C-Phycocyanin Extract Modulates Thermogenic and Inflammatory Markers in Brown Adipose Tissue of High-Fat Diet-Fed Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
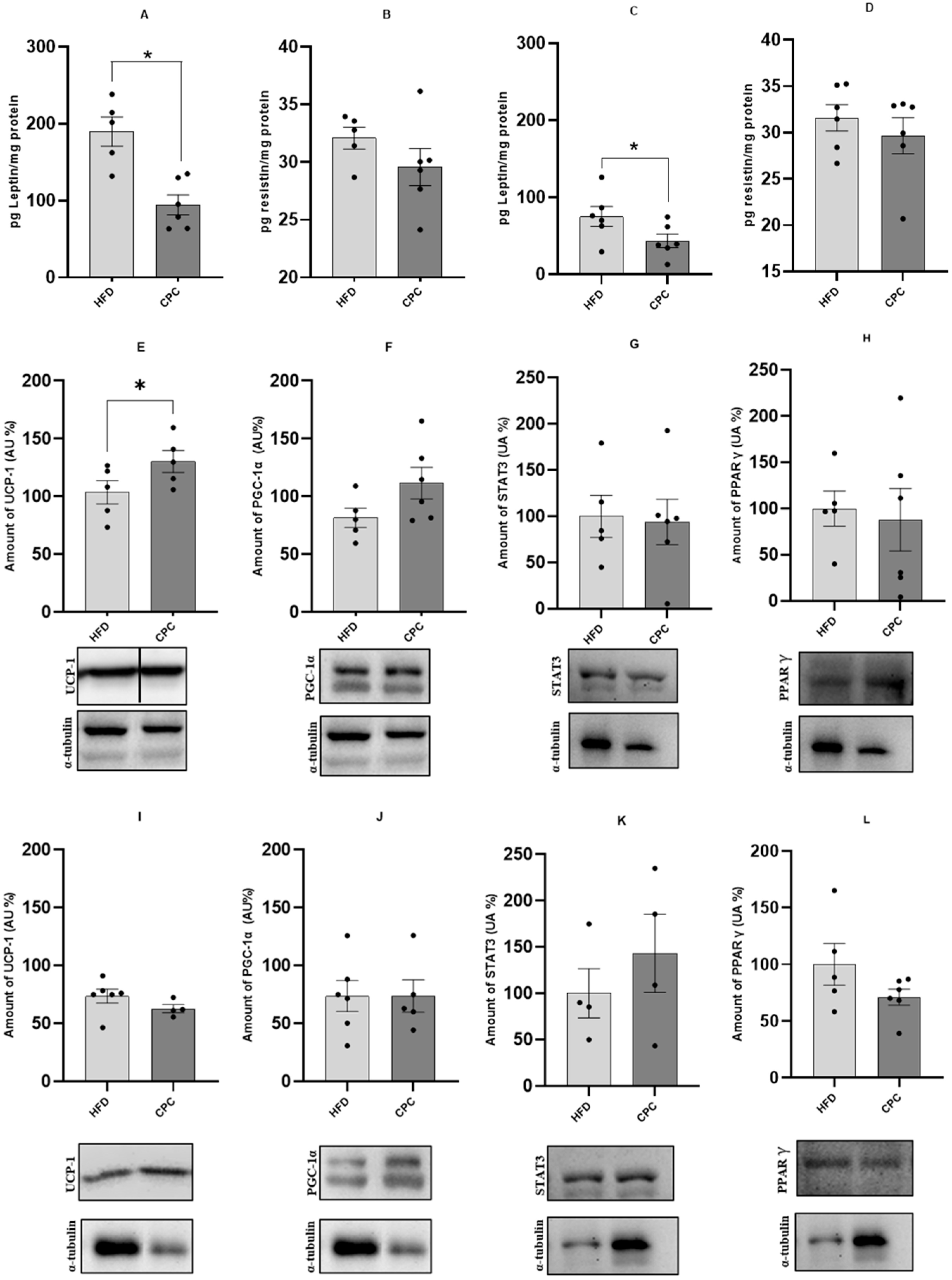
2. Results
Characterization of the Model and the Effect of CFC Extract on Thermogenesis Protein Expression and Inflammatory Processes in BAT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of C-Phycocyanin Extract
4.2. Animals
4.3. Protein Extraction for Western Blotting Method
4.4. Cytokines Concentration for ELISA Method
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling Protein 1 |
| CPC | C-phycocyanin |
| IL | Interleukine |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| ND | Normolipidic diet |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
References
- Castela, I.; Morais, J.; Barreiros-Mota, I.; Silvestre, M.P.; Marques, C.; Rodrigues, C.; Ismael, S.; Araújo, J.R.; Ângelo-Dias, M.; Martins, C.; et al. Decreased Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio Relates to Insulin Resistance in Adults with Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. -Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E115–E119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. -Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler-Vázquez, M.C.; Mera, P.; Zagmutt, S.; Serra, D.; Herrero, L. New Approaches Targeting Brown Adipose Tissue Transplantation as a Therapy in Obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghesmati, Z.; Rashid, M.; Fayezi, S.; Gieseler, F.; Alizadeh, E.; Darabi, M. An Update on the Secretory Functions of Brown, White, and Beige Adipose Tissue: Towards Therapeutic Applications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 25, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricquier, D. Uncoupling Protein 1 of Brown Adipocytes, the Only Uncoupler: A Historical Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown Adipose Tissue: Function and Physiological Significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontani, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kimura, K.; Inokuma, K.-I.; Saito, M.; Suzuki-Miura, T.; Wang, Z.; Sato, Y.; Mori, N.; Yamashita, H. UCP1 Deficiency Increases Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Obesity with Age. Aging Cell 2005, 4, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, H.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; et al. Differences in the Metabolic Status of Healthy Adults with and without Active Brown Adipose Tissue. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2013, 125, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, B.T.; Suchacki, K.J.; Stimson, R.H. Human Brown Adipose Tissue as a Therapeutic Target—Warming up or Cooling Down? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, R243–R259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesta, S.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Kahn, C.R. Developmental Origin of Fat: Tracking Obesity to Its Source. Cell 2007, 131, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Brown Adipose Tissue as a Secretory Organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Zorita, S.; Trepiana, J.; González-Arceo, M.; Aguirre, L.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; González, M.; Eseberri, I.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Portillo, M.P. Anti-Obesity Effects of Microalgae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, M.-C.; Sahebkar, A.; Dragan, S.; Stoichescu-Hogea, G.; Ursoniu, S.; Andrica, F.; Banach, M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Spirulina Supplementation on Plasma Lipid Concentrations. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Neto, A.F.; Fratelli, C.; Pucci, V.G.; Boldarine, V.T.; Ferreira, Y.A.M.; Telles, M.M.; Braga, A.R.C.; Oyama, L.M. C-Phycocyanin Extracted from Spirulina Using a Green Solvent Approach Presents an Anti-Obesity Characteristic in Mice Fed a Hyperlipidic Diet. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 108, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratelli, C.; Bürck, M.; Silva-Neto, A.F.; Oyama, L.M.; Braga, A.R.C. Green Extraction Process of Food Grade C-Phycocyanin: Biological Effects and Metabolic Study in Mice. Processes 2022, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-J.; Kim, K.-J.; Choi, J.; Koh, E.-J.; Lee, B.-Y. Spirulina Maxima Extract Reduces Obesity through Suppression of Adipogenesis and Activation of Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, Y.A.M.; Santamarina, A.B.; Mennitti, L.V.; de Souza, E.A.; Prado, C.M.; Pisani, L.P. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Enhance Mitochondrial Function and PGC1-α Expression in Brown Adipose Tissue of Obese Mice on a Low-Carbohydrate Diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 140, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Inflammation of Brown/Beige Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Wu, J.; Chang, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, X.; Sun, T.; Shang, D.; Yang, Y.; et al. Deciphering endocrine function of adipose tissue and its significant influences in obesity-related diseases caused by its dysfunction. Differentiation 2024, 141, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Thomou, T.; Boucher, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Lallukka, S.; Kim, J.K.; Torriani, M.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Cypess, A.M.; et al. Altered MiRNA Processing Disrupts Brown/White Adipocyte Determination and Associates with Lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Schultz, R.D.; Li, N.; He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Caron, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, K.; Xiong, W.; et al. Partial Leptin Reduction as an Insulin Sensitization and Weight Loss Strategy. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 706–719.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzbeck, P.; Giordano, A.; Mondini, E.; Murano, I.; Severi, I.; Venema, W.; Cecchini, M.P.; Kershaw, E.E.; Barbatelli, G.; Haemmerle, G.; et al. Brown Adipose Tissue Whitening Leads to Brown Adipocyte Death and Adipose Tissue Inflammation. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Amarante, M.C.A.; Braga, A.R.C.; Sala, L.; Moraes, C.C.; Kalil, S.J. Design strategies for C-phycocyanin purification: Process influence on purity grade. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.; Kuhn, K.R.; Moraes, C.C.; Burkert, C.A.V.; Kalil, S.J. Experimental design as a tool for optimization of C-phycocyanin purification by precipitation from Spirulina platensis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, D.A.; da Silva, F.P.; Carnier, M.; Mennitti, L.V.; Figuerêdo, R.G.; Hachul, A.C.L.; Boldarine, V.T.; Neto, N.I.P.; Seelaender, M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; et al. Chia Flour (Salvia hispanica L.) Did Not Improve the Deleterious Aspects of Hyperlipidic Diet Ingestion on Glucose Metabolism, but Worsened Glycaemia in Mice. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.F.; De Laquila, R.; Okuda, M.H.; Lira, F.S.; Souza, G.I.d.M.H.d.; de Souza, C.T.; Telles, M.M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Nascimento, C.M.O.D.; Oyama, L.M. Metabolic Profile Response to Administration of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in High-Fat-Fed Mice. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.F.; Silva, A.S.; de Oliveira, C.V.C.; de Souza, A.A.; Ferreira, P.B.; de Souza, I.L.L.; da Cunha Araujo, L.C.; da Silva Félix, G.; de Souza Sampaio, R.; Tavares, R.L.; et al. Spirulina platensis prevents oxidative stress and inflammation promoted by strength training in rats: Dose-response relation study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | ND 12-Week | HFD 12-Week | ND 16-Week | HFD 16-Week |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAT relative weight | 0.70 ± 0.07 | 0.93 ± 0.14 | 1.10 ± 0.11 | 0.89 ± 0.02 |
| UCP-1 | 100 ± 4.67 | 103.6 ± 10.13 | 100 ± 14.30 | 73.61 ± 5.99 * |
| PGC1-α | 100 ± 10.99 | 81.50 ± 8.35 | 100 ± 22.39 | 73.53 ± 13.32 |
| TNF-α | 3.46 ± 0.19 | 4.18 ± 0.39 | 4.00 ± 0.41 | 6.02 ± 0.85 * |
| STAT3 | 100 ± 21.18 | 70.05 ± 11.90 | 100 ± 19.95 | 81.54 ± 21.62 |
| PPARγ | 100 ± 21.54 | 71.48 ± 5.44 | 100 ± 5.76 | 113.8 ± 8.32 |
| IL-6 | 3.60 ± 0.22 | 4.07 ± 0.48 | 3.51 ± 0.27 | 4.13 ± 0.33 |
| IL10 | 21.93 ± 1.26 | 21.94 ± 0.97 | 29.02 ± 2.13 | 36.92 ± 2.61 * |
| TNFα/IL-10 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.01 * | 0.13 ± 0.005 | 0.15 ± 0.004 * |
| MCP-1 | 2.80 ± 0.29 | 3.20 ± 0.32 | 6.33 ± 0.31 | 7.34 ± 0.20 * |
| Leptin | 93.79 ± 27.08 | 189.8 ± 19.01 * | 24.71 ± 3.46 | 75.20 ± 12.89 * |
| Resistin | 30.12 ± 1.15 | 32.09 ± 0.95 | 27.75 ± 0.97 | 31.61 ± 1.43 * |
| Ingredients | ND (g/kg Diet) | HFD (g/kg Diet) |
|---|---|---|
| Maize starch | 720.7 | 450 |
| Sugar | – | 150 |
| Casein | 140 | 180 |
| Soy oil | 40 | 40 |
| Lard | – | 180 |
| Cellulose | 50 | – |
| Mix of vitamins/minerals | 10/35 | 10/35 |
| L-cystine/choline bitartrate/BHT | 1.8/2.5/0.008 | 1.8/2.5/0.008 |
| Caloric value (kcal/kg) | 3802.8 | 5100 |
| Carbohydrate (% energy) | 75.81% | 47.06% |
| Protein (% energy) | 14.73% | 14.12% |
| Lipids (% energy) | 9.47% | 38.82% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva-Neto, A.F.; Rocha, J.F.; Lima, G.O.; Oguma, J.M.; Pucci, V.C.G.S.; Ferreira, Y.A.M.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.; Oller do Nascimento, C.M.; Telles, M.M.; Braga, A.R.C.; et al. C-Phycocyanin Extract Modulates Thermogenic and Inflammatory Markers in Brown Adipose Tissue of High-Fat Diet-Fed Animals. Molecules 2025, 30, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122537
Silva-Neto AF, Rocha JF, Lima GO, Oguma JM, Pucci VCGS, Ferreira YAM, Alonso-Vale MI, Oller do Nascimento CM, Telles MM, Braga ARC, et al. C-Phycocyanin Extract Modulates Thermogenic and Inflammatory Markers in Brown Adipose Tissue of High-Fat Diet-Fed Animals. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122537
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva-Neto, Artur Francisco, Julia Ferreira Rocha, Gustavo Oliveira Lima, Juliana Miki Oguma, Vivien Cayres Giarola Suannes Pucci, Yasmin Alaby Martins Ferreira, Maria Isabel Alonso-Vale, Claudia Maria Oller do Nascimento, Mônica Marques Telles, Anna Rafaela Cavalcante Braga, and et al. 2025. "C-Phycocyanin Extract Modulates Thermogenic and Inflammatory Markers in Brown Adipose Tissue of High-Fat Diet-Fed Animals" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122537
APA StyleSilva-Neto, A. F., Rocha, J. F., Lima, G. O., Oguma, J. M., Pucci, V. C. G. S., Ferreira, Y. A. M., Alonso-Vale, M. I., Oller do Nascimento, C. M., Telles, M. M., Braga, A. R. C., Caperuto, L. C., & Oyama, L. M. (2025). C-Phycocyanin Extract Modulates Thermogenic and Inflammatory Markers in Brown Adipose Tissue of High-Fat Diet-Fed Animals. Molecules, 30(12), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122537











