Integrating NMR and MS for Improved Metabolomic Analysis: From Methodologies to Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Fusion in Metabolomics
2.1. Low-Level DF
2.2. Mid-Level DF
2.3. High-Level DF
2.4. Potential and Limitations of DF Levels in Data Integration
3. NMR-MS Data Fusion Applied in Metabolomics Studies
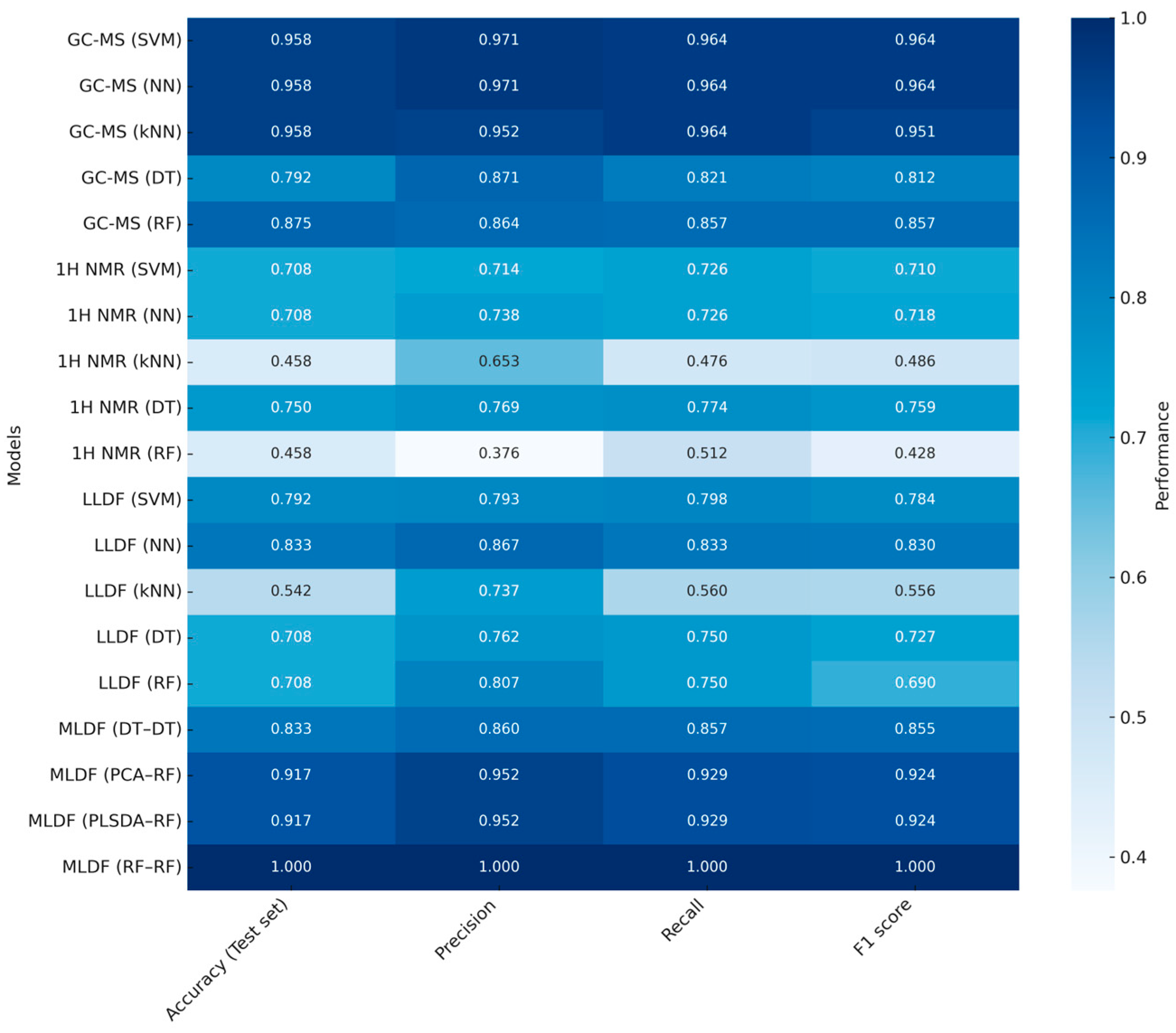
3.1. Importance of Evaluating Predictive Performance in NMR-MS Data Fusion
3.2. NMR and MS DF in Body Fluids—Clinical Studies
3.3. NMR and MS DF in Natural Product Matrices
3.4. NMR and MS DF in Food Matrices
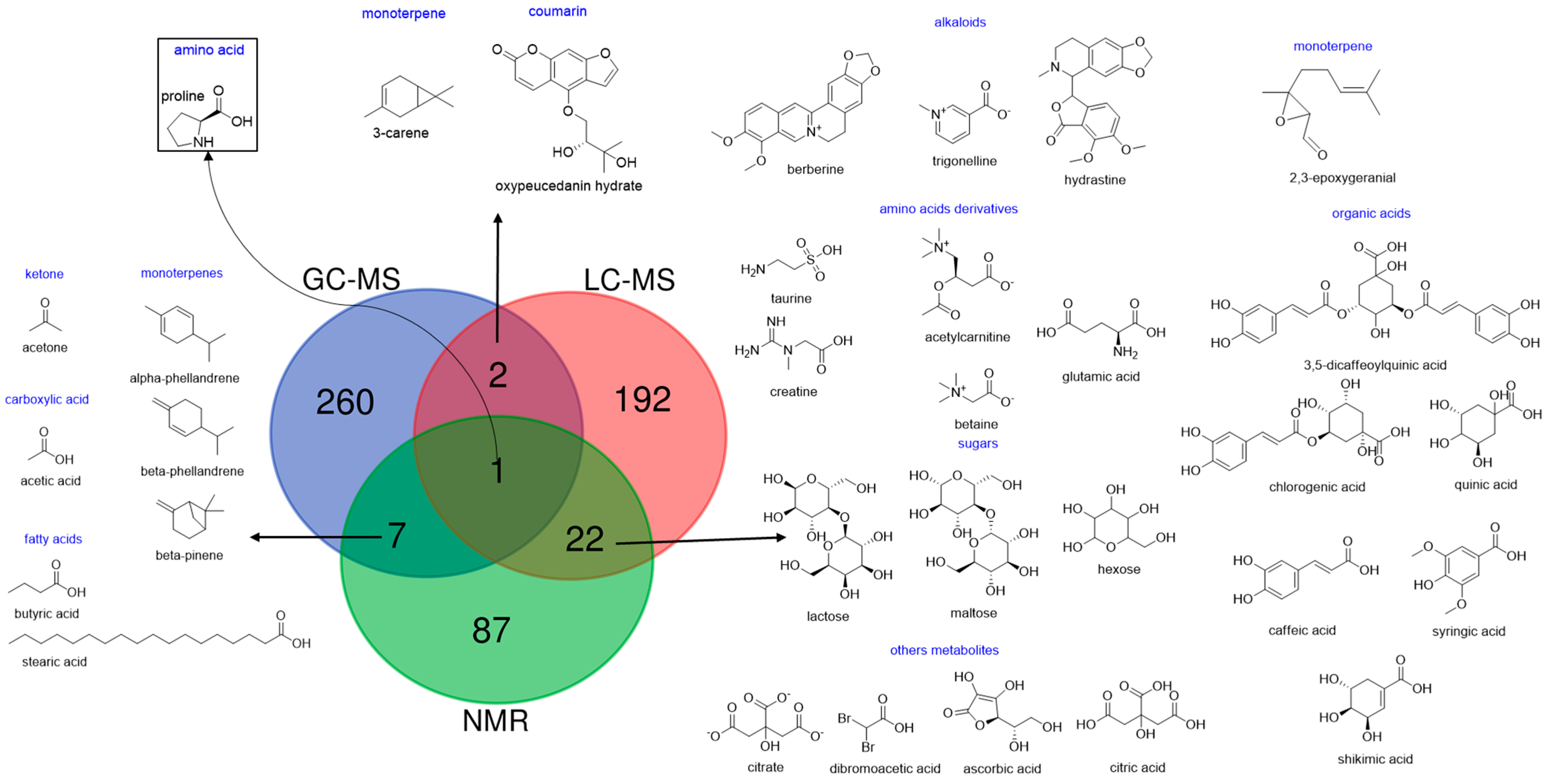
4. Metabolites Covered by NMR-MS Data Fusion
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vignoli, A.; Ghini, V.; Meoni, G.; Licari, C.; Takis, P.G.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. Hochdurchsatz-Metabolomik Mit 1D-NMR. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 980–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. “Metabonomics”: Understanding the Metabolic Responses of Living Systems to Pathophysiological Stimuli via Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Biological NMR Spectroscopic Data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Su, X.L.; Song, Y.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Wong, M.H.; Cai, Z.; Zheng, C. Metabolomics Reveal Nanoplastic-Induced Mitochondrial Damage in Human Liver and Lung Cells. Env. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12483–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.D.; Duvallet, C.; Chu, N.D.; Oberst, M.K.; Murphy, M.A.; Rockafellow, I.; Sontag, D.; Alm, E.J. Predicting Human Health from Biofluid-Based Metabolomics Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Li, Q.H.; Xu, Z.D.; Dou, J.J. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics in Health and Medical Science: A Systematic Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3092–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, C. Metabolomics in Environmental Toxicology: Applications and Challenges. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 34, e00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Corral, M.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Pereira, A.G.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Analytical Metabolomics and Applications in Health, Environmental and Food Science. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 712–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchev, A.S.; Vasileva, L.V.; Amirova, K.M.; Savova, M.S.; Balcheva-Sivenova, Z.P.; Georgiev, M.I. Metabolomics and Health: From Nutritional Crops and Plant-Based Pharmaceuticals to Profiling of Human Biofluids. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6487–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labine, L.M.; Simpson, M.J. The Use of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Mass Spectrometry (MS)–Based Metabolomics in Environmental Exposure Assessment. Curr. Opin. Env. Sci. Health 2020, 15, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letertre, M.P.M.; Dervilly, G.; Giraudeau, P. Combined Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.D.; Powers, R. Beyond the Paradigm: Combining Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Metabolomics. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson Spectrosc. 2017, 100, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Cheng, L.L.; Copié, V.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Hoch, J.C.; Gouveia, G.J.; Pathmasiri, W.; Powers, R.; Schock, T.B.; et al. NMR and Metabolomics—A Roadmap for the Future. Metabolites 2022, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.J. MS Based Foodomics: An Edge Tool Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics for Food Science. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfender, J.L.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Van Der Hooft, J.J.J.; Renault, J.H.; Bertrand, S. Accelerating Metabolite Identification in Natural Product Research: Toward an Ideal Combination of Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry and NMR Profiling, in Silico Databases, and Chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 704–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsedilin, A.M.; Fakhrutdinov, A.N.; Eremin, D.B.; Zalesskiy, S.S.; Chizhov, A.O.; Kolotyrkina, N.G.; Ananikov, V.P. How Sensitive and Accurate Are Routine NMR and MS Measurements? Mendeleev Commun. 2015, 25, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. NMR Metabolomics: A Look Ahead. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 306, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafar, S.Z.A.; Mediani, A.; Maulidiani, M.; Rudiyanto, R.; Mohd Ghazali, H.; Ramli, N.S.; Abas, F. Complementary NMR- and MS-Based Metabolomics Approaches Reveal the Correlations of Phytochemicals and Biological Activities in Phyllanthus Acidus Leaf Extracts. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.T.A.; Zainal, Z.A.; Maulidiani, M.; Shaari, K.; Zamri, Z.; Idrus, M.Z.M.; Khatib, A.; Abas, F.; Ling, Y.S.; Rui, L.L.; et al. Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR- and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Molecules 2018, 23, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Azcarate, S.M.; Camiña, J.M.; Goicoechea, H.C. Multi-Level Data Fusion Strategies for Modeling Three-Way Electrophoresis Capillary and Fluorescence Arrays Enhancing Geographical and Grape Variety Classification of Wines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1126, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo, F. A Review of Data Fusion Techniques. Sci. World J. 2013, 1, 704504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcarate, S.M.; Ríos-Reina, R.; Amigo, J.M.; Goicoechea, H.C. Data Handling in Data Fusion: Methodologies and Applications. TrAC–Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchi, M. Introduction: Ways and Means to Deal With Data From Multiple Sources. Data Handl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Smolinska, A.; Engel, J.; Szymanska, E.; Buydens, L.; Blanchet, L. General Framing of Low-, Mid-, and High-Level Data Fusion With Examples in the Life Sciences. Data Handl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 51–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.-Q.; Li, T.; Liu, H.-G.; Wang, Y. Application of UV-Vis and Infrared Spectroscopy on Wild Edible Bolete Mushrooms Discrimination and Evaluation: A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeswijk, T.G.; Smilde, A.K.; Hageman, J.A.; Westerhuis, J.A.; van Eeuwijk, F.A. On the Increase of Predictive Performance with High-Level Data Fusion. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2011, 705, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forshed, J.; Idborg, H.; Jacobsson, S.P. Evaluation of Different Techniques for Data Fusion of LC/MS and 1H-NMR. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2007, 85, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.P.; Reis, M.S. Data Preprocessing for Multiblock Modelling–A Systematization with New Methods. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 199, 103959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Roger, J.M.; Jouan-Rimbaud-Bouveresse, D.; Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F.; Nordon, A.; Rutledge, D.N. Recent Trends in Multi-Block Data Analysis in Chemometrics for Multi-Source Data Integration. TrAC–Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 137, 116206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bro, R. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems Tutorial PARAFAC. Tutor. Appl. 1997, 38, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Bilesio, A.R.; Batistelli, M.; García-Reiriz, A.G. Fusing Data of Different Orders for Environmental Monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1085, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiers, H.A.L.; ten Berge, J.M.F.; Bro, R. PARAFAC2—Part I. A Direct Fitting Algorithm for the PARAFAC2 Model. J. Chemom. 1999, 13, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalvand, A.R.; Goicoechea, H.C. Applications of Electrochemical Data Analysis by Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares. TrAC–Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 88, 134–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, F.; Jalalvand, A.R. Developing a Novel and Intelligent Chemometrics-Assisted Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor: Application to the Improvement of the Efficiency of the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2025, 259, 105351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Lee, H. MMMF: Multimodal Multitask Matrix Factorization for Classification and Feature Selection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 120155–120167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, D.; Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Recent Advances in High-Level Fusion Methods to Classify Multiple Analytical Chemical Data. Data Handl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 129–155. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova, O.; Pomerantsev, A. Multi-Block DD-SIMCA as a High-Level Data Fusion Tool. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1265, 341328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahat, D.; Adalý, T.; Jutten, C. Challenges in Multimodal Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Baky, M.H.; Badawy, M.T.; Bakr, A.F.; Hegazi, N.M.; Abdellatif, A.; Farag, M.A. Metabolome-Based Profiling of African Baobab Fruit (Adansonia digitata L.) Using a Multiplex Approach of MS and NMR Techniques in Relation to Its Biological Activity. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 39680–39695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Otify, A.; Porzel, A.; Michel, C.G.; Elsayed, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Comparative Metabolite Profiling and Fingerprinting of Genus Passiflora Leaves Using a Multiplex Approach of UPLC-MS and NMR Analyzed by Chemometric Tools. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3125–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Choi, B.R.; Ma, S.; Lee, J.W.; Jo, I.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.Y. Metabolomics for Age Discrimination of Ginseng Using a Multiplex Approach to HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy, UPLC-QTOF/MS, and GC × GC-TOF/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.D.; Lei, S.; Worley, B.; Huang, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, A.; Franco, R.; Dodds, E.D.; Powers, R. Combining DI-ESI–MS and NMR Datasets for Metabolic Profiling. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, T.; Mavel, S.; Emond, P.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Lefèvre, A.; Mattar, H.; Soufia, M.; Blasco, H.; Vourc’h, P.; Hleihel, W.; et al. Identification of Metabolic Pathway Disturbances Using Multimodal Metabolomics in Autistic Disorders in a Middle Eastern Population. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 152, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, İ.; Nørskov, N.P.; Yde, C.C.; Hedemann, M.S.; Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Kohler, A. Sparse Multi-Block PLSR for Biomarker Discovery When Integrating Data from LC–MS and NMR Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, K.; Baghel, R.; Bakhshi, R.; Dhariwal, S.; Tyagi, R.; Rana, P. An Integrative Chemometric Approach and Correlative Metabolite Networking of LC-MS and 1H NMR Based Urine Metabolomics for Radiation Signatures. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.A.; Filho, E.G.A.; Rodrigues, T.H.S.; Louredo, F.J.C.; Zocolo, G.J.; Canuto, K.M.; Mikich, S.B.; Liebsch, D.; De Almeida, A.; De Brito, E.S. Metabolomic Profiling of Phloem Sap from Different Pine Species and Implications on Black Capuchin. J. Chem. Ecol. 2022, 48, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, A.C.; Vieira, N.C.; Dantas-Medeiros, R.; Vilegas, W.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Understanding the Seasonal Effect of Metabolite Production in Terminalia Catappa L. Leaves through a Concatenated MS- and NMR-Based Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites 2023, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, A.C.; Vilegas, W.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. UHPLC-(ESI)-HRMS and NMR-Based Metabolomics Approach to Access the Seasonality of Byrsonima Intermedia and Serjania Marginata From Brazilian Cerrado Flora Diversity. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 710025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, B.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Da Costa, F.B. Effect of the Environment on the Secondary Metabolic Profile of Tithonia Diversifolia: A Model for Environmental Metabolomics of Plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniddir, M.A.; Le Moyec, L.; Triba, M.N.; Longeon, A.; Deville, A.; Blond, A.; Pham, V.C.; de Voogd, N.J.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Metabolomics with Multi-Block Modelling of Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Order to Discriminate Haplosclerida Marine Sponges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5929–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, F.; Marti, G.; Merle, P.; Delort, E.; Baroux, L.; Sommer, H.; Wolfender, J.L.; Rudaz, S.; Boccard, J. Integrating Metabolomic Data from Multiple Analytical Platforms for a Comprehensive Characterisation of Lemon Essential Oils. Flavour Fragr. J. 2015, 30, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaric, C.; Pilard, S.; Fontaine, J.X.; Boccard, J.; Mathiron, D.; Rigaud, S.; Cailleu, D.; Mesnard, F.; Gut, Y.; Renaud, T.; et al. Processing of NMR and MS Metabolomics Data Using Chemometrics Methods: A Global Tool for Fungi Biotransformation Reactions Monitoring. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchemin, C.; Raviglione, D.; Ghosson, H.; Salvia, M.V.; Goossens, C.; Sasal, P.; Faliex, E.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N. Development of a Multiblock Metabolomics Approach to Explore Metabolite Variations of Two Algae of the Genus Asparagopsis Linked to Interspecies and Temporal Factors. Algal Res. 2023, 72, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Delfi, G.O.; Rider, C.V.; Ferguson, S.S.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Mueller, G.A. Non-Targeted Chemical Analysis of Consumer Botanical Products Labeled as Blue Cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), Goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis), or Yohimbe Bark (Pausinystalia yohimbe) by NMR and MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, I.; Lolli, V.; Segato, S.; Caligiani, A.; Contiero, B.; Lotto, A.; Galaverna, G.; Magrin, L.; Cozzi, G. Use of GC–MS and 1H NMR Low-Level Data Fusion as an Advanced and Comprehensive Metabolomic Approach to Discriminate Milk from Dairy Chains Based on Different Types of Forage. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 123, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Filho, E.G.; Mara, L.; Silva, A.; De Brito, E.S.; Castro, D.R.G.; Bezerra, J.A.; Sanches, E.A.; Rodrigues, S.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Campelo, P.H. Effect of Glow and Dielectric Barrier Discharges Plasma on Volatile and Non-Volatile Chemical Profiling of Camu-Camu Juice. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2021, 14, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchi, P.P.; Lolli, V.; Zhang, L.; Pavanello, F.; Caligiani, A.; Lucini, L. Integration of LC-HRMS and 1H NMR Metabolomics Data Fusion Approaches for Classification of Amarone Wine Based on Withering Time and Yeast Strain. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Yan, G.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, J.; Han, L. A Novel Data Fusion Strategy of GC-MS and 1H NMR Spectra for the Identification of Different Vintages of Maotai-Flavor Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 14865–14873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, C.; Yang, C.; Hu, S.; Cai, H.; Ning, J.; Wei, C.; Li, A.; Hou, R. Tracing the Origin of Taiping Houkui Green Tea Using 1H NMR and HS-SPME-GC–MS Chemical Fingerprints, Data Fusion and Chemometrics. Food Chem. 2023, 425, 136538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte-Sánchez, J.R.; Romero-González, R.; Martínez Vidal, J.L.; Arrebola, F.J.; Garrido Frenich, A. 1H NMR and Multi-Technique Data Fusion as Metabolomic Tool for the Classification of Golden Rums by Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Filho, E.G.; Silva, L.M.A.; Wurlitzer, N.J.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Fonteles, T.V.; Rodrigues, S.; de Brito, E.S. An Integrated Analytical Approach Based on NMR, LC–MS and GC–MS to Evaluate Thermal and Non-Thermal Processing of Cashew Apple Juice. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, M.; Dubin, E.; Cotton, J.; Poirel, M.; Corman, B.; Jamin, E.; Lees, M.; Rutledge, D. Data Fusion between High Resolution 1H-NMR and Mass Spectrometry: A Synergetic Approach to Honey Botanical Origin Characterization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4389–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. MVAPACK: A Complete Data Handling Package for NMR Metabolomics. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Pérez, A.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido Frenich, A. Application of an Innovative Metabolomics Approach to Discriminate Geographical Origin and Processing of Black Pepper by Untargeted UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis and Mid-Level Data Fusion. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancolillo, A.; Liland, K.H.; Måge, I.; Næs, T.; Bro, R. Variable Selection in Multi-Block Regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 156, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Imran, M.; Kim, E.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Park, H.M.; Jung, J.W.; Ryu, T.H. Approach Strategies and Application of Metabolomics to Biotechnology in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1192235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, A.G.; Arbulu, A.A.; González, F.J.N.; Bermejo, J.V.D.; Vallejo, M.E.C. Discriminant Canonical Analysis as a Validation Tool for Multivariety Native Breed Egg Commercial Quality Classification. Foods 2021, 10, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, V.; Jouan-Rimbaud Bouveresse, D.; Qannari, E.M.; Rutledge, D.N. ComDim Methods for the Analysis of Multiblock Data in a Data Fusion Perspective. Data Handl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 31, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, M.T.; Razzaque, M.A.; Angione, C.; Scrivens, J.; Sawan, S.; Sarkar, M. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis of Ovarian Cancer Using Variational Autoencoders. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Song, L.; Wang, P.; Cui, L.; Lin, T. An Adaptive Data Fusion Strategy for Fault Diagnosis Based on the Convolutional Neural Network. Measurement 2020, 165, 108122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, A.; El-Rabbany, A. UAV-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Urban Land Cover Mapping Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, C.; Patin, F.; Bocca, C.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Bonnier, F.; Reynier, P.; Emond, P.; Vourc’h, P.; Joseph-Delafont, K.; Corcia, P.; et al. The Combination of Four Analytical Methods to Explore Skeletal Muscle Metabolomics: Better Coverage of Metabolic Pathways or a Marketing Argument? J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018, 148, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, K.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Yu, C.; Somogyi, A.; Zhang, F.; Brüschweiler, R. Metabolomics beyond Spectroscopic Databases: A Combined MS/NMR Strategy for the Rapid Identification of New Metabolites in Complex Mixtures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, R.M.; das Neves Costa, F.; Chagas, F.O.; Teixeira, A.M.; Yoon, J.; Weiss, M.B.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Pilon, A.C.; Garrido, B.C.; Betancur, L.A.; et al. Data Fusion-Based Discovery (DAFdiscovery) Pipeline to Aid Compound Annotation and Bioactive Compound Discovery across Diverse Spectral Data. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Criterion | Low-Level | Mid-Level | High-Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Simple, direct | Feature reduction needed | Separate models required |
| Data Richness | Full information | Compressed, relevant | Outputs only |
| Overfitting Risk | High (many variables) | Moderate | Low (if models are robust) |
| Interpretability | Moderate, variable-level | Component-based | Low, indirect |
| Data Compatibility | Low (scaling required) | Moderate (pre-processing helps) | High (platform-independent) |
| Application Focus | Exploration, trend mapping | Clustering, pattern discovery | Classification, decision support |
| Limitations | Sensitive to scale; risk of bias | Loss of nuance; method-dependent | Requires expertise; low traceability |
| Approach | Aim | Datasets | DF Level | Fusion Strategy | Stat. Modelling | Model Validation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Fluid Matrices—Clinical Studies | |||||||
| Targeted | Compare the metabolic profiles of patients affected by autistic disorders | LC-MS 1H-NMR 1H-13C (HSQC) | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | OPLS-DA | CV-ANOVA | [42] |
| Untargeted | Evaluate the effects of dietary variations on plasma responses in pigs | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed blocks | Sparse MB-PLS | RMSECV | [43] |
| Untargeted | Differentiate the urinary metabolic profiles of irradiated and non-irradiated mice | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | MB-OPLSDA | CV-ANOVA | [44] |
| Untargeted | Evaluate optimization methods for NMR and MS data fusion using multiblock bilinear factorization in neurotoxin analysis | DI-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | MB-PCA, MB-PLS | LOOCV | [41] |
| Natural Products Matrices (plant, marine, and fungal sources) | |||||||
| Untargeted | Evaluate the variability in primary metabolites and aroma compounds of pines | GC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PLS-DA | Permutation test | [45] |
| Untargeted | Evaluate the environmental factors driving seasonal variations of a medicinal plant | LC-MS 1H-1H (J-resolved) | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PLS-DA, OPLS-DA | Permutation test | [46] |
| Untargeted | Assess the influence of seasonal factors on the chemical composition of two medicinal plant species | LC-MS 1H-1H (J-resolved) | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PLS-DA | Permutation test | [47] |
| Untargeted | Examine the relationships between environmental factors and the growth of an invasive weed | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PCA, HCA, OPLS-DA | - | [48] |
| Untargeted | Discriminate marine sponges | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | Consensus PCA, MB-PLS | LOOCV | [49] |
| Untargeted | Classify lemon essential oils based on their extraction methods | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | MB-PLS, consensus K-OPLS-DA | LOOCV | [50] |
| Untargeted | Monitor the biotransformation medium of a potential histamine H3 antagonist | LC-MS 1H-NMR 1H-1H (J-resolved) | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | Consensus OPLS-DA | K-fold | [51] |
| Untargeted | Evaluate metabolic differences of algae | GC-MS LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | MB ComDim | Permutation test | [52] |
| Untargeted | Determine the botanical origin and authenticity of blue cohosh | LC-MS 1H-NMR | MLDF | This approach analyzed the top five principal components (i.e., latent variables) of the NMR and MS datasets | PCA | - | [53] |
| Food Matrices | |||||||
| Untargeted | Discriminate milk from dairy chains based on different dietary types | GC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of datasets | CDA | LOOCV | [54] |
| Untargeted | Investigate the effect of operating conditions on both non-volatile and volatile compounds in juice | GC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PCA, PLS-DA | RMSEC, RMSECV | [55] |
| Untargeted | Classify wines according to grape withering time and yeast strain | LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | MCIA, SPLS-DA | 3-fold cross validation | [56] |
| Untargeted | Investigate the different vintages of Baijiu beverage | GC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of datasets | PCA, PLS-DA machine learning: SVM, DT, RF, k-NN | 10-fold cross validation | [57] |
| MLDF | Extraction of features by: PCA, PLS-DA, Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF) | ||||||
| Untargeted | Discriminate geographical origin of green tea | GC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed datasets | PCA, ComDim-PLS | - | [58] |
| MLDF | Concatenation of 3D PCA loading plots (approach 1) | PCA | |||||
| Concatenation VIP scores (top 10-approach 2) | SVM | ||||||
| Untargeted | Classify rums based on fermentation barrel, raw material, distillation method, and aging | GC-MS LC-MS 1H-NMR | LLDF | Concatenation of pre-processed raw data | PLS-DA | RMSECV, CV ANOVA, permutation test | [59] |
| MLDF | Concatenation of features based on VIP scores | ||||||
| Untargeted | Evaluate the influence of two processing methods on juice composition | LC-MS 1H-NMR | MLDF | Pre-processed matrices of NMR and MS were converted to ASCII | PCA | - | [60] |
| Untargeted | Honey origin discrimination and comparative analysis of mid-level fusion strategies | LC-MS 1H-NMR | MLDF | Concatenation scores of PCAs of each analytical method (no variable selection) Selection of relevant variables of each analytical method using PLS | PCA, PLS-DA | - | [61] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Homobono Brito de Moura, P.; Leleu, G.; Da Costa, G.; Marti, G.; Pétriacq, P.; Valls Fonayet, J.; Richard, T. Integrating NMR and MS for Improved Metabolomic Analysis: From Methodologies to Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122624
Homobono Brito de Moura P, Leleu G, Da Costa G, Marti G, Pétriacq P, Valls Fonayet J, Richard T. Integrating NMR and MS for Improved Metabolomic Analysis: From Methodologies to Applications. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122624
Chicago/Turabian StyleHomobono Brito de Moura, Patricia, Guillaume Leleu, Grégory Da Costa, Guillaume Marti, Pierre Pétriacq, Josep Valls Fonayet, and Tristan Richard. 2025. "Integrating NMR and MS for Improved Metabolomic Analysis: From Methodologies to Applications" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122624
APA StyleHomobono Brito de Moura, P., Leleu, G., Da Costa, G., Marti, G., Pétriacq, P., Valls Fonayet, J., & Richard, T. (2025). Integrating NMR and MS for Improved Metabolomic Analysis: From Methodologies to Applications. Molecules, 30(12), 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122624









