The Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Dispersants Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Groups and Their Performance in Promoting Coal Particle Dispersion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Dispersant Structures
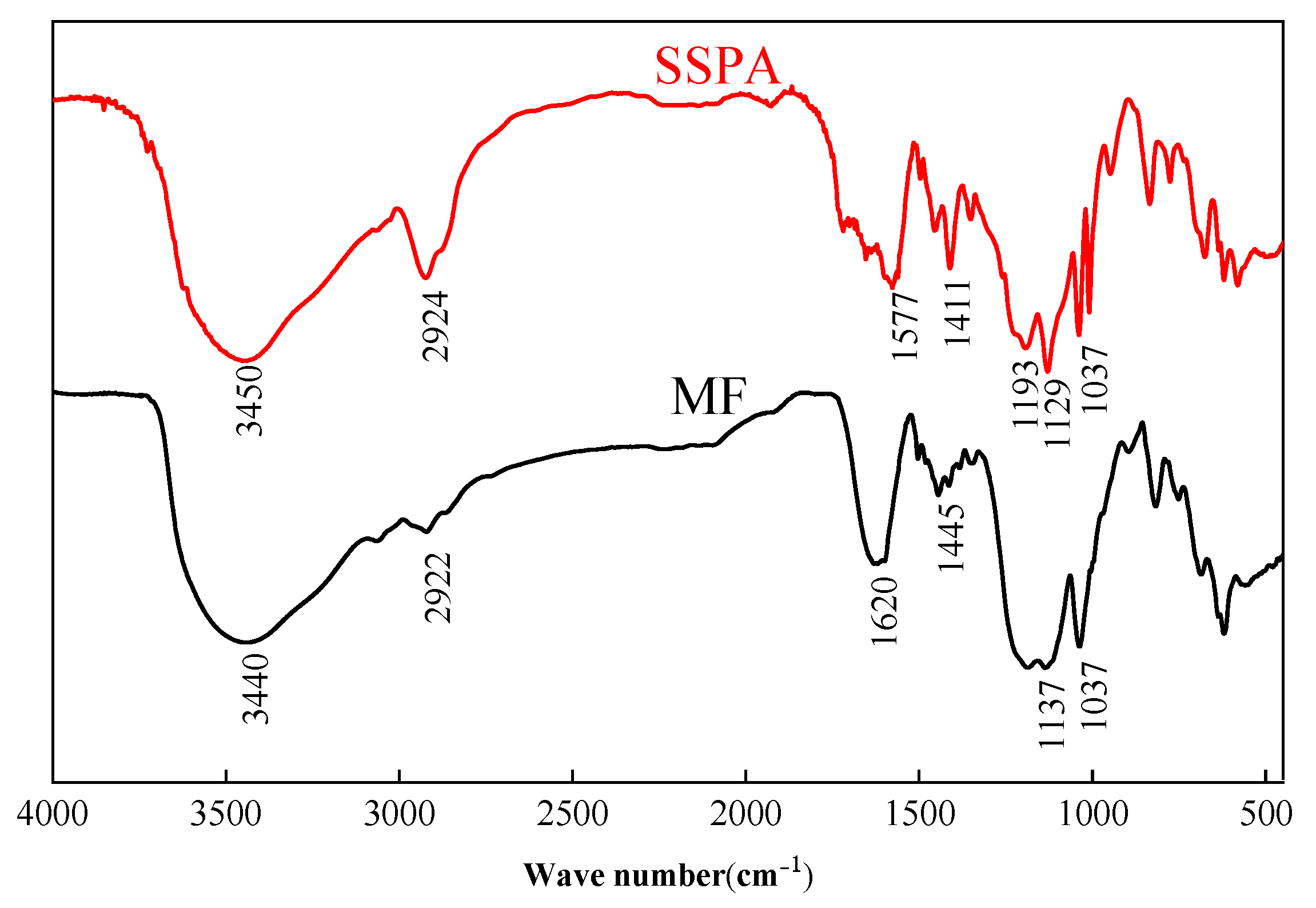
2.1.1. FT-IR Spectral Analysis
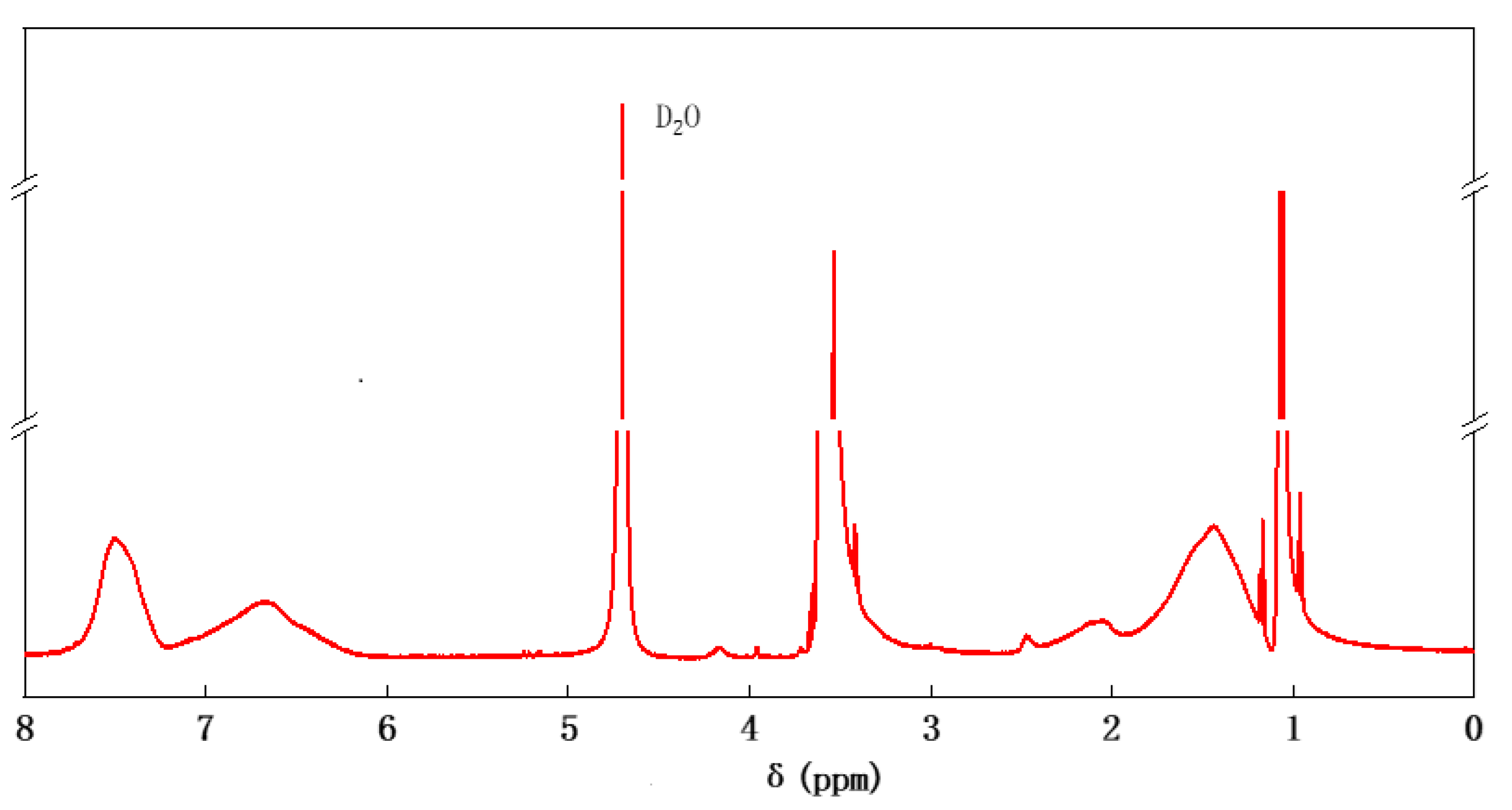
2.1.2. Nuclear Magnetic Hydrogen Spectroscopy Analysis
2.1.3. Molecular Weight Distribution Analysis
2.2. Analysis of Dispersion Performance
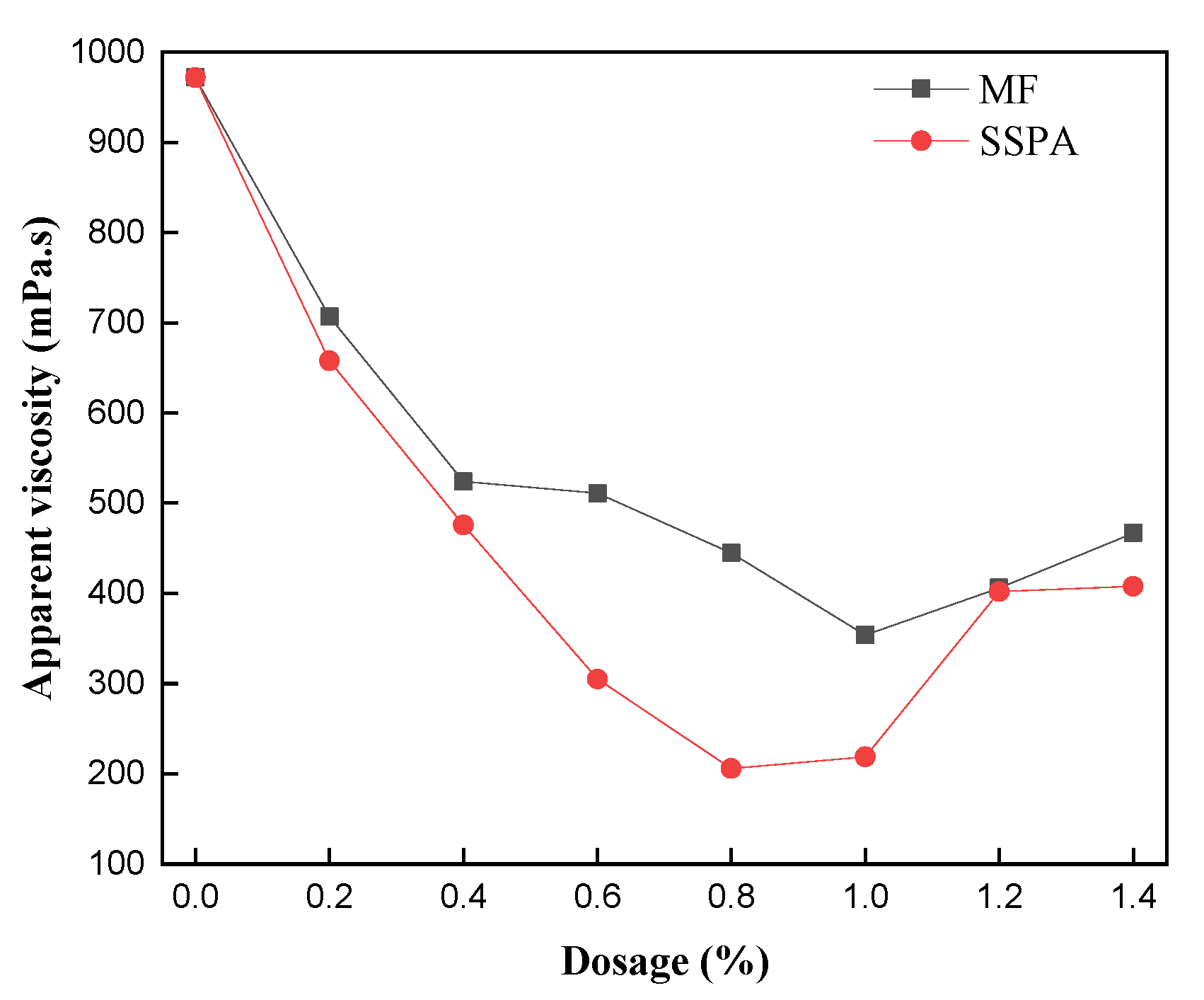
2.2.1. Dosage of Dispersant
2.2.2. Maximum Solid Content
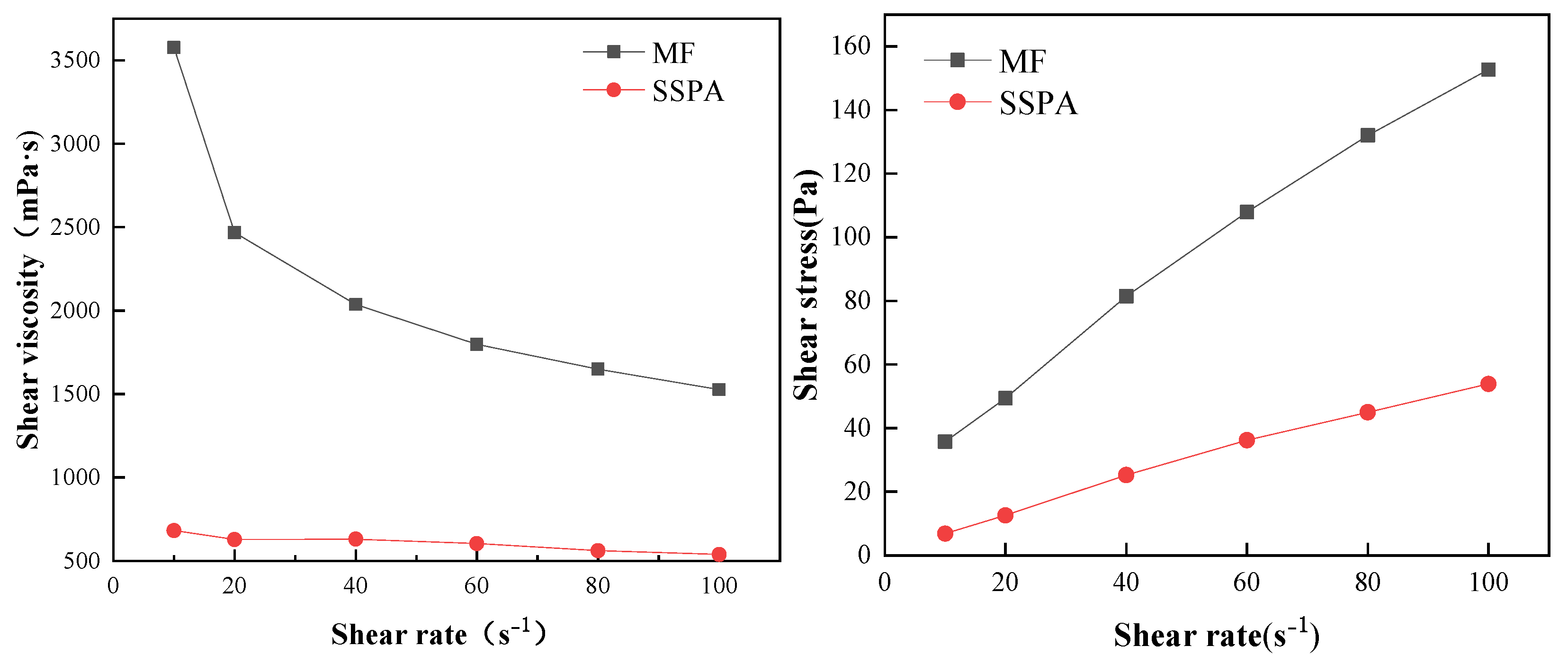
2.2.3. Rheological Analysis
2.2.4. Analysis of Stability
2.3. Mechanism Analysis
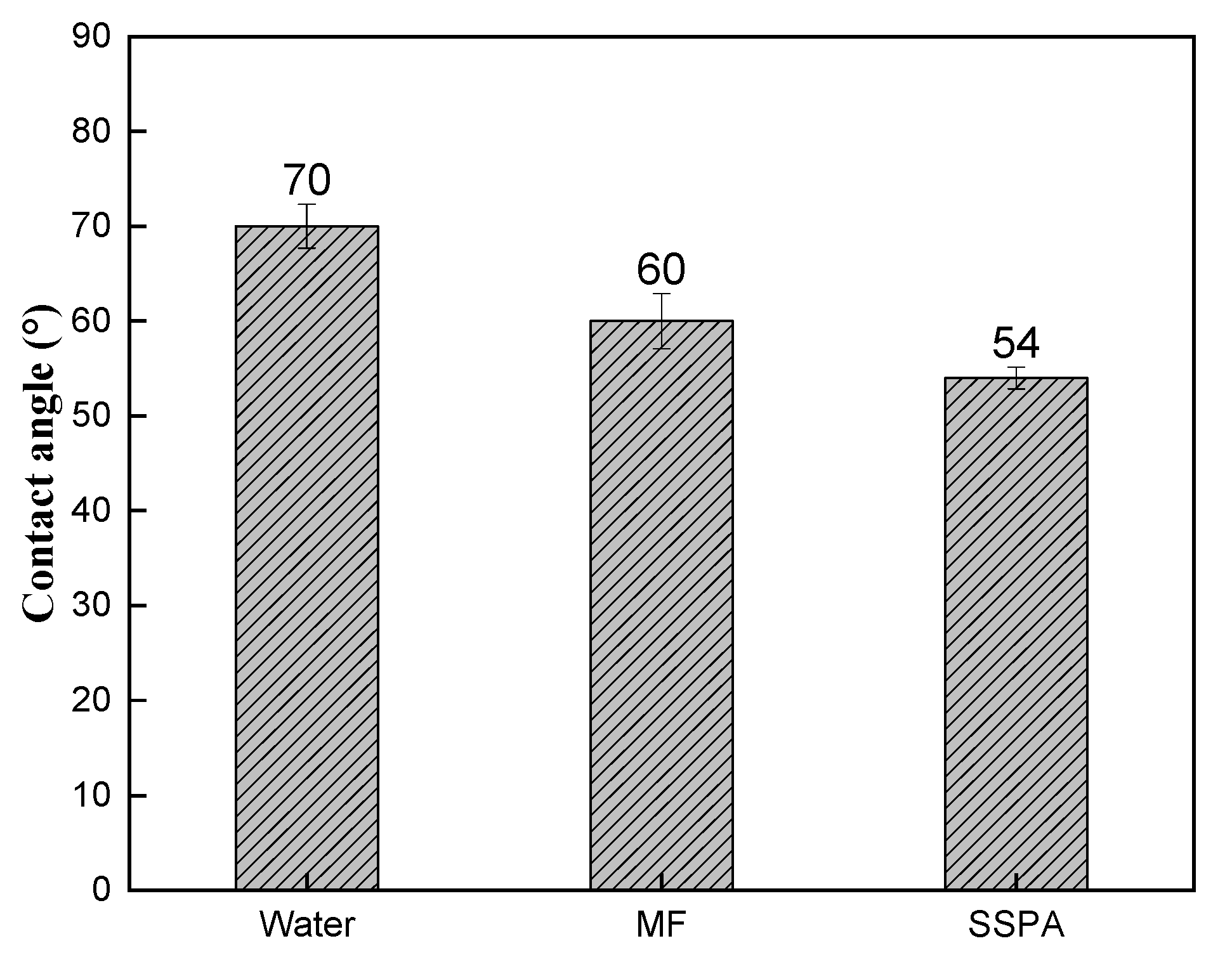
2.3.1. Wettability Analysis
2.3.2. Zeta Potential Analysis
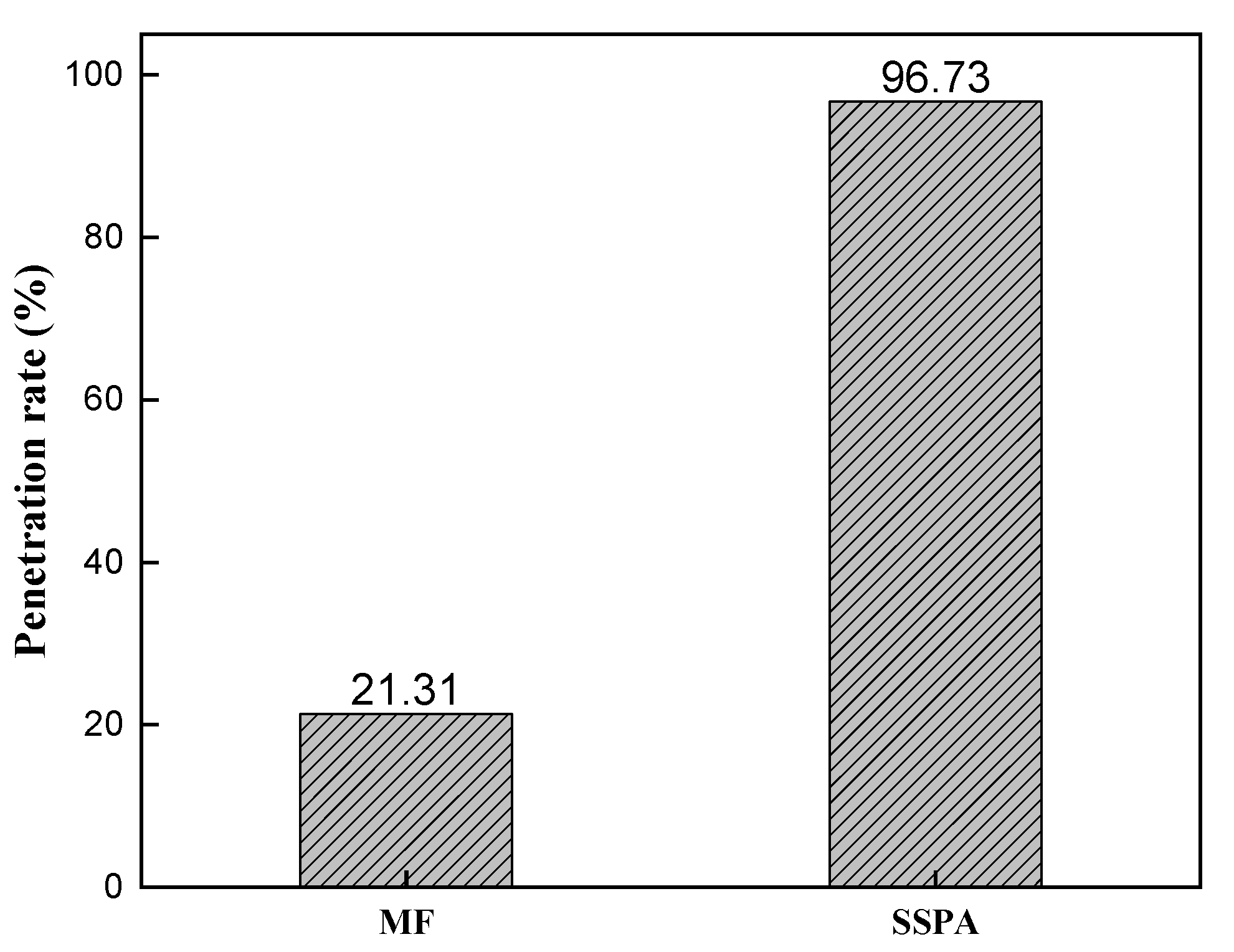
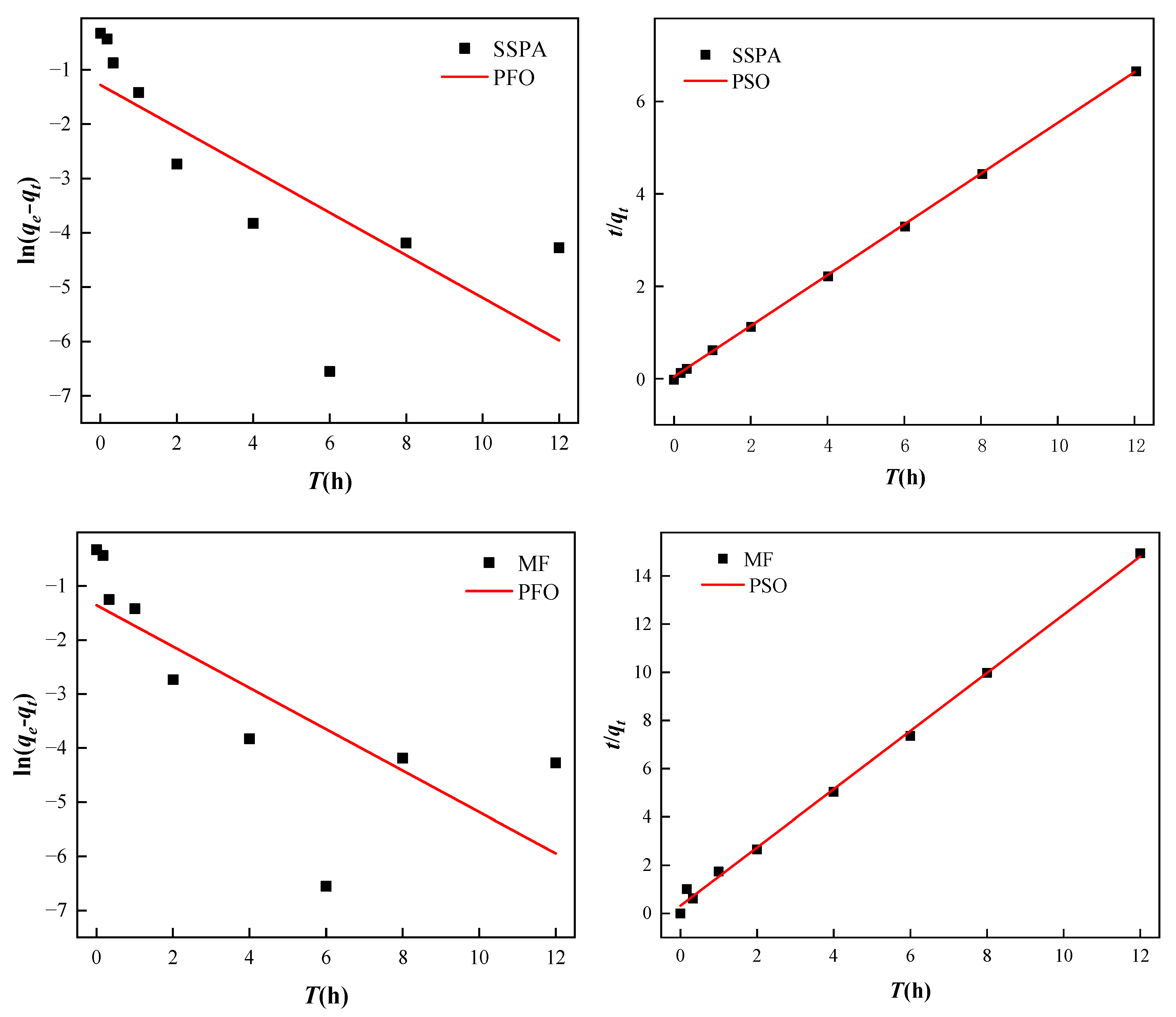
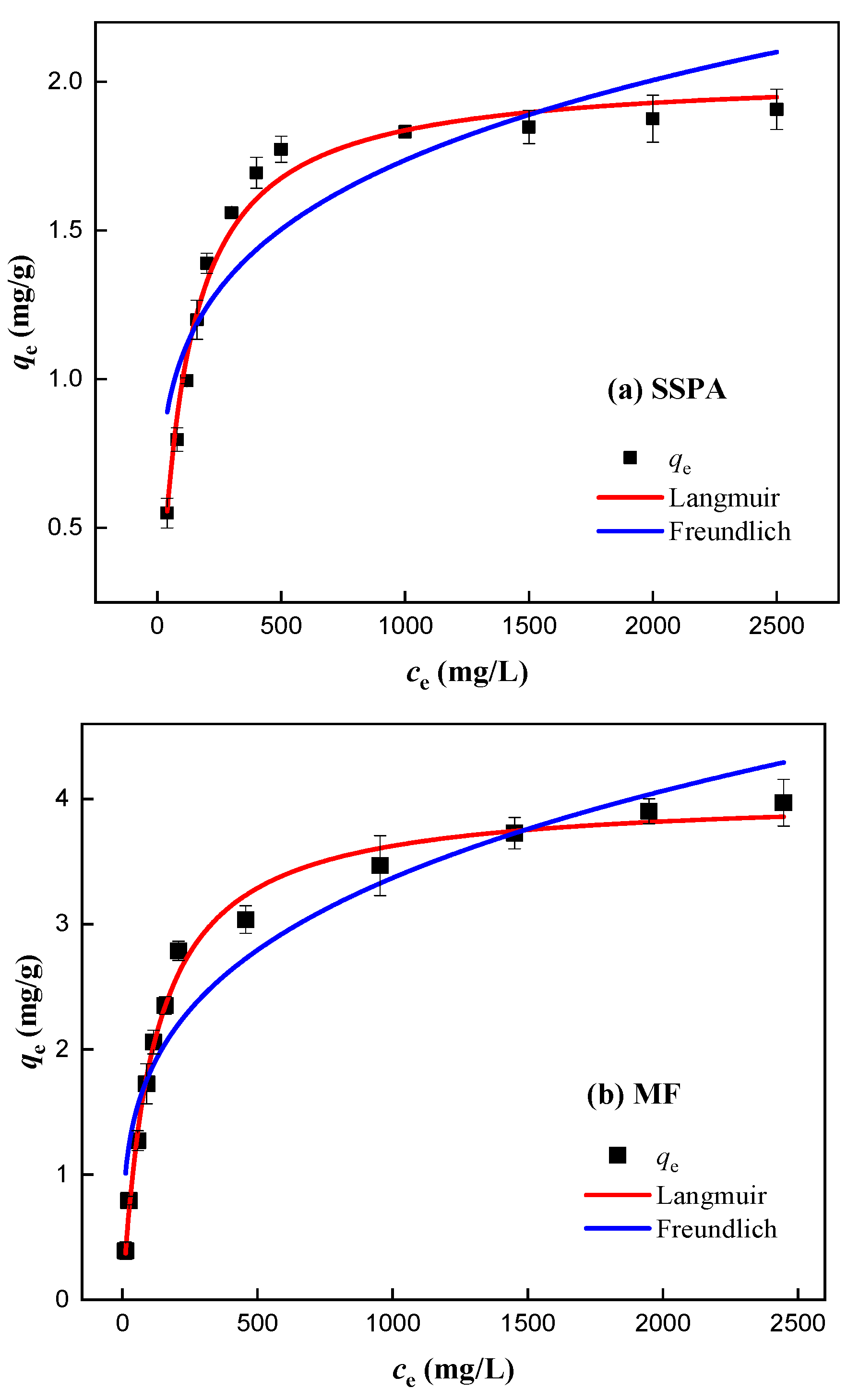
2.3.3. Adsorption Performance Study
- (1)
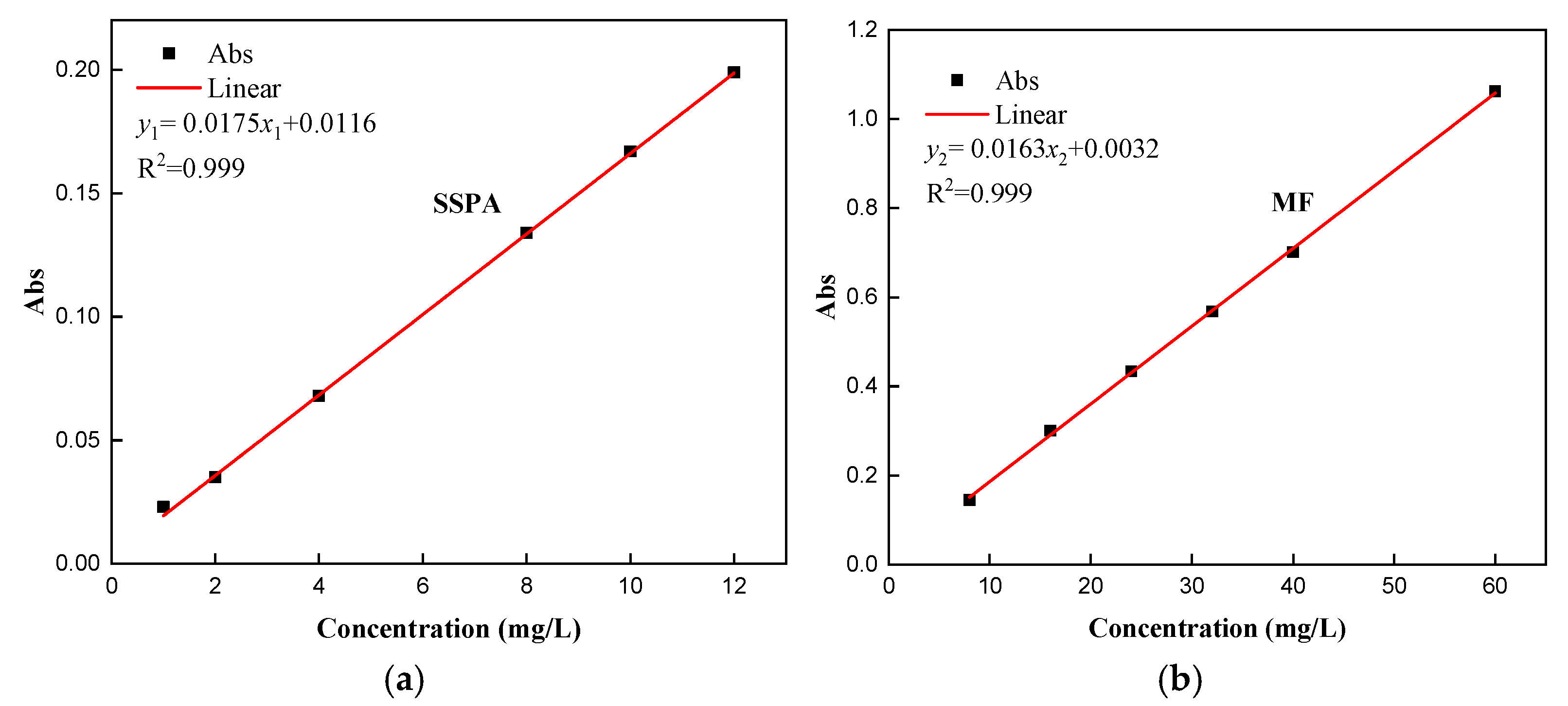
- Standard curve.
- (2)
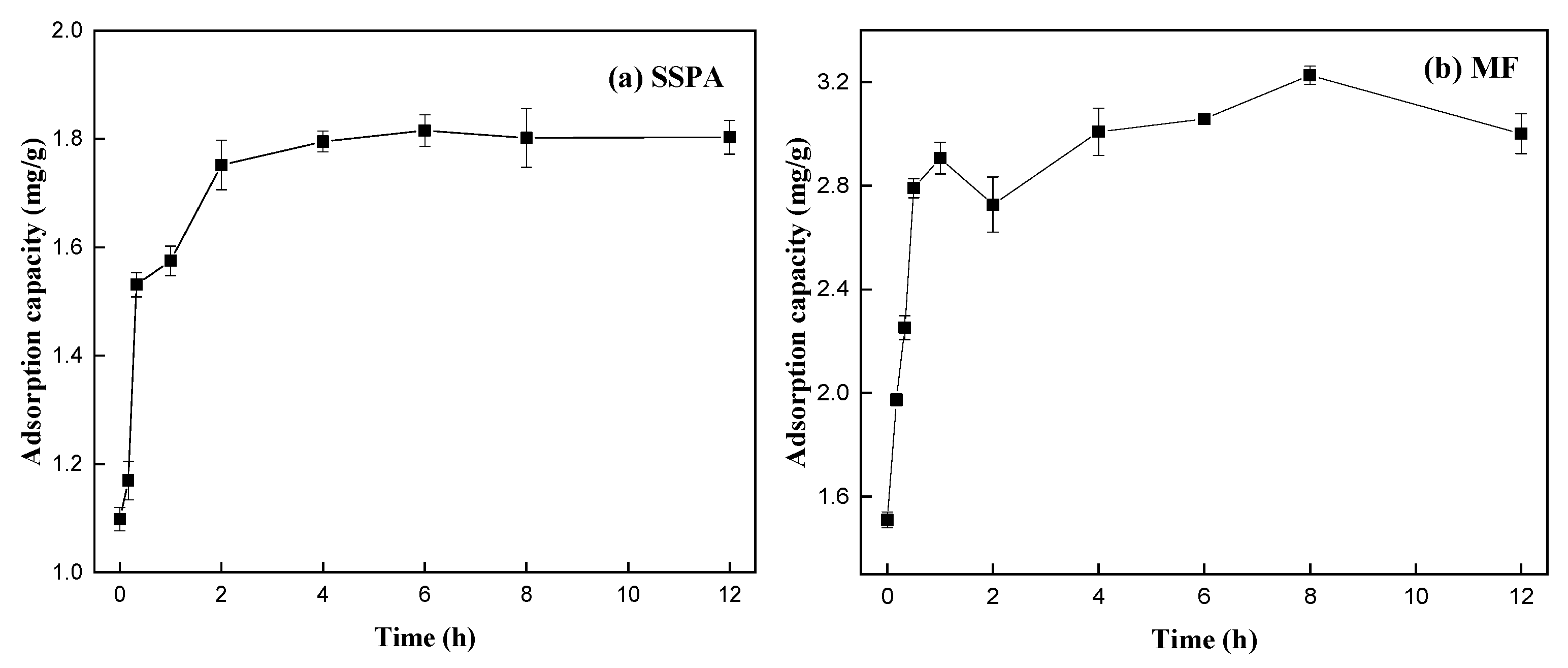
- Adsorption equilibrium and kinetic analysis.
- (3)
- Isothermal adsorption analysis.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Reagents
3.3. Methods
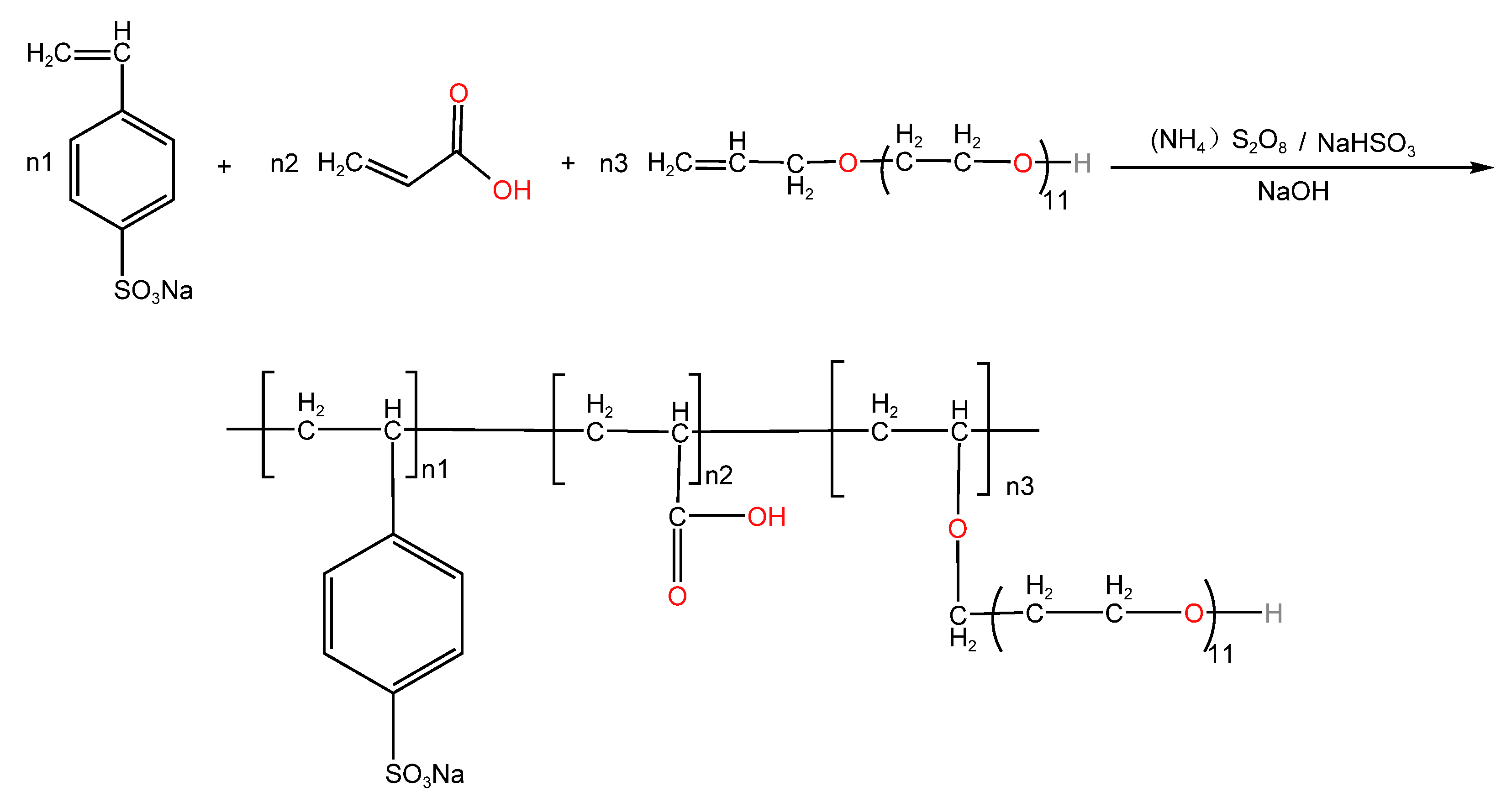
3.3.1. Preparation of Dispersants
3.3.2. Preparation of CWS
3.3.3. Contact Angle Test
3.3.4. Zeta Potential Test
3.3.5. Determination of Characteristic Functional Groups
3.3.6. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
3.3.7. Nuclear Magnetic Hydrogen Spectroscopy
3.3.8. Adsorption Experiment
- (1)
- Dsorption equilibrium and kinetics.
- (2)
- Isothermal adsorption experiment.
3.3.9. Stability Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, J.; Li, S. Clean Coal and Sustainable Energy; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Feng, Y.; He, Q.; Yan, W.; Yuan, M.; Hu, B. Review and perspectives of anionic dispersants for coal–water slurry. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 4816–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; You, X. Study on the slurry characteristics and surface microscopic interactions mechanism of diesel modified low-rank coal. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 37, 124237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Effects of coal structure and oxygen-containing functional groups on the wettability of low-rank coal. Fuel 2018, 217, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, S. Study on the influence of oxygen-containing groups and pore structure of low-rank coal on the stability of coal-water slurry. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, D.; Qiu, X.; Feng, W. Study on enhancing the slurry performance of coal–water slurry prepared with low-rank coal. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, C.; Lin, M.; Liu, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Cao, X.; You, X. Study of sodium lignosulfonate prepare low-rank coal-water slurry: Experiments and simulations. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 29, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Miao, Z.; Shang, T. Synthesis and performance of a comblike amphoteric polycarboxylate dispersant for coal–water slurry. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 412, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Wu, C.; Weng, L.; Liu, K. Influence of different dispersants on rheological behaviors of coal water slurry prepared from a low quality coal. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32911–32921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Sengupta, M. Nature and properties of humic acid prepared from different sources and its effect on nutrient availability. Plant Soil 1985, 88, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, M.; Lou, H. Properties of sodium lignosulfonate as dispersant of coal water slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qiu, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, M. Physicochemical properties of calcium lignosulfonate with different molecular weights as dispersant in aqueous suspension. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2008, 29, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, P.; Llorens, J. Understanding of naphthalene sulfonate formaldehyde condensates as a dispersing agent to stabilise raw porcelain gres suspensions: Surface adsorption and rheological behaviour. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 299, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhuang, W.; He, Q.; Cai, J.; Hu, B.; Shen, J. Effects of chemical structure on the properties of carboxylate-type copolymer dispersant for coal-water slurry. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Zhang, S.; Yi, C.; Qiu, X. Effect of polycarboxylic acid used as high-performance dispersant on low-rank coal-water slurry. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, P.; Yan, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, M. Effects of temperature and bleeding on rheology of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 403, 133085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Experimental Study of Alkali-Activated Cementitious Materials Using Thermally Activated Red Mud: Effect of the Si/Al Ratio on Fresh and Mechanical Properties. Buildings 2025, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Lyu, J.; He, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; You, X. Study on characteristics of coal gasification fine slag-coal water slurry slurrying, combustion, and ash fusion. Fuel 2023, 332, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Gao, X.; Feng, G.; Bai, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, X. Effect of biomass power plant ash on fresh properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussout, H.; Ahlafi, H.; Aazza, M.; Maghat, H. Critical of linear and nonlinear equations of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2018, 4, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, E.; Nas, M. Batch kinetic and equilibrium studies of adsorption of Reactive Blue 21 by fly ash and sepiolite. Desalination 2009, 243, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.E.; Matsumoto, M.R. Modeling cadmium adsorption by activated carbon using the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm expressions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-K.; Kim, W.-H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.; Jeong, T.-Y.; Park, P.-K. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms to predict adsorbate removal efficiency or required amount of adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, D. Adsorption behaviour of microplastics on the heavy metal Cr (VI) before and after ageing. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalkhal, F.; Negi, A.S.; Harrison, J.; Stokes, C.D.; Morgan, D.L.; Osuji, C.O. Evaluating the dispersant stabilization of colloidal suspensions from the scaling behavior of gel rheology and adsorption measurements. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Rulli, F.; Crestini, C. Gel permeation chromatography in determining molecular weights of lignins: Critical aspects revisited for improved utility in the development of novel materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dispersant | Mw [g/mol] | Mn [g/mol] | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSPA | 13,504 | 9443 | 1.43 |
| Dispersant | τ0/mPa | K/(mPa·sn) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | 9506 | 4294 | 0.7629 | 0.99907 |
| SSPA | 3614 | 1513 | 0.8280 | 0.99925 |
| Dispersant | PFO | PSO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe1, mg/g | K1 | R2 | qe2, mg/g | K2 | R2 | |
| PA | 1.817 | 0.3915 | 0.5301 | 1.817 | 0.5498 | 0.9977 |
| MF | 3.23 | 0.2722 | 0.4035 | 3.23 | 0.3244 | 0.9981 |
| Dispersant | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm, mg/g | KL, L/mg | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| SSPA | 2.03 | 0.0094 | 0.981 | 4.81 | 0.41 | 0.809 |
| MF | 4.03 | 0.0086 | 0.989 | 3.70 | 0.52 | 0.891 |
| Sample | Industrial Analysis, % | Elemental Analysis, % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FCad | Cad | Had | Nad | Sad | Oad | |
| Coal | 10.04 | 4.73 | 29.76 | 55.47 | 76.22 | 4.05 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 3.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; He, M.; You, X. The Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Dispersants Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Groups and Their Performance in Promoting Coal Particle Dispersion. Molecules 2025, 30, 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122493
Li L, Li Z, Yang S, Ma C, Zhang W, He M, You X. The Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Dispersants Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Groups and Their Performance in Promoting Coal Particle Dispersion. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122493
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Zhisen Li, Shuo Yang, Chuandong Ma, Wenqi Zhang, Meng He, and Xiaofang You. 2025. "The Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Dispersants Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Groups and Their Performance in Promoting Coal Particle Dispersion" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122493
APA StyleLi, L., Li, Z., Yang, S., Ma, C., Zhang, W., He, M., & You, X. (2025). The Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Dispersants Containing Benzenesulfonic Acid Groups and Their Performance in Promoting Coal Particle Dispersion. Molecules, 30(12), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122493





