Morphology-Engineered CeO2 as a Synergistic Flame Retardant in Polypropylene/Intumescent Systems: Mechanisms and Performance Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
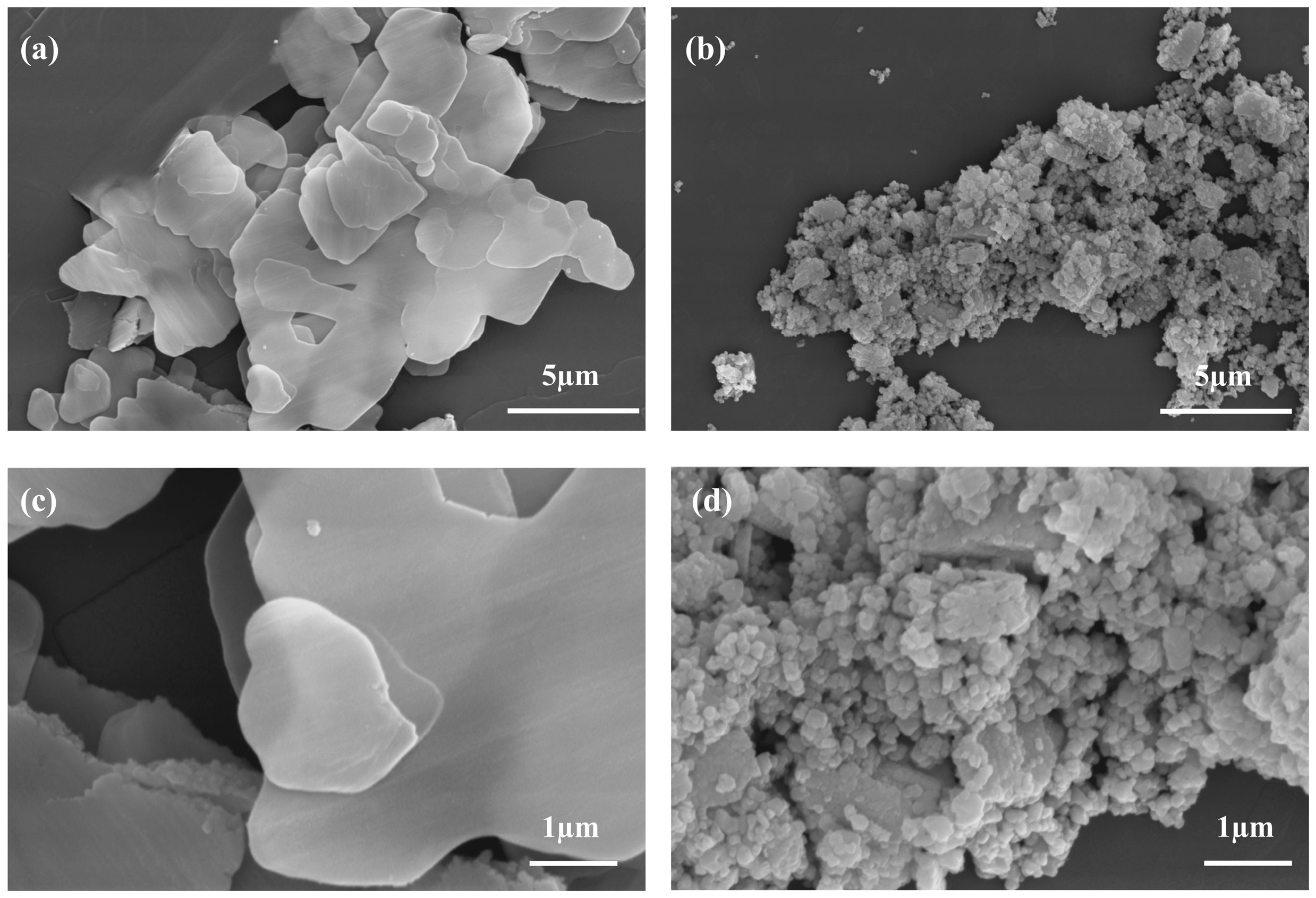
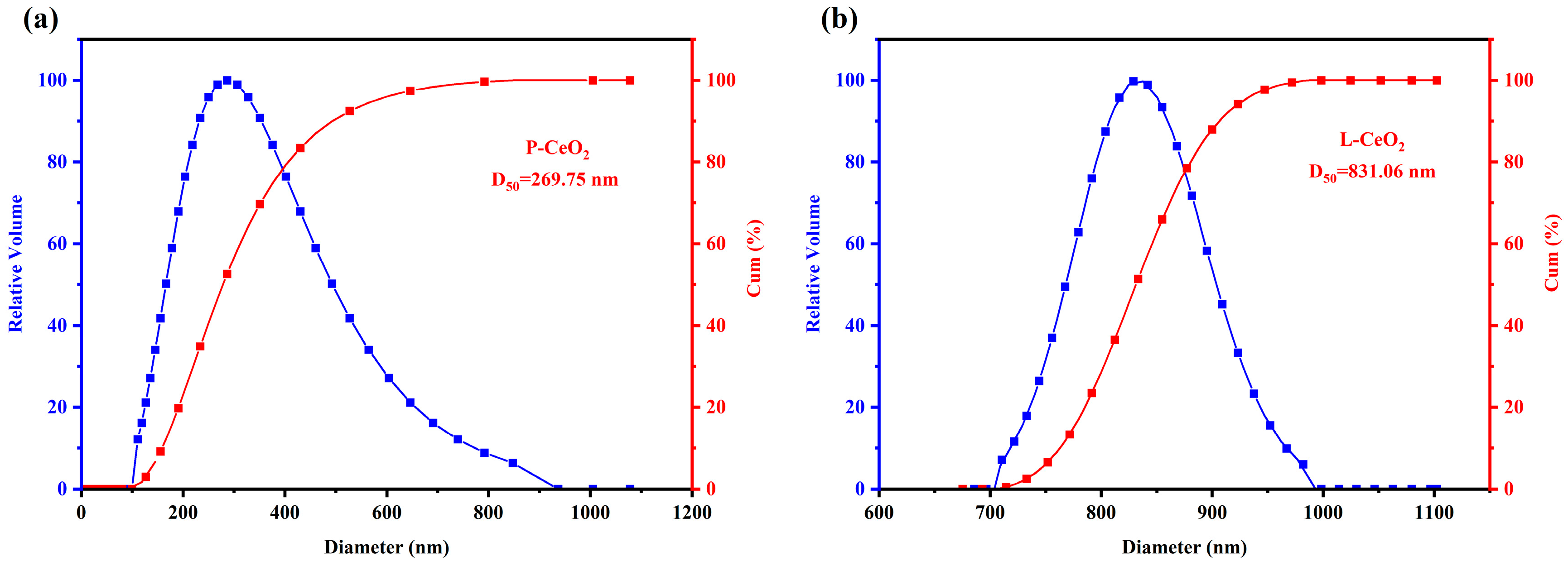
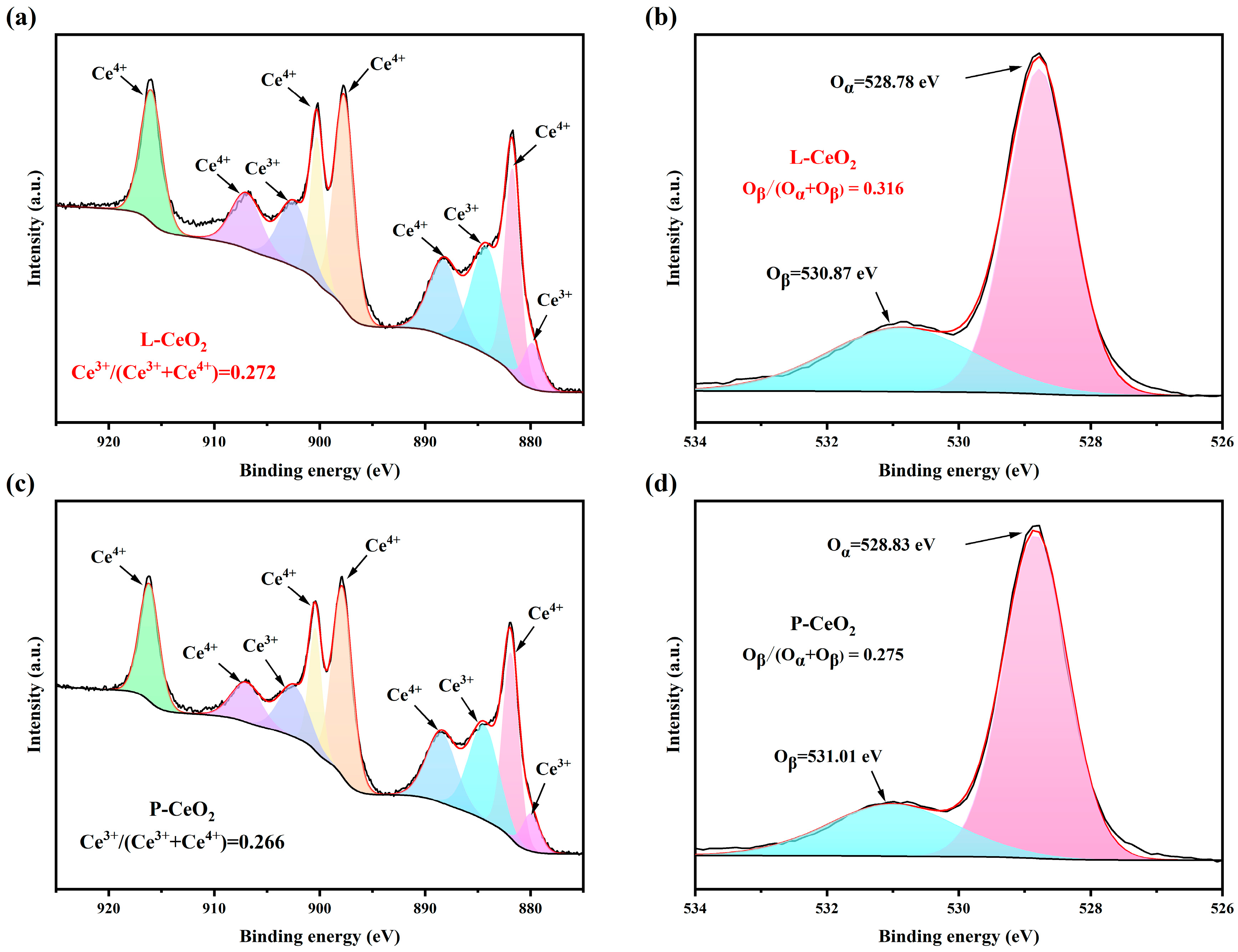
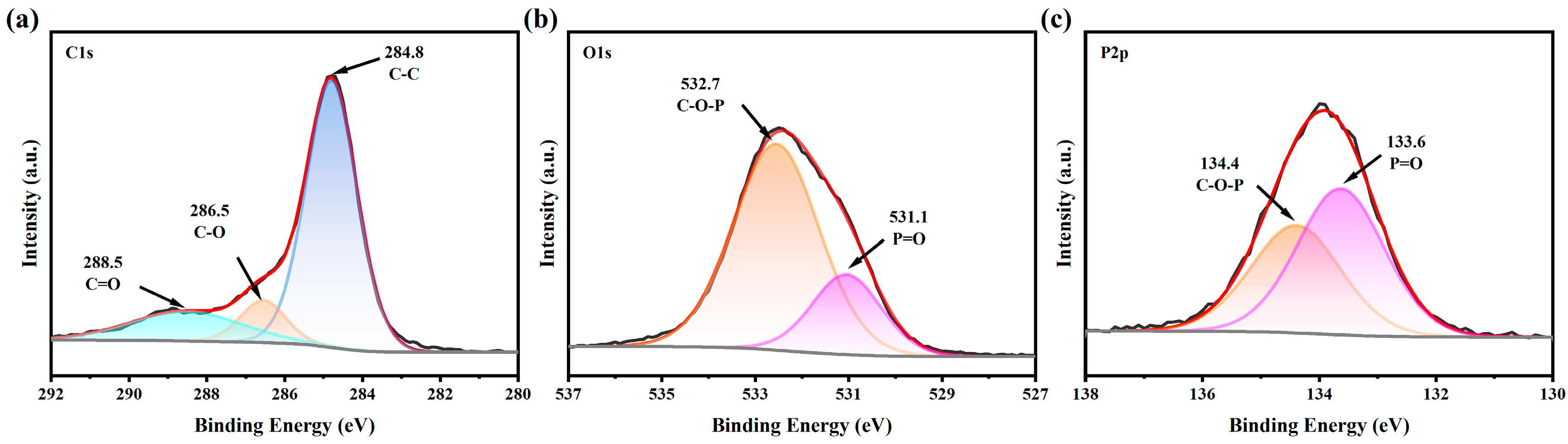
2.1. Characterization of CeO2
2.2. The Flame-Retardant Test
2.3. Characterization of Flame-Retardant Composites
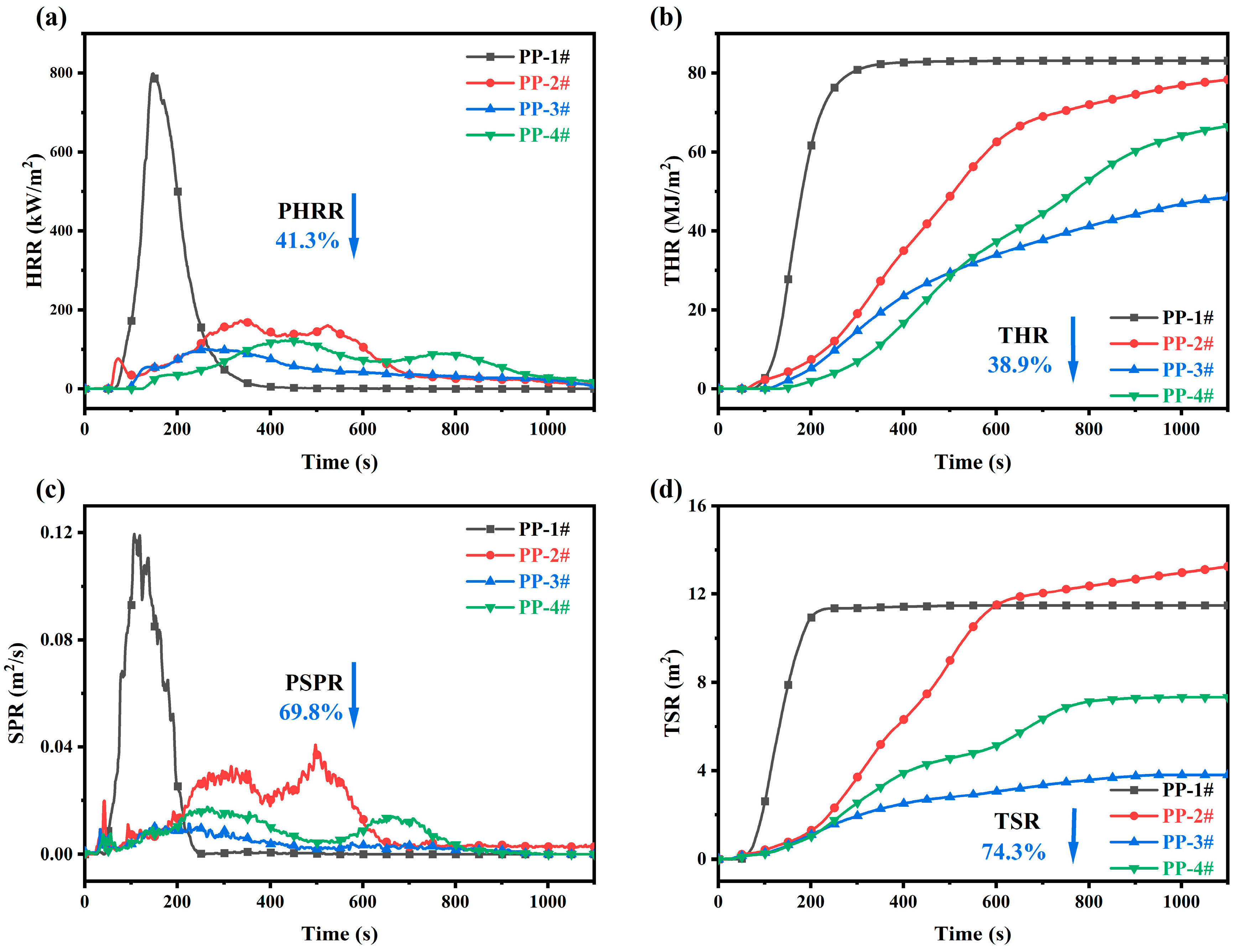
2.4. Cone Calorimeter Analysis of IFR Composites
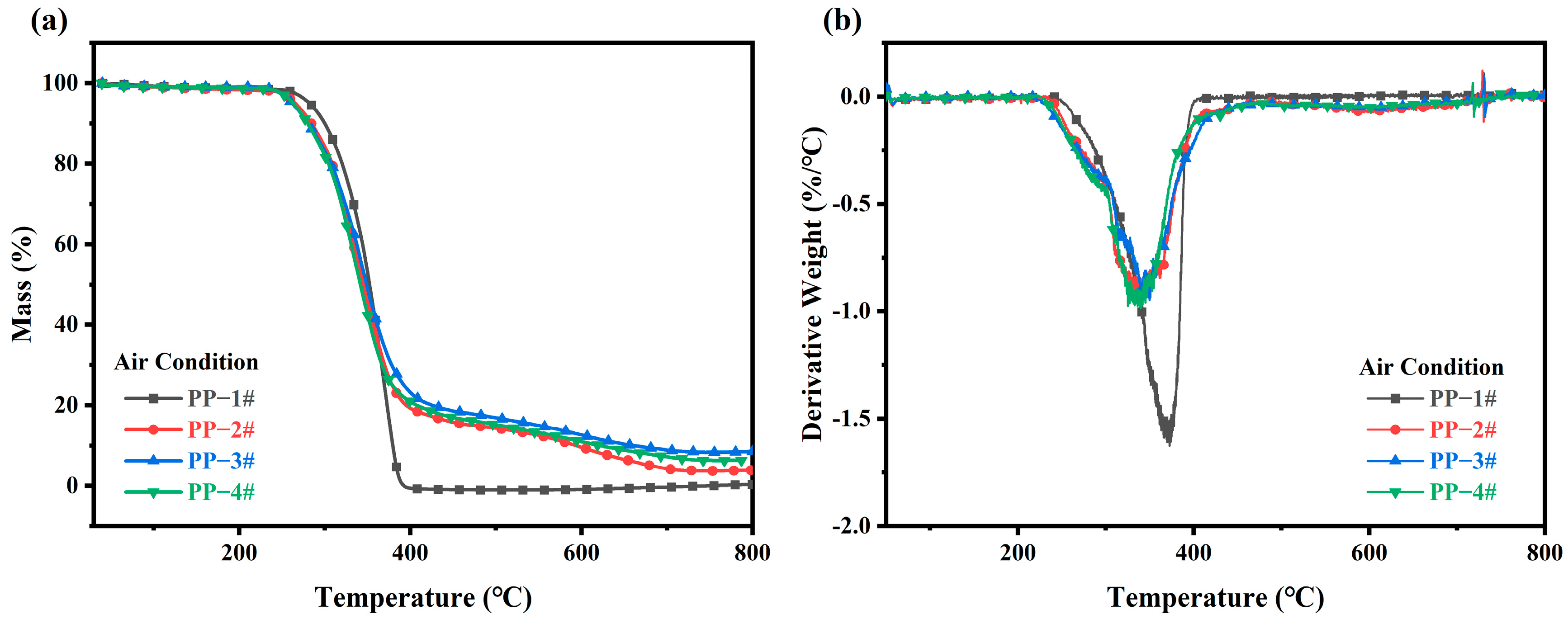
2.5. TGA of IFR Composites
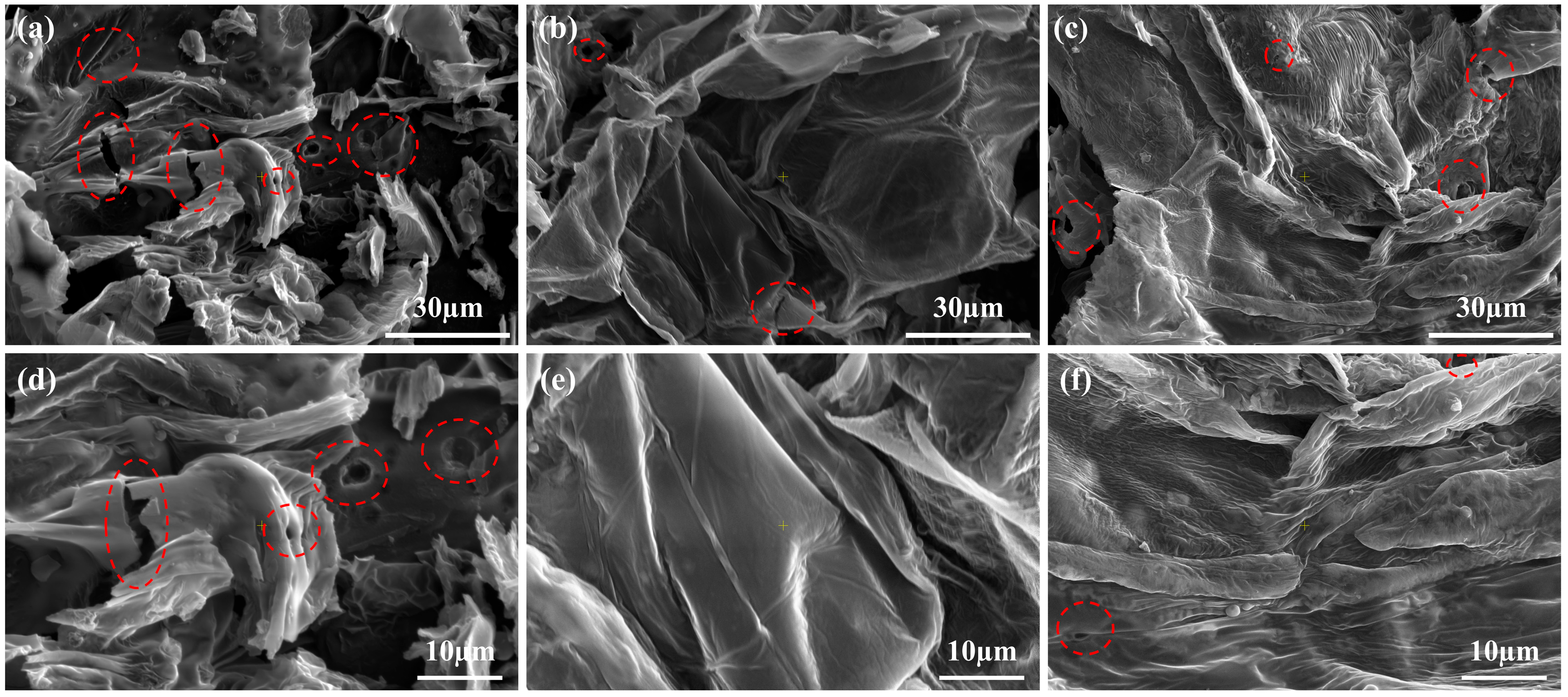
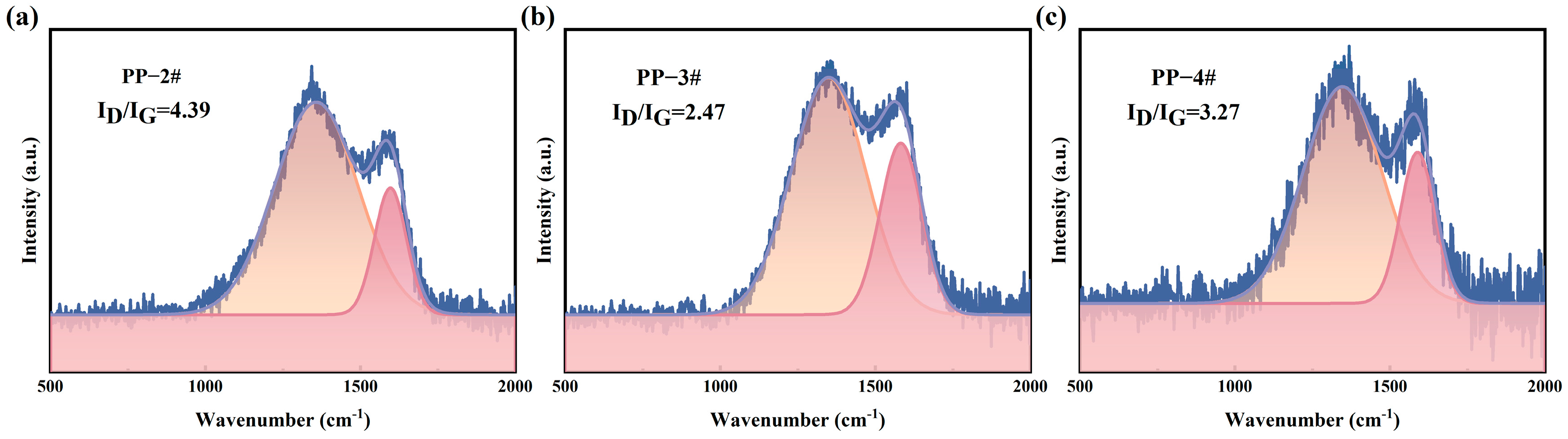
2.6. SEM and Raman Analysis of Carbon Layer Morphology
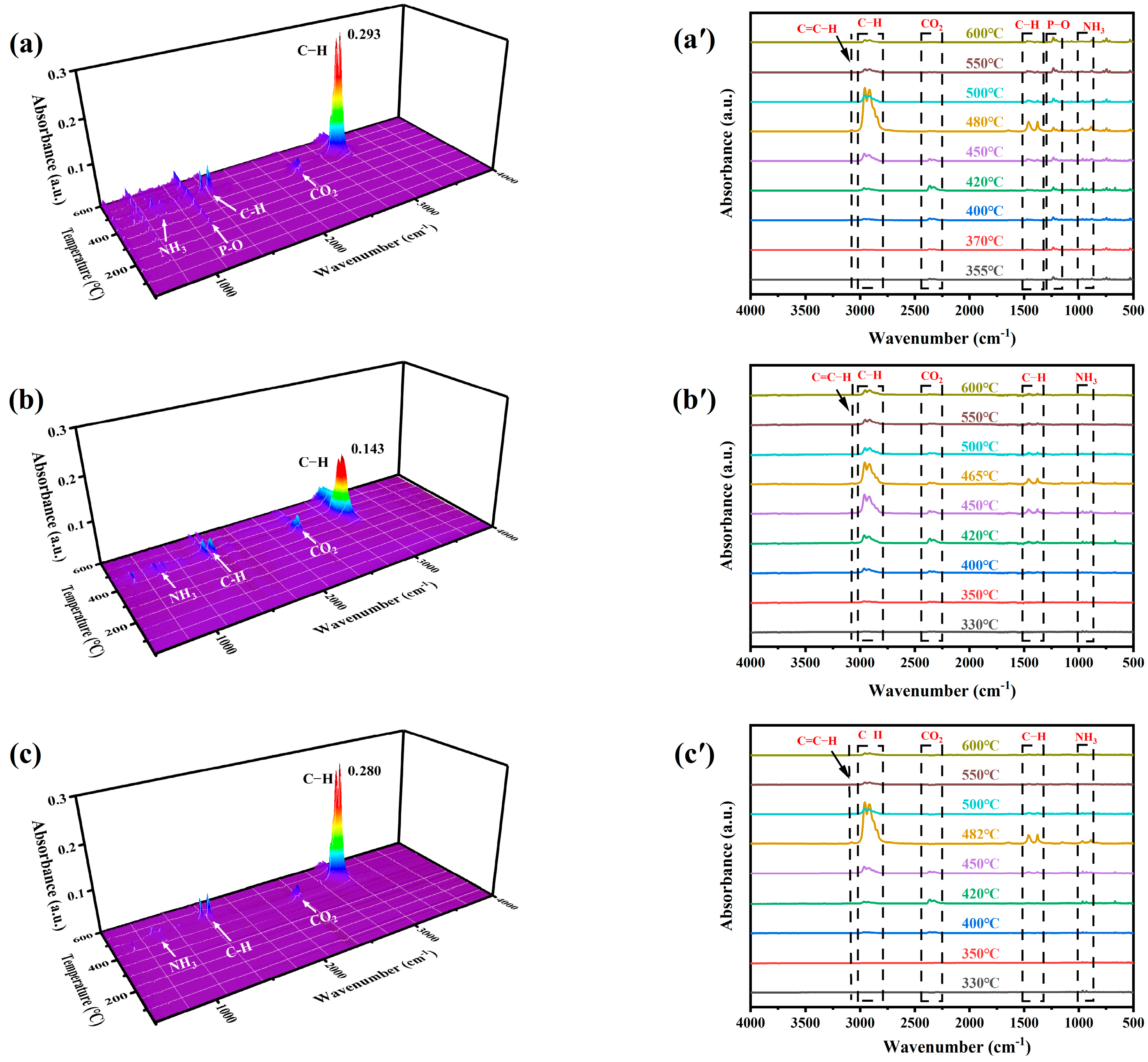
2.7. FTIR Analysis of IFR Composites
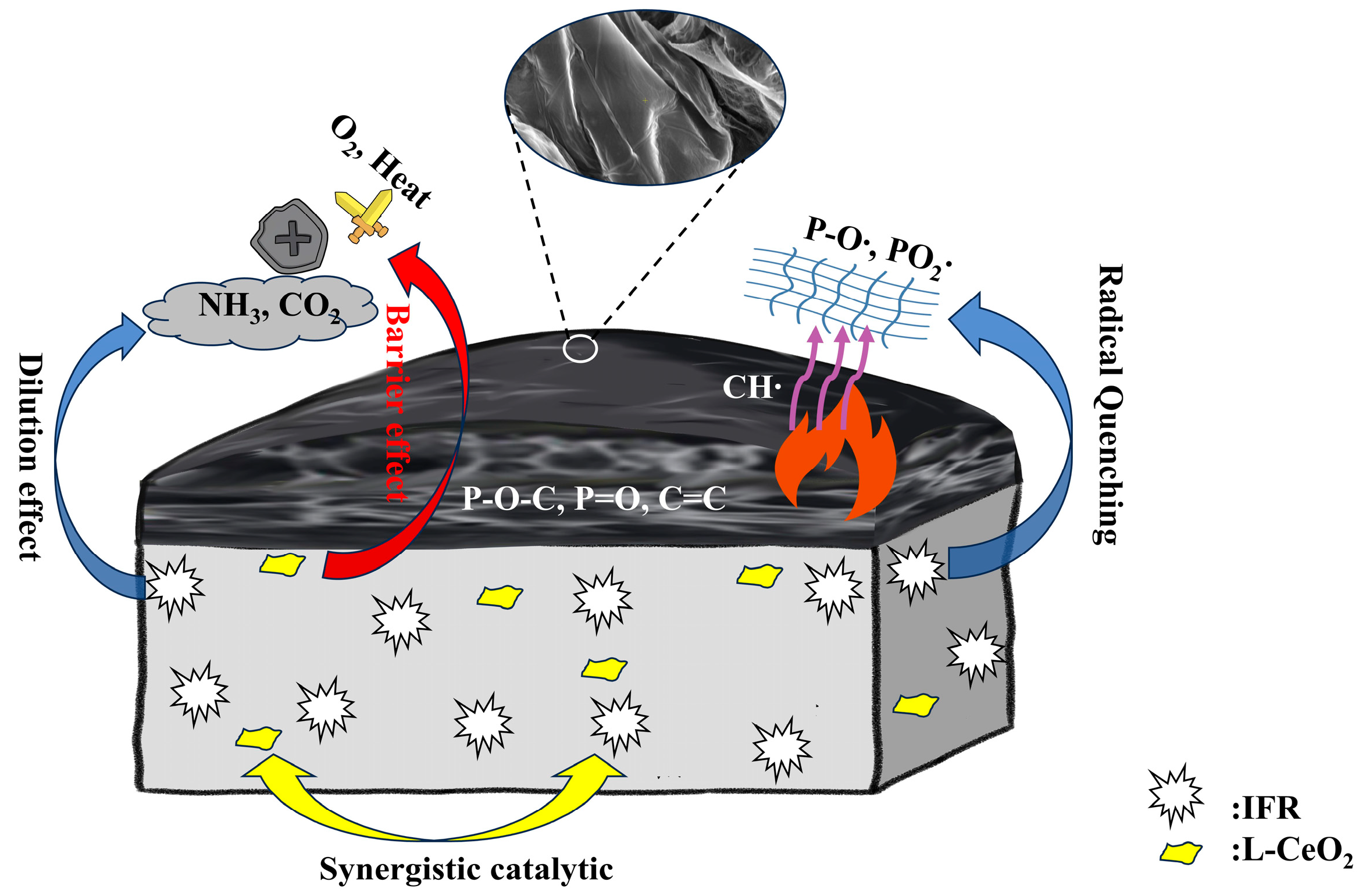
2.8. Synergistic Flame-Retardant Mechanism
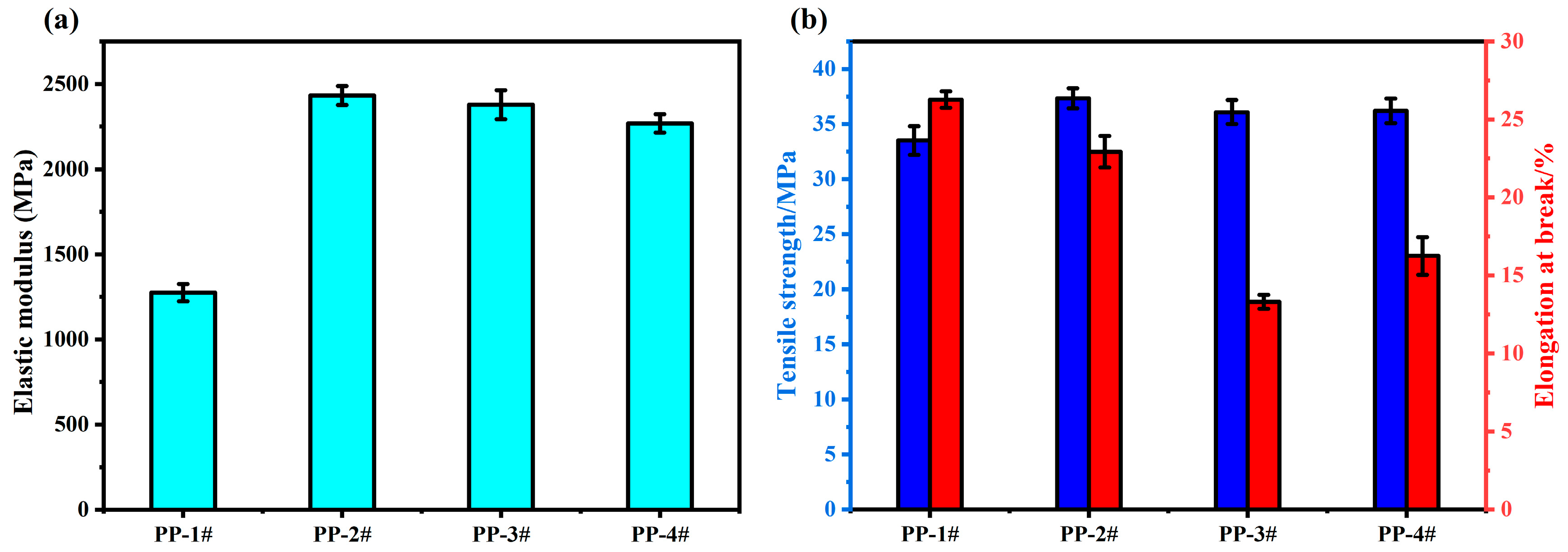
2.9. Mechanical Properties Analysis of IFR Composites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of L-CeO2
3.3. Preparation of Polypropylene Composites
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, X.; Tang, S.; Li, H.; Zeng, X. Flame-retardant mechanism of a novel polymeric intumescent flame retardant containing caged bicyclic phosphate for polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 113, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.-Y.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Tian, X.-Y.; Wu, K.; Hu, J.; Chen, C.-R.; Pan, Y. Intercalation of a novel containing nitrogen and sulfur anion into hydrotalcite and its highly efficient flame retardant performance for polypropylene. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 191, 105600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Synergistic effect of expandable graphite and intumescent flame retardants on the flame retardancy and thermal stability of polypropylene. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 5857–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, M.J. Effect of a novel charring-foaming agent on flame retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Cai, G.-P.; Mai, Y.-W. Recent developments in the fire retardancy of polymeric materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1357–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Martinasso, G. Intumescent fire-retardant systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1989, 23, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhong, Z.-Q.; Gong, X.-D. Flame retardancy, thermal properties, and combustion behaviors of intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene containing (poly) piperazine pyrophosphate and melamine polyphosphate. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Morgan, A.B.; Schiraldi, D.A.; Maia, J. Improving the flame retardancy of polypropylene foam with piperazine pyrophosphate via multilayering coextrusion of film/foam composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wen, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Synergistic effect between piperazine pyrophosphate and melamine polyphosphate in flame retarded glass fiber reinforced polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 184, 109477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B. Preparation of efficiently intumescent-flame-retarded polypropylene composite: Synergistic effect of novel phosphorus-containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2021, 50, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Ou, H.; Ran, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhu, F. Preparation and flame retardant properties of organic montmorillonite synergistic intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2024, 87, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Yu, T. Superior mechanical behavior and flame retardancy FRP via a distribution controllable 1D/2D hybrid nanoclay synergistic toughening strategy. Engineering 2024, 40, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, B.; Gao, X.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; You, T.; Lu, C.; Pang, X. Real-time monitoring of charcoal layer resistance for investigating the synergistic flame retardant mechanism of zinc oxide and intumescent flame retardants in SBS. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Meng, J.; Wang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y. Flame retardancy and smoke suppression effect of zinc borate-graphite intercalation compound/Fe2O3 on silicone rubber foams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yin, Z.; Yu, X.; Jia, P.; Zhou, X.; Lu, T.; Guo, L.; Song, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, B.; et al. A rare-earth-based nano-flame retardant with 2D MXene for improving fire safety and mechanical property of thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gong, K.; Yu, B.; Zhou, K. Rare earth-based flame retardants for polymer composites: Status and challenges. Compos. Part B 2023, 265, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, G.; Zou, Y.; Shang, S.; Sun, Y.; Yu, B.; He, S.; Chen, X. Alumina nanoflake-coated graphene nanohybrid as a novel flame retardant filler for polypropylene. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Hall, P. A comparative study on the mechanical and flammability properties of aluminum hydroxide and hollow glass beads-filled polypropylene composites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2025, 31, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Synergistic flame-retardant effects of aluminum oxide with layered double hydroxides in EVA/LDH composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2010, 23, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Liang, M.; Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, H. Synergism effect of CeO2 on the flame retardant performance of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites and its mechanism. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 122, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. An investigation into synergistic effects of rare earth oxides on intumescent flame retardancy of polypropylene/poly (octylene-co-ethylene) blends. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.H.; Yeh, H.C. A novel synthesis of α-MoO3 nanobelts and the characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Luo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Gao, W. Dispersion and agglomeration behaviors of submicron ceria particles in concentrated slurries. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021, 299, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, Y. Effect of surfactant types on particle size and morphology of flame-retardant zinc borate powder. Turk. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, H.; Mizoguchi, T.; Ohta, H.; Findlay, S.D.; Shibata, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Ikuhara, Y. Atomic structure of a CeO2 grain boundary: The role of oxygen vacancies. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4668–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Ran, R.; Li, M.; Weng, D. Soot oxidation over CeO2 and Ag/CeO2: Factors determining the catalyst activity and stability during reaction. J. Catal. 2016, 337, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Nanostructured ceria-based catalysts for soot combustion: Investigations on the surface sensitivity. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 165, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Bai, B.; Fu, L.; Li, Y. Ag/CeO2 nanospheres: Efficient catalysts for formaldehyde oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ren, Q.; Peng, R.; Mo, S.; Zhang, M.; Fu, M.; Chen, L.; Ye, D. Effect of CeO2 morphologies on toluene catalytic combustion. Catal. Today 2019, 332, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zou, L.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Yang, X. On the correlation between structure and catalytic activity of mesoporous ceria nanoparticles. J. Catal. 2021, 402, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Rational design of hierarchically micrometer scaled macro-mesoporous ceria-zirconia composites for enhancing diesel soot catalytic combustion performance. Mol. Catal. 2023, 535, 112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-T.; Castillo-Rodriguez, M.; Wang, D.-Y. Mesoporous metal oxide/pyrophosphate hybrid originated from reutilization of water treatment resin as a novel fire hazard suppressant. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wilkie, C.A.; O’Hare, D. Flame retardant polymer/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10996–11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, T.; Ran, S.; Guo, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, P.; Fang, Z. Transparent, highly thermostable and flame retardant polycarbonate enabled by rod-like phosphorous-containing metal complex aggregates. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qiu, S.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, F.; Wang, B.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of star-shaped allyl phosphazene small molecules for enhancing fire safety and toughness of high performance BMI resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, N.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Tang, T. Thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/carbon black nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lai, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, X. Fabrication of ZrP nanosheet decorated macromolecular charring agent and its efficient synergism with ammonium polyphosphate in flame-retarding polypropylene. Compos. Part A 2018, 105, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, A.; Abbenhuis, H.C.L.; Tabuani, D.; Camino, G. Metal functionalized POSS as fire retardants in polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gui, Z.; Jiang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, K. Carbonization of poly (methyl methacrylate) by incorporating hydroxyapatite nanorods during thermal degradation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10903–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qian, L. Enhancement of the intumescent flame retardant efficiency in polypropylene by synergistic charring effect of a hypophosphite/cyclotetrasiloxane bi-group compound. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 181, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-H.; Li, J.; Fang, K.-Y.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.-Z. Synergistic effect between a novel hyperbranched charring agent and ammonium polyphosphate on the flame retardant and anti-dripping properties of polylactide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.-Z. An S- and P-containing flame retardant for polypropylene. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2008, 26, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Chen, H.; He, D.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. An emerging mineral-based composite flame retardant coating: Preparation and enhanced fireproof performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 367, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Le Bras, M.; Delobel, R.; Gengembre, L. XPS study of an intumescent coating: II. Application to the ammonium polyphosphate/pentaerythritol/ethylenic terpolymer fire retardant system with and without synergistic agent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 120, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z. Fireproof performance of the intumescent fire retardant coatings with layered double hydroxides additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.S.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Chin, I.-J.; Jin, H.-J. Reinforcing effects of adding alkylated graphene oxide to polypropylene. Carbon 2011, 49, 3553–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraj, V.M.; Singh, S.; Devaraju, S.; Wadi, V.S.; Alhassan, S.; Anjum, D.H.; Mittal, V. Polypropylene/phosphazene nanotube nanocomposites: Thermal, mechanical, and flame retardation studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, T.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Improving flame retardancy of PP/MH/RP composites through synergistic effect of organic CoAl-layered double hydroxide. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Si, T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Improving flame retardancy of IFR/PP composites through the synergistic effect of organic montmorillonite intercalation cobalt hydroxides modified by acidified chitosan. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Improving the thermal stability and flame retardancy of PP/IFR composites by NiAl-layered double hydroxide. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 3660–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Y. Preparation of novel phosphorus-nitrogen-silicone grafted graphene oxide and its synergistic effect on intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene composites. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 36286–36297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Pei, H. Synergistic effect of 4A molecular sieve on intumescent ternary h-bonded complex in flame-retarding of polypropylene. Polymers 2023, 15, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, N.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Liu, S.; Zou, S.; Jin, F.; Tang, T. Synergistic effect of organo-modified montmorillonite and intumescent flame retardant on improving flame retardancy and thermal stability of polypropylene composites. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2025, 303, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, P. Synthesis of melamine phenyl hypophosphite and its synergistic flame retardance with SiO2 on polypropylene. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 6207–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Kang, W. Synergistic effect of lanthanum oxide on intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene-based formulations. J. Fire Sci. 2008, 26, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shuqian, S.; Mingmei, S.; Zhengwen, W.; Xingrong, Z.; Linsheng, T. Synergistic flame retardancy of ZnO with piperazine pyrophosphate/melamine polyphosphate in PP. Polym. Test. 2023, 117, 107878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4589-2:1996; Plastics-Determination of Burning Behaviour-by Oxygen Index. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- ASTM D3801-2020a; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Comparative Burning Characteristics of Solid Plastics in a Vertical Position. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ISO 5660-1:2015; Reaction-to-Fire Tests—Heat Release, Smoke Production and Mass Loss Rate. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 527-1-1993; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993.
| Sample | Components (wt.%) | UL 94 | t1/t2 (s) b | Dripping | Cotton Ignited | LOI (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | IFR a | L-CeO2 | P-CeO2 | ||||||
| PP-1# | 100 | NR | >60 | Y | Y | 17.8 | |||
| PP-2# | 81 | 19 | V-2 | 1.3/18.5 | Y | Y | 29.4 | ||
| PP-3# | 81 | 18 | 1 | V-0 | 0.5/7.2 | N | N | 32.6 | |
| PP-4# | 81 | 18 | 1 | V-0 | 0.5/5.5 | N | N | 31.0 | |
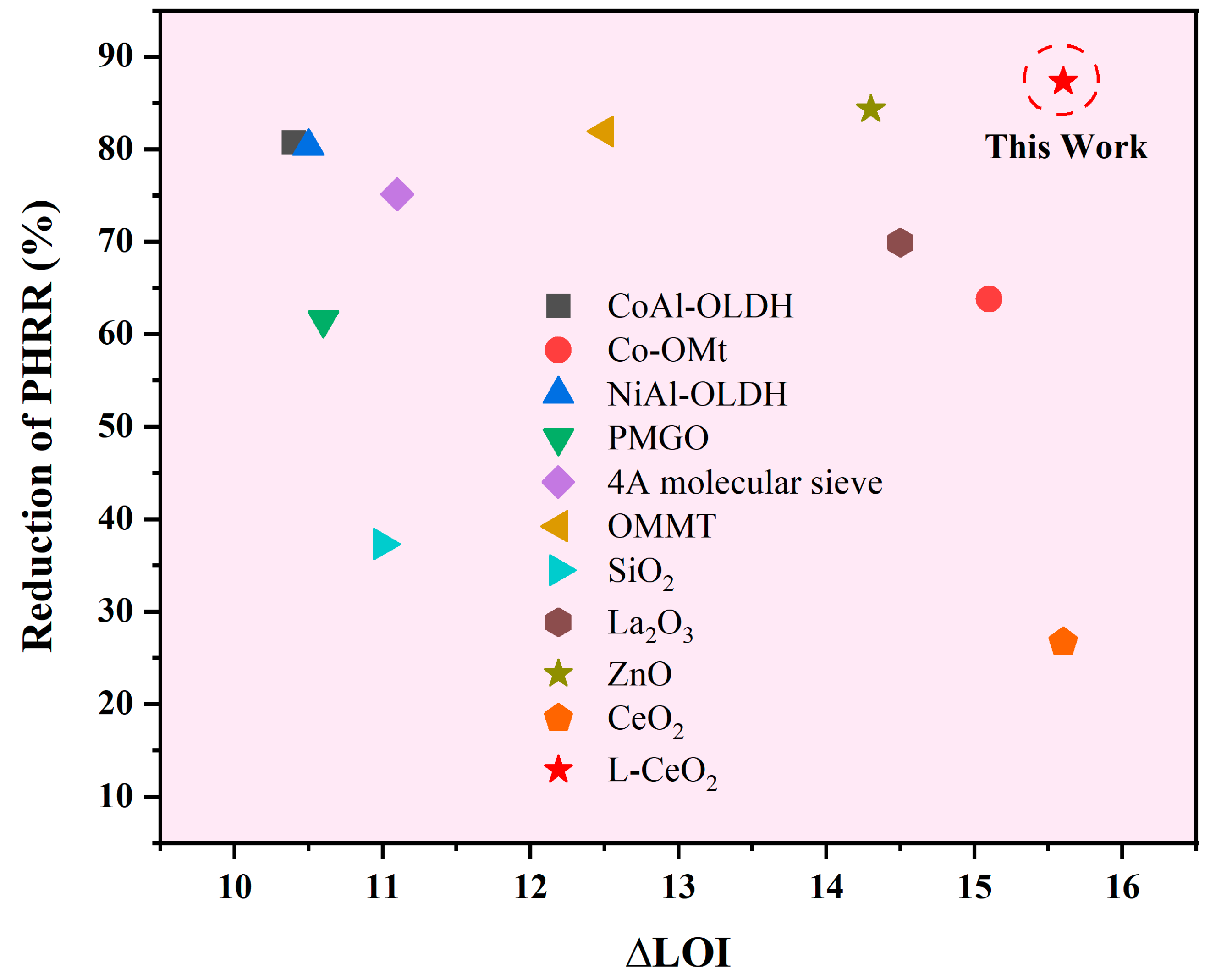
| Synergistic Flame Retardant | Content (wt.%) | Variation of THR (%) | Variation of PHRR (%) | ∆LOI | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoAl-OLDH | 3 | 36.9 | 80.7 | 10.4 | [49] |
| Co-OMt | 4 | 17.6 | 63.8 | 15.1 | [50] |
| NiAl-OLDH | 5 | 19.1 | 80.3 | 10.5 | [51] |
| PMGO | 5 | 40.2 | 61.5 | 10.6 | [52] |
| 4A molecular sieve | 1 | 17.1 | 75.1 | 11.1 | [53] |
| OMMT | 3 | 17.8 | 81.9 | 12.5 | [54] |
| SiO2 | 1 | 9.1 | 37.3 | 11.0 | [55] |
| La2O3 | 1 | 21.1 | 69.9 | 14.5 | [56] |
| ZnO | 0.5 | 28.1 | 84.3 | 14.3 | [57] |
| CeO2 | 1 | 16.5 | 26.7 | 15.6 | [20] |
| L-CeO2 | 1 | 41.6 | 87.3 | 14.8 | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Hsu, W.; Zheng, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, F.; Song, L.; Rao, X. Morphology-Engineered CeO2 as a Synergistic Flame Retardant in Polypropylene/Intumescent Systems: Mechanisms and Performance Enhancement. Molecules 2025, 30, 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102102
Li B, Hsu W, Zheng T, Wu Y, Wang S, Lin F, Song L, Rao X. Morphology-Engineered CeO2 as a Synergistic Flame Retardant in Polypropylene/Intumescent Systems: Mechanisms and Performance Enhancement. Molecules. 2025; 30(10):2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bangmin, Wayne Hsu, Tingyi Zheng, Yincai Wu, Shenglong Wang, Fenglong Lin, Lijun Song, and Xianfa Rao. 2025. "Morphology-Engineered CeO2 as a Synergistic Flame Retardant in Polypropylene/Intumescent Systems: Mechanisms and Performance Enhancement" Molecules 30, no. 10: 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102102
APA StyleLi, B., Hsu, W., Zheng, T., Wu, Y., Wang, S., Lin, F., Song, L., & Rao, X. (2025). Morphology-Engineered CeO2 as a Synergistic Flame Retardant in Polypropylene/Intumescent Systems: Mechanisms and Performance Enhancement. Molecules, 30(10), 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30102102







