The Effect of Quercetin Loading in Polylactic Acid-Based Electrospun Fibers on Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Electrospinning of Fibrous Mats
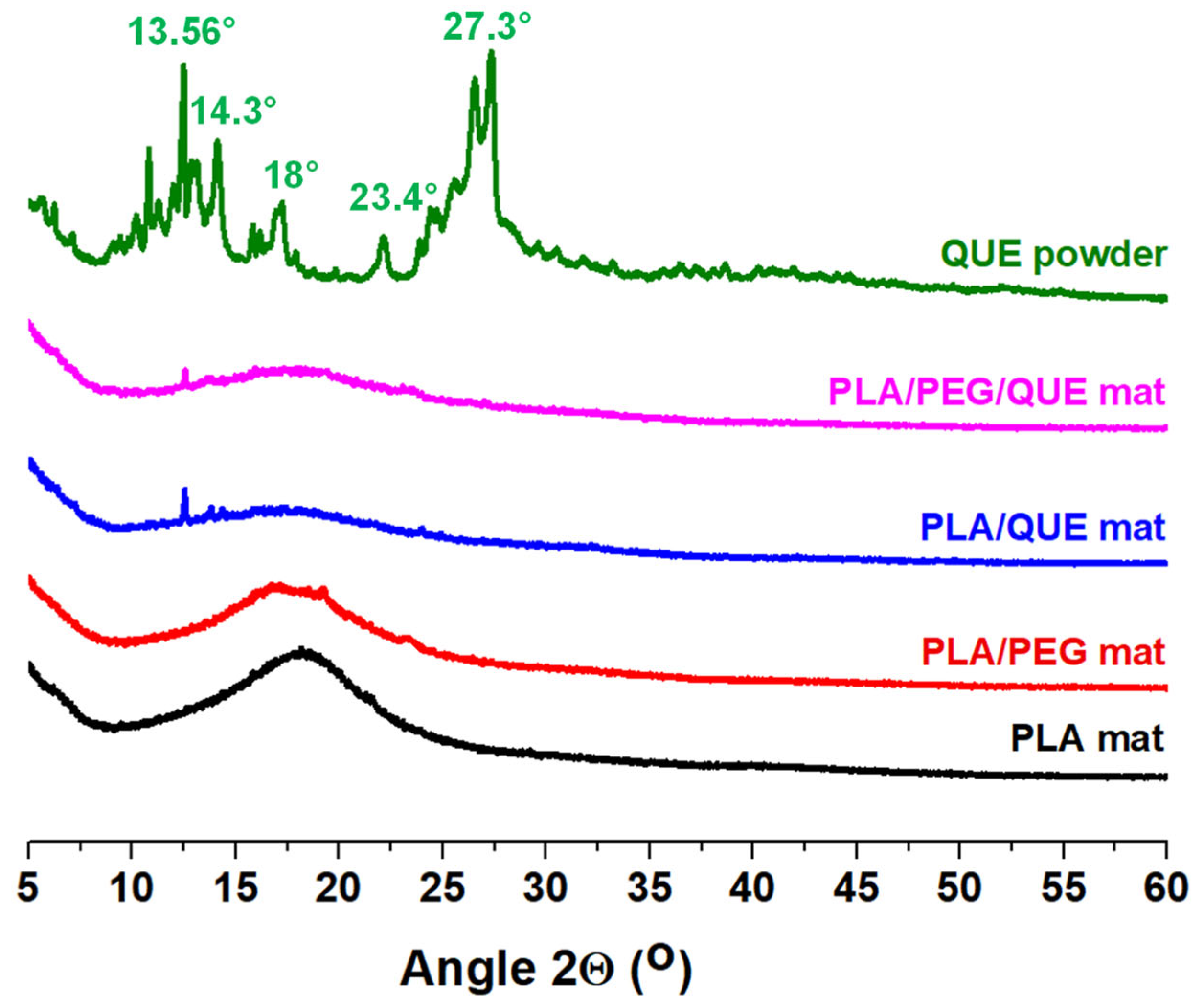
2.2. X-Ray Diffraction Characterization
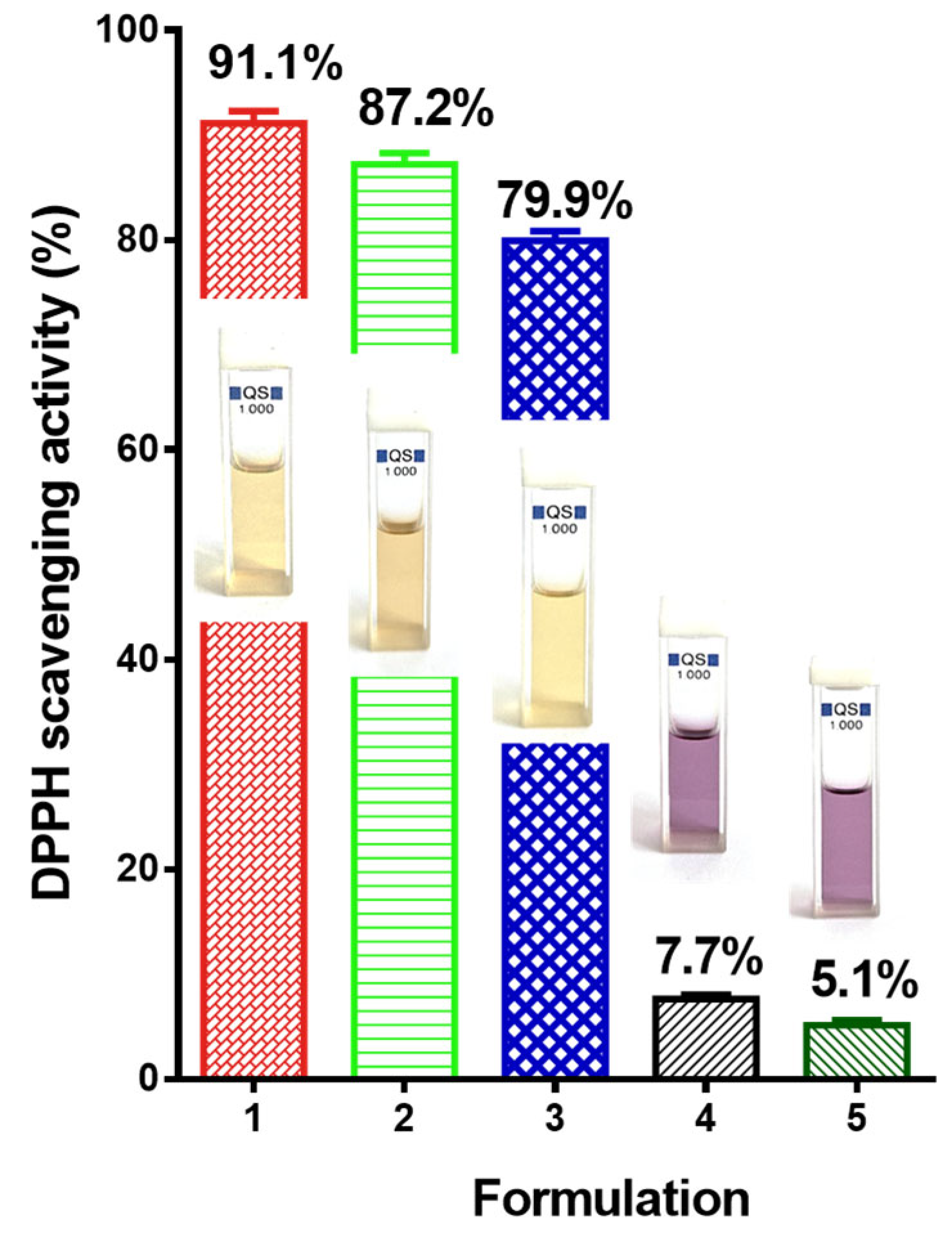
2.3. Determining Antioxidant Activity
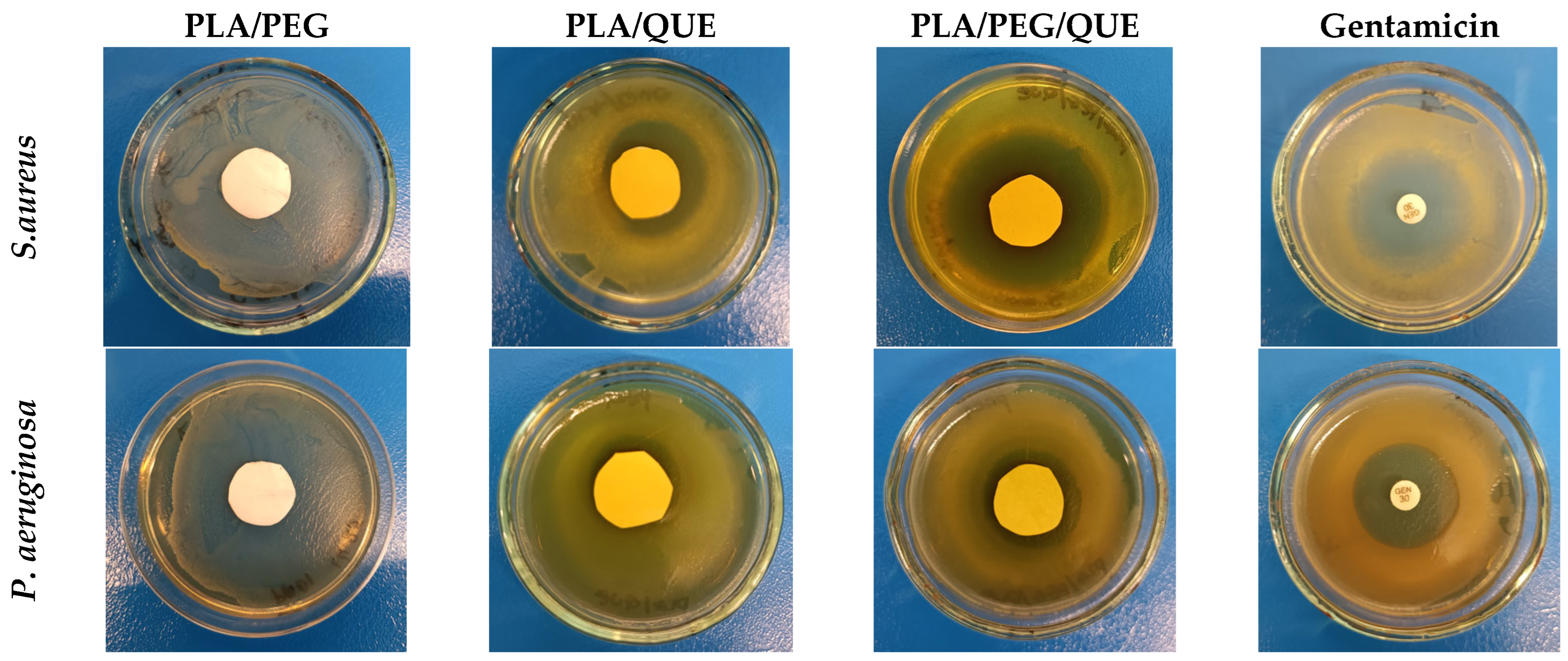
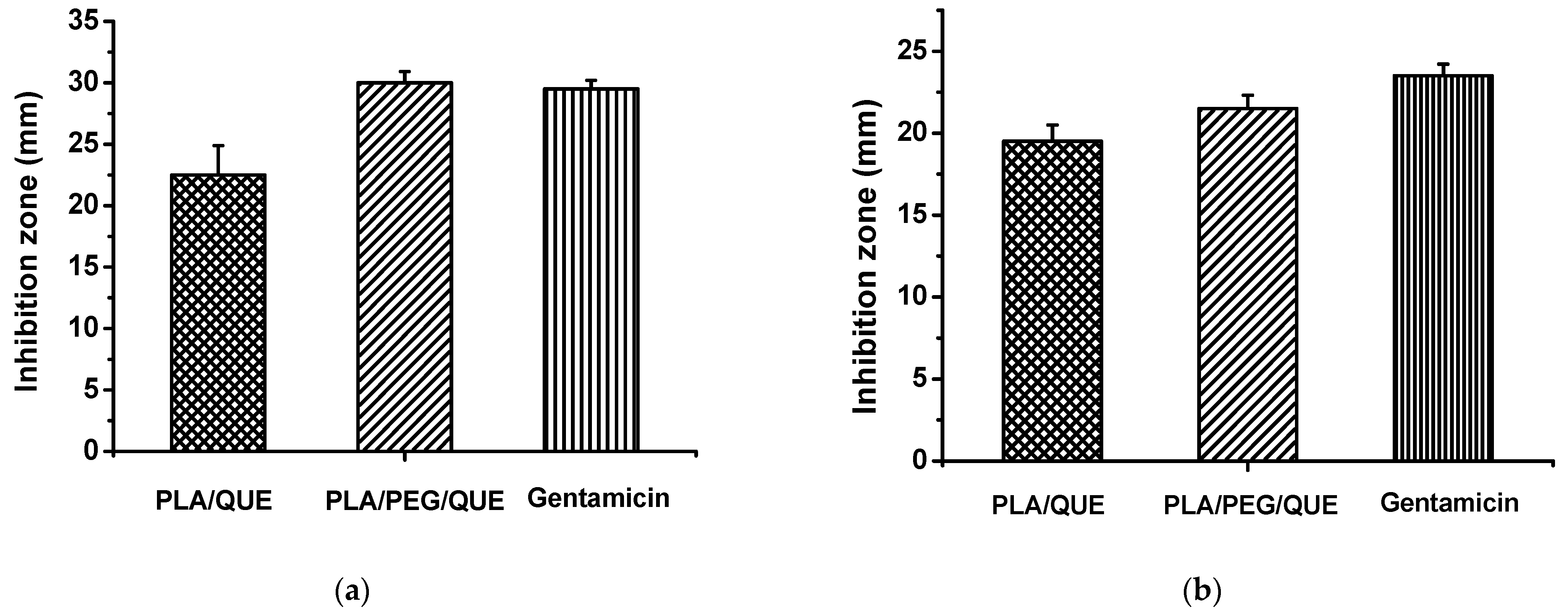
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
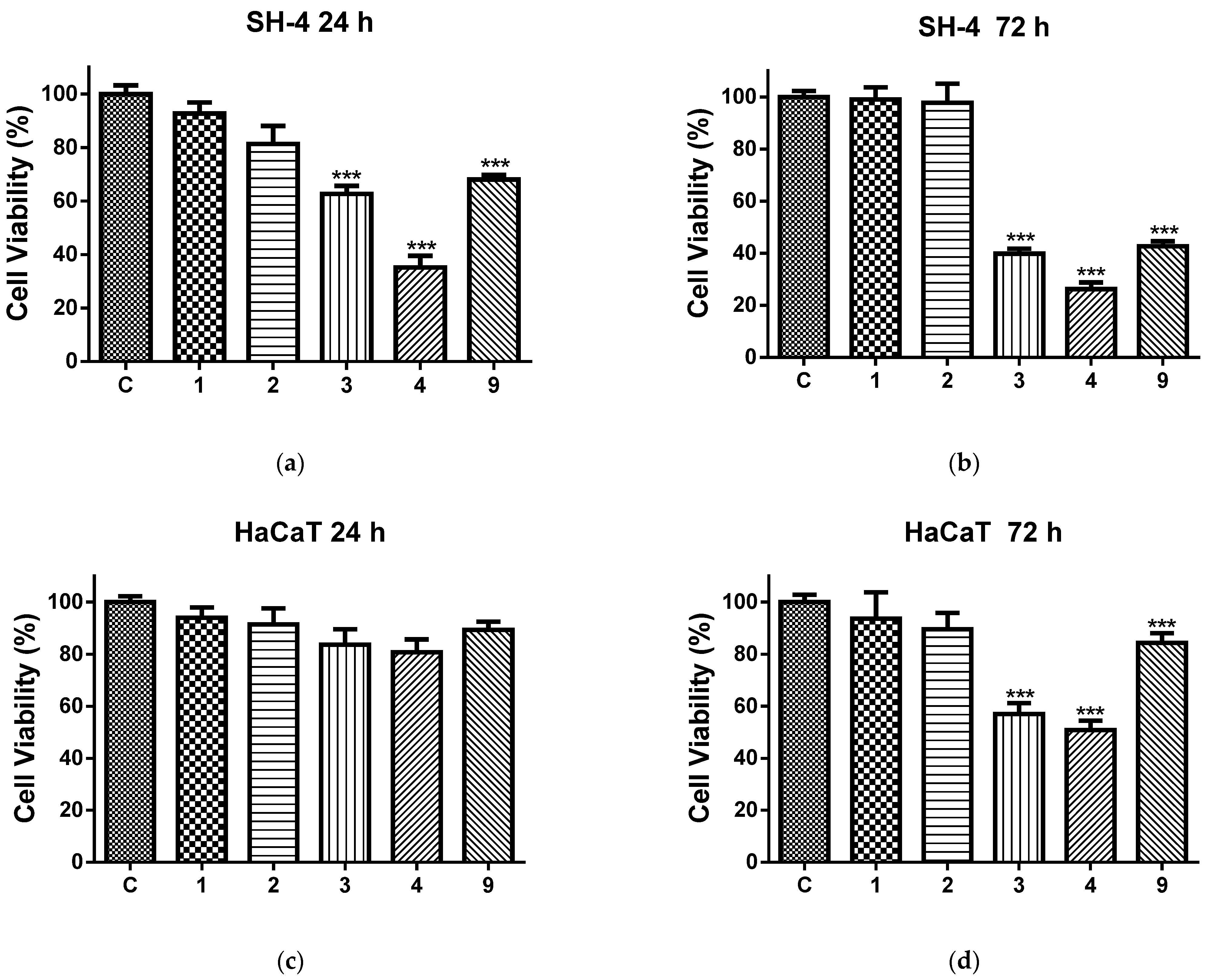
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Tests
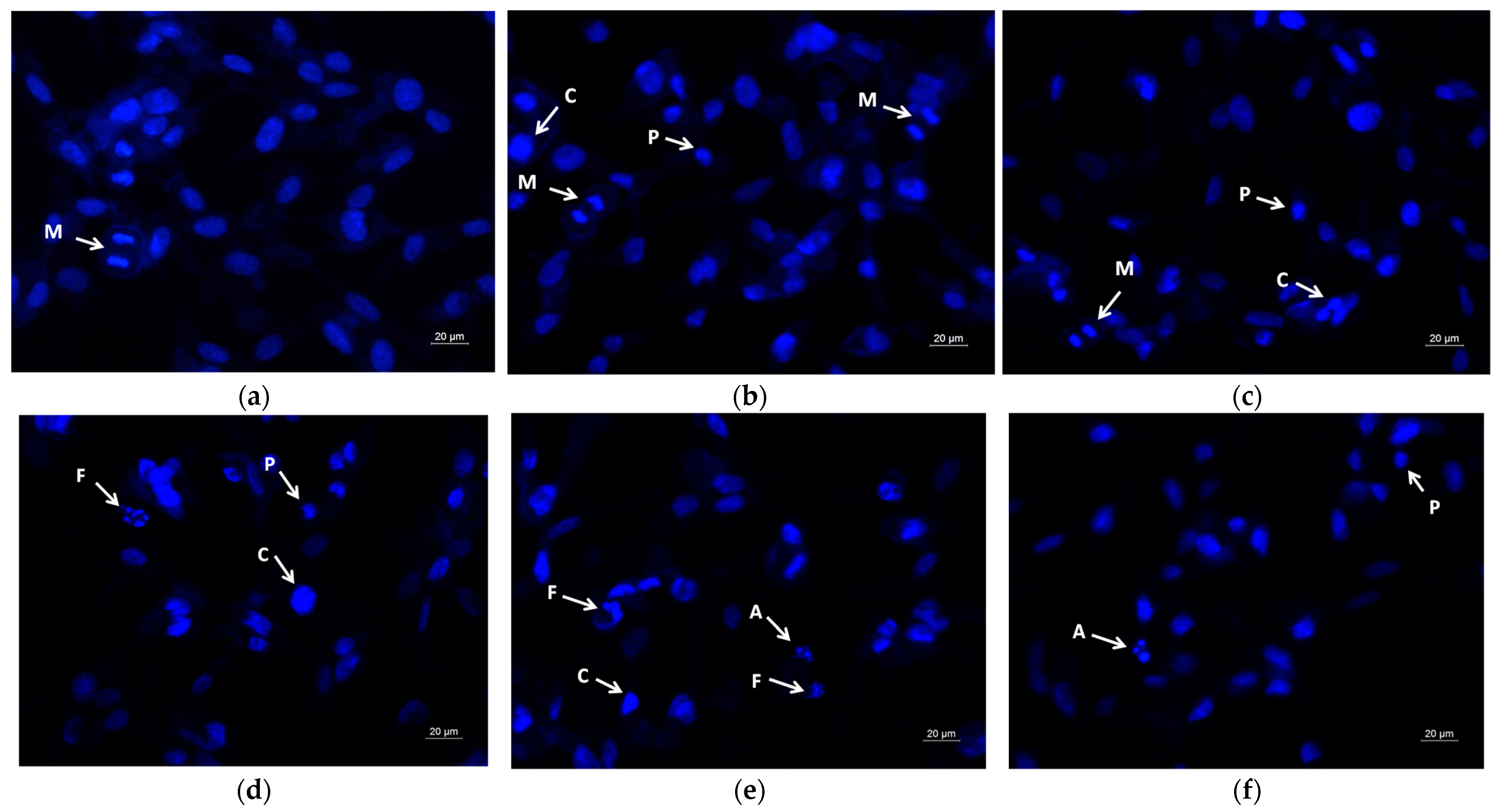
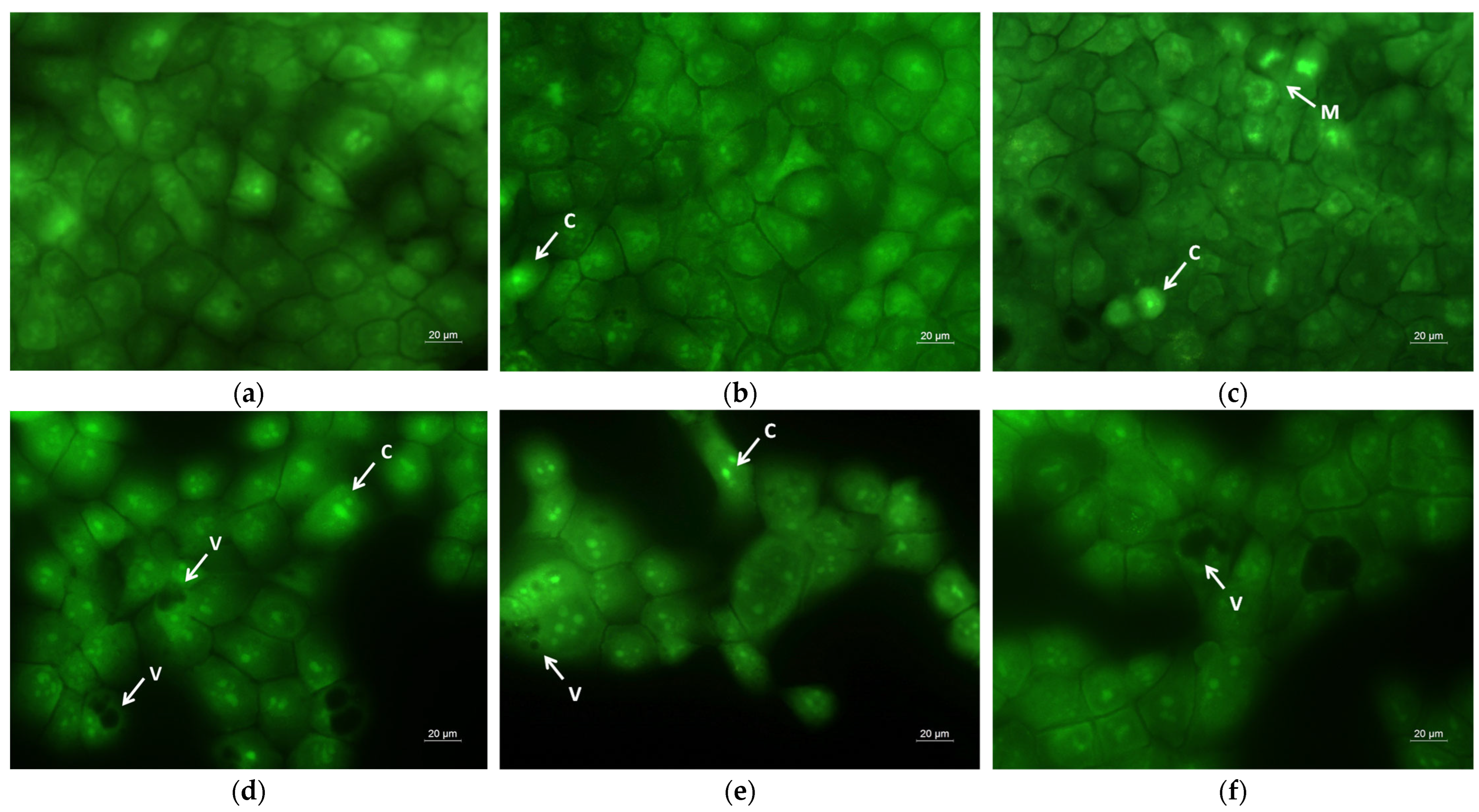
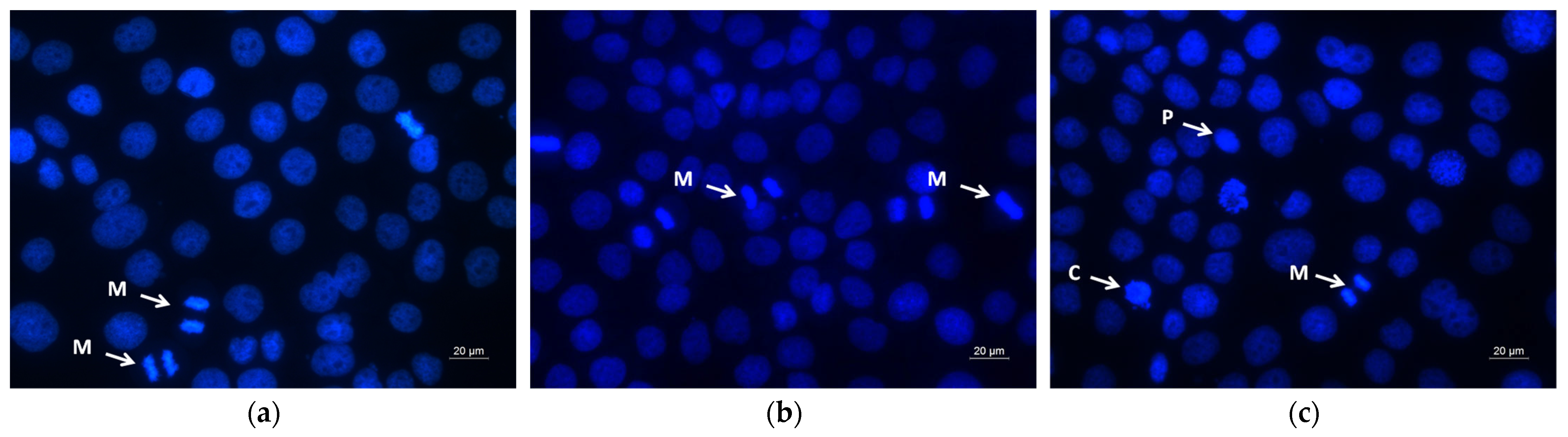
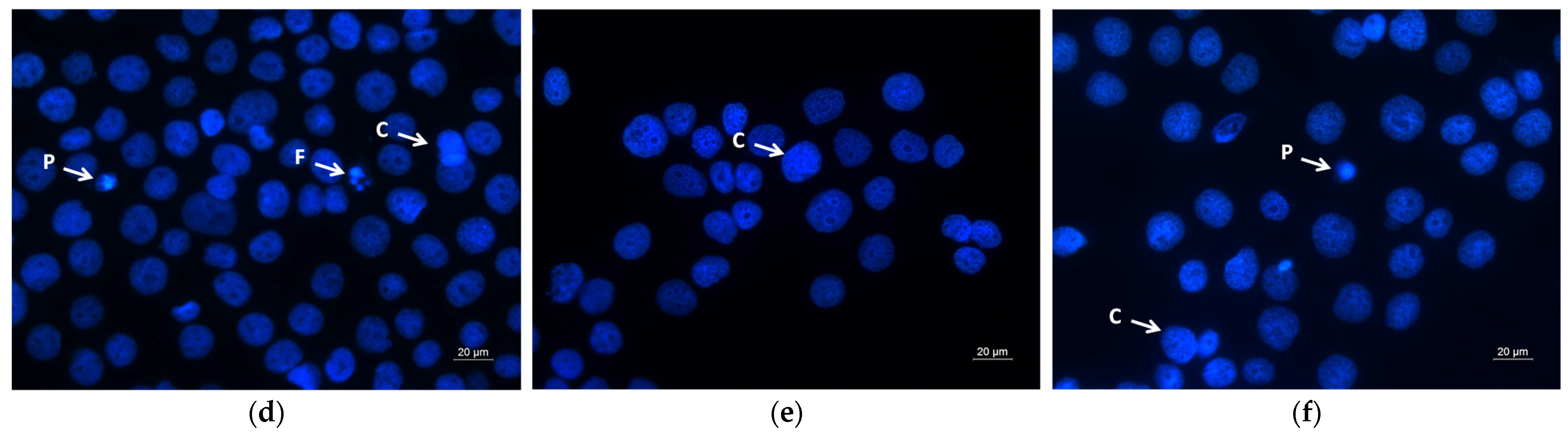
2.6. Assay of Cell Death by Fluorescent Staining Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.3. Preparation of Fibrous Mats by Electrospinning
3.4. Characterization
3.4.1. Dynamic Viscosity
3.4.2. SEM Analysis
3.4.3. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
3.4.4. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
3.5. Screening for Antimicrobial Activity—Disk Diffusion Assay
3.6. MTT Cytotoxicity Study
3.7. Dual Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide (AO/EtBr) Fluorescent Staining
3.8. DAPI—Fluorescent Staining
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colomer, R.; Sarrats, A.; Lupu, R.; Puig, T. Natural polyphenols and their synthetic analogs as emerging anticancer agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgal, V.; Madaan, N.; Mudgal, A.; Mishra, S. Dietary polyphenols and Human health. Asian J. Biochem. 2010, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, I.; Okuno, M.; Katsuma, R.; Arita, N.; Tachibana, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Characterisation of anti-Staphylococcus aureus activity of quercetin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; George, J.A.; Sahadevan, R.; Kothari, M.; Sadhukhan, S. Insights into one drug, multi-target aspects of polyphenols for diabetes management: In vitro, in vivo, and clinical evidence. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, V.N.; Spasov, A.A. Mechanisms of plant polyphenols anti-cancer effects. I. Blockade of carcinogenesis initiation. Biomed. Khim. 2012, 58, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, M.; Gluba, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Nowak, P.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A.; Rysz, J.; Banach, M. The role of polyphenols in cardiovascular disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2010, 16, RA110–RA119. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20424562/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Santos, C.N.; Gomes, A.; Oudot, C.; Dias-Pedroso, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Vieira, H.L.; Brenner, C. Pure polyphenols applications for cardiac health and disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2137–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Cui, X.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, B.; Xia, Y. Phenolic metabolites as therapeutic in inflammation and neoplasms: Molecular pathways explaining their efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalik, A.; Khan, F.A.; Mumtaz, A.; Mehmood, A.; Azhar, S.; Atif, M.; Karim, S.; Altaf, Y.; Tariq, I. Pharmacological applications of quercetin and its derivatives: A short review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A. The Pharmacological Activity, Biochemical Properties, and Pharmacokinetics of the Major Natural Polyphenolic Flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Ganesan, V.; Kannan, S. Antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy of quercetin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus associated with ICU infections. Biofouling 2025, 41, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musini, A.; Singh, H.N.; Vulise, J.; Pammi, S.S.; Giri, A. Quercetin’s antibiofilm effectiveness against drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus and its validation by in silico modeling. Res. Microbiol. 2024, 175, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkod, T.; Tobe, R.; Tragoolpua, Y.; Mihara, H. Medicinal plant extracts protect epithelial cells from infection and DNA damage caused by colibactin-producing Escherichia coli, and inhibit the growth of bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Kong, X. Synergistic Effect of Quercetin on Antibacterial Activity of Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophila In Vitro and In Vivo. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, D.; Prajapati, J.; Dabhi, M.; Sharkey, L.K.; Pidot, S.J. MurG as a potential target of quercetin in Staphylococcus aureus supported by evidence from subtractive proteomics and molecular dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham Hudson Mark, J.; Premkumar, R.; Sangeetha, R.; Lakshmi, A.; Langeswaran, K. Structural, quantum chemical, molecular docking, and dynamics studies of quercetin—A potent inhibitor for colon cancer. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2023, 43, 8426–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Chung, J.G.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, H.F.; Tsou, M.F.; Wood, W.G.; Kuo, S.J.; Chen, D.R. Quercetin-induced apoptosis acts through mitochondrial-and caspase-3-dependent pathways in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Chen, P.H.; Dai, H.Q.; Feng, J.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. Quercetin Induces Apoptosis via Downregulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor/Akt Signaling Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 534171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Tavakol, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Ashrafizadeh, M. Dual role of quercetin in enhancing the efficacy of cisplatin in chemotherapy and protection against its side effects: A review. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 1438–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z.; Cai, D. Quercetin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting Calcineurin in the Xenograft Model of Human Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 781, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezerji, S.; Robati, F.N.; Abdolazimi, H.; Fallah, A.; Talaei, B. Quercetin’s effects on colon cancer cells apoptosis and proliferation in a rat model of disease. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 48, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, D.; Yang, F.; Xing, N. Quercetin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process and promotes apoptosis in prostate cancer via downregulating lncRNA MALAT1. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teekaraman, D.; Elayapillai, S.P.; Viswanathan, M.P.; Jagadeesan, A. Quercetin inhibits human metastatic ovarian cancer cell growth and modulates components of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in PA-1 cell line. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2019, 300, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ding, H.; Tang, X.; Liang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J. Quercetin induces pro-apoptotic autophagy via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299 in vitro. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaei, A.; Mohammadzadeh, G.; Rashidi, M. Quercetin Improves the Anti-angiogenic Property of 5-Fluorouracil on the Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells HUVEC Cell Line. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2022, 15, e120315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanaraj, T.; Mohan, M.; Arunakaran, J. Quercetin attenuates metastatic ability of human metastatic ovarian cancer cells via modulating multiple signaling molecules involved in cell survival, proliferation, migration and adhesion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 701, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Luteolin and Quercetin combination therapy: Enhanced inhibition of H157 human lung cancer cells. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2024, 12, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Cui, Y.-L. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules 2019, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Martinez, E.J.; Flores-Hernández, F.Y.; Salazar-Montes, A.M.; Nario-Chaidez, H.F.; Hernández-Ortega, L.D. Quercetin, a Flavonoid with Great Pharmacological Capacity. Molecules 2024, 29, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarikwu, S.O.; Pant, A.B.; Farombi, E.O. Dietary antioxidant, quercetin, protects sertoli-germ cell coculture from atrazine-induced oxidative damage. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Ke, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, X. Quercetin inhibits inflammasome activation in diabetic rats and attenuates myocardial injury. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2019, 35, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xue, W.; Wu, Z.; Lu, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quercetin, a Compound of the Total Flavonoids of Periploca forrestii Schltr., Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting TNF-α. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 2025, 2879–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective effect of quercetin against the detrimental effects of LPS in the adult mouse brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhahebi, A.M.; Ling, J.; Krishnan, S.G.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Elumalai, N.K.; Saheed, M.S.M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Jose, R. Electrospinning research and products: The road and the way forward. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhan, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, H. A Mini Review: Electrospun Hierarchical Nanofibers. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, A.; Acevedo, F.; Cea, M.; Seeger, M.; Navia, R. Development and thermochemical characterization of an antioxidant material based on polyhydroxybutyrate electrospun microfibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecki, A.; Rzeszutek, I.; Lewińska, A.; Warski, T.; Korczyc, A.B.; Wojnarowska-Nowak, R.; Betlej, G.; Deręgowska, A.; Hudecki, J.; Łyko-Morawska, D.; et al. Electrospun fiber-based micro-and nano-system for delivery of high concentrated quercetin to cancer cells. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 153, 213582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, G.; Paolella, G.; Lamberti, E.; Caputo, I.; Gorrasi, G. Quercetin-Loaded Polycaprolactone-Polyvinylpyrrolidone Electrospun Membranes for Health Application: Design, Characterization, Modeling and Cytotoxicity Studies. Membranes 2023, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisth, P.; Singh, R.P.; Pruthi, V. A Controlled Release System for Quercetin from Biodegradable Poly (Lactide-Co-Glycolide)–Polycaprolactone Nanofibers and Its In Vitro Antitumor Activity. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2016, 31, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Novel Quercetin-Loaded Electrospun Cellulose Acetate/Polyethylene Glycol Fibrous Materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Nachev, N.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Spasova, M. Electrospun Quercetin-Loaded PLA and PLA/Polyethylene Glycol Fibers: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Kamenova-Nacheva, M.; Staleva, P.; Tavlinova-Kirilova, M. Electrospun PLA-Based Biomaterials Loaded with Melissa officinalis Extract with Strong Antioxidant Activity. Polymers 2023, 15, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, N.; Spasova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Taneva, S.; Momchilova, S.; Georgieva, A. Physico-Chemical, Mechanical, and Biological Properties of Polylactide/Portulaca oleracea Extract Electrospun Fibers. Membranes 2023, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, M.; Stoyanova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Taneva, S.; Momchilova, S.; Georgieva, A. Facile Preparation of Novel Antioxidant Fibrous Material Based on Natural Plant Extract from Portulaca oleracea and PLA by Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications. Polym. Int. 2022, 71, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, A.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. Mechanisms of Increased Bioavailability through Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review. Drug Deliv. 2019, 27, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghababaei, F.; Hadidi, M. Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Qi, W.; Xiong, D.; Long, M. Quercetin: Its Antioxidant Mechanism, Antibacterial Properties and Potential Application in Prevention and Control of Toxipathy. Molecules 2022, 27, 6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.A.; Bhattacharya, D. Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin: An Approach to Its Mechanistic Principle. Molecules 2022, 27, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Balakrishnan, J.; Govindasamy, A.; Arunagiri, R. New Insights into the Antibacterial Mode of Action of Quercetin against Uropathogen Serratia Marcescens in-vivo and in-vitro. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristo, F.; Valentino, A.; De Luca, I.; Peluso, G.; Bonadies, I.; Calarco, A.; Di Salle, A. PLA Nanofibers for Microenvironmental-Responsive Quercetin Release in Local Periodontal Treatment. Molecules 2022, 27, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Dai, L.; Ye, L.; Sun, X.; Enoch, O.; Hu, R.; Zan, X.; Lin, F.; Shen, J. A Vehicle-Free Antimicrobial Polymer Hybrid Gold Nanoparticle as Synergistically Therapeutic Platforms for Staphylococcus aureus Infected Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.G.; Basu, S.; Banerjee, T.; Shukla, V.K. Biofilm and Wound Healing: From Bench to Bedside. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damyanova, T.; Dimitrova, P.D.; Borisova, D.; Topouzova-Hristova, T.; Haladjova, E.; Paunova-Krasteva, T. An Overview of Biofilm-Associated Infections and the Role of Phytochemicals and Nanomaterials in Their Control and Prevention. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisova, D.; Strateva, T.; Dimov, S.G.; Atanassova, B.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Topouzova-Hristova, T.; Danova, S.T.; Tropcheva, R.; Stoitsova, S. Diversification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa After Inhaled Tobramycin Therapy for Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: Genotypic and Phenotypic Characteristics of Paired Pre- and Post-Treatment Isolates. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman Amin, M.; Khurram, M.; Khan, T.A.; Faidah, H.S.; Ullah Shah, Z.; Ur Rahman, S.; Haseeb, A.; Ilyas, M.; Ullah, N.; Umar Khayam, S.M.; et al. Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisinghani, R.N. Antibacterial Properties of Quercetin. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 8, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Gierszewska, M.; Richert, A.; Grabska-Zielińska, S.; Rudawska, A.; Bouaziz, M. Antibacterial Films Based on Polylactide with the Addition of Quercetin and Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Materials 2021, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.; Elhady, S.; Fathy, F.E.Z. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Properties of Quercetin against Clinical Isolates of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2024, 5, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin is an Effective Inhibitor of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasova, M.; Stoilova, O.; Manolova, N.; Altankov, G.; Rashkov, I. Preparation and Potential Application of Electrospun PLLA/PEG Nanofibers. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2007, 22, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Soyza, A.; Hall, A.J.; Mahenthiralingam, E.; Drevinek, P.; Kaca, W.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Stoitsova, S.R.; Toth, V.; Coenye, T.; Zlosnik, J.E.A.; et al. Developing an International Pseudomonas aeruginosa Reference Panel. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoyanova, N.; Damyanova, T.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Spasova, M. The Effect of Quercetin Loading in Polylactic Acid-Based Electrospun Fibers on Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties. Molecules 2025, 30, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112307
Stoyanova N, Damyanova T, Paunova-Krasteva T, Georgieva A, Toshkova R, Spasova M. The Effect of Quercetin Loading in Polylactic Acid-Based Electrospun Fibers on Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112307
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoyanova, Nikoleta, Tsvetozara Damyanova, Tsvetelina Paunova-Krasteva, Ani Georgieva, Reneta Toshkova, and Mariya Spasova. 2025. "The Effect of Quercetin Loading in Polylactic Acid-Based Electrospun Fibers on Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112307
APA StyleStoyanova, N., Damyanova, T., Paunova-Krasteva, T., Georgieva, A., Toshkova, R., & Spasova, M. (2025). The Effect of Quercetin Loading in Polylactic Acid-Based Electrospun Fibers on Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties. Molecules, 30(11), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112307







