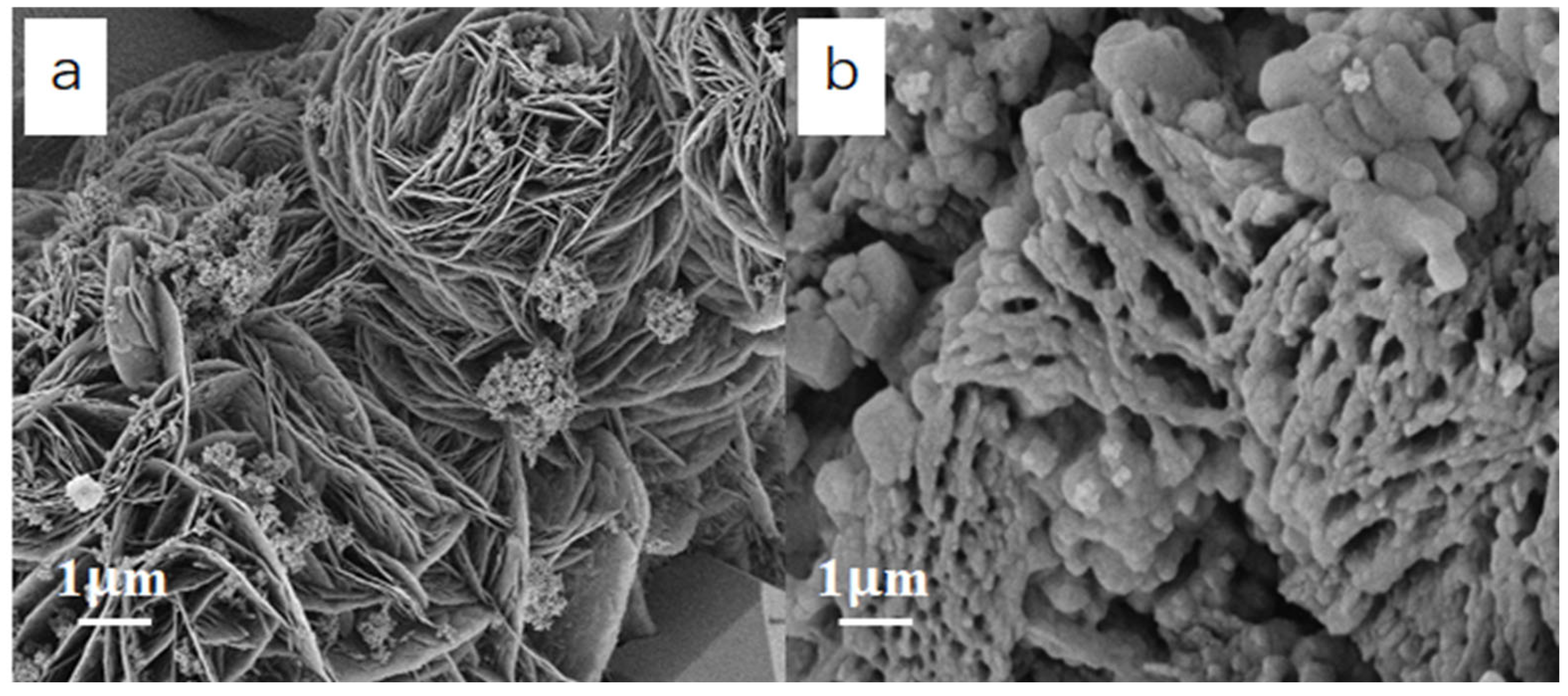
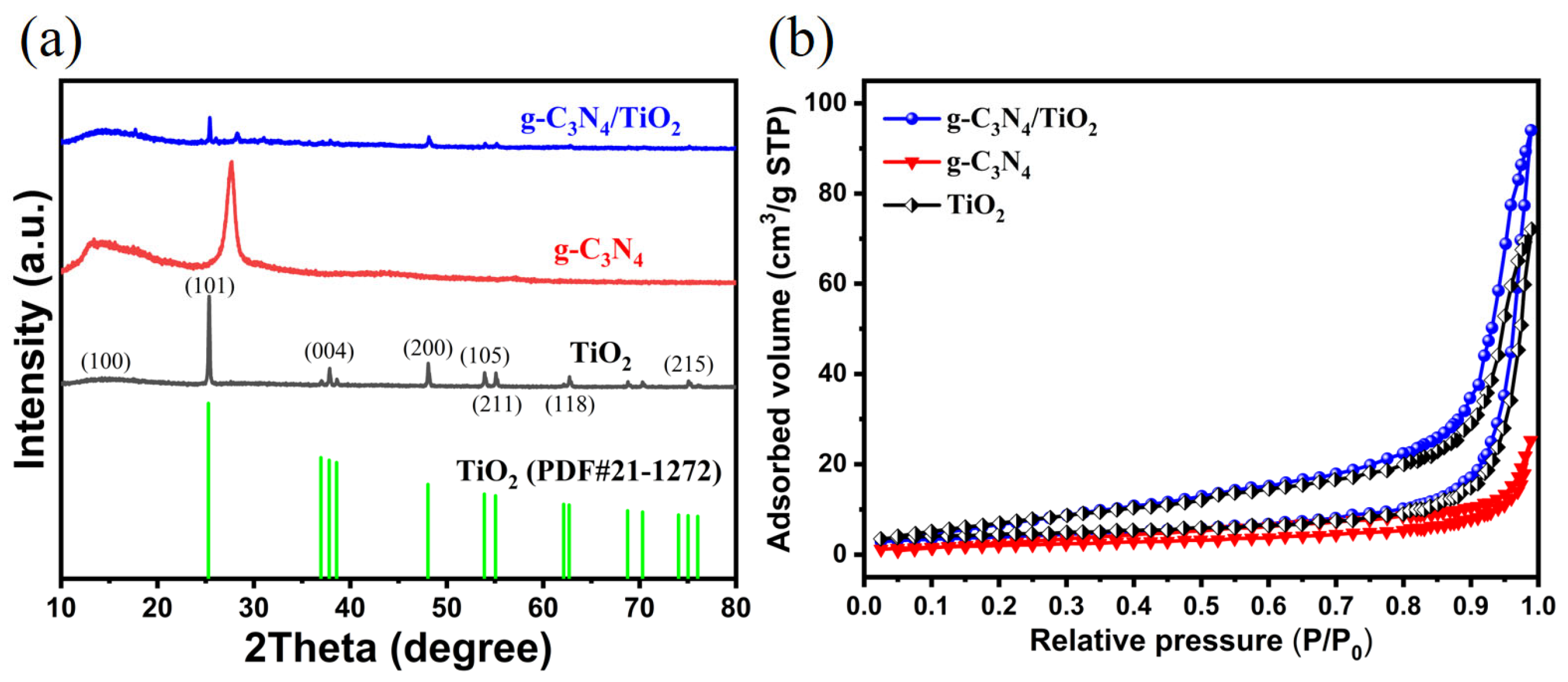
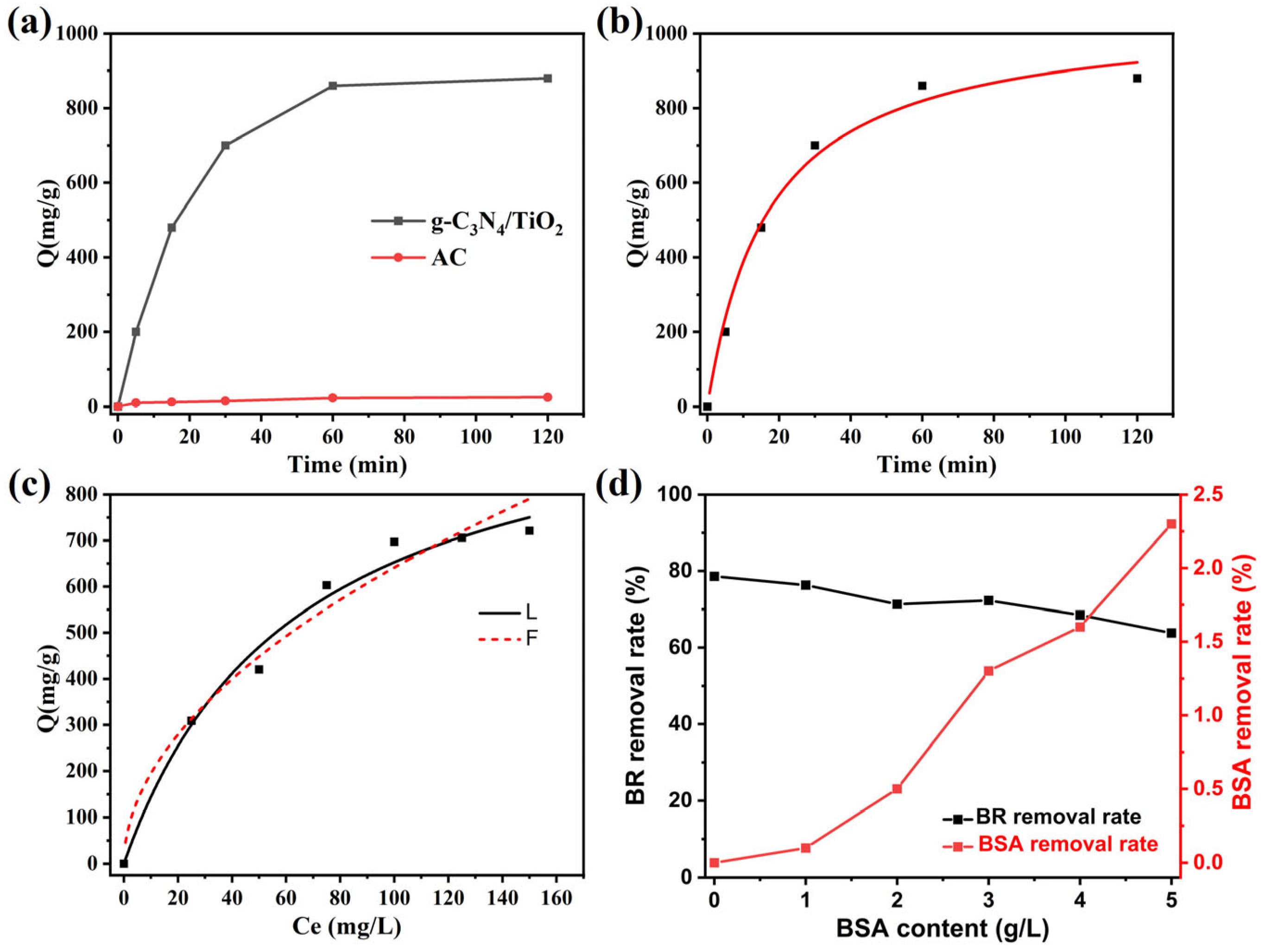
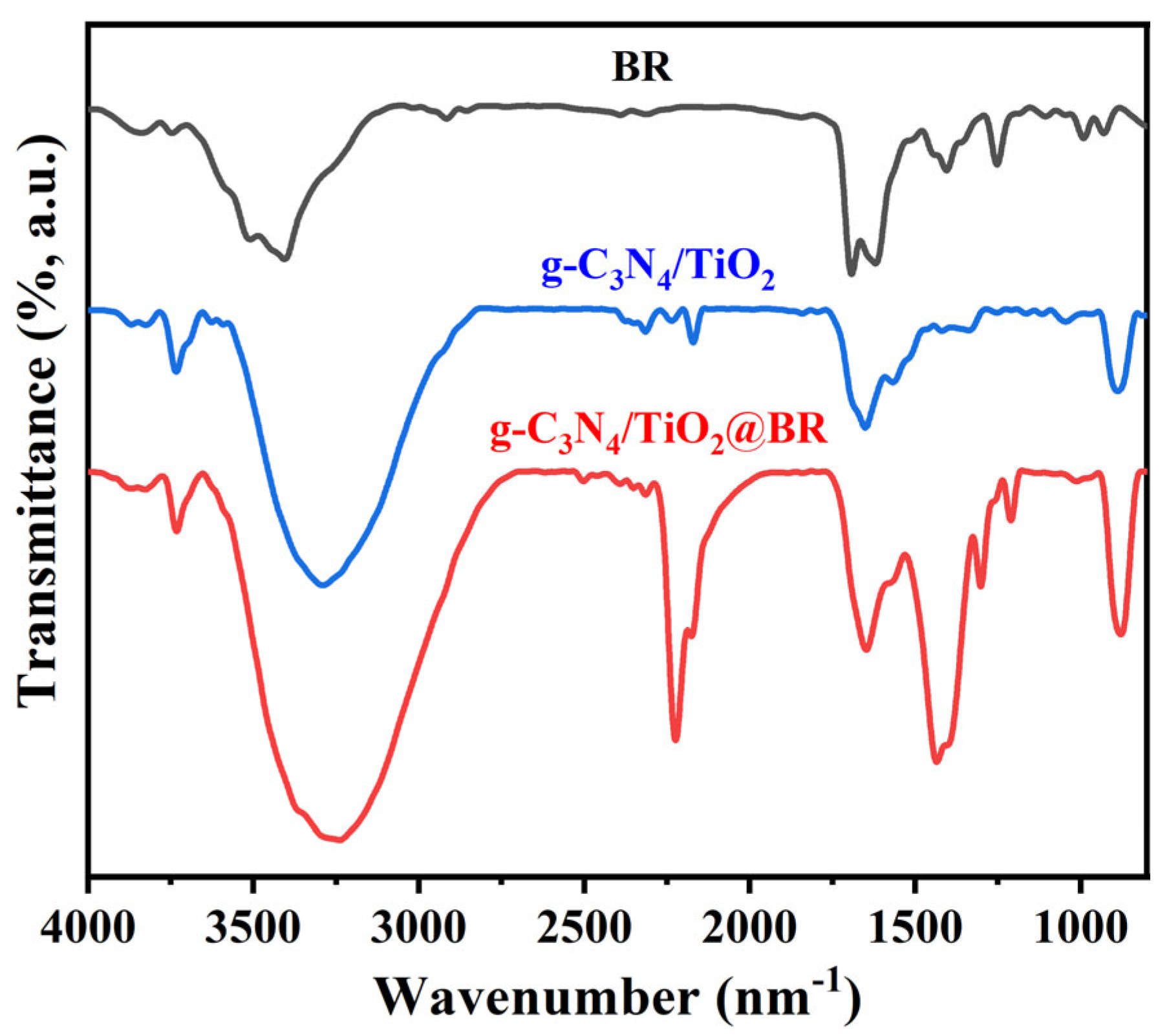
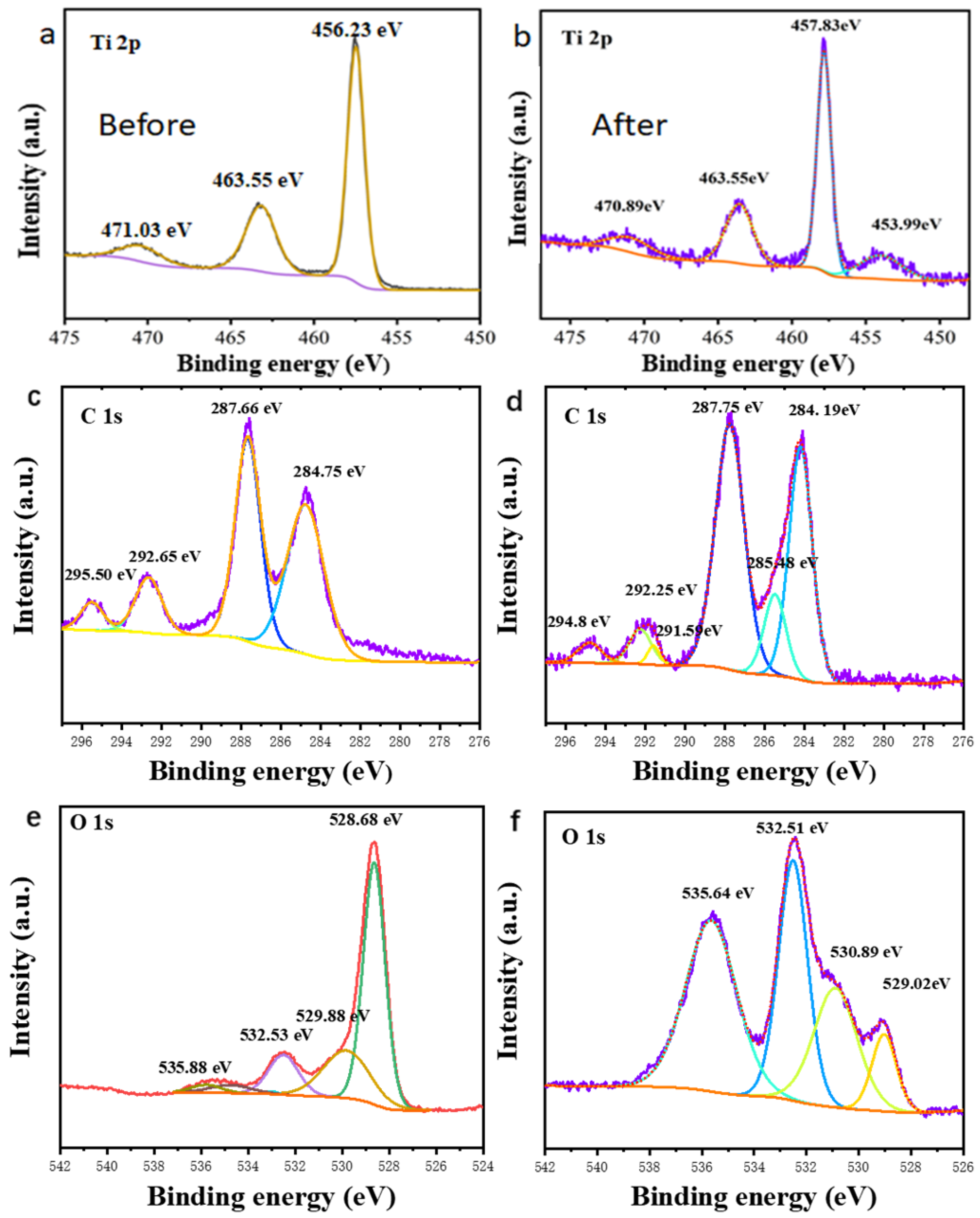
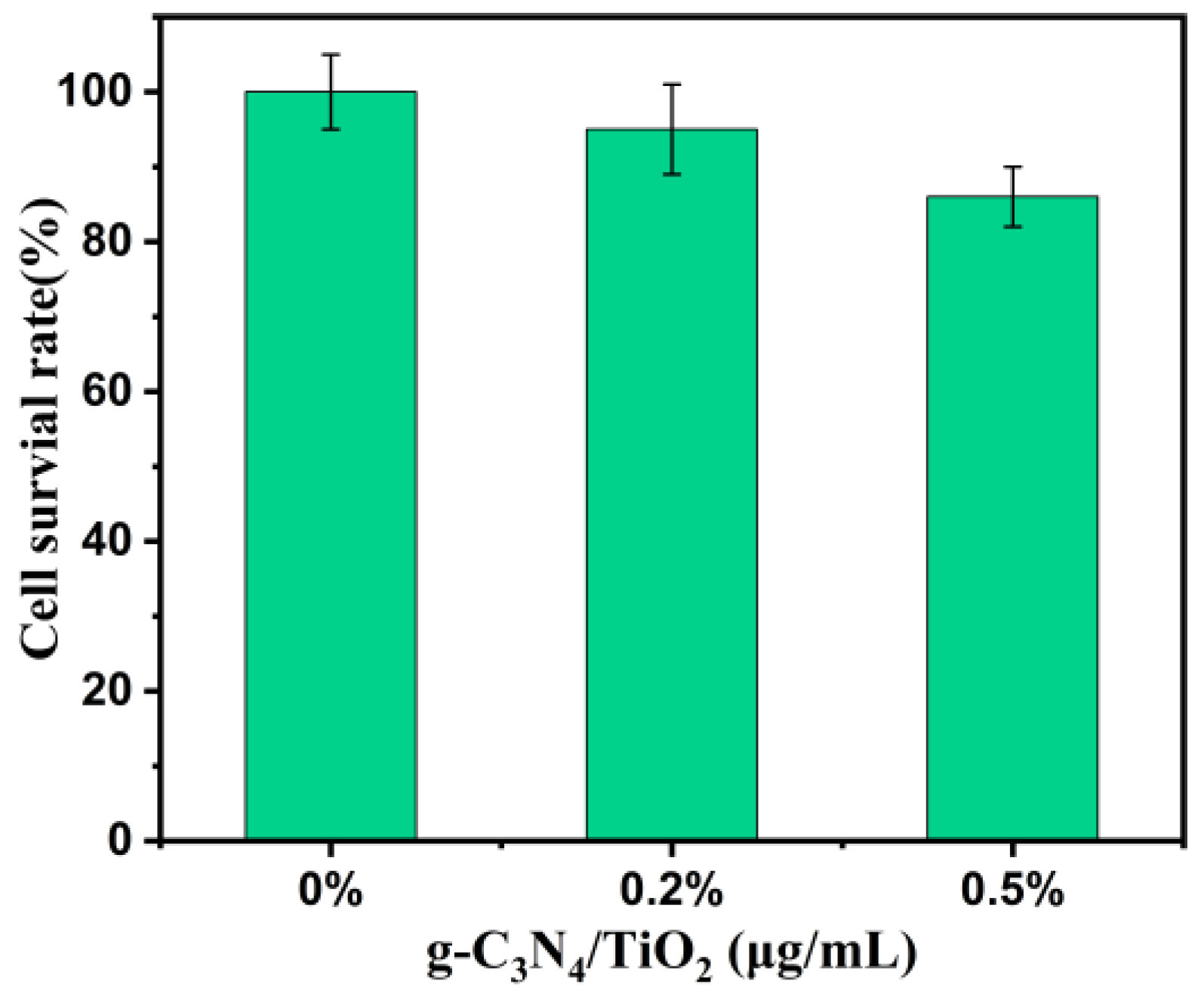
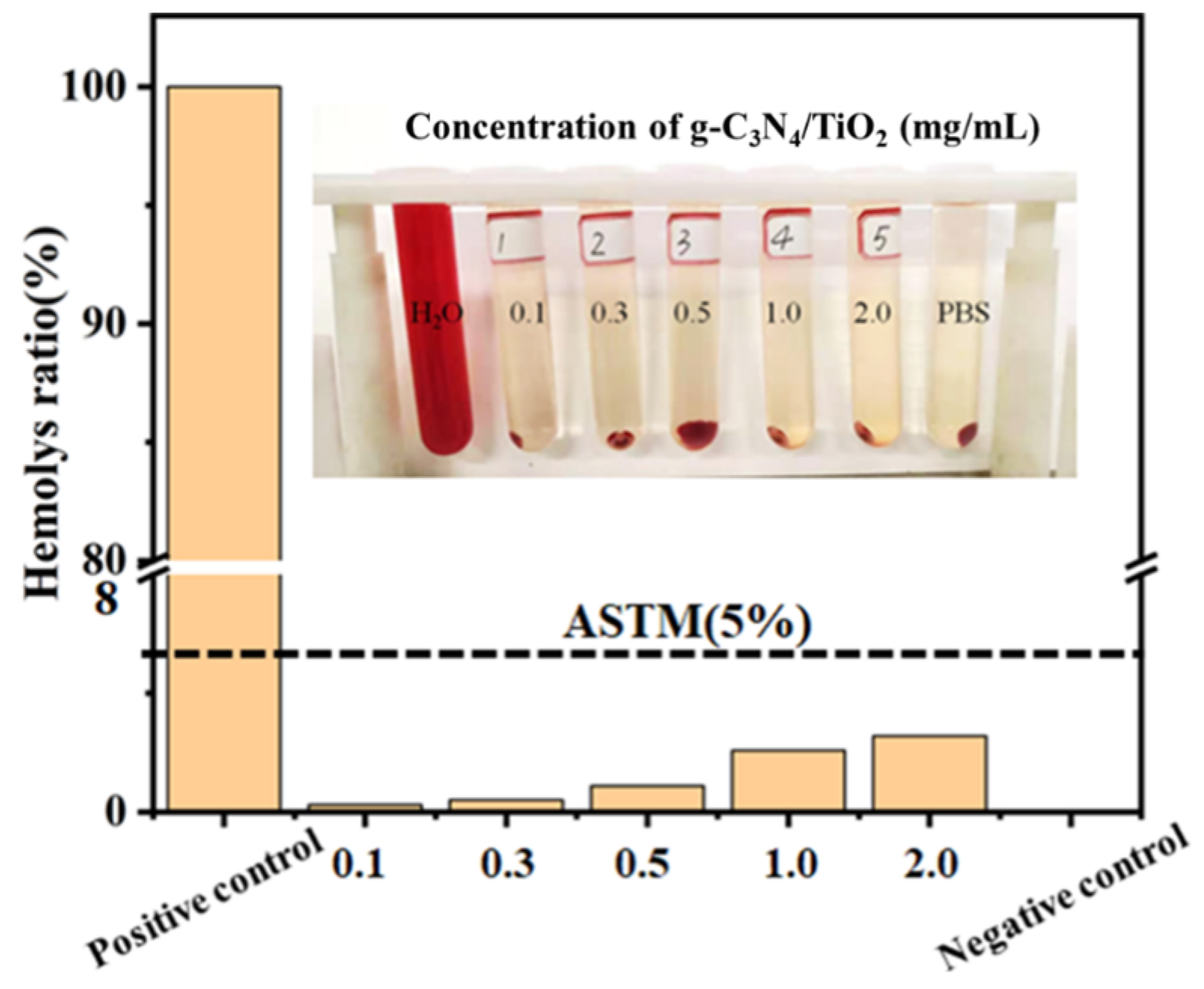
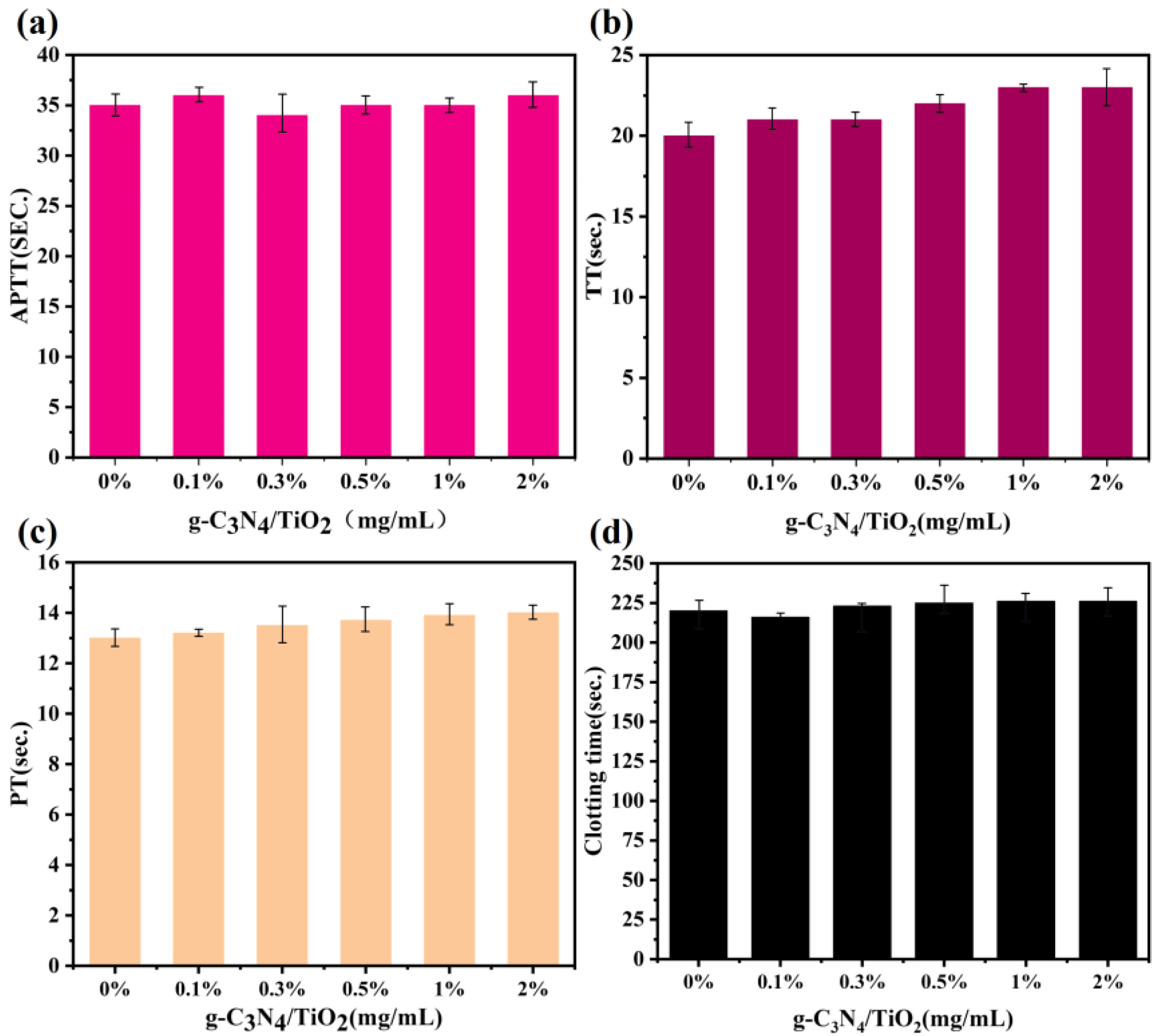
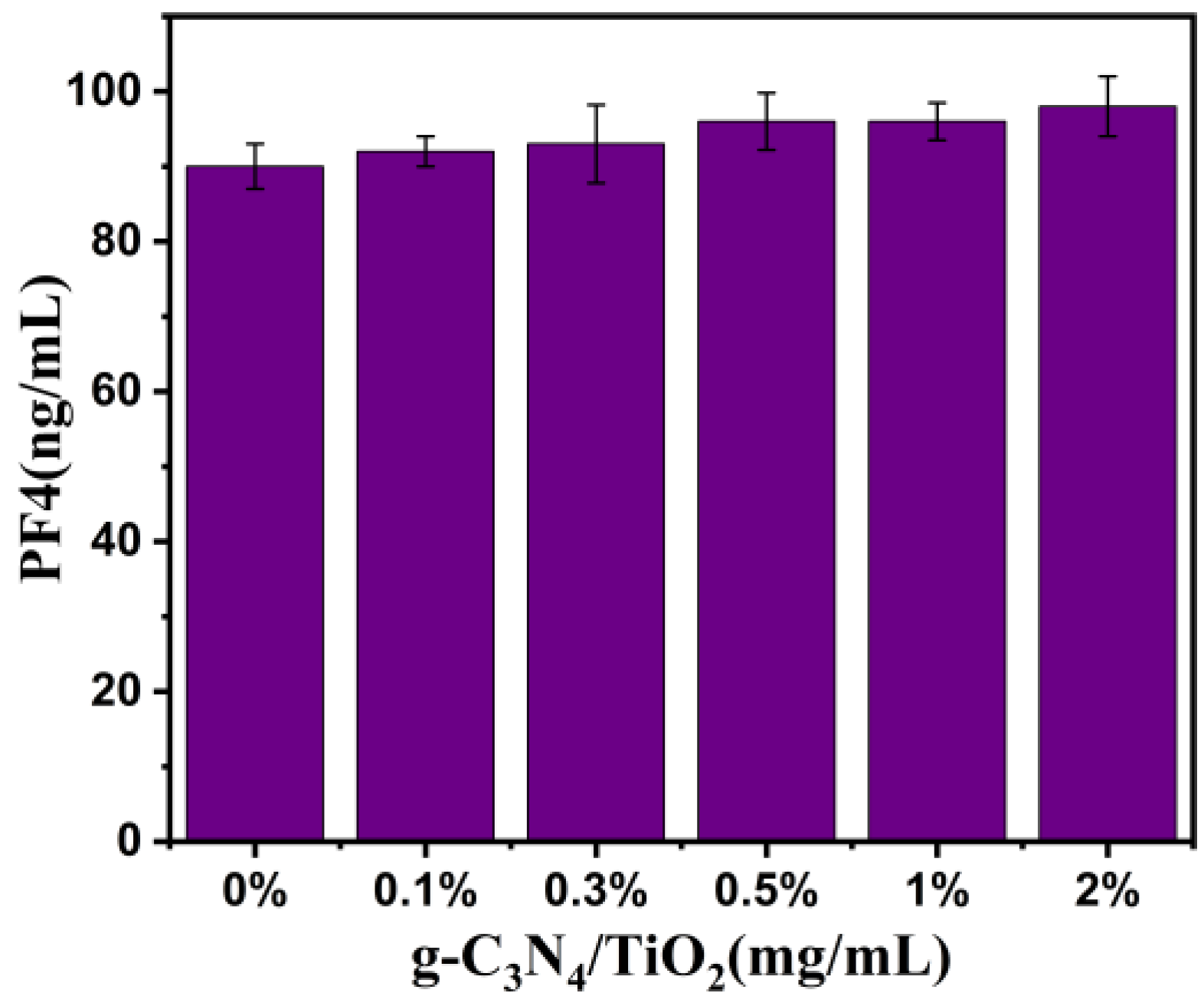
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. g-C3N4/TiO2 Absorbent Preparation
3.2. Adsorption Experiment
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics Experiment
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Experiment
3.5. Competitive Adsorption Experiment
3.6. Cell Toxicity Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwo, P.Y.; Cohen, S.M.; Lim, J.K. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironczuk, I.; Witkowska, A.M.; Zujko, M.E. Endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants in the human body. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Johnson, P.J. The ALBI score: From liver function in patients with HCC to a general measure of liver function. Jhep Rep. 2022, 4, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.; Levy, S.; Dufault-Thompson, K.; Arp, G.; Zhong, A.; Ndjite, G.M.; Weiss, A.; Braccia, D.; Jenkins, C.; Grant, M.R.; et al. BilR is a gut microbial enzyme that reduces bilirubin to urobilinogen. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhuang, W.; Ding, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Pang, D.-W.; Pu, K.; Xie, H.-Y. Molecularly Engineered Macrophage-Derived Exosomes with Inflammation Tropism and Intrinsic Heme Biosynthesis for Atherosclerosis Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2020, 59, 4068–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, K.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, H.; Zeng, R.; Jiang, R.; Li, J.; Wei, R.; Lian, Q.; et al. Targeted modulation of intestinal epithelial regeneration and immune response in ulcerative colitis using dual-targeting bilirubin nanoparticles. Theranostics 2024, 14, 528–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; El-Hais, A.M.; Olivier, A. Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by fermented rapeseed meal on growth, immune response and oxidative condition of red sea bream juvenile, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.J.; Taneja, A.; Niccum, D.; Kumar, G.; Jacobs, E.; Nanchal, R. The association of serum bilirubin levels on the outcomes of severe sepsis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 30, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodzimirow, K.A.; Eslami, S.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Nieuwoudt, M.; Chamuleau, R.A.F.M. A systematic review on prognostic indicators of acute on chronic liver failure and their predictive value for mortality. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Ouyang, G. Polydopamine decorated ordered mesoporous carbon for efficient removal of bilirubin under albumin-rich conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.M.; Carter, D.C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 1992, 358, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, B.; Chai, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, C.; Jiang, X.; et al. TiO2/Polystyrene nanocomposite antibacterial material as a hemoperfusion adsorbent for efficient bilirubin removal and prevention of bacterial infection. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Bao, Z.; Tian, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Reusable zwitterionic porous organic polymers for bilirubin removal in serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 56665–56677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.-K.; Liu, C.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Cui, F.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Z.-T. Supramolecular organic frameworks as adsorbents for efficient removal of excess bilirubin in hemoperfusion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 47397–47408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yue, P.; Ma, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liang, W.; Ye, Q. Hemoperfusion adsorbents for removal of common toxins in liver and kidney failure: Recent progress, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2305152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Hussain, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L. Novel hemoperfusion adsorbents based on collagen for efficient bilirubin removal—A thought from yellow skin of patients with hyperbilirubinemia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Fan, W.; Niu, J. Relationship between serum indirect bilirubin levels and cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, V.; de Ferris, M.E.D.-G.; Filler, G.; Kotanko, P. Novel extracorporeal treatment for severe neonatal jaundice: A mathematical modelling study of allo-hemodialysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.-H.; Kao, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Kao, C.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chen, K.-C.; Peng, C.-C.; Wu, M.-S. Relationship between serum total bilirubin levels and mortality in uremia patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis: A nationwide cohort study. Atherosclerosis 2017, 265, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Adamczak, M.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Massy, Z.A.; Sarafidis, P.; Agarwal, R.; Mark, P.B.; Kotanko, P.; Ferro, C.J.; et al. Cardiovascular complications in chronic kidney disease: A review from the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group of the European Renal Association. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Liu, X.J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhou, L. Ordered porous materials for blood purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Liu, G.H.; Xia, Q.P.; Deng, L. Research progress on blood compatibility of hemoperfusion adsorbent materials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1456694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.K.; Xiao, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L. A critical review of hemoperfusion adsorbents: Materials, functionalization and matrix structure selection. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Jiang, X.B.; Guo, X.F.; Ou, L.L. An Evolutionary Review of Hemoperfusion Adsorbents: Materials, Preparation, Functionalization, and Outlook. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 3599–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, A.M.; Abbas, S.; Ali, B.; Majeed, H.; Abouelwafa, M.Y.; Mousa, A.; Liang, L. Microencapsulation of Oils: A Comprehensive Review of Benefits, Techniques, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 143–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, K.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Qing, C.; Zou, D. Development and applications of multifunctional microencapsulated PCMs: A comprehensive review. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Mlambo, R.; Shaw, I.; Seid, Y.; Shah, H.; He, Y.; Kpegah, J.K.S.K.; Tan, S.; Zhou, W.; He, B. Cryopreservation of bioflavonoid-rich plant sources and bioflavonoid-microcapsules: Emerging technologies for preserving bioactivity and enhancing nutraceutical applications. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1232129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Yue, X.; Shao, J.; Li, M.; Li, Z. Polysaccharides, proteins, and their complex as microencapsulation carriers for delivery of probiotics: A review on carrier types and encapsulation techniques. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bao, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Porous Microspheres as Pathogen traps for sepsis therapy: Capturing active pathogens and alleviating inflammatory reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23855–23871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, B. Application of Hemoperfusion in the Treatment of Acute Poisoning. Blood Purif. 2024, 53, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, M.; Yang, M.; Su, B. Hemoperfusion with the HA330/HA380 Cartridge in Intensive Care Settings: A State-Of-The-Art Review. Blood Purif. 2024, 54, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Han, K.; Jiang, X.; Mao, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, M. Recent advances in blood toxin removal technology. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryata, O.; Akimov, O.; Riabushko, M.; Kostenko, H.; Kostenko, V.; Mishchenko, A.; Nazarenko, S.; Solovyova, N.; Kostenko, V. Therapeutic potential of 5-aminolevulinic acid in metabolic disorders: Current insights and future directions. Iscience 2024, 27, 111477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.K.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, S.Y. Influence of the acid groups on activated carbon on the adsorption of bilirubin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124133. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Y.; Shi, M.S.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Jiang, T.T.; Zhao, R. Theory-driven tailoring of the microenvironment of quaternary ammonium binding sites on electrospun nanofibers for efficient bilirubin removal in hemoperfusion. Polymers 2024, 16, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, X.; Lv, X.; Jia, Q. Highly Sensitive and selective sensing of free bilirubin using metal-organic frameworks-based energy transfer process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30925–30932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, J.; Cui, J.; Mei, Y.; Huang, G. Bimetallic mof-based fibrous device for noninvasive bilirubin sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Biswas, S. A recyclable post-synthetically modified Al(iii) based metal-organic framework for fast and selective fluorogenic recognition of bilirubin in human biofluids. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 9266–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Hou, J.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Yang, J.; Shan, S.; Hu, T.; Wang, C.; Su, H. Cyclodextrin metal-organic framework derived nano-cubic gel particles for the efficient removal of bilirubin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Nie, Y.; Du, Z.; Huang, Q.; Meng, P.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Enhanced adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate by bamboo-derived granular activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayathiri, M.; Pulingam, T.; Lee, K.T.; Sudesh, K. Activated carbon from biomass waste precursors: Factors affecting production and adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K.; Shinke, K.; Yamada, S.; Koyama, T.; Takai, T.; Nakaji, S.; Ogino, T. Fabrication of carbon nanotube sheets and their bilirubin adsorption capacity. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinke, K.; Ando, K.; Koyama, T.; Takai, T.; Nakaji, S.; Ogino, T. Properties of various carbon nanomaterial surfaces in bilirubin adsorption. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2010, 77, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-F.; Gao, Q.; Xia, K.-S.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Han, B.; Zhou, C.-G. Three-dimensionally porous graphene: A high-performance adsorbent for removal of albumin-bonded bilirubin. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.R.A.; Azenha, M.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Molecularly imprinted methyl-modified hollow TiO2 microspheres. Molecules 2022, 27, 8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of bilirubin on hydroxyapatite coatings with nanostructural surface. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 302, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhang, L.; Luo, C.; Lin, H.-J.; Han, D.-M.; Chen, F.-Z.; Huang, C. Molecule engineering metal-organic framework-based organic photoelectrochemical transistor sensor for ultrasensitive bilirubin detection. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 12739–12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinska, W.; Saska, V.; Siuzdak, K.; Karczewski, J.; Zaleski, K.; Coy, E.; de Poulpiquet, A.; Mazurenko, I.; Lojou, E. Interaction between bilirubin oxidase and Au nanoparticles distributed over dimpled titanium foil towards oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 474, 143535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (Mxene) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, L. Procion Blue H-5R functionalized cellulose membrane with specific removal of bilirubin. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8073–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, F.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, L. Development of amino acid-modified PET/PA6 segmented pie bicomponent spunbonded microfiber nonwoven for bilirubin affinity adsorption. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Sui, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. MOF-based anti-biofouling hemoadsorbent for highly efficient removal of protein-bound bilirubin. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8753–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, K.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, C. Fabrication of regular macro-mesoporous reduced graphene aerogel beads with ultra-high mechanical property for efficient bilirubin adsorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110282–110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Metal-organic framework traps with record-high bilirubin removal capacity for hemoperfusion therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25546–25556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Ma, T.; Cui, F.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, G. Porous aromatic framework with tailored binding sites and pore sizes as a high-performance hemoperfusion adsorbent for bilirubin removal. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001899–2001907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Tao, S.; Guan, J.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Ultraefficiently calming cytokine storm using Ti3C2T x MXene. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2001108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, T.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, R.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Self-anticoagulant nanocomposite spheres for the removal of bilirubin from whole blood: A step toward a wearable artificial liver. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S.Y.; Bjorkman, T.; Palgrave, R.G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y.Z.; Krasheninnikov, A.V.; Rabe, J.P.; et al. Triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride: A two-dimensional semiconductor. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53, 7450–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.X.; Wang, T.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, G.X. Removal of extremely low concentration cobalt by intercalation composite material of carbon nitride/titanium dioxide. J. Hazard. Mater 2021, 415, 125680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Han, L.; Tang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jia, L. Highly flexible heparin-modified chitosan/graphene oxide hybrid hydrogel as a super bilirubin adsorbent with excellent hemocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, C. Fabrication of chitosan/graphene oxide composite aerogel microspheres with high bilirubin removal performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves-Pedro, N.M.; Sugibayashi, K.; Ostrosky, E.A.; Ferrari, M.; Sufi, B.d.S.; Mathor, M.B.; Moreno, P.R.H.; Lourenco, F.R.; Consiglieri, V.O.; Baby, A.R.; et al. Validation cytotoxicity assay for lipophilic substances. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Tao, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, C. Heterojunction-Engineered g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites with Superior Bilirubin Removal Efficiency for Enhanced Hemoperfusion Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132729
Meng L, Tao S, Wang L, Cao Y, Hou J, Wang C. Heterojunction-Engineered g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites with Superior Bilirubin Removal Efficiency for Enhanced Hemoperfusion Therapy. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132729
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lingdong, Shouxuan Tao, Liyao Wang, Yu Cao, Jianhua Hou, and Chengyin Wang. 2025. "Heterojunction-Engineered g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites with Superior Bilirubin Removal Efficiency for Enhanced Hemoperfusion Therapy" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132729
APA StyleMeng, L., Tao, S., Wang, L., Cao, Y., Hou, J., & Wang, C. (2025). Heterojunction-Engineered g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites with Superior Bilirubin Removal Efficiency for Enhanced Hemoperfusion Therapy. Molecules, 30(13), 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132729






