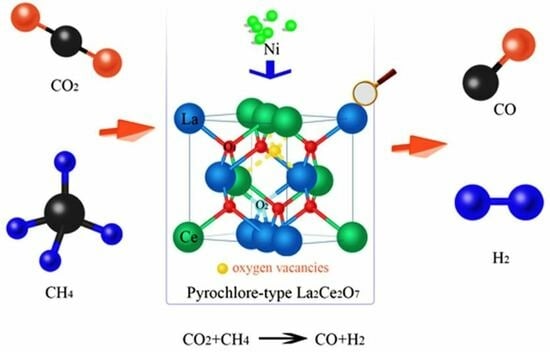
Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure and DRM Reaction Behaviors over the Catalysts Prepared with Different Methods
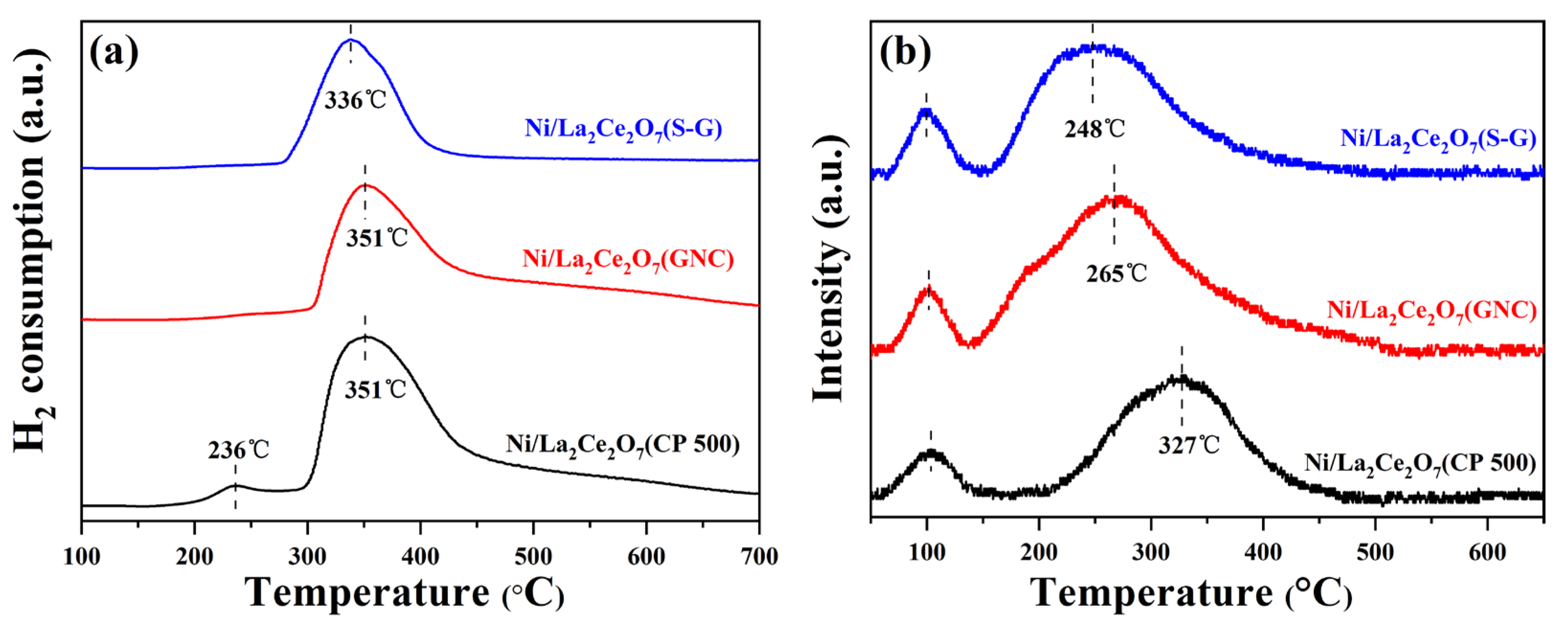
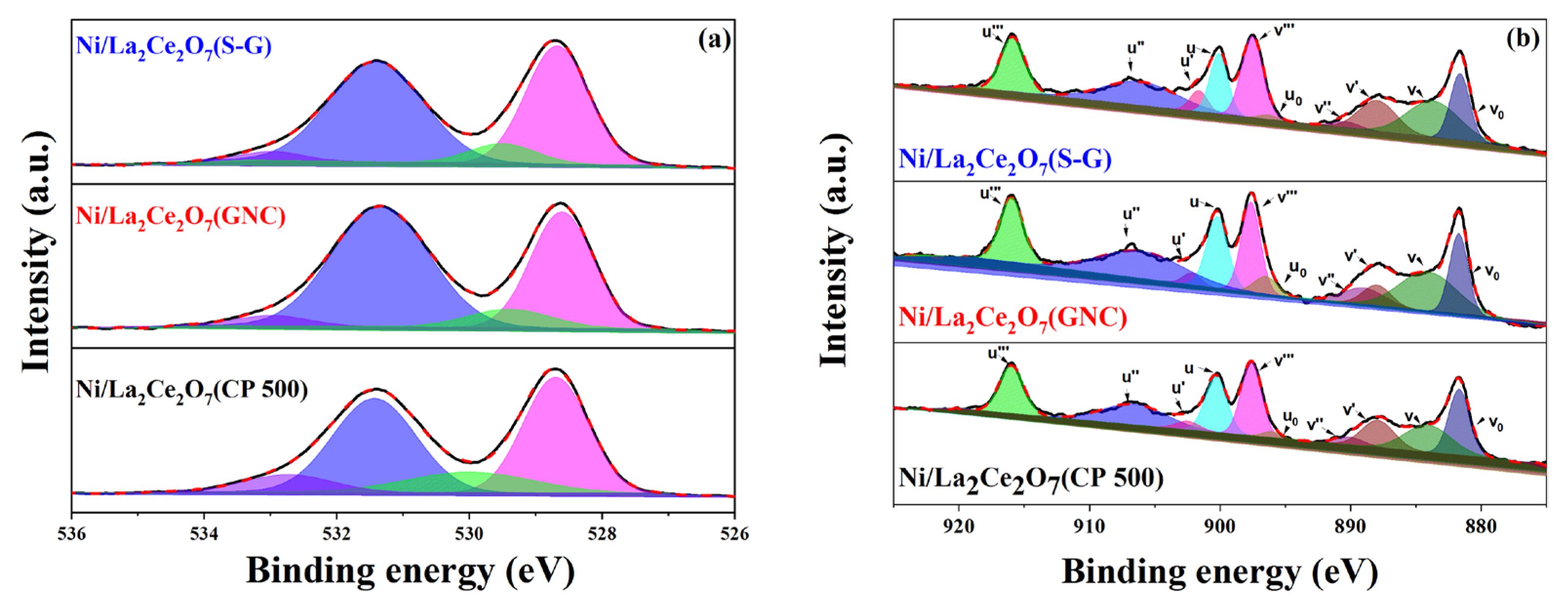
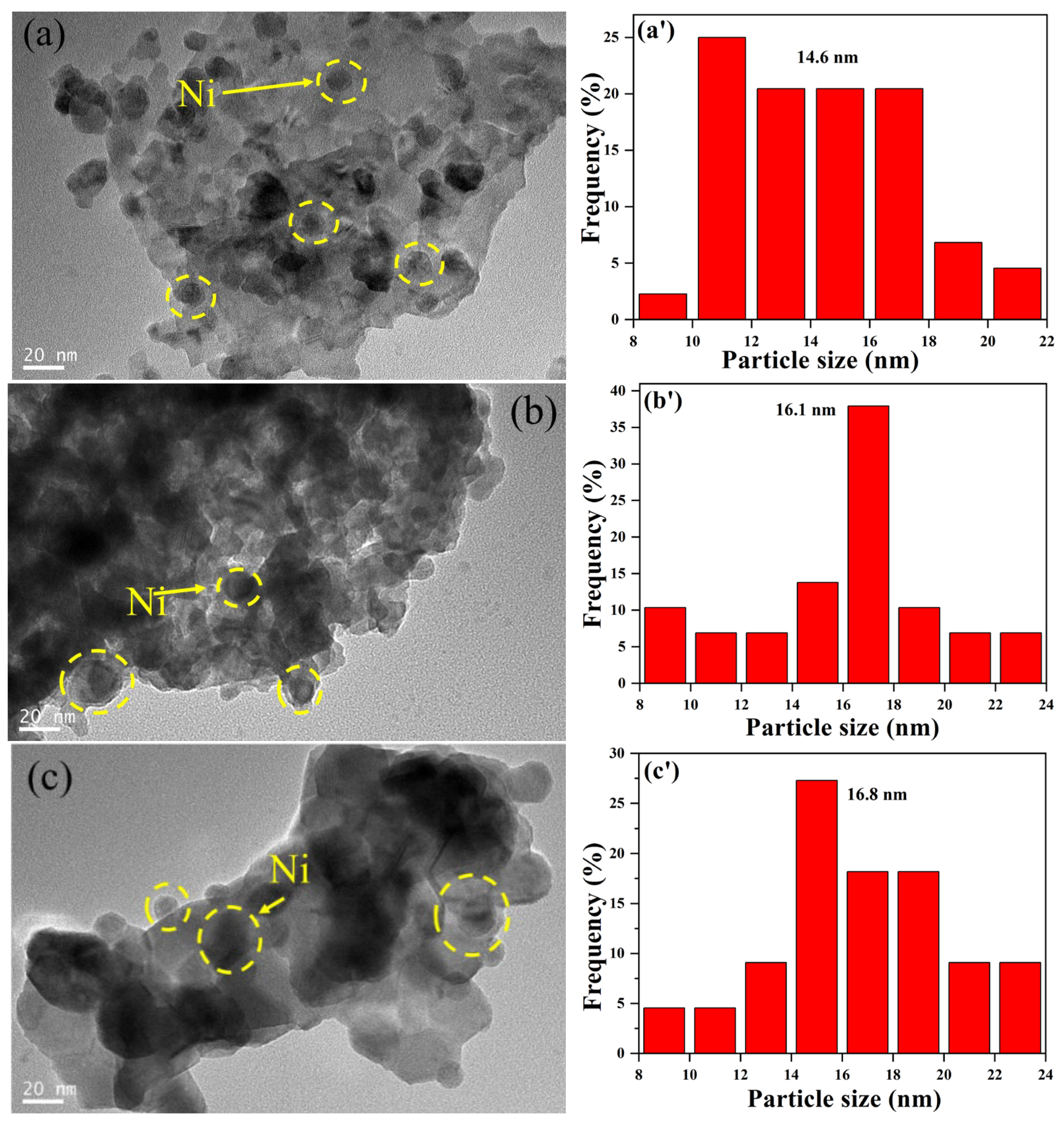
2.1.1. Sample Characterization
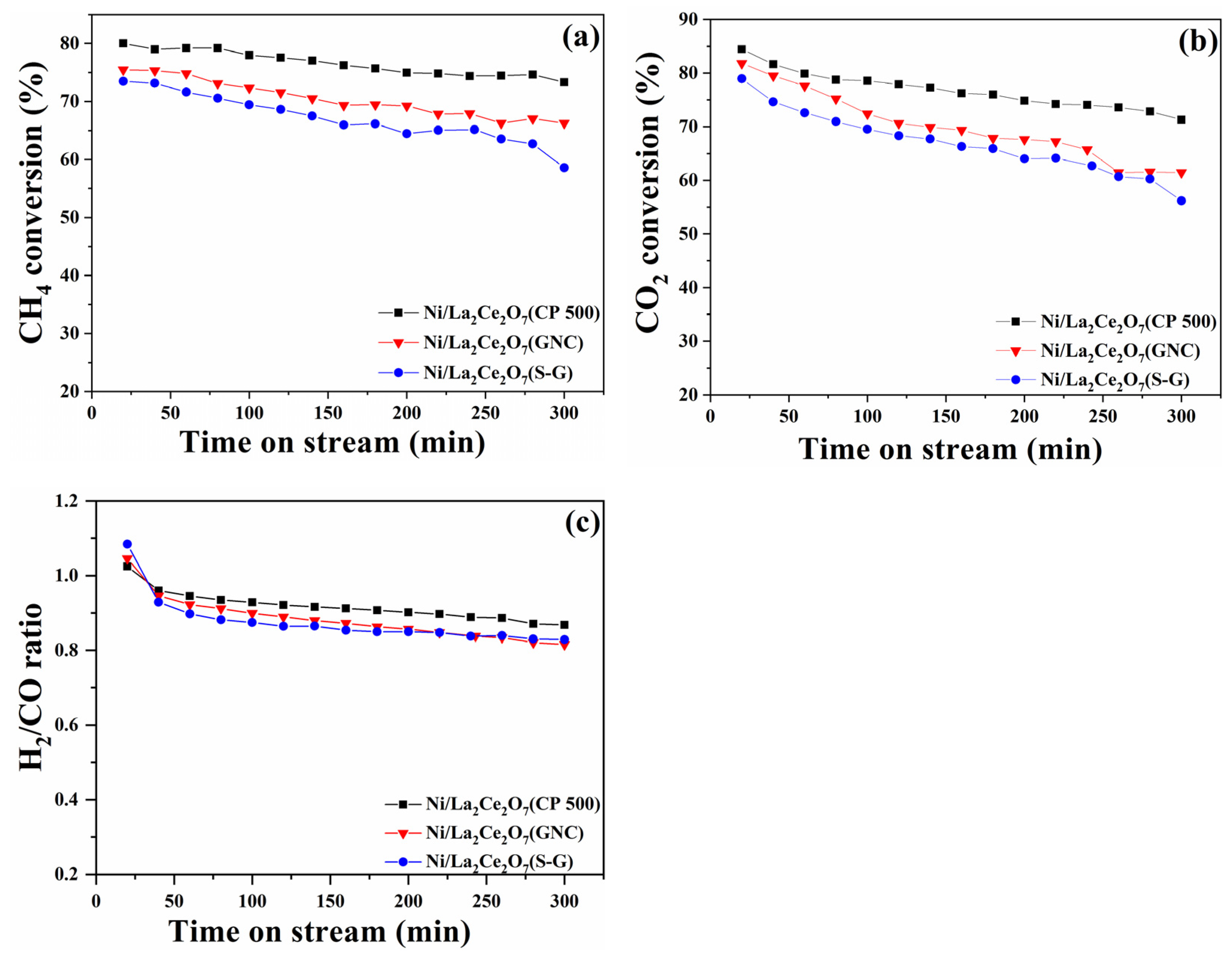
2.1.2. DRM Performance of the Ni/La2Ce2O7 Catalyst
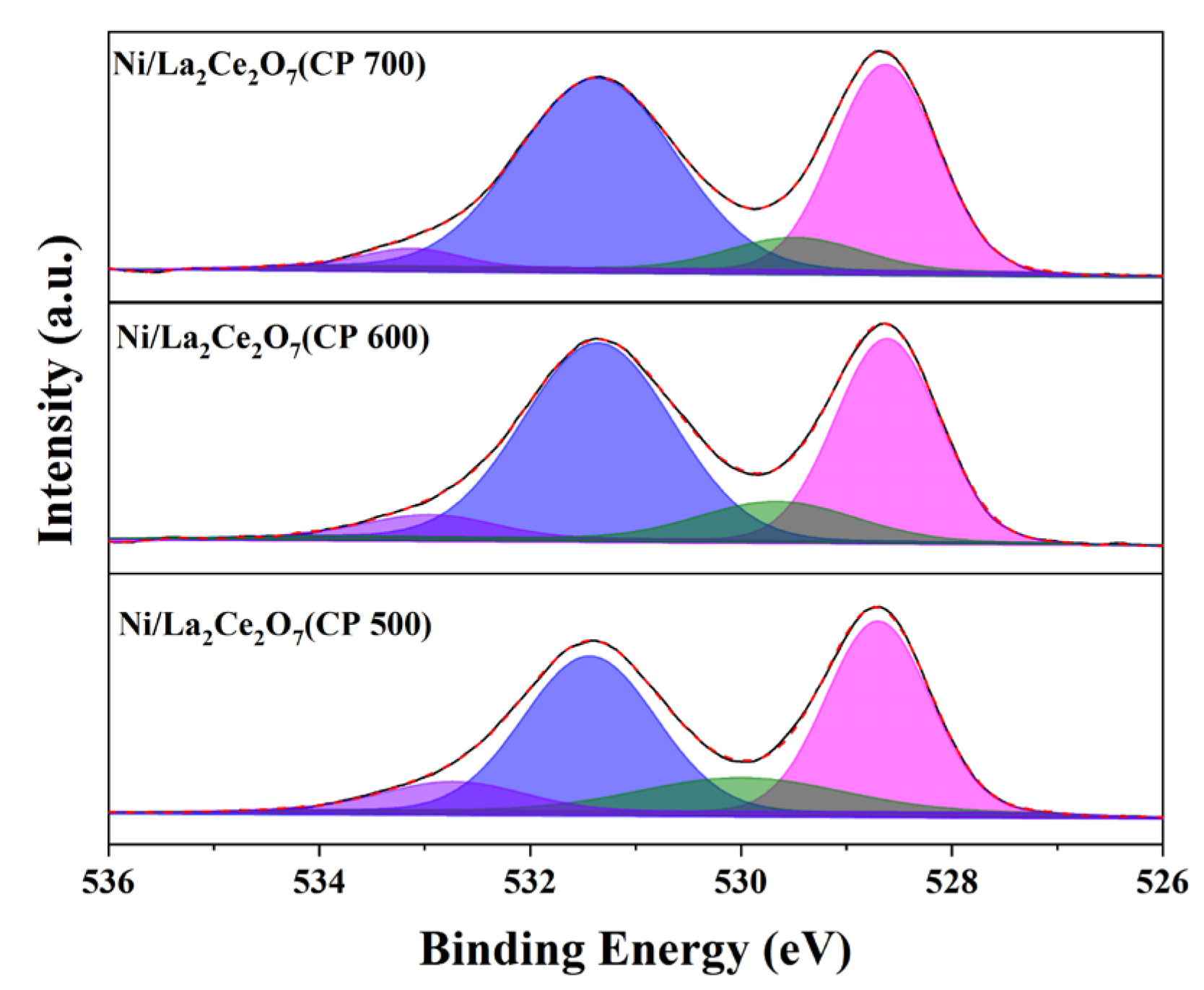
2.1.3. Characterization of the Spent Catalyst
2.2. DRM Reaction Behaviors over Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP T) Catalysts Obtained through Calcination at Different Temperatures
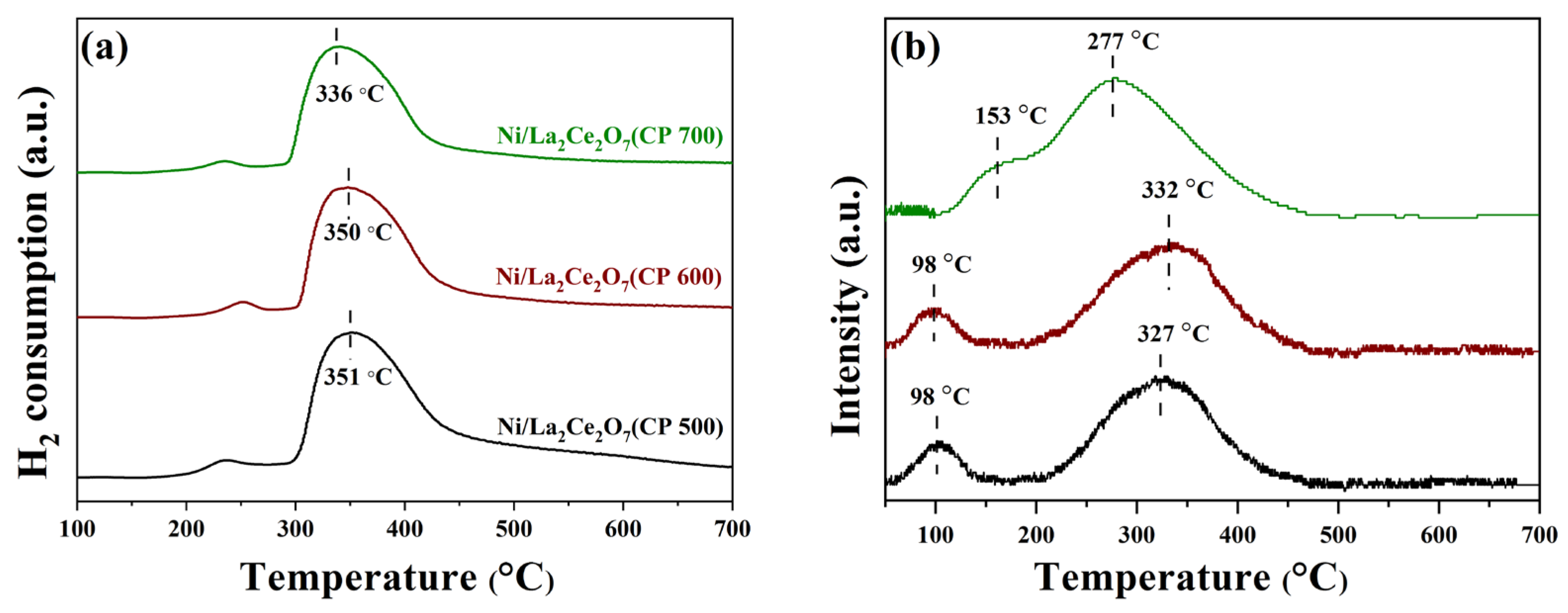
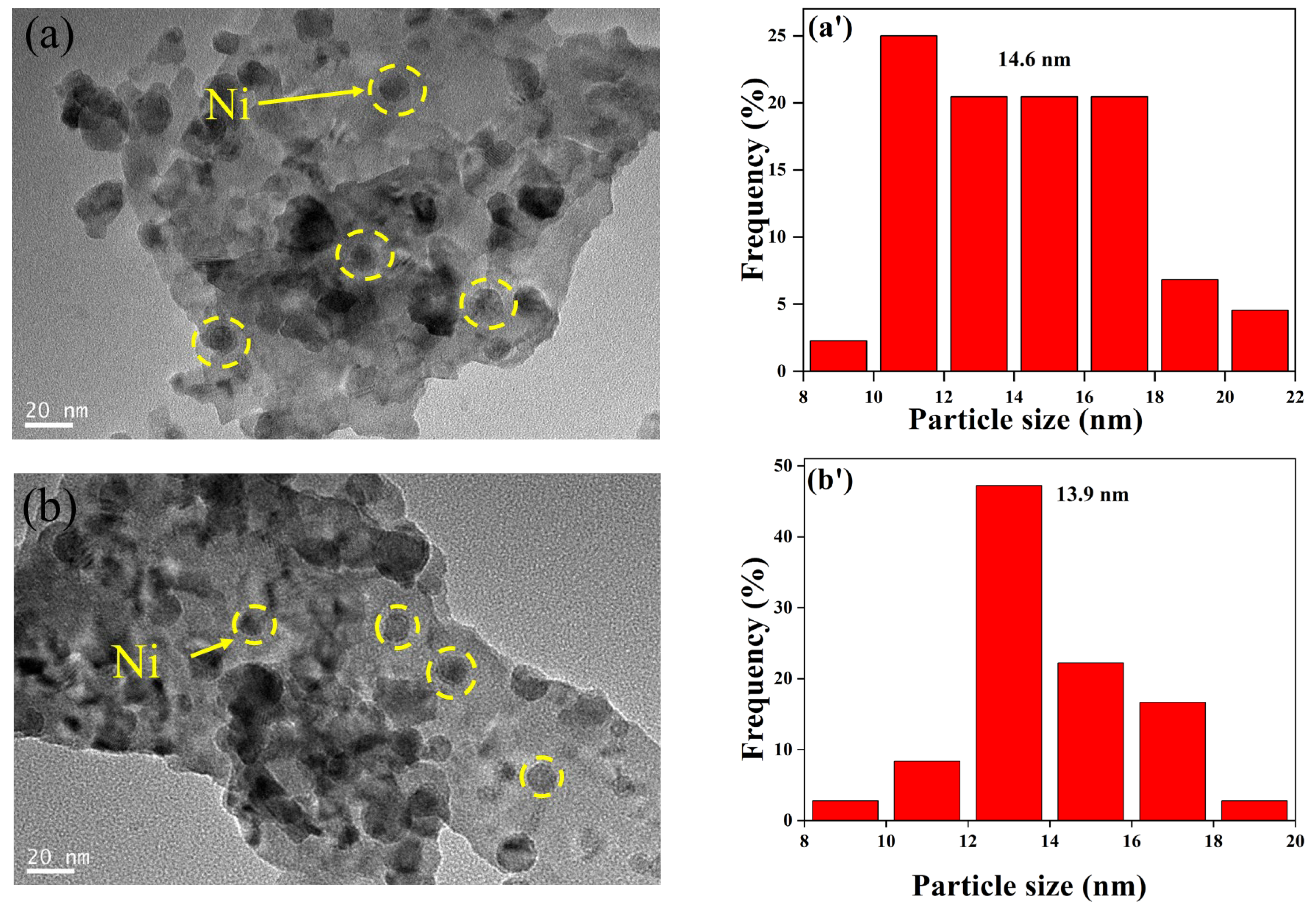
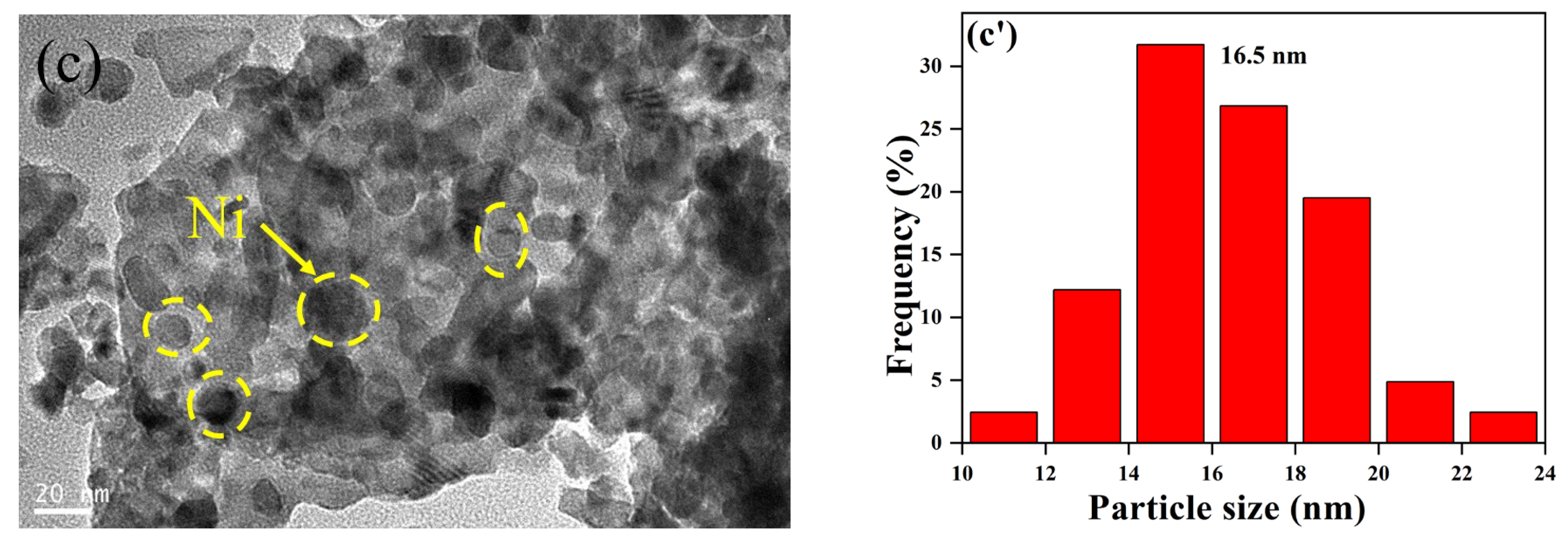
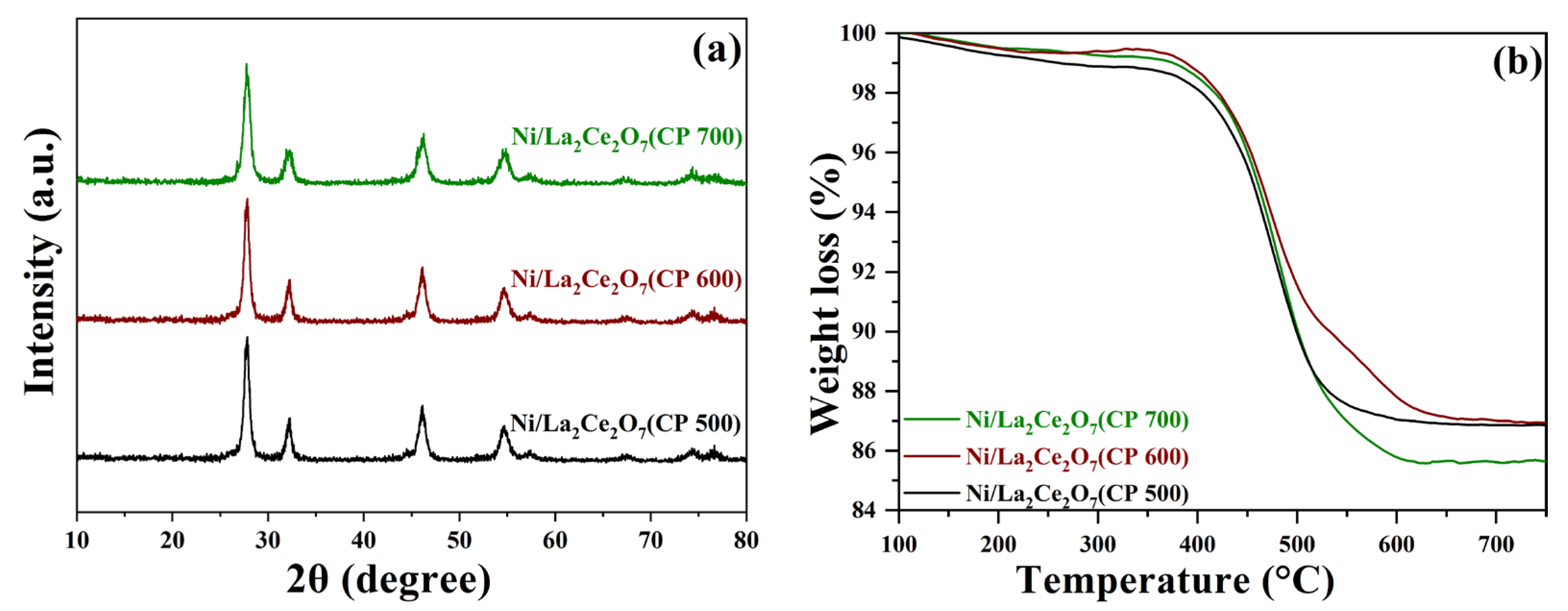
2.2.1. Sample Characterization
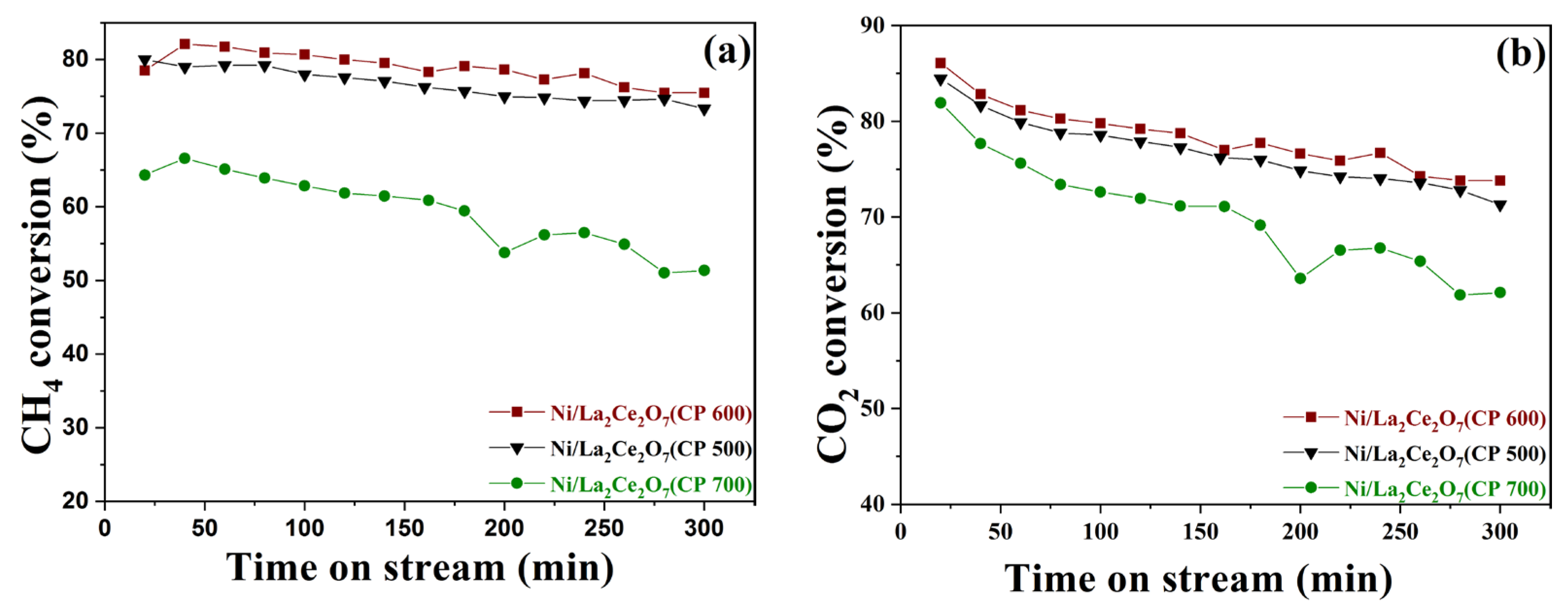
2.2.2. The Performance of Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP T)
2.2.3. Characterization of the Spent Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP T)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.1.1. La2Ce2O7 Supports Preparation
3.1.2. Preparation of Ni/La2Ce2O7 Catalysts
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalyst Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Compared with the catalysts prepared using sol–gel and combustion methods, the precipitated La2Ce2O7(CP 500) catalysts (Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 500)) show the best DRM reactivity and good stability after Ni loading.
- (2)
- The supports prepared through different methods have different particle sizes and surface properties. Moreover, improving the calcination temperature can promote the aggregation of the support with a small particle size (below 95 nm) but has no influence on the support with a large particle size (such as La2Ce2O7-SG with 229 nm). Pre-reduction at 700 °C also leads to the aggregation of La2Ce2O7 support particles calcined below 700 °C.
- (3)
- An appropriate particle size (68 nm) of the support is beneficial for enhancement of the metal–support interaction and improvement of Ni dispersion, effectively promoting the cracking of CH4. Meanwhile, supports with an appropriate particle size have more oxygen vacancies, leading to the presence of more surface-adsorbed oxygen species and basic sites for CO2 adsorption, accelerating carbon removal on the catalyst surface. Thus, the catalyst obtained with La2Ce2O7(CP 600), which has the most appropriate size, shows optimal catalytic performance in DRM among the representative catalysts.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Wongsakulphasatch, S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Understanding the role of surface basic sites of catalysts in CO2 activation in dry reforming of methane: A short review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentekakis, I.V.; Panagiotopoulou, P.; Artemakis, G. A review of recent efforts to promote dry reforming of methane (DRM) to syngas production via bimetallic catalyst formulations. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2021, 296, 120210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentekakis, I.V.; Goula, G.; Hatzisymeon, M.; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I.; Botzolaki, G.; Kousi, K.; Kondarides, D.I.; Taylor, M.J.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Osatiashtiani, A.; et al. Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 243, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, Q.D.; Tsubaki, N.; Tan, Y.S.; Han, Y.Z. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni nanoparticles incorporated into mesoporous amorphous ZrO2 matrix. Fuel 2015, 147, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ashok, J.; Bian, Z.; Dewangan, N.; Wai, M.H.; Du, Y.; Borgna, A.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Silica-Ceria sandwiched Ni core-shell catalyst for low temperature dry reforming of biogas: Coke resistance and mechanistic insights. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 230, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.P.; Lau, R.; Borgna, A.; Yang, Y.H. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane to synthesis gas over Ni-MCM-41 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2009, 358, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Song, H.L.; Chou, L.J. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over ordered mesoporous NiO-MgO-Al2O3 composite oxides. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2011, 108, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Han, Y.; Wei, Q.; Makpal, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.-S. Stabilizing Ni on bimodal mesoporous-macroporous alumina with enhanced coke tolerance in dry reforming of methane to syngas. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 35, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; He, F.; Han, S. Effects of preparation methods on properties of Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalysts for methane reforming with carbon dioxide. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 235, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Diéguez, M.; Pieta, I.S.; Herrera, M.C.; Larrubia, M.A.; Alemany, L.J. Nanostructured Pt- and Ni-based catalysts for CO2-reforming of methane. J. Catal. 2010, 270, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthiumporn, K.; Maneerung, T.; Kathiraser, Y.; Kawi, S. CO2 dry-reforming of methane over La0.8Sr0.2Ni0.8M0.2O3 perovskite (M = Bi, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe): Roles of lattice oxygen on C–H activation and carbon suppression. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 11195–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeling, Z.; Meng, Z.; Junfeng, Z.; Faen, S.; Qingde, Z.; Yisheng, T.; Yizhuo, H. Methane reforming with carbon dioxide over the perovskite supported Ni catalysts. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2020, 48, 833–841. [Google Scholar]
- Budiman, A.W.; Song, S.-H.; Chang, T.-S.; Shin, C.-H.; Choi, M.-J. Dry Reforming of Methane Over Cobalt Catalysts: A Literature Review of Catalyst Development. Catal. Surv. Asia 2012, 16, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Han, Y. Insight into the effects of the oxygen species over Ni/ZrO2 catalyst surface on methane reforming with carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 244, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, T.; Song, F.; Zhang, Q.; Tsubaki, N.; Tan, Y.; Han, Y. Effects of the surface adsorbed oxygen species tuned by rare-earth metal doping on dry reforming of methane over Ni/ZrO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 264, 118522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhare, D.; Shaw, C.; Haynes, D.; Shekhawat, D.; Spivey, J. Effect of reaction temperature on activity of Pt- and Ru-substituted lanthanum zirconate pyrochlores (La2Zr2O7) for dry (CO2) reforming of methane (DRM). J. CO2 Util. 2013, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhare, D.; Schwartz, V.; Abdelsayed, V.; Haynes, D.; Shekhawat, D.; Poston, J.; Spivey, J. Kinetic and mechanistic study of dry (CO2) reforming of methane over Rh-substituted La2Zr2O7 pyrochlores. J. Catal. 2014, 316, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Ni/Ln2Zr2O7 (Ln = La, Pr, Sm and Y) catalysts for methane steam reforming: The effects of A site replacement. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 2729–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Cheng, M.; Quan, C.; Zheng, Y. Syngas production via combined dry and steam reforming of methane over Ni-Ce/ZSM-5 catalyst. Fuel 2020, 273, 117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani Rad, S.J.; Haghighi, M.; Alizadeh Eslami, A.; Rahmani, F.; Rahemi, N. Sol–gel vs. impregnation preparation of MgO and CeO2 doped Ni/Al2O3 nanocatalysts used in dry reforming of methane: Effect of process conditions, synthesis method and support composition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 5335–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-Q.; He, D.-H.; Xu, B.-Q. Effects of preparation methods of ZrO2 support on catalytic performances of Ni/ZrO2 catalysts in methane partial oxidation to syngas. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2008, 337, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qiao, L.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-F.; Cui, G.-J.; Zong, S.-S.; Xu, D.-J.; Ye, R.-P.; Chen, R.-P.; Si, R.; Yao, Y.-G. Revealing the Synergistic Effects of Rh and Substituted La2B2O7 (B = Zr or Ti) for Preserving the Reactivity of Catalyst in Dry Reforming of Methane. ACS Catal. 2018, 9, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wei, C.; Junqiang, X.; Lin, Z. Glow discharge plasma-assisted preparation of nickel-based catalyst for carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 21, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y. Exploiting shape effects of La2O3 nanocatalysts for oxidative coupling of methane reaction. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10844–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Pei, C.; Chang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Mu, R.; Gong, J. FeO6 Octahedral Distortion Activates Lattice Oxygen in Perovskite Ferrite for Methane Partial Oxidation Coupled with CO2 Splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11540–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Shao, Z. Enhancing Electrocatalytic Activity of Perovskite Oxides by Tuning Cation Deficiency for Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.A.; Barbero, B.P.; Eloy, P.; Cadús, L.E. La1−xCaxCoO3 perovskite-type oxides: Identification of the surface oxygen species by XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Ge, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Jia, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z. Ultrathin Iron-Cobalt Oxide Nanosheets with Abundant Oxygen Vacancies for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shen, K.; Huang, L.; Yu, X.; Qian, W.; Chu, W. Facile Route for Synthesizing Ordered Mesoporous Ni–Ce–Al Oxide Materials and Their Catalytic Performance for Methane Dry Reforming to Hydrogen and Syngas. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1638–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfberg, A.; Guerrero-Caballero, J.; Kane, T.; Rubbens, A.; Jalowiecki-Duhamel, L. Ni/CeO2 based catalysts as oxygen vectors for the chemical looping dry reforming of methane for syngas production. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 212, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, D.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G. Effect of Ceria Crystal Plane on the Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Pd/Ceria for CO and Propane Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.J.; Tavares, P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L. Ce-Doped La2O3 based catalyst for the oxidative coupling of methane. Catal. Commun. 2013, 42, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.S.; Crnivec, I.G.O.; Pintar, A. Tunable ceria-zirconia support for nickel-cobalt catalyst in the enhancement of methane dry reforming with carbon dioxide. Catal. Commun. 2014, 52, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.J.; Shen, C.F.; Tan, P.J.; Huang, W. Ni based on dual-support Mg-Al mixed oxides and SBA-15 catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Catal. Commun. 2013, 41, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lou, H.; Zheng, X.M. The deposition of coke from methane on a Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst. Carbon 2007, 45, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guczi, L.; Stefler, G.; Geszti, O.; Sajo, I.; Paszti, Z.; Tompos, A.; Schay, Z. Methane dry reforming with CO2: A study on surface carbon species. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2010, 375, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, V.Y.; Tyulenin, Y.P.; Firsova, A.A.; Shafranovsky, E.A.; Gorenberg, A.Y.; Korchak, V.N. Carbonization of nickel catalysts and its effect on methane dry reforming. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2013, 453, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W.; Park, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, H. Uncoupling the size and support effects of Ni catalysIs for dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 203, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danghyan, V.; Novoa, S.C.; Mukasyan, A.; Wolf, E.E. Pressure dilution, a new method to prepare a stable Ni/fumed silica catalyst for the dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 234, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damyanova, S.; Pawelec, B.; Palcheva, R.; Karakirova, Y.; Sanchez, M.C.C.; Tyuliev, G.; Gaigneaux, E.; Fierro, J.L.G. Structure and surface properties of ceria-modified Ni-based catalysts for hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 225, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

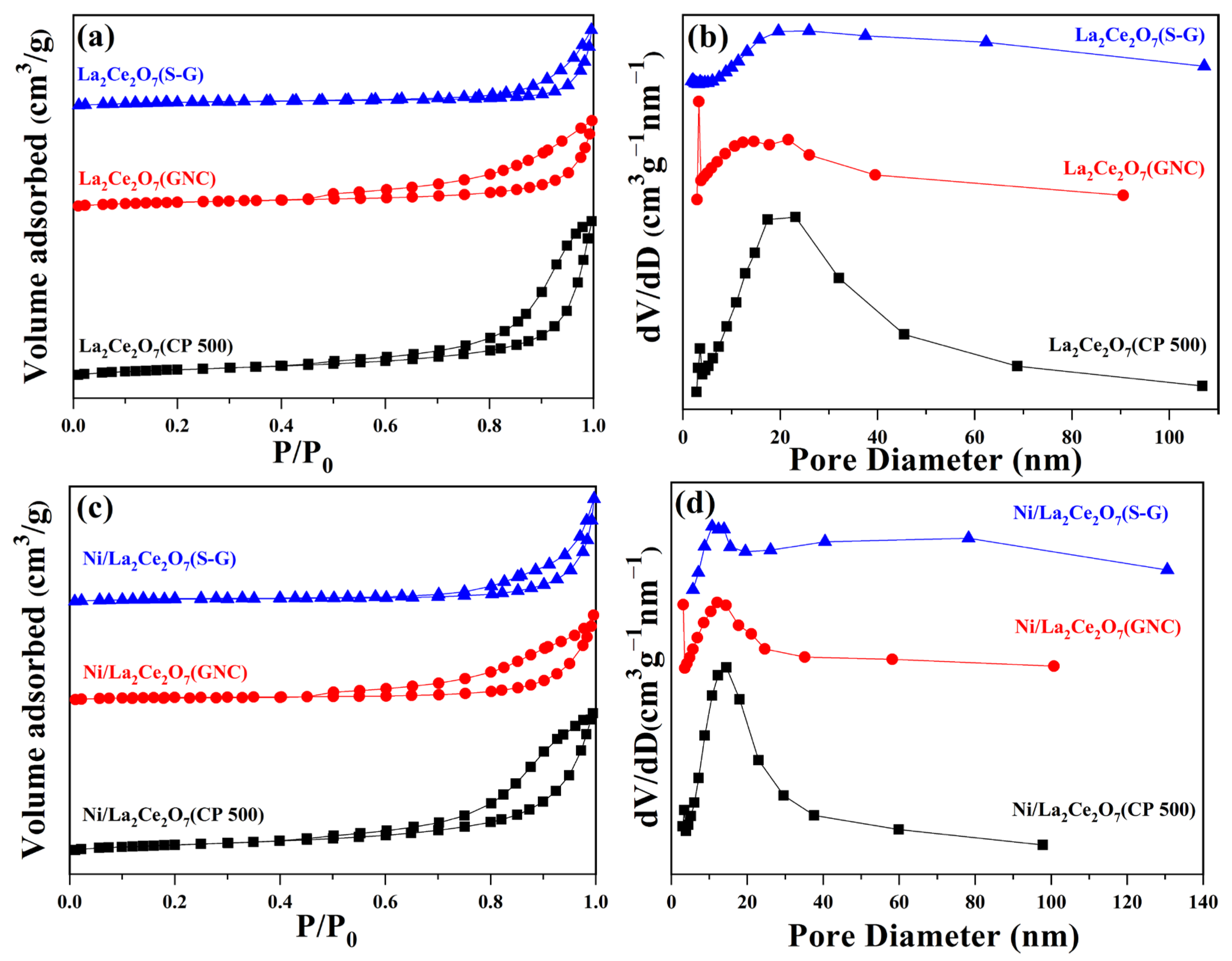


| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Crystalline Size a (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 35.2 | 0.1105 | 12.6 | 56 |
| La2Ce2O7(GNC) | 20.5 | 0.0575 | 11.2 | 60 |
| La2Ce2O7(S-G) | 12.9 | 0.0398 | 12.3 | 229 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 33.5 | 0.1127 | 13.4 | 95 * |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(GNC) | 16.7 | 0.0613 | 14.7 | 108 * |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(S-G) | 13.8 | 0.0549 | 15.9 | 224 * |
| Catalyst | Ce3+ (%) | Ni Atomic Concentration (%) | O 1s B.E (eV)/Relative Amount (%) | (α + β)/γ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2− (α) | CO32− | O22− (β) | O2− (γ) | ||||
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(S-G) | 21 | 4.06 | 533.0/2.9 | 531.4/50.3 | 529.5/7.0 | 528.7/39.8 | 0.25 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(GNC) | 25 | 4.66 | 533.0/3.6 | 531.3/55.1 | 529.4/7.2 | 528.6/34.1 | 0.32 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 27 | 4.69 | 533.0/7.8 | 531.4/40.2 | 530.0/13.4 | 528.7/38.6 | 0.54 |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Crystalline Size a (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 35.21 | 0.1105 | 12.55 | 56 |
| La2Ce2O7(CP 600) | 27.91 | 0.1142 | 16.36 | 68 |
| La2Ce2O7(CP 700) | 26.21 | 0.1065 | 16.26 | 88 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 33.53 | 0.1127 | 13.44 | 95 * |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 600) | 28.00 | 0.1156 | 16.51 | 87 * |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 700) | 28.24 | 0.1205 | 17.06 | 91 * |
| Catalyst | O 1s B.E (eV)/Relative Amount (%) | (O2− + O22−)/O2− | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2− | CO32− | O22− | O2− | ||
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 500) | 533.0/7.80 | 531.4/40.16 | 530.0/13.39 | 528.7/38.64 | 0.54 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 600) | 533.0/8.63 | 531.3/43.50 | 529.6/12.16 | 528.6/35.7 | 0.58 |
| Ni/La2Ce2O7(CP 700) | 533.1/2.89 | 531.3/52.43 | 529.4/7.55 | 528.6/37.12 | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y. Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support. Molecules 2024, 29, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081871
Zhou Z, Li C, Zhang J, Gao Q, Wang J, Zhang Q, Han Y. Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support. Molecules. 2024; 29(8):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081871
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zeling, Chao Li, Junfeng Zhang, Qiliang Gao, Jiahao Wang, Qingde Zhang, and Yizhuo Han. 2024. "Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support" Molecules 29, no. 8: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081871
APA StyleZhou, Z., Li, C., Zhang, J., Gao, Q., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., & Han, Y. (2024). Dry Reforming of Methane over Pyrochlore-Type La2Ce2O7-Supported Ni Catalyst: Effect of Particle Size of Support. Molecules, 29(8), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29081871