Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Poly(cyanoacrylates) and Poly(caprolactone)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of (PECA-PCL) Nanoparticles
2.1.1. Micelle Size Analysis
2.1.2. Surfactant Percentage and pH Analysis
2.1.3. Analysis of the PECA-PCL Copolymer via Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.1.4. 1H NMR and 13C NMR Analysis of the PECA-PCL Copolymer
2.1.5. Thermal Analysis
2.1.6. Particle Size Determined Using a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of (PECA-PCL) Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Ring-Opening of ε-Caprolactone
3.1.2. Synthesis of (PECA-PCL) Nanoparticles
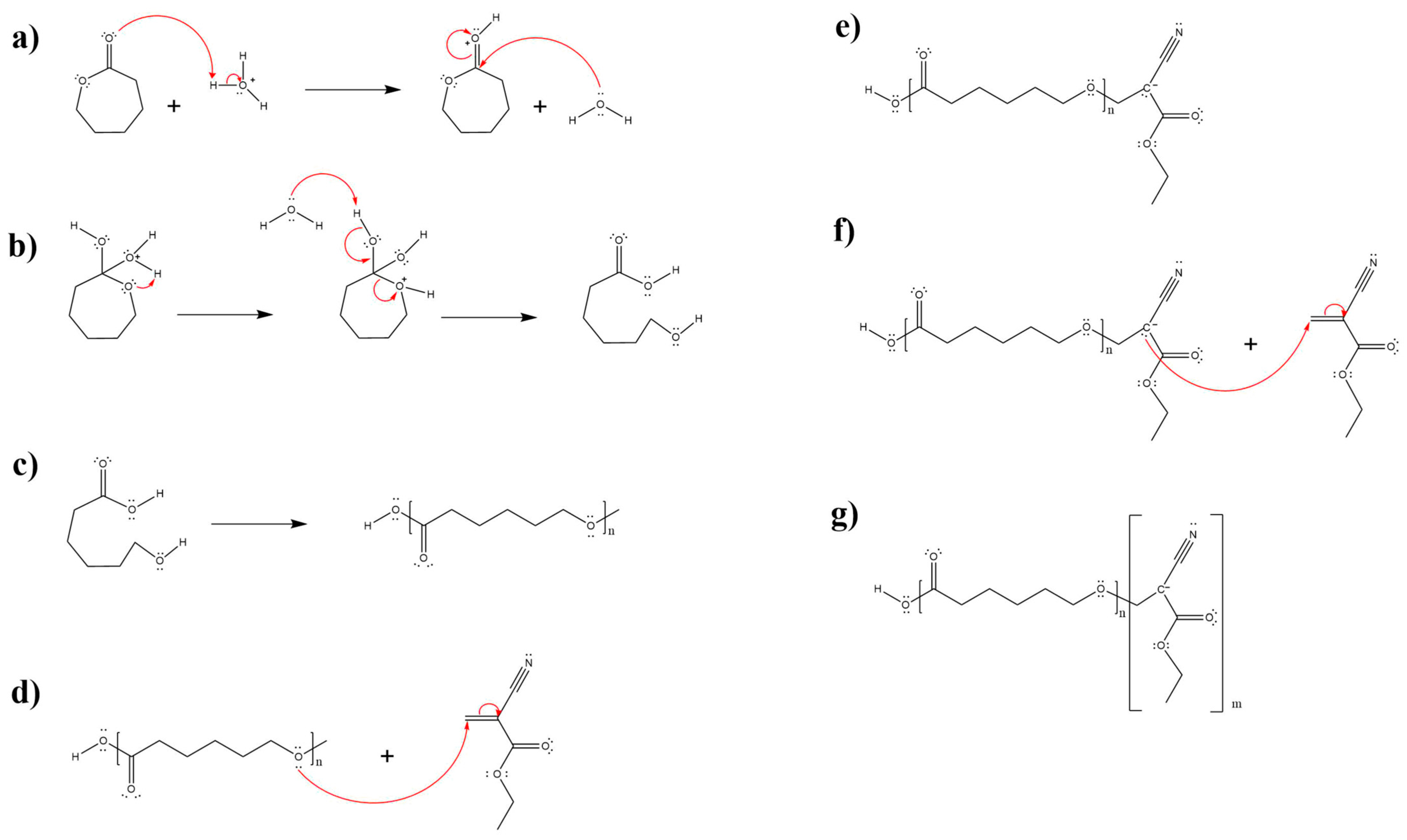
3.1.3. Copolymerization Mechanism (PECA-PCL)
3.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2.1. Micelle Size Measurement
3.2.2. Micelle Breakdown and Surfactant Removal
3.2.3. Thermal Analysis Procedure
3.2.4. Particle Size Analysis Using a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PECA | poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) |
| PCL | poly(ε-caprolactone) |
References
- Jones, D. Pharmaceutical Applications of Polymers for Drug Delivery; Rapra Technology: Shrewsbury, UK, 2004; ISBN 1-85957-479-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tekade, R.K. Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 9780128179093. [Google Scholar]
- Elsabahy, M.; Wooley, K.L. Design of polymeric nanoparticles for biomedical delivery applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2545–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yordanov, G.; Dushkin, C.D. Preparation of poly(butylcyanoacrylate) drug carriers by nanoprecipitation using a pre-synthesized polymer and different colloidal stabilizers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledezma, M.R.; Treviño, M.E.; Elizalde, L.E.; García, L.A. Semicontinuous heterophase polymerization under monomer starved conditions to prepare nanoparticles with narrow size distribution. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 102, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hamad, I. Factors controlling pharmacokinetics of intravenously injected nanoparticulate systems. In Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery; De Villiers, M.M., Aramwit, P., Kwon, G.S., Eds.; Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects, Volume X; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, R.; Florescu, I.P.; Coroiu, V.; Oancea, A.; Lungu, M. In vitro biocompatibility testing of some synthetic polymers used for the achievement of nervous conduits. J. Med. Life 2011, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lim, J.I.; Lee, Y.-K.; Shin, J.-S.; Lim, K.-J. Cyanoacrylate adhesives curable to flexible polymeric materials by poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone). Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2438–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Gong, C.; Gou, M.; Fu, S.; Guo, Q.; Shi, S.; Luo, F.; Guo, G.; Qian, Z. Biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.G.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H. Synthesis and degradation behavior of poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1234–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F.; Nanoencapsulation, I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, D.; Diget, J.S.; Nyström, B.; Gyulai, G.; Mészáros, R.; Gilányi, T.; Varga, T. Response of block copolyelectrolyte complexes to addition of ionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 532, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, J.E. Cómo obtener un polímero degradable en el laboratorio: Síntesis de la poli(D,L-lactida) y caracterización por RMN 1H. Educ. Quím. 2010, 21, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.K.; Porter, H.J.; Leonard, F. Glass transition temperatures of poly(alkyl cyanoacrylates). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1973, 17, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedalwafa, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) for tissue engineering applications: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2013, 34, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Watnasirichaikul, S.; Davies, N.M.; Rades, T.; Tucker, I.G. Effects of formulation variables on characteristics of poly(ethylcyanoacrylate) nanocapsules prepared from w/o microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D.J. Charged interfaces. In Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 174–209. ISBN 9780080509105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Abbas, Z.; Kleibert, A.; Green, R.G.; Goel, A.; May, S.; Squires, T.M. Determination of Surface Potenctial and Electrical Double-Layer Structure at the Aqueous Electrolyte-Nanoparticle Interface. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balleño, J.A.; Mendizábal-Ruiz, A.P.; Saade, H.; de León-Gómez, R.D.; Mendizábal, E.; Rios-Donato, N.; López, R.G. Ibuprofen Release from Poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) Nanoparticles Prepared by Semicontinuous Heterophase Polymerization. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, J.; Leng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Boric acid as biocatalyst for living ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Polymer 2015, 78, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, J. Organic Chemistry, 9th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781305080485. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, A.R.; López, M.; González, M. Poly(ε-caprolactone) degradation under acidic and alkaline conditions. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 3, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.; López, R.; Treviño, M.E.; Elizalde, L.E. Narrow size-distribution poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles made by semicontinuous heterophase polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, C.; Tripkovic, D.; Sun, S.; Markovic, N.M.; Stamenkovic, V.R. Surfactant removal for colloidal nanoparticles from solution synthesis: The effect on catalytic performance. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
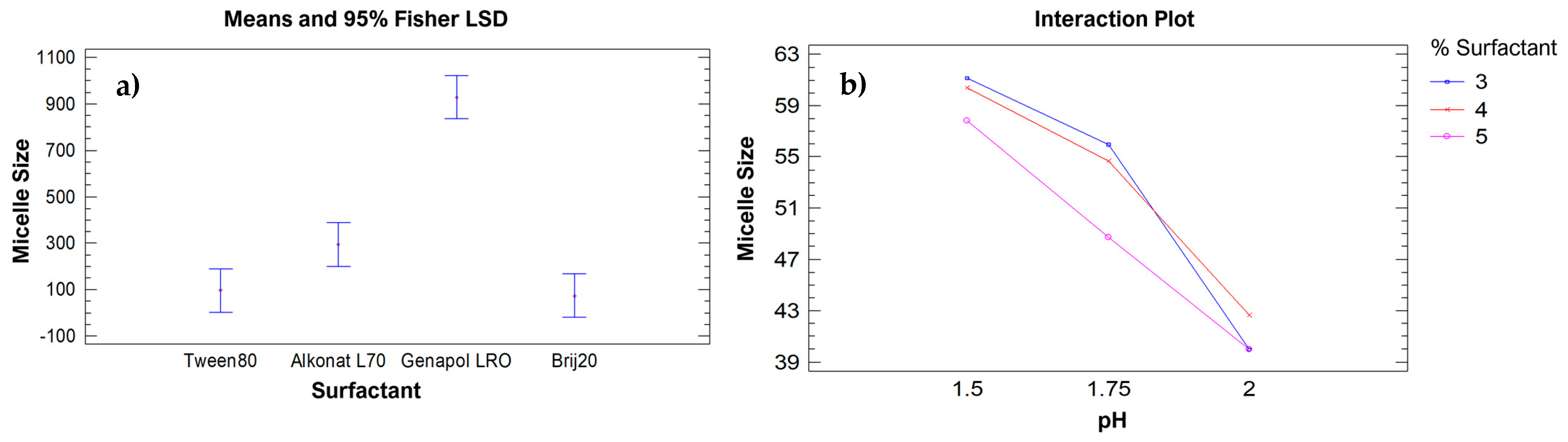
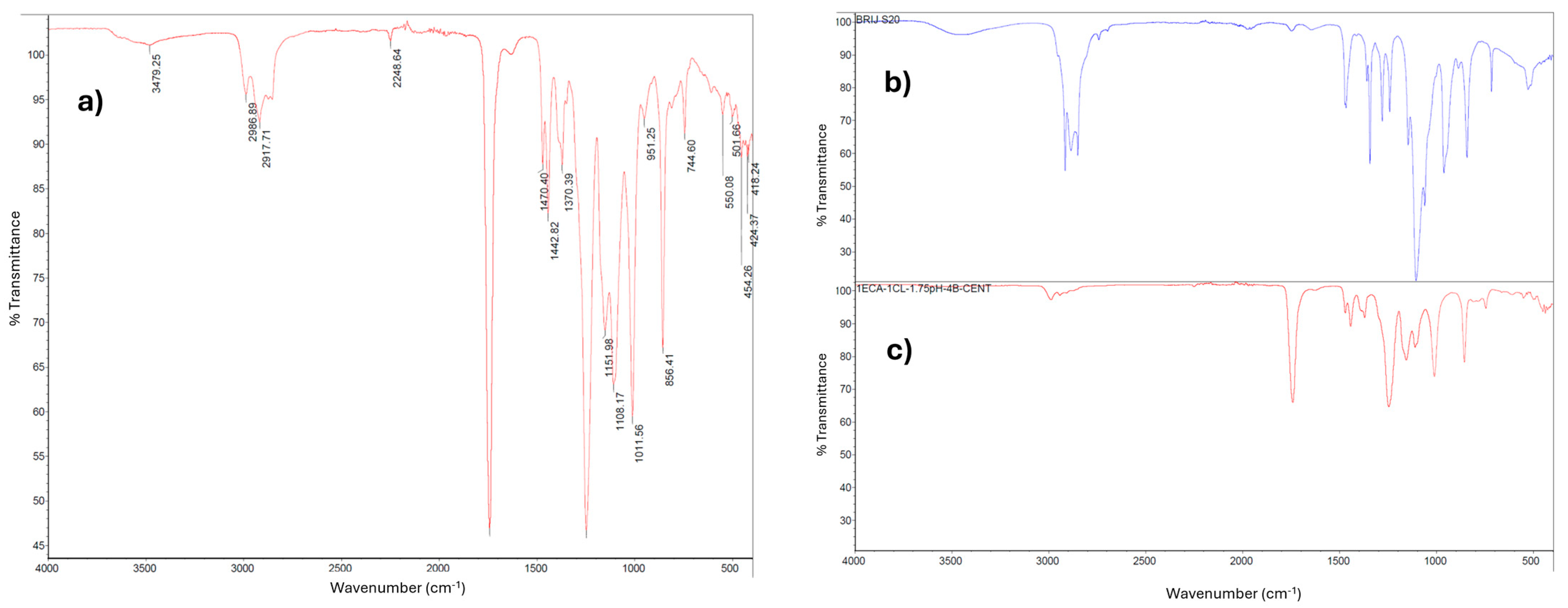

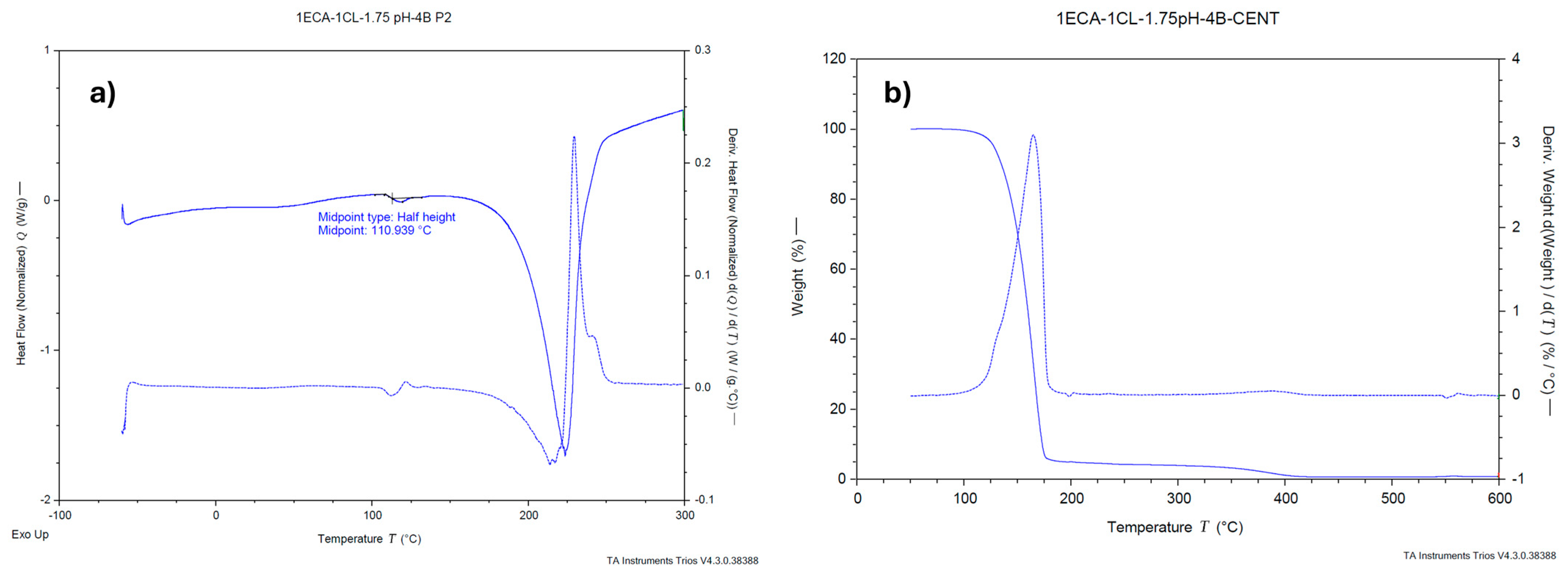
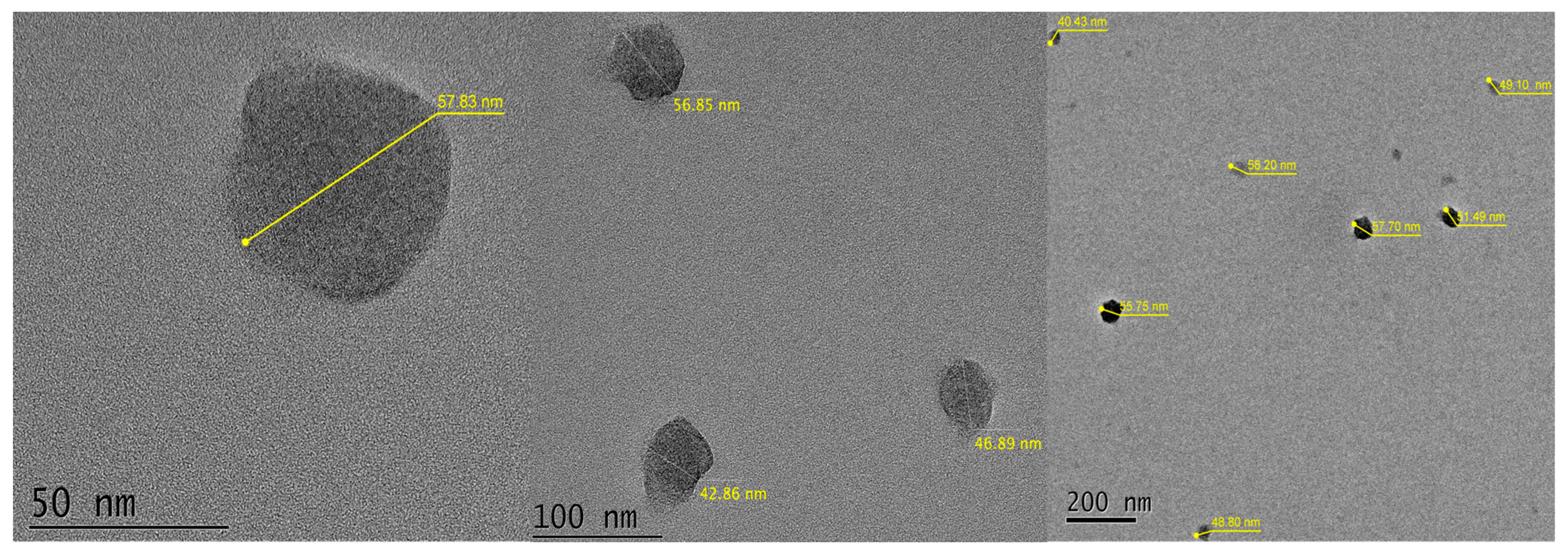
| PECA-PCL | % Brij20 | pH | Average Micelle Size a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 3 | 1.5 | 61.14 |
| 1:1 | 4 | 1.5 | 60.42 |
| 1:1 | 5 | 1.5 | 57.82 |
| 1:1 | 3 | 1.75 | 55.96 |
| 1:1 | 4 | 1.75 | 54.66 |
| 1:1 | 5 | 1.75 | 48.72 |
| 1:1 | 3 | 2 | 39.94 |
| 1:1 | 4 | 2 | 42.66 |
| 1:1 | 5 | 2 | 39.96 |
| [PCL] [m/m] | [PECA] [m/m] | % Tween80 | nm | Mean a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 502.2 | |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 549 | 530.5 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 540.2 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 96.84 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 96.76 | 96.7 |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 96.49 | |
| 2.5 | 0.5 | 5 | 737.4 | |
| 2.5 | 0.5 | 5 | 801 | 754.1 |
| 2.5 | 0.5 | 5 | 723.8 | |
| 1 | 1 | 6 | 203.1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 6 | 209.5 | 205.5 |
| 1 | 1 | 6 | 203.8 | |
| 2 | 1 | 7 | 179.5 | |
| 2 | 1 | 7 | 176.4 | 179.0 |
| 2 | 1 | 7 | 181 | |
| 1 | 1 | 7 | 274.2 | |
| 1 | 1 | 7 | 278.1 | 276.3 |
| 1 | 1 | 7 | 276.6 | |
| % Alkonat L70 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 279.4 | |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 302.5 | 294.0 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 300 | |
| % Genapol LRO | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 739.8 | |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 1135 | 928.8 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 911.6 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 1451 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 1653 | 1823.3 |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 2366 | |
| % Brij-20 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 74.08 | |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 75.04 | 74.0 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 72.76 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 52.85 | |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 52.85 | 51.9 |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 50.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-Sánchez, G.; Orozco-Guareño, E.; Zúñiga-González, O.G.; Briones-Márquez, L.F.; Quiñonez-López, R.R.; Campos-García, J.B.; Palacios-Sánchez, M.d.J. Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Poly(cyanoacrylates) and Poly(caprolactone). Molecules 2025, 30, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132668
León-Sánchez G, Orozco-Guareño E, Zúñiga-González OG, Briones-Márquez LF, Quiñonez-López RR, Campos-García JB, Palacios-Sánchez MdJ. Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Poly(cyanoacrylates) and Poly(caprolactone). Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-Sánchez, Gerardo, Eulogio Orozco-Guareño, Oscar Guillermo Zúñiga-González, Luisa Fernanda Briones-Márquez, Raúl R. Quiñonez-López, Jesús Baudelio Campos-García, and María de Jesús Palacios-Sánchez. 2025. "Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Poly(cyanoacrylates) and Poly(caprolactone)" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132668
APA StyleLeón-Sánchez, G., Orozco-Guareño, E., Zúñiga-González, O. G., Briones-Márquez, L. F., Quiñonez-López, R. R., Campos-García, J. B., & Palacios-Sánchez, M. d. J. (2025). Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization of Polymeric Nanoparticles of Poly(cyanoacrylates) and Poly(caprolactone). Molecules, 30(13), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132668






