Valerenic Acid and Pinoresinol as Positive Allosteric Modulators: Unlocking the Sleep-Promoting Potential of Valerian Extract Ze 911
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
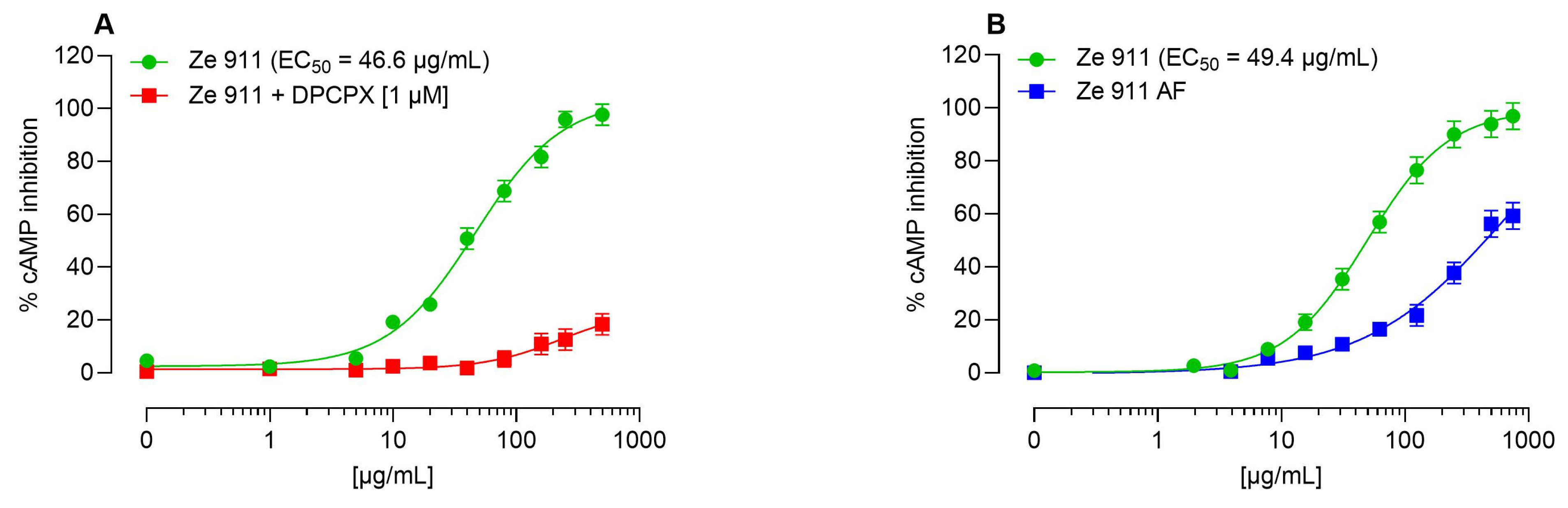
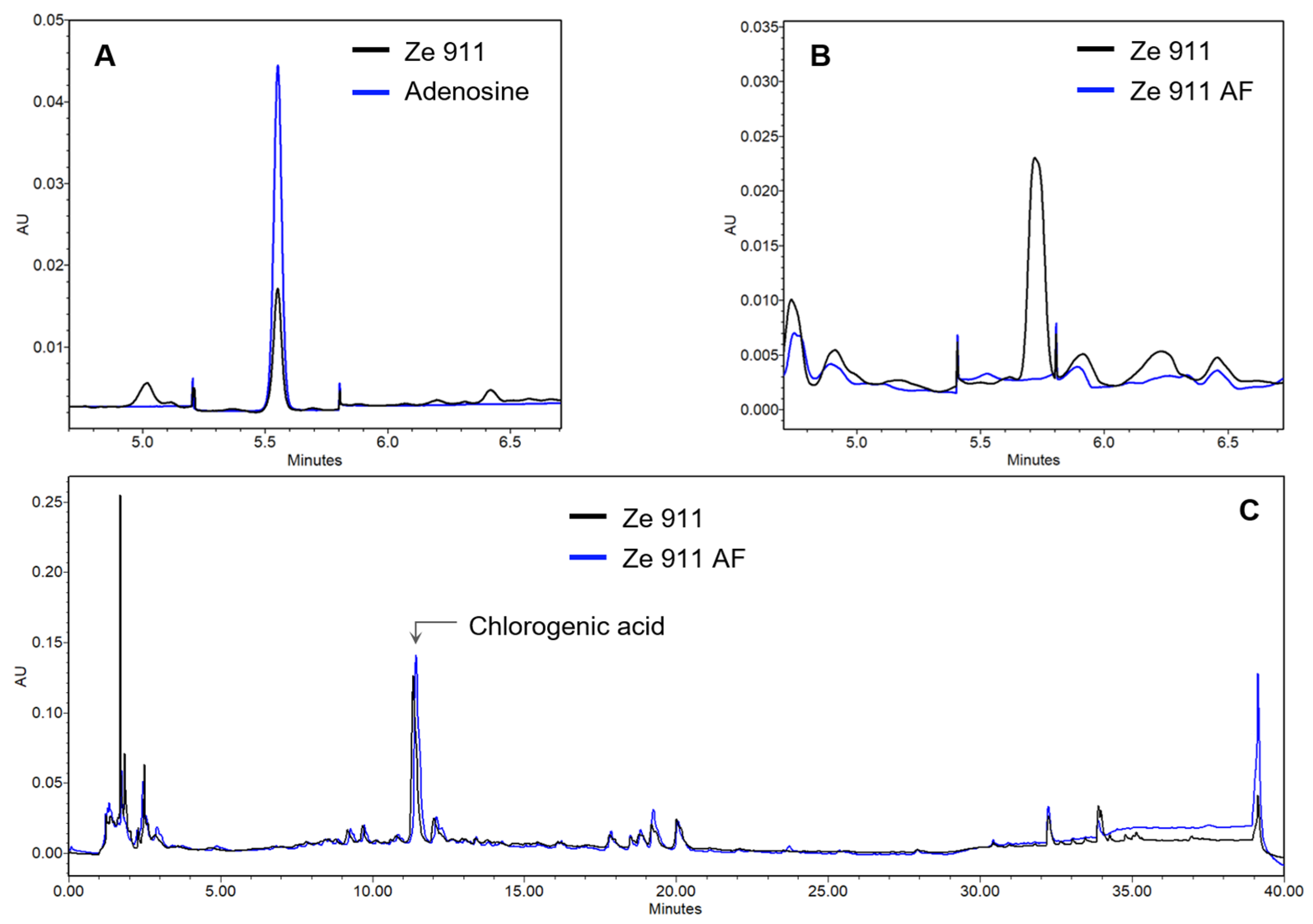
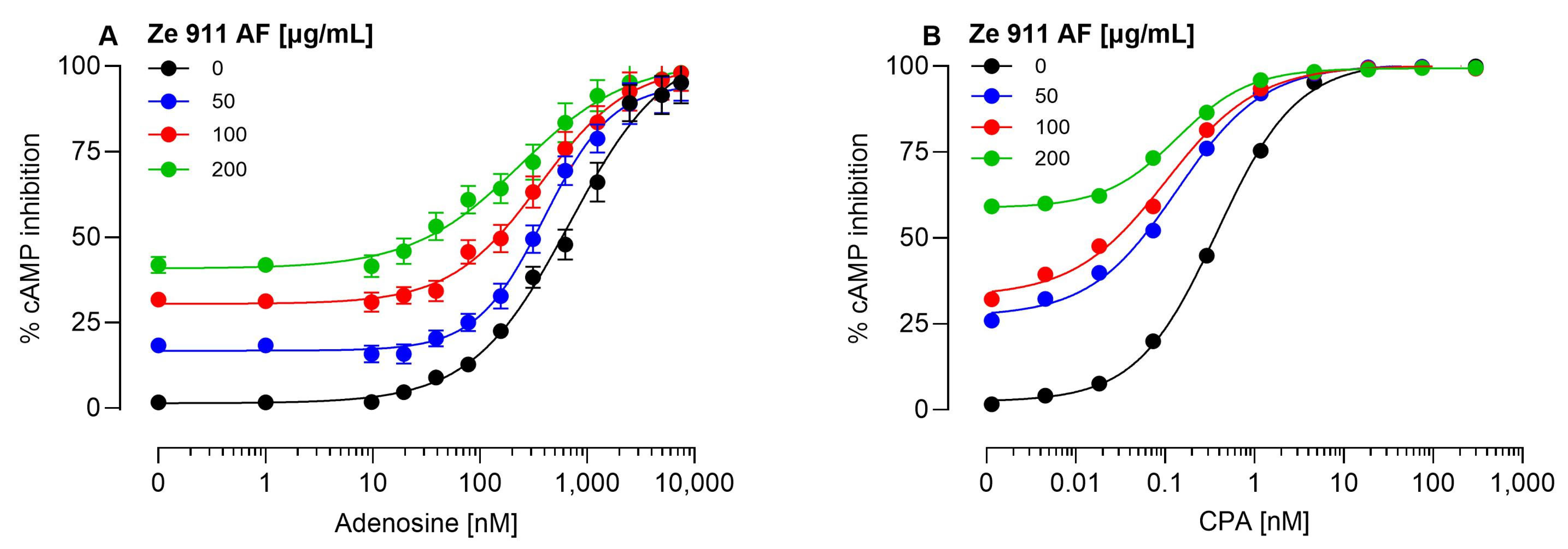
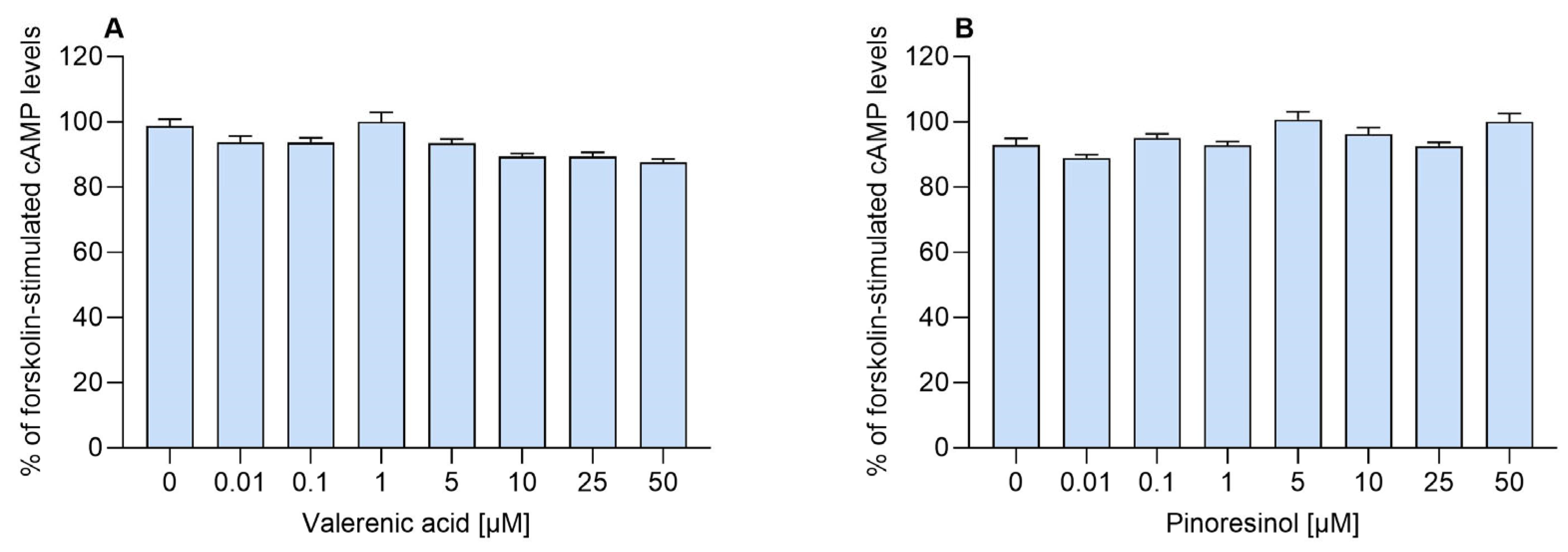
2.1. Direct Agonist Activity and the Role of Adenosine
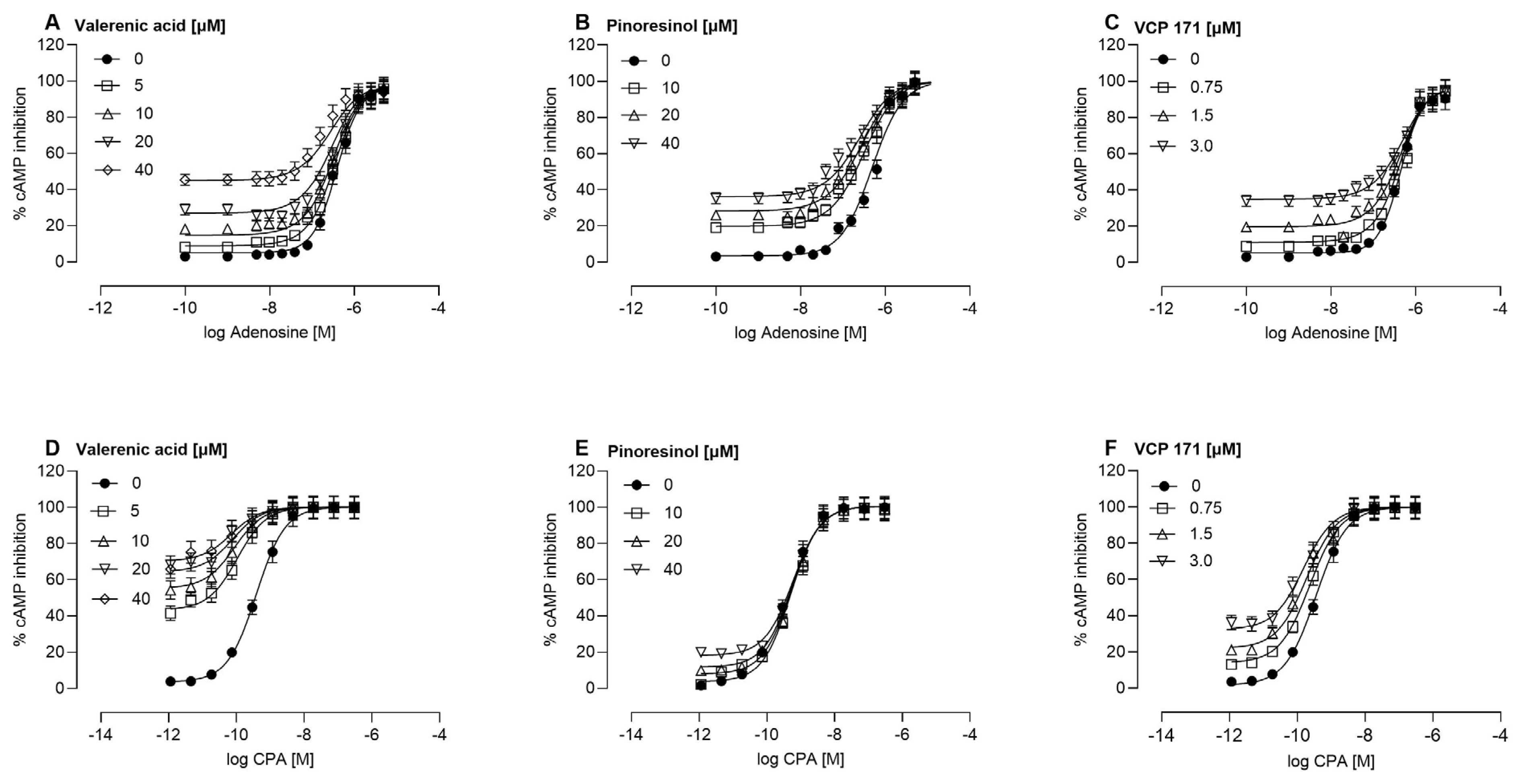
2.2. Allosteric Modulation of the A1AR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. cAMP Assay
4.4. Data Analysis
4.5. UPLC Analytics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A1AR | Adenosine A1 receptor |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CPA | N6-cyclopentyladenosine |
| GABA | Gamma aminobutyric acid |
| NAM | Negative allosteric modulator |
| PAM | Positive allosteric modulator |
References
- Bauer, R.B.W.; Buff, W.; CLassen, B.; Heise, E.M.; Hensel, A.; Krenn, L.; Lichius, J.J.; Lindequist, U.; Loew, D.; Melzig, M.F.; et al. Baldrianwurzel—Valeriana radix. In Wichtl—Teedrogen und Phytopharmaka, 6th ed.; Blaschek, W., Ed.; Wissenschaft liche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 2016; pp. 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- HMPC. Assessment Report on Valeriana officinalis L. Radix and Valeriana officinalis L. Aetheroleum; EMA/HMPC/150846/2015; EMA: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Benke, D.; Barberis, A.; Kopp, S.; Altmann, K.H.; Schubiger, M.; Vogt, K.E.; Rudolph, U.; Mohler, H. GABA A receptors as in vivo substrate for the anxiolytic action of valerenic acid, a major constituent of valerian root extracts. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, B.M.; Mahady, G.B.; Pauli, G.F.; Farnsworth, N.R. Valerian extract and valerenic acid are partial agonists of the 5-HT5a receptor in vitro. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 138, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khom, S.; Strommer, B.; Ramharter, J.; Schwarz, T.; Schwarzer, C.; Erker, T.; Ecker, G.F.; Mulzer, J.; Hering, S. Valerenic acid derivatives as novel subunit-selective GABAA receptor ligands—In vitro and in vivo characterization. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.E.; Schumacher, B.; Brattstrom, A.; Abourashed, E.A.; Koetter, U. Interactions of valerian extracts and a fixed valerian-hop extract combination with adenosine receptors. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sichardt, K.; Vissiennon, Z.; Koetter, U.; Brattstrom, A.; Nieber, K. Modulation of postsynaptic potentials in rat cortical neurons by valerian extracts macerated with different alcohols: Involvement of adenosine A(1)- and GABA(A)-receptors. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauner, G.; Khom, S.; Baburin, I.; Benedek, B.; Hering, S.; Kopp, B. Modulation of GABAA receptors by valerian extracts is related to the content of valerenic acid. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, A.; Avula, B.; Choi, Y.W.; Khan, I.A. Chemical fingerprinting of valeriana species: Simultaneous determination of valerenic acids, flavonoids, and phenylpropanoids using liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E. A Review Focused on Molecular Mechanisms of Anxiolytic Effect of Valerina officinalis L. in Connection with Its Phytochemistry through in vitro/in vivo Studies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinelli, A.L.; Arana, S.; Caceres, A.; di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R.; Rastrelli, L. New lignans from the roots of Valeriana prionophylla with antioxidative and vasorelaxant activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Ran, X.H.; Chen, R.; Luo, H.R.; Ma, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hu, J.M.; Huang, S.Z.; Jiang, H.Z.; Chen, Z.Q.; et al. Sesquiterpenoids and lignans from the roots of Valeriana officinalis L. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.P.; Wasowski, C.; Loscalzo, L.M.; Granger, R.E.; Johnston, G.A.; Paladini, A.C.; Marder, M. Central nervous system depressant action of flavonoid glycosides. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 539, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srednicka-Tober, D.; Hallmann, E.; Kopczynska, K.; Goralska-Walczak, R.; Baranski, M.; Grycz, A.; Seidler-Lozykowska, K.; Rembialkowska, E.; Kazimierczak, R. Profile of Selected Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Valerian and Lovage Grown in Organic and Low-Input Conventional System. Metabolites 2022, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintersteiner, J.; Haider, M.; Luger, D.; Schwarzer, C.; Reznicek, G.; Jager, W.; Khom, S.; Mihovilovic, M.D.; Hering, S. Esters of valerenic acid as potential prodrugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 735, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudal, D.; Guinobert, I.; Lafoux, A.; Bardot, V.; Cotte, C.; Ripoche, I.; Chalard, P.; Huchet, C. Skeletal muscle relaxant effect of a standardized extract of Valeriana officinalis L. after acute administration in mice. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacher, S.K.; Mayer, R.; Sichardt, K.; Nieber, K.; Muller, C.E. Interaction of valerian extracts of different polarity with adenosine receptors: Identification of isovaltrate as an inverse agonist at A1 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.; Scholle, S.; Holzl, J.; Khudeir, N.; Hess, S.; Muller, C.E. Lignans isolated from valerian: Identification and characterization of a new olivil derivative with partial agonistic activity at A(1) adenosine receptors. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissiennon, Z.; Sichardt, K.; Koetter, U.; Brattstrom, A.; Nieber, K. Valerian extract Ze 911 inhibits postsynaptic potentials by activation of adenosine A1 receptors in rat cortical neurons. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberg, R.; Sauer, S.; Abourashed, E.A.; Koetter, U.; Brattstrom, A. The fixed combination of valerian and hops (Ze91019) acts via a central adenosine mechanism. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorness, T.E.; Kelly, C.L.; Gao, T.; Poffenberger, V.; Greene, R.W. Control and function of the homeostatic sleep response by adenosine A1 receptors. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, S.; Contri, C.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F. Adenosine Receptors in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Fine Regulators of Neurotransmission and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Dai, W.; Li, S.; Xu, H. Functions and mechanisms of adenosine and its receptors in sleep regulation. Sleep Med. 2024, 115, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, S.; Contri, C.; Cappello, M.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F. Update on the recent development of allosteric modulators for adenosine receptors and their therapeutic applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1030895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.N.; Tran, Q.L.; Baltos, J.A.; McNeill, S.M.; Nguyen, D.T.N.; May, L.T. Small molecule allosteric modulation of the adenosine A(1) receptor. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1184360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.J.; May, L.T.; Kellam, B.; Woolard, J. Allosteric interactions at adenosine A(1) and A(3) receptors: New insights into the role of small molecules and receptor dimerization. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, C.J. Determining allosteric modulator mechanism of action: Integration of radioligand binding and functional assay data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 746, 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, S.L.; Soave, M.; Jorg, M.; Scammells, P.J.; Woolard, J.; Hill, S.J. Probe dependence of allosteric enhancers on the binding affinity of adenosine A(1)-receptor agonists at rat and human A(1)-receptors measured using NanoBRET. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.P.; Macleod, J.K.; Parker, C.W.; Letham, D.S.; Hunt, N.H. Identification and quantitation of adenosine-3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate in plants using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography. Planta 1981, 152, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper-Joyce, C.J.; Bhola, R.; Wang, J.; Bhattarai, A.; Nguyen, A.T.N.; Cowie-Kent, I.; O’Sullivan, K.; Chia, L.Y.; Venugopal, H.; Valant, C.; et al. Positive allosteric mechanisms of adenosine A(1) receptor-mediated analgesia. Nature 2021, 597, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.D.; Elmer, G.W.; Kantor, E.D.; Templeton, I.E.; Vitiello, M.V. Pharmacokinetics of valerenic acid after administration of valerian in healthy subjects. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, C.; Haug, K.; Thanei, S.; Hamburger, M.; Derendorf, H.; Frye, R.; Butterweck, V. Pharmacokinetics of valerenic acid in rats after intravenous and oral administrations. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Salamon, A.; Trauner, G.; Hiltscher, R.; Reznicek, G.; Kopp, B.; Thalhammer, T.; Jager, W. Hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion of valerenic acid in isolated perfused rat livers: Role of Mrp2 (Abcc2). J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, W.; Trauner, G.; Gruber, D.; Oelzant, S.; Klepal, W.; Kopp, B.; Noe, C.R. Transport of a GABAA receptor modulator and its derivatives from Valeriana officinalis L. s. l. across an in vitro cell culture model of the blood-brain barrier. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Vecchio, E.A.; Thomas, T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Aurelio, L.; Scammells, P.J.; White, P.J.; Sexton, P.M.; Gregory, K.J.; May, L.T.; et al. Role of the Second Extracellular Loop of the Adenosine A1 Receptor on Allosteric Modulator Binding, Signaling, and Cooperativity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimatrai-Salvador, M.; Baraldi, P.G.; Romagnoli, R. Allosteric modulation of A1-adenosine receptor: A review. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e285–e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.-G.; Tosh, D.K.; Jain, S.; Yu, J.; Suresh, R.R.; Jacobson, K.A. A1 Adenosine Receptor Agonists, Antagonists, and Allosteric Modulators. In The Adenosine Receptors; Borea, P.A., Varani, K., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 59–89. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Reitman, M.L. Adenosine-Related Mechanisms in Non-Adenosine Receptor Drugs. Cells 2020, 9, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, N.D.; Khatib, A.; Link-Struensee, A.M.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Rungkat-Zakaria, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Adenosine A1 receptor binding activity of methoxy flavonoids from Orthosiphon stamineus. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Xanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists. In Methylxanthines; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 151–199. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, E.D.; da Costa, P.F.; Medeiros, L.F.; Souza, A.; Battastini, A.M.; von Poser, G.L.; Bonan, C.; Torres, I.L.; Rates, S.M. Uliginosin B, a Possible New Analgesic Drug, Acts by Modulating the Adenosinergic System. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 5890590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.L.; Yu, G.; Yi, S.P.; Zhang, F.Y.; Wang, Z.T.; Huang, B.; Su, R.B.; Jia, Y.X.; Gong, Z.H. Antinociceptive effects of incarvillateine, a monoterpene alkaloid from Incarvillea sinensis, and possible involvement of the adenosine system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Valerenic Acid | Pinoresinol | VCP 171 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 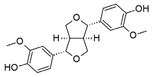 | 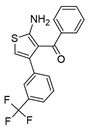 | ||||
| Adenosine | CPA | Adenosine | CPA | Adenosine | CPA | |
| a logKB | −3.61 | −4.75 | −4.58 | −3.5 | −5.02 | −4.96 |
| b KB [µM] | 243.78 | 17.42 | 25.82 | 316.23 | 9.38 | 10.76 |
| c LogτB | 0.77 | 0.49 | −0.03 | 0.22 | 0.42 | 0.3 |
| b τB | 5.98 | 3.14 | 0.93 | 1.66 | 2.66 | 1.99 |
| d Logαβ | 0.68 | 1.36 | 0.53 | −0.1 | −0.43 | 1.11 |
| b αβ | 4.79 | 23.38 | 3.42 | 0.79 | 0.37 | 12.73 |
| Goodness of fit (R2) | 0.9916 | 0.9963 | 0.9921 | 0.9956 | 0.9921 | 0.9961 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senn, R.; Schertler, L.; Bussmann, H.; Drewe, J.; Boonen, G.; Butterweck, V. Valerenic Acid and Pinoresinol as Positive Allosteric Modulators: Unlocking the Sleep-Promoting Potential of Valerian Extract Ze 911. Molecules 2025, 30, 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112344
Senn R, Schertler L, Bussmann H, Drewe J, Boonen G, Butterweck V. Valerenic Acid and Pinoresinol as Positive Allosteric Modulators: Unlocking the Sleep-Promoting Potential of Valerian Extract Ze 911. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112344
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenn, Roman, Lukas Schertler, Hendrik Bussmann, Juergen Drewe, Georg Boonen, and Veronika Butterweck. 2025. "Valerenic Acid and Pinoresinol as Positive Allosteric Modulators: Unlocking the Sleep-Promoting Potential of Valerian Extract Ze 911" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112344
APA StyleSenn, R., Schertler, L., Bussmann, H., Drewe, J., Boonen, G., & Butterweck, V. (2025). Valerenic Acid and Pinoresinol as Positive Allosteric Modulators: Unlocking the Sleep-Promoting Potential of Valerian Extract Ze 911. Molecules, 30(11), 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112344







