Metabolic Profile of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) Muscle: Effect of Fish–Macroalgae IMTA-RAS Aquaculture
Abstract
1. Introduction
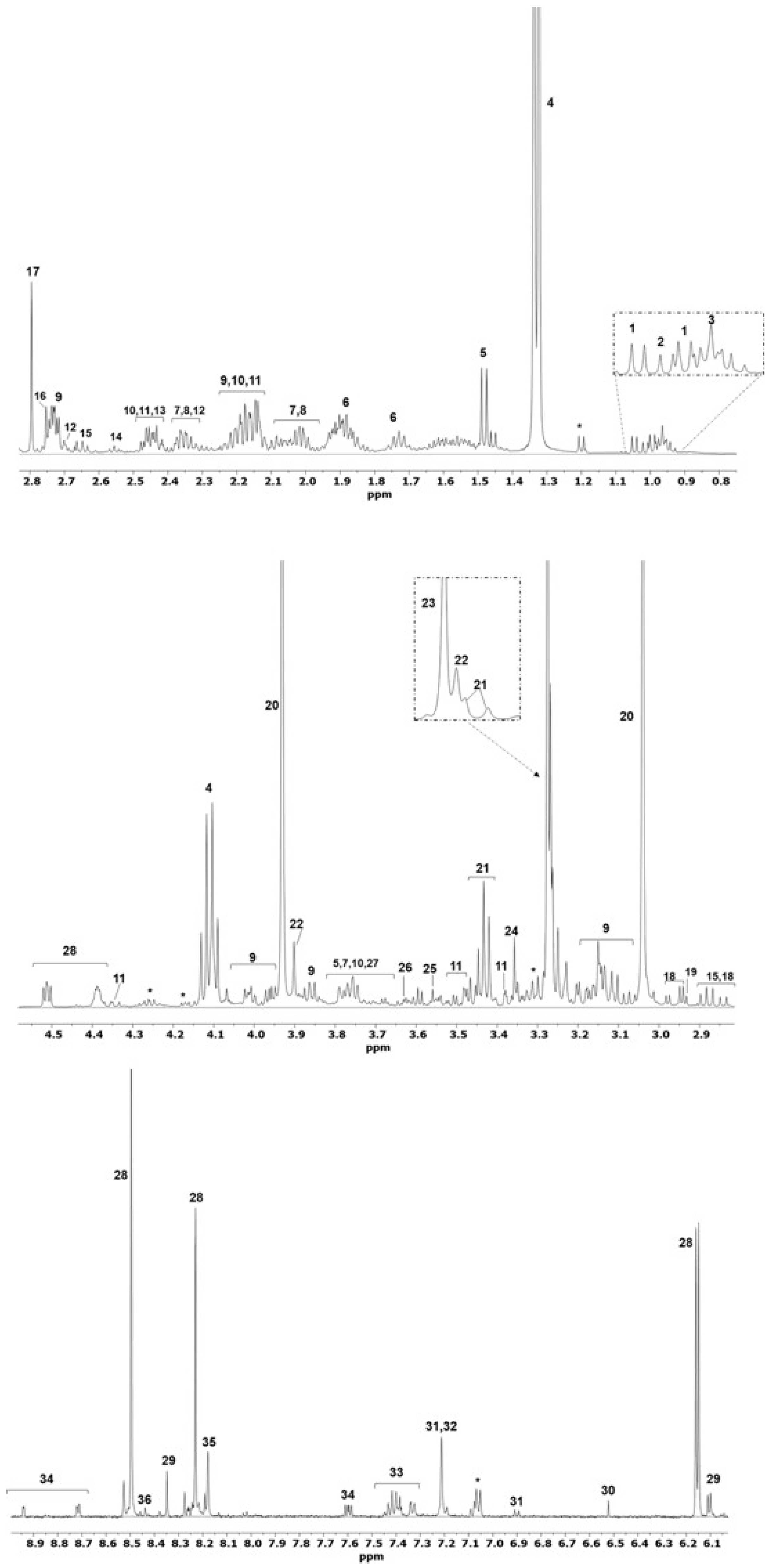
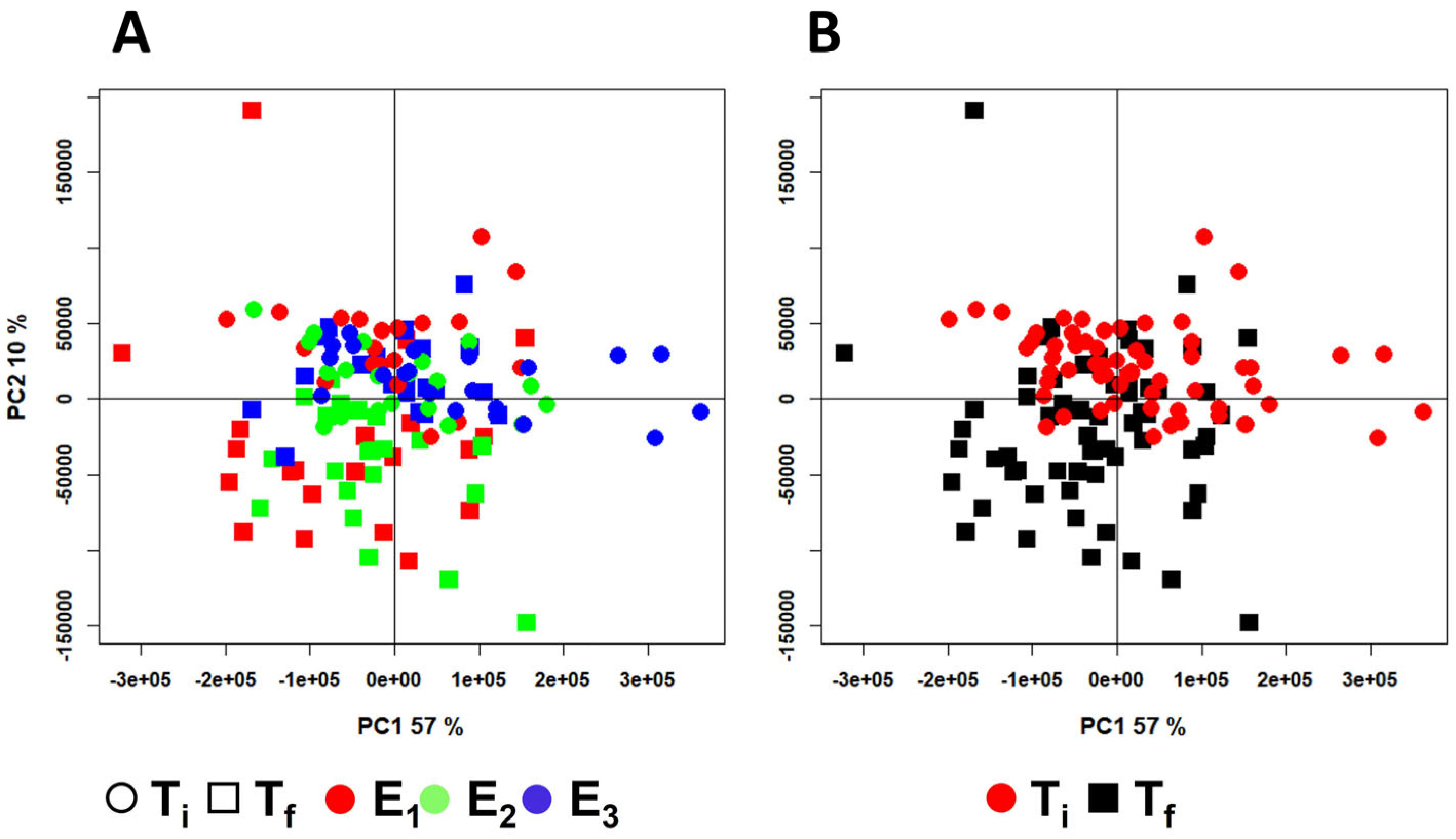
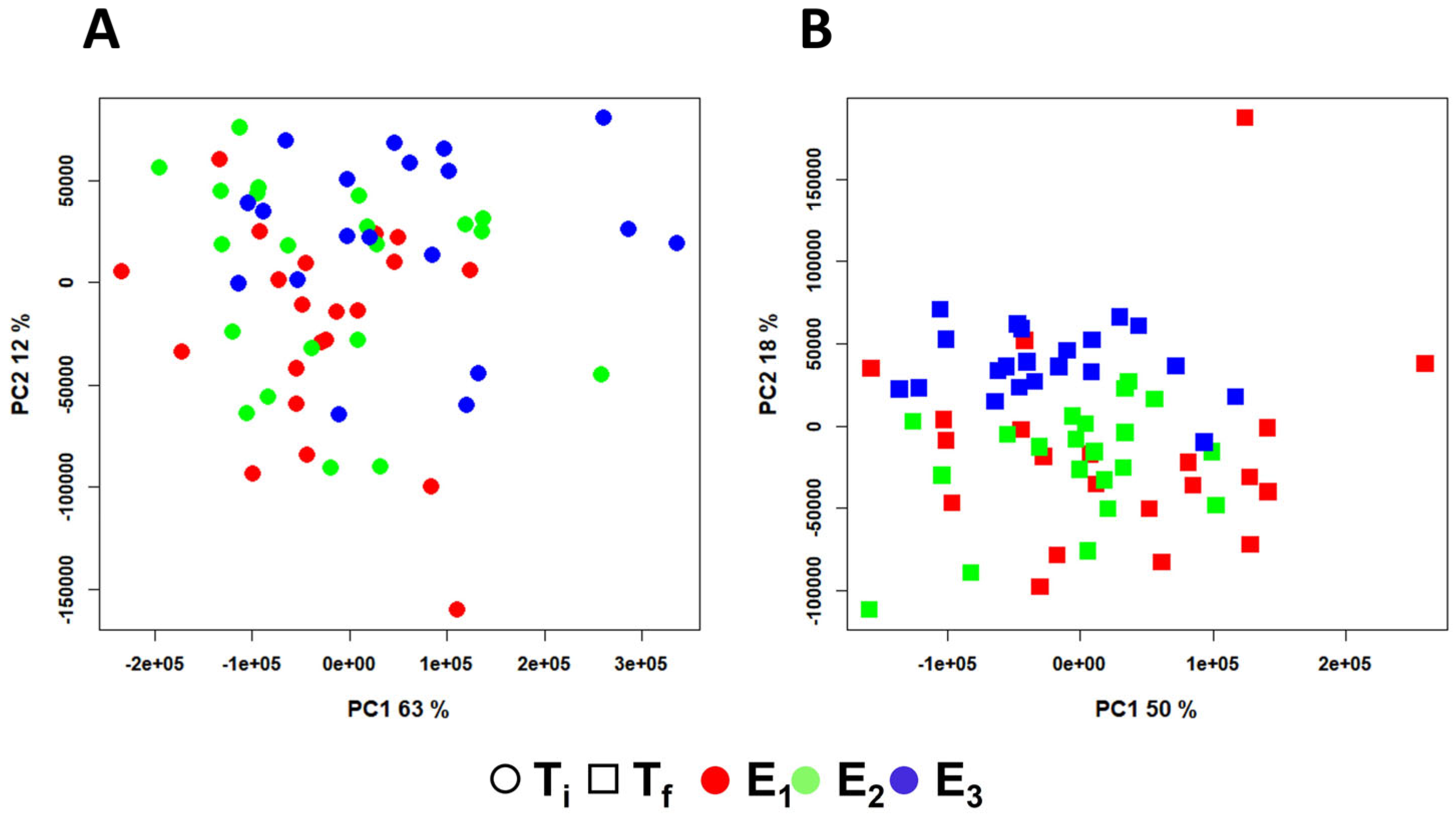
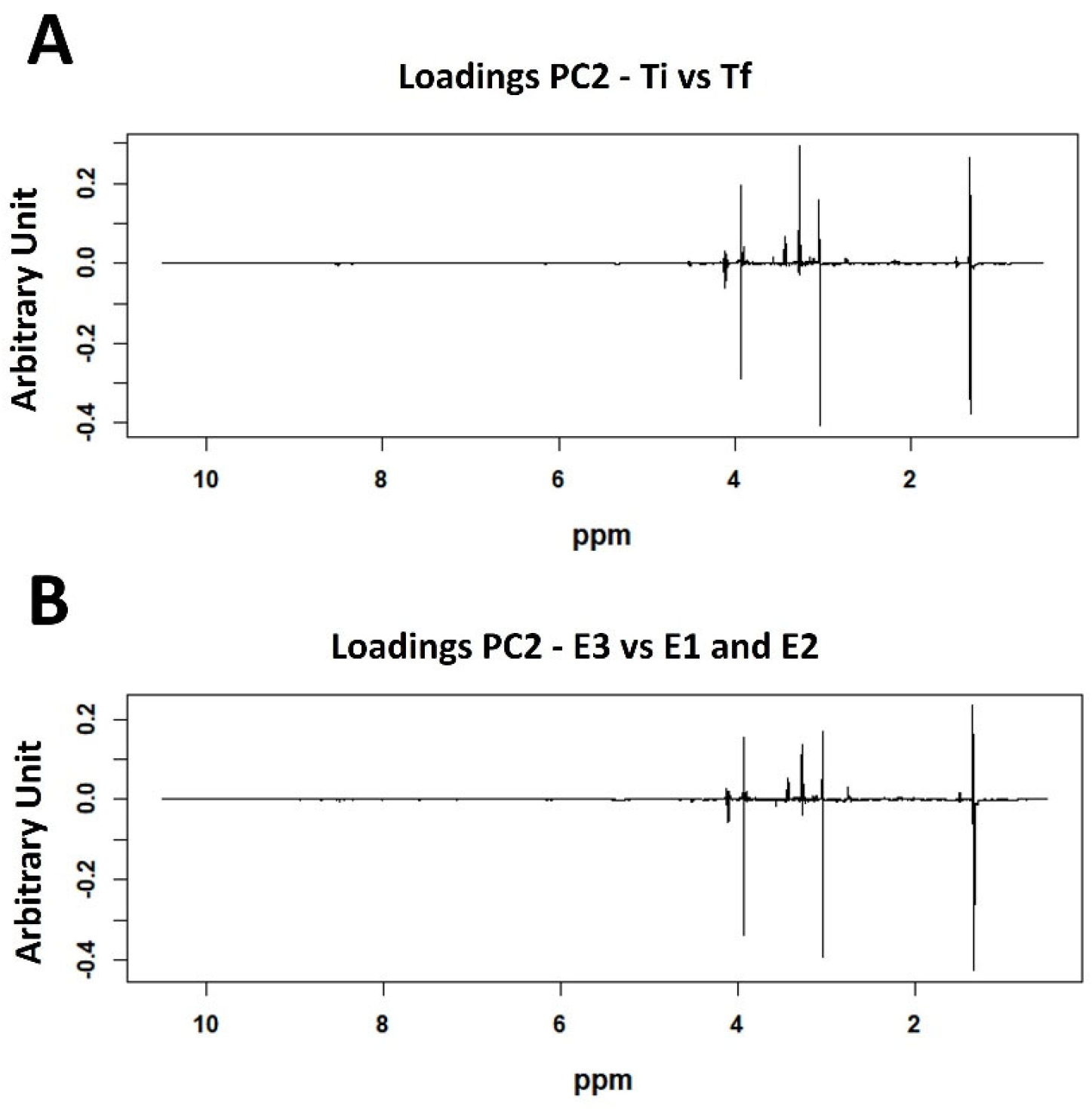
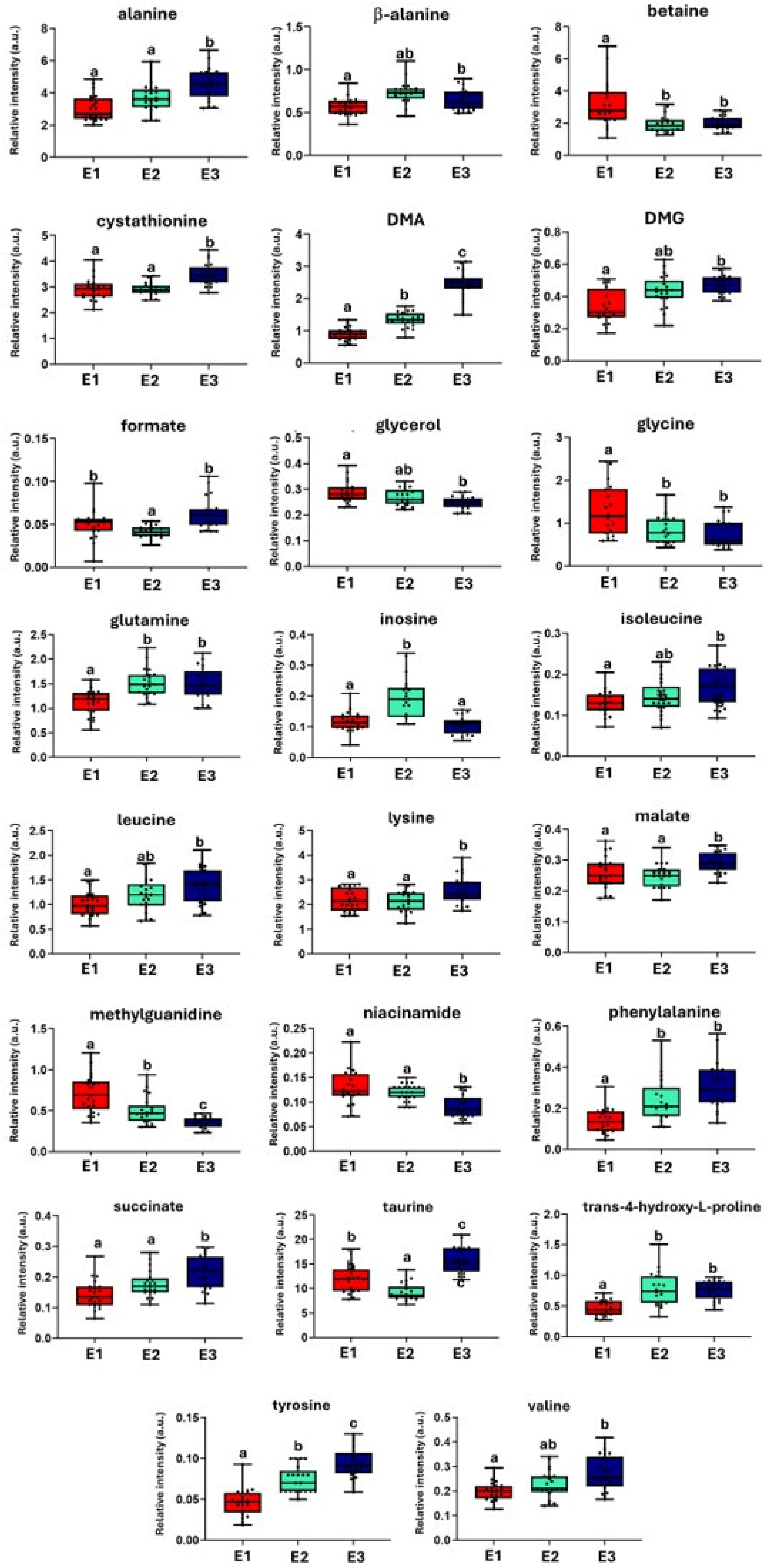
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. NMR Sample Preparation
4.4. NMR Spectroscopy
4.4.1. NMR Spectra Acquisition Parameters
4.4.2. NMR Spectra Processing
4.4.3. NMR Metabolic Profile
4.5. Multivariate and Univariate Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| DMA | Dimethylamine |
| DMG | Dimethylguanidine |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FID | Free Induction Decays |
| 1H NMR | High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| IMP | Inosine monophosphate |
| IMTA-RAS | Integrated Multitrophic Recirculating Aquaculture System |
| MVSDA | Multivariate Statistical Data Analysis |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PQN | Probabilistic Quotient Normalization |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid Krebs Cycle |
| TDA | Tropodithietic Acid |
| TMAO | Trimethylamine N-Oxide |
| TSP | 3-(Trimethylsilyl)-(2,2,3,3-2H4)-1-Propionate Sodium Salt |
| UVSDA | Univariate Statistical Data Analysis |
References
- Arora, N.K.; Mishra, I. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 2030 and environmental sustainability: Race against time. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molony, B.W.; Ford, A.T.; Sequeira, A.M.; Borja, A.; Zivian, A.M.; Robinson, C.; Lønborg, C.; Escobar-Briones, E.G.; Di Lorenzo, E.; Andersen, J.H. Sustainable development goal 14-life below water: Towards a sustainable ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 829610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturesson, A.; Weitz, N.; Persson, Å. SDG 14: Life Below Water. A Review of Research Needs. Technical Annex to the Formas Report Forskning for Agenda 2030; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrey, J. The 2030 Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals: The Challenge for Aquaculture Development and Management; FAO fisheries and aquaculture circular: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A. Aquaculture role in global food security with nutritional value: A review. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS): Environmental solution and climate change adaptation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, T.; Buschmann, A.H.; Halling, C.; Troell, M.; Kautsky, N.; Neori, A.; Kraemer, G.P.; Zertuche-González, J.A.; Yarish, C.; Neefus, C. Integrating seaweeds into marine aquaculture systems: A key toward sustainability. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Carter, C.G.; Hilder, P.E.; Hadley, S. A dynamic nutrient mass balance model for optimizing waste treatment in RAS and associated IMTA system. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, N.M.; Verreth, J.; Yusoff, F.M.; Nurulhuda, K.; Nagao, N.; Verdegem, M.C. Integration of algae to improve nitrogenous waste management in recirculating aquaculture systems: A review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, M.; Shimada, S.; Uenosono, M.; Masuda, M. A new green-tide-forming alga, Ulva ohnoi Hiraoka et Shimada sp. nov. (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae) from Japan. Phycol. Res. 2004, 52, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamrousi, A.; Casais, E.; García-Cardesín, É.; Masaló, I.; Pintado, J.; Cremades, J. Influence of pH, N, P, N: P ratio, and dissolved inorganic carbon on Ulva ohnoi growth and biomass quality: Potential implications in IMTA-RAS. Aquac. J. 2022, 2, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado, J.; Del Olmo, G.; Guinebert, T.; Ruiz, P.; Nappi, J.; Thomas, T.; Egan, S.; Masaló, I.; Cremades, J. Manipulating the Ulva holobiont: Co-culturing Ulva ohnoi with Phaeobacter bacteria as a strategy for disease control in fish-macroalgae IMTA-RAS aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 2017–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prol-García, M.J.; Gómez, M.; Sánchez, L.; Pintado, J. Phaeobacter grown in biofilters: A new strategy for the control of Vibrionaceae in aquaculture. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, E.C.; Jimenez, G.; Castex, M.; Gram, L. The Roseobacter-group bacterium Phaeobacter as a safe probiotic solution for aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02581-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, E.C.; Phippen, C.B.W.; Nielsen, K.F.; Mateiu, R.V.; Melchiorsen, J.; Gram, L.; Overmann, J.; Freese, H.M. Phaeobacter piscinae sp. nov., a species of the Roseobacter group and potential aquaculture probiont. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4559–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qui-Minet, Z.N.; Wichard, T.; Del Olmo, G.; Pereira, M.; Holbl, H.; Ruiz, P.; Cremades, J.; Pintado, J. Light-regulated interactions between Phaeobacter sp. and Ulva ohnoi (Chlorophyta): Effects on microbiome dynamics, metabolome composition, and tropodithietic acid production. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2025, 230, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K.J.; Krüger, R.; Scherz, V.; Münger, L.H.; Picone, G.; Vionnet, N.; Bertelli, C.; Greub, G.; Capozzi, F.; Vergères, G. Trimethylamine-N-oxide postprandial response in plasma and urine is lower after fermented compared to non-fermented dairy consumption in healthy adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, C.R.; Kavitake, D.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Jaiswal, K.S.; Reddy, G.B.; Agarwal, V.; Shetty, P.H. NMR-based metabolomics as a significant tool for human nutritional research and health applications. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, W.; Widmer, H. Protein NMR in biomedical research. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2004, 61, 580–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimigno, A.; Holderman, N.R.; Dong, C.; Boardman, K.D.; Zhao, J.; O’Day, E.M. NMR precision metabolomics: Dynamic peak sum thresholding and navigators for highly standardized and reproducible metabolite profiling of clinical urine samples. Metabolites 2024, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimigno, A.; Łoniewska, B.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Łoniewski, I.; Picone, G. The application of High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (HR NMR) in metabolomic analyses of meconium and stool in newborns. A preliminary pilot study of MABEL project: Metabolomics approach for the assessment of Baby-Mother Enteric Microbiota Legacy. PharmaNutrition 2024, 27, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo de Magalhães, C.S.F.; Cerqueira, M.A.C.; Schrama, D.; Moreira, M.J.V.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Rodrigues, P.M.L. A Proteomics and other Omics approach in the context of farmed fish welfare and biomarker discovery. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Solsona, R.; Nácher-Mestre, J.; Lacalle-Bergeron, L.; Sancho, J.V.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Hernández, F.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Untargeted metabolomics approach for unraveling robust biomarkers of nutritional status in fasted gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). PeerJ 2017, 5, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, G.; Engelsen, S.B.; Savorani, F.; Testi, S.; Badiani, A.; Capozzi, F. Metabolomics as a powerful tool for molecular quality assessment of the fish Sparus aurata. Nutrients 2011, 3, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roques, S.; Deborde, C.; Richard, N.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Moing, A.; Fauconneau, B. Metabolomics and fish nutrition: A review in the context of sustainable feed development. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liang, M.; Mai, K.; Zheng, K.; Xu, H. 1H NMR-based metabolomics studies on the effect of size-fractionated fish protein hydrolysate, fish meal and plant protein in diet for juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampa, A.; Laghi, L.; Picone, G. Validation of a 1H-NMR spectroscopy quantitative method to quantify trimethylamine content and K-index value in different species of fish. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 3612095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, E.; Lu, M.; Xie, J. Effects of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota as well as metabolite profiles within Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Men, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y. Probiotics mediate intestinal microbiome and microbiota-derived metabolites regulating the growth and immunity of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03980-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neissi, A.; Majidi Zahed, H.; Roshan, R. Probiotic performance of B. subtilis MS. 45 improves aquaculture of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss during acute hypoxia stress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; He, K.; Adam, A.A.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S. Combined exposure to hypoxia and ammonia aggravated biological effects on glucose metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Abo-Raya, M.H.; Jin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Metabolomic characterization of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) in semi-intensive and recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2024, 593, 741292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M. Multi-omics integrative analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of muscle adaptive changes in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) under water flow stress in recirculating aquaculture. Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morash, A.J.; Vanderveken, M.; McClelland, G.B. Muscle metabolic remodeling in response to endurance exercise in salmonids. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, F.; Stincone, P.; Cammarata, M.; Brandelli, A. Amino acids as the main energy source in fish tissues. Aquac. Fish. Stud. 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. Amino Acids: Biochemistry and Nutrition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Suehs, B.A.; Gatlin, D.M., 3rd; Wu, G. Glycine nutrition and biochemistry from an aquaculture perspective. Anim. Front. Rev. Mag. Anim. Agric. 2024, 14, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, P.M.; Holm, P.I.; Hustad, S. Betaine: A key modulator of one-carbon metabolism and homocysteine status. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2005, 43, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espe, M.; Adam, A.C.; Saito, T.; Skjærven, K.H. Methionine: An Indispensable Amino Acid in Cellular Metabolism and Health of Atlantic Salmon. Aquac. Nutr. 2023, 2023, 5706177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitvitsky, V.; Mosharov, E.; Tritt, M.; Ataullakhanov, F.; Banerjee, R. Redox regulation of homocysteine-dependent glutathione synthesis. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2003, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerwerk, M.T.; Zadinelo, I.V.; Meurer, F. Use of glycerol in fish nutrition: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Gram, L. Biotechnological applications of the Roseobacter clade. In Bioprospecting: Success, Potential and Constraints; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 137–166. [Google Scholar]
- Planas, M.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Hjelm, M.; Gram, L.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Bergh, Ø.; Pintado, J. Probiotic effect in vivo of Roseobacter strain 27-4 against Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum infections in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) larvae. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliou, S.; Adamaki, M.; Ioannou, P.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Spandidos, D.A.; Christodoulou, I.; Kyriakopoulos, A.M.; Zoumpourlis, V. Protective role of taurine against oxidative stress (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, H.; Fu, G.; Zhong, L. The Protective Effect of Taurine on Oxidized Fish-Oil-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Barrier-Function Impairment in Juvenile Ictalurus punctatus. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salze, G.P.; Davis, D.A. Taurine: A critical nutrient for future fish feeds. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.; Rønnestad, I.; Dinis, M.T.; Aragão, C. Taurine and fish development: Insights for the aquaculture industry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 776, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S.; Aragão, C.; Cabrita, E.; Conceição, L.E.; Constenla, M.; Costas, B.; Dias, J.; Duncan, N.; Engrola, S.; Estevez, A. New developments and biological insights into the farming of Solea senegalensis reinforcing its aquaculture potential. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 227–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.M.; Cabrita, E.; Fatsini, E. The use of sand substrate modulates dominance behaviour and brain gene expression in a flatfish species. Animals 2023, 13, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savorani, F.; Tomasi, G.; Engelsen, S.B. icoshift: A versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.; Bonaldo, A.; Di Biase, A.; Cerri, R.; Scicchitano, D.; Nanetti, E.; Candela, M.; Picone, G.; Capozzi, F.; Dondi, F. Towards a free wild-caught fishmeal, fish oil and soy protein in European sea bass diet using by-products from fishery and aquaculture. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampa, A.; Picone, G.; Laghi, L.; Nikzad, H.; Capozzi, F. Changes in the amino acid composition of Bogue (Boops boops) fish during storage at different temperatures by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Nutrients 2012, 4, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, C.; Scano, P.; Locci, E.; Sanna, R.; Marincola, F.C. Analysing the effects of frozen storage and processing on the metabolite profile of raw mullet roes using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, G.; Mezzetti, B.; Babini, E.; Capocasa, F.; Placucci, G.; Capozzi, F. Unsupervised principal component analysis of NMR metabolic profiles for the assessment of substantial equivalence of transgenic grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9271–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Junior, R.S.; Borges, E.M. Teaching statistics and chemometrics using an open source, free and graphical user interface software. ChemRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, A.M.; Romick-Rosendale, L.E.; Kennedy, M.A. Statistical significance analysis of nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics data. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 401, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloo, A.; Chairhany, S. Fostering students’ attitudes and achievement in probability using teams-games-tournaments. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 93, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends Sport Sci. 2014, 21, 19. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | E1 | E2 | E3 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight gain (g) | 26.0 ± 0.7 | 45.5 ± 15.3 | 43.4 ± 7.8 | ns |
| Specific growth rate | 0.61 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.24 | 0.99 ± 0.22 | ns |
| Fulton’s condition index K | 1.63 ± 0.18 | 1.67 ± 0.23 | 1.68 ± 0.14 | ns |
| Metabolite | p-Value | ε2 | q |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | <0.001 | 0.341 | 0.002 |
| β-Alanine | <0.001 | 0.243 | 0.002 |
| AMP/IMP | 0.239 | 0.046 | 0.265 |
| Asparagine | 0.415 | 0.028 | 0.444 |
| Aspartate | 0.063 | 0.202 | 0.076 |
| Betaine | <0.001 | 0.270 | 0.002 |
| Cystathionine | <0.001 | 0.370 | 0.002 |
| Creatine | 0.798 | 0.007 | 0.79 |
| DMA | <0.001 | 0.813 | 0.002 |
| DMG | 0.002 | 0.202 | 0.003 |
| Formate | <0.001 | 0.314 | 0.002 |
| Fumarate | 0.049 | 0.100 | 0.061 |
| Glycerol | 0.002 | 0.203 | 0.003 |
| Glycine | 0.003 | 0.203 | 0.004 |
| Glutamine | <0.001 | 0.305 | 0.002 |
| Inosine | <0.001 | 0.337 | 0.002 |
| Isoleucine | 0.027 | 0.118 | 0.035 |
| Lactate | 0.595 | 0.017 | 0.616 |
| Leucine | 0.009 | 0.155 | 0.013 |
| Lysine | 0.023 | 0.121 | 0.031 |
| Malate | 0.003 | 0.189 | 0.004 |
| Methylguanidine | <0.001 | 0.478 | 0.002 |
| Niacinamide | <0.001 | 0.284 | 0.002 |
| Phenylalanine | <0.001 | 0.448 | 0.002 |
| Succinate | <0.001 | 0.269 | 0.002 |
| Taurine | <0.001 | 0.588 | 0.002 |
| Tyrosine | <0.001 | 0.601 | 0.002 |
| TMAO | 0.232 | 0.047 | 0.265 |
| Trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline | <0.001 | 0.390 | 0.002 |
| Valine | 0.002 | 0.121 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cesare Marincola, F.; Palmas, C.; Lastres Couto, M.A.; Paz, I.; Cremades, J.; Pintado, J.; Bruni, L.; Picone, G. Metabolic Profile of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) Muscle: Effect of Fish–Macroalgae IMTA-RAS Aquaculture. Molecules 2025, 30, 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122518
Cesare Marincola F, Palmas C, Lastres Couto MA, Paz I, Cremades J, Pintado J, Bruni L, Picone G. Metabolic Profile of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) Muscle: Effect of Fish–Macroalgae IMTA-RAS Aquaculture. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122518
Chicago/Turabian StyleCesare Marincola, Flaminia, Chiara Palmas, Miguel A. Lastres Couto, Isabel Paz, Javier Cremades, José Pintado, Leonardo Bruni, and Gianfranco Picone. 2025. "Metabolic Profile of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) Muscle: Effect of Fish–Macroalgae IMTA-RAS Aquaculture" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122518
APA StyleCesare Marincola, F., Palmas, C., Lastres Couto, M. A., Paz, I., Cremades, J., Pintado, J., Bruni, L., & Picone, G. (2025). Metabolic Profile of Senegalese Sole (Solea senegalensis) Muscle: Effect of Fish–Macroalgae IMTA-RAS Aquaculture. Molecules, 30(12), 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122518







