Carbon Black Single Piece Electrodes for Nitrate Ion Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Membrane Characteristics
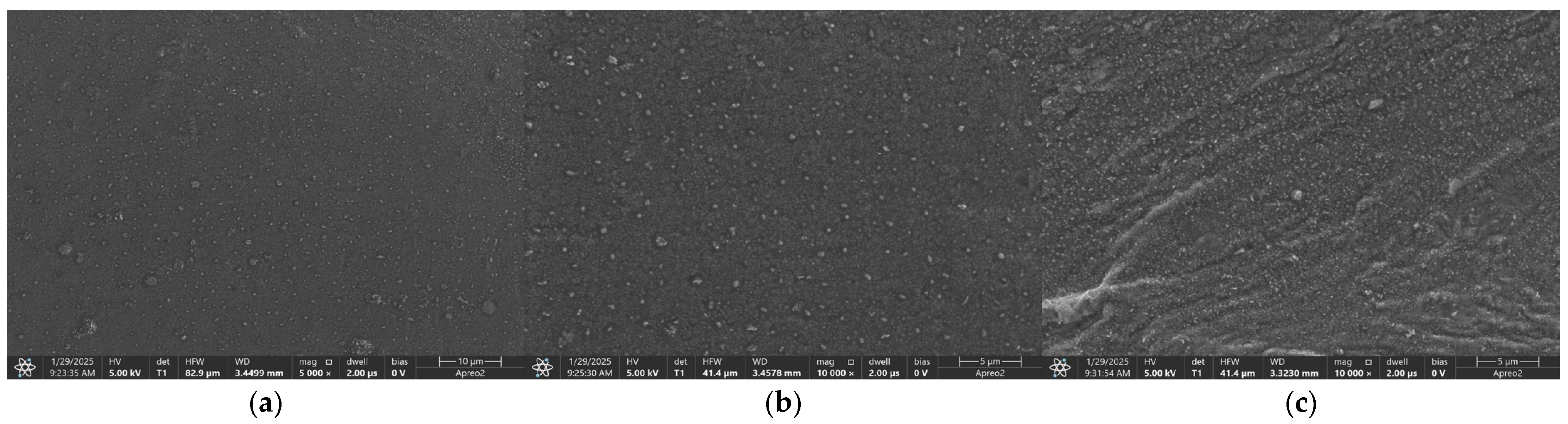
2.1.1. Microstructure
2.1.2. Wettability
2.1.3. Electrical Properties
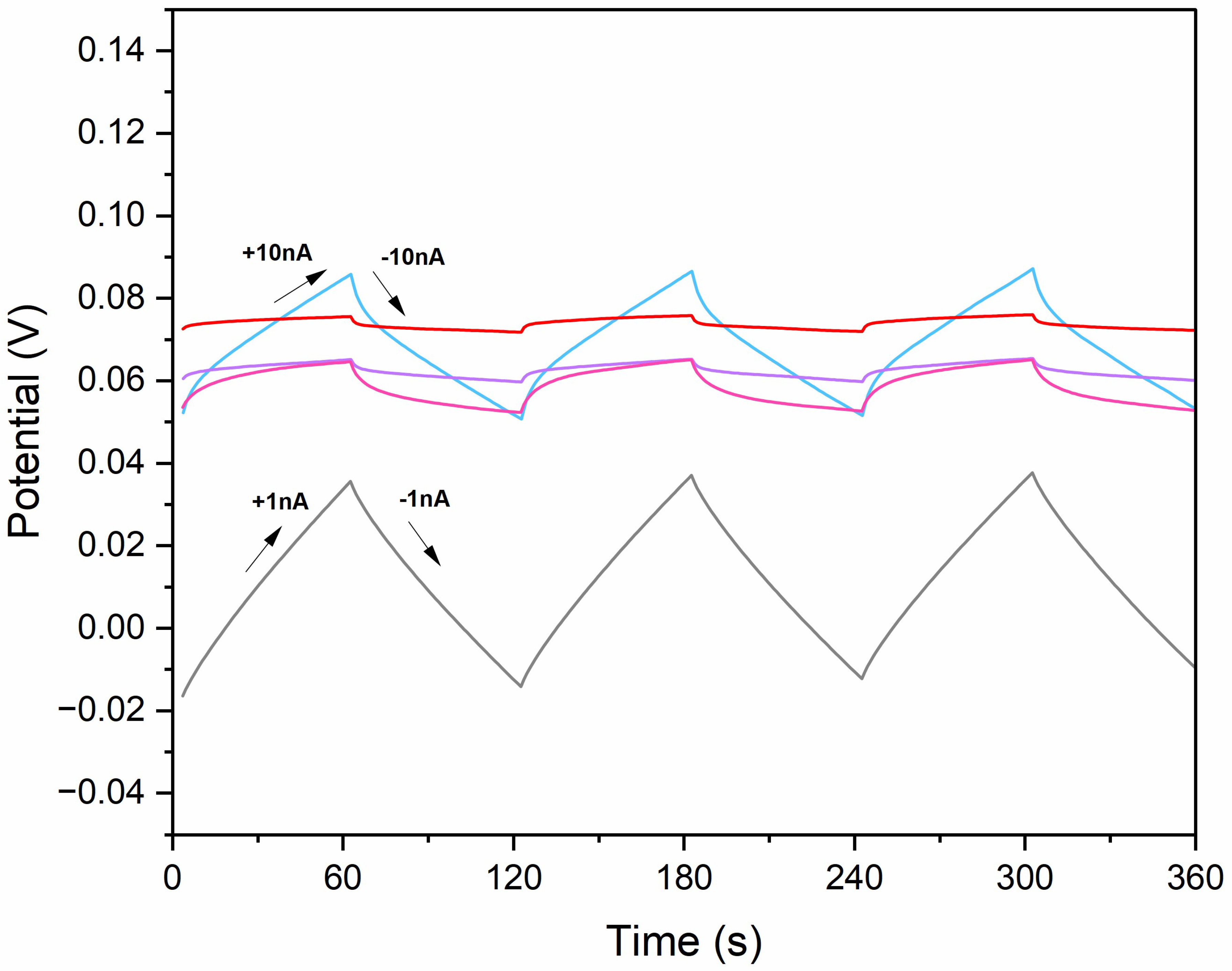
Chronopotentiometry
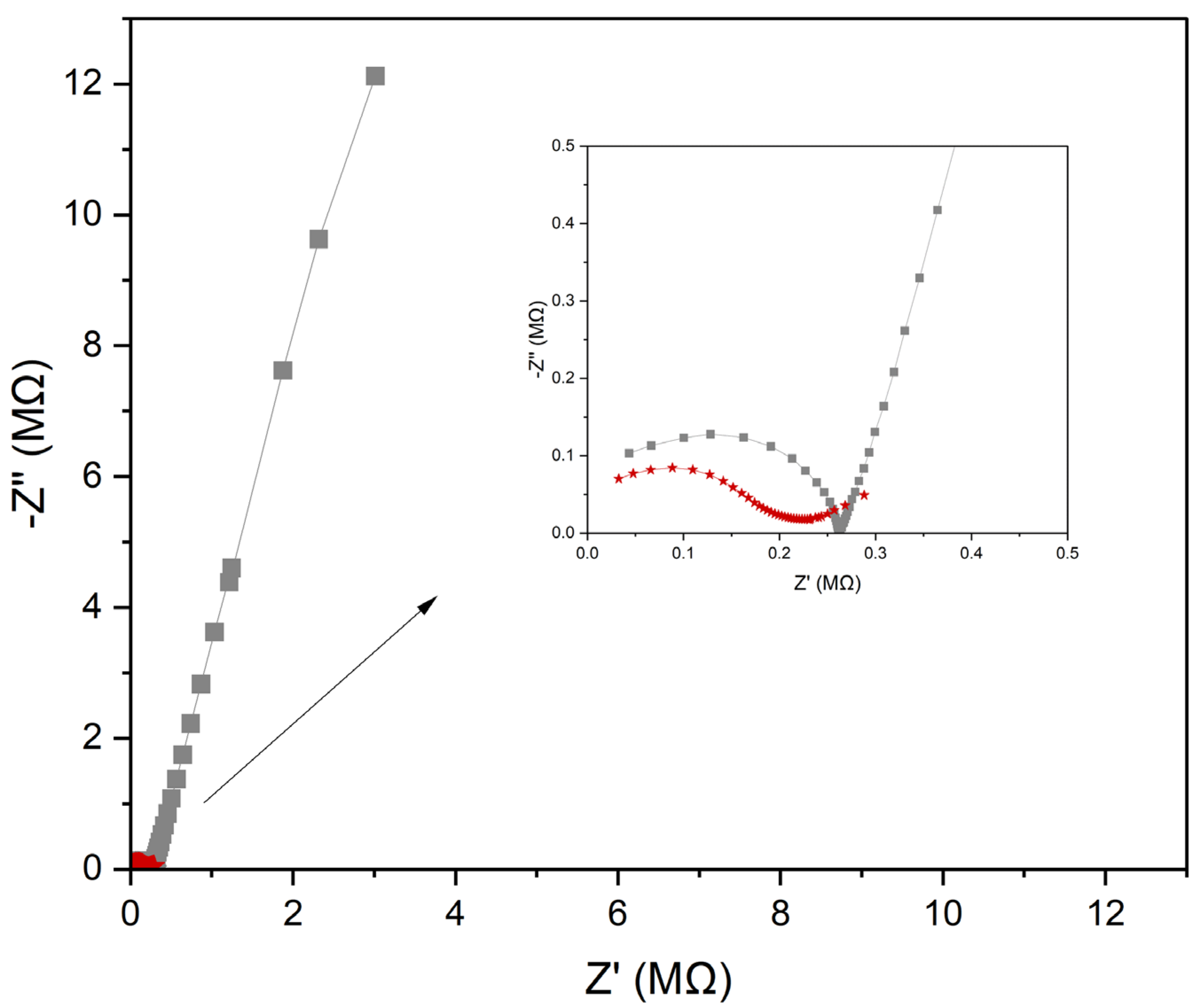
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
2.2. Analytical Properties of Sensor
2.2.1. Ionic Response
2.2.2. Water Layer Test
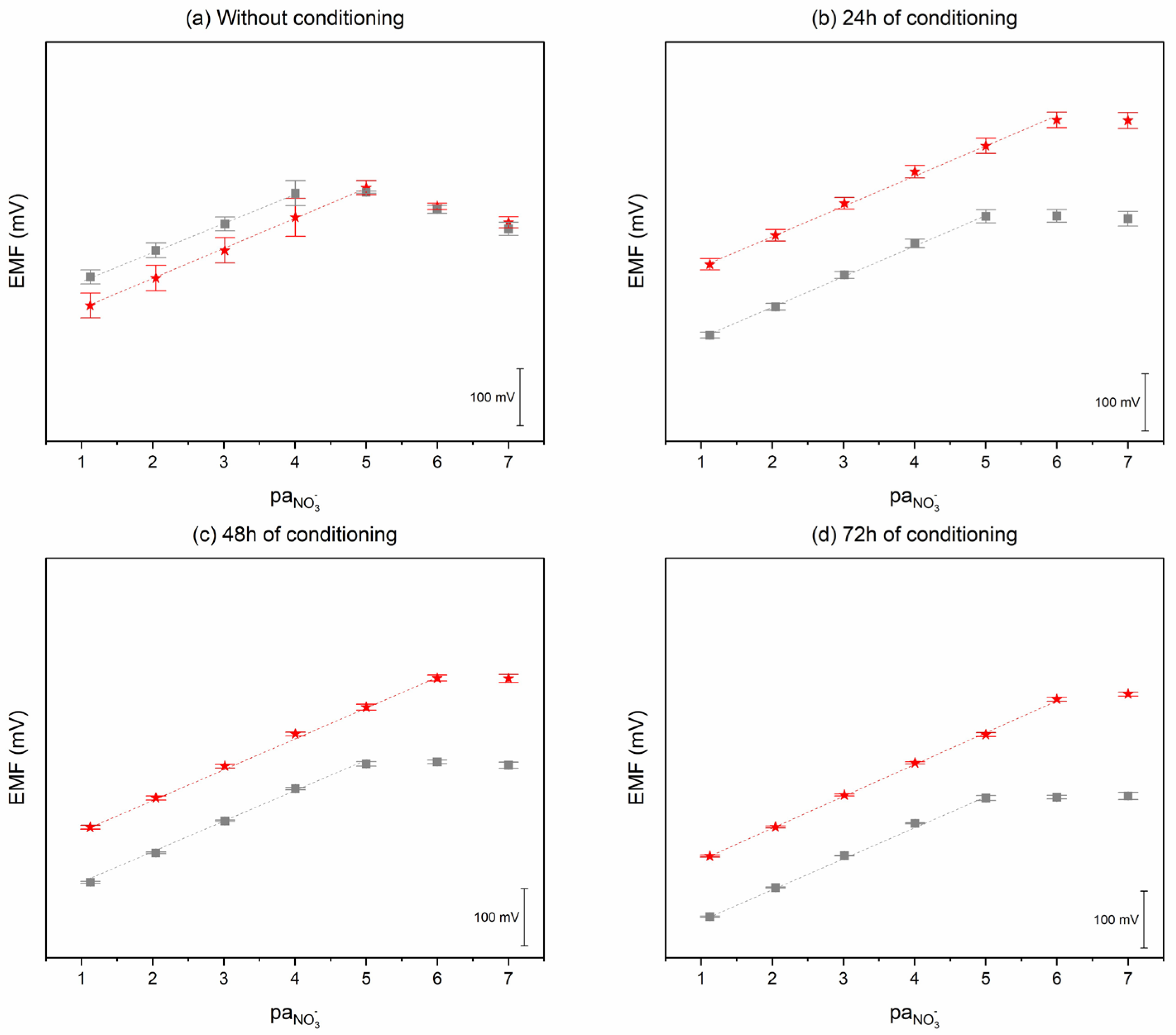
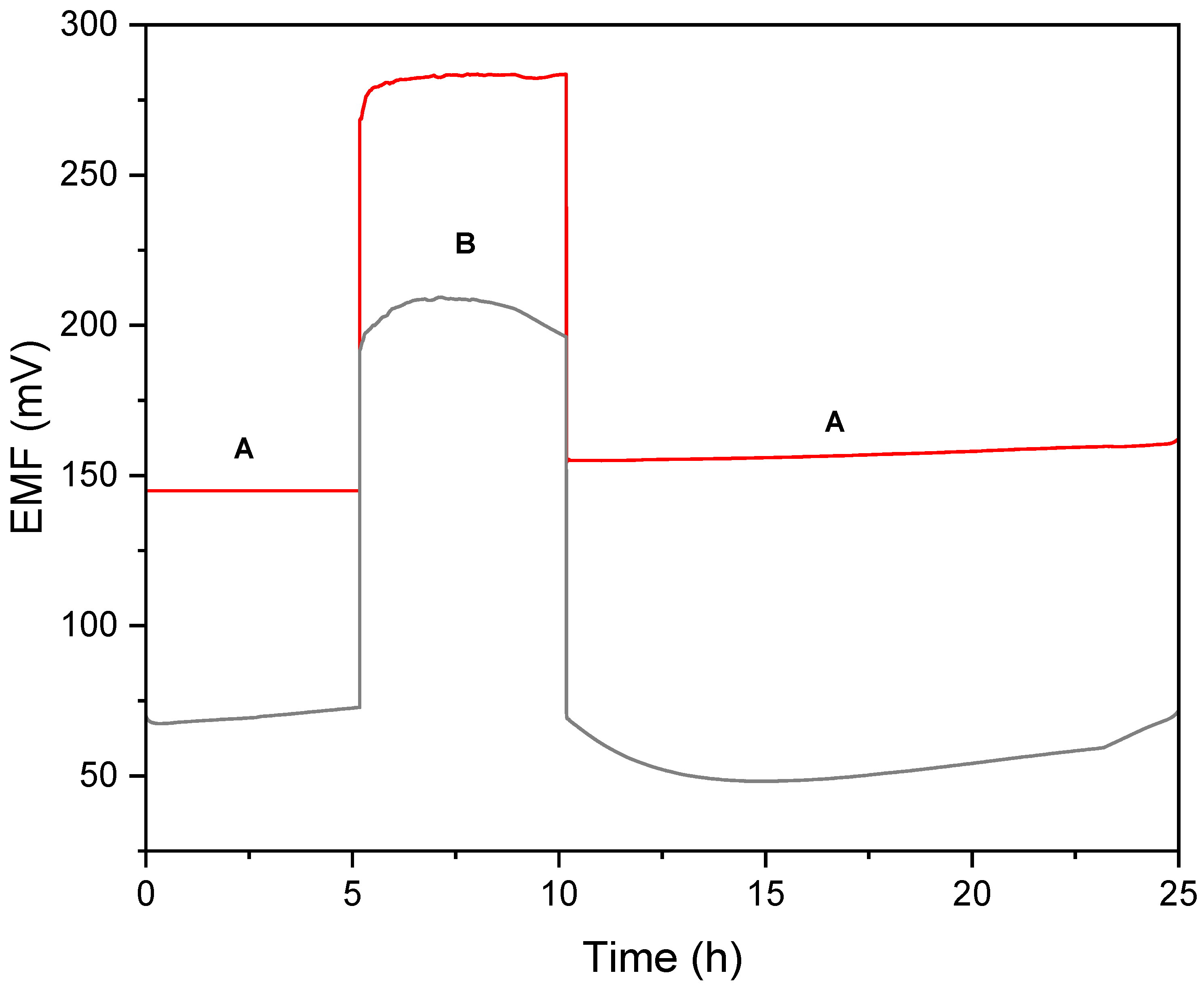
2.2.3. Potential Stability
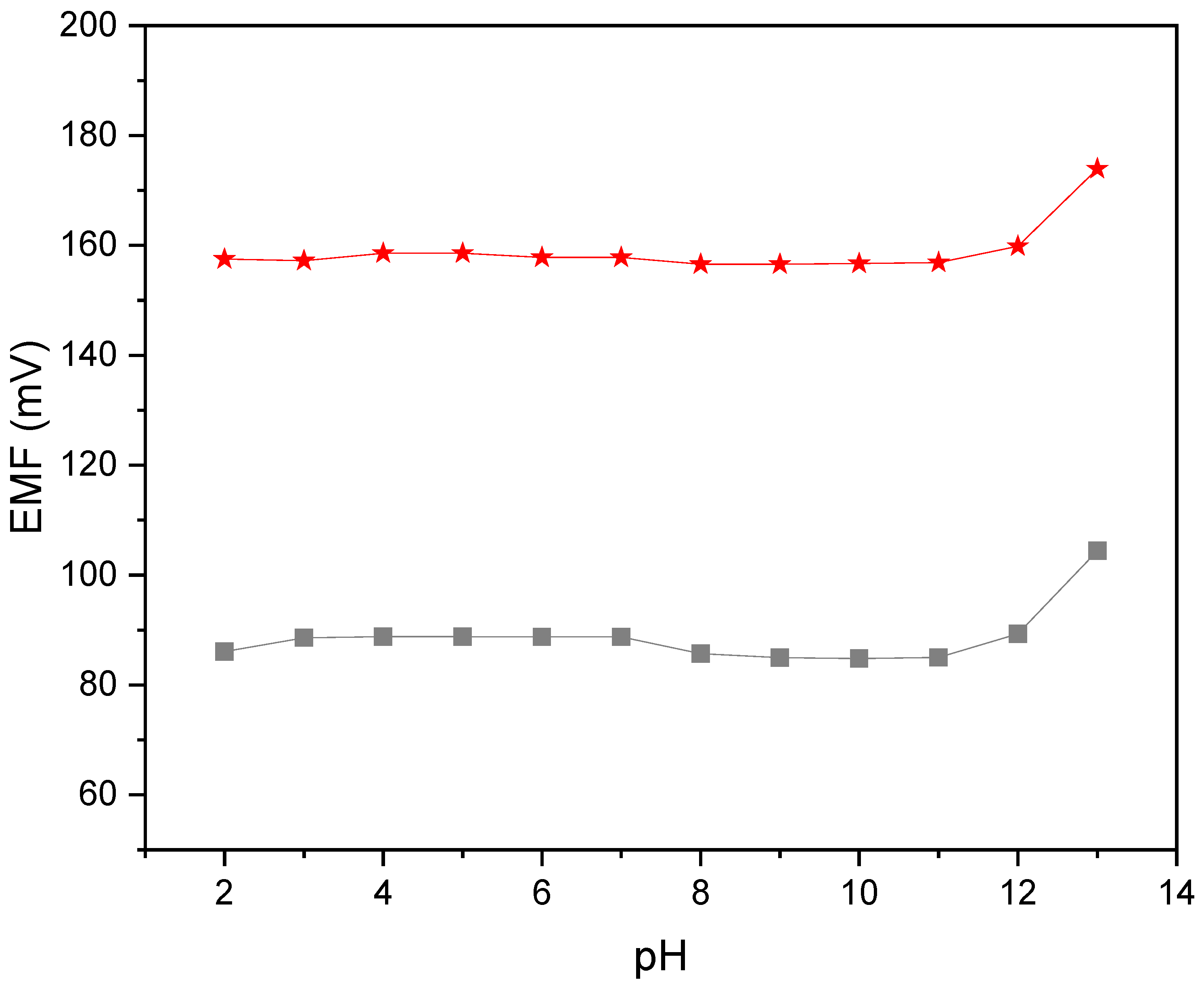
2.2.4. pH Sensitivity
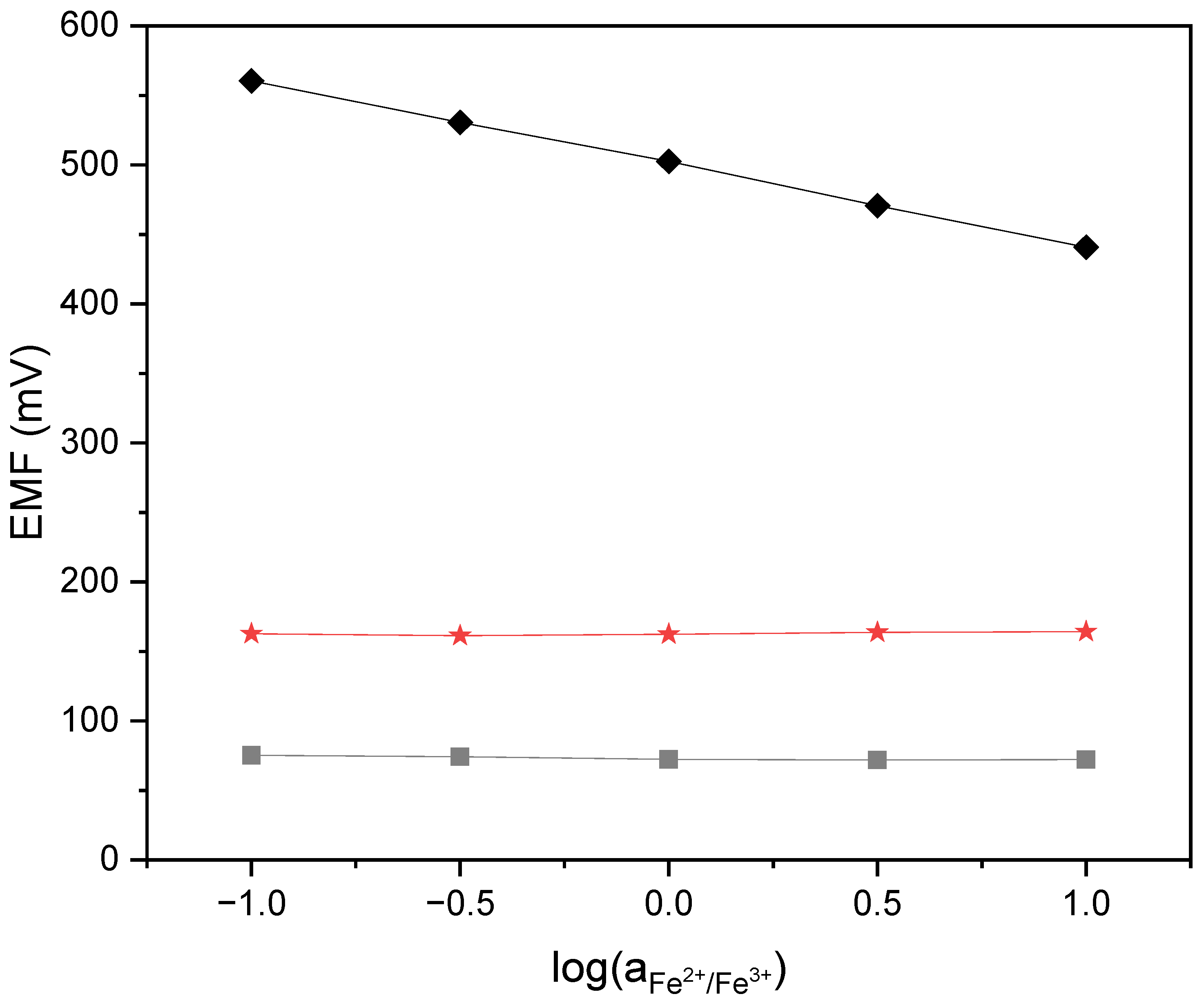
2.2.5. Redox Sensitivity
2.3. Application of Sensors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sensor Preparation
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.H.; DeKok, T.M.; Levallois, P.; Brender, J.; Gulis, G.; Nolan, B.T.; VanDerslice, J. Workgroup Report: Drinking-Water Nitrate and Health—Recent Findings and Research Needs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretsch, E. The new wave of ion-selective electrodes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Pretsch, E. Polymer Membrane Ion-Selective Electrodes-What are the Limits? Electroanalysis 1999, 11, 915–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, A.; Pyrzyńska, K.; Maksymiuk, K. Method of Achieving Desired Potentiometric Responses of Polyacrylate-Based Ion-Selective Membranes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3921–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Bakker, E. Spectral Imaging and Electrochemical Study on the Response Mechanism of Ionophore-Based Polymeric Membrane Amperometric pH Sensors. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, G.S.; Liu, D.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Cantor, H.C.; Midgley, A.R.; Goldberg, H.D.; Brown, R.B. Electrochemical performance, biocompatibility, and adhesion of new polymer matrixes for solid-state ion sensors. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbioli, M.; Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; de Rooij, N.F.; Pretsch, E. Potential Drifts of Solid-Contacted Ion-Selective Electrodes Due to Zero-Current Ion Fluxes Through the Sensor Membrane. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadogan, A.; Gao, Z.; Lewenstam, A.; Ivaska, A.; Diamond, D. All-solid-state sodium-selective electrode based on a calixarene ionophore in a poly(vinyl chloride) membrane with a polypyrrole solid contact. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenar, N.; Piech, R.; Paczosa-Bator, B. High Capacity Nanocomposite Layers Based on Nanoparticles of Carbon Materials and Ruthenium Dioxide for Potassium Sensitive Electrode. Materials 2021, 14, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J.; Lindfors, T.; McCarrick, M.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Single-piece all-solid-state ion-selective electrode. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 3819–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, E.; Maksymiuk, K.; Michalska, A. Adding Plasticizer Dispersible Conducting Polymer to the Ion-selective Membrane Composition—Revitalizing Single Piece Ion-selective Electrodes Concept. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, D.; Lu, M.; Lin, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Jiao, L.; Ye, Z.; Lu, J. Single-Piece Membrane Supercapacitor with Exceptional Areal/Volumetric Capacitance via Double-Face Print of Electrode/Electrolyte Active Ink. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P. A general approach to one-step fabrication of single-piece nanocomposite membrane based Pb2+-selective electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-D.; Wang, W.-J.; Wang, G.-J. Electrochemical Detection of Electrolytes Using a Solid-State Ion-Selective Electrode of Single-Piece Type Membrane. Biosensors 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.; Ahmed, M.A.; Amr, A.E.-G.E.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Kamel, A.H.; Khalifa, N.M. Single-Piece All-Solid-State Potential Ion-Selective Electrodes Integrated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) for Neutral 2,4-Dichlorophenol Assessment. Materials 2019, 12, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, C.; Grabarczyk, M. Single-piece all-solid-state Co(II) ion-selective electrode for cobalt monitoring in real samples. Int. Agrophys 2019, 1, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Jiao, L.; Jia, F.; Ye, J.; Li, F.; Gan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ivaska, A.; Niu, L. Robust single-piece all-solid-state potassium-selective electrode with monolayer-protected Au clusters. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Single-piece solid-contact ion-selective electrodes with polymer–carbon nanotube composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2010, 148, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Gupta, A.; Haque, B.; Qureshi, A.A.; Verma, D.; Sharma, K.; Lee, S.F.; Hee, C.W.; Roy, A.; Verma, R. An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity. Green Process. Synth. 2024, 13, 20240150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrott, G.S.J.; Thiessen, R. Carbon Black—Its Properties and Uses. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1920, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa-Bator, B. All-solid-state selective electrodes using carbon black. Talanta 2012, 93, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobacka, J. Potential Stability of All-Solid-State Ion-Selective Electrodes Using Conducting Polymers as Ion-to-Electron Transducers. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4932–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzinski, M.; Jarvis, J.M.; D’Orazio, P.; Izadyar, A.; Pendley, B.D.; Lindner, E. Solid-Contact pH Sensor without CO2 Interference with a Superhydrophobic PEDOT-C 14 as Solid Contact: The Ultimate ‘Water Layer’ Test. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8468–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Hao, H.; He, Z. Mechanisms and assessment of water eutrophication. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenar, N.; Drużyńska, M.; Piech, R.B. Paczosa-Bator. Ion-Selective Electrode for Nitrates Based on a Black PCV Membrane. Molecules 2024, 29, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Electrode Symbol | Current [nA] | Resistance ± SD [kΩ] | Electrical Capacitance ± SD [µF] |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC/NO3-ISM | 1 | 810 ± 12 | 1.22 ± 0.05 |
| GC/CB(1%)/NO3-ISM | 10 | 655 ± 10 | 23.2 ± 0.7 |
| GC/CB(2%)/NO3-ISM | 10 | 549 ± 9 | 227 ± 2 |
| GC/CB(4%)/NO3-ISM | 10 | 450 ± 8 | 302 ± 3 |
| GC/CB(5%)/NO3-ISM | 10 | 421 ± 8 | 610 ± 5 |
| Electrode Symbol | Sensitivity S ± SD [mV] | Standard Potential E0 ± SD [mV] | Linear Range [M] | Limit of Detection [M] | Potential Stability [mV/h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC/CB(5%)/NO3-ISM | 56.15 ± 0.50 | 115.1 ± 0.5 | 10−1–10−6 | 7 × 10−7 | 0.052 |
| GC/NO3-ISM | 56.60 ± 0.78 | 7.9 ± 2.2 | 10−1–10−5 | 1 × 10−5 | 2.18 |
| Water Body | Nitrate Concentration ± SD [µg/L] | Recovery [%] | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wisłok | 214 ± 1 | 102 | 7.6 |
| Wisła | 443 ± 7 | 99 | 7.7 |
| Rudawa | 358 ± 12 | 98 | 7.5 |
| Zakrzówek | 143 ± 7 | 101 | 8.0 |
| Additive to Membrane | Ion | Slope [mV/dec] | Linear Range [M] | Electrical Capacity [µF] | Potential Drift | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POT | Li+ | 56.80 | 10−1–10−3 | - | 0.8 mV/day | [11] |
| PANI | Ca2+ | 28.20 | 10−1–10−4 | - | 0.2 mV/day | |
| MWCNTs | Na+ | 58.00 | 10−1–10−6 | - | 0.3 mV/day | [19] |
| K+ | 59.10 | 10−1–10−6 | - | 0.5 mV/day | ||
| Cu2+ | 28.90 | 10−1–10−6 | - | 0.3 mV/day | ||
| Ca2+ | 29.20 | 10−1–10−6 | - | 0.3 mV/day | ||
| 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride | Co2+ | 31.80 | 10−1–10−7 | - | 0.15 mV/day | [17] |
| PANI | 2,4-dichlorophenol (DCP) | 0.47–13 µM | 15 | - | [16] | |
| MWCNTs | Pb2+ | 29.00 | 2 × 10−3–2 × 10−9 | 50 | - | [14] |
| CB | K+ | 58.80 | 10−1–10−6 | 429 | 0.009 mV/h | [23] |
| CB | NO3− | 54.22 | 10−1–10−6 | 211 | 0.087 mV/h | [27] |
| CNTs | 54.15 | 10−1–10−6 | 88 | 0.082 mV/h | ||
| GR | 54.32 | 10−1–10−6 | 931 | 0.065 mV/h | ||
| CB | NO3− | 56.15 | 10−1–10−6 | 610 | 0.052 mV/h | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drużyńska, M.; Kikas, T.; Lenar, N.; Paczosa-Bator, B. Carbon Black Single Piece Electrodes for Nitrate Ion Sensing. Molecules 2025, 30, 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112405
Drużyńska M, Kikas T, Lenar N, Paczosa-Bator B. Carbon Black Single Piece Electrodes for Nitrate Ion Sensing. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112405
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrużyńska, Martyna, Timo Kikas, Nikola Lenar, and Beata Paczosa-Bator. 2025. "Carbon Black Single Piece Electrodes for Nitrate Ion Sensing" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112405
APA StyleDrużyńska, M., Kikas, T., Lenar, N., & Paczosa-Bator, B. (2025). Carbon Black Single Piece Electrodes for Nitrate Ion Sensing. Molecules, 30(11), 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112405








