In this section, we report the experimental results on the interfacial properties of the mixed saponin–chitosan systems at the water–MCT interface as well as on the behavior of the respective emulsions. Such results are obtained by different experimental approaches and are discussed in order to understand the role of the adsorption properties of the emulsifiers in emulsion evolution and stabilization.
2.1. Interfacial Properties
2.1.1. Adsorption Properties of Saponin with and Without Acetic Acid
The results obtained in [
19] prove that, for neutral pH, saponin behaves as an ionic surfactant because its charge groups are predominantly dissociated, while, in acidic conditions obtained by adding acetic acid, the dissociation of carboxylic groups is strongly reduced, implying a non-ionic surfactant behavior with increased surface activity at the same bulk concentration.
Thus, as the adsorption properties of saponin are expected to be pH-dependent, the aqueous solutions of saponin plus acetic acid have been preliminarily investigated by measuring interfacial tension and dilational viscoelasticity, and the results are compared with those obtained with saponin dissolved in pure water.
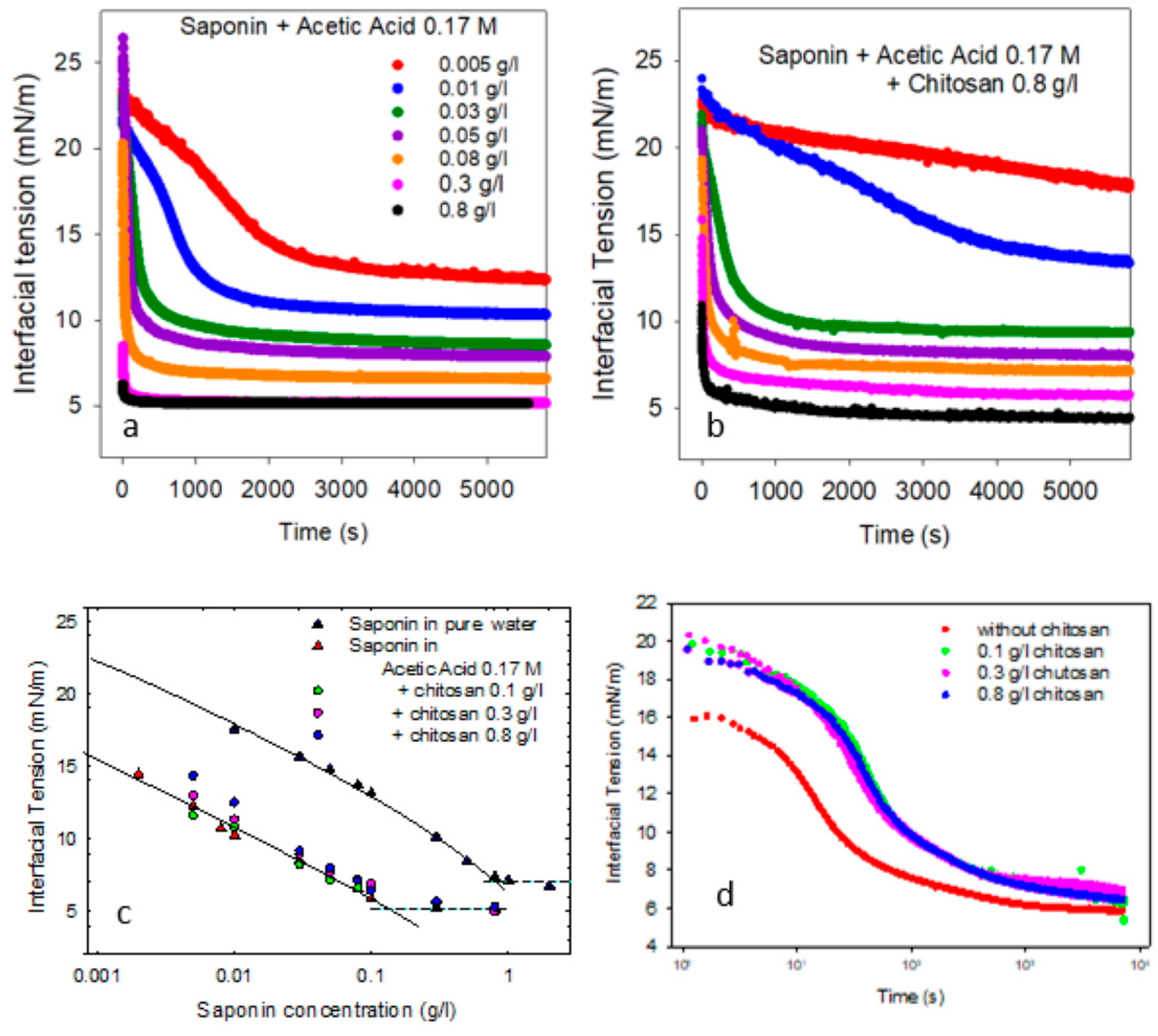
Figure 1a shows the trend of the interfacial tension, γ, of saponin solution in acetic acid against MCT, for different concentrations of saponin. The corresponding equilibrium values versus concentration and the resulting adsorption isotherm are reported in
Figure 1c, and are compared with those obtained in [
21] for saponin in pure water. Some key parameters, such as the maximum adsorption, critical micellar concentration (cmc), and the interfacial tension above the cmc, derived from the analysis of these equilibrium data, are reported in
Table 1 and compared with those obtained previously for saponin adsorption at water–air interfaces. Note that, as the saponin used here consists of a mixture of components with molecular weights distributed from 1070 to 1700 g/mol, in this work, where it is necessary to express adsorption properties in significant units, we assume the value of 1650 g/mol as the average molecular weight, as in previous reference studies on saponins or mixtures of saponins [
12,
13,
14].
The solid curves in
Figure 1c are the best fit adsorption isotherms derived from the reorientation adsorption model [
22]. In the framework of this model, the adsorbed molecules can assume different orientations with respect to the interface, corresponding to different occupational areas at the interface. The theoretical equation used for the fitting is as follows:
where Π = γ
0 − γ is the equilibrium interfacial pressure and γ
0 is the interfacial tension of the pure interface, and
ω1 and
ω2 are the maximum and minimum areas per mole, corresponding to the horizontal and vertical orientations, respectively.
b and
α are further isotherm parameters, described in detail in [
22,
23].
b expresses the surface activity of the adsorbing component;
α is directly related to the relative weight of the limit orientation states. Moreover, according to well-established classical thermodynamic treatments of surfactant adsorption, a direct relation between the surface activity of adsorbing molecules and their molar area is assumed [
23]. This condition leads to an expression for the average molar area in terms of the equilibrium interfacial tension [
22,
24,
25], which, in the case of a two-state or reorientation model, reads as follows:
Thus, the average molar area, ω, decreases with the decreasing of the equilibrium interfacial tension, corresponding to the advancement of the surfactant adsorption, and approaches the value associated to the vertical orientation with respect to the interface.
More sophisticated thermodynamic models have been recently developed for re-orientable surfactants adsorbing at liquid–air interfaces, taking into account different molecular reorientation modes [
26]. However, the model assumed here appears to be appropriate for describing the adsorption of saponin at the water–MCT interface, independently of the presence of acetic acid. The use of Equation (2), which is a limiting case of more general theoretical expressions, provides physically realistic values for the thermodynamic parameters, enabling a coherent interpretation of the acquired data.
Based on these results, it is clear that saponin, when dissolved in acetic acid, presents higher surface activity and lower cmc. The best fit value found for the isotherm parameter b (
Table 2) is one order of magnitude lower compared with that found for pure water. As in the water–air interface, this reduction is the result of the suppression of the charge of saponin at a low pH, which makes it predominantly behave as non-ionic surfactants. Additionally, at that pH, the carboxylic groups of fatty acids of MCT at the interface with water are protonated; therefore, the repulsive electrostatic interaction between saponin and the MCT interface is diminished.
The other isotherm parameters are of the same order of magnitude, even if ω2 is slightly reduced in acetic acid. This effect is explainable considering that, being adsorbed saponin predominantly uncharged, as expected at a low pH, the reduction of repulsive forces between the adsorbed molecules results in a lower value of the area per adsorbed molecules.
2.1.2. Partitioning
To complement this study on the adsorption properties of saponin, the possibility of the transfer into the oil phase was investigated. As underlined in many previous studies [
6,
25], the surfactant partitioning in liquid–liquid systems is an important aspect that must be taken into account because it can affect the dynamics of the interfacial layers and modify the morphology and stability of the corresponding emulsions.
For saponin in the water–MCT system, different behaviors are expected depending on whether saponin is dissolved in pure water or in acetic acid solutions. In the first case, as saponin is predominantly dissociated, the transfer across the water–oil interface can be neglected. On the other hand, at a low pH, when saponin is essentially a non-ionic surfactant, such partitioning can be relevant.
Methods to quantitatively evaluate the partition coefficient; that is, the ratio between the surfactant concentrations in oil and in water at equilibrium, have been developed and widely used [
25,
27]. However, the occurrence of the surfactant transfer across the water–oil interface can be preliminarily checked by an effective and easy method relying on the comparison of the interfacial tension trends obtained with two different configurations: a drop of oil immersed in the aqueous surfactant solution and a pendant drop of solution in an initially surfactant oil-free phase. In the case of surfactant transfer, the second configuration provides higher values of interfacial tension, due to the impoverishment of the drop phase because of the much higher volume of the initially pure external phase, or even, when the partitioning is very favored, a typical minimum trend [
25].
As shown in
Figure S1 of the Supplementary Materials (SM), for saponin dissolved in pure water, the trends of interfacial tension are coincident, while, in the presence of acetic acid, the interfacial tension in the second configuration remains slightly higher during adsorption. Therefore, we can conclude that, while in the first case the transfer of surfactant is not relevant, in acetic acid, a slight surfactant transfer can be hypothesized; however, it does not appreciably influence the adsorption dynamics of the system.
2.1.3. Effect of Chitosan on Interfacial Properties
The interfacial properties of the mixed saponin–chitosan solutions against MCT have been investigated for different concentrations of chitosan, ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 g/L. As an example,
Figure 1b shows the trends of the dynamic interfacial tension of mixed solutions containing chitosan at 0.8 g/L and different concentrations of saponin. The corresponding equilibrium values versus saponin concentration are reported in
Figure 1c, in order to evidence the effect of the presence of chitosan on the saponin adsorption isotherm.
From these results, it is evident that the adsorption process in the presence of chitosan is, in general, slower and, depending on the composition, produces higher equilibrium values of interfacial tension. This is especially true for concentrations of chitosan around 0.3 g/L and higher. In fact, from
Figure 1c, it is clear that, while for 0.1 g/L of chitosan, the equilibrium interfacial tension versus saponin concentration is essentially unchanged, for higher concentrations of chitosan, the equilibrium interfacial tension tends to be increasingly larger while reducing the saponin concentration. Moreover, as shown in
Figure 1d for 0.1 g/L of saponin, the presence of chitosan tends to slow down the kinetic process, also in cases where the final equilibrium interfacial tension is not affected. This behavior may be explained considering that chitosan, under low-pH conditions, is essentially a cationic polymer, well dissolved in water and without any particular amphiphilicity at the water–oil interface; therefore, its effect on the interfacial tension is essentially due to the interaction with saponin and, in particular, with the small fraction of dissociated molecules of saponin. That implies the formation of non-amphiphilic chitosan–saponin complexes, which impoverishes the surfactant content in the aqueous solution. Such depletion is more important at low-saponin concentrations than at high ones, where the amphiphilicity of saponin in the complex with the chitosan molecule can prevail.
A second effect that may contribute to the slowing down of the saponin adsorption kinetics is the increase in bulk viscosity due to the presence of chitosan. Some data on the increase of the viscosity due to the presence of chitosan are reported in [
19], with the composition of the aqueous phase in the same range as the present study. In that study, it was found that, with a chitosan concentration of 0.8 g/L, the viscosity can reach a value of 3.092 ± 0.004 mm
2/s. This increase in viscosity may slow down the bulk diffusion of saponin, inducing consequentially longer equilibration times of adsorption. Similar effects were observed in [
19] in relation to the adsorption at water–air interfaces and attributed, also in that case, to the slowing down of the bulk diffusion process.
2.1.4. Dilational Rheology
To obtain more information on the adsorption dynamics of these composite systems, interfacial rheology studies have been carried out against the composition of the aqueous phase. In particular, the frequency dependence of dilational viscoelasticity,
E(
ν), were measured by varying the saponin bulk concentration and evidencing the effects of acetic acid and chitosan.
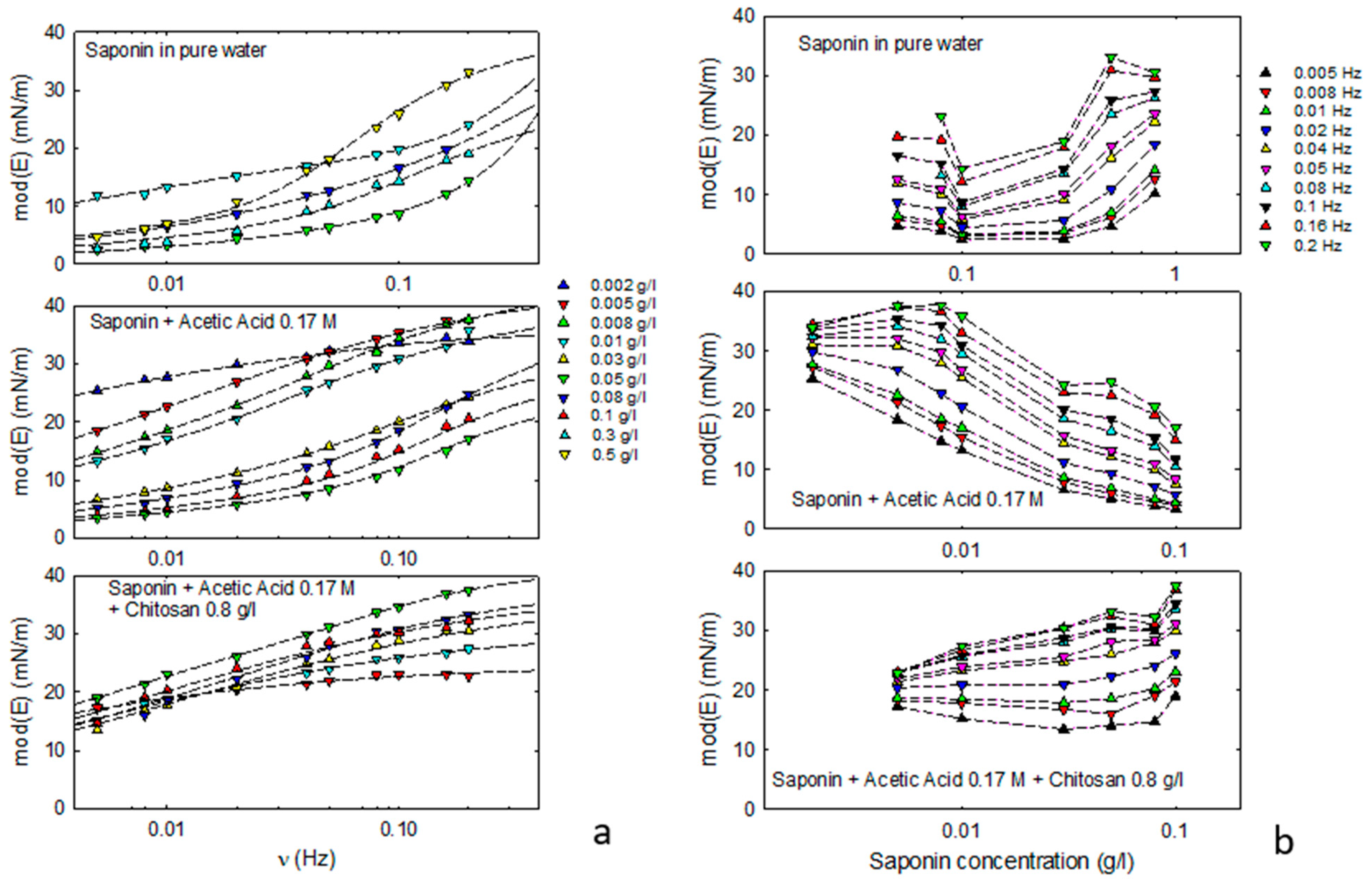
Figure 2 reports the modulus of the viscoelasticity, mod(E), as obtained by the oscillating drop method in the case of saponin dissolved in acetic acid solution, with and without chitosan, compared to mod(E) values obtained in [
21] for pure water. The frequency dependence of these data (
Figure 2a) shows that, for all the investigated compositions, the interfacial layer presents a viscoelastic behavior in the investigated frequency range coherent with the coexistence of the bulk diffusion and a further re-arrangement surface process.
The obtained mod(E) data are, in fact, well-fitted by the theoretical curves calculated by the following extended Lucassen–Van der Tempel equation [
24,
28]:
where
,
,
and
νk are the characteristic frequencies of diffusion and the interfacial kinetic process, respectively.
is the thermodynamic Gibbs elasticity and
E1 is the high frequency limit of
E.Equation (3) has been widely used in many studies dealing with common soluble surfactants where adsorption is not only governed by bulk diffusion, but also by further relaxation interfacial processes [
29]. The classical Lucassen–Van der Tempel equation expression is as follows:
It is found as the limit case of Equation (3) for , which corresponds to the instantaneous equilibration of the relaxation process, or diffusion-controlled adsorption.
For the systems investigated here, as in [
21], the re-arrangement process occurring in the adsorption layer in response to surface perturbation is expected to be strictly related to the variation of the average molar area under dynamic conditions, likely due to the reorientation of the adsorbed molecules.
Figure 2a shows that the observed frequency dependence of the viscoelasticity is in good agreement with the extended Lucassen–Van der Tempel model. The best fit parameters obtained and, in particular, the characteristic frequencies associated with the occurring dynamic processes (diffusion and surface re-organization), provide information on the mechanisms governing the adsorption dynamics.
Figure S2 of the Supplementary Materials reports the best fit values of some key parameters, such as the characteristic frequencies of the diffusion and interfacial processes and the high-frequency limit of the dilational elasticity.
For saponin plus acetic acid, the characteristic frequency of the surface re-arrangement is found to vary from 0.03 Hz to 0.14 Hz, slightly increasing with the concentration of saponin above 0.05 g/L. The characteristic frequency of the diffusional transport process was found to be in the 0.001–0.2 Hz range, increasing with concentration.
In the presence of chitosan at 0.8 g/L, the re-arrangement at the interface does not appear relevant. The best fit theoretical curves correspond, in fact, to the limit case of the Lucassen–Van der Tempel model (Equation (4)), meaning that the diffusion transport is the main process governing the rheological response. In this case, the diffusional characteristic frequency is around 10−3–10−2 Hz, reduced of about one order of magnitude with respect to the previous cases without chitosan, but with the same increasing trend versus concentration.
These results can be interpreted considering the formation of saponin–chitosan complexes in the aqueous phase, where adsorption at the interface is controlled by a diffusion process slower than that governing the adsorption of saponin molecules and for which the surface reorientation kinetics are not significant.
The trend of the viscoelasticity against frequency is also important because it is related to the capacity of adsorbed components to hinder the phenomenon of droplet coalescence in emulsions. Higher values of mod(E), in fact, due to Marangoni effects, tend to hamper the thinning of the liquid films between droplets, preventing their breakage. As coalescence has a major role in emulsion destabilization [
6], the results presented in this section are expected to be correlated with the long-time stability of the respective emulsions.
In this area, to know the trend of the elasticity in a wide frequency range is important. When this range is rather limited, as in the present work, fitting appropriate theoretical curves to the experimental rheological data enables the behavior at a high frequency to be accessed. In particular, fitting Equation (3) to the obtained E(ν) data provides the high-frequency limit of the dilational elasticity as a best fit parameter. From this kind of analysis, it was found that, while in the case of saponin in pure water [
21], the high-frequency elasticity from the best fit curves reaches rather high values, of the order of 50–100 mN/m, this is not true for saponin in acetic acid, for which the limit values of the elasticity at high frequency are found to be lower than 50 mN/m (see
Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials). In the presence of chitosan, the high frequency values of the elasticity are slightly increasing with the concentration but are always below those of saponin in pure water.
Figure 2b shows the values of mod(E) versus the composition of the aqueous phase in the investigated frequency range. From these data, it is evident that maximum values of mod(E) are found at different concentrations of saponin, depending on the presence of acetic acid and chitosan. More specifically, while for saponin in pure water, mod(E) increases with concentration and seems to reach a maximum at a concentration close to the cmc, in the presence of acetic acid, a maximum appears at concentrations almost two orders of magnitude lower. Increasing the concentration above that value, mod(E) tends to decrease. Adding chitosan, the trend of mod(E) is to slightly increase with the concentration, and it maintains at rather high values in almost all the concentration ranges investigated.
The correlations of these results with the long-time stability of the respective emulsions are discussed in the following sections.
2.3. Emulsion Properties
The first analysis of emulsion behavior has been carried out by monitoring the volume of the emulsified phase, referred to as the total volume of the liquid–liquid system, V
rel = V
emul/V
tot, after the emulsion formation. For this first study, as well as for all the other emulsion investigations reported below, the method of emulsification adopted is the double-syringe method, described in
Section 4.2. In all cases, the emulsification method adopted provides the total emulsification of the liquid–liquid system so that, for all the systems investigated, V
rel = 1 at the initial monitoring time. The morphology of the obtained emulsions, just after the formation, has been checked by microscope visualization. By this analysis, even if rather qualitative, it was possible to verify that, in all cases, the used emulsification method provides oil-in-water emulsions with droplet sizes of the same order as those found in [
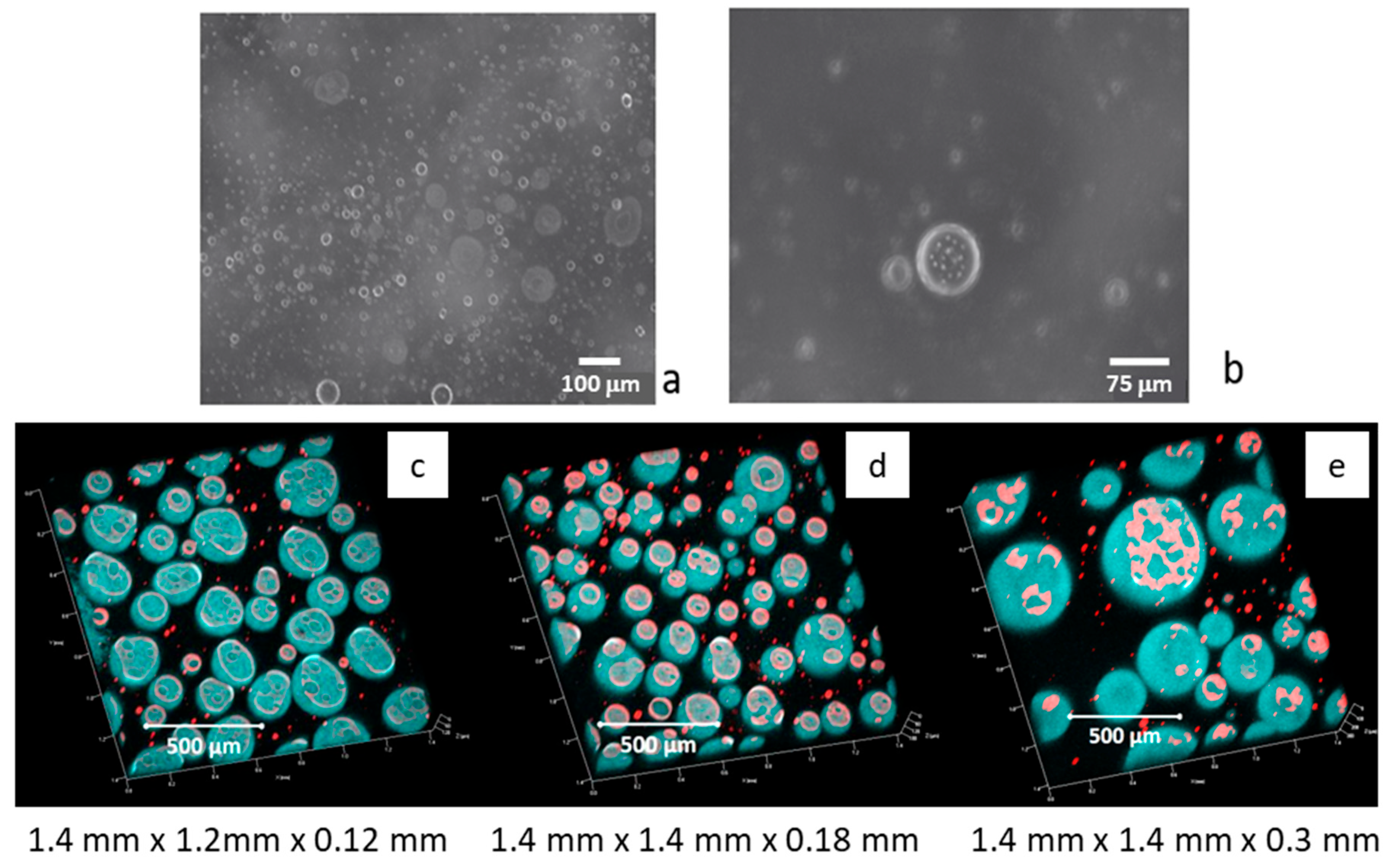
21] for saponin dissolved in pure water; that is, 5–10 μm, and with the presence of some bigger droplets in presence of chitosan, which can reach diameters of about 50 μm. A typical microscope image obtained with saponin and chitosan, of a freshly formed emulsion diluted 1:10 in water, is reported in
Figure 4 for visualization. At closer observation, the presence of very small droplets inside the bigger ones is observed. This leads us to hypothesizing the onset of double emulsification, which will be discussed below.
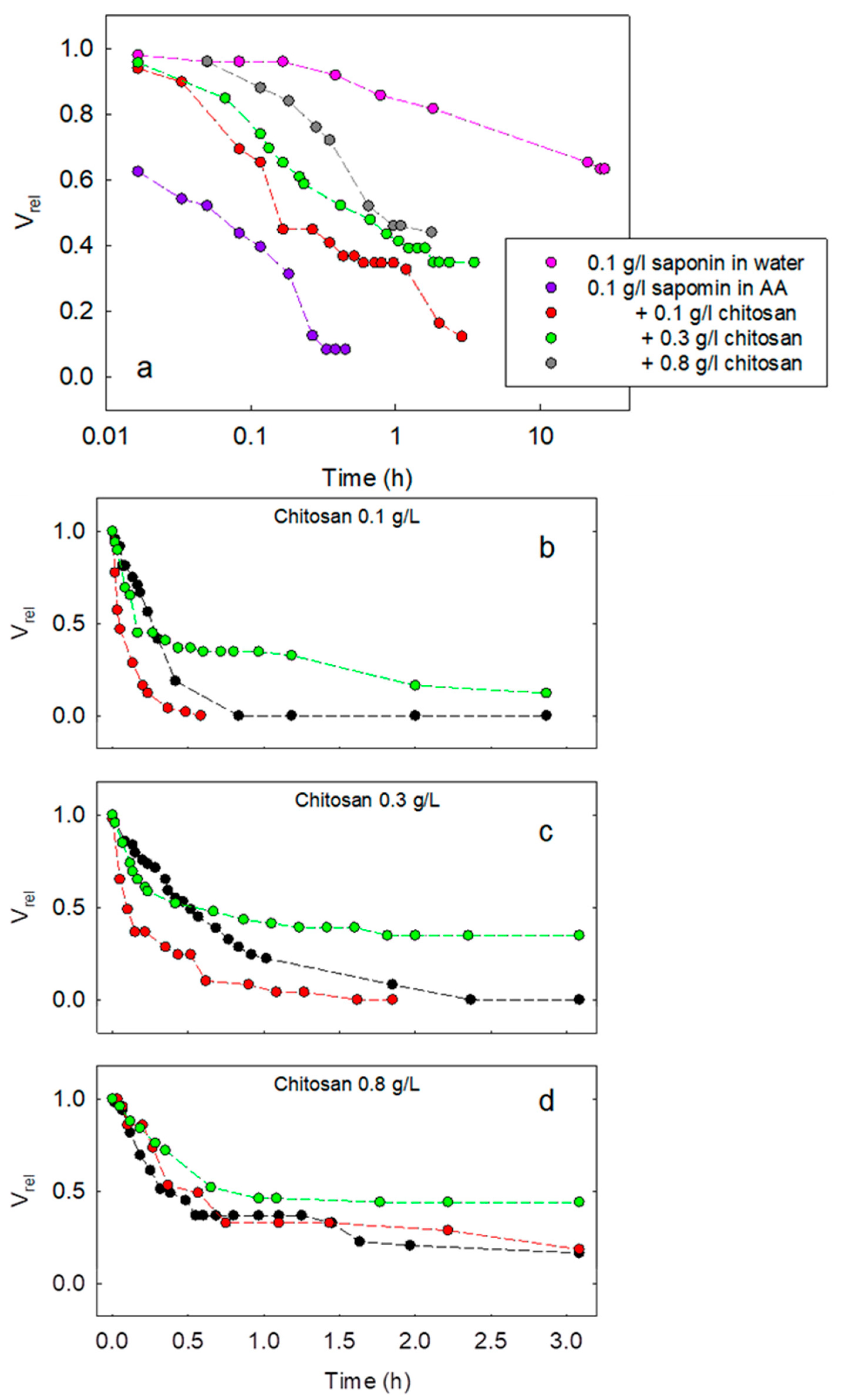
Figure 5 reports the main results obtained on the variation of V
rel with time for different compositions of the aqueous phase of the emulsions during their destabilization.
Figure 5a illustrates the effect of pH, or the presence of acetic acid, on the evolution of the emulsion as well as that of the content of chitosan. It is evident that, for saponin at 0.1 g/L with acetic acid, emulsions destabilize much earlier than those obtained with saponin in pure water. Note that the cases for saponin concentration below 0.1 g/L in acetic acid without chitosan are not reported in the figure because emulsions separate immediately. This behavior can be ascribed to the fact that saponin in pure water presents higher values of dilational viscoelasticity modulus at a high frequency, which likely favours the prevention of droplet coalescence due to the Marangoni effect. Moreover, the ionic character of saponin in pure water induces repulsive interactions between the adsorbed layers at MCT droplet surfaces. Such electrostatic repulsions play an important role in hindering coalescence [
6]. In the presence of acetic acid, these two stabilizing effects are not relevant. In fact, the adsorbed layer can be assumed to be neutral because of saponin’s non-ionic character, which, at low pH, is predominantly not dissociated, and dilational viscoelasticity does not increase appreciably with the frequency.
The effect of chitosan is, instead, to increase the lifetime of the emulsions. This improvement in emulsion stability, which appears to be proportional to the chitosan concentration, is correlated with the trend of dilational viscoelasticity. Mod(E) presents, in fact, values slightly higher than those for saponin at the same concentration solely in acetic acid. Steric effects should be also taken into consideration due to the expected formation of chitosan–saponin complexes adsorbing at the aqueous phase–MCT interface. Moreover, in these cases, the ionic character of these complexes, due to chitosan, may increase the stability against coalescence by electrostatic repulsion.
In
Figure 5b–d, the trends of V
rel, obtained for fixed chitosan concentration and varying saponin concentration from 0.01 g/L to 0.1 g/L, are compared. It is interesting to note that, apart from the chitosan concentration of 0.8 g/L, in which increasing the saponin concentration increases the emulsion lifetime, for the lower chitosan concentrations, this proportionality with the saponin concentration is not observed. This behavior is coherent with a scenario characterized by an interplay between the two main mechanisms contrasting droplet coalescence: the fluid dynamic effect governed by dilational rheology and electrostatic repulsion between the adsorbed layers. Depending on the composition of the aqueous phase, one of the effects can be predominant over the other. For a rather low concentration of chitosan, in fact, the electrostatic and steric effects are possibly ineffective in counteracting coalescence. At the same time, mod(E) is expected to have the same decreasing trend with saponin concentration as in the case of saponin in acetic acid. Thus, while the interfacial rheology may have a role for saponin at 0.01 g/L, it becomes less effective for higher saponin concentrations. Meanwhile, when further increasing saponin concentration, the formation of charged amphiphilic complexes with chitosan is favored. Such complexes adsorb at the interfaces and hamper coalescence.
To go into more detail about the effect of chitosan and, in general, the dependence of the emulsion stability on the emulsion composition, the same systems reported in
Figure 4 have been investigated by multiple light scattering measurements, according to the method reported in
Section 4.2.
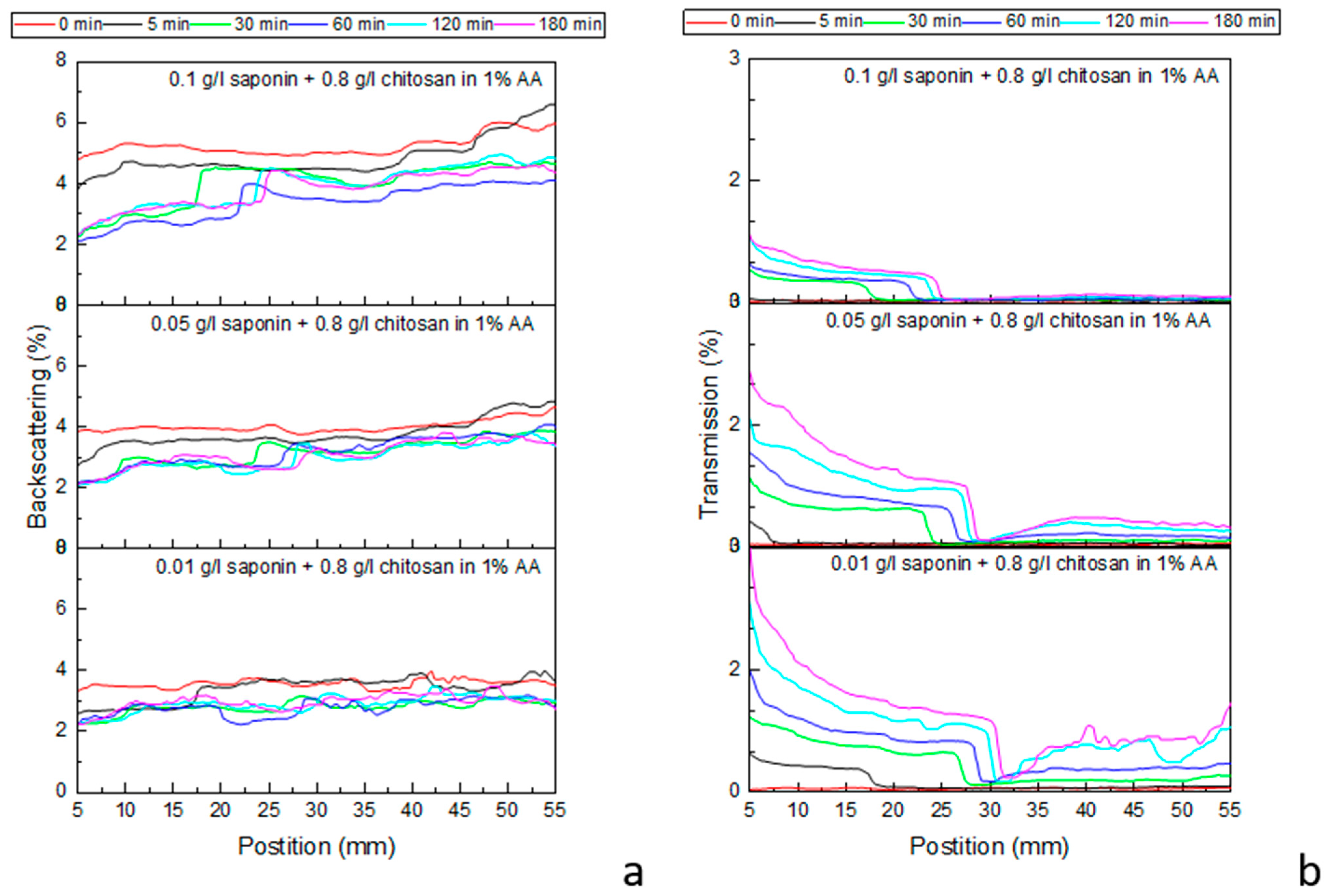
Figure 6 shows the profiles recorded by a Multiscan MS 20 during the destabilization of emulsions, obtained with chitosan at 0.8 g/L and different saponin concentrations (compositions corresponding to
Figure 5d) within 3 h of their generation. The results for lower concentrations of chitosan are reported in
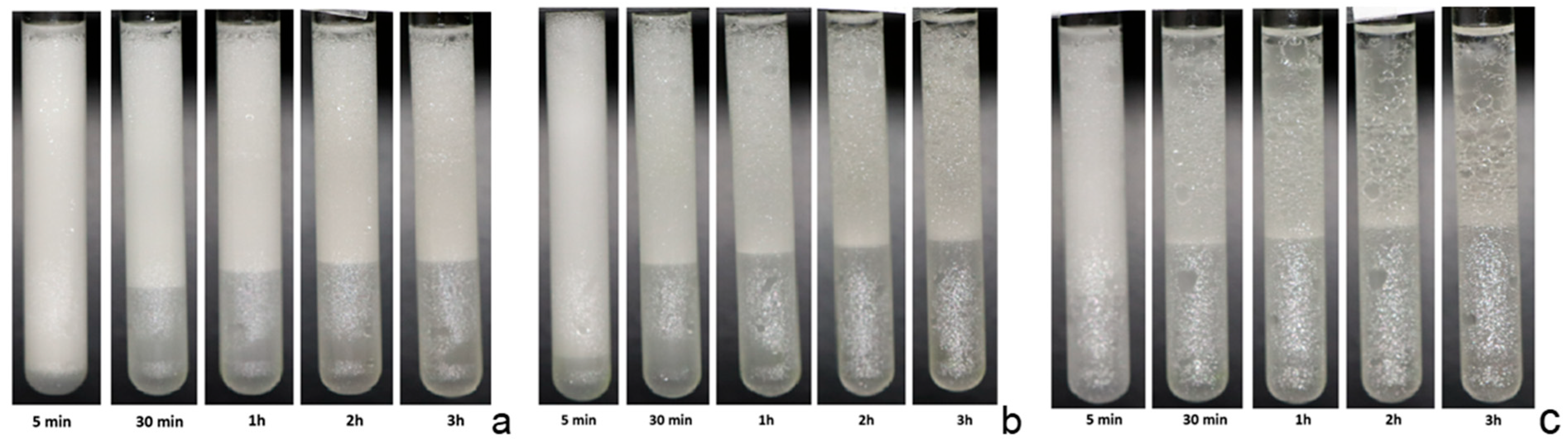
Supplementary Materials (Figures S5 and S6). Additional information on the evolution and stability of the emulsion can be obtained from the photos of the samples analyzed in the Multiscan apparatus (
Figure 7,
Figures S7 and S8). These photos provide a qualitative monitoring of the emulsion changes during their ageing, which is important in validating the spectra interpretation. Analysis of the acquired spectra confirms the emulsion behavior reported in
Figure 5, providing further interesting details about the development of the investigated emulsions.
For all studied cases, the recorded transmission profiles prove that the evolution of the emulsions is characterized by an evident separation into two phases after a short time from the introduction of the emulsion into the cell. The spectra acquired immediately after the generation are, in fact, coherent with the presence of one emulsion initially occupying the whole measurement cell, while the spectra acquired after 5 min demonstrate the separation of the system into two different phases: an emulsion with droplet sizes of the order of some microns in the superior part of the cell (impenetrable to the Multiscan NIR radiation wavelength), and an initially wholly opaque phase in the lower part of the cell. This latter phase is expected to also be an emulsified phase that, as time progresses, becomes more and more transparent to light radiation as oil drops tend to flow out under the influence of buoyancy. In accordance with the previously carried out microscope observation, we found that all the emulsions obtained in this work are oil-in-water emulsions; therefore, we can assume that the emulsified phases observed during the Multiscan MS 20 measurements are oil-in-water emulsions as well.
Note that, in the previous more qualitative analysis of emulsion ageing, the results of which are reported in
Figure 5, this lower phase was not recognized as an emulsified phase but considered from the beginning to be an aqueous phase, separated from the emulsions due to their destabilization. After 30 min from the formation, the boundary between the two detected phases is at a 25–30 mm level and only slightly increases during succeeding evolution. The backscattering spectra confirm this dynamic behavior, even if only qualitatively, due to the low percentage of reflection radiation. The images reported in
Figure 7 provide further confirmation of this behavior.
With a more rigorous analysis of the spectra, also confirmed by the emulsion images, one can assert that a boundary phase is formed between these two emulsions, which are completely impermeable to radiation, as evidenced in
Figure 6b (transmission is equal to zero), and slightly increase in thickness over time. The formation of this further layer between the two principal emulsified phases is most likely due to the chemical or physicochemical processes occurring in these areas under the dynamic conditions of the early destabilization process, such as aggregation, coagulation, or gelation processes, as well as involving the components of the oil fraction.
A common behavior observed in all the emulsions investigated here, with different concentrations of saponin and chitosan in the period of up to 180 min from generation, consists of a noticeable change of the emulsions in the lower part of the cell from the beginning of the acquisition, while the emulsions composed of bigger droplets in the upper part seem to be more stable, especially those obtained with saponin at 0.1 g/L (see
Figure 6,
Figures S5 and S6). This can be explained by assuming that the smaller droplets in the lower emulsion layer aggregate and/or coalesce, and that the resulting bigger droplets or aggregates tend to transfer into the boundary phase. This implies that part of the aqueous phase is displaced downwards, increasing the content of water in the emulsion in the lower part of the cell, which results in the observed changes in the transmission curves. Meanwhile, the upper emulsion becomes increasingly rich in the oil phase but with a longer destabilization time.
In summary, we can say that the obtained spectra and their variations in time are coherent with a scenario where an initially uniform emulsion separates, mainly driven by the buoyancy effect, into two oil-in-water emulsions: the lower part of the cell contains smaller (micrometric) droplets; whatever coalesced into bigger droplets under the effect of gravity tend to rise towards the emulsion in the upper part of the cell. The upper emulsion becomes more and more dense; its slower destabilization is driven by the coalescence of oil drops.
To complement the results reported so far, the morphology of the emulsions was analyzed by confocal microscopy, using Coumarin 6 and Rhodamine B as dyes dissolved in the MCT oil and aqueous phase, respectively. The concentrations of dyes adopted in this study were optimized by interfacial tension measurements and optical observations. The concentration of Rhodamine B in aqueous solution was 3 × 10
−7 M, while the MCT solution of Coumarin 6 was obtained by dissolving 10 μL of a saturated solution of Coumarin 6 in 1 mL of MCT. At these concentrations, the measurements of the interfacial tension indicated negligible effects on the adsorption properties of emulsifiers (see
Table S1). Additional emulsification tests also demonstrated the negligible influence of these concentrations on emulsion behavior. The emulsions for the confocal analysis were prepared using the double-syringe technique, as described in the previous section, and micrographs were taken for freshly formed emulsions diluted with water 1:10. In
Figure 4c–e, the confocal microscopy images from emulsions obtained with saponin at 0.1 g/L and chitosan are reported for different concentrations.
These images evidence the presence of a certain amount of aqueous phases inside the oil droplets, confirming the onset of double emulsification that was already observed by optical microscopy. Moreover, this phenomenon appears to become more important with the increasing of the chitosan concentration, which also induces an increase in the oil droplet size.