Novel Star-Shaped Viologens Containing Phenyl and Triphenylamine Moieties for Electrochromic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
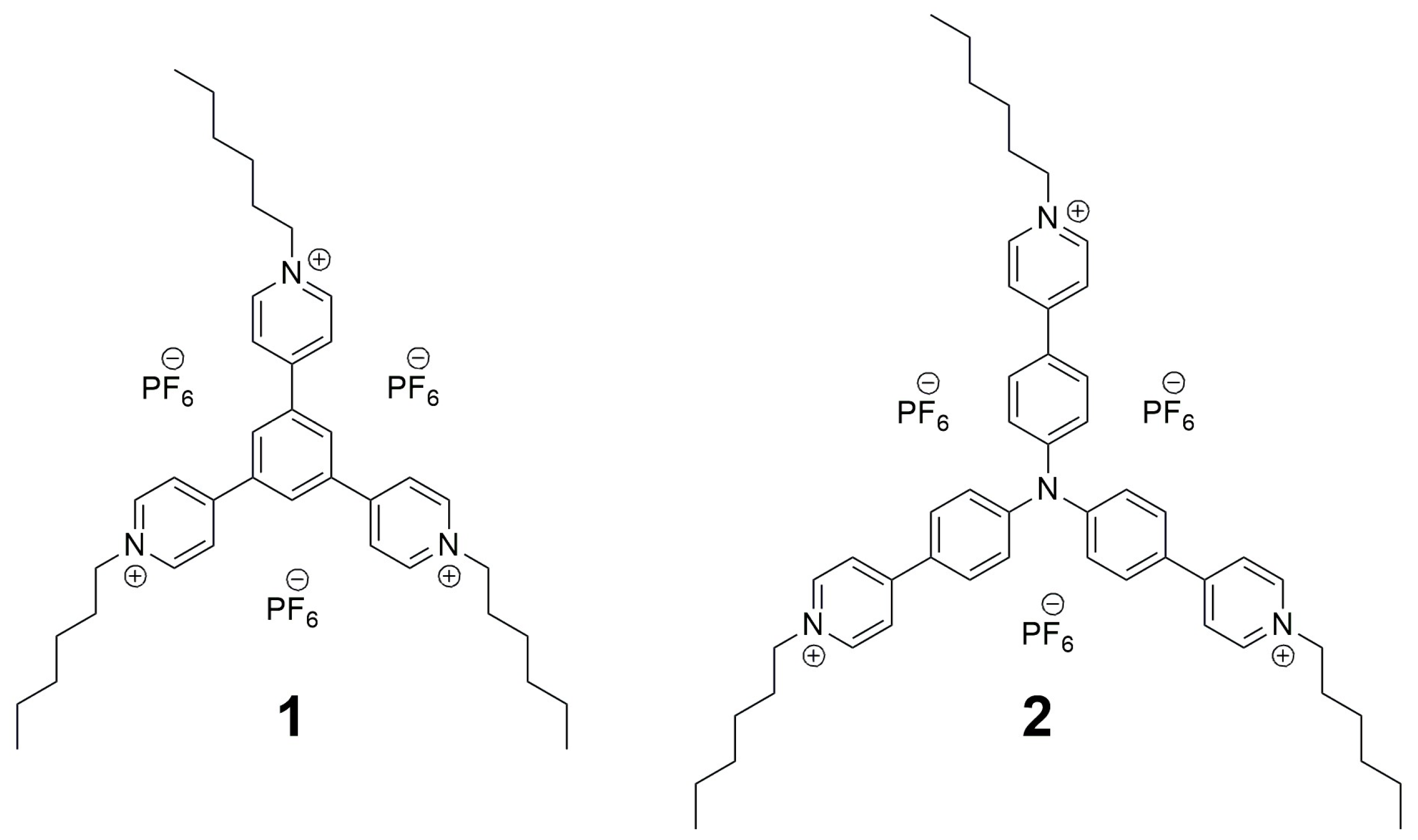
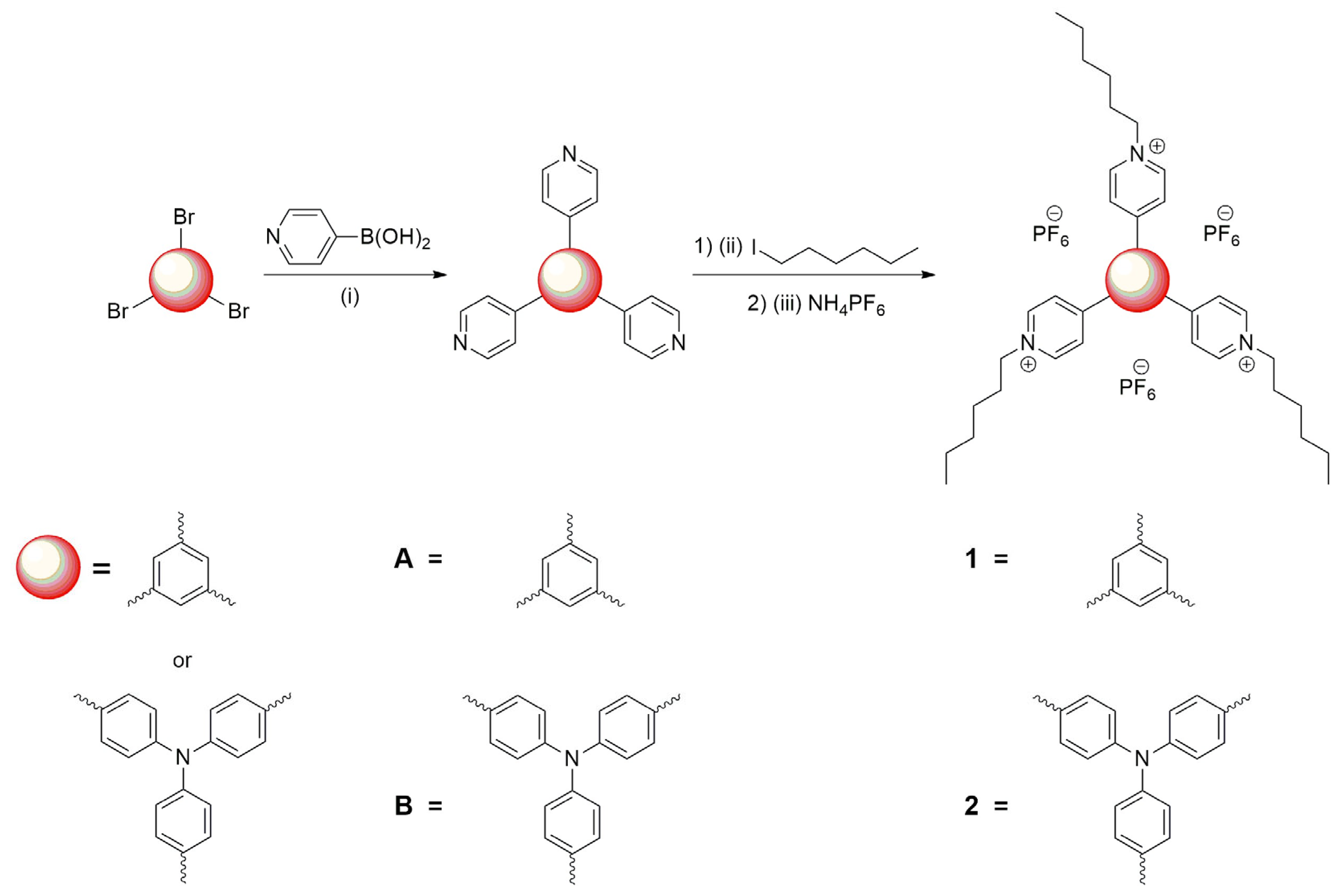
2.1. Synthesis
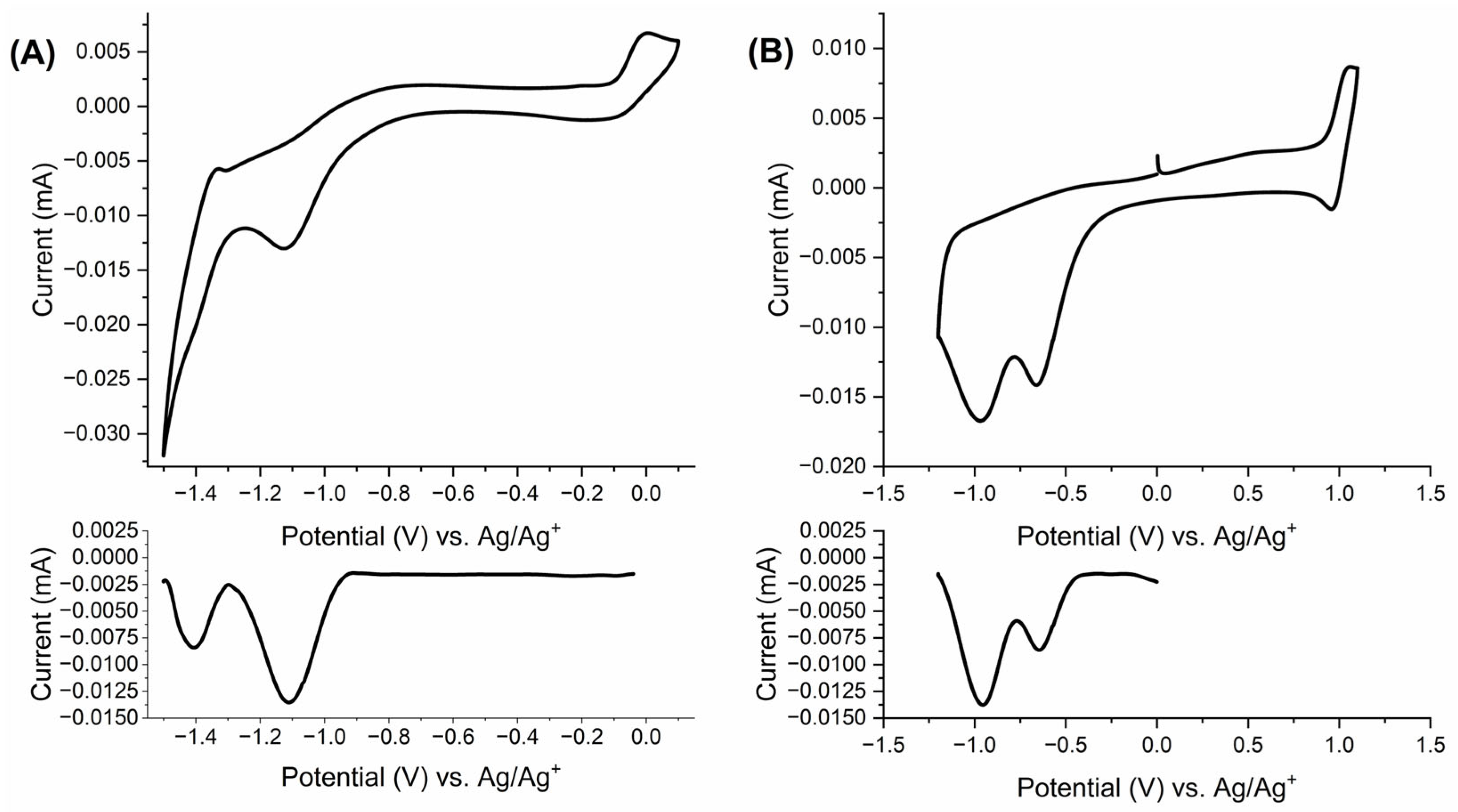
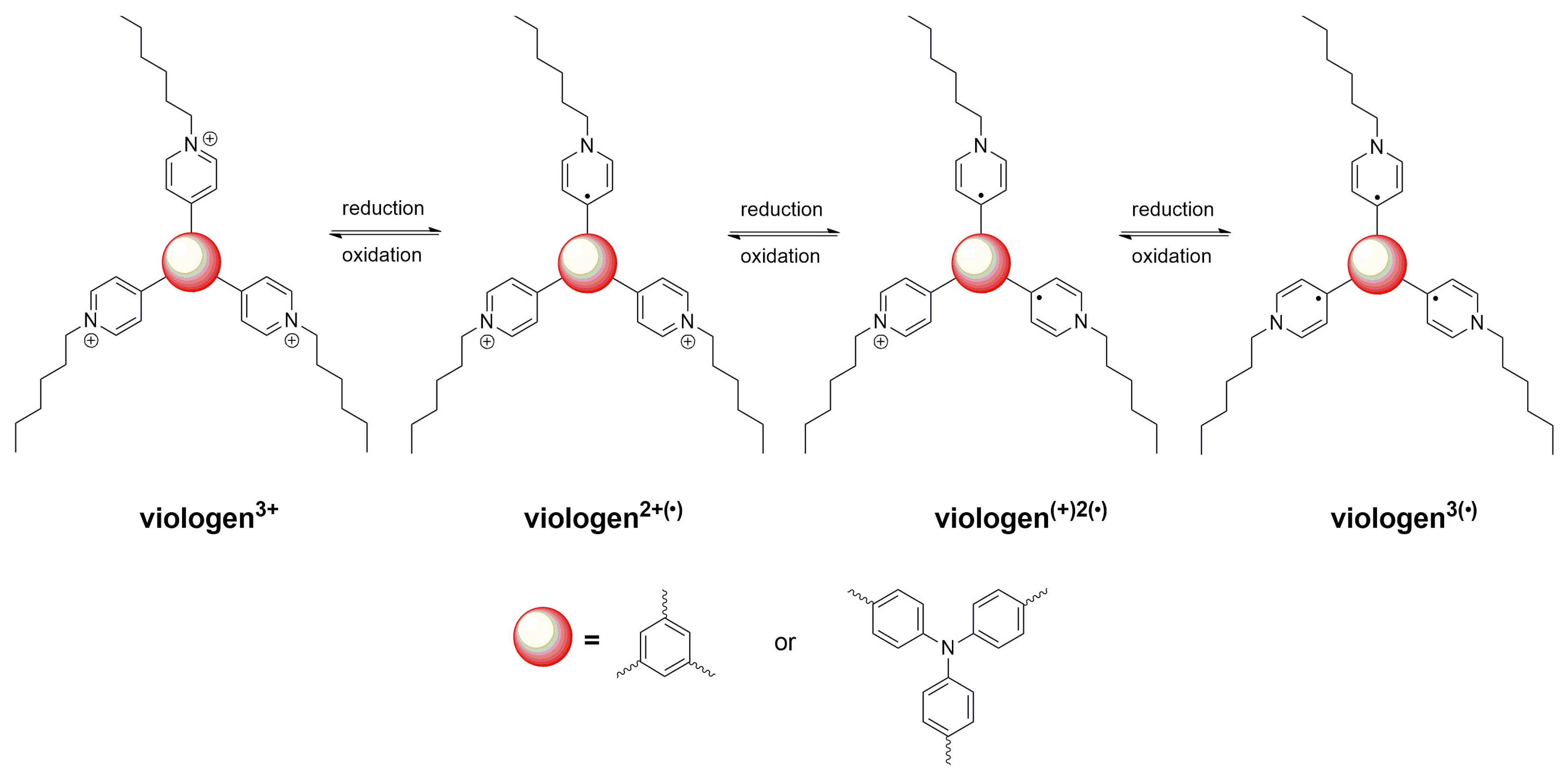
2.2. Electrochemical Properties
2.3. Spectroelectrochemistry
2.4. Luminescent Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. 4,4′,4″-(Benzene-1,3,5-Triyl)Tris(1-Hexylpyridin-1-Ium) Tris(Hexafluorophosphate(V)) (1)
3.3. 4,4′,4″-(Nitrilotris(Benzene-4,1-Diyl))Tris(1-Hexylpyridin-1-Ium) Tris(Hexafluorophosphate(V)) (2)
3.4. Tris(4-Bromophenyl)Amine (TPA)Br3
3.5. 1,3,5-Tri(Pyridine-4-yl)Benzene (A)
3.6. Tris(4-(Pyridine-4-yl)Phenyl)Amine) (B)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Striepe, L.; Baumgartner, T. Viologens and Their Application as Functional Materials. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 16924–16940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Zhai, G.; Zhuang, X. Viologen-inspired functional materials: Synthetic strategies and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 23337–23360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-H.; Fan, Y.; Li, W.-X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, R.-R.; Lin, F.; Zhan, T.-G.; Cui, J.; Liu, L.-J.; Zhao, X.; et al. Viologen derivatives with extended π-conjugation structures: From supra-/molecular building blocks to organic porous materials. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madasamy, K.; Velayutham, D.; Suryanarayanan, V.; Kathiresan, M.; Ho, K.-C. Viologen-based electrochromic materials and devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 4622–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasz, R.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Photolithographic patterning of viologens containing styrene groups. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 16206–16210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedernikov, A.I.; Lobova, N.A.; Kuz’mina, L.G.; Howard, J.A.K.; Strelenko, Y.A.; Alfimov, M.V.; Gromov, S.P. Pseudorotaxane complexes between viologen vinylogues and cucurbit [7]uril: New prototype of photocontrolled molecular machine. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 989, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Nassar, M.S.; Botros, Y.Y.; Stoddart, J.F. Radically promoted formation of a molecular lasso. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2562–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.-C. Viologen radical stabilization by molecular spectators for aqueous organic redox flow batteries. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tripathi, B.P. A high-capacity viologen-based anolyte for high energy density neutral pH aqueous redox-flow batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 78, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabolsi, A.; Das, G.; Prakasam, T.; Nuryyeva, S.; Han, D.S.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Olsen, J.-C.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Platas-Iglesias, C.; Jouiad, M.; et al. Multifunctional redox-tuned viologen-based covalent organic polymers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15361–15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, S.; Bian, J.; He, X.; Li, H.; Li, J. Viologen-based flexible electrochromic devices. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 93, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolar, M. Organic electrochromic molecules: Synthesis, properties, applications and impact. Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 92, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraskina, M.R.; Dutton, A.S.; Juetten, M.J.; Wood, S.A.; Winter, A.H. The Viologen Cation Radical Pimer: A Case of Dispersion-Driven Bonding. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9563–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.W.; Wang, S.-X.; Soo, D.X.; Xu, J. Viologen-Based Electrochromic Materials: From Small Molecules, Polymers and Composites to Their Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-C.; Kao, S.-Y.; Yu, H.-F.; Chang, T.-H.; Kung, C.-W.; Ho, K.-C. Achieving Low-Energy Driven Viologens-Based Electrochromic Devices Utilizing Polymeric Ionic Liquids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30351–30361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.C.; Kim, C.-H.; Lodge, T.P.; Frisbie, C.D. Multicolored, Low-Power, Flexible Electrochromic Devices Based on Ion Gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6252–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidin, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.-L.; Liaw, D.-J. Recent advances in electrochromic polymers. Polymer 2014, 55, 5293–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Wu, X.; Li, K.; Su, F.; Tian, Y.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y.J.; Sun, X.W. Air-stable, high contrast solution-phase electrochromic device based on an A-D-A viologen derivative. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 851, 113447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cospito, S.; Beneduci, A.; Veltri, L.; Salamonczyk, M.; Chidichimo, G. Mesomorphism and electrochemistry of thienoviologen liquid crystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 17670–17678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.N.; Kolesar, J.M.; Hall, S.R.; Saleh, N.-A.; Jones, D.S.; Walter, M.G. Thiazolothiazole Fluorophores Exhibiting Strong Fluorescence and Viologen-Like Reversible Electrochromism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8467–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, G.A.; Di Maio, G.; La Deda, M.; Ruiz de Ballesteros, O.; Gabriele, B.; Veltri, L.; Auriemma, F.; Beneduci, A. The Rainbow Arching over the Fluorescent Thienoviologen Mesophases. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltri, L.; Cavallo, G.; Beneduci, A.; Metrangolo, P.; Corrente, G.A.; Ursini, M.; Romeo, R.; Terraneo, G.; Gabriele, B. Synthesis and thermotropic properties of new green electrochromic ionic liquid crystals. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 18285–18293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibiri, I.; Beneduci, A.; Carraro, M.; Causin, V.; Casella, G.; Corrente, G.A.; Chidichimo, G.; Pace, A.; Riccobono, A.; Saielli, G. Mesomorphic and electrooptical properties of viologens based on non-symmetric alkyl/polyfluoroalkyl functionalization and on an oxadiazolyl-extended bent core. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 7974–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.; Seo, S.; Bak, S.; Lee, H.; Min, M.; Lee, H. An Electrolyte-Free Flexible Electrochromic Device Using Electrostatically Strong Graphene Quantum Dot–Viologen Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5129–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgil, B.; Damlin, P.; Heinonen, M.; Kvarnström, C. A facile one step electrostatically driven electrocodeposition of polyviologen–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite films for enhanced electrochromic performance. Carbon 2015, 89, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichugov, R.D.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Keshtov, M.L. Fast switching electrochromic nanocomposite based on Poly(pyridinium salt) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Qin, Y.; Lei, Z.; Chang, L.; Lei, L.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y. Aggregation-induced emission (AIE)-active fluorescent probes with multiple binding sites toward ATP sensing and live cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8525–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.-Y.; Niu, J.; Liu, Y. Polymerization boosting cascade energy transfer based on opened glucopyranosyl β-cyclodextrin. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Qi, C.; Ma, H. Positive charge-dependent cell targeted staining and DNA detection. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 18251–18258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Bu, R.; Piao, X.; Gao, E. Metal-Organic Frameworks with Novel Catenane-like Interlocking: Metal-Determined Photoresponse and Uranyl Sensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 16415–16421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madasamy, K.; Shanmugam, V.M.; Velayutham, D.; Kathiresan, M. Reversible 2D Supramolecular Organic Frameworks encompassing Viologen Cation Radicals and CB [8]. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Cai, W.; Tan, L.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Kong, Y. A Liquid–Liquid Interfacial Strategy for Construction of Electroactive Chiral Covalent–Organic Frameworks with the Aim to Enlarge the Testing Scope of Chiral Electroanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 3200–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, L.; Du, Q. Synthesis of a new star-shaped 4,4′-bipyridine derivative and its multicolor solid electrochromic devices. Org. Electron. 2011, 12, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Rao, B.; Wei, J.; Wei, Z.; Xu, L.; He, G. Star-shaped thienoviologens for electrochromism and detection of picric acid in aqueous medium. Dyes Pigment. 2020, 178, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Bao, Z. Side Chain Engineering in Solution-Processable Conjugated Polymers. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Minemawari, H.; Tsutsumi, J.; Chikamatsu, M.; Yamada, T.; Horiuchi, S.; Tanaka, M.; Kumai, R.; Yoneya, M.; Hasegawa, T. Effects of Substituted Alkyl Chain Length on Solution-Processable Layered Organic Semiconductor Crystals. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3809–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Leenaers, P.J.; Wienk, M.M.; Janssen, R.A.J. The effect of alkyl side chain length on the formation of two semi-crystalline phases in low band gap conjugated polymers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5856–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęsa-Chorab, M.; Tremblay, M.H.; Skene, W.G. Hydrogen-Bond and Supramolecular-Contact Mediated Fluorescence Enhancement of Electrochromic Azomethines. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11382–11393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, L. {[Ru(bda)] x L y } n cross-linked coordination polymers: Toward efficient heterogeneous catalysis for water oxidation in an organic solvent-free system. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Turner, P.; D’Alessandro, D.M. Electrochemical and optical properties of a redox-active Cu(ii) coordination framework incorporating the tris(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)amine ligand. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, W.; Shen, F.; Liu, D.; Yang, B.; Ma, Y. Highly efficient deep-blue electroluminescence based on the triphenylamine-cored and peripheral blue emitters with segregative HOMO–LUMO characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4401–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.T.; Liu, H.; Lv, X.; Jin, S.; Li, W.; Feng, D. Viologen Hydrothermal Synthesis and Structure–Property Relationships for Redox Flow Battery Optimization. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 202203919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumura, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Kawanami, H.; Tamaoki, N.; Yoshida, M. Tuning of solubility and gelation ability of oligomeric electrolyte by anion exchange. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, L.; West, K.; Wintherjensen, B.; Jacobsen, T. Electrochemical reaction rates in a dye-sensitised solar cell—The iodide/tri-iodide redox system. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, C.; Dai, S.; Kong, F.; Hu, L.; Sui, Y. Influence of Different Electrolytes on the Reaction Mechanism of a Triiodide/Iodide Redox Couple on the Platinized FTO Glass Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Chaudhuri, D. Rapid and Efficient Electrochemical Actuation in a Flexible Perylene Bisimide Dimer. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasz, R.; Kubicki, M.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Electrochemistry and Electrochromic Performance of a Metallopolymer Formed by Electropolymerization of a Fe(II) Complex with a Triphenylamine-Hydrazone Ligand. ChemPhysChem 2022, 23, e202100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napierała, S.; Kubicki, M.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Toward Electrochromic Metallopolymers: Synthesis and Properties of Polyazomethines Based on Complexes of Transition-Metal Ions. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 14011–14021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęsa-Chorab, M.; Skene, W.G. Investigation of an electroactive immobilized azomethine for potential electrochromic use. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 200, 109977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęsa-Chorab, M.; Banasz, R.; Kubicki, M.; Patroniak, V. Dipyrromethane functionalized monomers as precursors of electrochromic polymers. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Perepichka, I.F.; Xing, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Meng, H. Multicolored Cathodically Coloring Electrochromism and Electrofluorochromism in Regioisomeric Star-Shaped Carbazole Dibenzofurans. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24156–24164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Luo, F.; Chen, L.; Yuan, F.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, S.; Dai, Y.; Ouyang, M.; Zhang, C. Multi-color electrochromism containing green color based on electrochemically polymerized star-shaped phenyl bithiophene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 12923–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striepe, L.; Vespa, M.; Baumgartner, T. Synthesis and properties of electron accepting star-shaped phosphaviologen oligomers. Org. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, P. Synthesis and Electrochromic Properties of Star-Shaped Oligomers with Phenyl Cores. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2202–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesanco, Y.; Viñuales, A.; Palenzuela, J.; Odriozola, I.; Cabañero, G.; Rodriguez, J.; Tena-Zaera, R. Multicolor Electrochromics: Rainbow-Like Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14795–14801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Berda, E.B.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Chao, D. Design and synthesis of multicolor electrochromic polymers based on oligoaniline and viologen/phenothiazine groups. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hu, J.; Yin, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, R.-T. Recent progress in transmissive and reflective electrochromic devices for multi-color modulation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 267, 112706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasz, R.; Kubicki, M.; Wałȩsa-Chorab, M. Yellow-to-brown and yellow-to-green electrochromic devices based on complexes of transition metal ions with a triphenylamine-based ligand. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 15041–15053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wałęsa-Chorab, M.; Skene, W.G. Leveraging reversible bonds for property modification of electrochromes and their immobilization by dual modes: Thermal and electrochemical polymerization. Prog. Org. Coatings 2024, 187, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muras, K.; Kubicki, M.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Benzochalcodiazole-based donor-acceptor-donor non-symmetric small molecules as dual-functioning electrochromic and electrofluorochromic materials. Dyes Pigment. 2023, 212, 111098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, A.V.; P, C.A.S. Fine-tuning the acceptor–donor ability of star shaped triarylborane–triphenylamine conjugates: Synthesis, characterization and anion binding studies. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 20299–20310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, P.M.S. The Viologens: Physicochemical Properties, Synthesis and Applications of the Salts of 4,4′-Bipyridine; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Clennan, E. Viologen embedded zeolites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Gundlach, L.; Piotrowiak, P.; Galoppini, E. Fluorescence Enhancement of Di- p -tolyl Viologen by Complexation in Cucurbit [7]uril. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tsarevsky, N.V. Well-defined polymers containing a single mid-chain viologen group: Synthesis, environment-sensitive fluorescence, and redox activity. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 4402–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Freunberger, S.A.; Peng, Z.; Fontaine, O.; Bruce, P.G. Charging a Li–O2 battery using a redox mediator. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhzhukhina, N.; Calvo, E.J. Perspective—The Correct Assessment of Standard Potentials of Reference Electrodes in Non-Aqueous Solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A2295–A2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) (black), −0.9 (
) (black), −0.9 ( ) (green), −1.0 V (
) (green), −1.0 V ( ) (blue); (B) −1.0 V (
) (blue); (B) −1.0 V ( ) (blue), −1.1 V (
) (blue), −1.1 V ( ) (red), −1.2 V (
) (red), −1.2 V ( ) (cyan); (C) −1.2 V (
) (cyan); (C) −1.2 V ( ) (cyan), −1.3 V (
) (cyan), −1.3 V ( ) (orange), −1.4 V (
) (orange), −1.4 V ( ) (grey-green); (D) photographs of the trication, radical dication, diradical cation and triradical (from left to right).
) (grey-green); (D) photographs of the trication, radical dication, diradical cation and triradical (from left to right).
 ) (black), −0.9 (
) (black), −0.9 ( ) (green), −1.0 V (
) (green), −1.0 V ( ) (blue); (B) −1.0 V (
) (blue); (B) −1.0 V ( ) (blue), −1.1 V (
) (blue), −1.1 V ( ) (red), −1.2 V (
) (red), −1.2 V ( ) (cyan); (C) −1.2 V (
) (cyan); (C) −1.2 V ( ) (cyan), −1.3 V (
) (cyan), −1.3 V ( ) (orange), −1.4 V (
) (orange), −1.4 V ( ) (grey-green); (D) photographs of the trication, radical dication, diradical cation and triradical (from left to right).
) (grey-green); (D) photographs of the trication, radical dication, diradical cation and triradical (from left to right).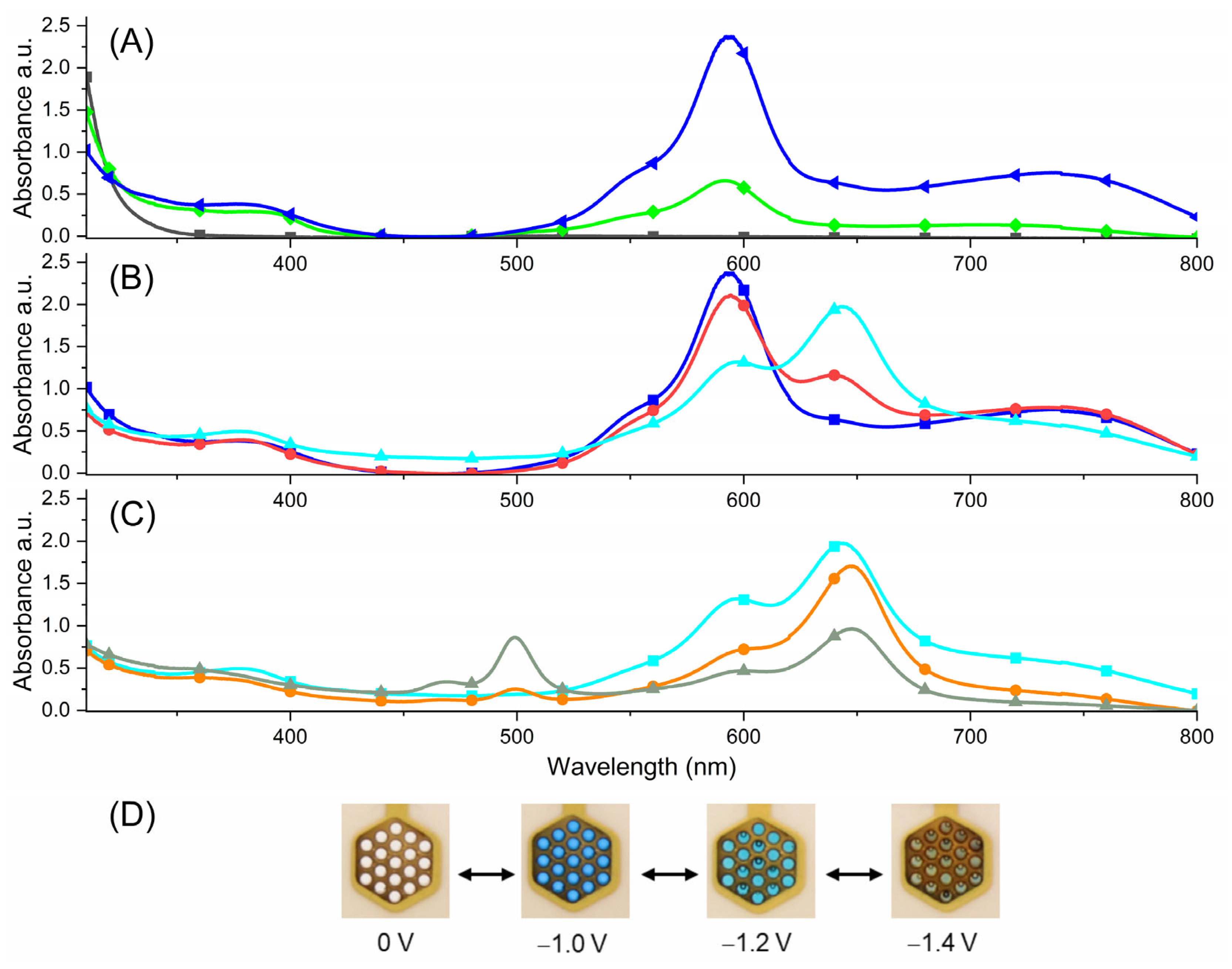
 ) (black), −0.3 V (
) (black), −0.3 V ( ) (green), −0.5 V (
) (green), −0.5 V ( ) (violet), −0.9 V (
) (violet), −0.9 V ( ) (red), −1.0 V (
) (red), −1.0 V ( ) (cyan); −1.1 V (
) (cyan); −1.1 V ( ) (brown) (B) 0.8 V (
) (brown) (B) 0.8 V ( ) (black), 1.0 V (
) (black), 1.0 V ( ) (blue), 1.1 V (
) (blue), 1.1 V ( ) (yellow), 1.3 V (
) (yellow), 1.3 V ( ) (red), 1.4 V (
) (red), 1.4 V ( ) (green); (C) photographs of the compound in reduced state (left), trication form (middle) and oxidized state (right).
) (green); (C) photographs of the compound in reduced state (left), trication form (middle) and oxidized state (right).
 ) (black), −0.3 V (
) (black), −0.3 V ( ) (green), −0.5 V (
) (green), −0.5 V ( ) (violet), −0.9 V (
) (violet), −0.9 V ( ) (red), −1.0 V (
) (red), −1.0 V ( ) (cyan); −1.1 V (
) (cyan); −1.1 V ( ) (brown) (B) 0.8 V (
) (brown) (B) 0.8 V ( ) (black), 1.0 V (
) (black), 1.0 V ( ) (blue), 1.1 V (
) (blue), 1.1 V ( ) (yellow), 1.3 V (
) (yellow), 1.3 V ( ) (red), 1.4 V (
) (red), 1.4 V ( ) (green); (C) photographs of the compound in reduced state (left), trication form (middle) and oxidized state (right).
) (green); (C) photographs of the compound in reduced state (left), trication form (middle) and oxidized state (right).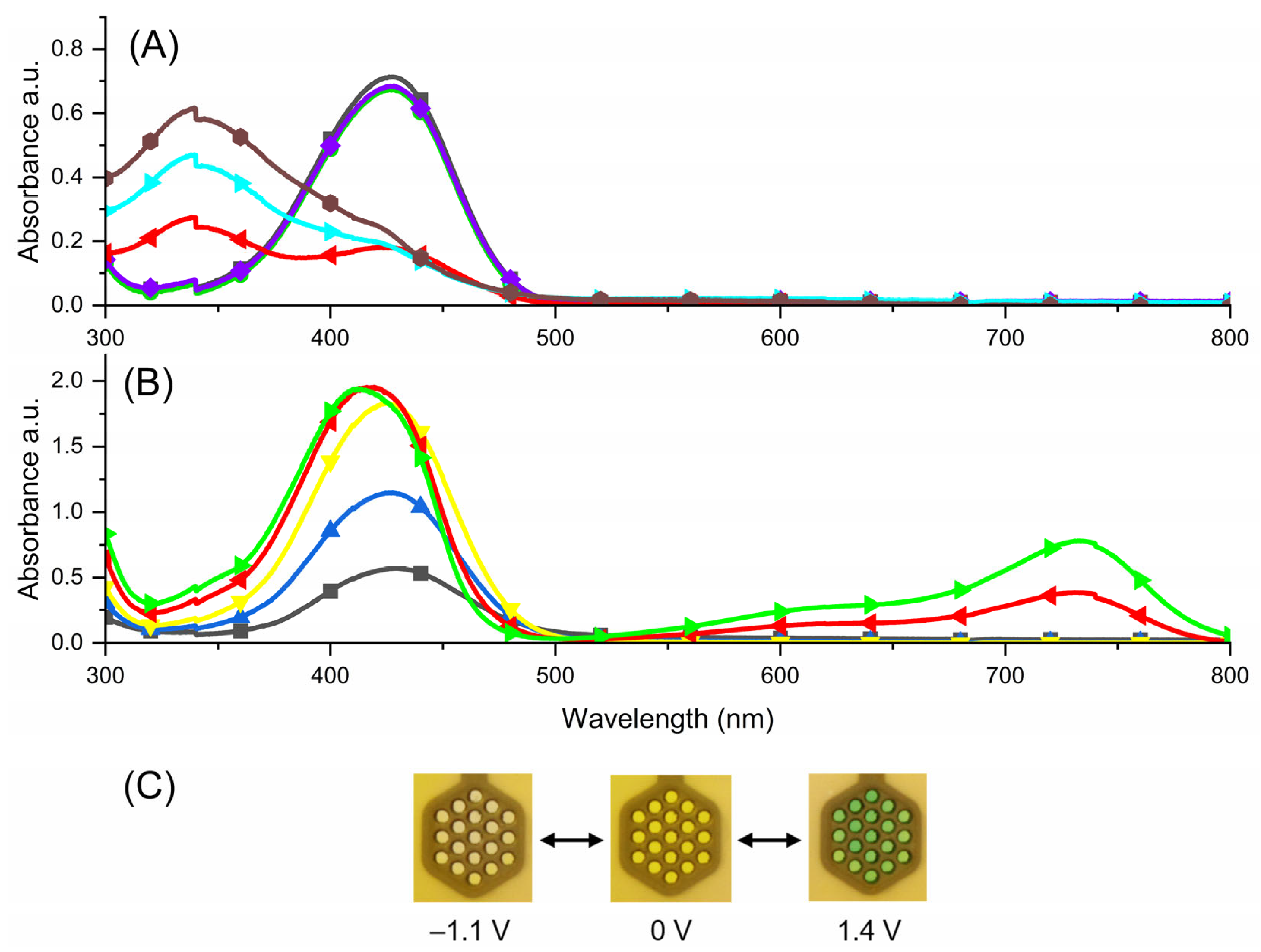
 ) (green), tetrahydrofuran (
) (green), tetrahydrofuran ( ) (red), dichloromethane (
) (red), dichloromethane ( ) (yellow), methanol (
) (yellow), methanol ( ) (orange) and acetonitrile (
) (orange) and acetonitrile ( ) (black-grey). Insert: A photograph showing the emission of 2 in different solvents: 1—ethyl acetate, 2—tetrahydrofuran, 3—dichloromethane, 4—methanol and 5—acetonitrile, when excited with a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
) (black-grey). Insert: A photograph showing the emission of 2 in different solvents: 1—ethyl acetate, 2—tetrahydrofuran, 3—dichloromethane, 4—methanol and 5—acetonitrile, when excited with a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
 ) (green), tetrahydrofuran (
) (green), tetrahydrofuran ( ) (red), dichloromethane (
) (red), dichloromethane ( ) (yellow), methanol (
) (yellow), methanol ( ) (orange) and acetonitrile (
) (orange) and acetonitrile ( ) (black-grey). Insert: A photograph showing the emission of 2 in different solvents: 1—ethyl acetate, 2—tetrahydrofuran, 3—dichloromethane, 4—methanol and 5—acetonitrile, when excited with a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
) (black-grey). Insert: A photograph showing the emission of 2 in different solvents: 1—ethyl acetate, 2—tetrahydrofuran, 3—dichloromethane, 4—methanol and 5—acetonitrile, when excited with a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).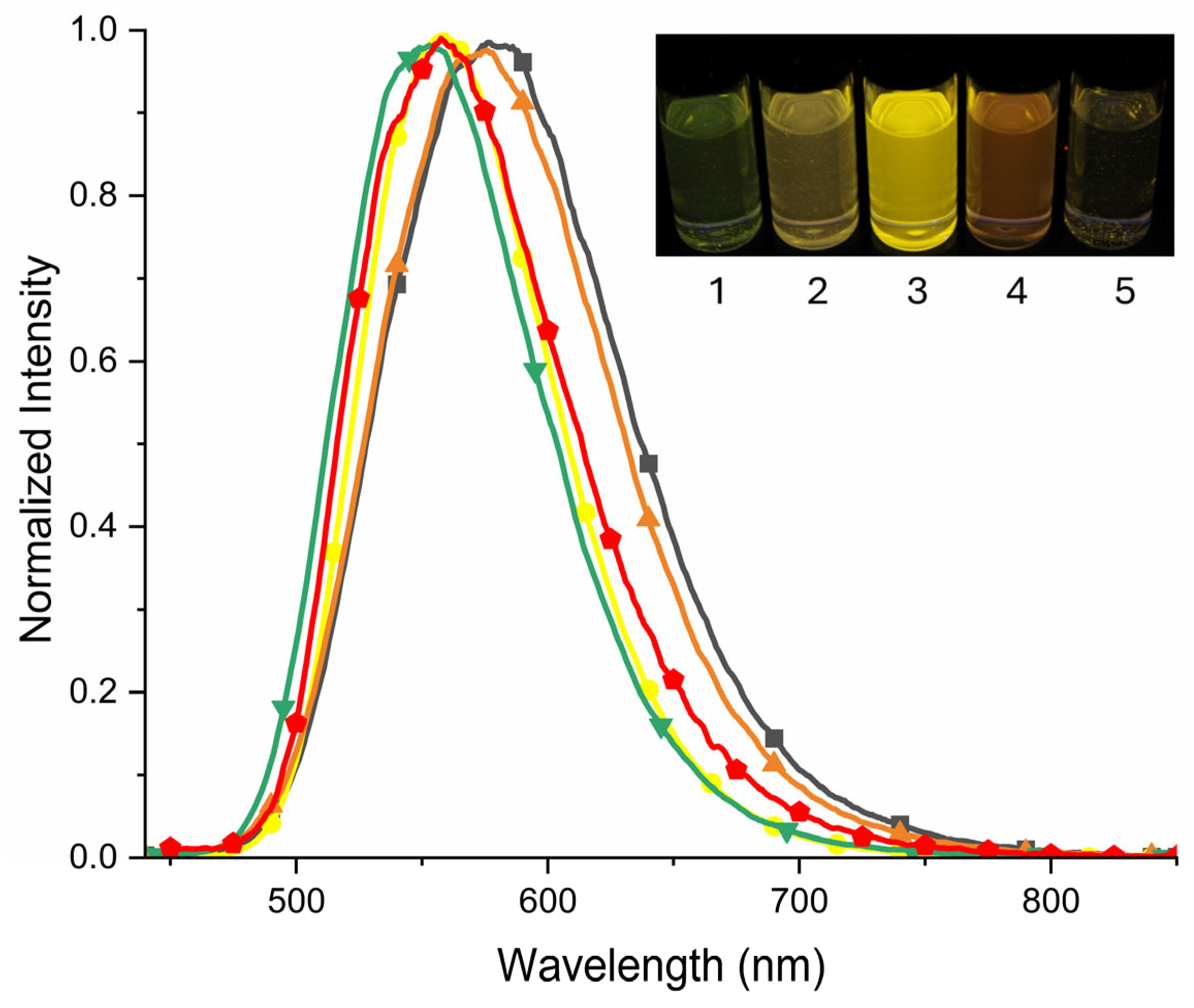
 ) (black-grey) (λem = 657 nm) and emission spectra (
) (black-grey) (λem = 657 nm) and emission spectra ( ) (red) (λex = 560 nm) of 2 in the solid state. Insert: photo showing the emission of 2 in the solid state during excitation using a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
) (red) (λex = 560 nm) of 2 in the solid state. Insert: photo showing the emission of 2 in the solid state during excitation using a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
 ) (black-grey) (λem = 657 nm) and emission spectra (
) (black-grey) (λem = 657 nm) and emission spectra ( ) (red) (λex = 560 nm) of 2 in the solid state. Insert: photo showing the emission of 2 in the solid state during excitation using a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).
) (red) (λex = 560 nm) of 2 in the solid state. Insert: photo showing the emission of 2 in the solid state during excitation using a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm).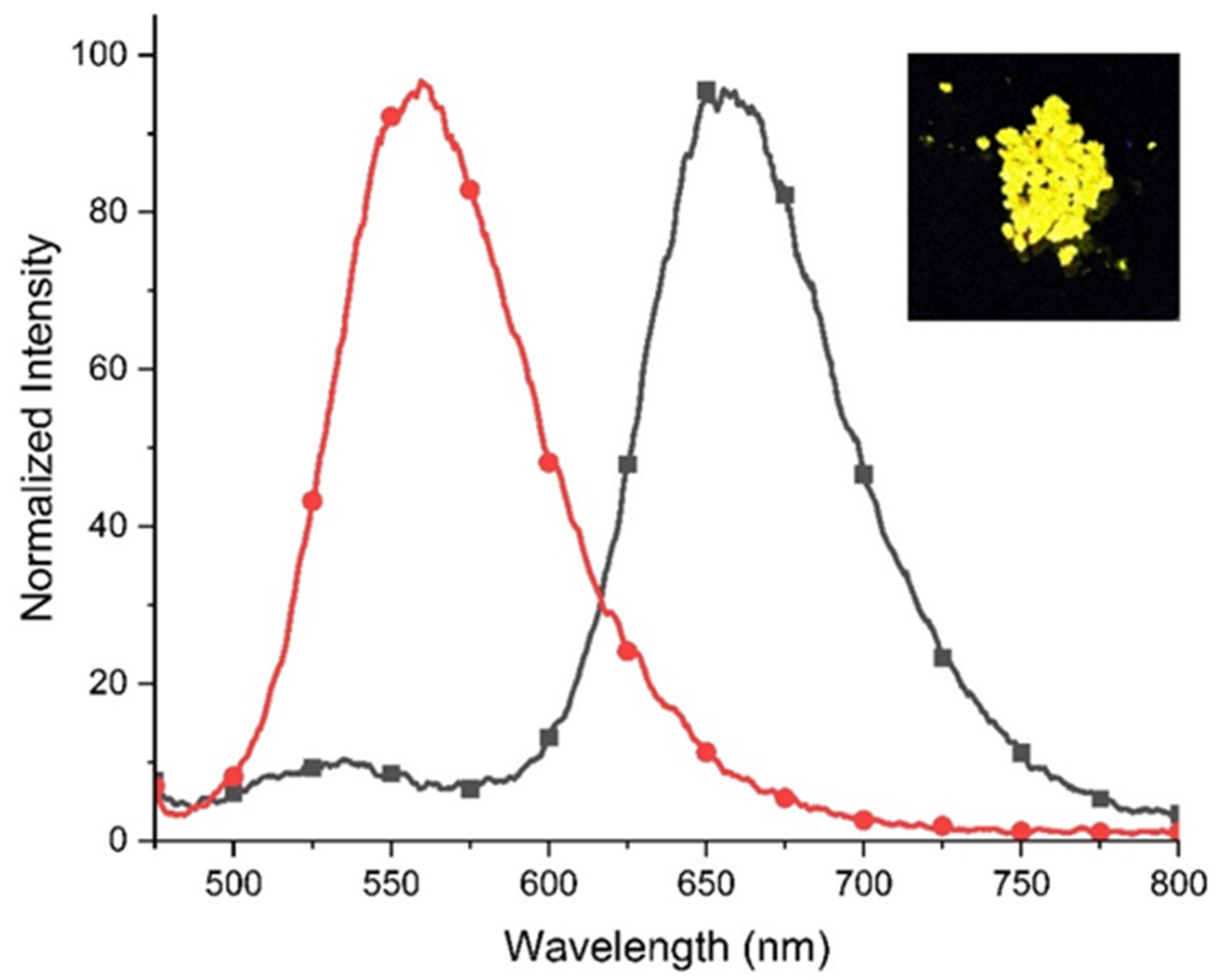
| Solvent | λabs [nm] | λem [nm] | Stokes Shift [cm−1] | QY [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl acetate | 432 nm | 550 nm | 4966 cm−1 | 5% |
| THF | 433 nm | 557 nm | 5141 cm−1 | 7% |
| Dichloromethane | 450 nm | 558 nm | 4301 cm−1 | 14% |
| Acetonitrile | 427 nm | 577 nm | 6088 cm−1 | <1% |
| Methanol | 429 nm | 572 nm | 5828 cm−1 | 4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banasz, R.; Wałęsa-Chorab, M. Novel Star-Shaped Viologens Containing Phenyl and Triphenylamine Moieties for Electrochromic Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092006
Banasz R, Wałęsa-Chorab M. Novel Star-Shaped Viologens Containing Phenyl and Triphenylamine Moieties for Electrochromic Applications. Molecules. 2024; 29(9):2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092006
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanasz, Radosław, and Monika Wałęsa-Chorab. 2024. "Novel Star-Shaped Viologens Containing Phenyl and Triphenylamine Moieties for Electrochromic Applications" Molecules 29, no. 9: 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092006
APA StyleBanasz, R., & Wałęsa-Chorab, M. (2024). Novel Star-Shaped Viologens Containing Phenyl and Triphenylamine Moieties for Electrochromic Applications. Molecules, 29(9), 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092006








