Selected Metabolites of Biofunctional Importance from Edible Fruits of Forest Shrubs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antioxidant Activity, the Total Phenolic Content, Total Phenolic Acid Content, and Total Flavonoid Content
2.2. Natural Pigments
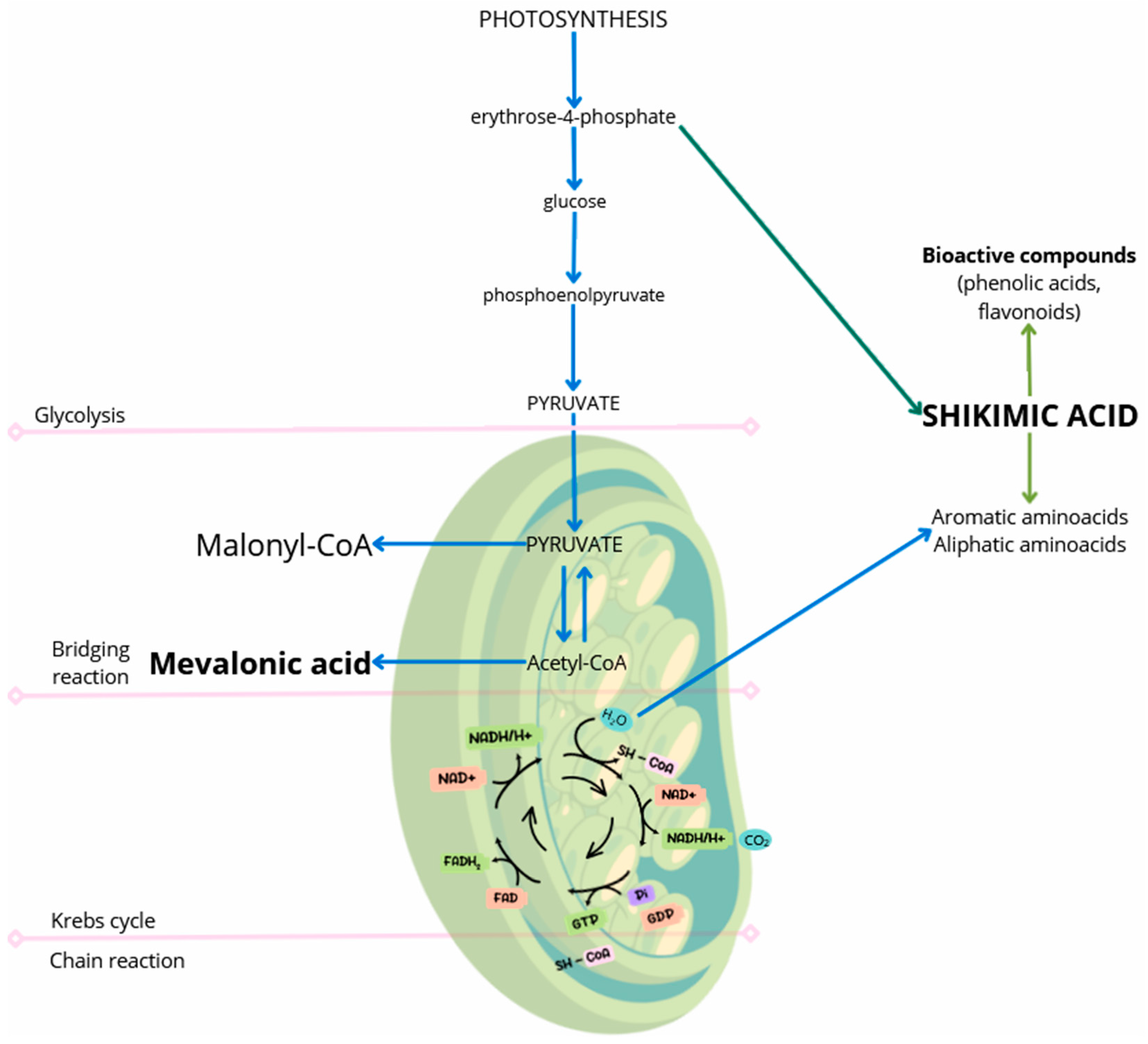
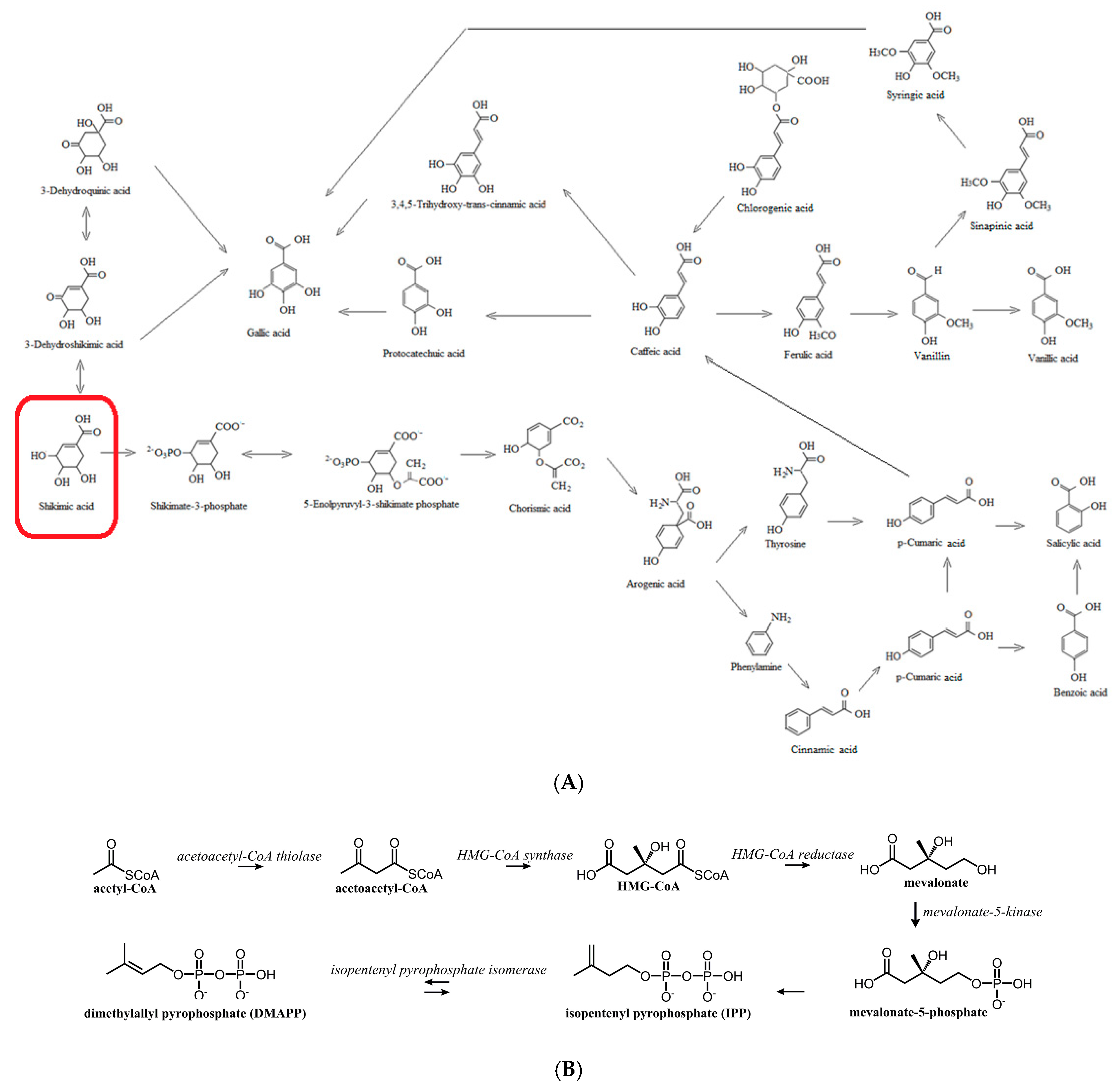
2.3. Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids, Organic Acids, and Flavonoid Glycosides
2.4. Elemental Composition of Soil
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Material
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. ABTS+ Radical-Scavenging Capacity
3.2.2. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds
3.2.3. Chromatographic Analysis
3.2.4. Total Phenolic Content (TPC, TAC, TFC)
3.2.5. Total Chlorophyll Content
- A645–665—absorbance measured at a wavelength of 649–665 nm;
- V—total volume of the extract (mL);
- W—weight of the sample (g) [71].
3.2.6. Total Carotenoid Content
3.2.7. Total Anthocyanin Content
3.2.8. Analyses of Insolation
3.2.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kroymann, J. Natural diversity and adaptation in plant secondary metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M. Albrecht Kossel, a biographical sketch. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1953, 26, 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gawlik-Dziki, U. Phenolic acids as bioactive food ingredients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 4, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kandar, C.C. Secondary Metabolites from Plant Sources. In Bioactive Natural Products for Pharmaceutical Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 329–377. [Google Scholar]
- Szweykowska, A. Fizjologia Roślin; Scientific Publishing House: Poznan, Poland, 1998; pp. 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katarzyna, N.-C.; Dariusz, L.; Natalia, G.-W. Secondary Metabolites Synthesized by Selected Tree and Shrub Species: Use in Medicine; TYGIEL Scientific Publishing House: Lublin, Poland, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The effect of phenolic acids on living organisms. Indian J. Med. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dudka, K.; Baran, M.; Karpik, E. Roślinne metabolity wtórne i ich za-stosowanie w kosmetyce. In Przegląd Wybranych Prac z Zakresu Enzymologii; Foundation for the Promotion of Science and Development TYGIEL: Lublin, Poland, 2016; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Keser, S.; Celik, S.; Turkoglu, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Turkogul, I. The Investigation of Some Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Properties of Hawthorn (Crataegus monogyna subsp. monogyna jacq.). J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadić, V.M.; Dobrić, S.; Marković, G.M.; Ðorđević, S.M.; Arsić, I.A.; Menković, N.R.; Stević, T. Anti-inflammatory, Gastroprotective, Free-Radical-Scavenging, and Antimicrobial Activities of Hawthorn Berries Ethanol Extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7700–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant Activity/Capacity Measurement. 2. Hydrogen Atom Transfer (HAT)-Based, Mixed-Mode (Electron Transfer (ET)/HAT), and Lipid Peroxidation Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1028–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarv, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Rätsep, R.; Aluvee, A.; Kazernavičiūtė, R.; Bhat, R. Antioxidants Characterization of the Fruit, Juice, and Pomace of Sweet Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Cultivated in Estonia. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juríková, T.; Sochor, J.; Mlček, J.; Balla, Š.; Klejdus, B.; Baroň, M.; Ercisli, S.; Yilmaz, S.O. Polyphenolic profile of interspecific crosses of rowan (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Ital. J. Food Sci. 2014, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kampuss, K.; Kampuse, S.; Berņa, E.; Krūma, Z.; Krasnova, I.; Drudze, I. Biochemical Composition and Antiradical Activity of Rowanberry (Sorbus L.) Cultivars and Hybrids with Different Rosaceae L. Cultivars Pīlādžu (Sorbus L.) Šėirĥu Un to Hibrīdu Ar Citiem Rosaceae L. Augěaugiem Antioksidatīvā Aktivitāte Un Bioėīmiskais Sastāvs. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2009, 59, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Szablewski, T.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Świerk, D.; Cegielska-Radziejewska, R.; Krejpcio, Z.; Suchowilska, E.; Tomczyk, Ł.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Sambucus nigra Extracts–Natural Antioxidants and Antimicrobial Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobinaitė, R.; Kraujalis, P.; Tamkutė, L.; Urbonavičienė, D.; Viškelis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R. Recovery of bioactive substances from rowanberry pomace by consecutive extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide and pressurized solvents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávalos, A.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Bartolomé, B. Extending Applicability of the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC−Fluorescein) Assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarczyk, K.; Walkowiak-Tomczak, D.; Staniek, H.; Kidoń, M.; Łysiak, G.P. The Content of Selected Minerals, Bioactive Compounds, and the Antioxidant Properties of the Flowers and Fruit of Selected Cultivars and Wildly Growing Plants of Sambucus nigra L. Molecules 2020, 25, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozos, K.; Ochmian-Nyćkowiak, J. Porównanie Jakości Kilku Gatunków Owoców o Ciemnym Zabarwieniu Skórki Uprawnych i Pozyskanych Ze Stanowisk Naturalnych; Wyd Młodzi Naukowcy: Poznań, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Młynarczyk, K.; Walkowiak-Tomczak, D.; Łysiak, G.P. Bioactive properties of Sambucus nigra L. as a functional ingredient for food and pharmaceutical industry. J. Funct. Foods. 2018, 40, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochmian, I.; Oszmianski, J.; Skupien, K. Chemical composition, phenolics, and firmness of small black fruits. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2009, 83, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hukkanen, A.T.; Pölönen, S.S.; Kärenlampi, S.O.; Kokko, H.I. Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Content of Sweet Rowanberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polka, D.; Podsędek, A.; Koziołkiewicz, M. Comparison of Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruit, Flower and Bark of Viburnum opulus. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rop, O.; Reznicek, V.; Valsikova, M.; Jurikova, T.; Mlcek, J.; Kramarova, D. Antioxidant Properties of European Cranberrybush Fruit (Viburnum opulus var. edule). Molecules 2010, 15, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, O.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Szablewski, T.; Cegielska-Radziejewska, R.; Świerk, D.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. New Insights into Bioactive Compounds of Wild-Growing Medicinal Plants. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Česonienė, L.; Daubaras, R.; Venclovienė, J.; Viškelis, P. Biochemical and agro-biological diversity of Viburnum opulus genotypes. Open Life Sci. 2010, 5, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudjil, S.; Boussekine, S.; Goudjil, S.; Goudjil, H.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Ola, M.S.; Ali, A.; Cakir, O. Investigation of Algerian Crataegus monogyna Jacq Phenolic Compounds (Using LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis, Antioxidant Activity, and Enzyme Inhibition) and Their Potential Implications for Food and Nutraceutical Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveci, E.; Tel Çayan, G.; Karakurt, S.; Duru, M.E. Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Agropyron repens and Crataegus monogyna Species. Eur. J. Biol. 2020, 79, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, A.M.; Mertoğlu, K.; Alan, F.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Bulduk, İ.; Akbel, E.; Kahramanoğlu, I. Screening of Naturally Grown European Cranberrybush (Viburnum opulus L.) Genotypes Based on Physico-Chemical Characteristics. Foods 2022, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, N.; Ercisli, S.; Gundogdu, M. Evaluation of European Cranberrybush (Viburnum opulus L.) genotypes for agro-morphological, biochemical and bioactive characteristics in Turkey. Folia Hortic. 2017, 29, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurori, M.; Niculae, M.; Hanganu, D.; Pall, E.; Cenariu, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Fiţ, N.; Andrei, S. The Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Cell-Protective Properties of Bioactive Compounds Extracted from Rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits In Vitro. Plants 2024, 13, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, E.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Patras, A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A.; Tudor, C.; Sturza, R. The Influence of Temperature, Storage Conditions, pH, and Ionic Strength on the Antioxidant Activity and Color Parameters of Rowan Berry Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šavikin, K.P.; Zdunić, G.M.; Krstić-Milošević, D.B.; Šircelj, H.J.; Stešević, D.D.; Pljevljakušić, D.S. Sorbus aucuparia and Sorbus aria as a Source of Antioxidant Phenolics, Tocopherols, and Pigments. Chem. Biodivers 2017, 14, e1700329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajszczak, D.; Zakłos-Szyda, M.; Podsędek, A. Viburnum opulus L.—A Review of Phytochemistry and Biological Effects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnum-Hansen, K.; Jacobsen, F.; Flink, J.M. Anthocyanin colourants from elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.). 1. Process considerations for production of the liquid extract. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1985, 20, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.M.; Pintea, A.M.; Rugina, D.O.; Sconta, Z.M.; Hanganu, D.; Vlase, L.; Benedec, D. Preliminary studies on the chemical characterization an antioxidant capacity of polyphenols from Sambucus sp. J. Nanometer Bios. 2013, 8, 973–980. [Google Scholar]
- Vulic, J.; Vracar, L.; Sumic, Z. Chemical characteristics of cultivated elderberry fruit. Acta Period. Technol. 2008, 39, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawirska-Olszańska, A. A plant not without potential. Black elderberry—A weed, or maybe a medicinal plant? Dir. Food 2016, 2, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bobinaitė, R.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J.; Šarkinas, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Žvikas, V.; Viškelis, P.; Venskutonis, P.R. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of the extracts isolated from the pomace of rowanberry (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Ivancic, A.; Schmitzer, V.; Veberic, R.; Stampar, F. Comparison of major taste compounds and antioxidative properties of fruits and flowers of different Sambucus species and interspecific hybrids. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goławska, S.; Łukasik, I.; Chojnacki, A.A.; Chrzanowski, G. Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids Content in Cultivation and Wild Collection of European Cranberry Bush Viburnum opulus L. Molecules 2023, 28, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perova, I.B.; Zhogova, A.A.; Cherkashin, A.V.; Éller, K.I.; Ramenskaya, G.V.; Samylina, I.A. Biologically Active Substances from European Guelder Berry Fruits. Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 48, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özrenk, K.; Gündoğdu, M.; Keskin, N.; Kaya, T. Some physical and chemical characteristics of gilaburu (Viburnum opulus L.) fruits in Erzincan region. Iğdır Univ. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sedat Velioglu, Y.; Ekici, L.; Poyrazoglu, E.S. Phenolic composition of European cranberrybush (Viburnum opulus L.) berries and astringency removal of its commercial juice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsou, K.; Magopoulou, D.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Sfougaris, A.I.; Lalas, S.I. Enhancing the Nutritional Profile of Crataegus monogyna Fruits by Optimizing the Extraction Conditions. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chai, X.; Zhao, F.; Hou, G.; Meng, Q. Food Applications and Potential Health Benefits of Hawthorn. Foods 2022, 11, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muradoğlu, F.; Gürsoy, S.; Yıldız, K. Quantification Analysis of Biochemical and Phenolic Composition in Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) Fruits. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2019, 61, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolatova, E.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Baj, T.; Stasiak, N.; Ibadullayeva, G.; Koch, W.; Głowniak, K.; Tulemissov, S.; Sakipova, Z.; Boylan, F. Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čulum, D.; Čopra-Janićijević, A.; Vidic, D. The investigation of selected bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties of Crataegus monogyna L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez-Zahra Amrati, F.; Mssillou, I.; Boukhira, S.; Djiddi Bichara, M.; El Abdali, Y.; de Azevedo, R.G.; Mohamed, C.; Slighoua, M.; Conte, R.; Kiokias, S.; et al. Phenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq. Extract and Its Anti-Inflammatory, Hepatoprotective, and Antileukemia Effects. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Song, M.; Qiu, P.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; Xiao, H. A metabolite of nobiletin, 4′-demethylnobiletin and atorvastatin synergistically inhibits human colon cancer cell growth by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Yuan, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Hanna, M.; Yuan, L. Evaluation of physicochemical characteristics, nutritional composition and antioxidant capacity of Chinese organic hawthorn berry (Crataegus pinnatifida). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlicher, T.; Hennebelle, T.; Martin-Nizard, F.; Cleenewerck, P.; Hilbert, J.L.; Trotin, F.; Grec, S. Phenolic profiles and antioxidative effects of hawthorn cell suspensions, fresh fruits, and medicinal dried parts. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, F.; Ning, C.; Chen, G. Pectin oligosaccharides from hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge. Var. major): Molecular characterization and potential antiglycation activities. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, G.; Senizza, B.; Zengin, G.; Mahomodally, M.F.; Senkardes, I.; Lobine, D.; Lucini, L. Untargeted metabolomic profiling of three Crataegus species (hawthorn) and their in vitro biological activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwajkowska-Michalek, L.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Rogoziński, T.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Bioactive Substances in Trees and Shrubs of Central Europe. Preprints 2019, 2019060156. [Google Scholar]
- Zymone, K.; Raudone, L.; Žvikas, V.; Jakštas, V.; Janulis, V. Phytoprofiling of Sorbus L. Inflorescences: A Valuable and Promising Resource for Phenolics. Plants 2022, 11, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsavová, J.; Juríková, T.; Bednaříková, R.; Mlček, J. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content, Individual Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Sweet Rowanberry Cultivars. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M.; Owczarek-Januszkiewicz, A.; Magiera, A.; Gieleta, M.; Olszewska, M.A. Chemometrics-Driven Variability Evaluation of Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Capacity, and α-Glucosidase Inhibition of Sorbus aucuparia L. Fruits from Poland: Identification of Variability Markers for Plant Material Valorization. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvinte, O.; Senila, L.; Becze, A.; Amariei, S. Rowanberry—A Source of Bioactive Compounds and Their Biopharmaceutical Properties. Plants 2023, 12, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.; Bonesi, M.; Sicari, V.; Ursino, C.; Manfredi, I.; Conidi, C.; Figoli, A.; Cassano, A. Concentration of Bioactive Compounds from Elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) Juice by Nanofiltration Membranes. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, E.V.; Andrushchenko, O.A.; Kononenko, A.V. Carboxylic Acids from Sorbus aucuparia and S. aria. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Krska, B.; Kiprovski, B.; Veberic, R. Bioactive Components and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruits from Nine Sorbus Genotypes. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimler, D.; Romani, A.; Ieri, F. Plant polyphenol content, soil fertilization and agricultural management: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Tattini, M. Multiple functional roles of flavonoids in photoprotection. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisa, M.; Bonnet, S.L.; Ferreira, D.; Van der Westhuizen, J.H. Photochemistry of Flavonoids. Molecules 2010, 15, 5196–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Frankowski, J.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Bioactive compounds in sorghum. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Kurasiak-Popowska, D.; Nawracała, J.; Perkowski, J. Quantitative profile of phenolic acids and antioxidant activity of wheat grain exposed to stress. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Szablewski, T.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Świerk, D.; Cegielska-Radziejewska, R.; Krejpcio, Z. Antimicrobial Activities Evaluation and Phytochemical Screening of Some Selected Plant Materials Used in Traditional Medicine. Molecules 2022, 28, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, F.; Jafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S.; Wan Maznah, W.O. Laboratory measurement: Chlorophyll-a concentration measurement with acetone method using spectrophotometer. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Kurasiak-Popowska, D.; Ryńska, B.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Analysis of Distribution of Selected Bioactive Compounds in Camelina sativa from Seeds to Pomace and Oil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.M.; Wrolstad, R.E. Characterization and Measurement of Anthocyanins by UV-Visible Spectroscopy. In Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
| Family of Plants | Rosaceae Juss. | Adoxaceae | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Species | Crataegus monogyna Jacq. | Sorbus aucuparia L. | Viburnum opulus L. | Sambucus nigra | ||||
| Location | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina |
| ABTS+ (μmol Trolox equivalents/kg d.m. fruit) | 2844 ± 54 a | 2537 ± 38 b | 1244 ± 31 c | 1204 ± 28 c | 1349 ± 29 d | 1257 ± 32 c | 1255 ± 39 c | 1387 ± 29 d |
| TPC (mg GAE/100 g d.m. fruit) | 4322 ± 43 a | 4299 ± 53 a | 1855 ± 34 b | 1948 ± 42 b | 722 ± 37 c | 761 ± 33 c | 4177 ± 58 a | 5042 ± 62 d |
| TAC (mg CAE/100 g d.m. fruit) | 122 ± 19 a | 130 ± 17 a | 100 ± 14 a | 355 ± 17 b | 106 ± 16 a | 111 ± 13 a | 324 ± 23 b | 102 ± 23 a |
| TFC (mg RUTE/100 g d.m. fruit) | 1041.6 ± 46.3 a | 1057.1 ± 36.4 a | 758.3 ± 41.7 b | 519.2 ± 33.5 c | 148.5 ± 18.3 d | 119.3 ± 14.2 d | 550.2 ± 26.4 c | 765.8 ± 28.3 b |
| Family of Plants | Rosaceae Juss. | Adoxaceae | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Species | Crataegus monogyna Jacq. | Sorbus aucuparia L. | Viburnum opulus L. | Sambucus nigra | ||||
| Location | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina |
| Carothenoids | 211.5 ± 19.2 a | 206.3 ± 12.3 a | 134.2 ± 18.3 b | 151.1 ± 14.6 b | 51.8 ± 8.5 c | 56.3 ± 5.6 c | 142.1 ± 13.6 b | 133.7 ± 15.2 b |
| Chlorophyll | 0.65 ± 0.07 a | 0.59 ± 0.09 a | 0.27 ± 0.08 b | 1.24 ± 0.11 c | 3.11 ± 0.97 d | 1.88 ± 0.09 c | 1.66 ± 0.09 c | 0.22 ± 0.08 b |
| Anthocyanins | 21.3 ± 4.5 a | 20.7 ± 5.6 a | 50.8 ± 7.2 b | 58.9 ± 8.3 b | 8.7 ± 2.5 c | 5.6 ± 1.2 c | 579.6 ± 53.8 d | 517.4 ± 42.6 d |
| No. | Family of Plants | Rosaceae Juss. | Adoxaceae | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Species | Crataegus monogyna Jacq. | Sorbus aucuparia L. | Viburnum opulus L. | Sambucus nigra | |||||
| Location | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | |
| 1 | Gallic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 8.22 ± 0.87 a | 12.01 ± 1.01 b |
| 2 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 7.15 ± 1.00 a | 3.94 ± 0.52 b |
| 3 | 2.5-dihydroksobenzoic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 4 | Vanilic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.02 b |
| 5 | Caffeic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 2.45 ± 0.65 a | 6.09 ± 0.07 b |
| 6 | Syringic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 4.37 ± 0,74 a | 5.27 ± 0.28 b |
| 7 | Coumaric acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 8 | Vanilin | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 8.16 ± 1.01 a | 10.55 ± 1.12 b |
| 9 | p-Cumaric acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.56 ± 0.12 a | 1.74 ± 0.12 a |
| 10 | Benzoic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 33.77 ± 3.12 a | 16.04 ± 2.11 b |
| 11 | Ferulic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 93.08 ± 5.10 a | 65.76 ± 4.01 b |
| 12 | Sinapic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 188.25 ± 8.12 a | 197.99 ± 7.45 a |
| 13 | t-Cinnamic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.89 ± 0.21 a | 1.55 ± 0.13 a | 131.54 ± 7.45 b | 135.51 ± 6.38 b |
| 14 | Chlorogenic acid | 1158.22 ± 15.54 a | 1199.7 ± 17.59 a | 6.55 ± 0.71 b | 8.01 ± 0.61 b | 58.22 ± 7.18 c | 601.41 ± 14.32 c | 405.88 ± 12.05 d | 389.84 ± 12.69 d |
| 15 | Protocatechuic acid | 85.24 ± 84.11 a | 88.79 ± 4.98 a | 233.5 ± 8.54 b | 238.54 ± 6.39 b | 50.22 ± 6.25 c | 53.47 ± 5.18 c | 1.77 ± 0.07 d | 2.53 ± 0.04 d |
| 16 | Rozmaric acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.44 ± 0.01 a | 2.17 ± 0.02 b |
| 17 | Salicylic acid | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 3.11 ± 0.05 a | 2.86 ± 0.05 a | 7.03 ± 0.10 b | 7.17 ± 0.11 b |
| 18 | Apigenin | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 177.29 ± 10.05 a | 188.19 ± 7.98 a |
| 19 | Katechin | 165.2 ± 4.75 a | 170.47 ± 4.95 a | <LOD | <LOD | 219.3 ± 8.84 b | 195.24 ± 4.85 b | 0.49 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 c |
| 20 | Kempferol | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.79 ± 0.02 a | 3.47 ± 0.02 b |
| 21 | Luteolin | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 36.81 ± 1.38 a | 74.4 ± 2.02 b |
| 22 | Naringenin | <LOD | <LOD | 613.5 ± 7.15 a | 610.77 ± 7.26 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 77.22 ± 3.29 c | 83.23 ± 4.05 c |
| 23 | Quercetin | 1057.2 ± 10.54 a | 1102.74 ± 11.15 a | 180.22 ± 7.12 b | 182.1 ± 5.54 b | 1.97 ± 0.02 c | 1.25 ± 0.02 c | 819.33 ± 8.13 d | 956.38 ± 7.48 d |
| 24 | Rutin | 588.21 ± 5.56 a | 549.33 ± 7.32 a | 66.84 ± 3.78 b | 68.39 ± 6.48 b | 0.88 ± 0.02 c | 0.79 ± 0.01 c | 1798.22 ± 14.15 d | 2044.51 ± 15.65 e |
| 25 | Vitexin | 287.35 ± 7.24 a | 271.4 ± 6.69 a | 55.74 ± 5.56 b | 58.27 ± 5.65 b | <LOD | <LOD | 5.31 ± 0.08 c | 2.11 ± 0.04 c |
| 26 | Citric acid | 322.5 ± 3.28 a | 330.77 ± 6.26 a | 135.2 ± 3.39 b | 133.9 ± 3.45 b | 821.18 ± 5.89 c | 865.2 ± 6.68 c | 3.96 ± 0.12 d | 4.16 ± 0.14 d |
| 27 | Malic acid | 7.59 ± 1.01 a | 6.58 ± 0.81 a | 120.7 ± 4.52 b | 121.8 ± 4.56 b | 1340 ± 10.18 c | 1502.0 ± 10.65 d | 1.01 ± 0.01 e | 1.02 ± 0.01 e |
| 28 | Quinic acid | 20.55 ± 1.02 a | 19.36 ± 1.02 a | 6.85 ± 0.84 b | 6.99 ± 0.89 b | 150 ± 7.14 c | 138.0 ± 7.58 c | <LOD | <LOD |
| 29 | Shikimic acid | 1.44 ± 0.15 a | 1.28 ± 0.12 a | 0.79 ± 0.08 b | 0.85 ± 0.02 b | 49.0 ± 2.32 c | 53.0 ± 3.25 c | 0.13 ± 0.03 d | 0.33 ± 0.01 d |
| 30 | Fumaric acid | 6.88 ± 1.01 a | 7.02 ± 1.02 a | 3.44 ± 0.51 b | 3.58 ± 0.32 b | <LOD | <LOD | 0.23 ± 0.01 c | 0.78 ± 0.02 c |
| No. | Family of Plants | Rosaceae Juss. | Adoxaceae | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Species | Crataegus monogyna Jacq. | Sorbus aucuparia L. | Viburnum opulus L. | Sambucus nigra | |||||
| Location | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Siemianice | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | Laski | Murowana Goślina | |
| 1 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | <LOD | 1.87 ± 0.02 b | 2.33 ± 0.41 c | <LOD | 14.71 ± 1.23 d | 0.16 ± 0.08 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 a |
| 2 | quercetin 3-O-β-d-galactoside | 0.45 ± 0.02 a | 12.51 ± 0.51 b | 4.22 ± 0.05 c | 6.34 ± 0.42 c | 11.52 ± 0.75 b | 1.28 ± 0.13 d | 0.45 ± 0.08 a | 0.42 ± 0.02 a |
| 3 | quercetin 3-O-β-d-glucoside | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 7.43 ± 0.56 b | 1.87 ± 0.02 c | 2.44 ± 0.32 d | 6.88 ± 0.65 b | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.07 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 a |
| 4 | 1-O-feruloylquinic acid | 1.33 ± 0.08 a | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 1.33 ± 0.09 a | 1.16 ± 0.03 a |
| 5 | caffeoyl-maloyl-quinic acid | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.41 ± 0.01 b | <LOD | <LOD | 0.37 ± 0.06 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a |
| 6 | 1-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 1.23 ± 0.07 a | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 2.11 ± 0.05 b | 1.23 ± 0.06 a | 1.11 ± 0.09 a |
| 7 | 5-caffeoylshikimic acid | 0.34 ± 0.07 a | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 1.38 ± 0.05 b | 0.34 ± 0.02 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 a |
| 8 | caffeoyl-maloyl-quinic acid | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 0.55 ± 0.02 b | <LOD | <LOD | 0.61 ± 0.08 b | 2.34 ± 0.06 c | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 a |
| 9 | 3-caffeoylshikimic acid | 1.31 ± 0.04 a | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.31 ± 0.02 b | 1.31 ± 0.02 a | 1.39 ± 0.03 a |
| 10 | 3-O-feruloylquinic acid | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | <LOD | 1.98 ± 0.21 b | 1.33 ± 0.12 c | <LOD | <LOD | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 a |
| 11 | feruloyl-maloyl-quinic acid | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | <LOD | 0.33 ± 0.03 b | 0.87 ± 0.06 c | <LOD | <LOD | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| 12 | 5-O-feruloylquinic acid | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | <LOD | 3.55 ± 0.12 b | 1.11 ± 0.05 c | <LOD | <LOD | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a |
| 13 | Kaempferol-O-dihexoside | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 5.51 ± 0.06 b | 4.64 ± 0.15 b | 3.61 ± 0.51 c | 5.81 ± 0.12 b | 12.51 ± 0.98 d | 1.01 ± 0.02 a | 1.16 ± 0.03 a |
| Location | Chemical Elements | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | K | Mg | B | Cu | Zn | Mn | Fe | S | Na | Ca | |
| Siemianice | 73.2 ± 2.74 a | 73.5 ± 2.95 b | 10.1 ± 1.12 a | 0.75 ± 0.05 a | 1.59 ± 0.07 a | 7.12 ± 0.51 a | 197 ± 5.75 a | 683 ± 5.84 b | 12.6 ± 1.12 a | 0.42 ± 0.02 a | 6.30 ± 0.47 a |
| Laski | 76.2 ± 2.15 a | 66.5 ± 1.81 a | 13.8 ± 0.59 b | 0.71 ± 0.02 a | 1.58 ± 0.05 a | 7.50 ± 1.05 a | 196 ± 4.25 a | 715 ± 5.28 c | 13.9 ± 1.12 b | 0.68 ± 0.02 b | 6.59 ± 0.26 a |
| Murowana Goślina | 87.4 ± 2.32 b | 78.0 ± 1.18 c | 12.5 ± 0.54 b | 0.89 ± 0.03 b | 1.74 ± 0.04 b | 7.26 ± 1.01 a | 191 ± 4.35 a | 613 ± 5.65 a | 12.4 ± 1.02 a | 0.71 ± 0.02 b | 6.46 ± 2.13 a |
| Family of Plants | Plant Species | Location | Number of Bushes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosaceae Juss. | Crataegus monogyna Jacq. |  | Siemianice 51°05′38″ N 18°11′87″ E | 4 |
| Murowana Goślina 52°34′27.02″ N 17°00′32.14″ E | 3 | |||
| Sorbus aucuparia L. |  | Siemianice 51°05′38″ N 18°11′87″ E | 5 | |
| Murowana Goślina 52°34′27.02″ N 17°00′32.14″ E | 4 | |||
| Adoxaceae | Viburnum opulus L. |  | Laski 51°35′26″ N 19°07′58″ E | 7 |
| Murowana Goślina 52°34′27.02″ N 17°00′32.14″ E | 3 | |||
| Sambucus nigra |  | Laski 51°35′26″ N 19°07′58″ E | 7 | |
| Murowana Goślina 52°34′27.02″ N 17°00′32.14″ E | 3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Selected Metabolites of Biofunctional Importance from Edible Fruits of Forest Shrubs. Molecules 2025, 30, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010073
Przybylska-Balcerek A, Stuper-Szablewska K. Selected Metabolites of Biofunctional Importance from Edible Fruits of Forest Shrubs. Molecules. 2025; 30(1):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010073
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzybylska-Balcerek, Anna, and Kinga Stuper-Szablewska. 2025. "Selected Metabolites of Biofunctional Importance from Edible Fruits of Forest Shrubs" Molecules 30, no. 1: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010073
APA StylePrzybylska-Balcerek, A., & Stuper-Szablewska, K. (2025). Selected Metabolites of Biofunctional Importance from Edible Fruits of Forest Shrubs. Molecules, 30(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010073






