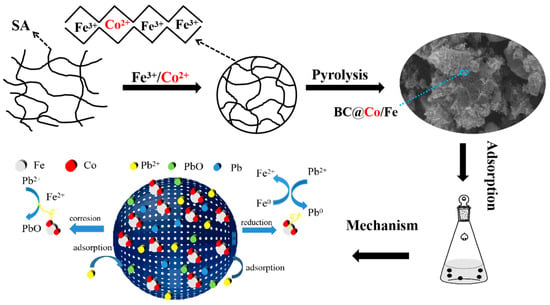
Cobalt/Iron Bimetallic Biochar Composites for Lead(II) Adsorption: Mechanism and Remediation Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
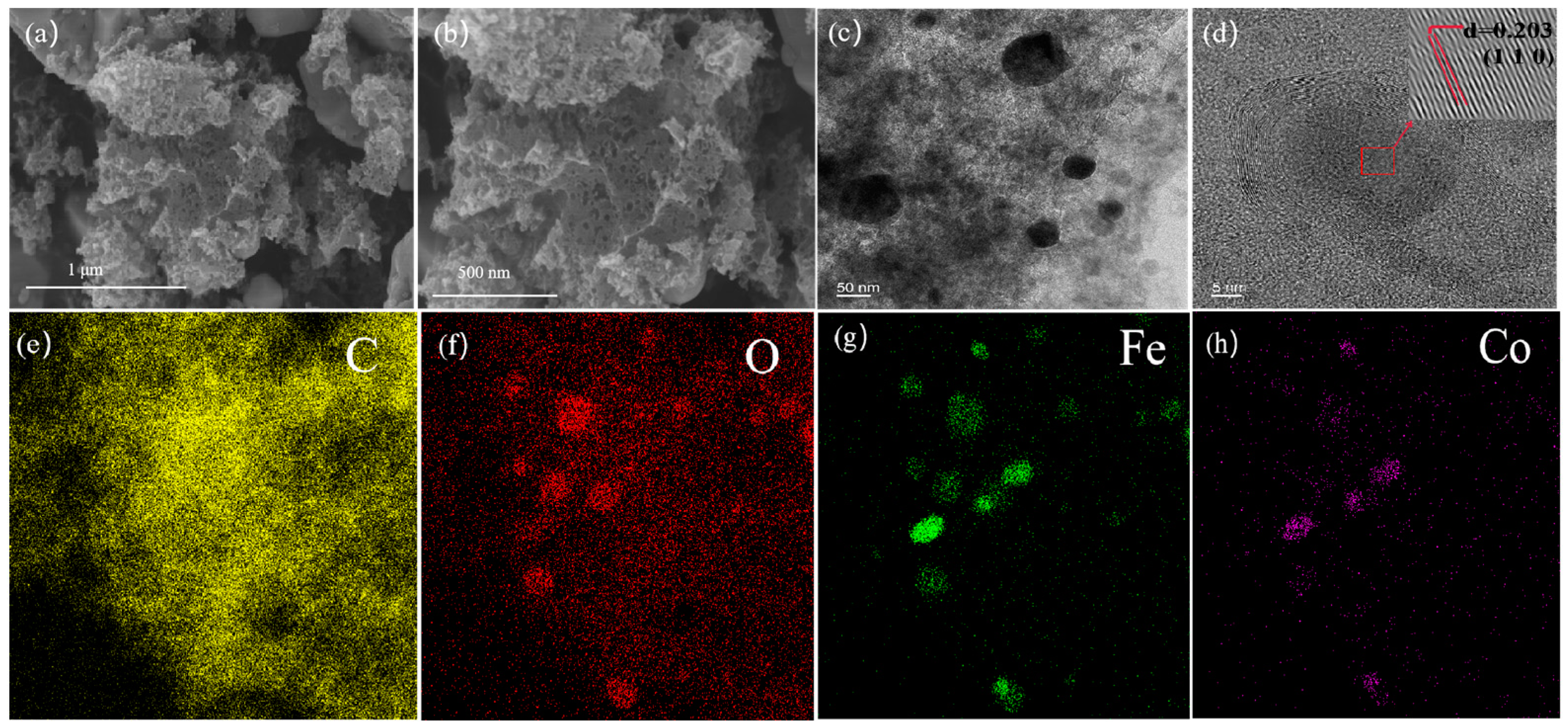
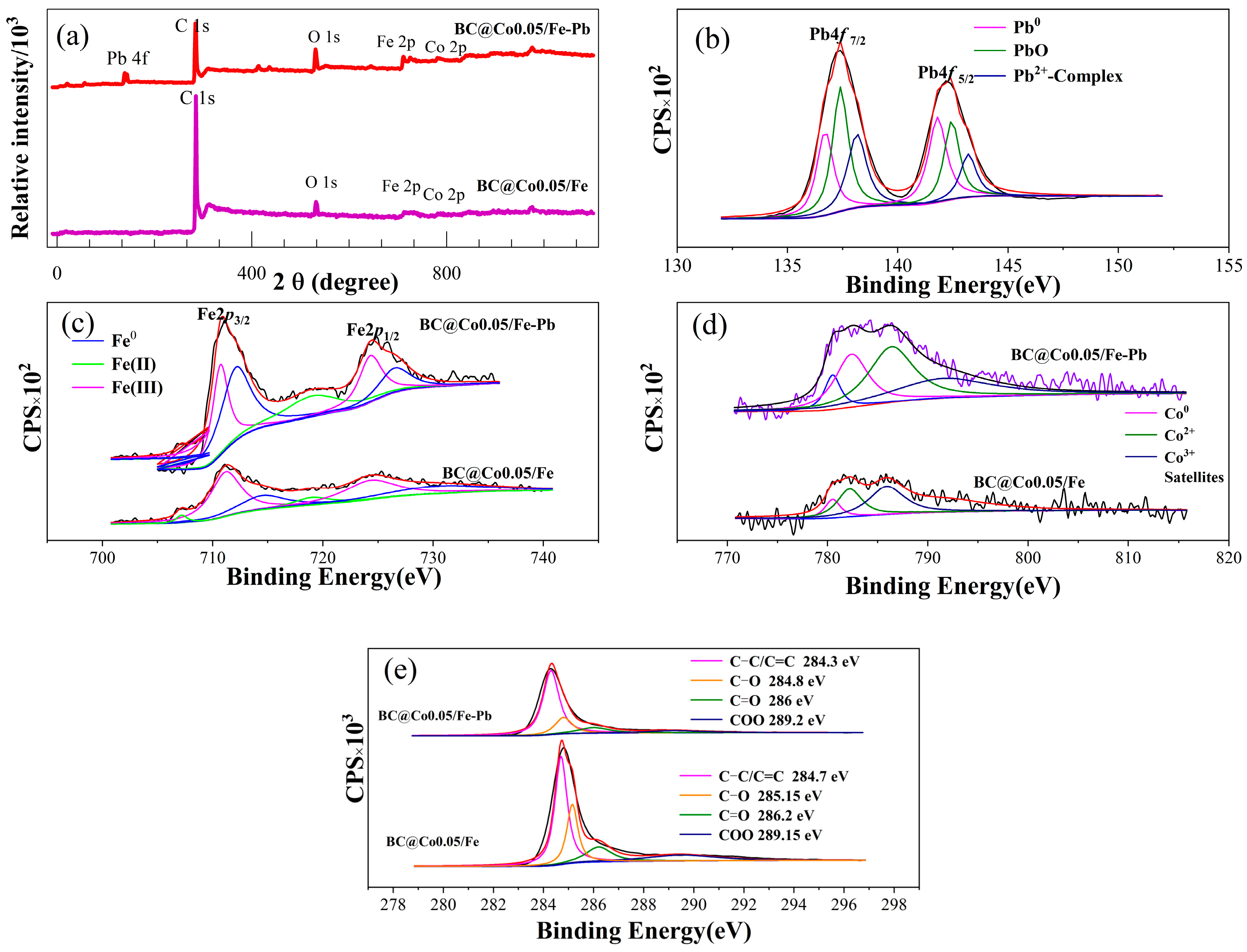
2.1. Characterisation
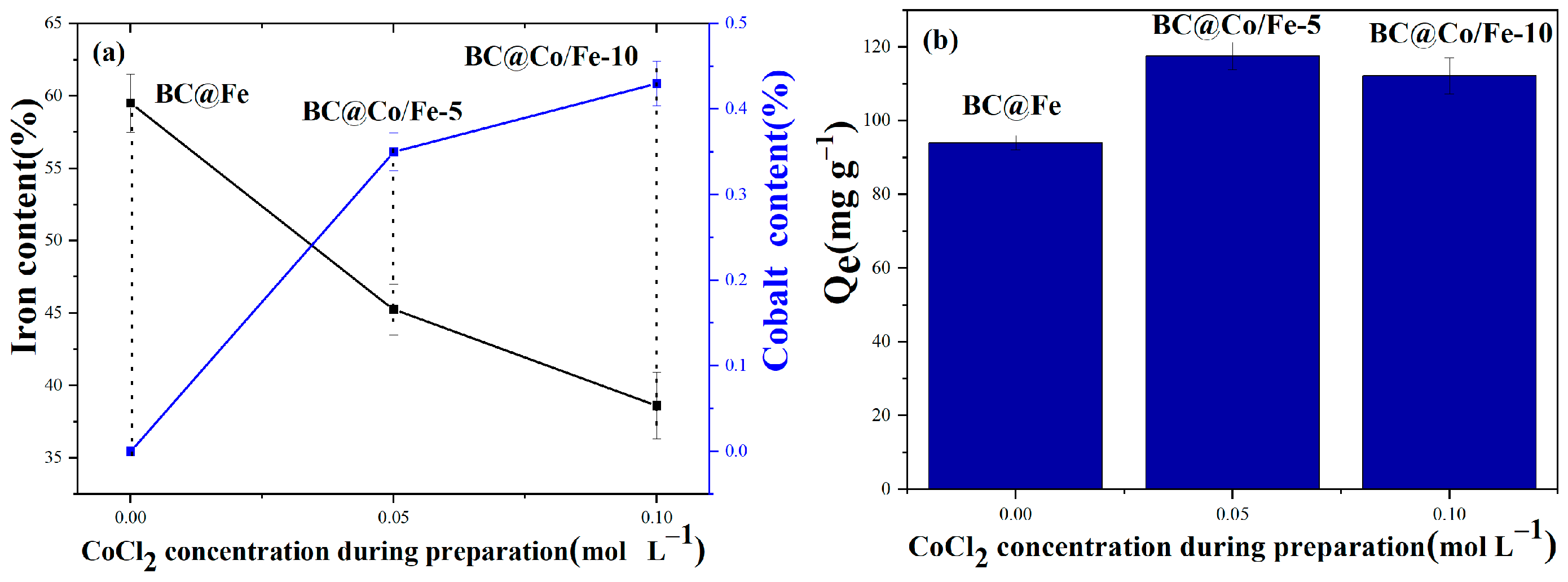
2.2. Performance of BC@Fe and BC@Co/Fe-X
2.3. Effect of pH on Pb2+ Adsorption
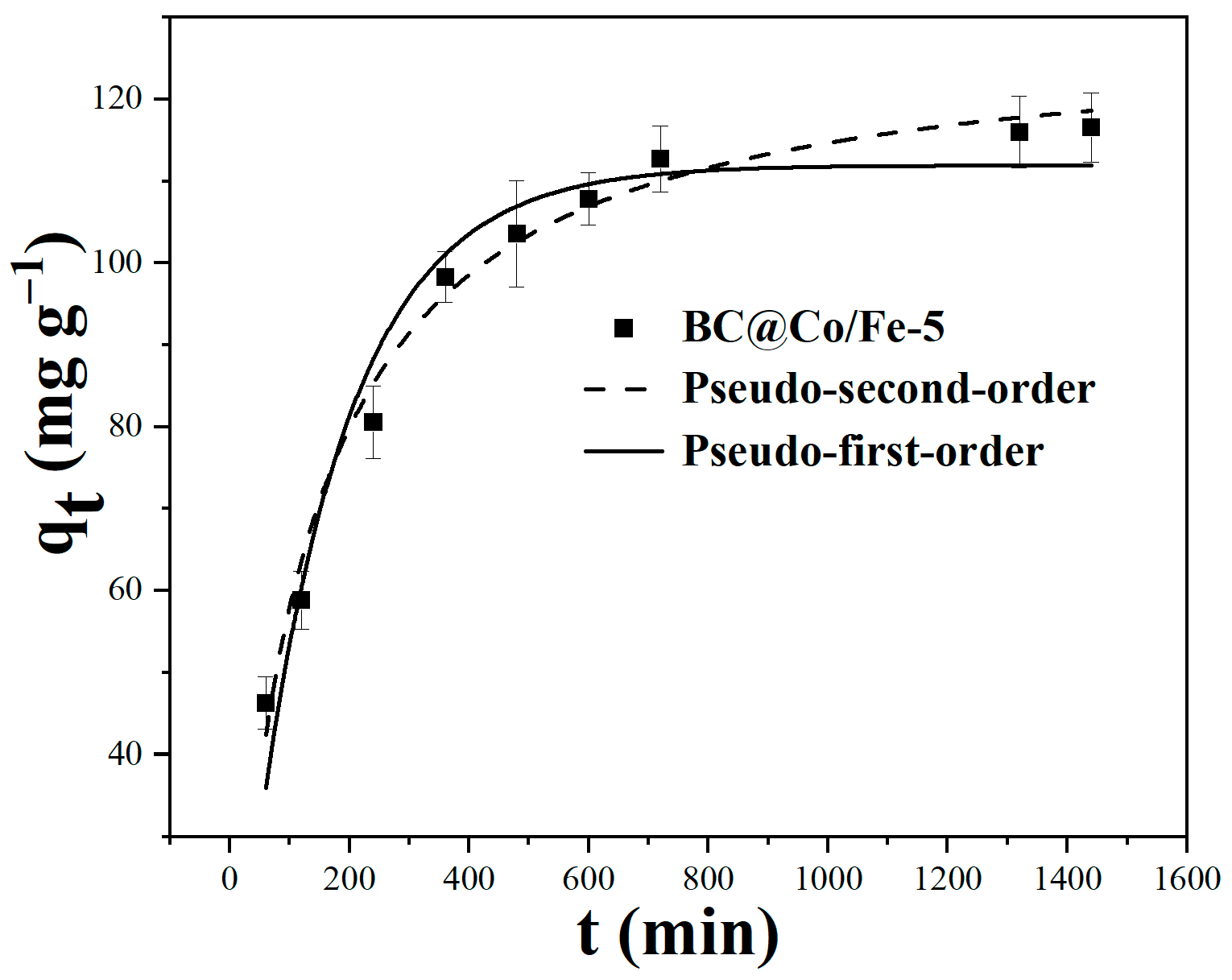
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics
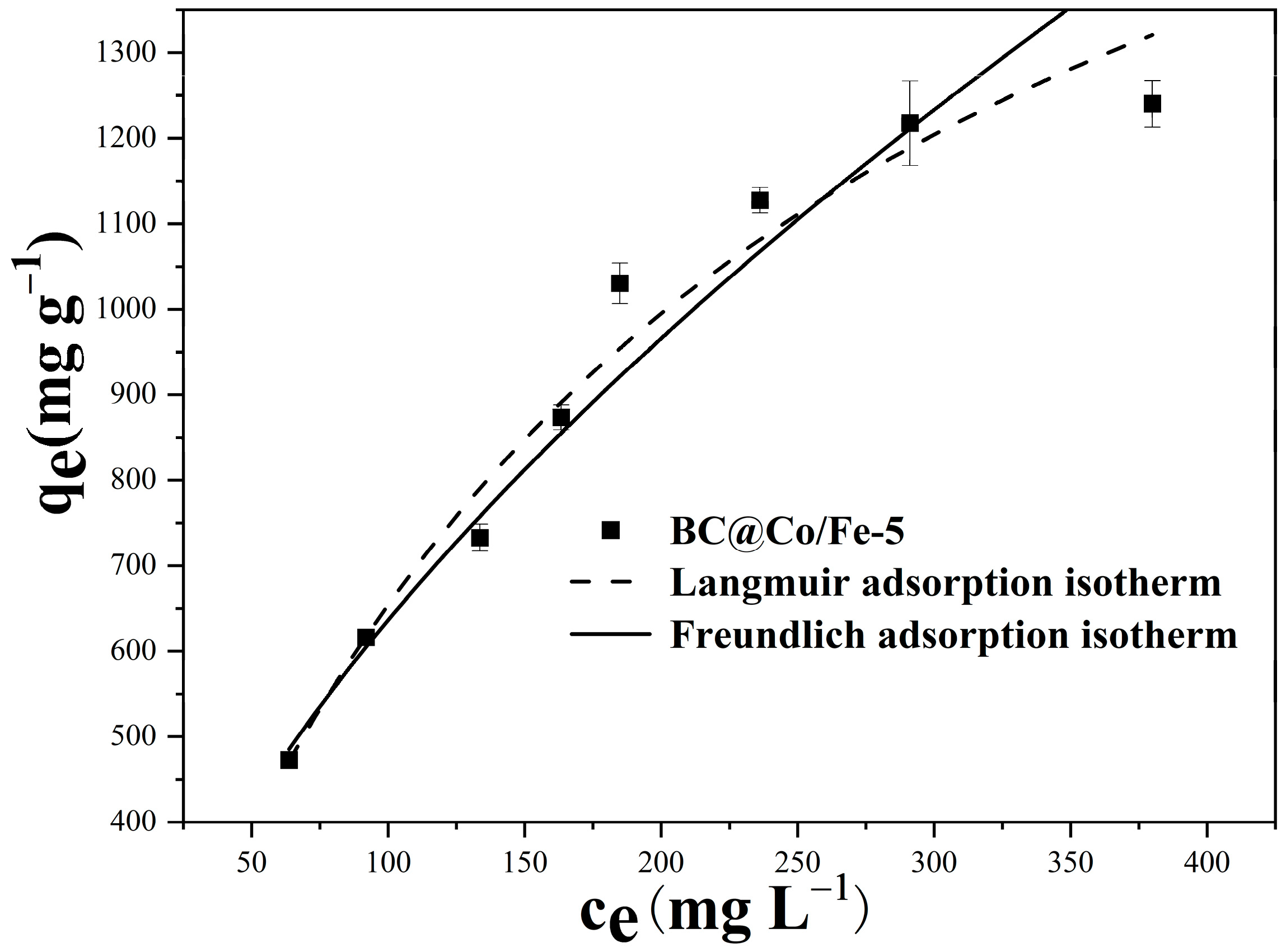
2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
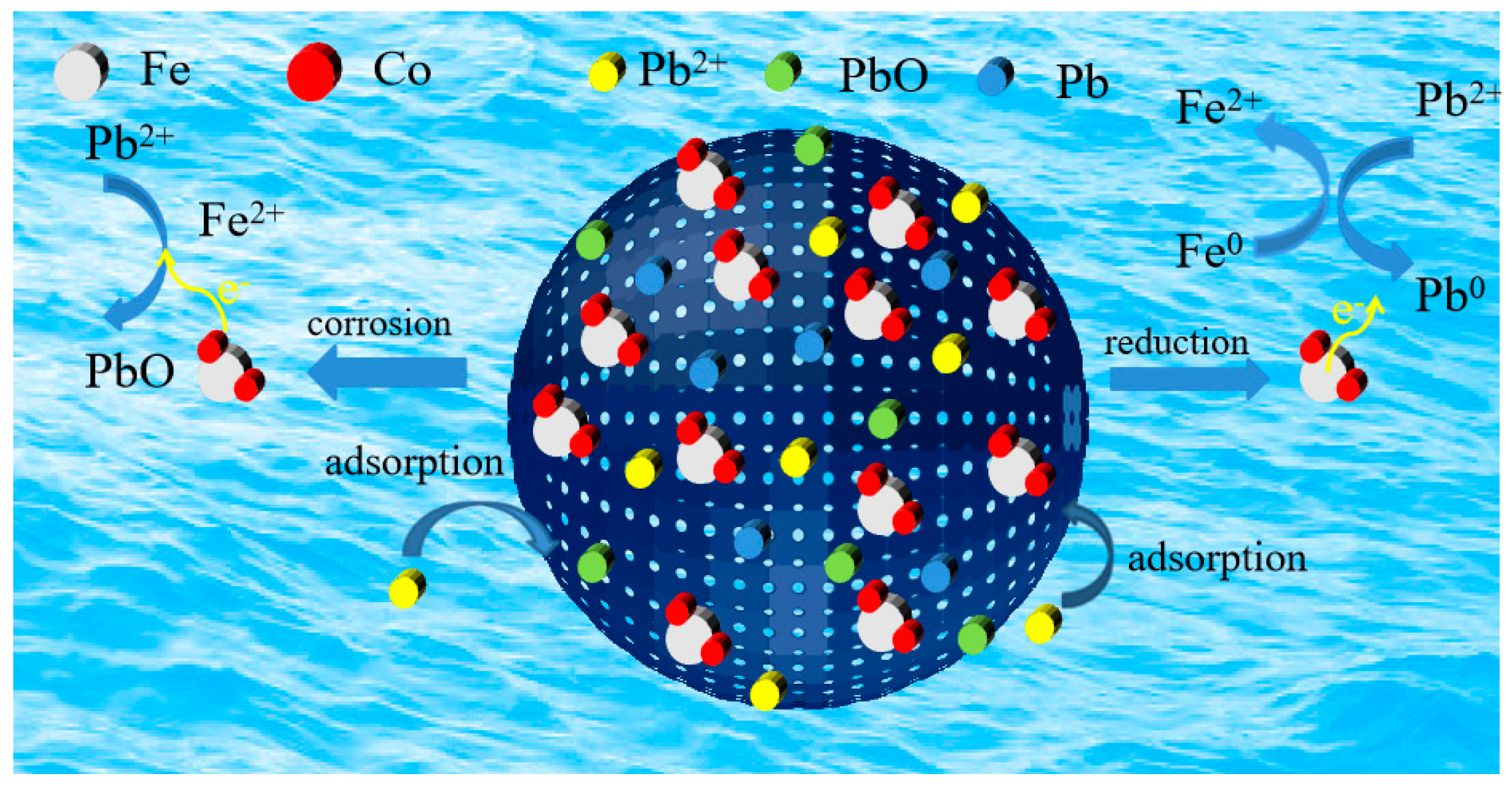
2.6. Pb2+ Adsorption Mechanisms
2.7. Recyclability of BC@Co/Fe-5
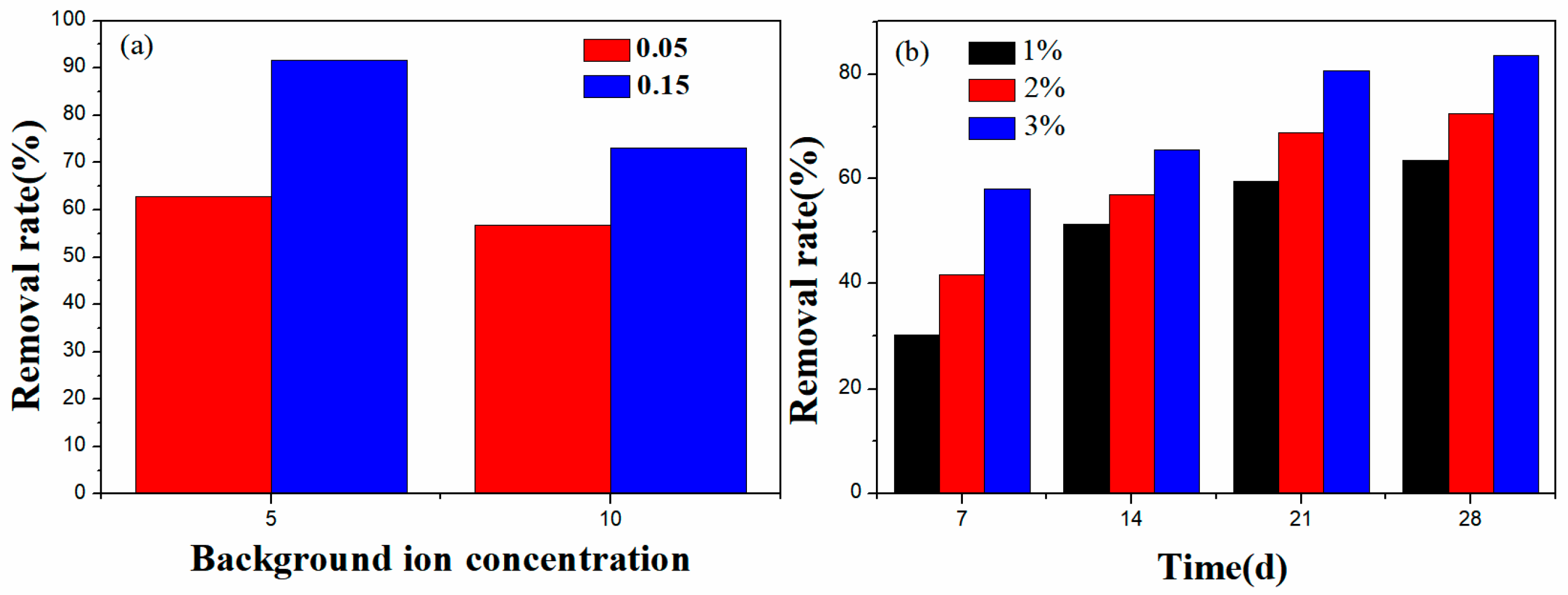
2.8. Pb2+ Removal from Contaminated Wastewater and Soil
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of BC@Co/Fe-X
3.3. Characterisation
3.4. Batch Sorption Experiments
3.5. Pb2+ Adsorption by BC@Co/Fe-5 in Simulated Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC@Co/Fe-X | Co/Fe biochar composite |
| CBC | corn cob biochar |
| ce | concentration at adsorption equilibrium (mg L−1) |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| HRTEM | high-resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| k1 | first-order rate constant (min−1) |
| k2 | second-order rate constant (g mg−1 min−1) |
| KL | Langmuir adsorption constant (L g−1) |
| KF | Freundlich adsorption constant (mg g−1) |
| nZVI | nano-zero-valent iron |
| qe | adsorption capacity at equilibrium (mg g−1) |
| qm | adsorption capacity at saturation (mg g−1) |
| qt | adsorption capacity at time t (mg g−1) |
| SEx | standard error |
| RSS | residual sum of squares |
| SA | sodium alginate |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| t | time (min) |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Zhang, X.; Lin, J.H.; Li, T.T.; Wang, Z.K.; Shiu, B.C.; Lou, C.W. A study on modified fabric-contained melamine/bentonite polyurethane foam: Pb2+ adsorption and mechanical properties. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neskoromnaya, E.A.; Khamizov, R.K.; Melezhyk, A.V.; Memetova, A.E.; Mkrtchan, E.S.; Babkin, A.V. Adsorption of lead ions (Pb2+) from wastewater using effective nanocomposite GO/CMC/FeNPs: Kinetic, isotherm, and desorption studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 655, 130224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Liang, Y. Adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ in wastewater by modified chitosan hydrogel. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lv, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Cost-effective microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of analcime-activated carbon composite from coal gangue used for Pb2+ adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 77788–77799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Z.; Zhou, W.-H.; Liu, F.; Yi, S.; Geng, X. Microstructure and morphological characterization of lead-contaminated clay with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) treatment. Eng. Geol. 2019, 256, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.-F.; Hao, D.; Shen, H.; You, N.; Long, W.-Y. Amino-carboxyl cellulose for adsorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagbi, Y.; Sarswat, A.; Tiwari, S.; Mohan, D.; Pandey, A.; Solanki, P.R. Synthesis of l -cysteine stabilized zero-valent iron (nZVI) nanoparticles for lead remediation from water. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chang, G.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y. Nanoscale zero-valent iron modified with carboxymethyl cellulose in an impinging stream-rotating packed bed for the removal of lead(II). Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Deng, Q. Shell biomass material supported nano-zero valent iron to remove Pb2+ and Cd2+ in water. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 201192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Mpouras, T.; Dermatas, D.; Verdone, N.; Polydera, A.; Di Palma, L. Nanomaterials application for heavy metals recovery from polluted water: The combination of nano zero-valent iron and carbon nanotubes. Competitive adsorption non-linear modeling. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtbari, Y.; Sher, F.; Afshin, S.; Hamzezadeh, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Azhar, O.; Rastegar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Poureshgh, Y. Green synthesis of zero-valent iron nanoparticles and loading effect on activated carbon for furfural adsorption. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouli, F.; Ezzat, A.O.; Sabantina, L.; Benyoucef, A.; Zehhaf, A. Optimization Conditions of Malachite Green Adsorption onto Almond Shell Carbon Waste Using Process Design. Molecules 2023, 29, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, J. Biochar loaded with cobalt ferrate activated persulfate to degrade naphthalene. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5283–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, R.; Rong, R.; Dai, M.; Ali, I.; Naz, I.; Peng, C. Fe-C-based materials: Synthesis modulation for the remediation of environmental pollutants-a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 64345–64369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ren, X.; Alharbi, N.S.; Chen, C. Efficient adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by Santa Barbara Amorphous-15 (SBA-15) supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Lai, B. Efficient reduction of hexavalent chromium with microscale Fe/Cu bimetals: Efficiency and the role of Cu. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Lu, J. Activation of persulfate by highly dispersed FeCo bimetallic alloy for in-situ remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Wu, Z.L.; Duan, W.J.; Zhang, W.Z. Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of triclosan by Ginkgo biloba L. stabilized Fe/Co bimetallic nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Geng, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G. Enhanced removal of trace Cr(VI) from neutral and alkaline aqueous solution by FeCo bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kang, L.; Shi, X.; Wei, R.; Mai, X.; Pan, D.; Naik, N.; Guo, Z. Highly efficient removal of trace lead (II) from wastewater by 1,4-dicarboxybenzene modified Fe/Co metal organic nanosheets. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 98, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Banik, C.; Rathke, S.J.; Laird, D.A. Arsenic sorption on zero-valent iron-biochar complexes. Water Res. 2018, 137, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Chen, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Chromium(VI) removal from synthetic solution using novel zero-valent iron biochar composites derived from iron-rich sludge via one-pot synthesis. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Rao, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, M.; Su, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, N. A green in-situ synthesis of biochar-supported Fe0/Cu0 bimetallic catalyst for the efficient oxidation antibacterial in water: Performance and mechanism analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Long, L.; Gong, T.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Xue, Y. Enhanced alginate-based microsphere with the pore-forming agent for efficient removal of Cu2+. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, Y.; Azhar, M.R.; Zhong, Y.; O’Hayre, R.; Tadé, M.O.; Shao, Z. Organic ligand-facilitatedin situexsolution of CoFe alloys over Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δperovskite toward enhanced oxygen electrocatalysis for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 12856–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, L.; Steinhauer, S.; Lazarov, V.K. In situ TEM oxidation study of Fe thin-film transformation to single-crystal magnetite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 12897–12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-F.; Ling, L.-L.; Chen, W.-J.; Liu, W.-J.; Li, D.-C.; Jiang, H. High efficient removal of bisphenol A in a peroxymonosulfate/iron functionalized biochar system: Mechanistic elucidation and quantification of the contributors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J. nZVI-biochar derived from Fe3O4-loaded rabbit manure for activation of peroxymonosulfate to degrade sulfamethoxazole. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansuri, H.; Supriadi, W.; Ediati, R.; Utomo, W.P.; Hidayati, R.E.; Iqbal, R.M.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Subaer. Immobilization and leaching behavior of Cd2+ and Pb2+ heavy metal ions in Indonesian fly ash-based geopolymers. Environ. Adv. 2024, 15, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.A.H.; Harun, N.Y.; Sufian, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Zakaria, Z.Y.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Mohammed, H.G. Pristine and Magnetic Kenaf Fiber Biochar for Cd2+ Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Gen, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Qi, W.; Wang, F. Synthesis of zero-valent iron/biochar by carbothermal reduction from wood waste and iron mud for removing rhodamine B. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 48556–48568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Luo, L.; Fu, L.; Yang, H. Ion responsiveness of polyacrylamide/sodium alginate (PAM/SA) shape memory hydrogel. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Selective adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ on amino-modified attapulgite: Kinetic, thermal dynamic and DFT studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, E.; Wang, K.; Muhammad, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, D.; Wei, Y.; Fujita, T. Preparation and conversion mechanism of different geopolymer-based zeolite microspheres and their adsorption properties for Pb2+. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 119971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Bai, T.; Yi, X.; Zhao, K.; Shi, W.; Dai, F.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, C. Polypropylene fiber grafted calcium alginate with mesoporous silica for adsorption of Bisphenol A and Pb2+. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, M.; Lin, Q.; Lei, M.; Wang, D.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Jia, Z. One-pot synthesis of spherical nanoscale zero-valent iron/biochar composites for efficient removal of Pb(ii). RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36826–36835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinterinwa, A.; Oladele, E.; Adebayo, A.; Adamu, M. Characterization of aqueous Pb2+ adsorption onto cross-linked-carboxymethyl legume starch phosphate using FTIR and SEM-EDX. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Yan, L.; Du, B.; Pei, Z. Removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions by magnetic alginate microsphere based on Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; Lyu, Q.; Hu, S. Efficient adsorption of BPA and Pb2+ by sulfhydryl-rich β-cyclodextrin polymers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 122913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, R.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Che, D. Investigation on Pb2+ adsorption characteristics by AAEMs-rich biochar in aqueous solution: Performance and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2023, 236 Pt 1, 116731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.A.; Abo-Aly, M.M.; Salaheldin, T.A. Modified mesoporous zeolite-A/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for dual removal of methylene blue and Pb2+ ions from wastewater. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 126, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Bakry, B.M.; Adlii, A.; Yakout, S.M.; El-Zaidy, M.E. Facile conversion of kaolinite into clay nanotubes (KNTs) of enhanced adsorption properties for toxic heavy metals (Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cr6+) from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L. Adsorption/desorption performance of Pb2+ and Cd2+ with super adsorption capacity of PASP/CMS hydrogel. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Yao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Su, L.; Ren, S.; Li, S. Removal of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Ni2+ from water by adsorption onto magnetic composites prepared using humic acid from waste biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 411, 137237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaraweera, H.; Nawalage, S.; Nayanathara, R.M.O.; Peiris, C.; Karunaratne, T.N.; Gunatilake, S.R.; Thirumalai, R.V.K.G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Mlsna, T. In Situ Synthesis of Zero-Valent Iron-Decorated Lignite Carbon for Aqueous Heavy Metal Remediation. Processes 2022, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Chen, B.; Lin, Y.; Guan, Y. Aromatic and hydrophobic surfaces of wood-derived biochar enhance perchlorate adsorption via hydrogen bonding to oxygen-containing organic groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q. Characteristics and mechanism of Cu(II) adsorption on prepared calcium alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose@MnFe2O4. Polym. Bull. 2021, 76, 1201–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Ning, F.; Yi, J. Facile synthesis of lead-tin nanoparticles for electrocatalyzing carbon dioxide reduction to formate. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 4136–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Gou, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Xiao, L.; Hao, G.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, W. CuO/PbO Nanocomposite: Preparation and Catalysis for Ammonium Perchlorate Thermal Decomposition. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32667–32676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yu, L.; McElhenny, B.; Xing, X.; Luo, D.; Zhang, F.; Bao, J.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Rational design of core-shell-structured CoP @FeOOH for efficient seawater electrolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 294, 120256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Z.H.; Du, J.J.; Jiang, D.; Kong, L.J.; Huo, W.Y.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, Q.H.; Xu, X.R. Insights into the simultaneous removal of Cr6+ and Pb2+ by a novel sewage sludge-derived biochar immobilized nanoscale zero valent iron: Coexistence effect and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Liu, R.; Wang, C.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Sun, W. A novel scheme for the utilization of Cu slag flotation tailings in preparing internal electrolysis materials to degrade printing and dyeing wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.C.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Shi, Z.; Hou, P.X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.M.; Shao, M. Dual-Phasic Carbon with Co Single Atoms and Nanoparticles as a Bifunctional Oxygen Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Zn–Air Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, W.; Bao, N. Top-Level Design Strategy to Construct an Advanced High-Entropy Co–Cu–Fe–Mo (Oxy)Hydroxide Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Li, J.; Kang, L.; Gao, L.; Shi, X. Preparation of novel terephthalic acid modified Fe/Ni metal organic nanosheet with high adsorption performance for trace Pb2+. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 579, 152268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ye, Z.; Xie, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Yao, M. Rapid magnetic removal of aqueous heavy metals and their relevant mechanisms using nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) particles. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4050–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Walker, H.; Zhu, Q. Reduction of nitrate by NaY zeolite supported Fe, Cu/Fe and Mn/Fe nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Tang, A. Effect of the occurrence state of magnesium in talc on the adsorption of Pb(II). J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 161288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Luo, J.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Cai, W.; Zhai, S.; Li, Z. Efficiently selective adsorption of Pb(II) with functionalized alginate-based adsorbent in batch/column systems: Mechanism and application simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Rawat, B.S.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, N.; Upadhyay, S.; Chetana, S.; Gururani, P.; Kimothi, S. Sustainable synthetic approach and applications of ZnO/r-GO in the adsorption of toxic Pb2+ and Cr6+ ions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Pang, L.; Li, M.; Song, X.; Wen, J.; Zhao, H. Preparation of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Poly(acrylamide) Nanocomposite and Its Adsorption of Pb(II) and Methylene Blue. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10727–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China.
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Groundwater Quality and Source Apportionment Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques for the Hutuo River Alluvial-Pluvial Fan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, H.; Tardif, S.; Kandeler, E.; Holm, P.E.; Brandt, K.K. Assessment of biochar and zero-valent iron for in-situ remediation of chromated copper arsenate contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aborisade, M.A.; Feng, A.; Oba, B.T.; Kumar, A.; Battamo, A.Y.; Huang, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhao, L. Pyrolytic synthesis and performance efficacy comparison of biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron on soil polluted with toxic metals. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 69, 2249–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
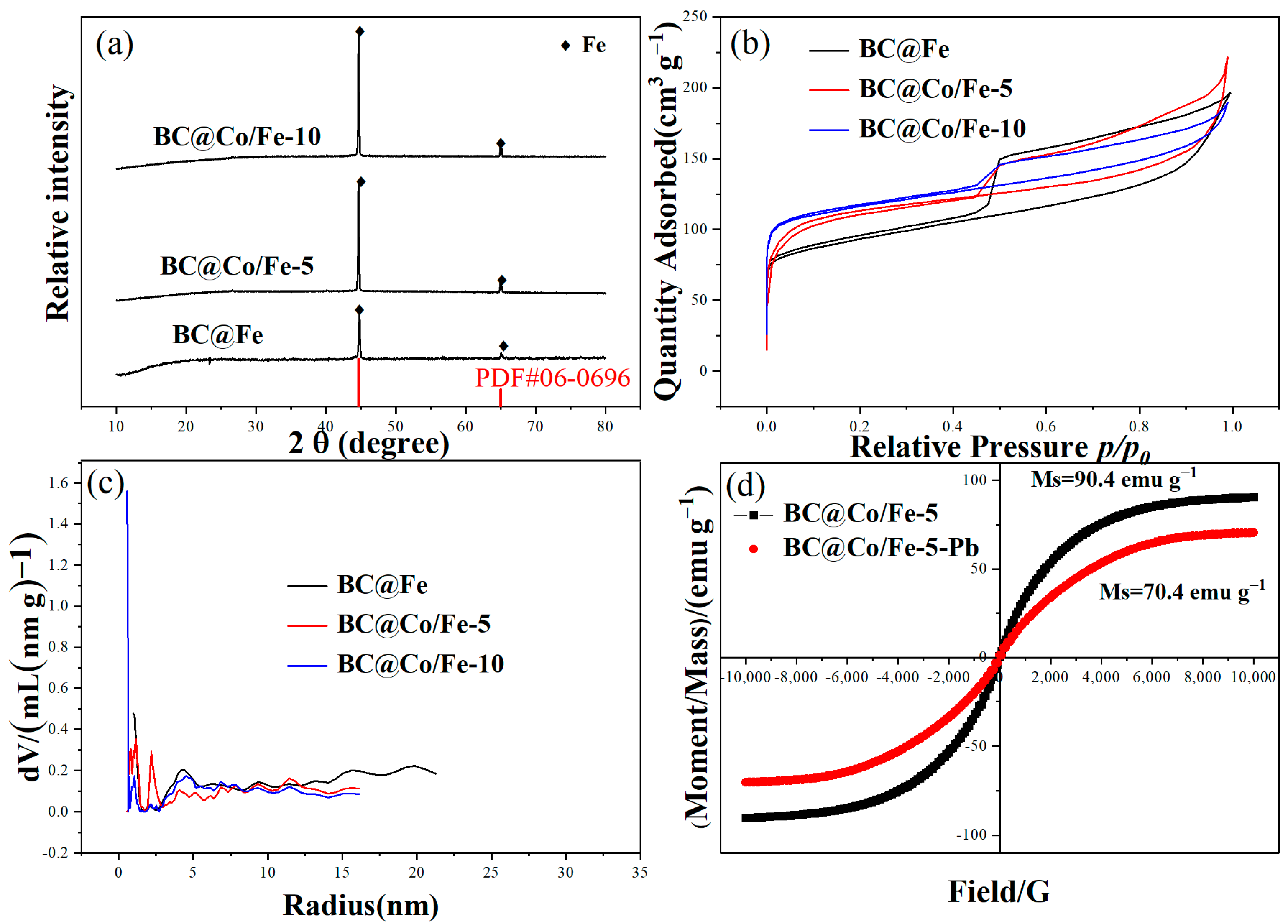



| Sample | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Total Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Size Parameters (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC@Fe | 464 | 0.303 | 3.53 |
| BC@Co/Fe-5 | 429 | 0.294 | 3.21 |
| BC@Co/Fe-10 | 547 | 0.343 | 2.65 |
| Sample | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC@Co/Fe-5 | qe,cal (mg g−1) | SEx | k1 (10−3 min−1) | R2 | RSS | Reduced chi-squared | qe,cal (mg g−1) | SEx | k2 (10−5 g mg−1 min−1) | R2 | RSS | Reduced chi-squared |
| 111.9 | 3.09 | 6.48 | 0.95 | 17.2 | 2.5 | 128.7 | 2.92 | 6.36 | 0.98 | 6.0 | 0.87 | |
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC@Co/Fe-5 | qm,cal (mg g−1) | SEx | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | RSS | Reduced chi-squared | n | KF (mg1−n Ln g−1) | SEx | R2 | RSS | Reduced chi-squared |
| 2076.6 | 155.8 | 0.0046 | 0.98 | 43.3 | 7.22 | 1.66 | 39.76 | 7.63 | 0.967 | 91.2 | 15.20 | |
| Adsorbent | pH | Concentration Range (mg L−1) | qm (mg g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified chitosan hydrogel | 5 | 100–1100 | 420.98 | [3] |
| Amino-carboxyl cellulose | 5 | 100–1000 | 117.6 | [6] |
| Analcime-activated carbon composite | 5.5 | 100 | 125.57 | [4] |
| Sulfhydryl-rich β-cyclodextrin polymers | - | - | 604.64 | [39] |
| Alkali and alkaline earth metal-rich biochar | 5.5 | 10–4000 | 226.64 | [40] |
| Mesoporous zeolite-A/reduced graphene oxide | 6.5 | - | 416.7 | [41] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose-nZVI | 6 | 100–1000 | 1376 | [8] |
| Geopolymer-based zeolite microspheres | 5 | 100–600 | 529.7 | [34] |
| Carboxymethylcellulose/graphene oxide + Fe 18% | 6 | 55–1050 | 1850 | [2] |
| Kaolinite nanotubes | 6 | 25–350 | 1428 | [42] |
| Polyaspartic acid/carboxymethyl salix psammophila hydrogel | 5.5 | 2000–10,000 | 1954 | [43] |
| BC@Co/Fe-5 | 5 | 300–1000 | 1240 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Q.; Cai, M.; Jia, Z.; Yu, C.; Shang, A.; Fei, Y.; et al. Cobalt/Iron Bimetallic Biochar Composites for Lead(II) Adsorption: Mechanism and Remediation Performance. Molecules 2024, 29, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071595
Zhao J, Qin Y, Liu Y, Shi Y, Lin Q, Cai M, Jia Z, Yu C, Shang A, Fei Y, et al. Cobalt/Iron Bimetallic Biochar Composites for Lead(II) Adsorption: Mechanism and Remediation Performance. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071595
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingyu, Yuhong Qin, Yue Liu, Yunlong Shi, Qiang Lin, Miao Cai, Zhenya Jia, Changjiang Yu, Anqi Shang, Yuxiao Fei, and et al. 2024. "Cobalt/Iron Bimetallic Biochar Composites for Lead(II) Adsorption: Mechanism and Remediation Performance" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071595
APA StyleZhao, J., Qin, Y., Liu, Y., Shi, Y., Lin, Q., Cai, M., Jia, Z., Yu, C., Shang, A., Fei, Y., & Zhang, J. (2024). Cobalt/Iron Bimetallic Biochar Composites for Lead(II) Adsorption: Mechanism and Remediation Performance. Molecules, 29(7), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071595