Abstract
It is a valid path to realize the zero discharge of coal chemical wastewater by using the fractional crystallization method to recycle the miscellaneous salt in high-salinity wastewater. In this study, the thermodynamics and nucleation kinetics of sodium chloride (NaCl) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) crystallization in coal chemical wastewater were systematically studied. Through analyses of solubility, metastable zone width, and induction period, it was found that the impurity dimethoxymethane would increase the solid–liquid interface energy and critical crystal size during the nucleation of Na2SO4. Ternary phase diagrams of the pseudo-ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O systems in simulated wastewater were plotted in the temperature range of 303.15 to 333.15 K, indicating that a co-ionization effect existed between NaCl and Na2SO4, and NaCl had a strong salting out effect on Na2SO4. Finally, the nucleation rate and growth rate of Na2SO4 crystals under simulated wastewater conditions were determined by the intermittent dynamic method, and the crystallization kinetic models of Na2SO4 were established. The crystallization nucleation of Na2SO4 crystals was found to be secondary nucleation controlled by surface reactions. The basic theoretical research of crystallization in this study is expected to fundamentally promote the application of fractional crystallization to realize the resource utilization of high-salinity wastewater in the coal chemical industry.
1. Introduction
The contradiction between the modern coal chemical industry and the requirements of saving resources and protecting the environment is becoming increasingly prominent [1,2]. Large amounts of high-salinity wastewater and organic wastewater are produced during the modern coal chemical production process, usually containing various soluble inorganic salts, such as Cl−, Na+, and SO42−, etc. The discharge of such wastewater inevitably leads to the mineralization of freshwater resources and soil alkalization [3]. The effective treatment and separation of miscellaneous salt resources are of great significance for improving the utilization value of high-salinity wastewater in the coal chemical industry and achieving zero discharge [4,5].
High-salinity wastewater from the coal chemical industry is characterized by high contents of inorganic salt ions, a poor biodegradability, and a complex composition [6]. Generally, wastewater with salinity in the range of 1 to 3.5% w/w salts is termed as highly saline, while that containing more than 3.5% w/w salts present in oceans is termed hypersaline [7]. The treatment methods for such wastewater in China mainly include evaporation crystallization and evaporation pond salt drying [8]. However, both methods produce mixed crystalline salts with high contents of heavy metals and organic matter, which are complex in composition and difficult to use, resulting in a low degree of resource utilization [9]. In this context, the zero-discharge technological requirement with the core concept of fractional crystallization was proposed, which not only concerns the water treatment, but also focuses more on the recycling of the dissolved inorganics [10].
The theory of fractional crystallization is of great significance for guiding its practical application, mainly including crystallization thermodynamics and nucleation kinetic properties. It is known that typical coal chemical wastewater is rich in sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and sodium chloride (NaCl), which is considered as a classical water-salt system. To date, the crystallization processes of ternary, quaternary, and pluralistic systems containing Na2SO4 or NaCl have been extensively studied, involving phase equilibrium [11,12,13], crystallization kinetics [14], and process optimization [15]. Zhang et al. [16] investigated the solid-liquid equilibrium for the ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system at 313.15 K. Zeng et al. [17] estimated the primary nucleation kinetics during Na2SO4 crystallization at temperatures ranging from 313.15 to 353.15 K. Bian et al. [15] conducted process parameters optimization on Na2SO4 fractional crystallization in a quaternary NaCl-NaNO3-Na2SO4-H2O system. Despite a lot of published studies, only some of crystallization fundamentals have been involved, either thermodynamics or nucleation kinetics, and few studies have been reported that cover both aspects. Compared to thermodynamics, fewer studies on nucleation kinetics have been published, even in the classical Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system. In this study, thermodynamic properties, phase equilibrium regularity, and nucleation kinetics were comprehensively investigated in a ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system covering temperatures ranging from 278.15 to 303.15 K.
The existence of non-negligible organic impurities in wastewater will inevitably influence the crystallization process and the quality of subsequent salts [18]. Previous studies have shown that additives have influences on the thermodynamics, kinetics, and morphology of salt crystallization [19,20,21]. Zhu et al. [22] plotted the phase diagrams of NaCl and Na2SO4 in the presence of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone and obtained different influence trends. Rajesh studied the effect of EDTA on the metastable zone of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) [23], indicating that EDTA significantly increased the metastable zone width of ADP and decreased the nucleation rate. The above reports not only prove that organic impurities affect the crystallization of salts more or less, but also imply that the corresponding research in the water-salt system cannot be generalized. Wastewater composition varies greatly, and fundamental crystallization research on different wastewater systems is necessary to supplement the high-salinity wastewater system theory [14]. The influences of different organic impurities on solubility, metastable zone width, induction period, and nucleation kinetics should be further studied [24].
Based on the above considerations, targeting high-salinity wastewater from the coal chemical industry in Ningxia, for the first time, this study theoretically revealed the influence of dimethoxymethane on the crystallization thermodynamic properties and crystal nucleation process of Na2SO4 and NaCl. According to the analysis report, the main inorganic salts involved in the Nixia wastewater were Na2SO4 and NaCl, with content ranges of 1.2 to 2.0% and 2.3 to 3.0% w/w, respectively. The most abundant organic compositions included dimethoxymethane, diethyl ether, 1,1 dichloroethane, and dibromomethane et al., among which, dimethoxymethane ranked the first. Therefore, in the present study, dimethoxymethane was selected as a typical organic impurity in a classical Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system to conduct the research. It is expected that the results could provide theoretical guidance for the separation and resource utilization of Na2SO4 and NaCl.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Dimethoxymethane on Thermodynamics Properties of NaCl and Na2SO4 Crystallization
2.1.1. Solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl
The solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl in water at different temperatures and dimethoxymethane concentrations in the temperature range of 278.15 to 303.15 K are shown in Figure 1. The solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl increase with a rise in temperature. The solubility data of Na2SO4 were linearly fitted by the Apelblat equation, Van ‘t Hoff equation, and polynomial equation, respectively, among which, the Van ‘t Hoff model was the most suitable (Table S1). Based on the Van ‘t Hoff model, the Gibbs free energy of the dissolution of Na2SO4 in dimethoxymethane solution at different concentrations was estimated (Table S2). All the dissolution enthalpy and Gibbs free energy values were positive, indicating that the dissolution of Na2SO4 in dimethoxymethane solutions was an endothermic reaction. The solubility of Na2SO4 increased with an increase in temperature, which was consistent with previous experimental results [25]. At the same time, all the dissolution enthalpy values were greater than those of the dissolution entropy, indicating that the main driving force of Na2SO4 in the dissolution process was the dissolution enthalpy.
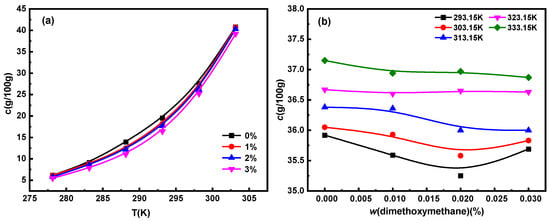
Figure 1.
Solubility of (a) Na2SO4 and (b) NaCl at different temperatures and dimethoxymethane concentrations.
At the same temperature, with an increase in dimethoxymethane concentration, the solubility of Na2SO4 decreased significantly, while that of NaCl first decreased and then increased. As a whole, dimethoxymethane inhibited the dissolution of Na2SO4 and NaCl. When Na2SO4 and NaCl were dissolved in water, Cl−, SO42−, and Na+ were ionized, forming three unstable hydrated ions by binding water molecules through intermolecular forces and electrostatic interactions [26]. The ether group –O– in the structure of dimethoxymethane is a hydrophilic group [27], which could have competed with hydrated ions for water molecules in the solvent, thereby reducing the solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl. The slightly increased solubility of NaCl at 3% dimethoxymethane might have been caused by the interaction between NaCl and Na2SO4.
2.1.2. The Metastable Zone Width of Na2SO4 Solution
The metastable zone width is an important parameter of crystallization thermodynamics [17]. The effects of temperature, dimethoxymethane concentration, and cooling rate on the metastable zone width of Na2SO4 are shown in Figure 2. The metastable zone width of Na2SO4 solution widened with an increase in cooling rate, saturation temperature, and dimethoxymethane concentration, making it difficult for Na2SO4 to crystallize in water. As the cooling rate increased, the time for the solute to pass through the nucleation temperature zone was too short for the crystals to precipitate in time, resulting in a lag in crystal precipitation and, thus, a widening of the metastable zone [28].
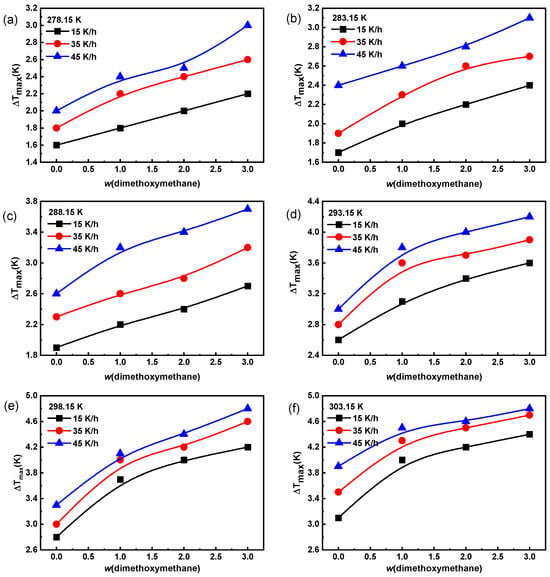
Figure 2.
The effect of dimethoxymethane on the metastable zone width of Na2SO4 in water with different cooling rates at saturation temperatures: (a) 278.15 K; (b) 283.15 K; (c) 288.15 K; (d) 293.15 K; (e) 298.15 K; and (f) 303.15 K.
In order to investigate the effect of dimethoxymethane on the nucleation mechanism of Na2SO4, the classical 3D nucleation theory model was employed to fit the metastable zone width data of Na2SO4, as shown in Figure 3. The calculated results of the solid–liquid interface energy γ and pre-exponential factor A of Na2SO4 under different conditions are shown in Tables S3 and S4. Increases in saturation temperature and dimethoxymethane concentration increased the solid–liquid interface energy γ, which made crystal nucleation more difficult and led to experimental broadening of the metastable zone with an increase in the saturation temperature and dimethoxymethane concentration.
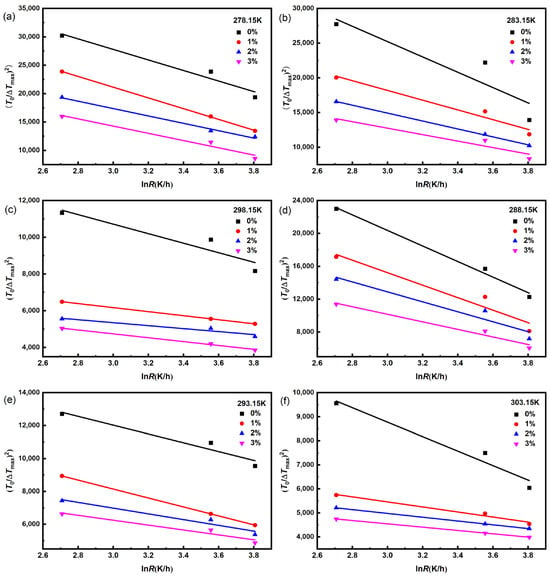
Figure 3.
The fitting curves of (T0/ΔTmax)2 and ln R of Na2SO4 at different dimethoxymethane concentrations by using Classical 3D nucleation theory model with different saturation temperatures: (a) 278.15 K; (b) 283.15 K; (c) 288.15 K; (d) 293.15 K; (e) 298.15 K; and (f) 303.15 K.
2.1.3. The Induction Period of Na2SO4 Solution
The induction period is mainly controlled by the experimental environment where the material is located [29,30]. The effects of the saturation temperature, dimethoxymethane concentration, and supersaturation on the induction period of Na2SO4 are shown in Figure 4. The induction period of Na2SO4 increased with decreasing supersaturation, an increasing saturation temperature, and an increasing dimethoxymethane concentration, making crystal nucleation difficult, which was similar to the trend of the previously measured metastable zone width.
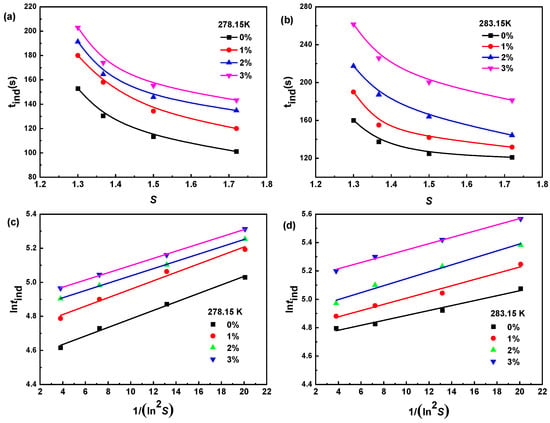
Figure 4.
Effect of dimethoxymethane concentration and supersaturation on induction period of Na2SO4 and the fitting results of induction period data based on classical nucleation theory at different saturation temperatures: (a,c) 278.15 K and (b,d) 283.15 K.
The classical nucleation theory was used to fit the induction period data, as shown in Figure 4. The solid–liquid interface energy (γ), critical nucleus size (r*), and critical Gibbs free energy ΔG* of the Na2SO4 crystallization system with different concentrations of dimethoxymethane and different supersaturations were calculated, as shown in Table 1. The γ decreased with increasing supersaturation, increased with an increasing dimethoxymethane concentration, and increased with an increasing temperature. The variation trends of r* and ΔG* were similar to those of γ. The above results indicate that crystal nucleation became difficult with decreasing solution supersaturation, an increasing dimethoxymethane concentration, and an increasing temperature. This theoretically explains the experimental phenomenon of the induction period data, which was consistent with the conclusion of the metastable zone.

Table 1.
The solid–liquid interfacial energy γ and critical nucleus size r* of Na2SO4 in water at different temperatures, supersaturations, and dimethoxymethane concentrations.
In summary, the results of the analysis of the metastable zone width and induction period data indicated an effect on the nucleation mechanism of Na2SO4. The increase in dimethoxymethane concentration increased the solid–liquid interfacial energy and critical nucleation size, making crystal nucleation difficult.
2.2. Phase Equilibrium of Pseudo-Ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O System in Simulated High-Salinity Wastewater
In the temperature range of 293.15 to 333.15 K, the equilibrium composition and solution density of the pseudo-ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system in simulated wastewater were determined, as listed in Table S5. The equilibrium phase diagrams of the pseudo-ternary system are shown in Figure 5. The composition of the simulated wastewater is shown in Table 2. In the temperature range of 303.15 to 333.15 K, the system had a co-saturation point, two solubility curves, an unsaturated zone, and three crystallization zones. The crystallization zone of Na2SO4 was larger than that of NaCl. The dissolution trends of NaCl and Na2SO4 in the simulated wastewater were the same as those in pure water. The solubility of Na2SO4 decreased with the addition of NaCl, which might have been due to the co-ionization effect. In addition, compared with the binary saturated solution, the decrease in the solubility of Na2SO4 at the ternary co-saturation point was much larger than that of NaCl, indicating that NaCl had a stronger salting out effect on Na2SO4 in the simulated wastewater system.
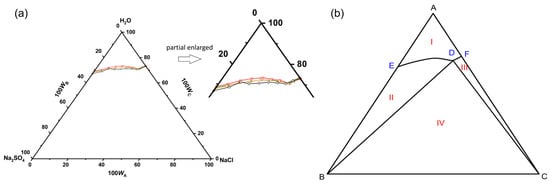
Figure 5.
(a) The equilibrium phase diagrams and (b) schematic diagram of pseudo-ternary Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system in simulated wastewater at 303.15 K (black line), 313.15 K (orange line), 323.15K (green line) and 333.15 K (red line). Wa, Wb, and Wc are the mass fractions of NaCl, Na2SO4, and H2O, respectively. Points: A, H2O; B, Na2SO4; C, NaCl; D, the co-saturated point of Na2SO4 and NaCl; E and F, the saturated points of Na2SO4 and NaCl in the solution, respectively. Curves: DE and DF, the solubility curves of Na2SO4 and NaCl, respectively. Regions: AEDF (I), unsaturated solution; BDE (II), crystalline regions of Na2SO4; CDF (III), crystalline regions of NaCl; BDC (IV), crystalline regions of Na2SO4 and NaCl.

Table 2.
Composition of simulated wastewater system.
As shown in Figure S1, in the temperature range of 303.15 to 333.15 K, the co-saturation points position of Na2SO4 and NaCl shifted to the lower right as the temperature increased, indicating that the crystallization zone of Na2SO4 became larger while that of NaCl became smaller. In addition, the shift of the co-saturation point demonstrated that the salting out strength of NaCl to Na2SO4 became stronger with an increasing temperature, while the salting out effect of Na2SO4 to NaCl weakened. Therefore, in the salt recovery process of high-salinity wastewater from the coal chemical industry, NaCl could be added to the wastewater at a higher temperature until it reaches saturation, followed by being concentrated to reduce the water content and precipitate a large amount of Na2SO4 crystals, with the co-saturated wastewater being treated.
The morphologies of the NaCl crystals and Na2SO4 crystals were observed in the simulated wastewater, as shown in Figure 6. The NaCl crystal was a cube with fork depression, gradually transforming from a cube to an ellipsoid with a layered and relatively flat surface. As a contrast, the Na2SO4 crystal morphology was linear ellipsoid with a rough and uneven crystal surface and no obvious hierarchy. Under the simulated wastewater conditions, the addition of NaCl had a strong salting out effect on the saturated solution of Na2SO4 and the solubility of Na2SO4 decreased significantly, resulting in the nucleation rate of Na2SO4 crystal precipitation being greater than the growth rate, with a damaged crystal morphology.
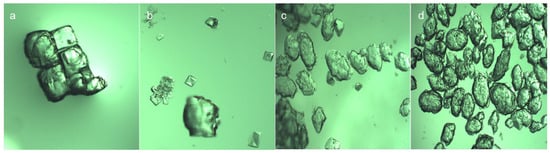
Figure 6.
NaCl and Na2SO4 crystals observed under metallographic digital microscope. (a,b) are NaCl crystals and (c,d) are Na2SO4 crystals.
2.3. Crystallization Kinetics of Na2SO4 in Simulated High-Salinity Wastewater
The results of the particle size analysis of the Na2SO4 crystals indicated that the crystal growth was independent of particle size. The kinetic equation of the Na2SO4 crystals in the simulated wastewater solution was obtained by an intermittent dynamic method, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Crystallization kinetics data of Na2SO4 at different temperatures.
According to the nucleation rate model in Equation (13) and growth rate model in Equation (14), the 1stOpt software 5.0 was used to fit the kinetic experimental data. The crystal nucleation rate and growth rate equations of the kinetic model in simulated high-salinity wastewater were obtained as shown below.
where B0 is the nucleation rate, n·m−3·s−1; MT is the suspension density, kg·m−3; ΔC is the supersaturation, mol·L−1; R is the gas constant, J·K·mol−1; and T is the temperature, K.
where G refers to the growth rate, m·s−1; T is the temperature, K; R is the gas constant, J·K·mol−1; and ΔC is the supersaturation, mol·L−1.
According to the nucleation kinetics equation, the index of supersaturation was 1.91, which is less than 10. Therefore, the Na2SO4 crystallization was a secondary nucleation process. The growth kinetic equation showed that the supersaturation index was −0.64, which is less than 1, indicating that the growth of Na2SO4 crystals was controlled by surface reactions [31].
Both the growth rate and nucleation rate of Na2SO4 increased with an increasing temperature, especially the growth rate. The influence of supersaturation on the nucleation rate of Na2SO4 was greater than that on the growth rate, and the nucleation of Na2SO4 crystals was more likely to occur [32]. The nucleation rate of Na2SO4 was squared to the suspension density, i.e., the nucleation rate increased with an increase in the suspension density of Na2SO4. The crystallization rate of sodium salt in high-salt wastewater directly affects the desalting efficiency, and the grain size of sodium salt crystals also affects the selection of separation equipment and the setting of parameters [33]. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out research on crystallization kinetics and the identification of influencing factors to provide a basis for equipment selection and the optimization of process parameters.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
The main chemical reagents, including NaCl, Na2SO4, dimethoxymethane, silver nitrate, potassium chromate, barium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and absolute ethyl alcohol, etc., were used as-received from various chemical suppliers and were all analytically pure. All solutions were prepared with Milli-Q water.
3.2. Experimental and Analysis Methods
Methods for water quality analysis of coal chemical wastewater. A qualitative analysis of the total composition was performed to understand the unknown components and composition of the Ningxia coal chemical wastewater. Common inorganic salt ions, including SO42−, Cl−, NO3−, Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, etc., were detected by ion chromatography. The total component analysis of organic compounds, including volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds, was performed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) after different pretreat methods, such as extraction, drying, concentration, or dilution, etc.
Solubility determination. In this study, the solubility was determined by the static equilibrium method [34]. Different concentrations of dimethoxymethane solutions were prepared, with excessive solute added. After being incubated in a programmed constant temperature and humidity incubator for 8 h and left to stand for 1 h, the supernatant was quickly filtered with a 0.45 μm filter membrane to determine the contents of SO42− and Cl−, and the solute content was analyzed and calculated. Each experimental point was repeatedly analyzed 3 times, and the average value was taken as the final experimental value. The SO42− contents were measured by the gravimetric method with excess barium chloride solution, while the Cl− contents were quantified by the argentometric method with standard silver nitrate solution in the presence of potassium chromate (see the Supplementary Materials for the details), according to the national standard of China (GB/T 13025.8-2012 [35] and GB/T 13025.5-2012 [36]), respectively.
Determination of metastable zone. The laser method was applied [29]. According to the measured solubility data, the saturated solution of Na2SO4 was accurately prepared, added to the glass jacketed crystallizer, and connected to the laser monitoring system. The stirring rate was set as constant, and the low-temperature thermostat was controlled to cool down at a certain cooling rate. When the crystal was observed, the temperature was recorded at this time, and the metastable zone was obtained by combining with the solubility curve. The experiment was repeated 3~5 times.
Determination of induction period [37]. The measurement method of the induction period was the same as that of the metastable zone, which was also determined by the laser analysis method. After connecting the laser monitoring system, the solution was kept at a constant temperature for half an hour, and the readings of the thermometer and the digital laser power were recorded until they tended to be stable. The stopwatch was turned on when the solution reached the corresponding supersaturation and the changes in the digital laser power device were monitored until the turbidity phenomenon occurred. The experiment was repeated 3~5 times.
Determination of phase equilibrium data. With the saturated solution of one salt as the initial solution, a series of pseudo-ternary system solutions were prepared by adding another new salt with gradient concentrations [38]. The simulated wastewater solution with different ratios was placed in a constant-temperature oscillation box, oscillating for 9 h and standing for 1 h. The supernatant was then taken and filtered for the measurements of SO42−, Cl−, and the liquid density. The solid was rapidly filtered, and the morphology of the crystal was observed by a metallographic digital microscope.
Determination of crystallization kinetics data. The intermittent dynamic method was used [39]. The simulated wastewater solution was prepared with saturated Na2SO4 added. The temperature was set according to the undercooling data, and the time of crystal nucleus appearance was judged by temperature changes and visual observation of whether there was crystal precipitation in the solution. With a large number of crystals precipitated, samples were taken, filtered, and dried every 5 min for analysis. The suspension density, solution supersaturation, and crystal particle size distribution were measured, and the sampling volume and sampling time were recorded at the same time.
3.3. Theoretical Models
3.3.1. Thermodynamic Models for Solubility [40]
- The Apelblat model
The Apelblat model was obtained on the basis of the Keck equation. The expression is as follows:
where x is the molar fraction of the solute; T is the absolute temperature, K; and A, B, and C represent different parameters to be estimated.
- 2.
- The Van ‘t Hoff model
The Van ‘t Hoff model was originally used to calculate the reaction equilibrium constant, and its expression is as follows:
where x is the molar fraction of the solute; T is the absolute temperature, K; and a and b represent different parameters to be estimated.
- 3.
- The polynomial model
The expression of the polynomial model is as follows:
where x is the molar fraction of the solute; T is the absolute temperature, K; and A, B, and C represent different parameters to be estimated.
3.3.2. Models for Metastable Zone Width
Based on the Nyvlt’s equation [41] and the self-consistent Nyvlt-like model [42], the relationship between the width of the metastable zone and the cooling rate under the condition of a constant stirring rate is shown as follows:
where ΔTmax is the width of the metastable zone; m is the nucleation order; RG and ΔHs are the ideal gas constant and dissolution enthalpy, respectively; Tlim represents the nucleation temperature; f is the number of entities per unit volume; K is the nucleation constant; and R is the cooling rate [43].
Classical nucleation theory [44] is widely used to fit metastable region data, and the expression is as follows:
where J is the nucleation rate; A is the pre-exponential factor; γ is the solid–liquid interface energy; Vs represents the volume of solute molecules; Tlim represents the nucleation temperature; and S represents supersaturation.
Combining Equations (6) and (7) and taking the logarithm, the following equations can be obtained.
where A refers to the pre-factor; γ is the solid–liquid interfacial energy; Vs stands for the solute molecular volume; Tlim stands for the nucleation temperature; and S stands for the supersaturation. The solid–liquid interface energy γ and the pre-exponential factor A can be obtained from the slope and intercept.
3.3.3. Models for Induction Period
Based on classical nucleation theory and the Gibbs–Thompson equation [44], the following equation can be obtained. The interface energy can be expressed by Equation (12), where α is the slope of Equation (11).
where tind is the induction time; γ is the solid–liquid interfacial energy; Vs stands for the solute molecular volume; Tlim stands for the nucleation temperature; and S stands for the supersaturation.
3.3.4. Nucleation Kinetics Models [45]
The secondary nucleation of crystals is a common phenomenon in production and life, and the following empirical equation is usually used:
where B is the nucleation rate, n·m−3·s−1; MT is the suspension density, kg·m−3; ΔC is the supersaturation, mol·L−1; R is the gas constant, J·K·mol−1; T is the temperature, K; c and d are kinetic equation parameters; Kb is the nucleation rate constant; and EB is the nucleation activation energy, J·mol−1.
In the whole range of the particle size distribution, the relationship between the grain size of the Na2SO4 crystals and the logarithm of the particle number density is approximately linear, so the growth of Na2SO4 crystals complies with the law of ΔL, showing a grain-size-independent growth law. Industrial production often adopts the following empirical equation:
where G refers to the growth rate, m·s−1; Kg is the growth rate constant; T is the temperature, K; R is the gas constant, J·K·mol−1; Ea is the growth activation energy, J·mol−1; and ΔC is the supersaturation, mol·L−1.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The effects of temperature and organic impurities on the solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl were investigated. The solubility of Na2SO4 and NaCl increased with a rising temperature. Under certain temperature conditions, the solubility of Na2SO4 decreased with an increasing dimethoxymethane content in the solution.
- (2)
- The metastable zone width and induction period of Na2SO4 increased with an increasing dimethoxymethane content, saturation temperature, and cooling rate. The theoretical reasons for this could be that the increase in the saturation temperature and dimethoxymethane content increased the solid–liquid interface energy and the critical crystal nucleation size, which was unfavorable for the nucleation of Na2SO4.
- (3)
- The phase diagrams of the NaCl-Na2SO4-H2O pseudo-ternary system in the simulated wastewater were plotted in the temperature range of 303.15 to 333.15 K. Under the simulated wastewater conditions, the crystallization zone of Na2SO4 was larger than that of NaCl, and the density of the system was positively correlated with the amount of Na2SO4. The nucleation rate of Na2SO4 was greater than the growth rate due to the salting out effect.
- (4)
- The crystallization kinetics equations of Na2SO4 in the simulated wastewater solution were obtained through kinetic experiments. The crystallization nucleation of Na2SO4 was a secondary nucleation process, controlled by surface reactions. A higher solution temperature and suspension density would be favorable for the crystallization and nucleation of Na2SO4.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29091928/s1, Table S1: Experimental and theoretical values of mole fraction of Na2SO4; Table S2: Van’t Hoff equation parameters of Na2SO4 at different concentrations of dimethoxymethane; Table S3: The γ for Na2SO4 in water at different temperatures and concentrations of dimethoxymethane; Table S4: The A for Na2SO4 in water at different temperatures and concentrations of dimethoxymethane; Table S5: Phase equilibrium solubility data of the pseudo-ternary system (NaCl-Na2SO4-H2O) in simulated wastewater; Figure S1: The co-saturated points of the pseudo-ternary system (NaCl-Na2SO4-H2O) of simulated wastewater at T = (303.15 to 333.15) K. (WA, WB and WC are the mass fractions of NaCl, Na2SO4 and H2O, respectively; Text S1: Determination of sulfate ion and chloride ion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S. and B.W.; methodology, B.Z. and H.D.; software, B.Z. and Y.R.; validation, B.S. and J.T.; formal analysis, H.D. and Y.L.; investigation, B.S. and Q.H.; data curation, H.D. and B.W.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S.; writing—review and editing, B.S. and B.W.; funding acquisition, B.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of High-efficiency Utilization of Coal and Green Chemical Engineering (Grant No. 2017-K14), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22278381), the Key R&D Program of Henan Province (Grant No. 231111320502), and the Young Backbone Teacher Training Program of Zhengzhou University (Grant No. 2021ZDGGJS015).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shi, J.; Huang, W.; Han, H.; Xu, C. Pollution control of wastewater from the coal chemical industry in China: Environmental management policy and technical standards. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Cao, Q.; Qian, Y. Life cycle economic assessment of coal chemical wastewater treatment facing the ‘Zero liquid discharge’ industrial water policies in China: Discharge or reuse? Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaissa, M.; Rouane-Hacene, O.; Boutiba, Z.; Guibbolini-Sabatier, M.E.; Faverney, C.R.D. Ecotoxicological impact assessment of the brine discharges from a desalination plant in the marine waters of the Algerian west coast, using a multibiomarker approach in a limpet, Patella rustica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24521–24532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulos, A. Brine management (saline water & wastewater effluents): Sustainable utilization and resource recovery strategy through Minimal and Zero Liquid Discharge (MLD & ZLD) desalination systems. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 176, 108944. [Google Scholar]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Giannika, V. Decarbonized and circular brine management/valorization for water & valuable resource recovery via minimal/zero liquid discharge (MLD/ZLD) strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116239. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, P. A comprehensive review of saline effluent disposal and treatment: Conventional practices, emerging technologies, and future potential. Water Reuse 2020, 11, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Parida, V.K.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Treatment of saline wastewater using physicochemical, biological, and hybrid processes: Insights into inhibition mechanisms, treatment efficiencies and performance enhancement. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xie, Y.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y. Research Progress of High-Salinity Wastewater Treatment Technology. Water 2023, 15, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmardeh, H.; Akhlaghi Amiri, H.A.; Nowee, S.M. Evaluation of mechanical vapor recompression crystallization process for treatment of high salinity wastewater. Chem. Eng. Process. 2019, 145, 107682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Bao, Y.; Hao, H. Crystallization techniques in wastewater treatment: An overview of applications. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, H.; Wu, X.; Deng, T. Metastable Phase Equilibrium in the Aqueous Quaternary System (NaCl + MgCl2 + Na2SO4 + MgSO4 + H2O) at 323.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4216–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bian, C.; Bian, J.; Song, X.; Yu, J. Stable Solid—Liquid Equilibrium of the Quaternary System Na+//Cl−, NO3−, and SO42−—H2O at 333.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3569–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Bao, Y.; Ma, D.; Hao, H. Phase equilibria for the pseudo-ternary system (NaCl+ Na2SO4+H2O) of coal gasification wastewater at T= (268.15 to 373.15) K. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.-Y.; Ma, Y.-L.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, X.-X.; Ren, Y.-S.; Ma, R.; Gao, J. Study of the Solubility, Supersolubility, and Metastable Zone Width of Ternary System (NaCl + Na2SO4 + H2O) Containing Organic Impurity at 333.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 5113–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Chen, H.; Song, X.; Yu, J. Process Parameters Optimal Investigation on the Na2SO4 Fractional Crystallization from Coal Chemical Industry High-saline Wastewater. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, H.; Ma, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.N.; Kong, L.; Shen, W. Solid–Liquid Equilibrium for the Ternary Systems (Na2SO4 + NaH2PO4 + H2O) and (Na2SO4 + NaCl + H2O) at 313.15 K and Atmospheric Pressure. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 3969–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Li, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Determination of metastable zone width and the primary nucleation kinetics of sodium sulfate. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, H.; Lou, Y.; Huang, J.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Hao, H. Mechanism of Influence of Organic Impurity on Crystallization of Sodium Sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K. Effect of impurities on the metastable zone width of solute-solvent systems. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4050–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, T.; Wen, G. Experimental study on the effects of different factors on the crystallization rate and products of Mn–Ca co-crystallization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 13521–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielitz, T.R.; Phenicie, C.M.; Holmes, R.J. Effects of Additives on Crystallization in Thin Organic Films. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4522–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, Y.; Ge, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Wu, D.; Che, C. Determination of NaCl and Na2SO4 Equilibrium Solubility in Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Aqueous Solutions at 323.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, N.P.; Meera, K.; Srinivasan, K.; Raghavan, P.S.; Ramasamy, P. Effect of EDTA on the metastable zone width of ADP. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 213, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Doki, N.; Kubota, N. The Effect of an Additive on Morphology of Sodium Chloride Crystals in Seeded Batch Cooling Crystallization. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Chemical and Process Engineering (ICheaP), Milano, Italy, 19–22 May 2015; pp. 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Nanev, C.N. Thermodynamic and molecular-kinetic considerations of the initial growth of newly born crystals; crystal size distribution; Dissolution of small crystals during Ostwald ripening due to temperature changes. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2023, 69, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Lu, W.; Chen, N. Chemical Bond-Parametric Analysis of Formation Regularities of Salt Hydrates. J. Shanghai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2004, 10, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Menger, F.M.; Chlebowski, M.E. Is the ether group hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Langmuir 2005, 21, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.S.; Kulkarni, S.A.; Ribera, R.C.; Stankiewicz, A.I.; Ter Horst, J.H.; Kramer, H.J.M. A new view on the metastable zone width during cooling crystallization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 72, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K.; Wójcik, K. Investigation of metastable zone width of ammonium oxalate aqueous solutions. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2009, 44, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K.; Mielniczek-Brzóska, E.; Borc, J. On the induction period for crystallization in solute-solvent systems by polythermal method. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2013, 48, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, J.M.; MacIver, D.; Jolliffe, H.; Haw, M.D.; Sefcik, J. Nucleation and Growth Kinetics of Sodium Chloride Crystallization from Water and Deuterium Oxide. Crystals 2023, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custelcean, R.; Sloop, F.V., Jr.; Rajbanshi, A.; Wan, S.; Moyer, B.A. Sodium Sulfate Separation from Aqueous Alkaline Solutions via Crystalline Urea-Functionalized Capsules: Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frawley, P.J.; Mitchell, N.A.; O‘Ciardhá, C.T.; Hutton, K.W. The effects of supersaturation, temperature, agitation and seed surface area on the secondary nucleation of paracetamol in ethanol solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 75, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Du, S.; Wu, S.; Cai, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, K.; Yang, P.; Yu, B.; Guo, B.; et al. Determination and correlation of solubility and solution thermodynamics of oxiracetam in three (alcohol + water) binary solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 96, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 13025.8-2012; General Test Method in Salt Industry-Determination of Sulfate. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB/T 13025.5-2012; General Test Method in Salt Industry-Determination of Chloride Ion. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Kuldipkumar, A.; Kwon, G.S.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Determining the growth mechanism of tolazamide by induction time measurement. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, Y.L.; Ge, S.Y.; Wu, D.; Che, C.; Liu, E.; Zhao, K.H. Study of the stable and metastable phase equilibrium of a ternary system (NaCl + Na2SO4+H2O) in coal-to-liquids wastewater at 323.15 K. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 197, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivanek, J.; Pekarek, V.; Hostomsky, J. Crystallization studies in thermometric methods. II. Calorimetric determination of crystallization kinetics of sodium sulfate and sodium carbonate decahydrates. Krist. Tech. 1975, 10, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirheydari, S.N.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Acree, W.E.; Shekaari, H.; Shayanfar, A.; Jouyban, A. Comparison of the Models for Correlation of Drug Solubility in Ethanol plus Water Binary Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 1079–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nývlt, J. Kinetics of nucleation in solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 1968, 3, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, A.; Sarkar, D. Effects of Ultrasound and Its Amplitude on the Metastable Zone Width, Induction Time, and Nucleation Kinetics of Pyrazinamide in Acetone. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 11262–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K. Recent developments in understanding of the metastable zone width of different solute-solvent systems. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 318, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.W.; Hofmeister, W.H.; Bayuzick, R.J.; Rulison, A.J.; Watkins, J.L. The kinetics of solid nucleation in zirconium. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 6033–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, M.; Lin, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Rohani, S. Secondary nucleation and growth kinetics of aluminum hydroxide crystallization from potassium aluminate solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2019, 507, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).