Overview of Some Second- and Third-Row Late Transition Metal Pincer-Type N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation and Reactivities of d6 Late Transition Metal-NHC Complexes
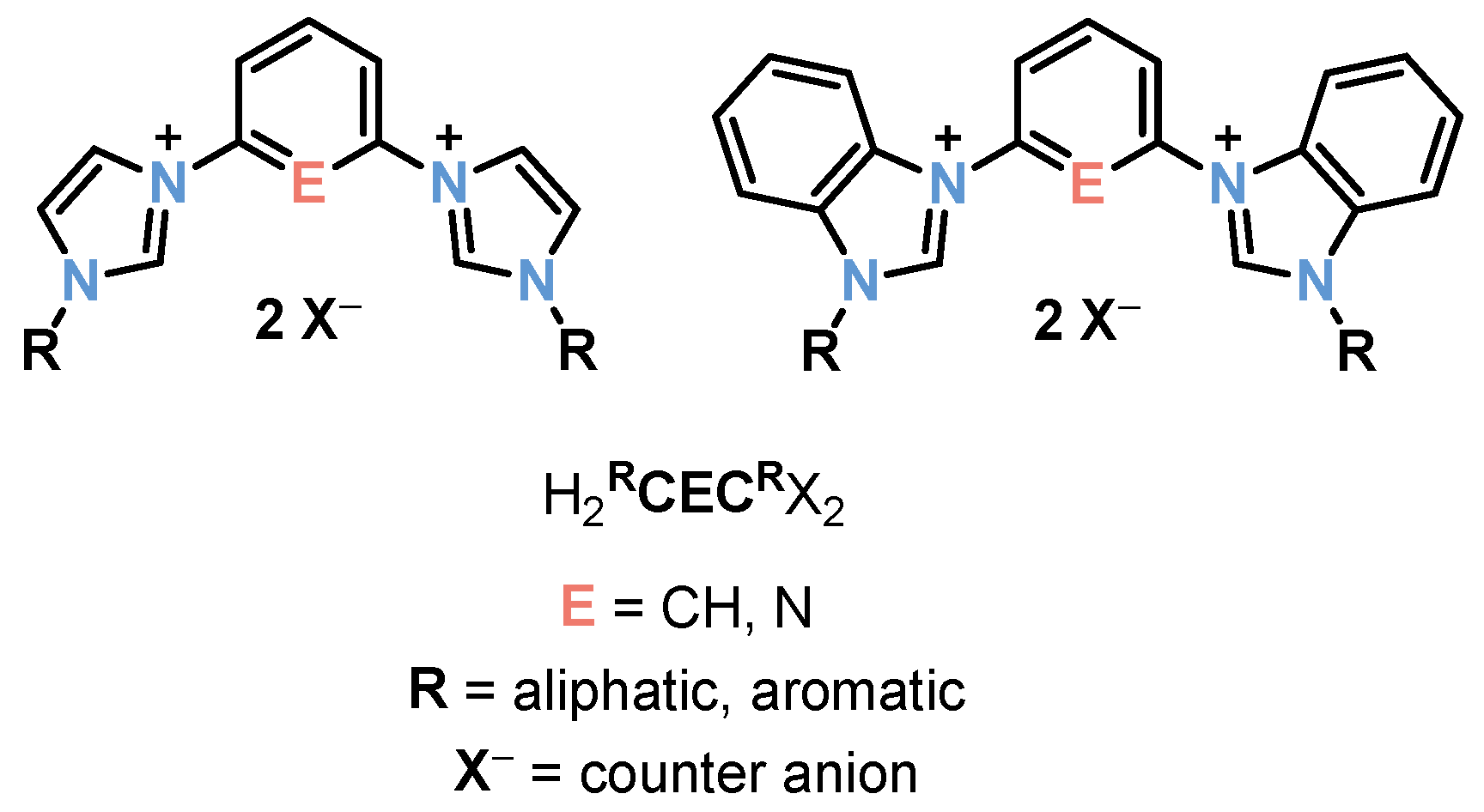
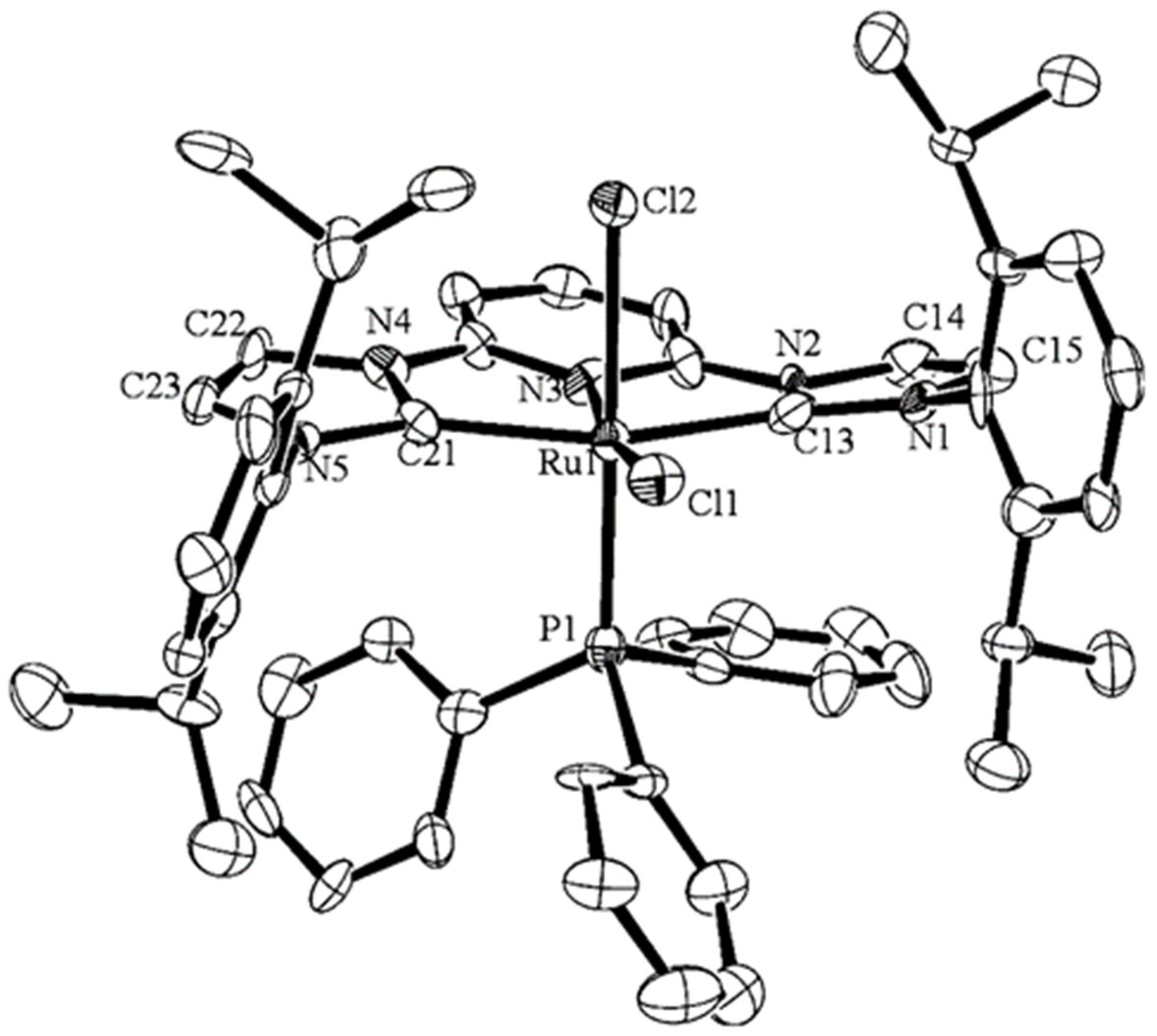
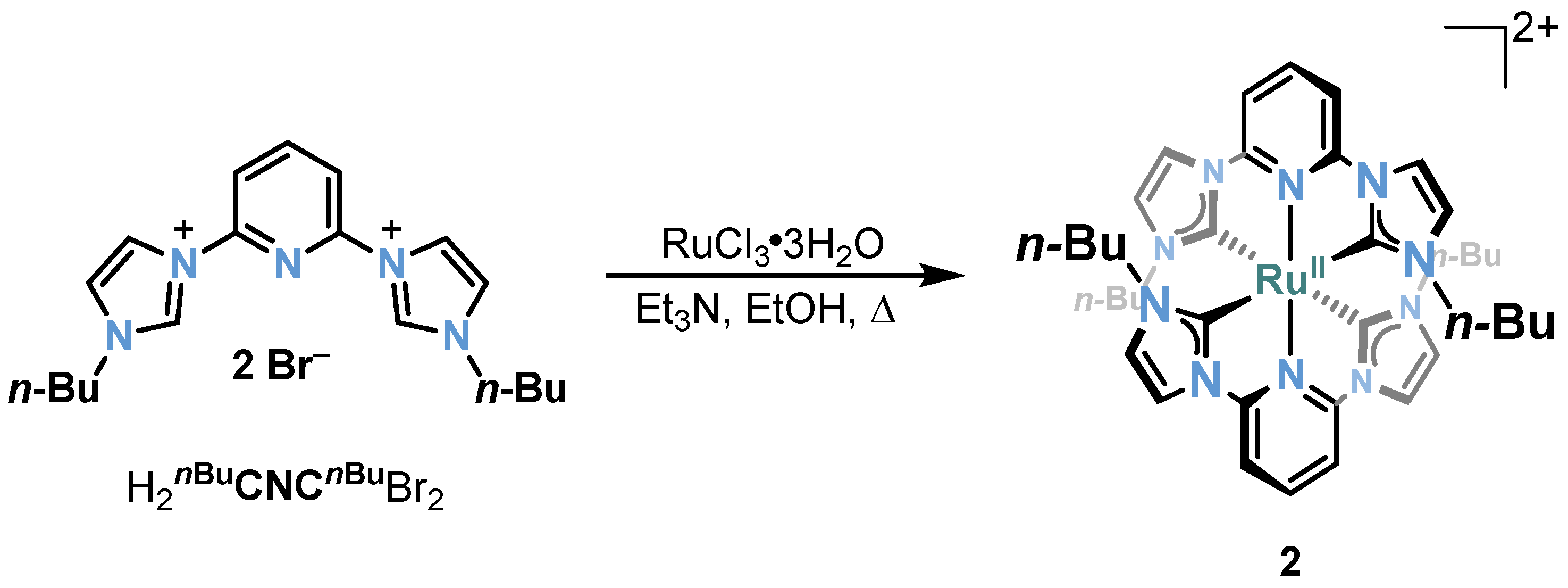
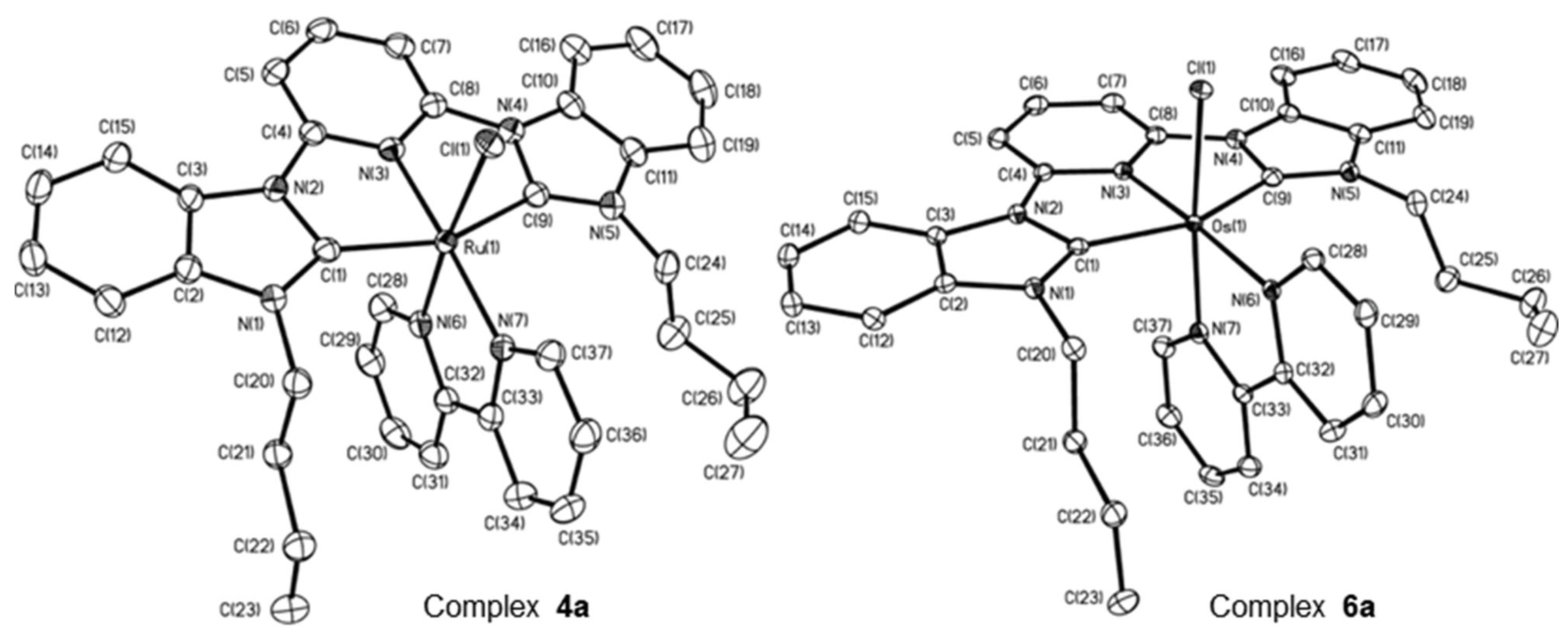
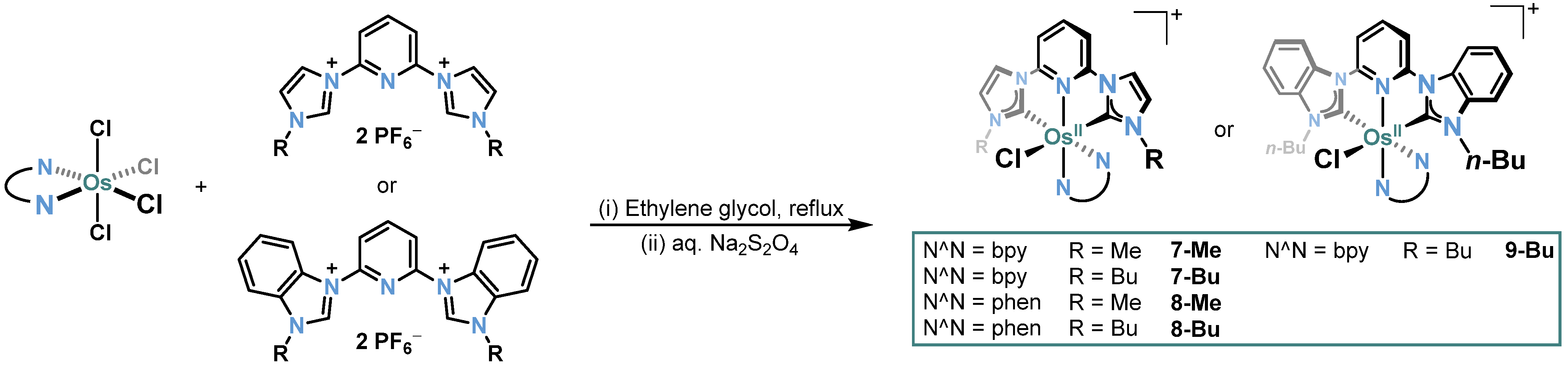
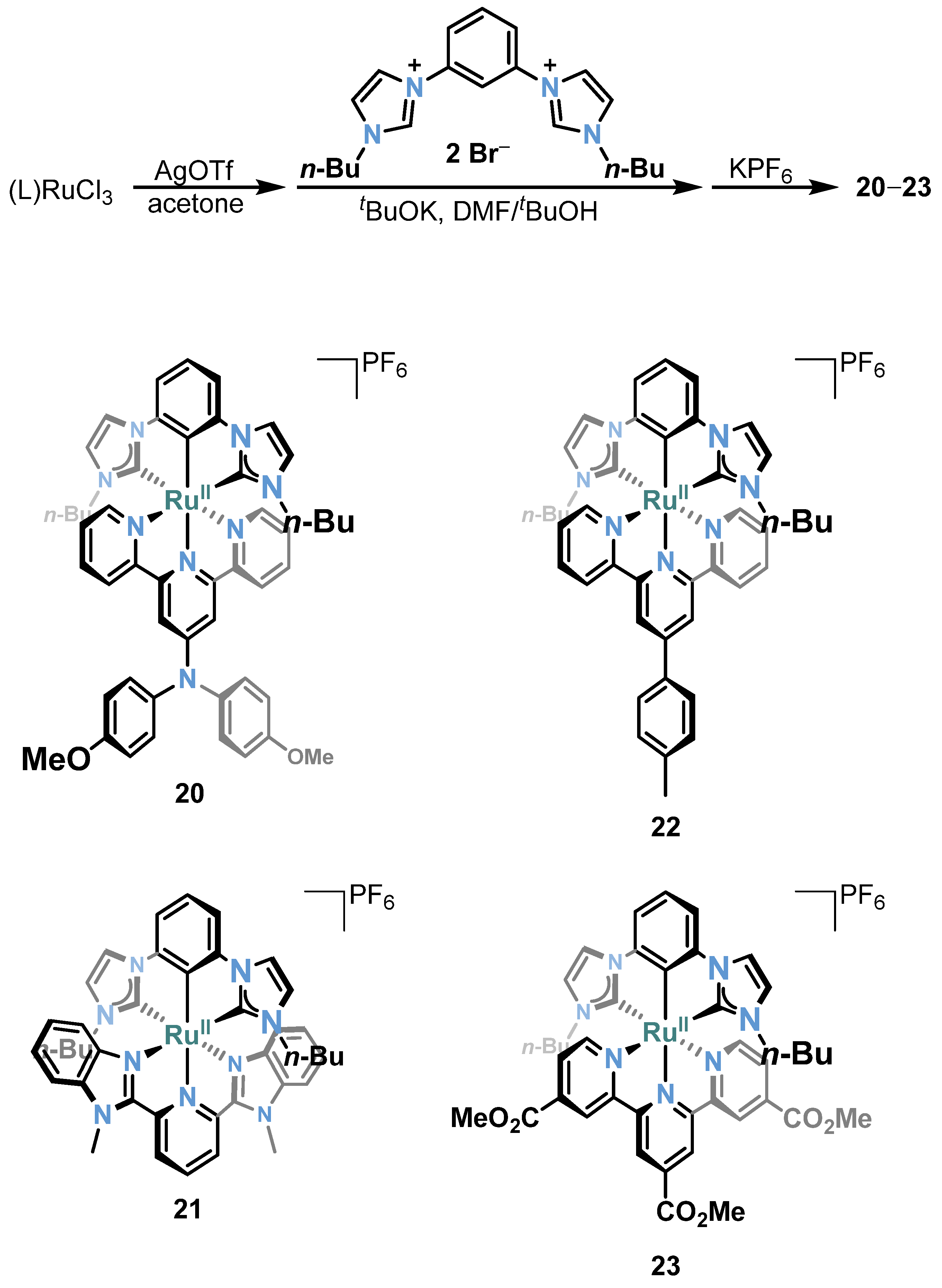
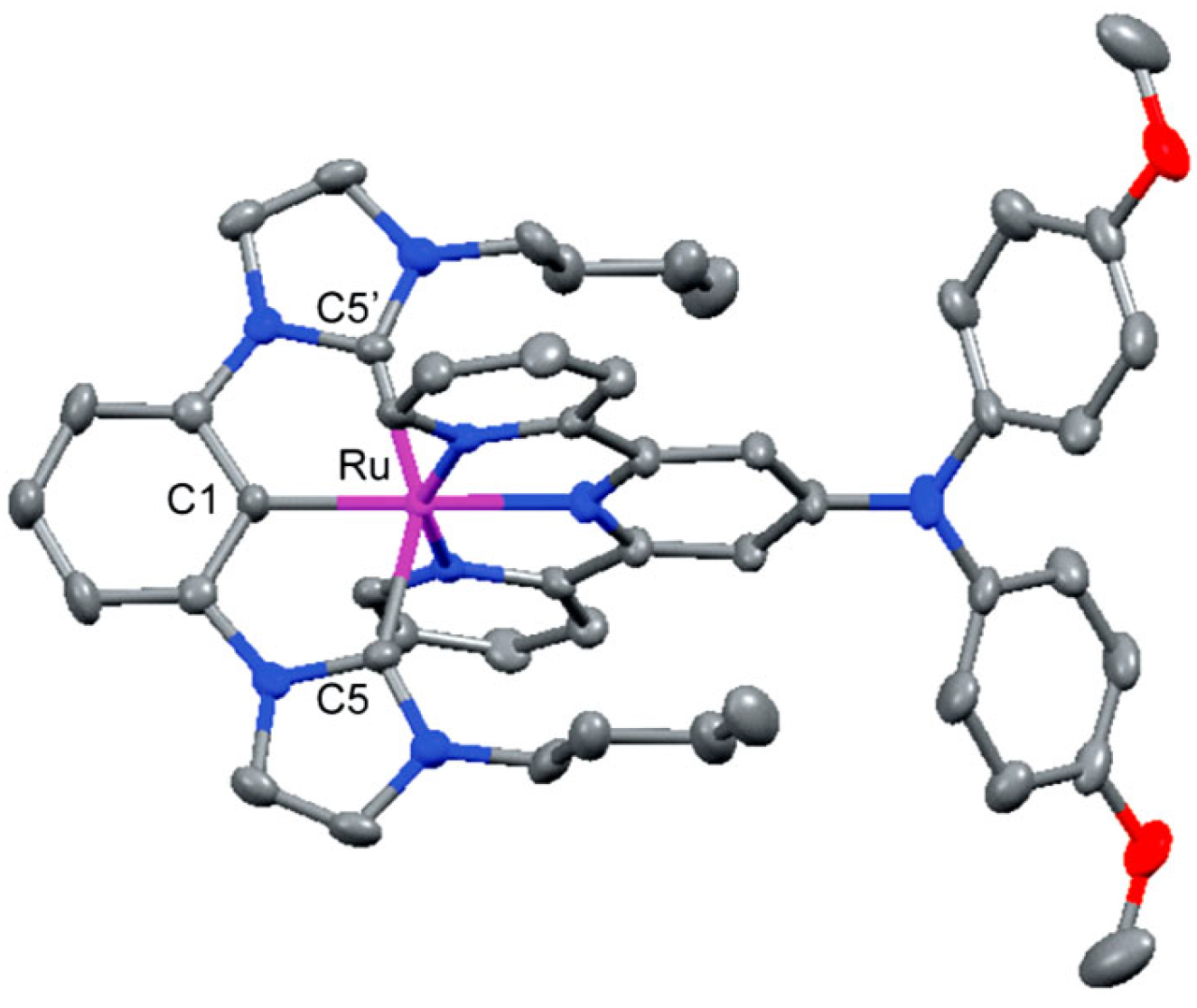
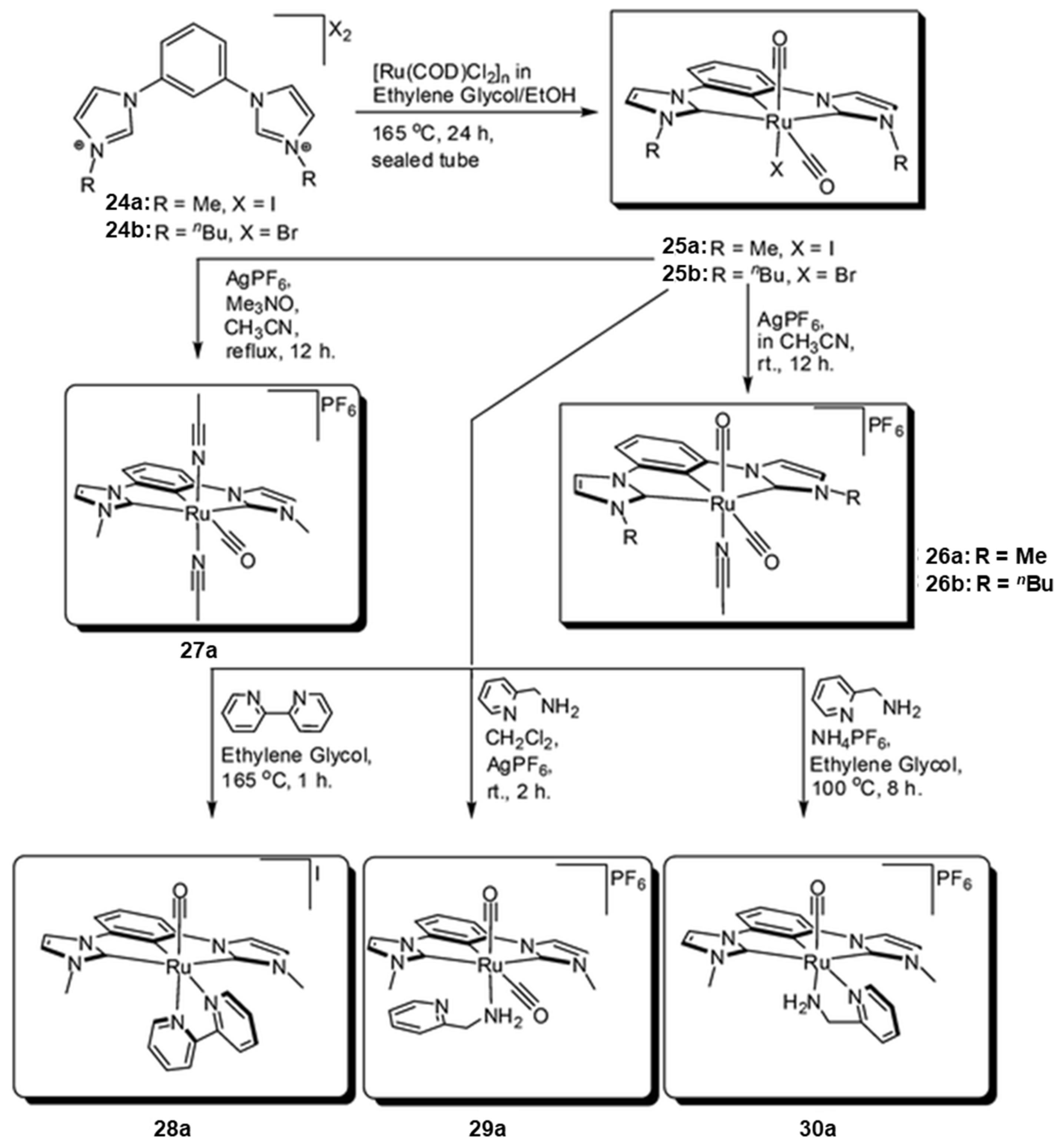
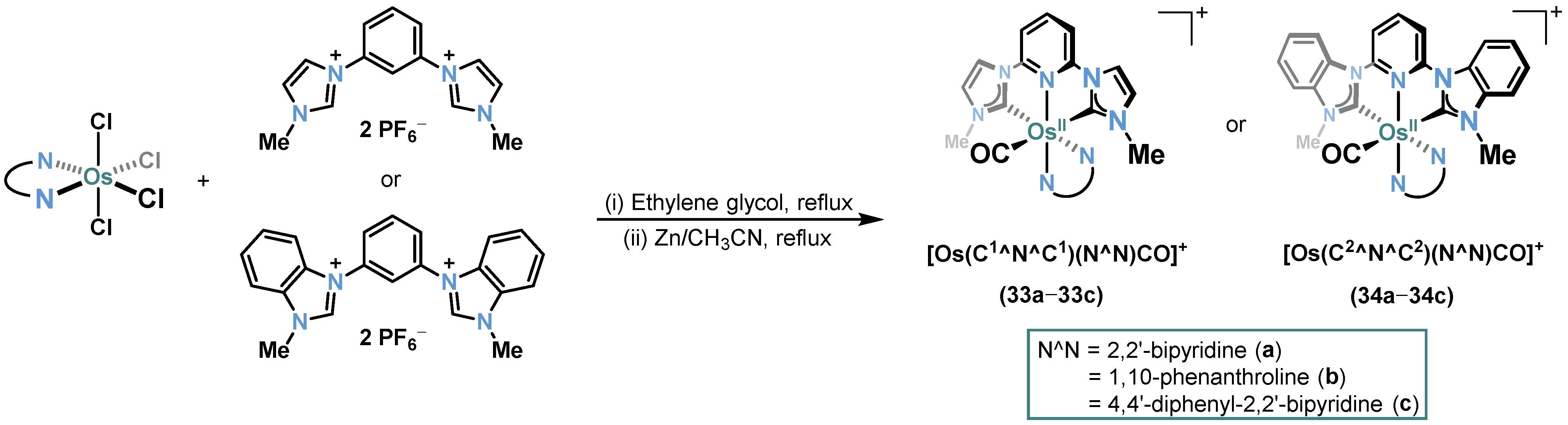
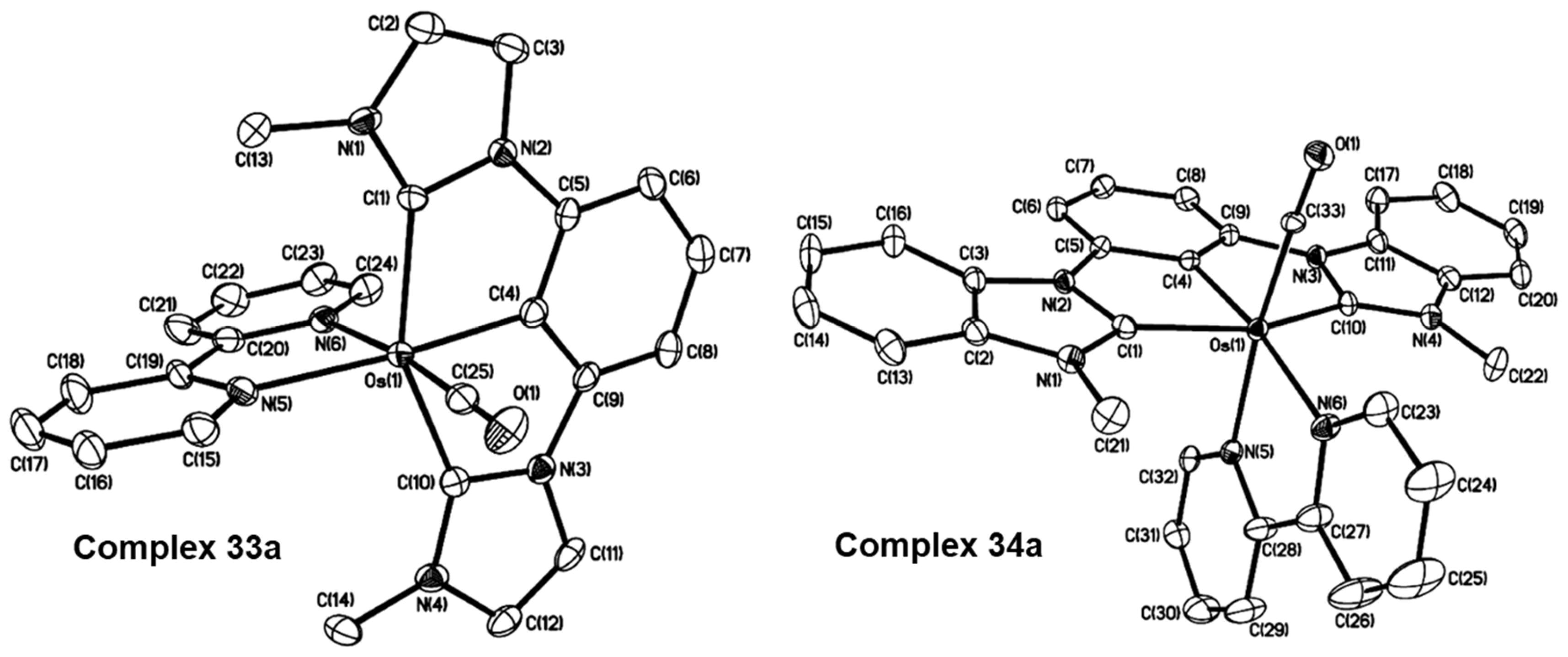
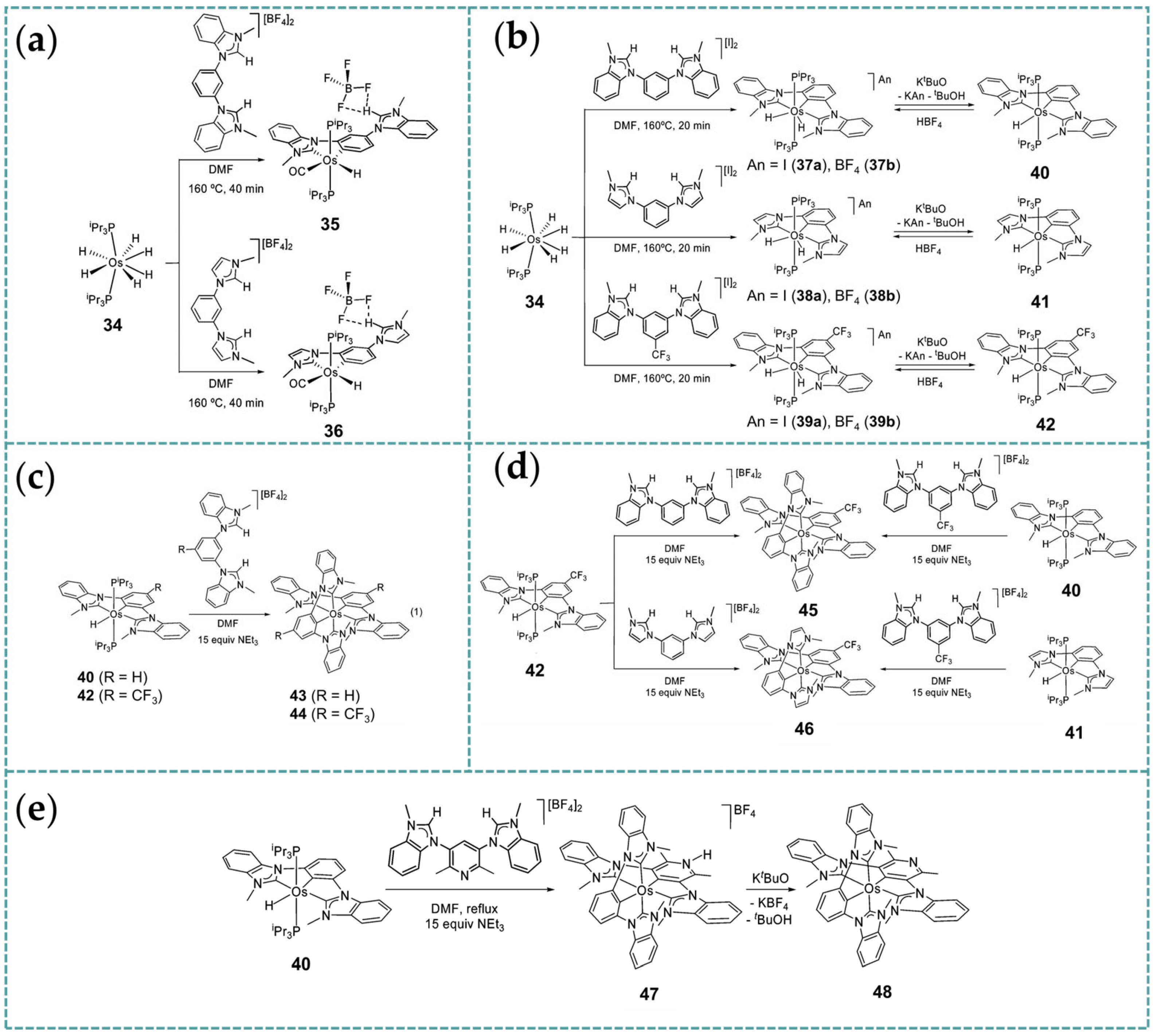
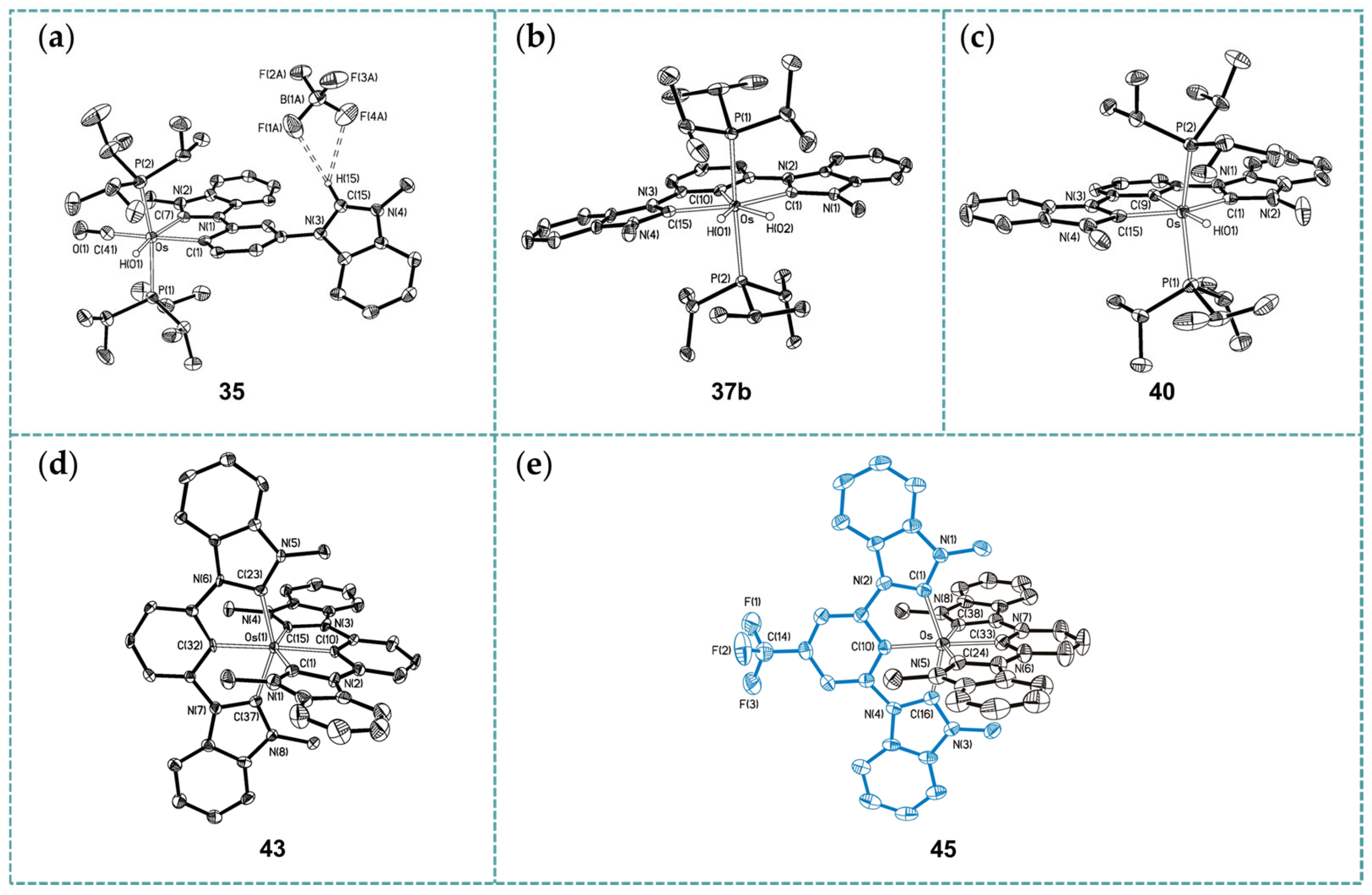
2.1. Ru/Os-RCNCR Complex
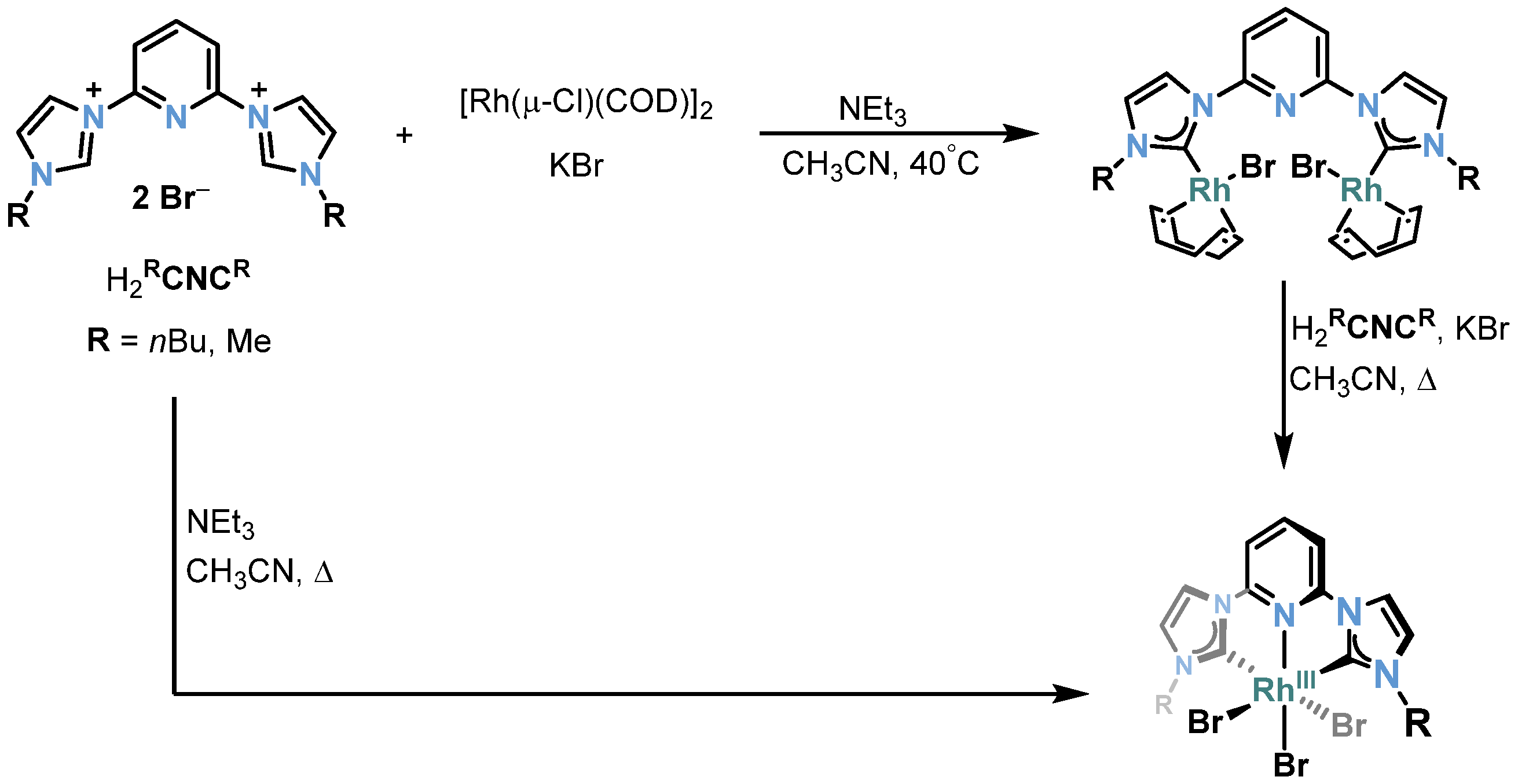
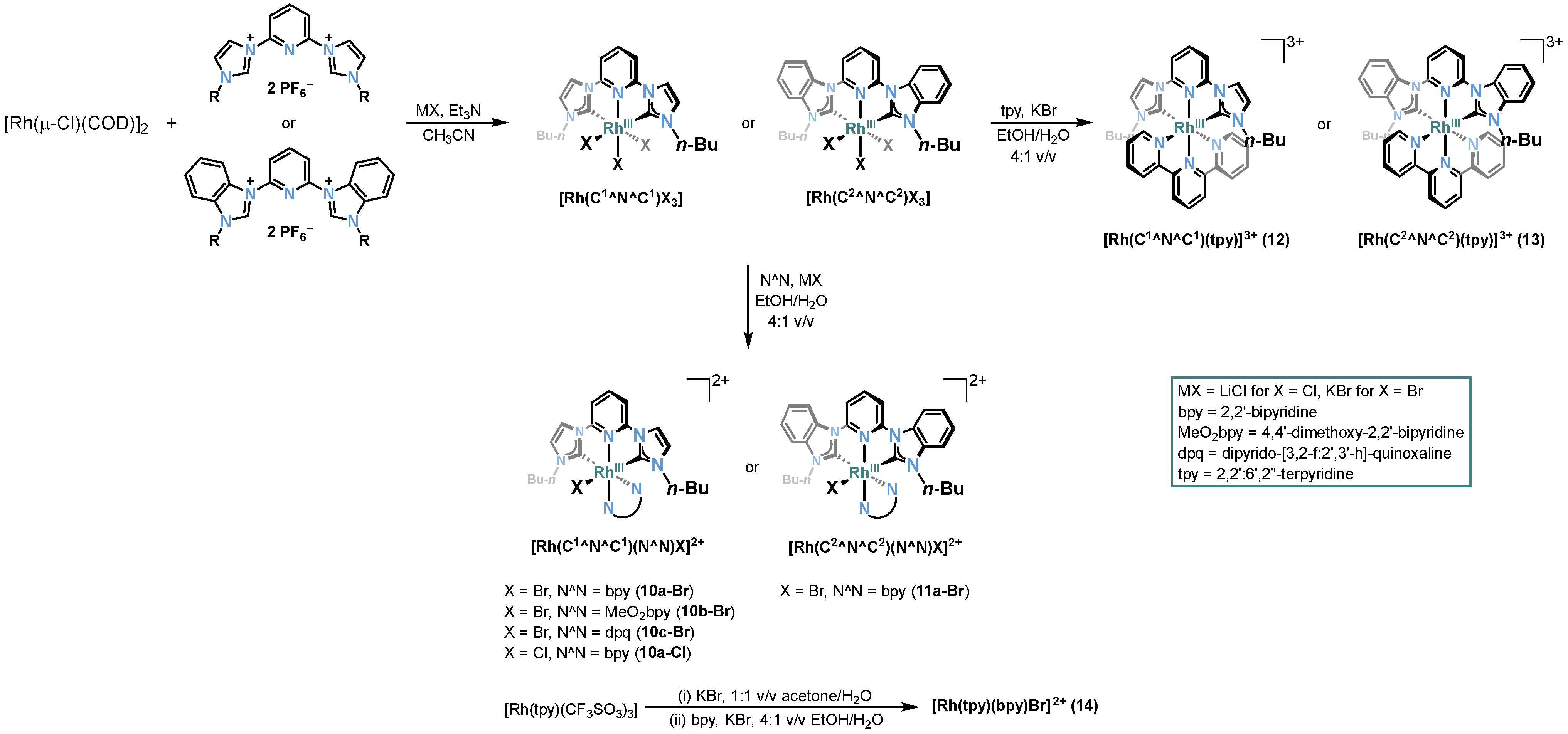
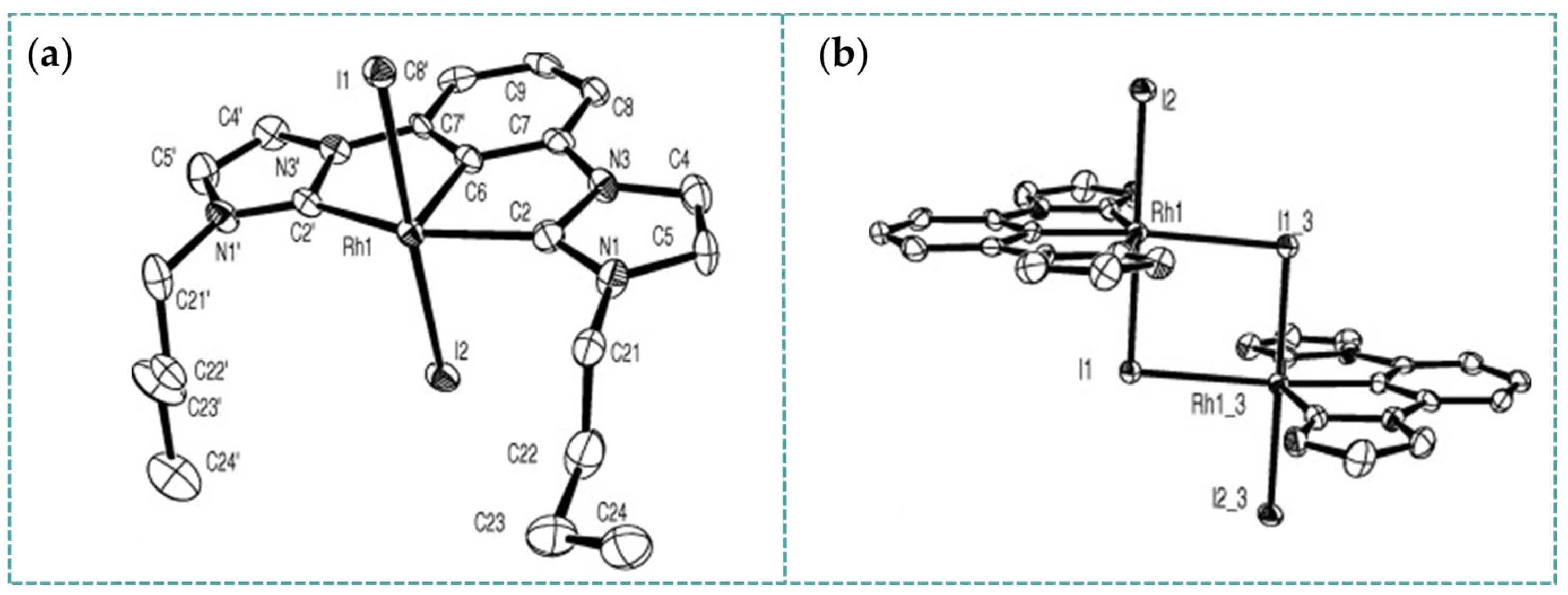
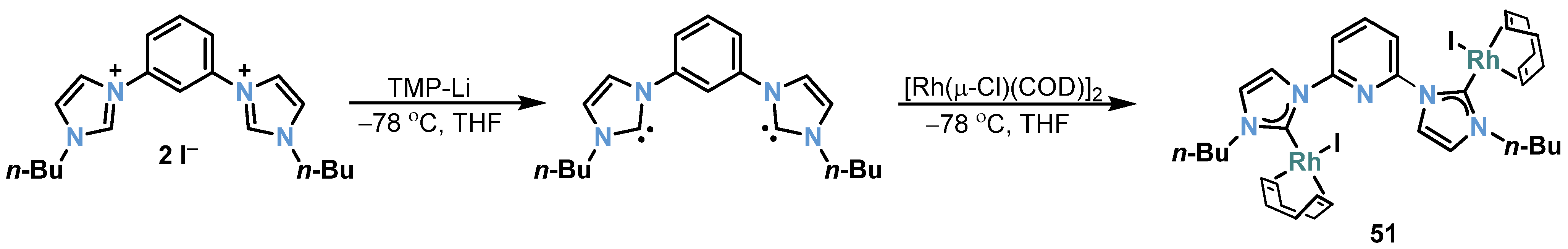
2.2. Rh-RCNCR Complexes
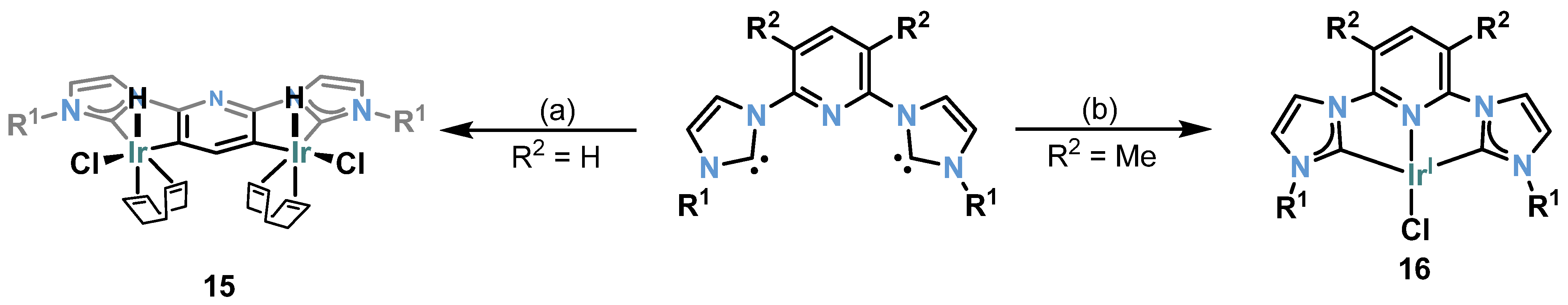
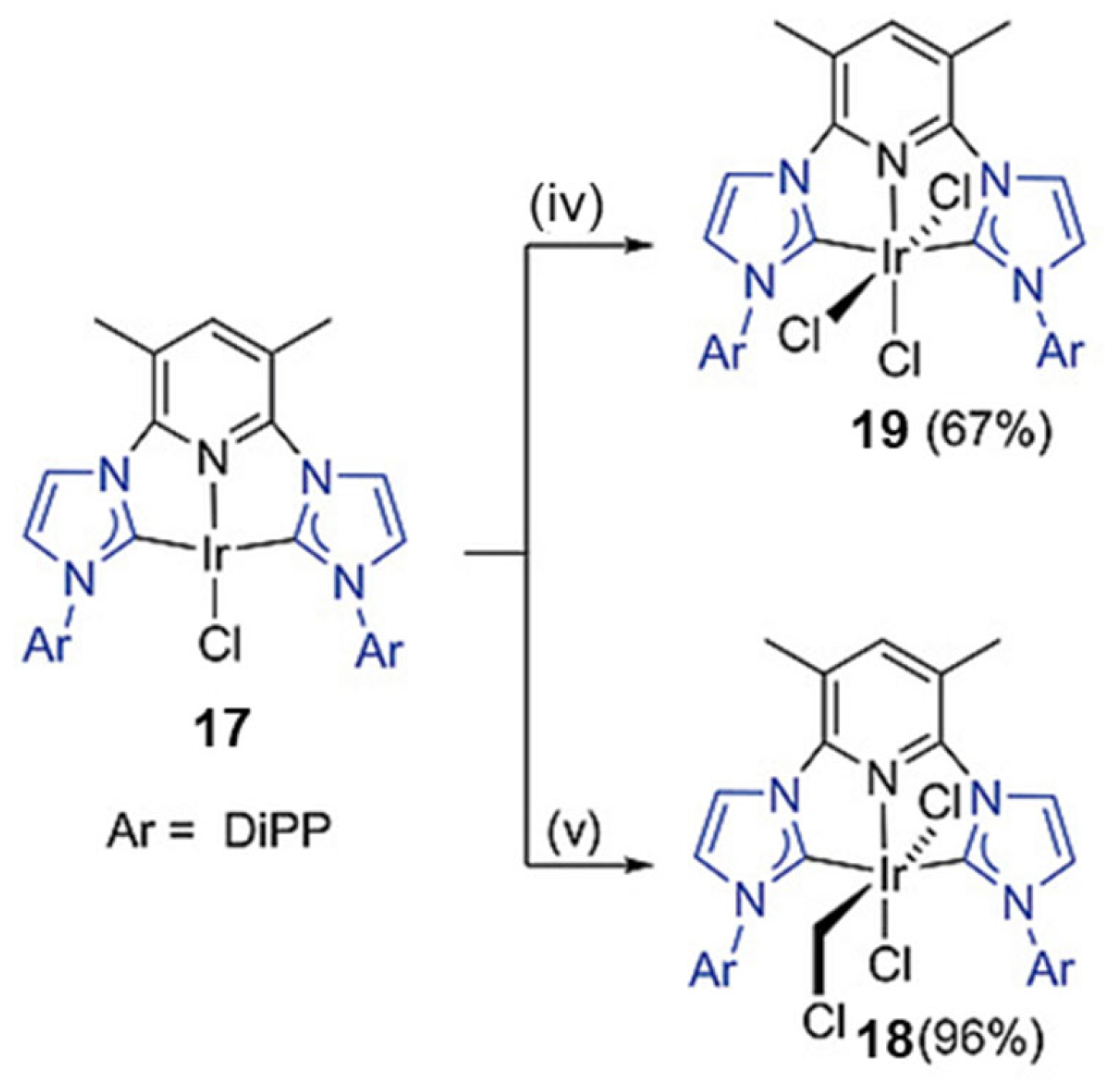
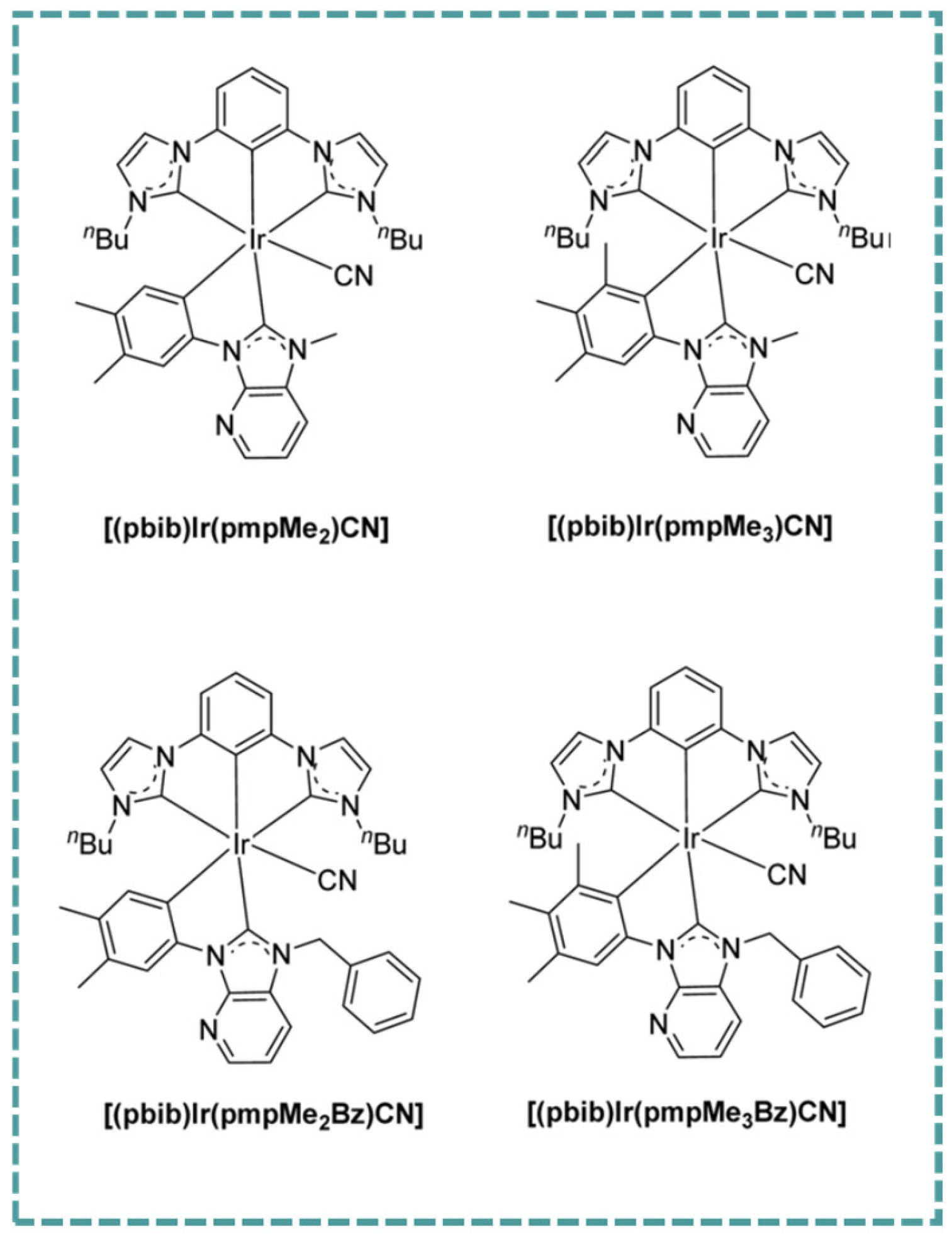
2.3. Ir-RCNCR Complexes
2.4. Ru/Os-RCCCR Complexes
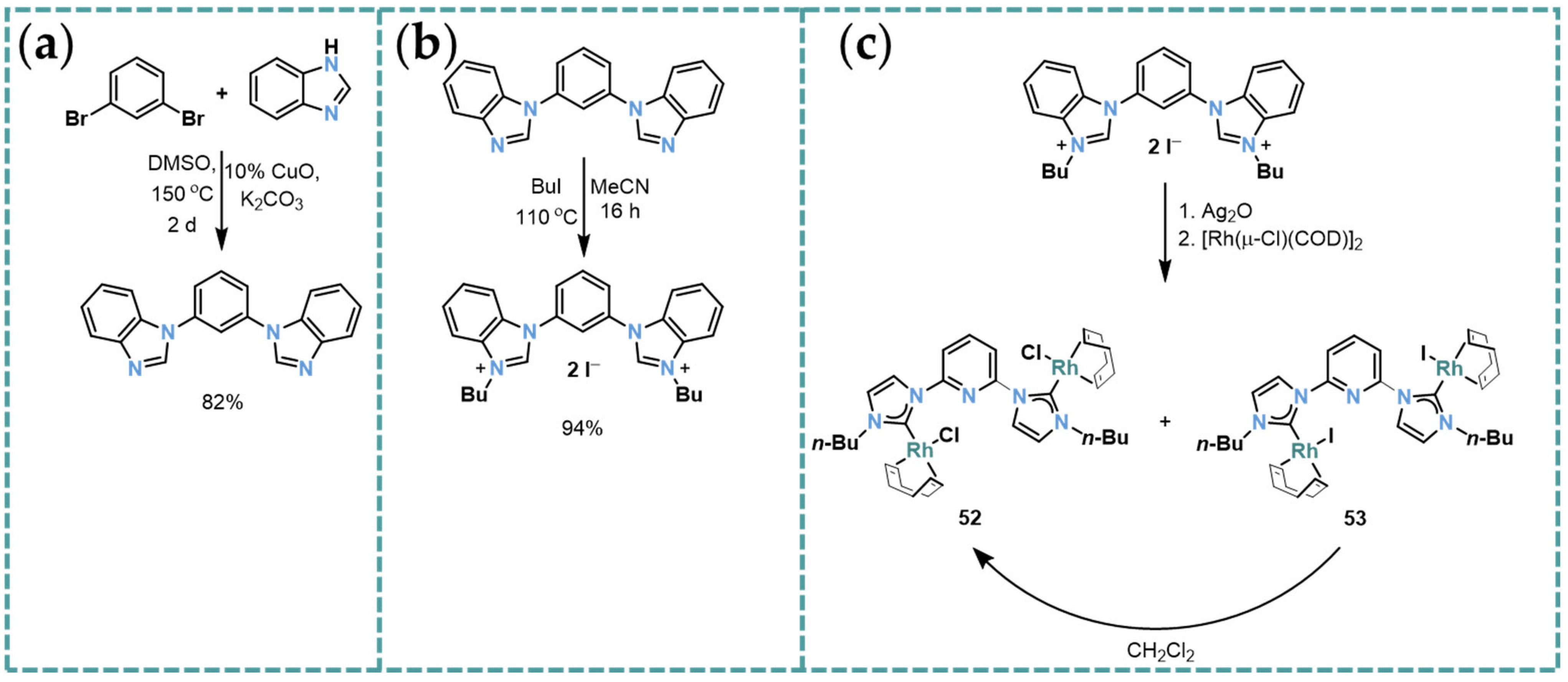
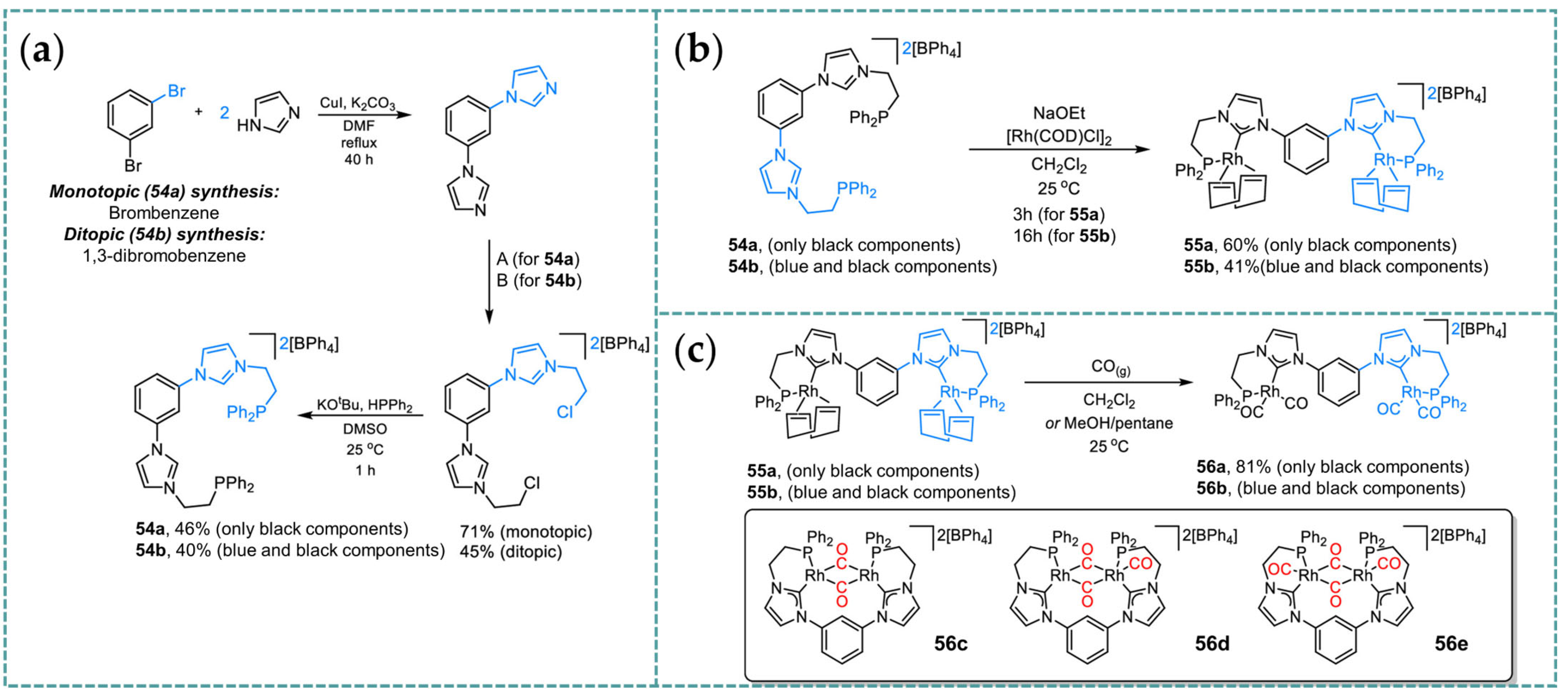
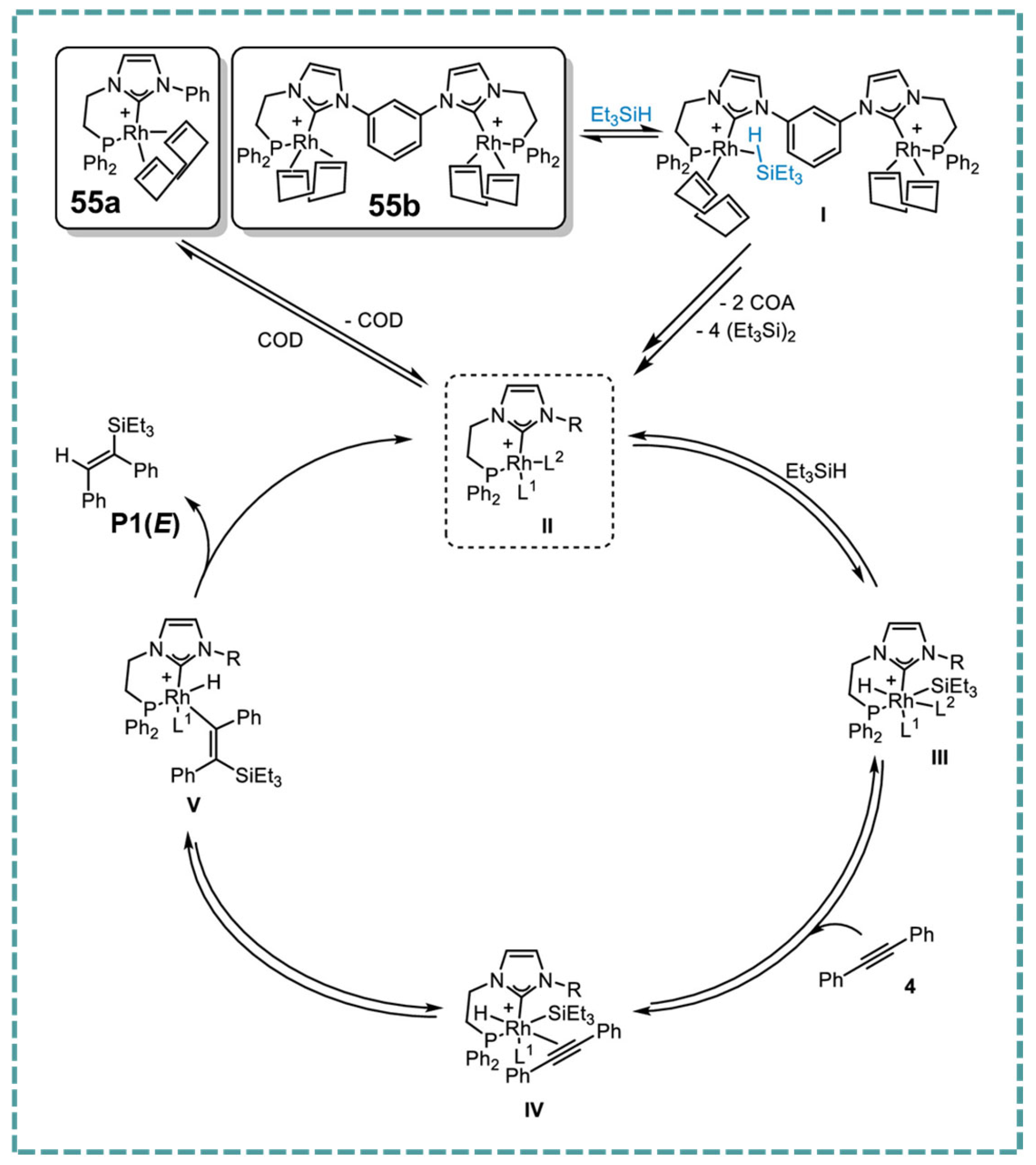
2.5. Rh-RCCCR Complexes
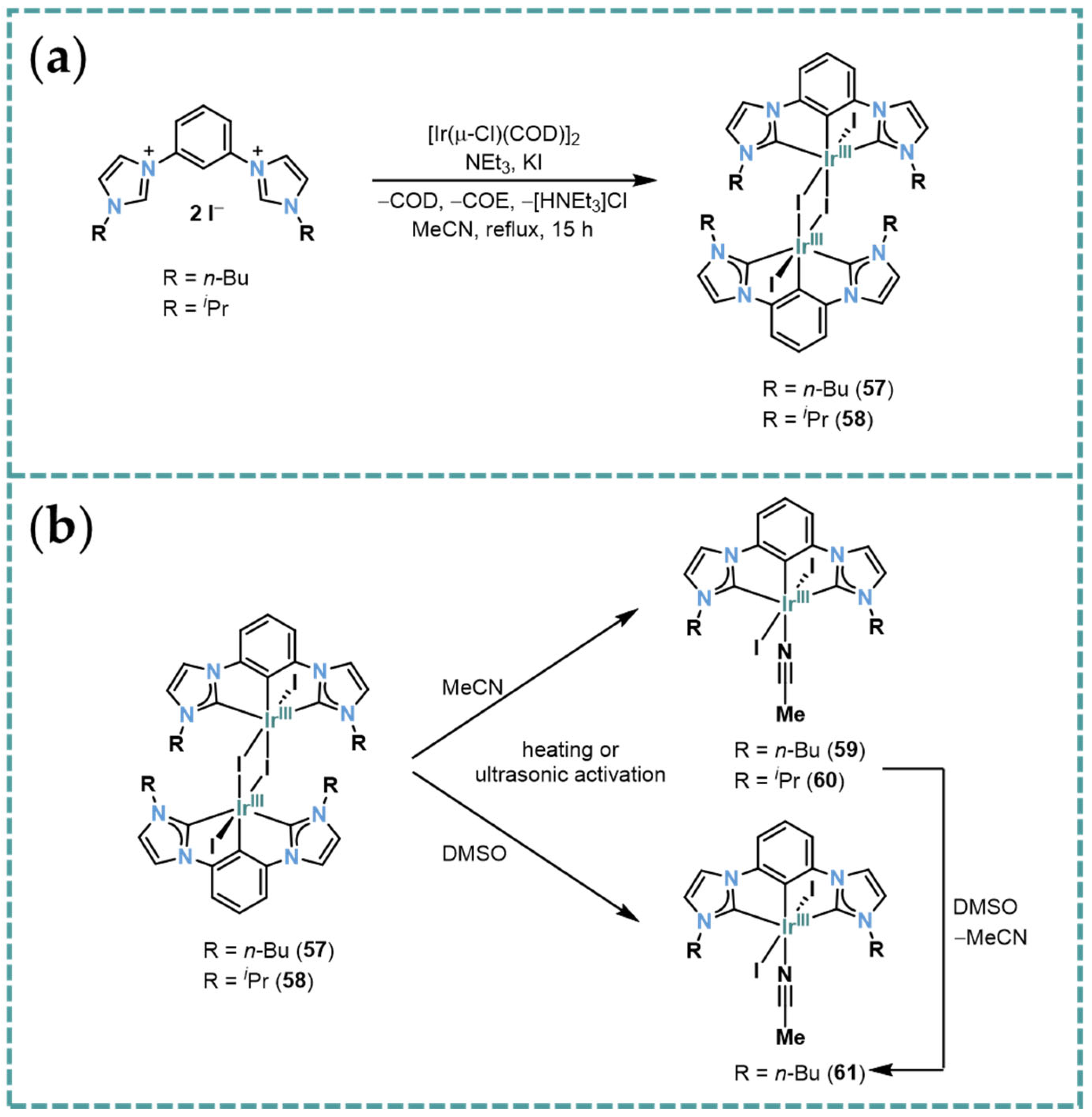
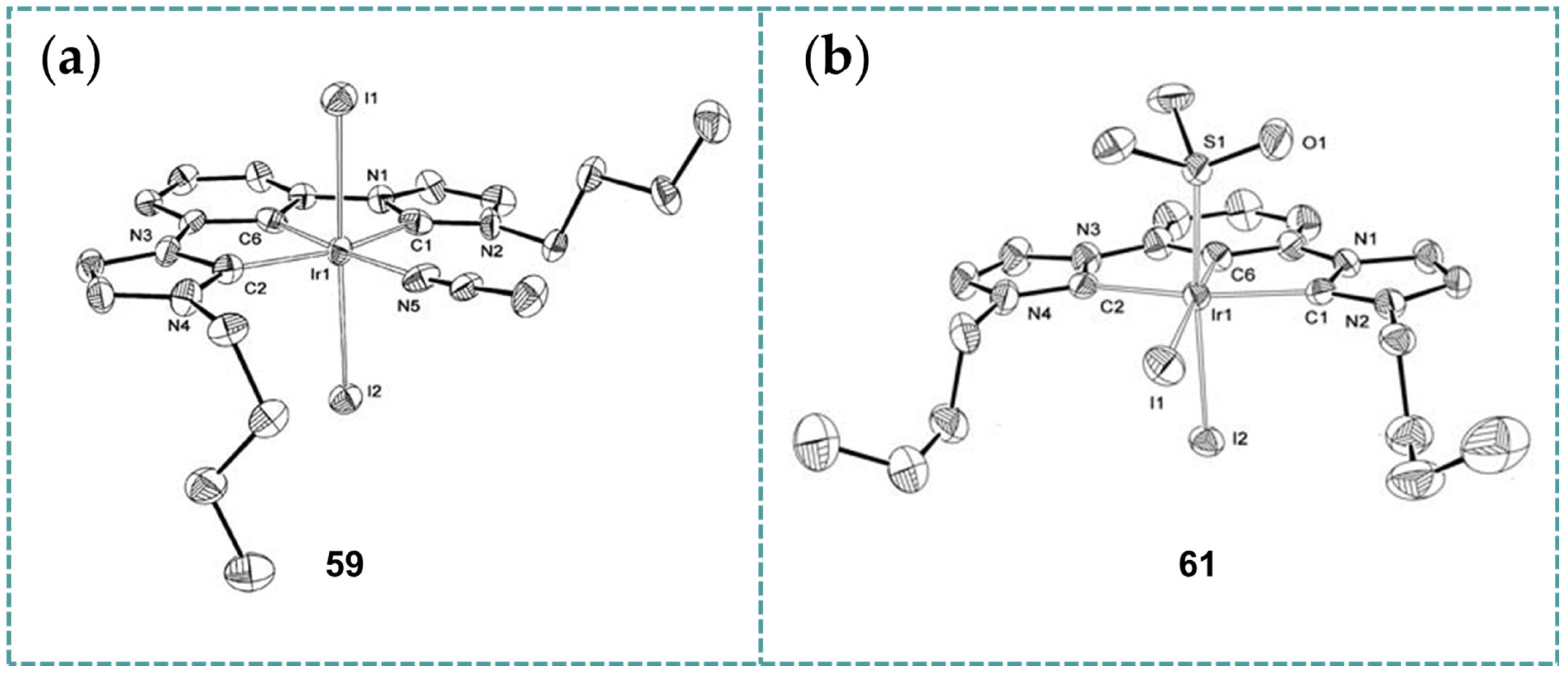
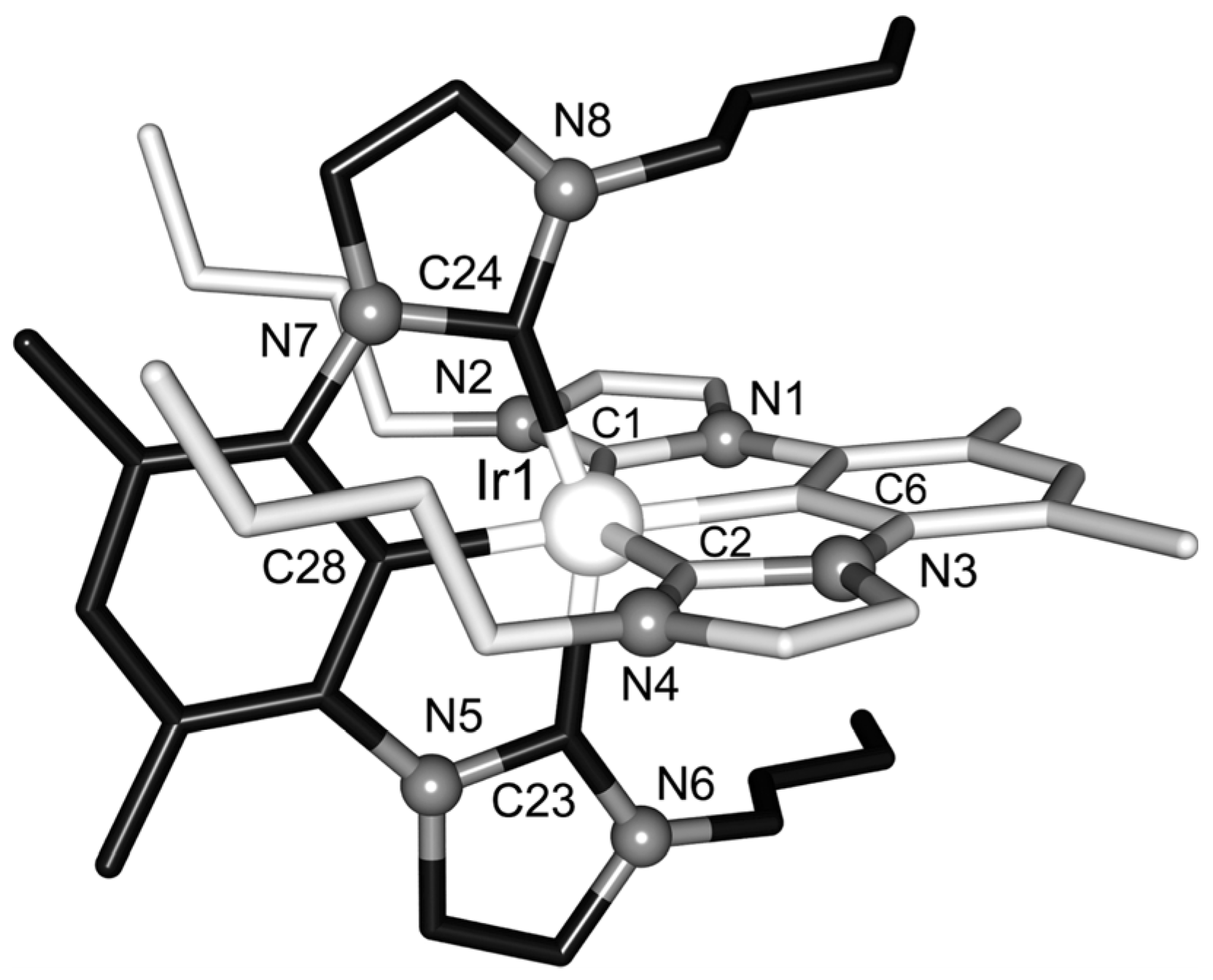
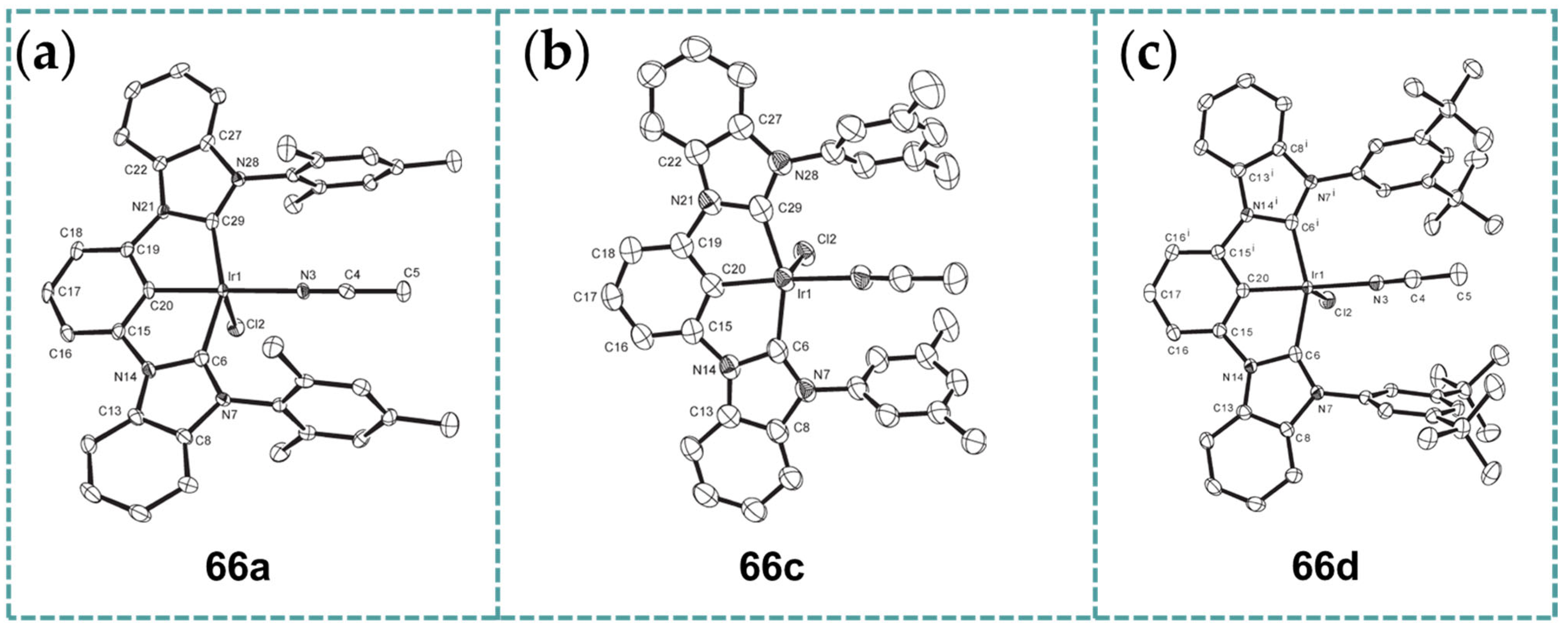
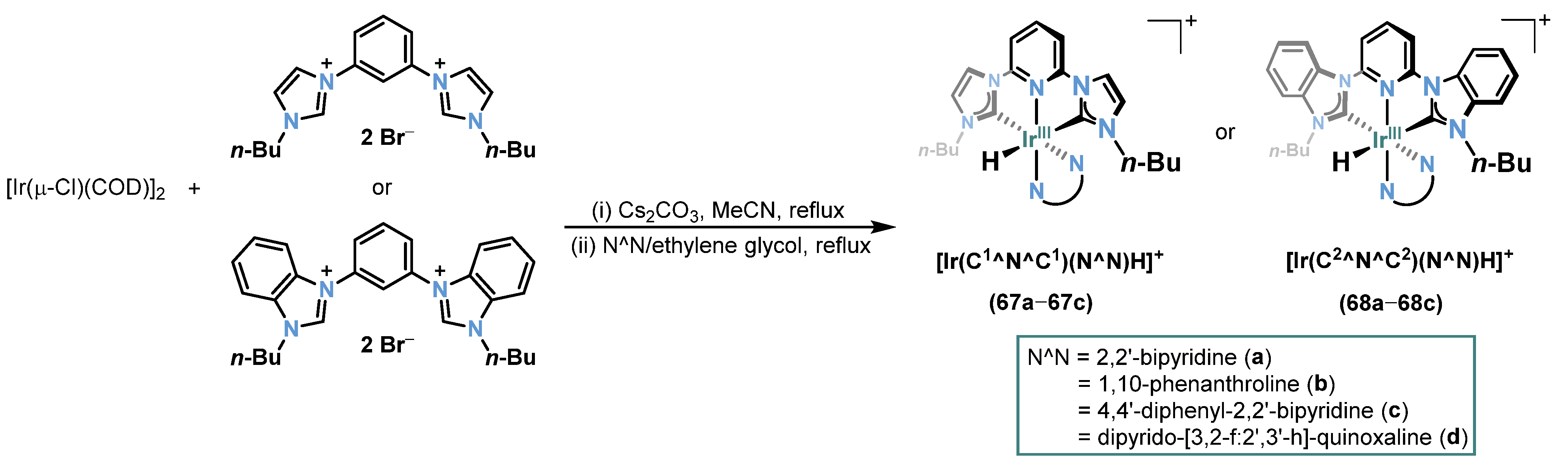
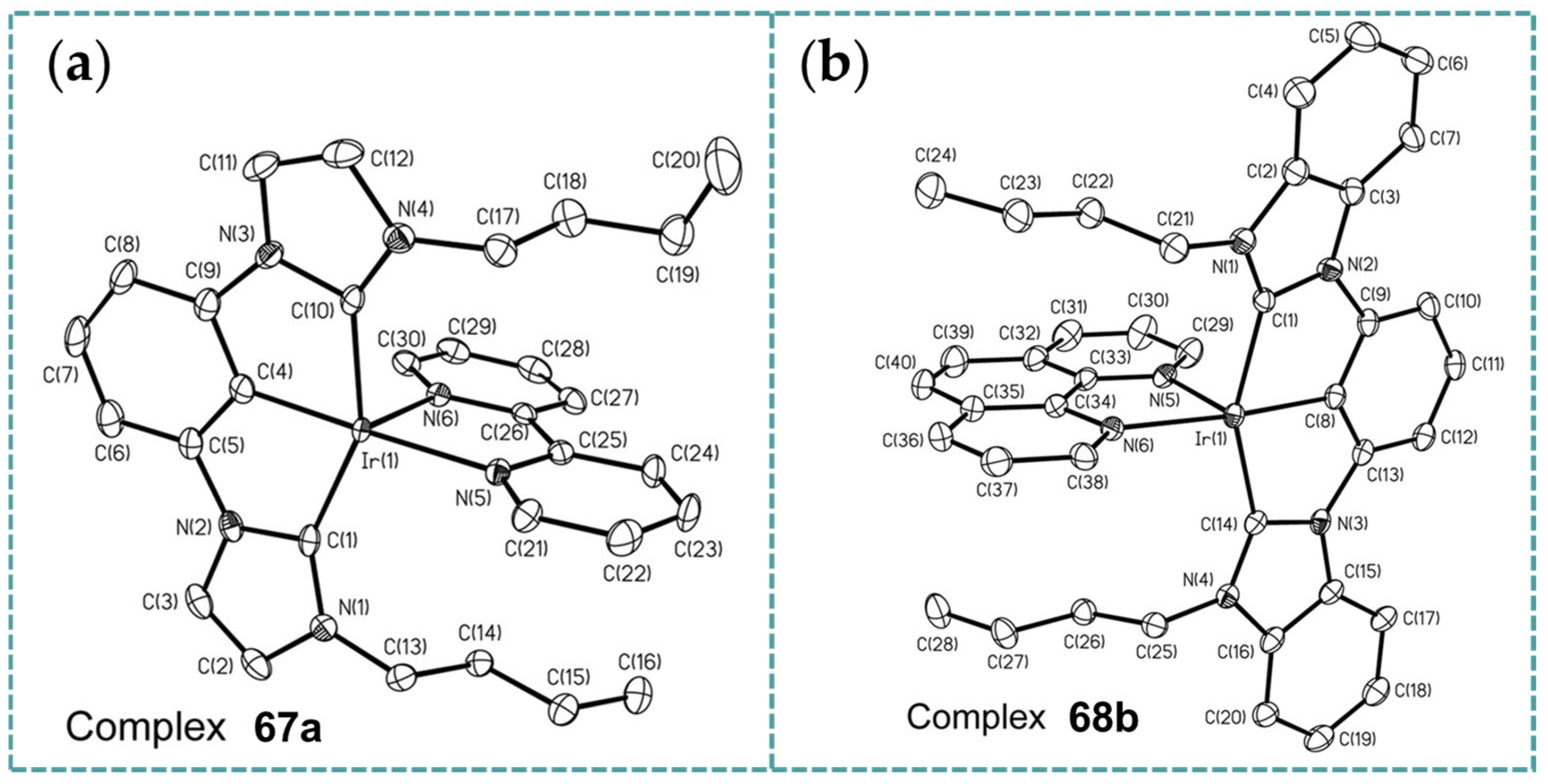
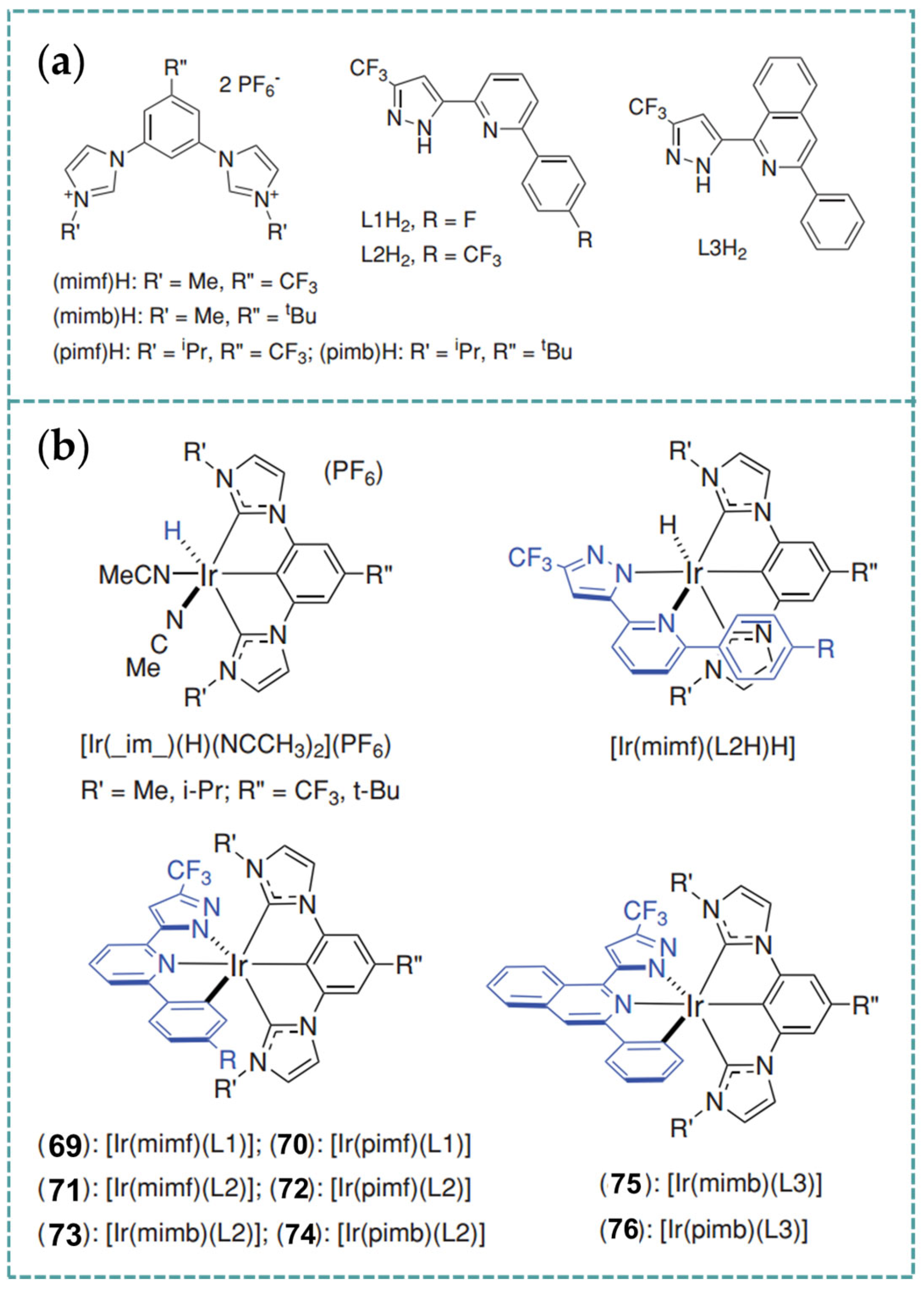
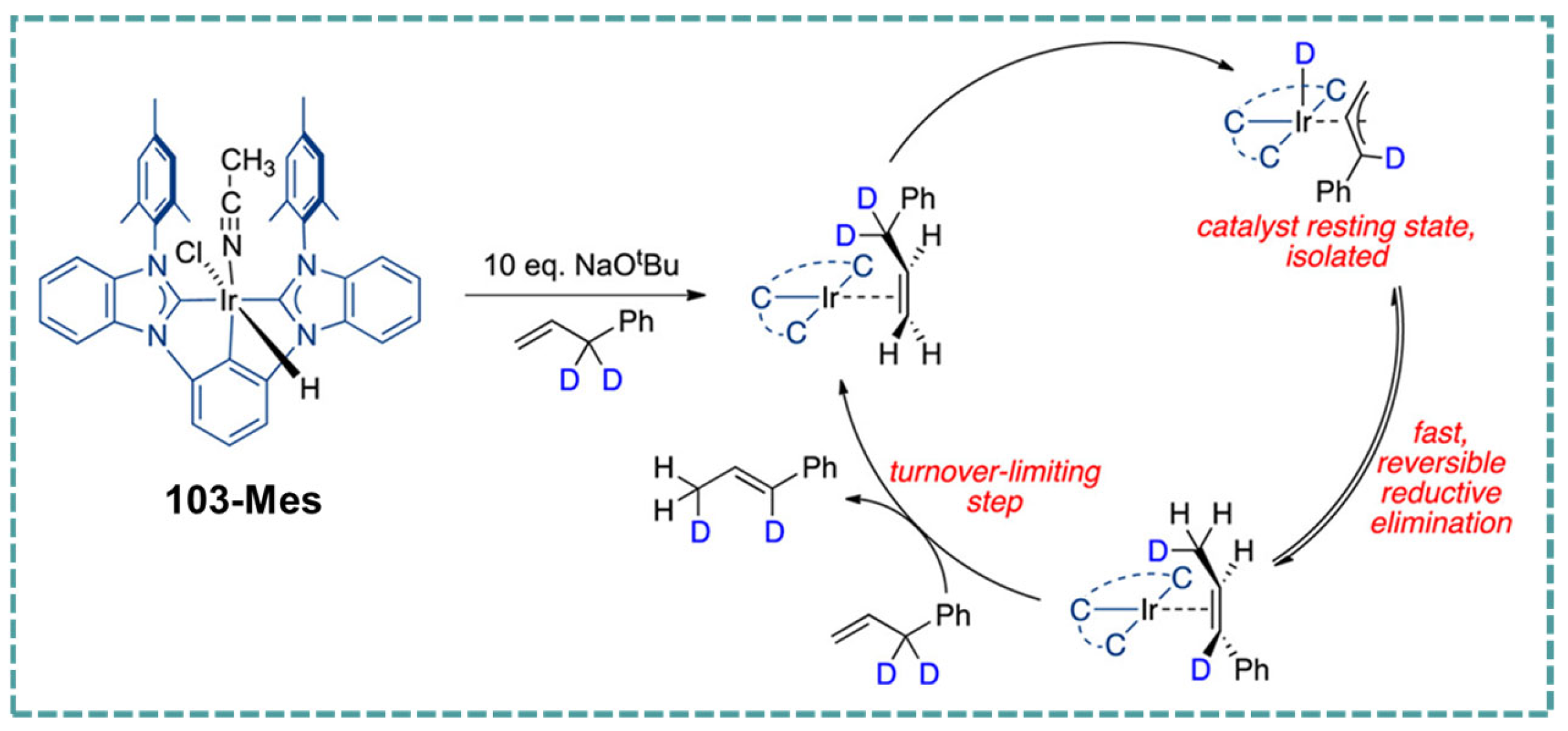
2.6. Ir-RCCCR Complexes
3. Photophysical Property of d6 Transition Metal-NHC Complexes
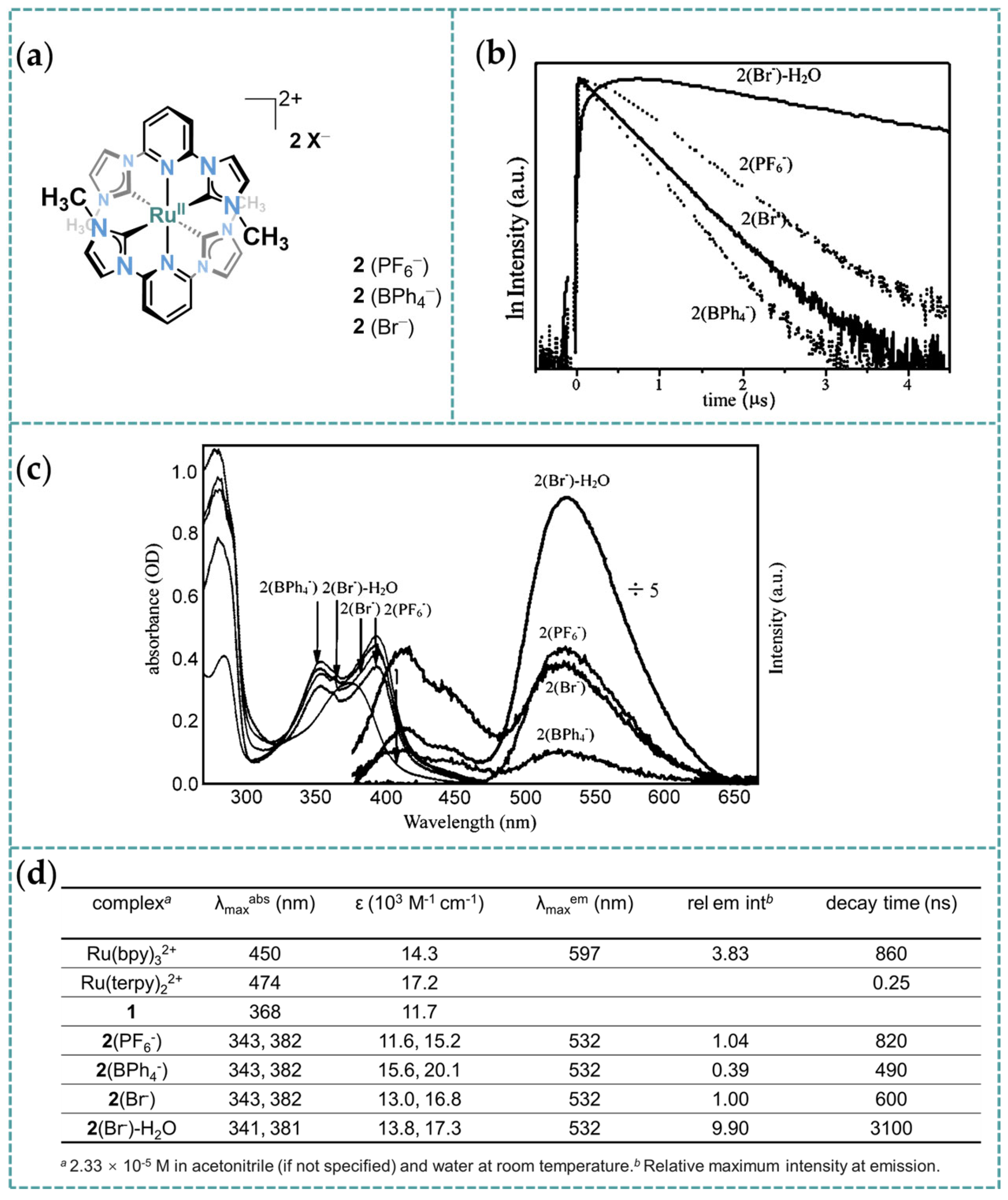
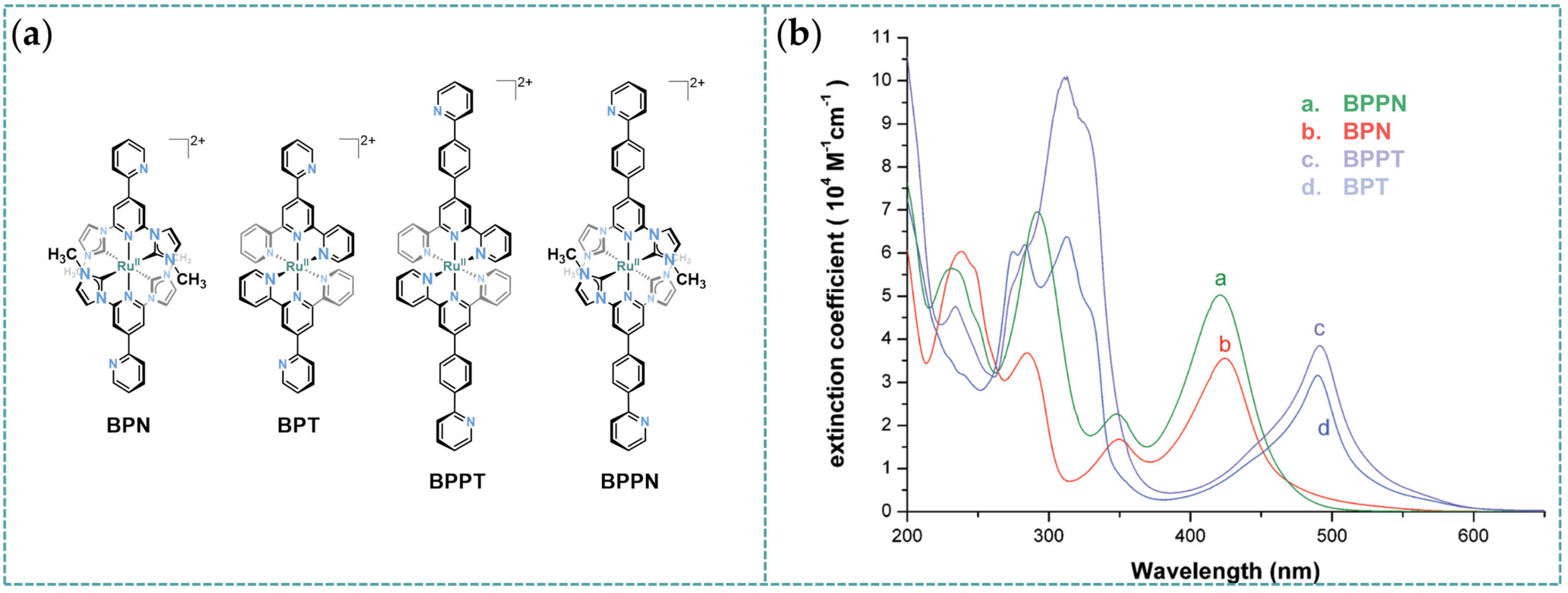
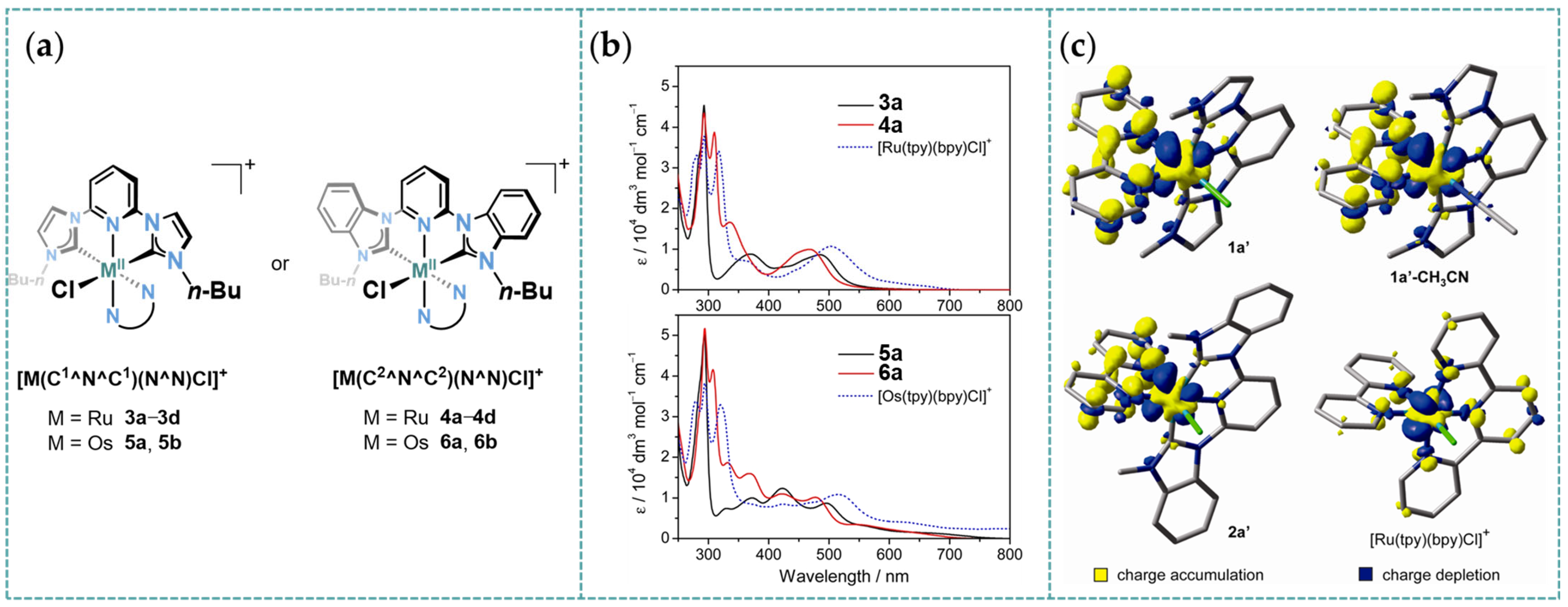
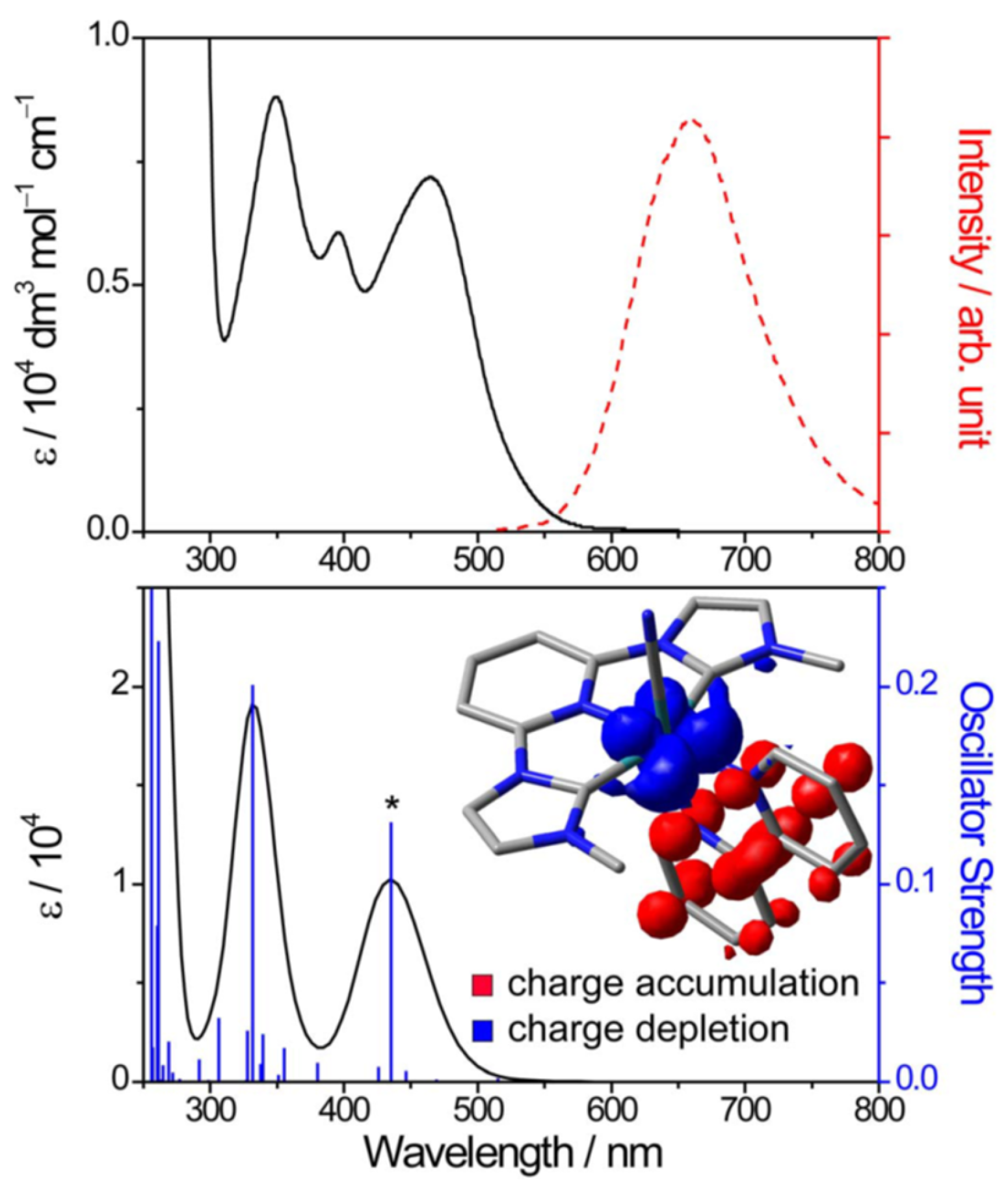
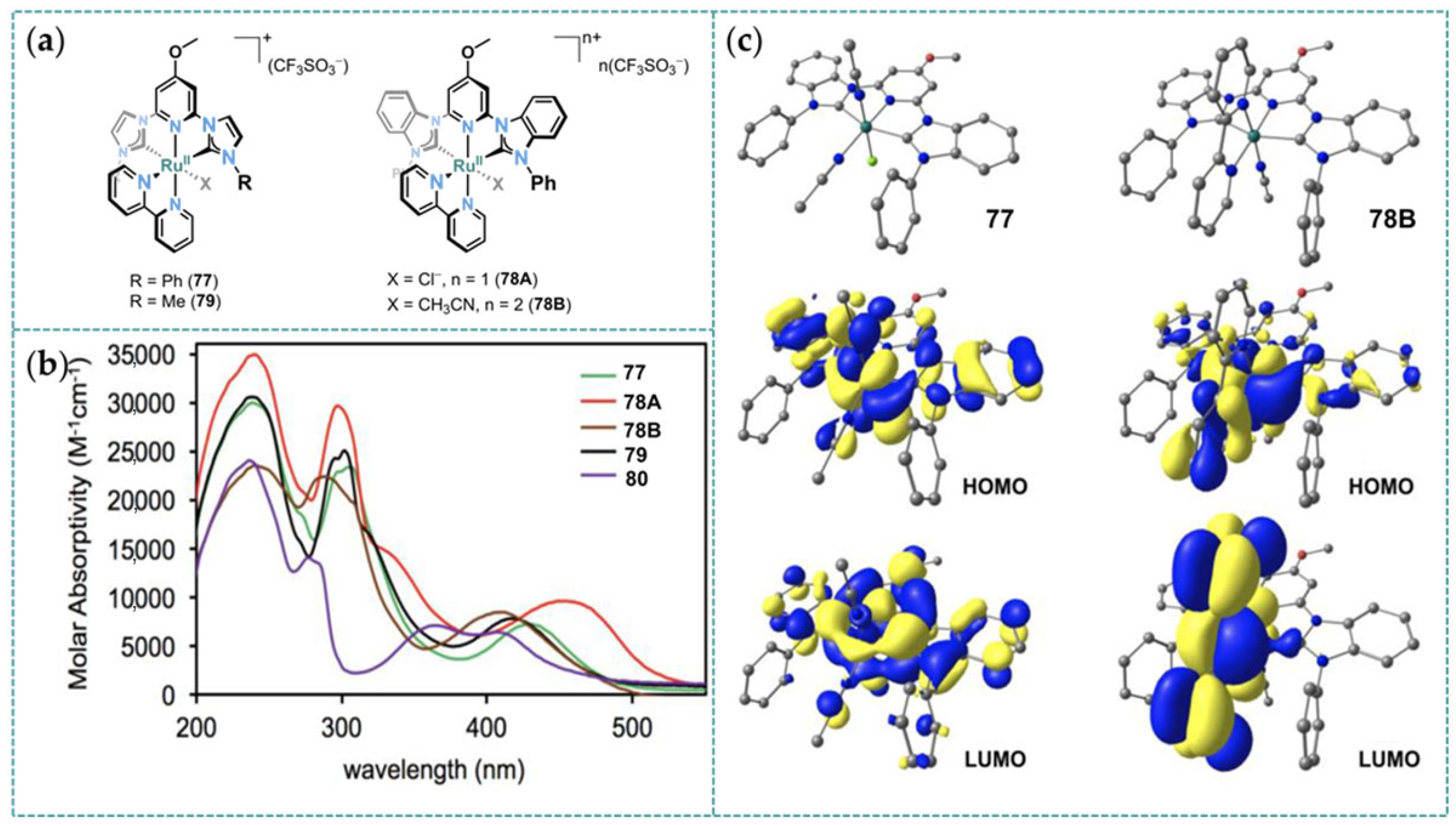
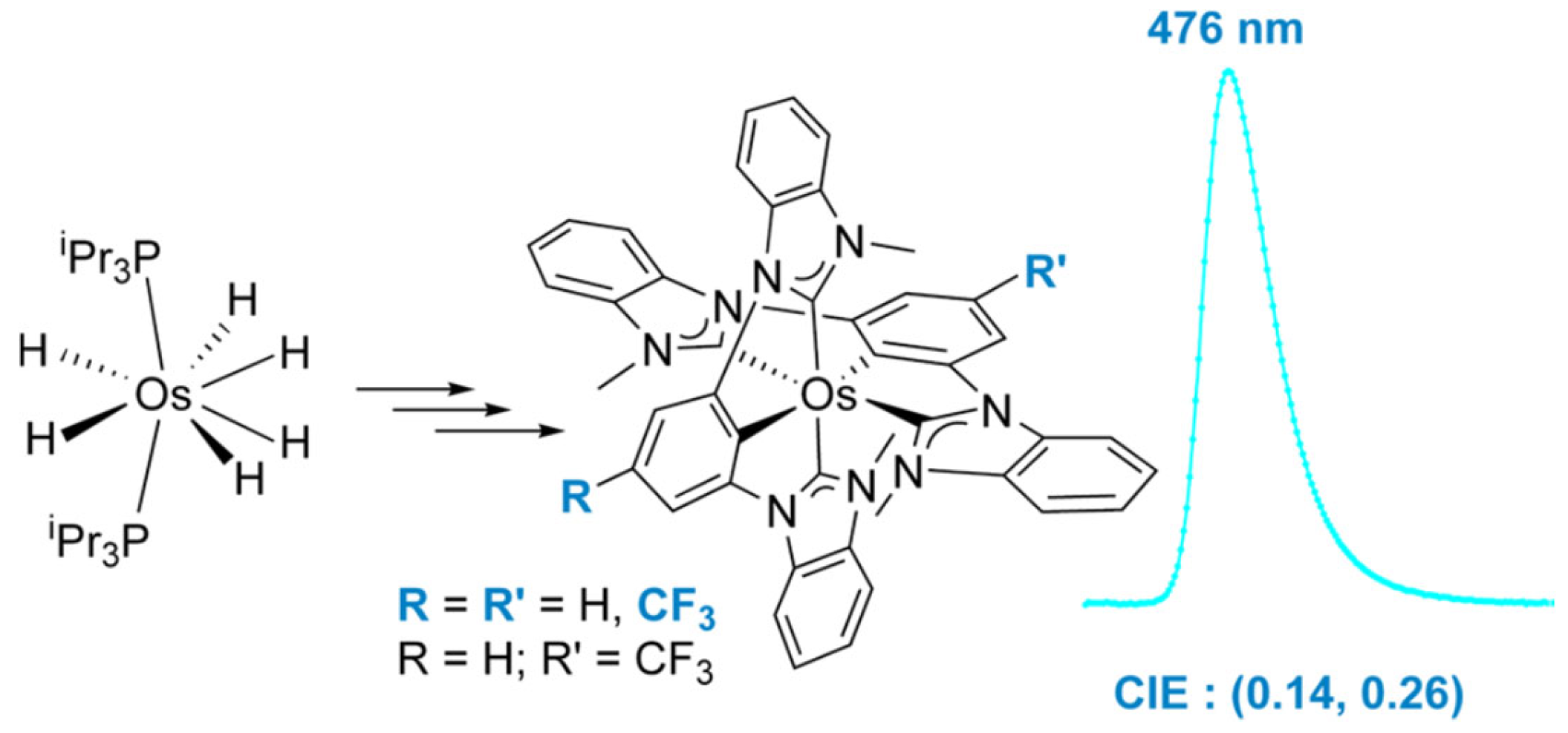
3.1. Photophysical Property of Ru/Os-CNC Pincer Complexes
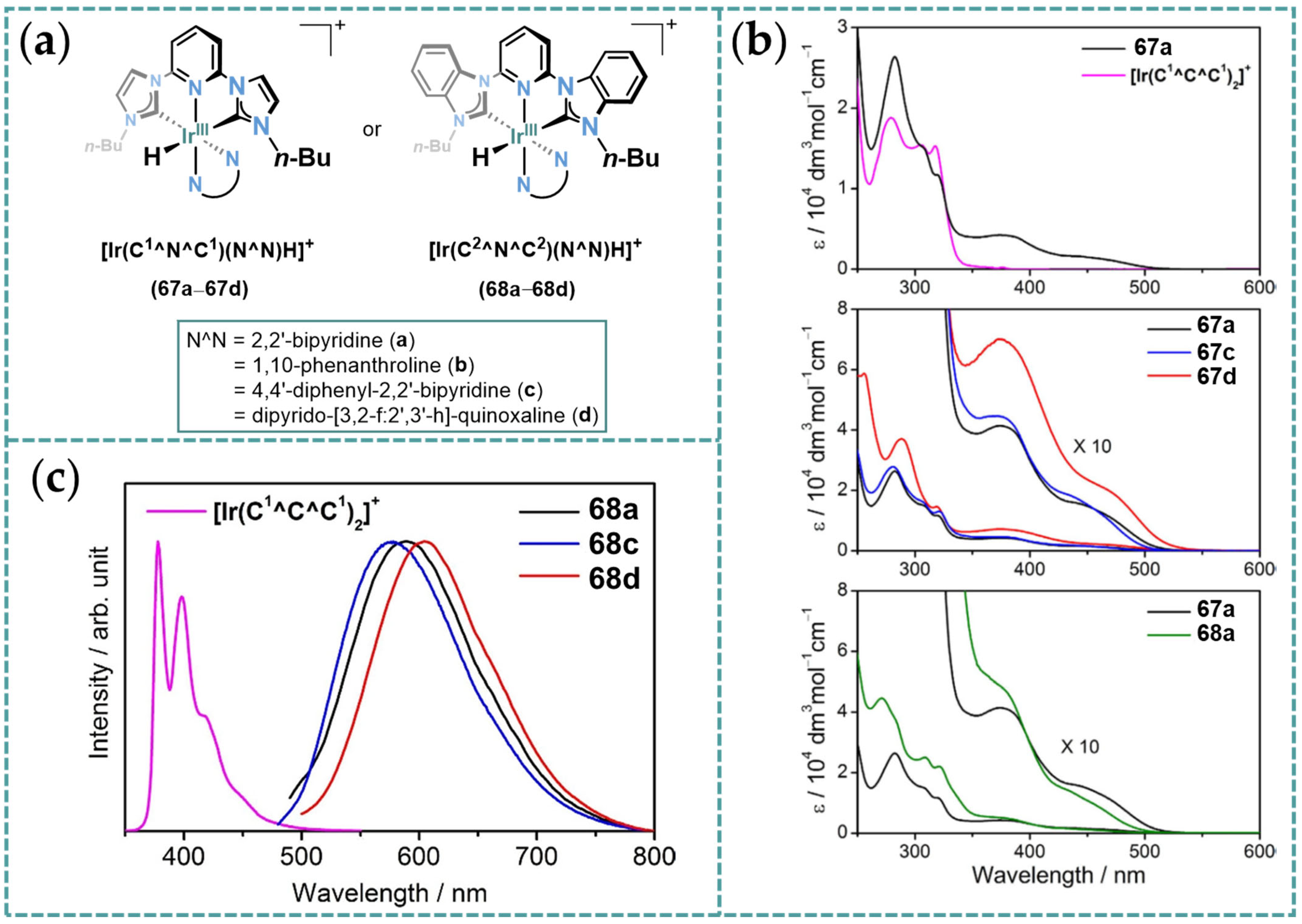
3.2. Photophysical Properties of Ir-CCC Complexes
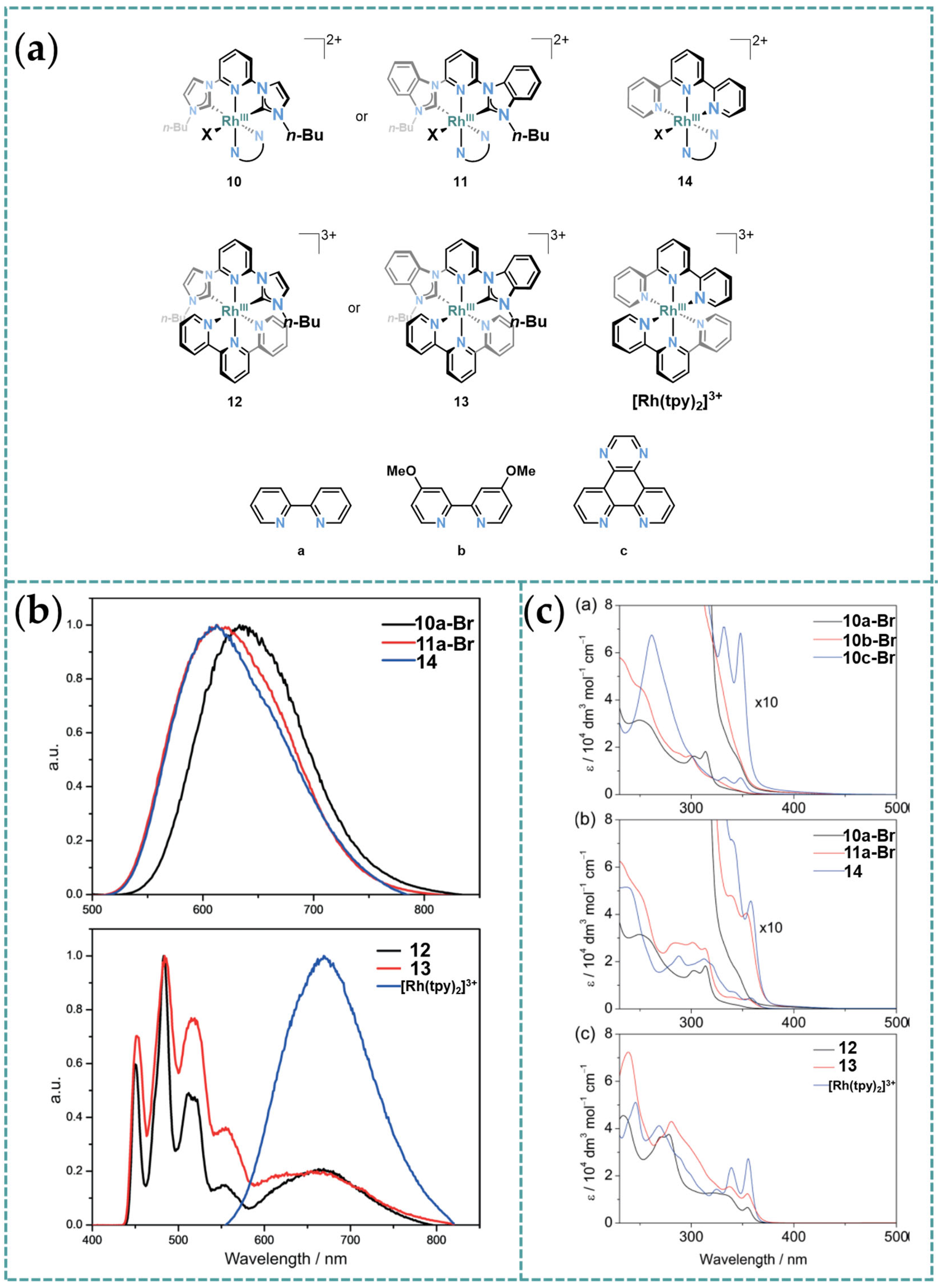
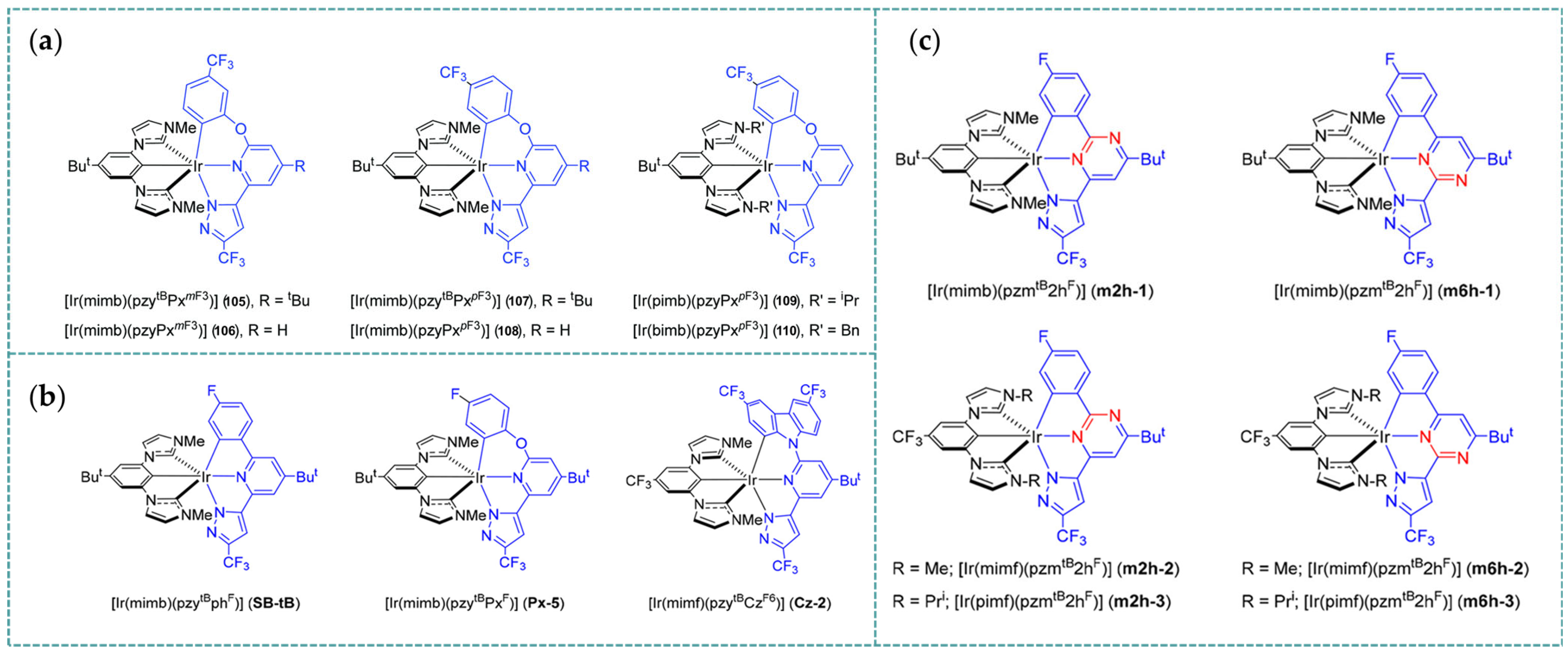
3.3. Photophysical Property of Rh-RCNCR Complexes
4. Application of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Metal Complex
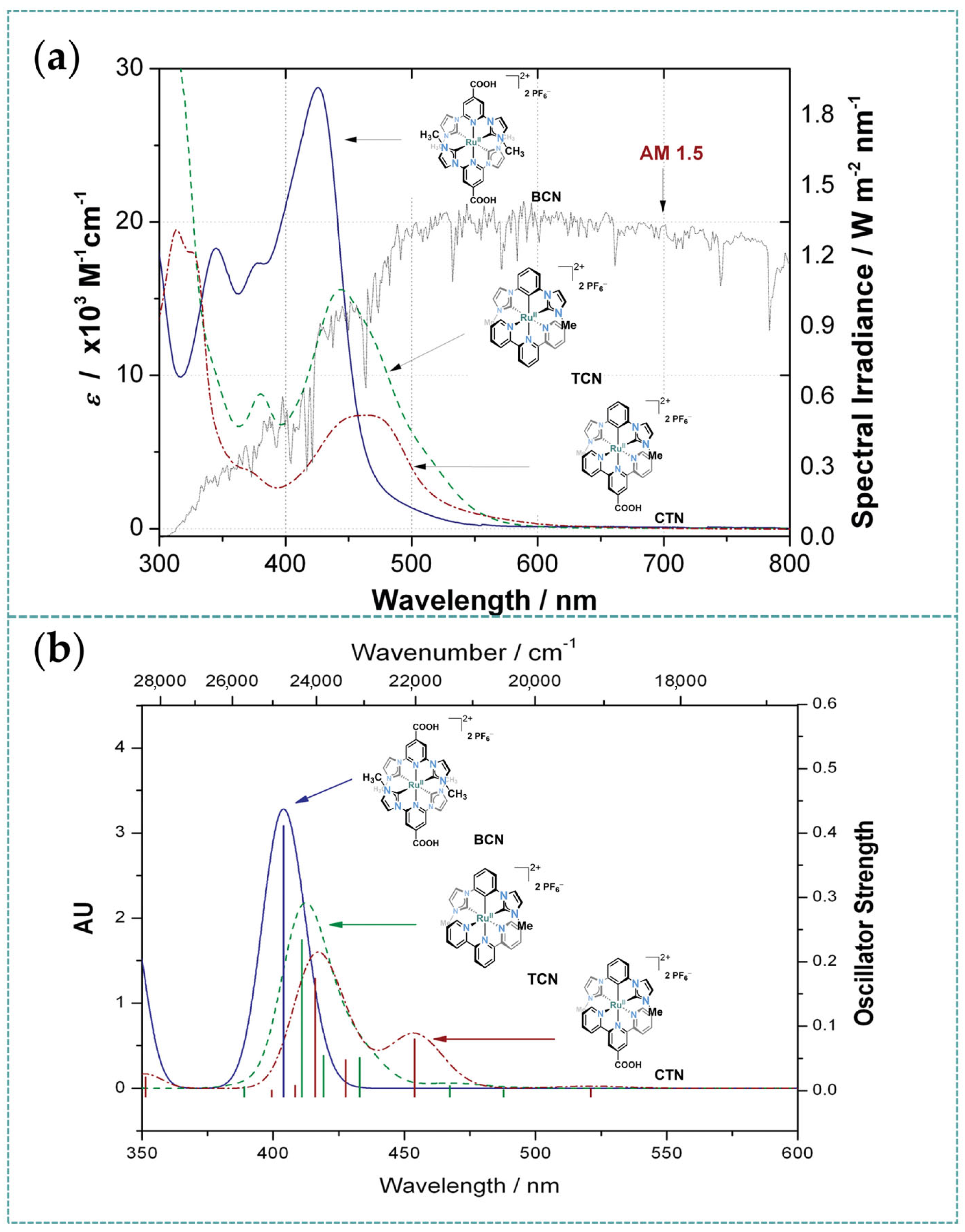
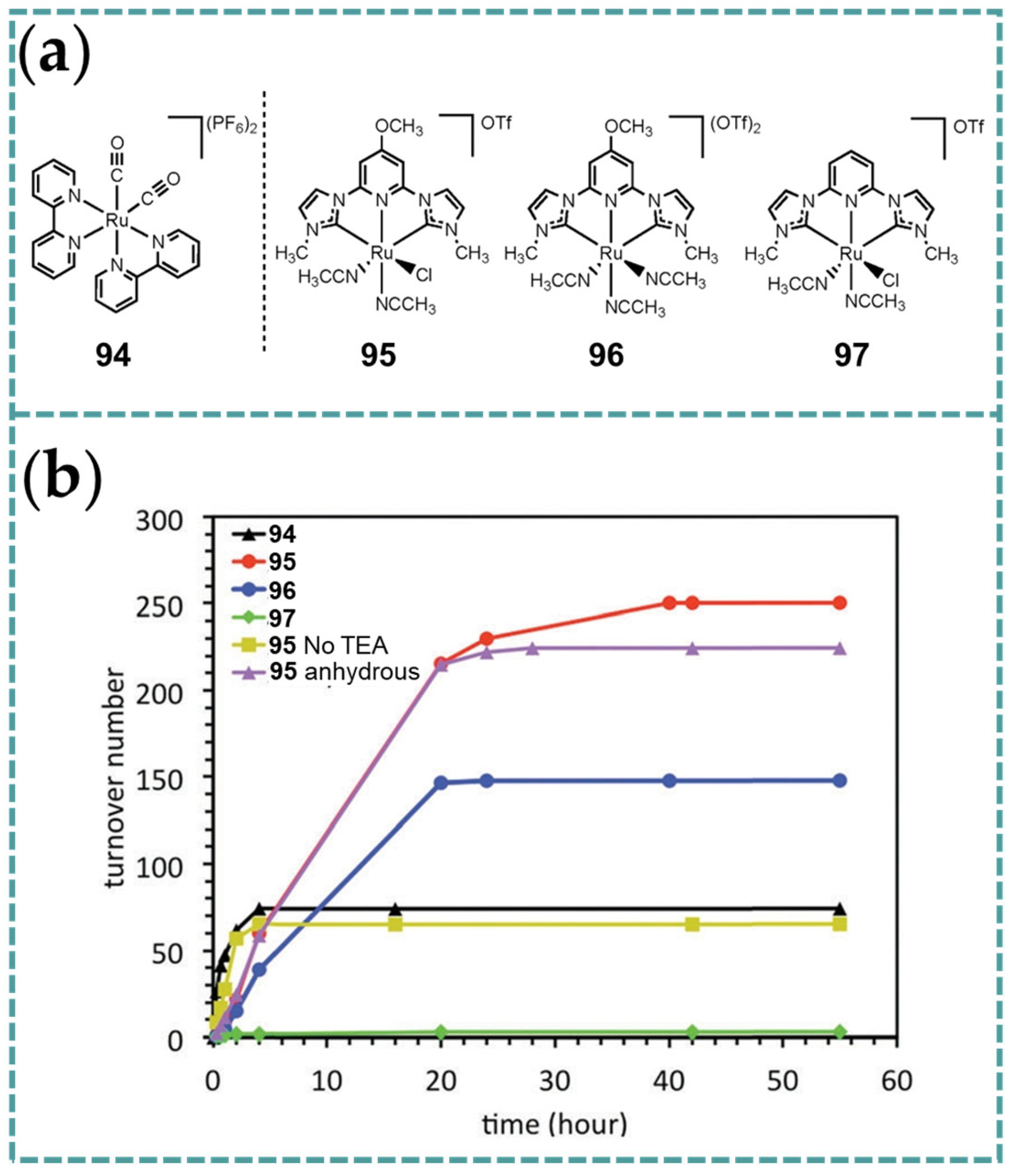
4.1. Photocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Reduction
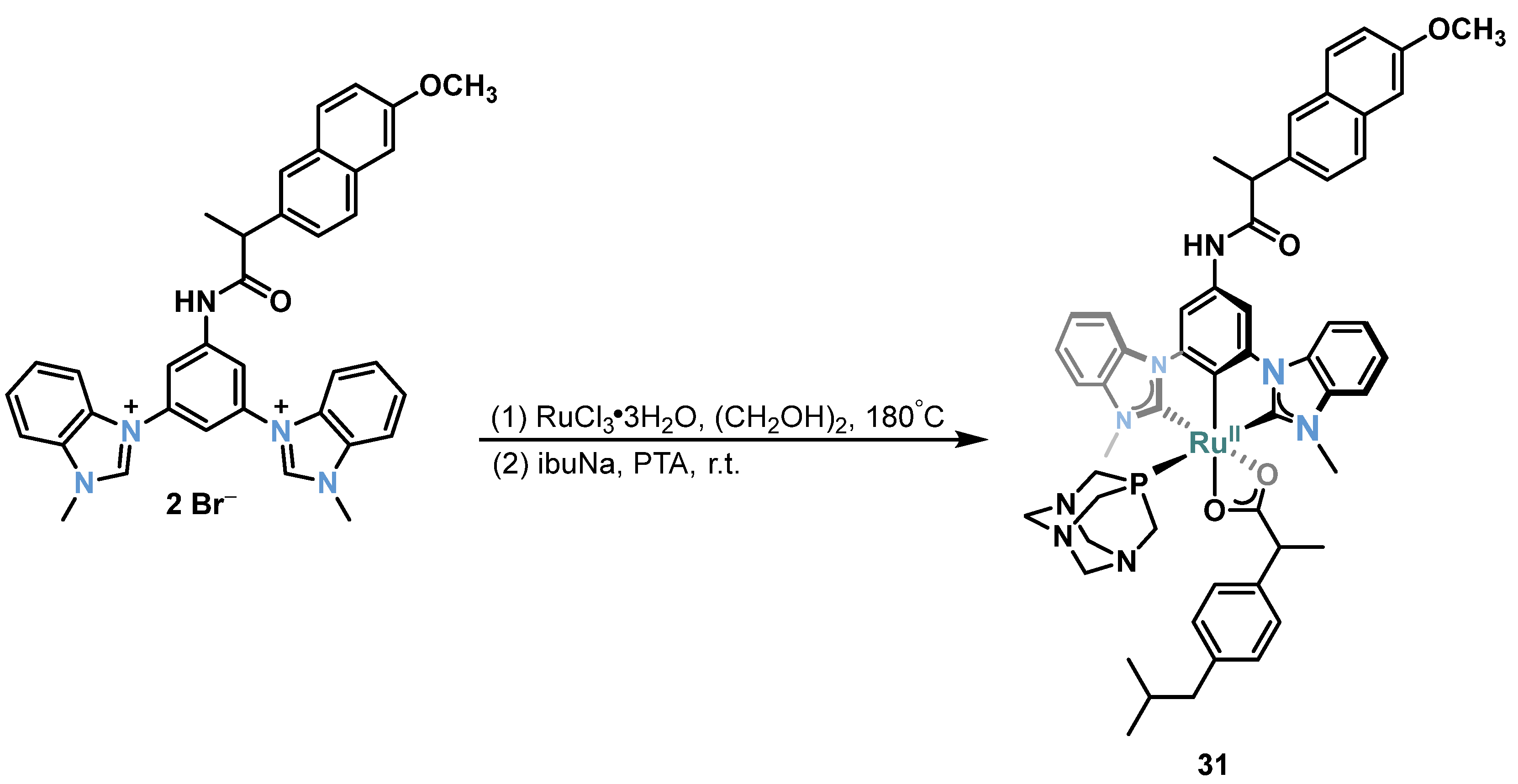
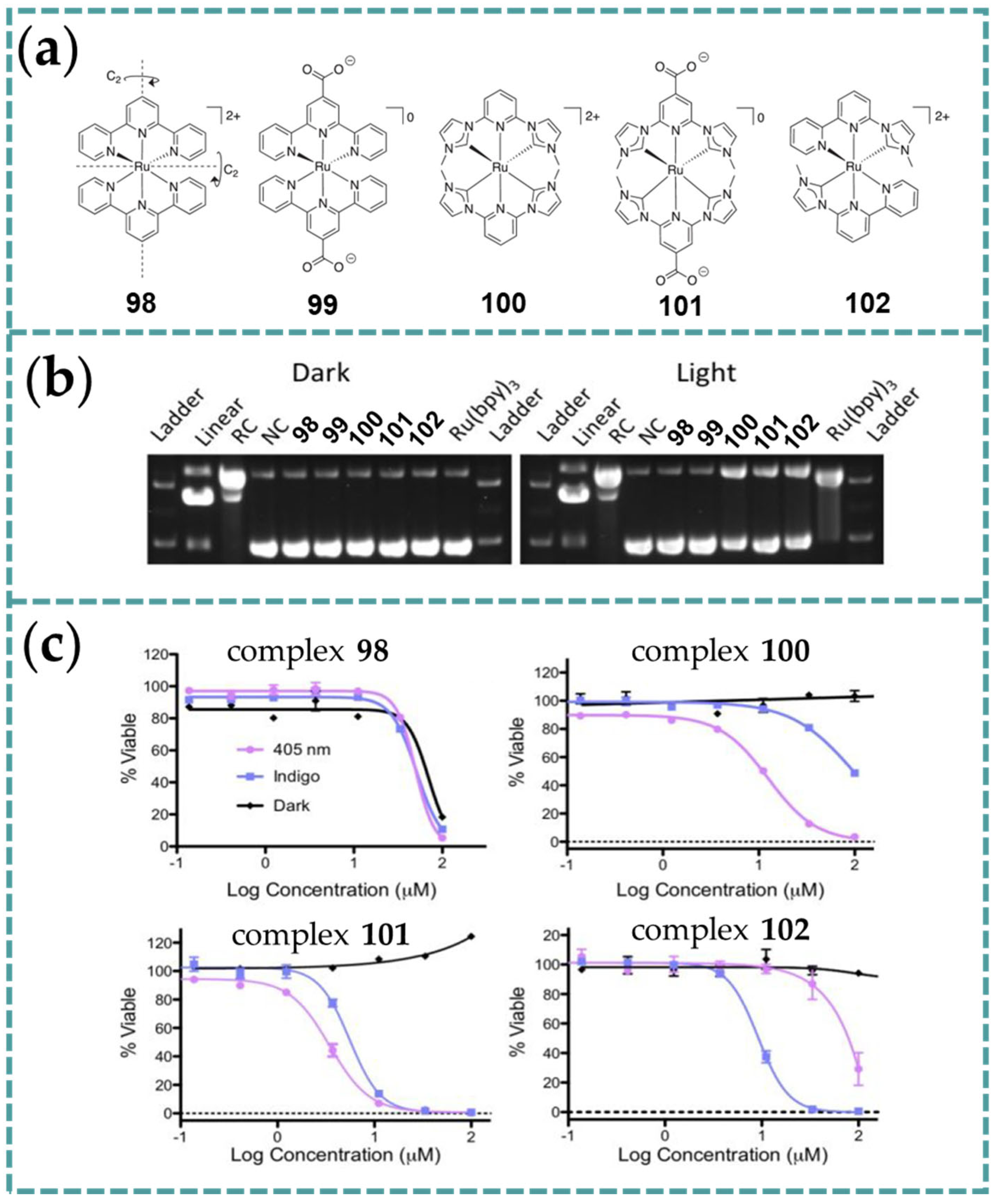
4.2. Bio-Imaging Study
4.3. Catalytic Organic Reactions
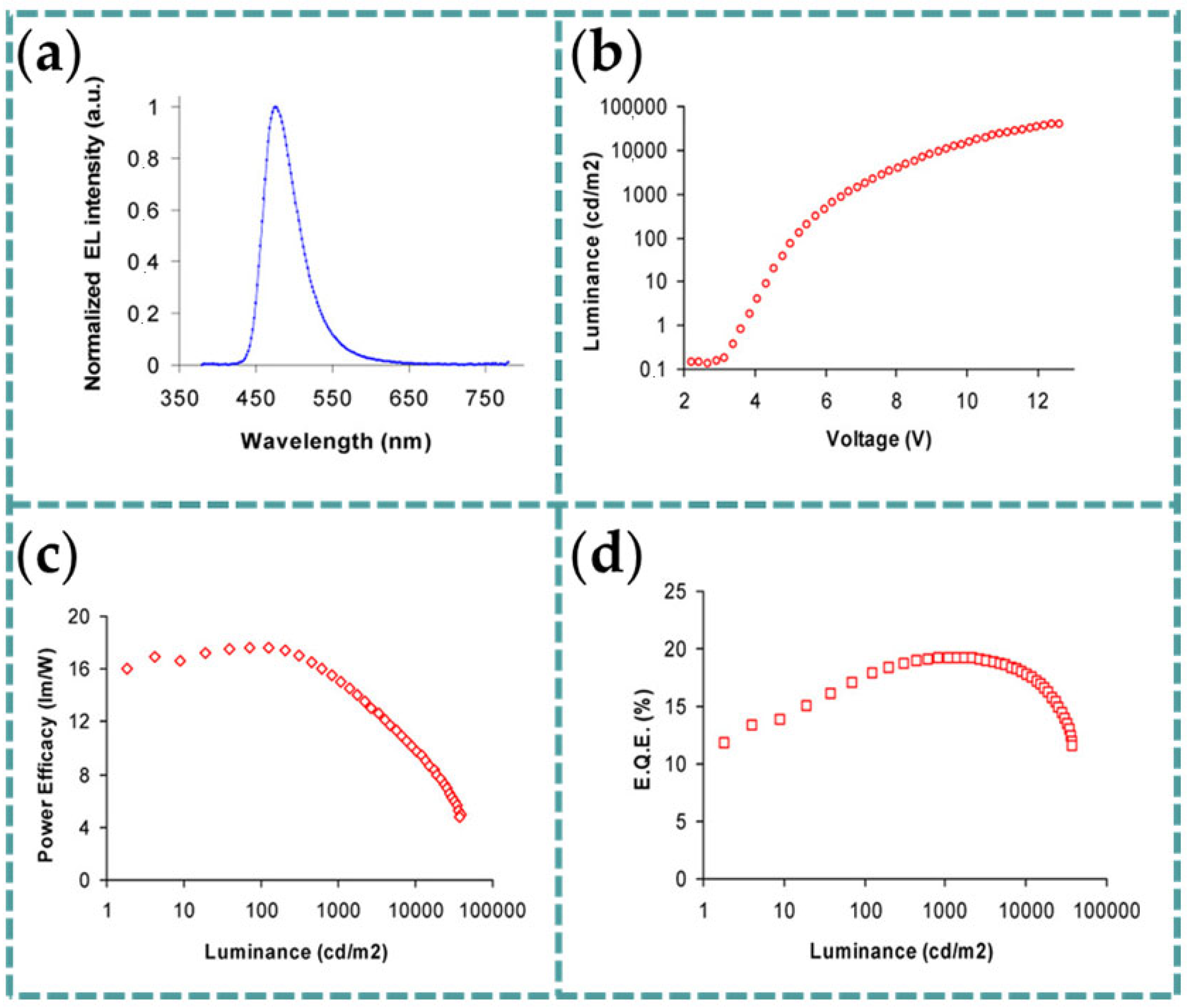
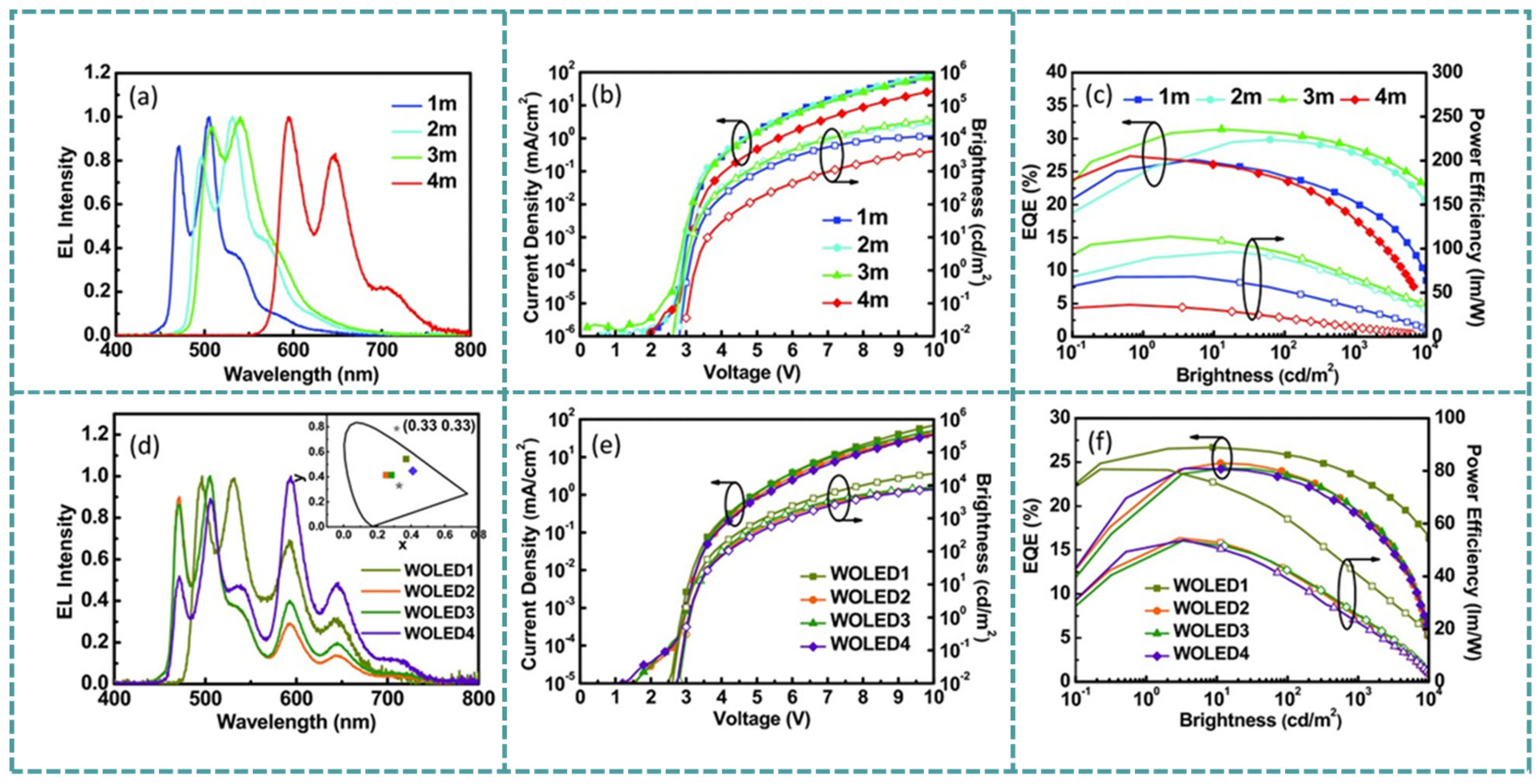
4.4. Organic Light-Emitting Devices
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arduengo, A.J., III; Harlow, R.L.; Kline, M. A stable crystalline carbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpaen, J.; Manguin, R.; Baslé, O. Chiral N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands Enable Asymmetric C−H Bond Functionalization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10242–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazzar, R.; Soleilhavoup, M.; Bertrand, G. Cyclic (Alkyl)- and (Aryl)-(amino)carbene Coinage Metal Complexes and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4141–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amouri, H. Luminescent Complexes of Platinum, Iridium, and Coinage Metals Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Design, Structural Diversity, and Photophysical Properties. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 230–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisnetti, F.; Gautier, A. Metal/N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Opportunities for the Development of Anticancer Metallodrugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11976–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Gimeno, M.C.; Visbal, R. Recent advances in gold–NHC complexes with biological properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.V. Electronic Properties of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes and Their Experimental Determination. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9457–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visbal, R.; Gimeno, M.C. N-Heterocyclic carbene metal complexes: Photoluminescence and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3551–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, V.; Reiter, D.; Bag, P.; Frisch, P.; Holzner, R.; Porzelt, A.; Inoue, S. NHCs in Main Group Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9678–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, A.A.; Simler, T.; Braunstein, P. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Copper, Nickel, and Cobalt. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3730–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, E.; Crabtree, R.H. Key factors in pincer ligand design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, D.; Danopoulos, A.A. Metal complexes with ‘pincer’-type ligands incorporating N-Heterocyclic carbene functionalities. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 610–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, M.; Mata, J.A.; Peris, E. Complexes with Poly(N-Heterocyclic carbene) Ligands: Structural Features and Catalytic Applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3677–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameury, S.; de Frémont, P.; Braunstein, P. Metal complexes with oxygen-functionalized NHC ligands: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 632–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, A.A.; Winston, S.; Motherwell, W.B. Stable N-functionalised ‘pincer’ bis carbene ligands and their ruthenium complexes; synthesis and catalytic studies. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1376–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, M.; Mata, J.A.; Falomir, E.; Crabtree, R.H.; Peris, E. New Ruthenium(II) CNC-Pincer Bis(carbene) Complexes: Synthesis and Catalytic Activity. Organometallics 2003, 22, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.-H.; Cho, K.-S.; England, J.; Chan, S.-C.; Wieghardt, K.; Wong, C.-Y. Ruthenium(II) and Osmium(II) Complexes Bearing Bipyridine and the N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Based C^N^C Pincer Ligand: An Experimental and Density Functional Theory Study. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9885–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-Y.; Lai, L.-M.; Pat, P.-K.; Chung, L.-H. Osmium Complexes Containing N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Based C,N,C-Pincer Ligands. Organometallics 2010, 29, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, M.; Mas-Marzá, E.; Mata, J.A.; Sanaú, M.; Peris, E. Synthesis, Reactivity, Crystal Structures and Catalytic Activity of New Chelating Bisimidazolium-Carbene Complexes of Rh. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Io, K.-W.; Ng, S.-W.; Yeung, C.-F.; Wong, C.-Y. Synthesis, Spectroscopic and Computational Studies of Rhodium(III) Complexes Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Based C^N^C Pincer Ligand and Bipyridine/Terpyridine. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, A.A.; Pugh, D.; Wright, J.A. “Pincer” Pyridine-Dicarbene-Iridium Complexes: Facile C-H Activation and Unexpected η2-Imidazol-2-ylidene Coordination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9765–9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, A.A.; Braunstein, P.; Saßmannshausen, J.; Pugh, D.; Wright, J.A. “Pincer” Pyridine-Dicarbene-Iridium and -Ruthenium Complexes and Derivatives Thereof. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Shao, J.-Y.; Yao, C.-J.; Zhong, Y.-W. Cyclometalated ruthenium(II) complexes with a bis-carbene CCC-pincer ligand. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9280–9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziruddin, A.R.; Huang, Z.-J.; Lai, W.-C.; Lin, W.-J.; Hwang, W.-S. Ruthenium(II) carbonyl complexes bearing CCC-pincer bis-(carbene) ligands: Synthesis, structures and activities toward recycle transfer hydrogenation reactions. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 13161–13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, L.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Fadare, O.A. Experimental and theoretical investigations of cyclometalated ruthenium(ii) complex containing CCC-pincer and anti-inflammatory drugs as ligands: Synthesis, characterization, inhibition of cyclooxygenase and in vitro cytotoxicity activities in various cancer cell lines. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 728–740. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, L.-H.; Chan, S.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Wong, C.-Y. Emissive Osmium(II) Complexes Supported by N-Heterocyclic Carbene-based C∧C∧C-Pincer Ligands and Aromatic Diimines. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 8693–8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabau, R.G.; Eguillor, B.; Esler, J.; Esteruelas, M.A.; Oliván, M.; Oñate, E.; Tsai, J.-Y.; Xia, C. CCC-Pincer-NHC Osmium Complexes: New Types of Blue-Green Emissive Neutral Compounds for Organic Light-Emitting Devices (OLEDs). Organometallics 2014, 33, 5582–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, R.J.; Andavan, G.T.S.; Bauer, E.B.; Hollis, T.K.; Cho, J.; Tham, F.S.; Donnadieu, B. Toward a general method for CCC N-Heterocyclic carbene pincer synthesis: Metallation and transmetallation strategies for concurrent activation of three C–H bonds. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5353–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andavan, G.T.S.; Bauer, E.B.; Letko, C.S.; Hollis, T.K.; Tham, F.S. Synthesis and characterization of a free phenylene bis(N-Heterocyclic carbene) and its di-Rh complex: Catalytic activity of the di-Rh and CCC–NHC Rh pincer complexes in intermolecular hydrosilylation of alkynes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5938–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huckaba, A.J.; Hollis, T.K.; Howell, T.O.; Valle, H.U.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of a 1,3-Phenylene-Bridged N-Alkyl Bis(benzimidazole) CCC-NHC Pincer Ligand Precursor: Homobimetallic Silver and Rhodium Complexes and the Catalytic Hydrosilylation of Phenylacetylene. Organometallics 2013, 32, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.H.; Keaveney, S.T.; Messerle, B.A.; Pernik, I. Bimetallic Rhodium Complexes: Precatalyst Activation-Triggered Bimetallic Enhancement for the Hydrosilylation Transformation. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynal, M.; Cazin, C.S.J.; Vallée, C.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Braunstein, P. An unprecedented, figure-of-eight, dinuclear iridium(I) dicarbene and new iridium(III) ‘pincer’ complexes. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3983–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynal, M.; Pattacini, R.; Cazin, C.S.J.; Vallée, C.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Braunstein, P. Reaction Intermediates in the Synthesis of New Hydrido, N-Heterocyclic Dicarbene Iridium(III) Pincer Complexes. Organometallics 2009, 28, 4028–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, A.R.; Mo, A.; Lampland, N.L.; Swartz, R.L.; Bremer, P.T. Iridium Complexes of CCC-Pincer N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands: Synthesis and Catalytic C-H Functionalization. Organometallics 2010, 29, 3019–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.-H.; Lo, H.-S.; Ng, S.-W.; Ma, D.-L.; Leung, C.-H.; Wong, C.-Y. Luminescent Iridium(III) Complexes Supported by N-Heterocyclic Carbene-based C^C^C-Pincer Ligands and Aromatic Diimines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuei, C.-Y.; Tsai, W.-L.; Tong, B.; Jiao, M.; Lee, W.-K.; Chi, Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Chou, P.-T. Bis-Tridentate Ir(III) Complexes with Nearly Unitary RGB Phosphorescence and Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with External Quantum Efficiency Exceeding 31%. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.U.; Park, K.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, B.Y.; Choi, C.H.; Lah, M.S.; Jang, Y.H.; Jang, D.-J.; Chung, Y.K. Synthesis of Ru(II) Complexes of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes and Their Promising Photoluminescence Properties in Water. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 6896–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, W.I.; Kang, Y.K.; Chung, Y.K. Unsymmetric Ru(II) Complexes with N-Heterocyclic Carbene and/or Terpyridine Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, Ground- and Excited-State Electronic Structures and Their Application for DSSC Sensitizers. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 7340–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Chung, Y.K. Ru(II) complexes with N-Heterocyclic carbene ligands or terpyridine analogues: Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical and proton-dependent spectrometric properties. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5678–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, W.-K.; Chung, L.-H.; Wong, M.M.-K.; Tsang, W.-H.; Lo, H.-S.; Liu, Y.; Leung, C.-H.; Ma, D.-L.; Chiu, S.-K.; Wong, C.-Y. Luminescent Ruthenium(II) Complex Bearing Bipyridine and N-Heterocyclic Carbene-based C^N^C Pincer Ligand for Live-Cell Imaging of Endocytosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Lamb, R.W.; Qu, F.; Reinheimer, E.; Boudreaux, C.M.; Webster, C.E.; Delcamp, J.H.; Papish, E.T. Highly Active Ruthenium CNC Pincer Photocatalysts for Visible-Light-Driven Carbon Dioxide Reduction. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8012–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Carrión, M.C.; Leal, J.; Castañeda, G.; Manzano, B.R.; Jalón, F.A. Homoleptic ruthenium complexes with N-Heterocyclic carbene ligands as photosensitizers in the photocatalytic generation of H2 from water. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 898, 120880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Nugegoda, D.; Qu, F.; Boudreaux, C.M.; Burrow, P.E.; Figgins, M.T.; Lamb, R.W.; Webster, C.E.; Delcamp, J.H.; Papish, E.T. Structure Function Relationships in Ruthenium Carbon Dioxide Reduction Catalysts with CNC Pincers Containing Donor Groups. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmawan, N.; Yang, C.-H.; Mauro, M.; Raynal, M.; Heun, S.; Pan, J.; Buchholz, H.; Braunstein, P.; De Cola, L. Efficient Near-UV Emitters Based on Cationic Bis-Pincer Iridium(III) Carbene Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10756–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuei, C.-Y.; Liu, S.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; Lee, G.-H.; Chi, Y. Room temperature blue phosphorescence: A combined experimental and theoretical study on the bis-tridentate Ir(III) metal complexes. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 15364–15373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Devereux, L.R.; Wu, C.-C.; Fox, M.A.; Kuei, C.-Y.; Chi, Y.; Lee, G.-H. Bis-Tridentate Ir(III) Metal Phosphors for Efficient Deep-Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-H.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Tso, J.-Y.; Hung, W.-Y.; Liu, S.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; Wong, K.-T.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Lee, C.-S.; Jen, A.K.Y.; et al. Blue-emitting bis-tridentate Ir(III) phosphors: OLED performances vs. substituent effects. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10486–10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.-S.; Gnanasekaran, P.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Hung, W.-Y.; Zhou, X.; Chou, T.-C.; Lee, G.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; You, C.; Chi, Y. Rational Tuning of Bis-Tridentate Ir(III) Phosphors to Deep-Blue with High Efficiency and Sub-microsecond Lifetime. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 15437–15447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-Y.; Chen, D.-G.; Liu, S.-H.; Chiu, T.-Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Jen, A.K.Y.; Chou, P.-T.; Chi, Y. Roles of Ancillary Chelates and Overall Charges of Bis-tridentate Ir(III) Phosphors for OLED Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreaux, C.M.; Liyanage, N.P.; Shirley, H.; Siek, S.; Gerlach, D.L.; Qu, F.; Delcamp, J.H.; Papish, E.T. Ruthenium(ii) complexes of pyridinol and N-Heterocyclic carbene derived pincers as robust catalysts for selective carbon dioxide reduction. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11217–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.R.; Boudreaux, C.M.; Papish, E.T.; Delcamp, J.H. Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO and Formate: Do Reaction Conditions or Ruthenium Catalysts Control Product Selectivity? ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.T.; Stevens, K.C.; Calabro, R.; Parkin, S.; Mahmoud, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Heidary, D.K.; Glazer, E.C.; Selegue, J.P. Bis-tridentate N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ru(II) Complexes are Promising New Agents for Photodynamic Therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8882–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Das, S.; DeLucia, N.A.; Qu, F.; Boudreaux, C.M.; Vannucci, A.K.; Papish, E.T. Determining the Catalyst Properties That Lead to High Activity and Selectivity for Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation with Ruthenium Pincer Complexes. Organometallics 2020, 39, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.M.M.; Shaner, S.E.; Kim, D.; Shopov, D.Y.; Tendler, J.A.; Pudalov, D.M.; Chianese, A.R. Mechanistic Studies of Alkene Isomerization Catalyzed by CCC-Pincer Complexes of Iridium. Organometallics 2014, 33, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-K.; Kuo, H.-H.; Luo, D.; Lai, Y.-N.; Li, W.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Escudero, D.; Jen, A.K.Y.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Chi, Y. Phenyl- and Pyrazolyl-Functionalized Pyrimidine: Versatile Chromophore of Bis-Tridentate Ir(III) Phosphors for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 6453–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ng, M.; Wu, C.; Tong, K.-N.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, M.; Tang, M.-C.; Wei, G. Correction: Saturated-blue-emitting [3+2+1] coordinated iridium(III) complexes for vacuum-deposited organic light-emitting devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Lindhorst, A.C.; Groche, F.J.; Kühn, F.E. Immobilization of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Compounds: A Synthetic Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 1970–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cui, L.; Sun, P.; Shi, L.; Yue, C.; Li, F. Reusable N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complex Catalysts and Beyond: A Perspective on Recycling Strategies. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9843–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Narouz, M.R.; Lummis, P.A.; Singh, I.; Nazemi, A.; Li, C.-H.; Crudden, C.M. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Materials Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4986–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koy, M.; Bellotti, P.; Das, M.; Glorius, F. N-Heterocyclic carbenes as tunable ligands for catalytic metal surfaces. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
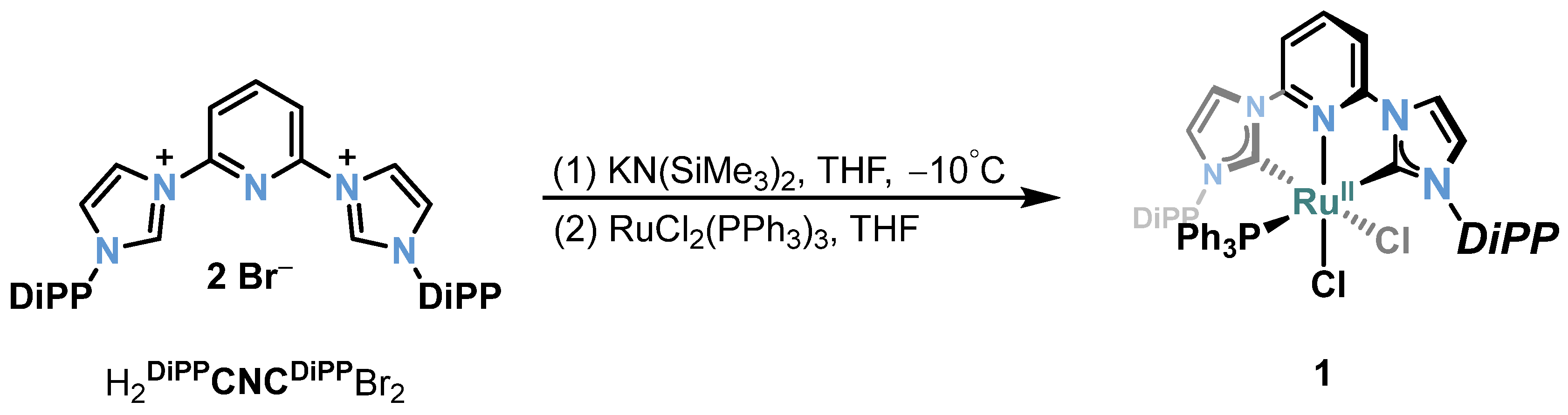


















| Catalyst[1] | TONmax | TOFmax [h−1] |
|---|---|---|
| RuOMe | 1006 | 174 |
| RuMe | 639 | 104 |
| Ru3OMe | 565 | 32 |
| RuH | 440 | 31 |
| RuH[2] | 120 | 14 |
| RuNPh2 | 337 | 13 |
| RuNMe2 | 38 | 4 |
| RuOH | 15 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, D.-L.; Li, K.-K.; Chung, L.-H.; He, J.; Wong, C.-Y. Overview of Some Second- and Third-Row Late Transition Metal Pincer-Type N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122640
Kuang D-L, Li K-K, Chung L-H, He J, Wong C-Y. Overview of Some Second- and Third-Row Late Transition Metal Pincer-Type N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122640
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Dong-Ling, Ka-Kit Li, Lai-Hon Chung, Jun He, and Chun-Yuen Wong. 2025. "Overview of Some Second- and Third-Row Late Transition Metal Pincer-Type N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122640
APA StyleKuang, D.-L., Li, K.-K., Chung, L.-H., He, J., & Wong, C.-Y. (2025). Overview of Some Second- and Third-Row Late Transition Metal Pincer-Type N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications. Molecules, 30(12), 2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122640







