Enhanced Oxidation of Carbamazepine Using Mn(II)-Activated Peracetic Acid: A Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Involving the Significant Role of Ligand Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
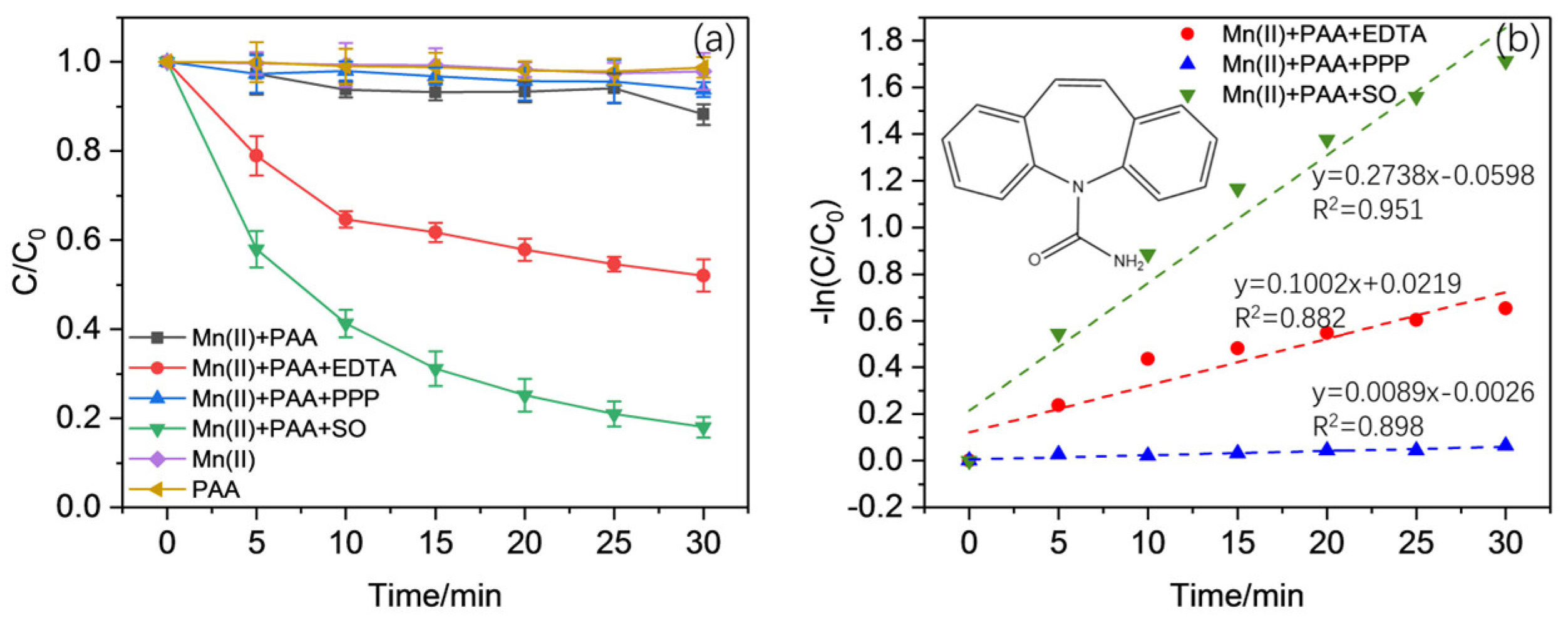
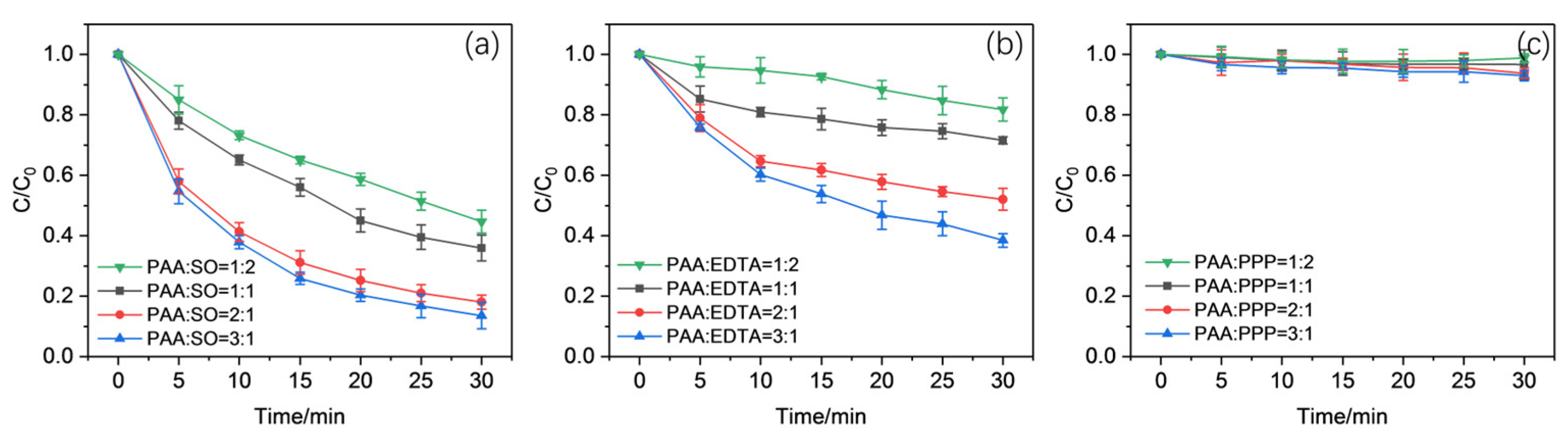
2.1. Effect of Complexing Ligands in the Activation of PAA Using Mn(II)
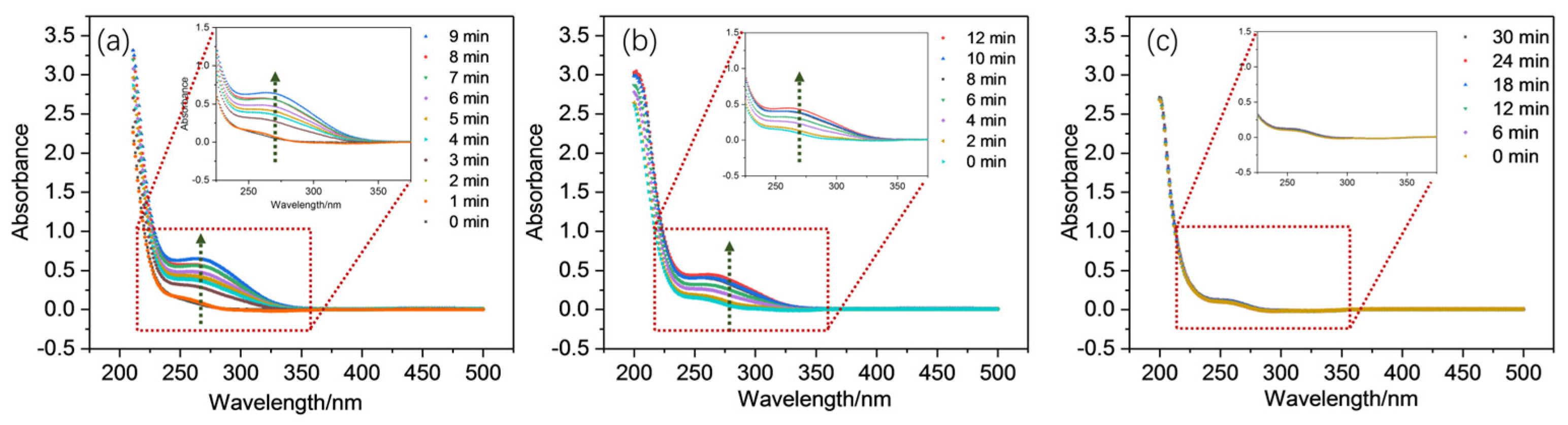
2.2. Generation and Involvement of Mn(III) Complex
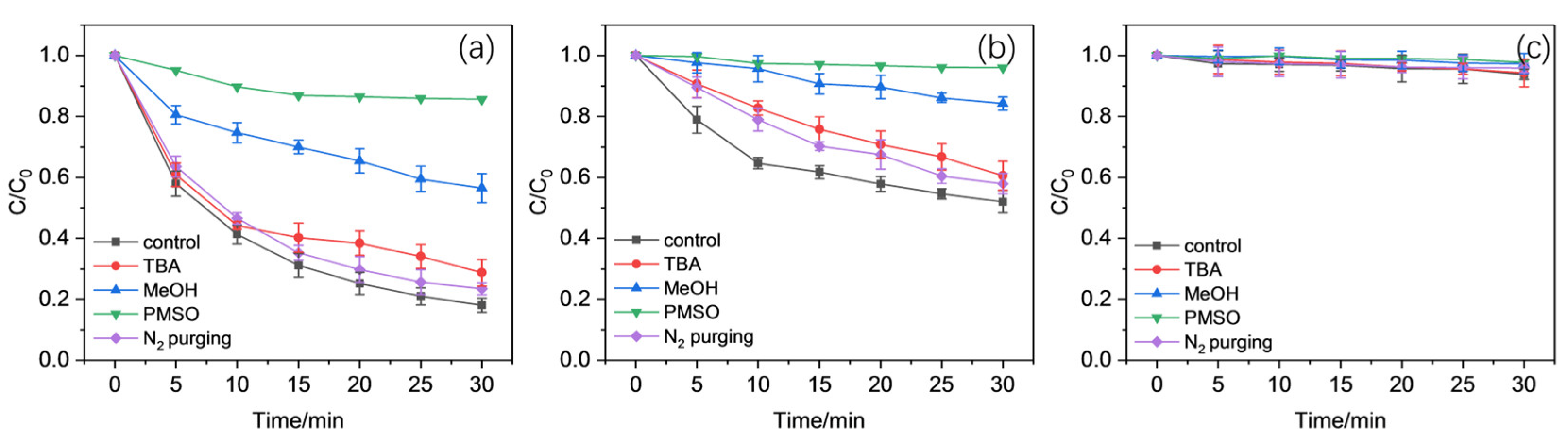
2.3. Identification of ROS
2.4. Proposed Oxidation Pathway of CBZ
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of PAA
3.3. Batch Experiments
3.4. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eloranta, J.; Li, C.; Ao, X.-W.; Lu, Z.-D.; Huang, C.-H.; Santoro, D.; Sun, W.-J. Peracetic acid-based advanced oxidation processes for decontamination and disinfection of water: A review. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116479. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, M.; Cao, H. The reactivity of organic radicals in the performic, peracetic, perpropionic acids-based advanced oxidation process: A case study of sulfamethoxazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Sanchez, S.; Peñuela, G.A. Peracetic acid-based advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of emerging pollutants: A critical review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Fegan, N.; Kocharunchitt, C.; Bowman, J.P.; Duffy, L.L. Effect of peracetic acid on Campylobacter in food matrices mimicking commercial poultry processing. Food Control 2020, 113, 107185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zou, J.; Cai, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, B.; Ma, J. Hydroxylamine enhanced Fe (II)-activated peracetic acid process for diclofenac degradation: Efficiency, mechanism and effects of various parameters. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, J.; Heinonen-Tanski, H. Peracetic acid (PAA) disinfection of primary, secondary and tertiary treated municipal wastewaters. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4445–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, X. A review of measurement methods for peracetic acid (PAA). Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, E.M.; Pantea, O.; Gologan, D.; Doukeh, R. Hydrogen Peroxide and Peracetic Acid Oxidizing Potential in the Treatment of Water. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Brown, P.J.; Hu, Z. Thermodynamic properties of an emerging chemical disinfectant, peracetic acid. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 621, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Huo, J.; Ji, W.; Cui, N.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, X.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on heterogeneous catalysts-mediated activation of peracetic acid for micropollutants degradation: Classification of reaction pathways, mechanisms, influencing factors and DFT calculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Z. Comprehensive understanding of fluoroquinolone degradation via MPUV/PAA process: Radical chemistry, matrix effects, degradation pathways, and toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 445, 130480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H. Insight into Three-Dimensional Electro-Fenton system with Fe0 activated Peroxyacetic acid for sulfadiazine degradation under neutral Condition: Performance and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 158968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-R.; He, C.-S.; Xie, Z.-H.; Li, L.-L.; Xiong, Z.-K.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, F.; Mu, Y.; Lai, B. Efficient activation of PAA by FeS for fast removal of pharmaceuticals: The dual role of sulfur species in regulating the reactive oxidized species. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, X. The diverse roles of halide ions in the degradation of bisphenol A via UV/peracetic acid process at different pH values: Radical chemistry, and transformation pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 465, 133053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cai, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L. Effects of water matrices on the degradation of naproxen by reactive radicals in the UV/peracetic acid process. Water Res. 2019, 150, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Zhang, T. Modeling the kinetics of UV/peracetic acid advanced oxidation process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7579–7590. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, R. (Invited) Design Principle of Multi-Electron Water Oxidation Catalysts Composed of Mn Oxides. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2013, MA2013-01, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.A.; Li, J.; Stalick, J.K.; Subramanian, M. Intense turquoise colors of apatite-type compounds with Mn5+ in tetrahedral coordination. Solid State Sci. 2016, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.J. Manganese in natural waters and earth’s crust: Its availability to organisms. Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 2000, 37, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Pan, B.; Shan, C.; Pignatello, J.J. Mn(II) acceleration of the picolinic acid-assisted Fenton reaction: New insight into the role of manganese in homogeneous Fenton AOPs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6621–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tong, S. Mn2+/H2O2/O3, a high efficient advanced oxidation process in acidic solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yuan, S.; Liao, W.; Tong, M.; Xie, W. Ligand-Enhanced Electron Utilization for Trichloroethylene Degradation by ·OH during Sediment Oxygenation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7044–7051. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, X. Effect of ligands on the production of oxidants from oxygenation of reduced Fe-bearing clay mineral nontronite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 251, 136–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.-Y.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Guan, C.; Jiang, J. Aqueous iron (IV)–oxo complex: An emerging powerful reactive oxidant formed by iron (II)-based advanced oxidation processes for oxidative water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1492–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Wu, D. High-valent cobalt-oxo species triggers hydroxyl radical for collaborative environmental decontamination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 300, 120722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Sun, K.; Wu, S.; Lu, W.; Xu, J.; Li, N.; Pei, K.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, W. Insights into the generation of high-valent copper-oxo species in ligand-modulated catalytic system for oxidizing organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shan, C.; Li, W.; Pan, B. Peroxymonosulfate activation by iron(III)-tetraamidomacrocyclic ligand for degradation of organic pollutants via high-valent iron-oxo complex. Water Res. 2018, 147, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Effect of inorganic, synthetic and naturally occurring chelating agents on Fe(II) mediated advanced oxidation of chlorophenols. Water Res. 2009, 43, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.E.; Bohrer, B.M.; Mejia, S.M.V. Phosphate alternatives for meat processing and challenges for the industry: A critical review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Zhao, X.-N.; Bai, Y.; Ma, J. Ferrate self-decomposition in water is also a self-activation process: Role of Fe(V) species and enhancement with Fe(III) in methyl phenyl sulfoxide oxidation by excess ferrate. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Brusseau, M.L. Effect of pyrophosphate on the dechlorination of tetrachloroethene by the Fenton reaction. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Hanna, K.; Despas, C.; Wu, F.; Deng, N. Effect of chelating agent on the oxidation rate of PCP in the magnetite/H2O2 system at neutral pH. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 311, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, C.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B. In situ ligand-modulated activation of inert Ce(III/IV) into ozonation catalyst for efficient water treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2305255120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufan, M.; Deborde, M.; Delmont, A.; Legube, B. Aqueous chlorination of carbamazepine: Kinetic study and transformation product identification. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5076–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M. A critical review of the application of chelating agents to enable Fenton and Fenton-like reactions at high pH values. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, D.; Xiao, J.; Dong, J.; Li, L.; Dong, H. Enhanced Degradation of Micropollutants in a Peracetic Acid/Mn(II) System with EDDS: An Investigation of the Role of Mn Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12179–12188. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, W.; Guan, X.; Sun, B. Influence of Pyrophosphate on the Generation of Soluble Mn(III) from Reactions Involving Mn Oxides and Mn(VII). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10227–10235. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, C.; Chu, W. The role of organic ligands in ferrous-induced photochemical degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ligand-Enhanced Zero-Valent Iron for Organic Contaminants Degradation: A Mini Review. Processes 2023, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiejza, D.; Kotowska, U.; Polińska, W.; Karpińska, J. Peracids-New oxidants in advanced oxidation processes: The use of peracetic acid, peroxymonosulfate, and persulfate salts in the removal of organic micropollutants of emerging concern—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Zhang, T.; Du, P.; Dobson, J.T.; Huang, C.-H.; Liu, W. Advanced Oxidation Process with Peracetic Acid and Fe(II) for Contaminant Degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13312–13322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Nie, Y.; Tian, X.; Dai, C.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Surface weak acid-base pair of FeOOH/Al2O3 for enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation in degradation of humic substances from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-H.; Li, H.-T.; Xia, K.-S.; Gao, Q.; Han, B.; Zhou, C.-G. Partial-Redox-Promoted Mn Cycling of Mn(II)-Doped Heterogeneous Catalyst for Efficient H2O2-Mediated Oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Sharma, V.K.; Huang, C.-H.; Wang, J.; Ashley, D.C. Picolinic Acid-Mediated Catalysis of Mn(II) for Peracetic Acid Oxidation Processes: Formation of High-Valent Mn Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18929–18939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, S.-Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.-M.; Song, Y.; Duan, J.-B.; Guo, Q. Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation via complexed Mn(II): A novel non-radical oxidation mechanism involving manganese intermediates. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, S.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Qu, R.; Wang, Z. Enhanced Removal of Chlorophene and 17β-estradiol by Mn(III) in a Mixture Solution with Humic Acid: Investigation of Reaction Kinetics and Formation of Co-oligomerization Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13222–13230. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pang, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Duan, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, J. Oxidative transformation of emerging organic contaminants by aqueous permanganate: Kinetics, products, toxicity changes, and effects of manganese products. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Lai, B.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, Z.; He, C.-S.; Du, Y.; Zhou, H. In Situ Regulation of MnO2 Structural Characteristics by Oxyanions to Boost Permanganate Autocatalysis for Phenol Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 12847–12857. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; DiSalvo, F.J.; Abruña, H.D.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Y. A Strategy for Increasing the Efficiency of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Mn-Doped Cobalt Ferrites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Kavadiya, S.; Karakocak, B.B.; Nie, Y.; Raliya, R.; Wang, S.T.; Berezin, M.Y.; Biswas, P. ZnO1−x/carbon dots composite hollow spheres: Facile aerosol synthesis and superior CO2 photoreduction under UV, visible and near-infrared irradiation. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 230, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, H.; Ma, J.; Kong, Y.; Qin, Y.; Komarneni, S. Decolorization of methyl orange by MnO2/organic acid system: The role of Mn (III). Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 122, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, K.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Cui, M. Enhanced removal of phenolic pollutants over MnO2 initiated by peracetic acid: In situ generation of a heterogeneous Mn(III)-hydroperoxo complex. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-X.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.-H.; Xie, M.; Li, N.; Zhao, R.-S. Effectively removing indole-3-butyric acid from aqueous solution with magnetic layered double hydroxide-based adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.J.; Schlautman, M.A.; Bilinski, H. Rates of abiotic MnII oxidation by O2: Influence of various multidentate ligands at high pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14426–14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Ai, W.; Luo, S.-P.; Liu, Q. Reversible interconversion between methanol-diamine and diamide for hydrogen storage based on manganese catalyzed (de)hydrogenation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richtrová, K.; Votinský, J.; Kalousová, J.; Beneš, L.; Zima, V. Synthesis, Characterization, and Intercalation of Vanadyl Phosphate Modified with Manganese. J. Solid State Chem. 1995, 116, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Irie, H.; Nakamura, R. In situ UV-vis Absorption Spectra of Intermediate Species for Oxygen-Evolution Reaction on the Surface of MnO2 in Neutral and Alkaline Media. Electrochemistry 2014, 82, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Archipov, T.; Maheswari, R.; Hanefeld, U.; Roduner, E.; Gläser, R. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties of the Novel Manganese-Containing Amorphous Mesoporous Material MnTUD-1. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 7468–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klewicki, J.K.; Morgan, J.J. Kinetic behavior of Mn (III) complexes of pyrophosphate, EDTA, and citrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2916–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jones, M.R.; Pan, Z.; Lu, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z. Trivalent manganese in dissolved forms: Occurrence, speciation, reactivity and environmental geochemical impact. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, G. The General, Selective, and Specific Formation of Complexes by Metallic Cations. In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry; Emeleus, H.J., Sharpe, A.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1961; pp. 257–285. [Google Scholar]
- Law, S.K. Role of Ligand Design on the Stability of Metal Complexes and Its Catalytic Properties-A Mini-Review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2024, 14, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Lu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Gong, B.; Ma, J. Nitrilotriacetic acid-assisted Mn(II) activated periodate for rapid and long-lasting degradation of carbamazepine: The importance of Mn(IV)-oxo species. Water Res. 2023, 241, 120156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aken, B.; Agathos, S. Implication of manganese (III), oxalate, and oxygen in the degradation of nitroaromatic compounds by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Fu, Y. Enhanced Mn(II)/peracetic acid by nitrilotriacetic acid to degrade organic contaminants: Role of Mn(V) and organic radicals. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-R.; Liu, C.; Boyd, S.A.; Teppen, B.J.; Li, H. Reduction of Carbadox Mediated by Reaction of Mn(III) with Oxalic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Stone, A.T. Reaction of MnIII,IV (hydr)oxides with oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid, phosphonoformic acid, and structurally-related organic compounds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4477–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Manoli, K.; Kim, J.; Feng, M.; Huang, C.H.; Sharma, V.K. Peracetic Acid–Ruthenium(III) Oxidation Process for the Degradation of Micropollutants in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9150–9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Wang, S.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xie, P.; Wiesner, M.R.; Wan, Y. Application of cobalt/peracetic acid to degrade sulfamethoxazole at neutral condition: Efficiency and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 464–475. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Yang, K.; Pan, S.; Xiang, Y.; Tang, S.; Huang, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Peracetic acid enhanced electrochemical advanced oxidation for organic pollutant elimination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiao, S.; Qian, Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Revisiting the synergistic oxidation of peracetic acid and permanganate(Ⅶ) towards micropollutants: The enhanced electron transfer mechanism of reactive manganese species. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pang, S.; Guan, C.; Qiu, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y. Is sulfate radical really generated from peroxydisulfate activated by iron(II) for environmental decontamination? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11276–11284. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kim, J.; Ashley, D.C.; Sharma, V.K.; Huang, C.-H. Peracetic Acid Enhances Micropollutant Degradation by Ferrate(VI) through Promotion of Electron Transfer Efficiency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11683–11693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xu, X.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, M.; Huang, Y. Role of Mn(III) intermediates in the degradation of carbamazepine via peroxymonosulfate activation by manganese single-atom catalysts: Radical and non-radical synergistic effects. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 373, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y. Picolinic acid-mediated Mn(II) activated periodate for ultrafast and selective degradation of emerging contaminants: Key role of high-valent Mn-oxo species. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D. Preparation of peracetic acid from hydrogen peroxide. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 271, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Hao, J.; Liu, D. Preparation of peracetic acid from hydrogen peroxide, part II: Kinetics for spontaneous decomposition of peracetic acid in the liquid phase. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 284, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; He, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Blaney, L.; Peng, G. The role of Fe(IV) in the zero-valent iron biochar activated persulfate system for treatment of contaminants of emerging concern. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Hong, L.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Yao, X.; Qiu, Y. Enhanced Oxidation of Carbamazepine Using Mn(II)-Activated Peracetic Acid: A Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Involving the Significant Role of Ligand Effects. Molecules 2025, 30, 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132690
Yang X, Yu H, Hong L, Huang Z, Zeng Q, Yao X, Qiu Y. Enhanced Oxidation of Carbamazepine Using Mn(II)-Activated Peracetic Acid: A Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Involving the Significant Role of Ligand Effects. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132690
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xue, Hai Yu, Liang Hong, Zhihang Huang, Qinda Zeng, Xiao Yao, and Yinyuan Qiu. 2025. "Enhanced Oxidation of Carbamazepine Using Mn(II)-Activated Peracetic Acid: A Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Involving the Significant Role of Ligand Effects" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132690
APA StyleYang, X., Yu, H., Hong, L., Huang, Z., Zeng, Q., Yao, X., & Qiu, Y. (2025). Enhanced Oxidation of Carbamazepine Using Mn(II)-Activated Peracetic Acid: A Novel Advanced Oxidation Process Involving the Significant Role of Ligand Effects. Molecules, 30(13), 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132690






