Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill—Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment—A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
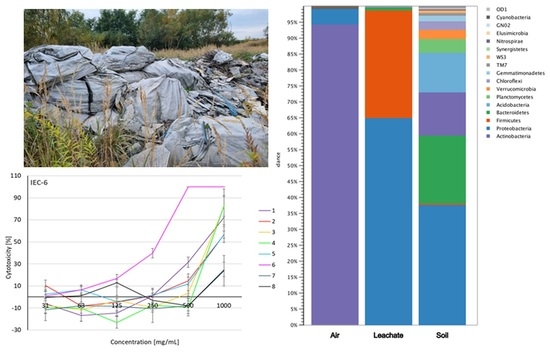
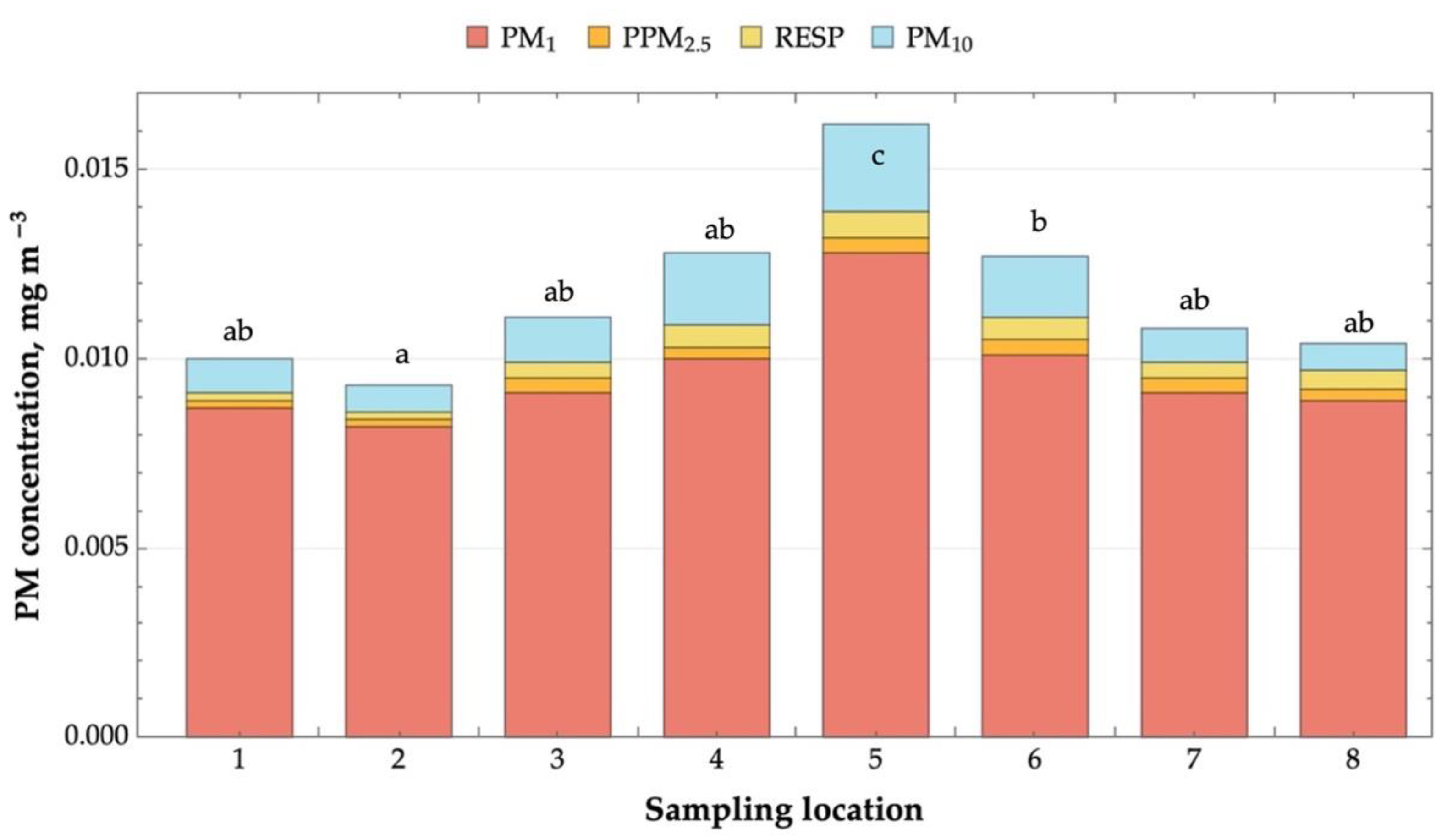
2.1. Microclimate and Airborne Dust Concentration
2.2. Metal Concentration in Soil Samples
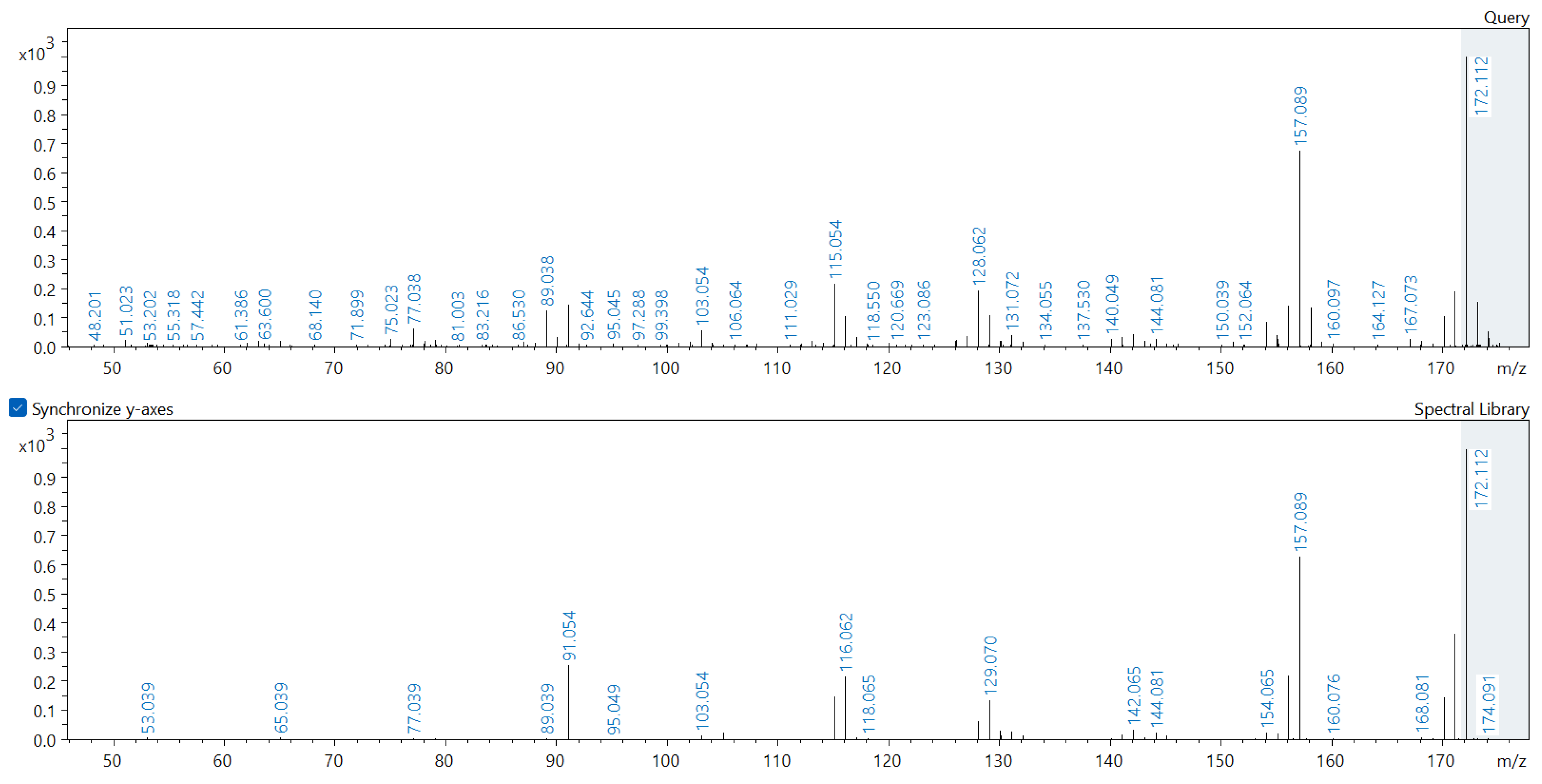
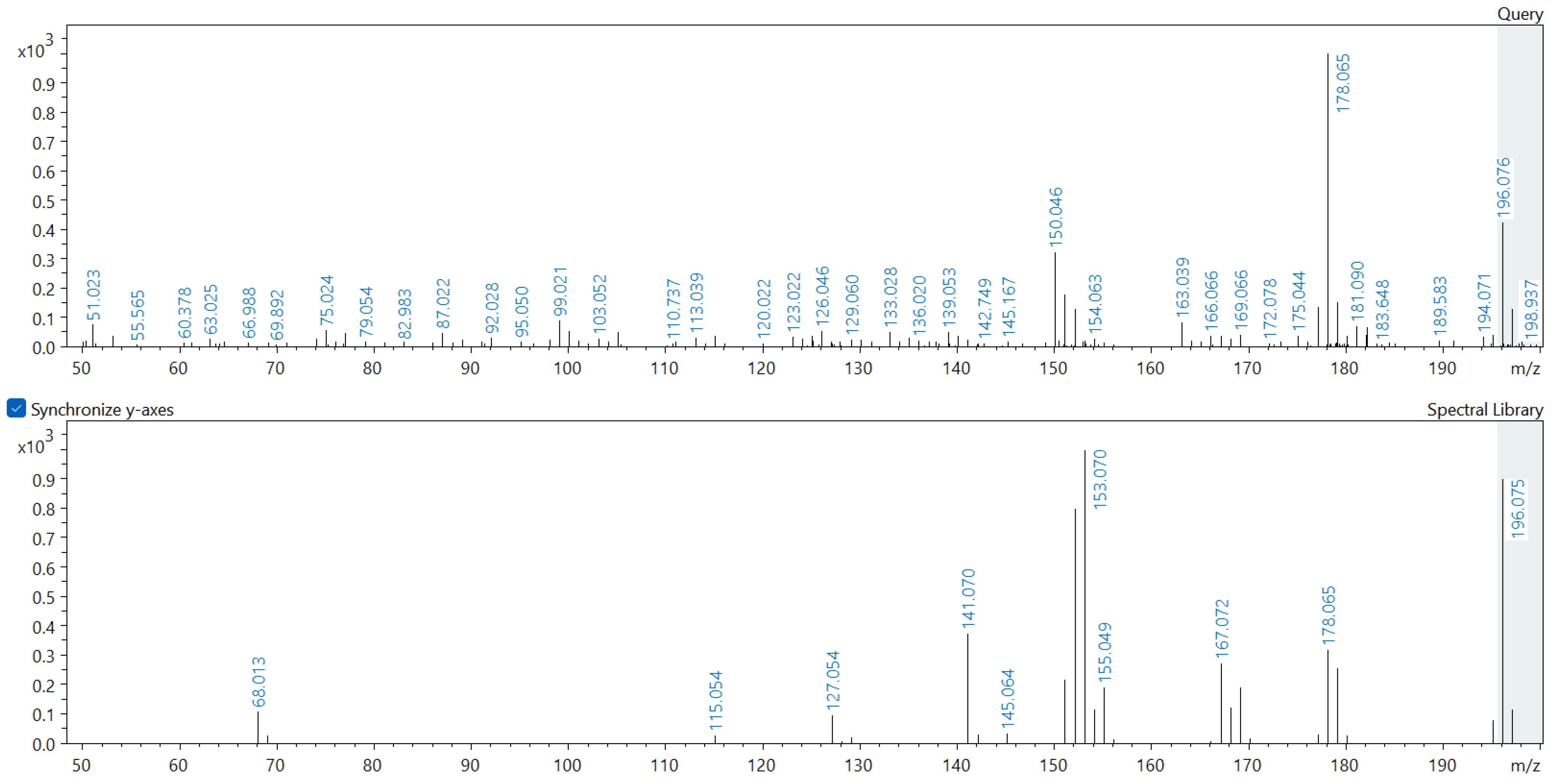
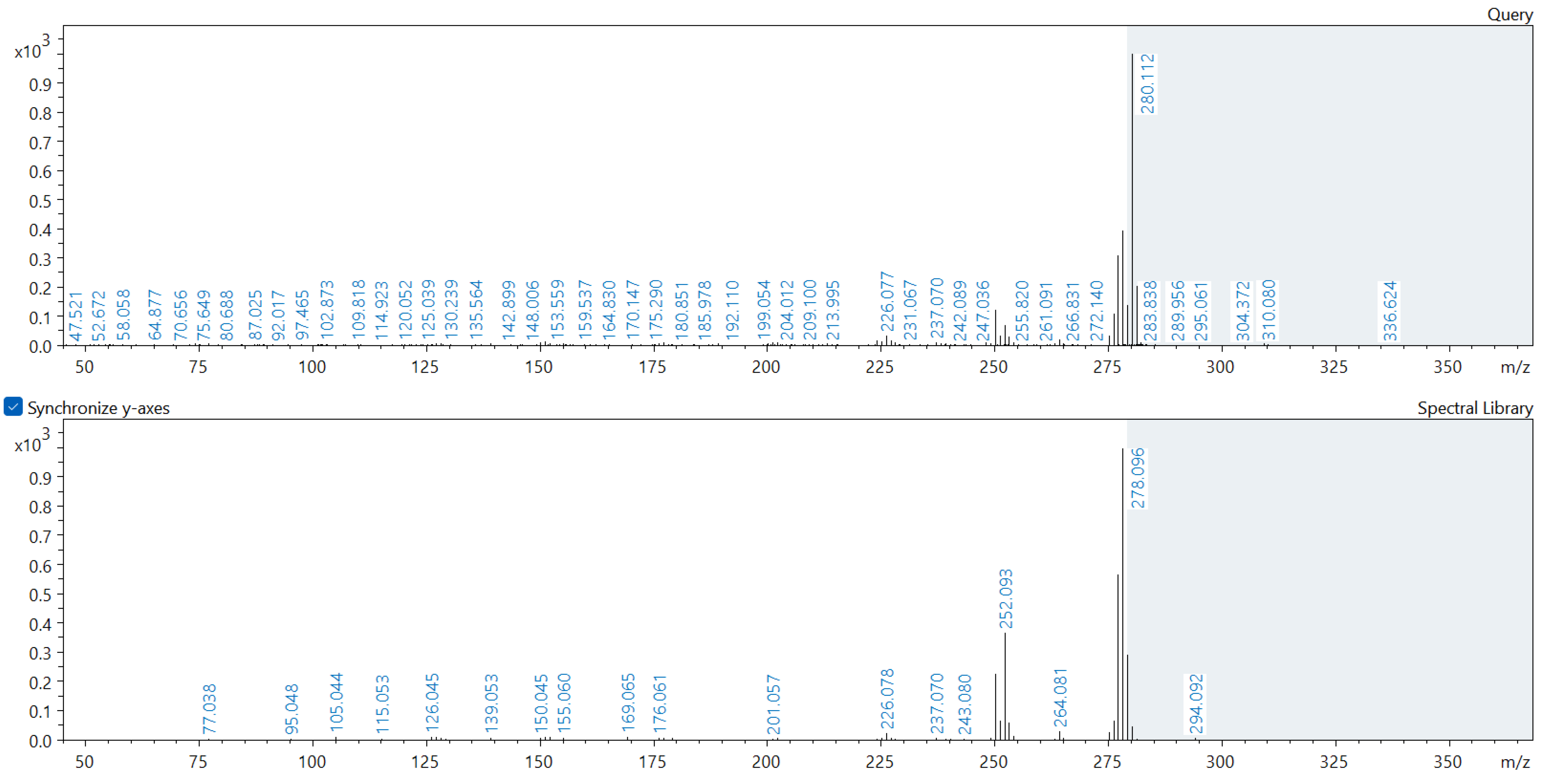
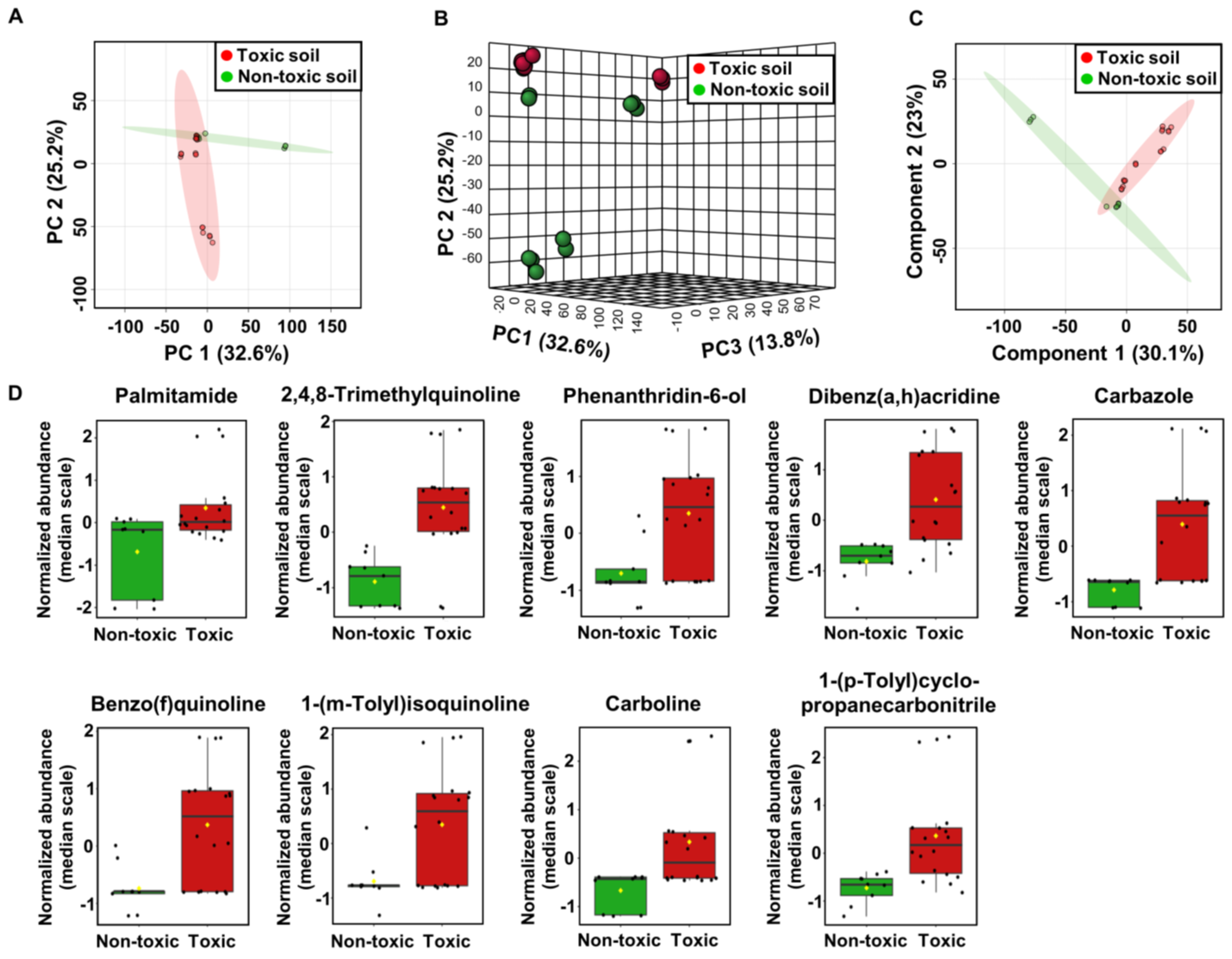
2.3. Metabolome Analysis of Soil Samples
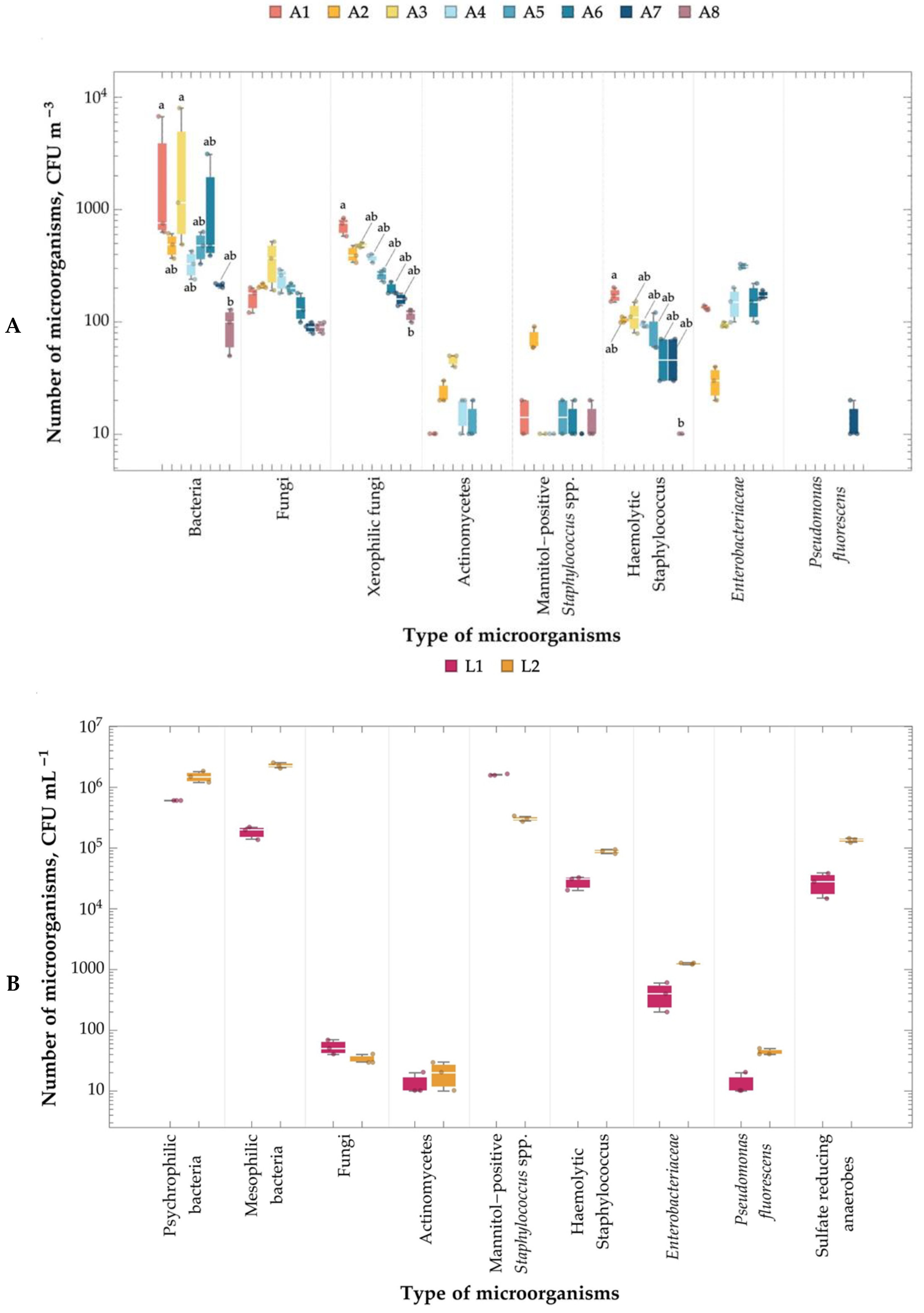
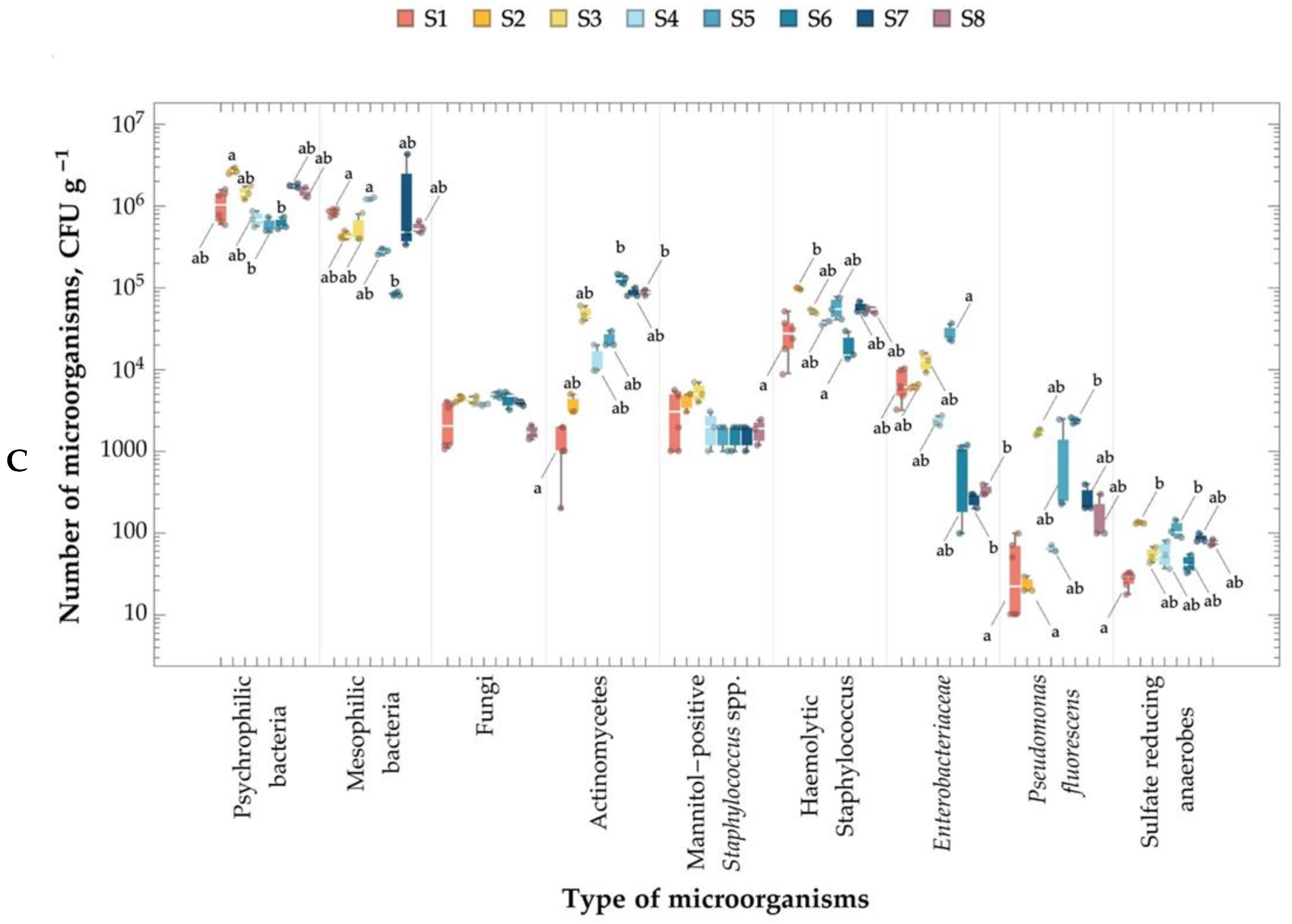
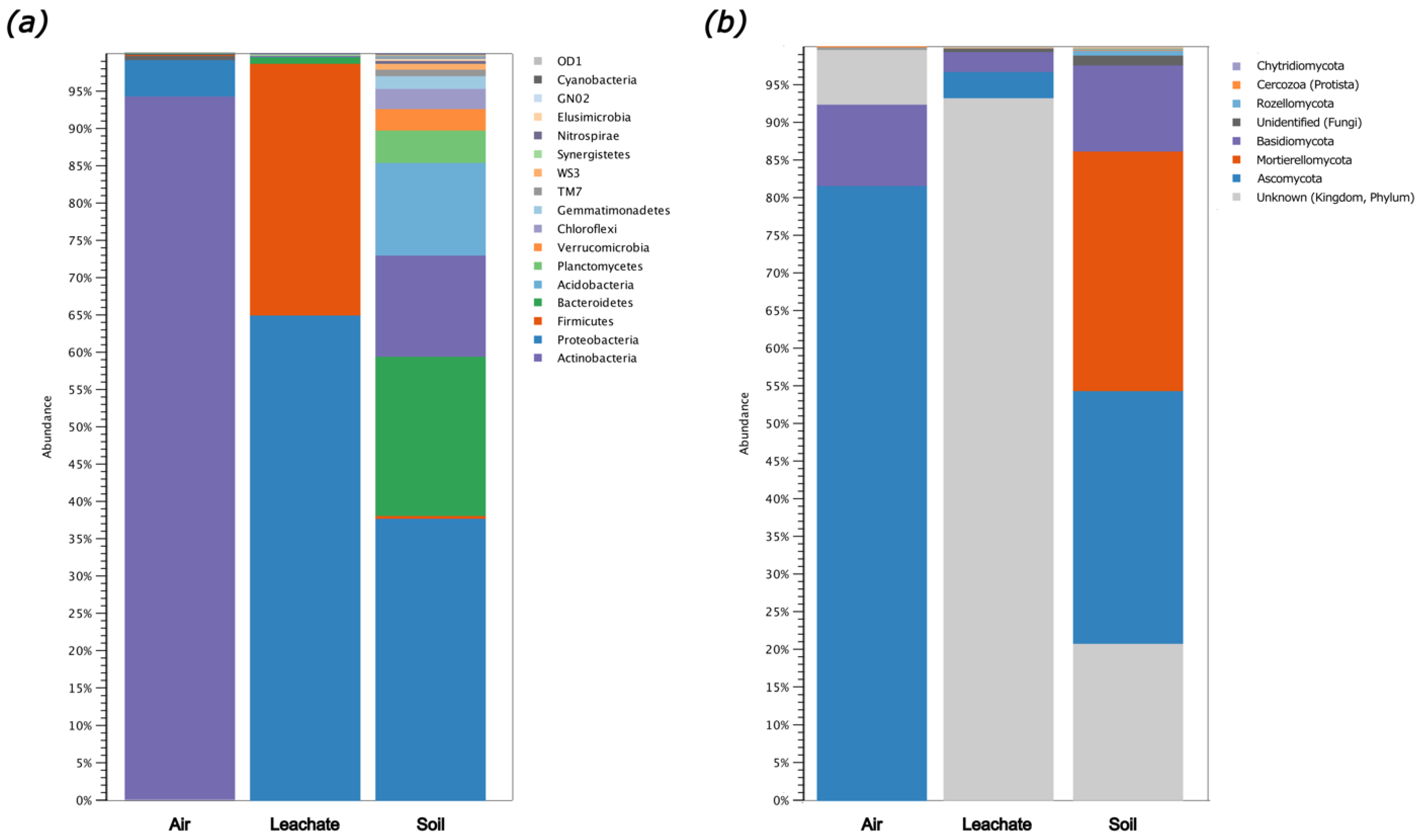
2.4. Number of Microorganisms in the Air, Leachate, and Soil
2.5. Biodiversity of Air, Leachate, and Soil
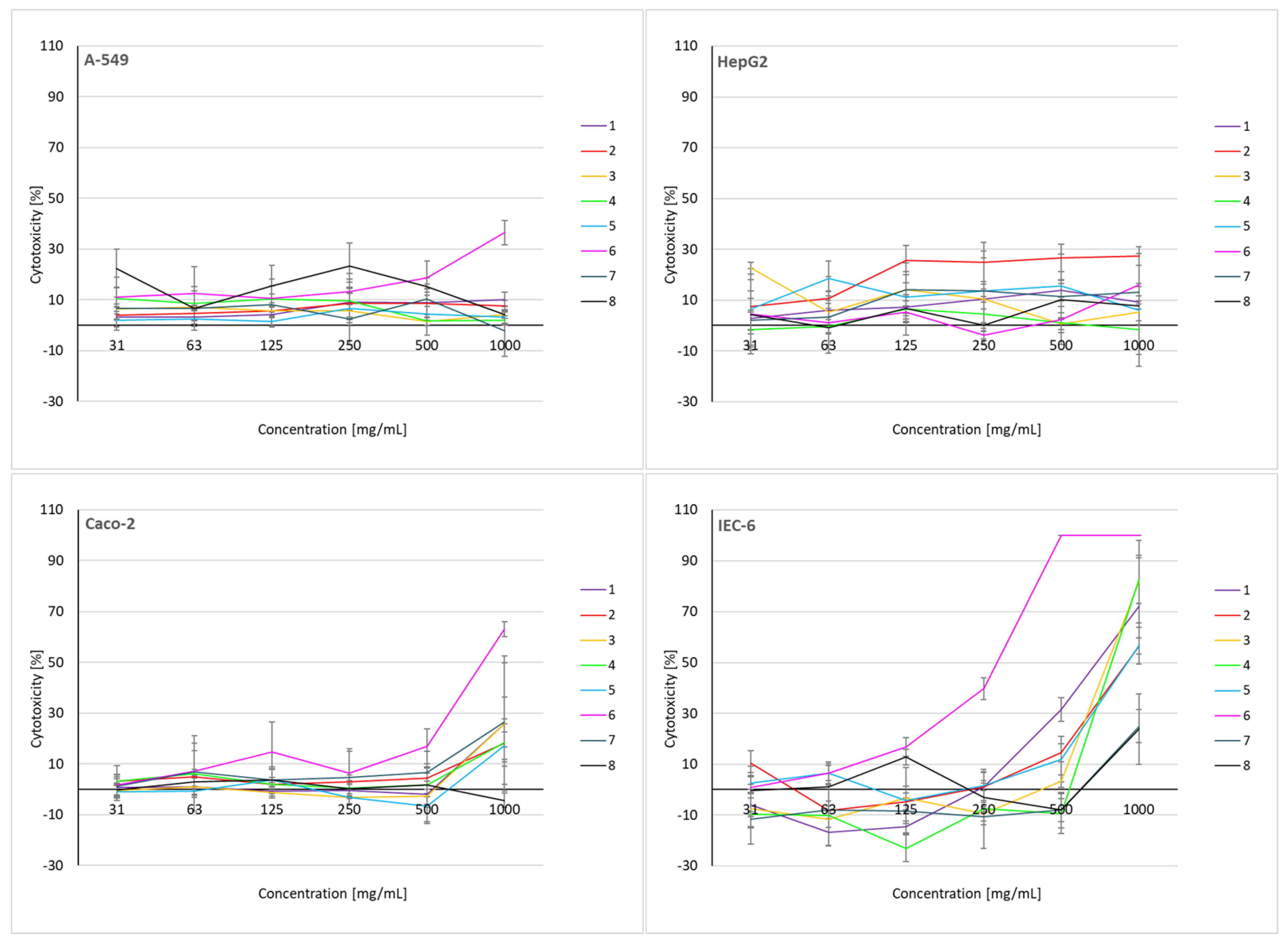
2.6. Cytotoxicity Assessment of Soil Extracts
2.7. Proposed Solutions and Recommendations including New Insights or Recommendations Based on Our Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Landfill Characterization
| No. | Name | Description | Samples (N) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | The northern part of the landfill at the foot of the escarpment | At the foot of the slope of the landfill there are abandoned big bags with unidentified content and visible traces of seepage water with greasy stains on the surface. There was an unpleasant “chemical” smell in the air. | A1 (28) S1 (4) L1 (3) L2 (3) |
| 2 |  | In front of the entrance gate to the landfill site | The area is overgrown with vegetation, a damaged fence is visible | A2 (28) S2 (4) |
| 3 |  | On the left, at the top of the landfill | Visibly broken, unsecured piles of asbestos | A3 (28) S3 (4) |
| 4 |  | On the right, at the top of the landfill | There is deposited construction waste in bags, visible piles of crushed Eternit | A4 (28) S4 (4) |
| 5 |  | Between heaps of municipal waste | On a heap overgrown with grass, various types of municipal waste are visible | A5 (28) S5 (4) |
| 6 |  | By the river | Plant succession occurs in the study area, greasy stains are visible on the water surface | A6 (28) S6 (4) |
| 7 |  | Clearing located near residential buildings | Visible vegetation, scattered municipal waste | A7 (28) S7 (4) |
| 8 |  | Control samples | 5 km from tested landfill site | A8 (27) S8 (4) |
3.2. Microclimate and Airborne Dust Concentration Measurements
3.3. Collection of Environmental Samples
3.4. Metal Concentration Analysis
3.5. Metabolome Analysis of Soil Samples
3.5.1. Preparation of Samples
3.5.2. UHPLC-Q-ToF-UHRMS Instrumentation
3.6. Determination of Number of Microorganisms
3.7. Determination of Biodiversity
3.8. Cytotoxicity Study of the Soil Samples
3.8.1. Cell Propagation and Culturing
3.8.2. Sample Preparation
3.8.3. PrestoBlue Assay and IC50 Calculation
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Comparison of Spectral Database (Lower Spectrum) and Experimental (Upper Spectrum) MS/MS Spectra of Detected Compounds

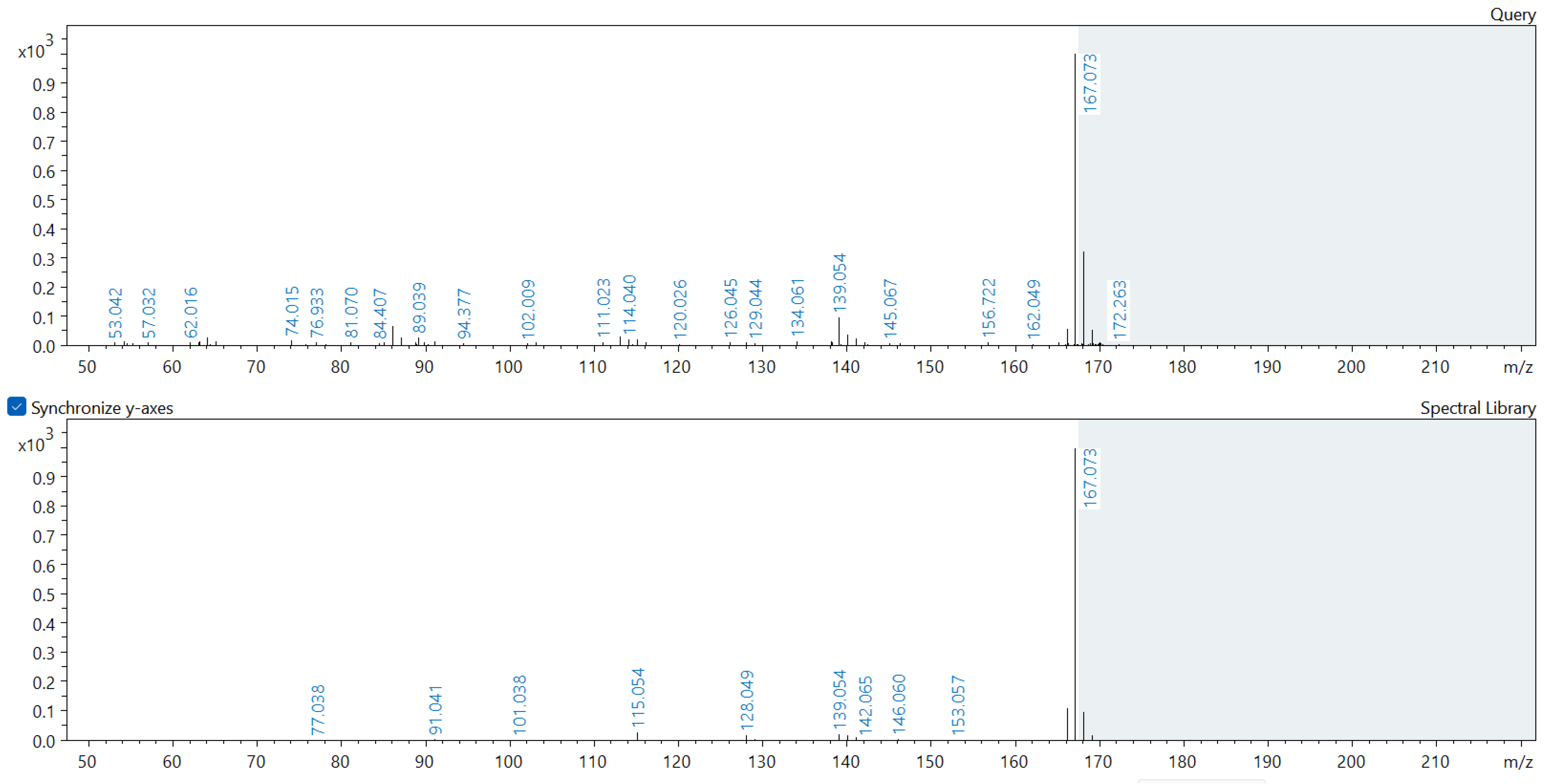
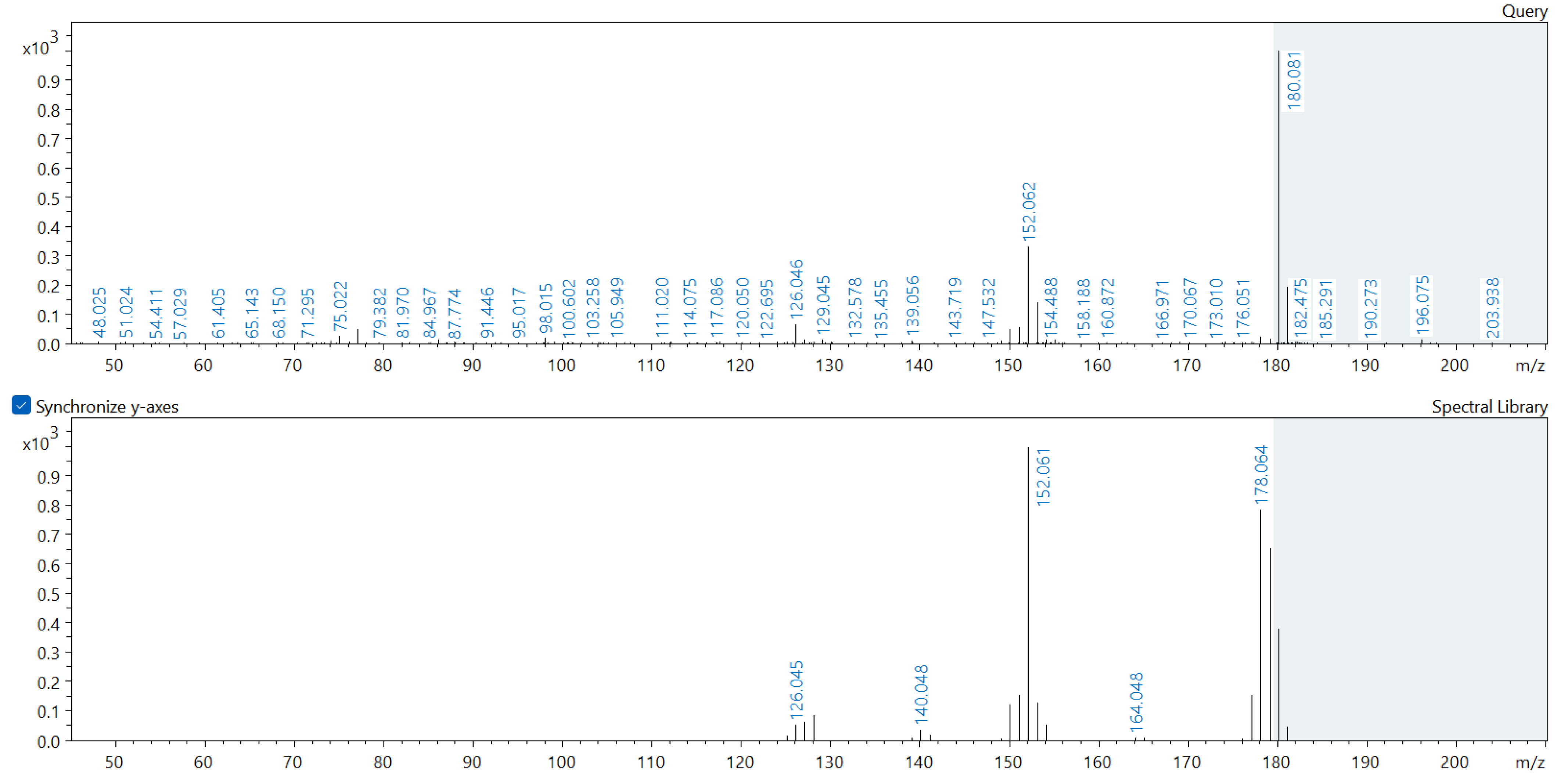
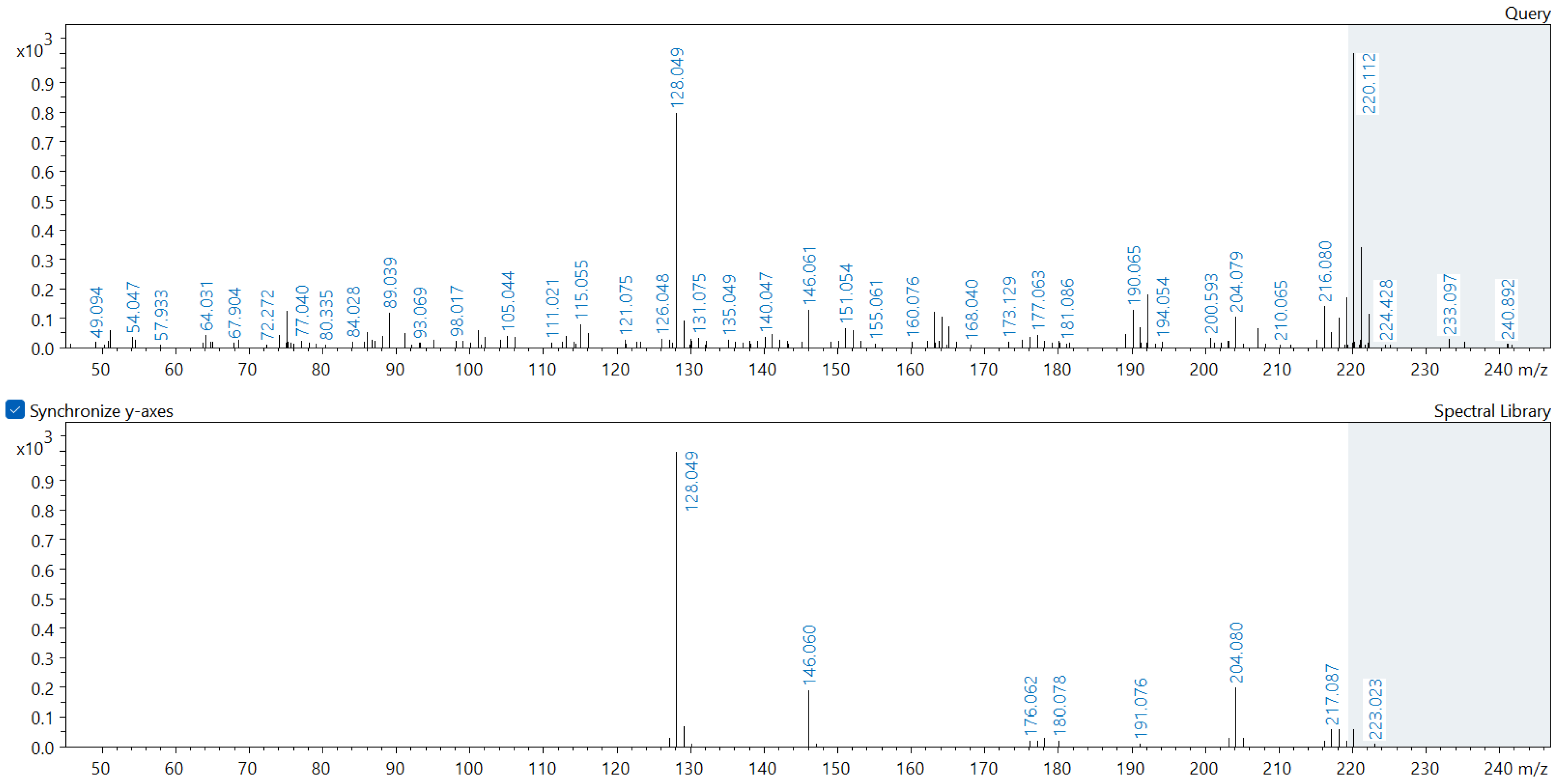

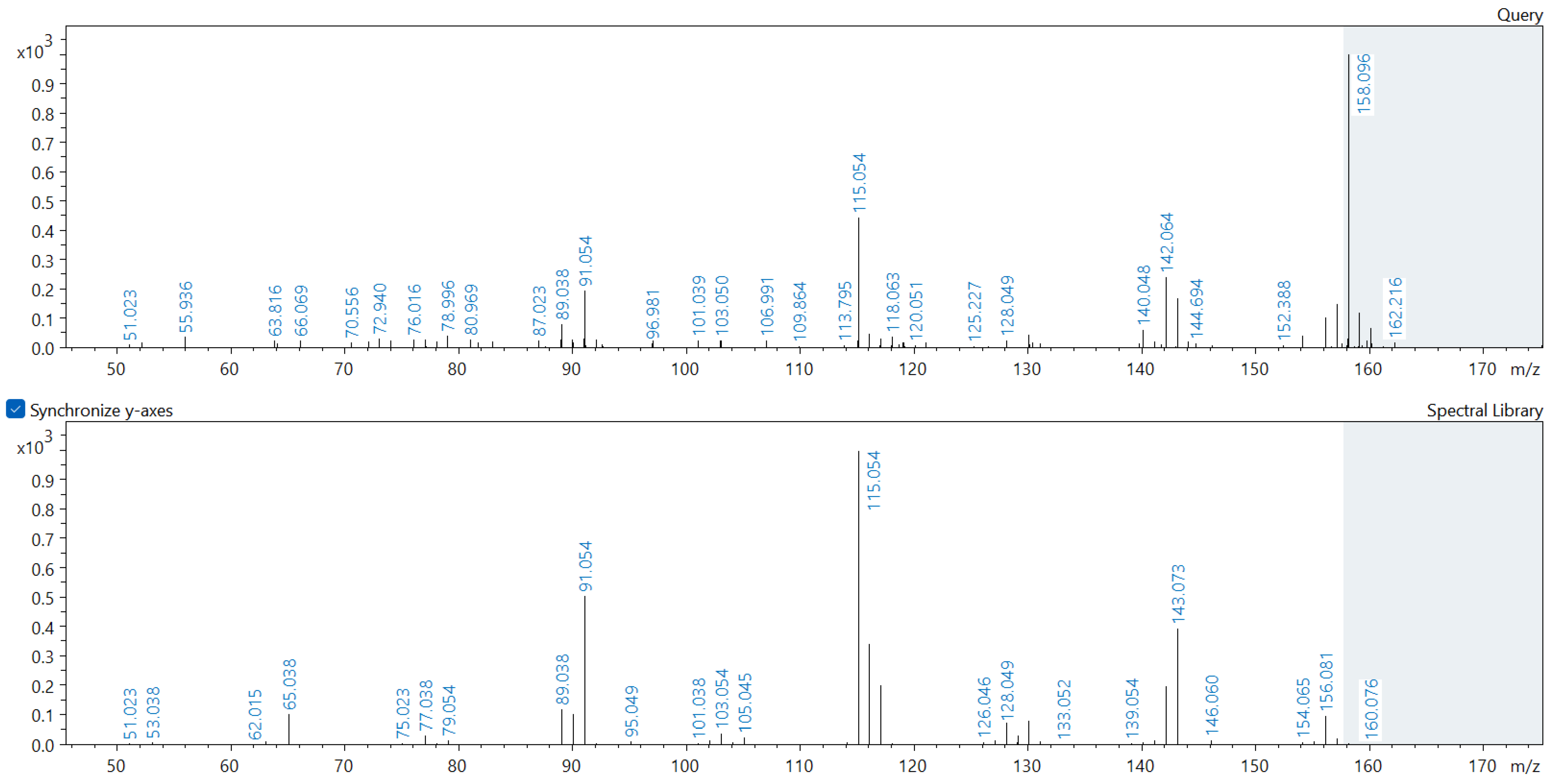
References
- Vinti, G.; Bauza, V.; Clasen, T.; Medlicott, K.; Tudor, T.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vaccari, M. Municipal Solid Waste Management and Adverse Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Poland. Environment 2021. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/environment-energy/environment/environment-2021,1,13.html (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Statistics Poland. Environment 2020. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/environment-energy/environment/environment-2020,1,12.html (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Srivastava, A.N.; Chakma, S. Dry tomb—Bioreactor landfilling approach for enhanced biodegradation and biomethane generation from municipal solid waste Co-disposed with sugar mill pressmud. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Poland. Stan i Ochrona Środowiska, Składowiska Odpadów. Available online: https://bdl.stat.gov.pl/bdl/metadane/metryka/3196# (accessed on 26 October 2022). (In Polish)
- Naveen, B.P.; Mahapatra, D.M.; Sitharam, T.G.; Sivapullaiah, P.V.; Ramachandra, T.V. Physico-chemical and biological characterization of urban municipal landfill leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordean, D.-M.; Pirvulescu, L.; Poiana, M.-A.; Alexa, E.; Cozma, A.; Raba, D.N.; Borozan, A.B.; Misca, C.D.; Morar, A.; Obistioiu, D.; et al. An Innovative Approach to Assess the Ecotoxicological Risks of Soil Exposed to Solid Waste. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravanian, A.; Ravari, S.O. Types of Contamination in Landfills and Effects on the Environment: A Review Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 614, 012083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Watson, A.; Forter, M.; Oliaei, F. Review Article: Persistent organic pollutants and landfills—A review of past experiences and future challenges. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2011, 29, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggen, T.; Moeder, M.; Arukwe, A. Municipal landfill leachates: A significant source for new and emerging pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, J.; Okrasa, M.; Nowak, A.; Nizioł, J.; Ruman, T.; Kuberski, S. Assessment of Physicochemical, Microbiological and Toxicological Hazards at an Illegal Landfill in Central Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Huang, X.; Xue, Q.; Liu, L.; Wan, Y. In-situ biodegradation of harmful pollutants in landfill by sludge modified biochar used as biocover. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, J.; Okrasa, M.; Majchrzycka, K.; Sulyok, M.; Nowak, A.; Ruman, T.; Nizioł, J.; Szponar, B.; Gutarowska, B. Microbiological and Toxicological Hazards in Sewage Treatment Plant Bioaerosol and Dust. Toxins 2021, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brągoszewska, E.; Pawlak, M. Health Risks Associated with Occupational Exposure to Biological Air Pollutants Occurring during the Processing of Biomass for Energy Purposes: A Case Study. Energies 2021, 14, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, O.; Robert, S.; Noyon, N. Airborne mycotoxins in waste recycling and recovery facilities: Occupational exposure and health risk assessment. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado-Gamero, W.B.; Parody, A.; Medina, J.; Rodriguez-Villamizar, L.A.; Agudelo-Castañeda, D. Multi-antibiotic resistant bacteria in landfill bioaerosols: Environmental conditions and biological risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, N.M.; Giorgetti, G.; Magrini, C.; Capitani, G.C.; Galimberti, L.; Cavallo, A.; Salvini, R.; Vanneschi, C.; Viti, C. From hazardous asbestos containing wastes (ACW) to new secondary raw material through a new sustainable inertization process: A multimethodological mineralogical study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulc, J.; Nizioł, J.; Ruman, T.; Kuźniar, A.; Nowak, A.; Okrasa, M.; Nowak, I.; Szponar, B.; Kuberski, S. Biological and chemical contamination of illegal, uncontrolled refuse storage areas in Poland. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csuros, M.; Csuros, C. Environmental Sampling and Analysis for Metals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780429186981. [Google Scholar]
- Skóra, J.; Gutarowska, B.; Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Stępień, Ł.; Pietrzak, K.; Piotrowska, M.; Pietrowski, P. Assessment of microbiological contamination in the work environments of museums, archives and libraries. Aerobiologia 2015, 31, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on ambient air quality and cleaner air for Europe. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L152, 1–44.
- Regulation of the Minister of the Environment Regulation of the Minister of the Environment of 1 September 2016 on the Method of Assessing Pollution of the Earth’s Surface (Dz.U. z 2016 r. poz. 1395) 2016. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20160001395/O/D20161395.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022). (In Polish)
- Rovira, J.; Domingo, J.L. Human health risks due to exposure to inorganic and organic chemicals from textiles: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council Directive (EU) 2018/850 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 amending Directive 1999/31/EC on the landfill of waste. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, 2018, 100–108.
- Ozbay, G.; Jones, M.; Gadde, M.; Isah, S.; Attarwala, T. Design and Operation of Effective Landfills with Minimal Effects on the Environment and Human Health. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 6921607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Voie, E.J.; Defauw, J.; Fealy, M.; Way, B.M.; Mcqueen, C.A. Genotoxicity of fluoroquinolines and methyiquinolines. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.M.; Royer, R.E.; Galvin, J.B.; Shimizu, R.W. Metabolism of phenanthridine to phenanthridone by rat lung and liver microsomes after induction with benzo[a]pyrene and aroclor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1983, 68, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. PARP inhibitors: Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 2017, 355, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buening, M.K.; Levin, W.; Wood, A.W.; Chang, R.L.; Yagi, H.; Karle, J.M.; Jerina, D.M.; Conney, A.H. Tumorigenicity of the Dihydrodiols of Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene on Mouse Skin and in Newborn Mice. Cancer Res. 1979, 39, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Duuren, B.L.; Langseth, L.; Goldschmidt, B.M.; Orris, L. Carcinogenicity of Epoxides, Lactones, and Peroxy Compounds. VI. Structure and Carcinogenic Activity. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1967, 39, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluszynska, A. Biological potential of carbazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, D.O.; Ulfig, K.; Wlazło, A.; Pastuszka, J.S. Microbial Air Quality in Offices at Municipal Landfills. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2004, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breza-Boruta, B. Bioaerosols of the municipal waste landfill site as a source of microbiological air pollution and health hazard. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2012, 19, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breza-Boruta, B.; Lemanowicz, J.; Bartkowiak, A. Variation in biological and physicochemical parameters of the soil affected by uncontrolled landfill sites. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.T. Bioaerosols in the landfill environment: An overview of microbial diversity and potential health hazards. Aerobiologia 2021, 37, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legon, N. Fungal Portraits No. 50 Lindtneria trachyspora. Field Mycol. 2012, 13, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Lei, Y. Bacterial community diversity in municipal waste landfill sites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7745–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kuila, A. Bioremediation of heavy metals by microbial process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, S.-J.; Schumann, P.; Oh, T.-K. Cellulosimicrobium terreum sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, H.H.; Gralnick, J.A. Ecology and Biotechnology of the Genus Shewanella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees-Hill, S.; Douglas, P.; Pashley, C.H.; Hansell, A.; Marczylo, E.L. A systematic review of outdoor airborne fungal spore seasonality across Europe and the implications for health. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Mahanty, B.; Dasu, V.V. Modeling growth of Cellulomonas cellulans NRRL B 4567 under substrate inhibition during cellulase production. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2009, 23, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwuma, O.B.; Rafatullah, M.; Tajarudin, H.A.; Ismail, N. Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure of a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill: A Source of Lignocellulolytic Potential. Life 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, E.; Hanaka, A. Mortierella Species as the Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi Present in the Agricultural Soils. Agriculture 2020, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, T.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, N.; Singh, R.; Fuloria, A.; Waziri, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Purty, R. Assessment of Bioremediation Potential of Cellulosimicrobium sp. for Treatment of Multiple Heavy Metals. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 47, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Monchy, S.; Cardinale, M.; Taghavi, S.; Crossman, L.; Avison, M.B.; Berg, G.; van der Lelie, D.; Dow, J.M. The versatility and adaptation of bacteria from the genus Stenotrophomonas. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Lal, R. (Meta)genomic insights into the pathogenome of Cellulosimicrobium cellulans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, U.; Paul, K.; Gupta, S. The multifaceted genus Acinetobacter: From infection to bioremediation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Q.; Chen, D.; Wei, L.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H. Microbial community in a hydrogenotrophic denitrification reactor based on pyrosequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10829–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; He, J. Proteiniclasticum sediminis sp. nov., an obligate anaerobic bacterium isolated from anaerobic sludge. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Qiu, J.; Li, N.; He, J. Anaerobic biodegradation and detoxification of chloroacetamide herbicides by a novel Proteiniclasticum sediminis BAD-10T. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Tian, X.; Cao, S. Identification of an anaerobic bacterial consortium that degrades roxarsone. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasi, S.; Tabrez, S.; Ahmad, M. Use of Pseudomonas spp. for the bioremediation of environmental pollutants: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8147–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Thakur, I.S. Enzymatic Dehalogenation of Pentachlorophenol by Pseudomonas fluorescens of the Microbial Community from Tannery Effluent. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Shah, S.B.; Zanaroli, G.; Xu, P.; Tang, H. Phenol biodegradation by Acinetobacter radioresistens APH1 and its application in soil bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banar, M.; Sattari-Maraji, A.; Bayatinejad, G.; Ebrahimi, E.; Jabalameli, L.; Beigverdi, R.; Emaneini, M.; Jabalameli, F. Global prevalence and antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1163439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.W.; St Leger, R.J. Metarhizium spp., Cosmopolitan Insect-Pathogenic Fungi: Mycological Aspects. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Golzar, H.; Thomas, G.; Jayasena, K.W.; Wright, D.; Wang, C.; Kehoe, M. Neoascochyta species cause leaf scorch on wheat in Australia. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2019, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.M.; Schaffer, P.A.; Bander, N.B. Chalastospora gossypii in a Maine Coon cat: Case report and literature review. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Engqvist, H.; Biermann, J.; Werner Rönnerman, E.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Kovács, A.; Karlsson, P.; Helou, K.; Parris, T.Z. Optimization of cell viability assays to improve replicability and reproducibility of cancer drug sensitivity screens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkowska, K.; Nowak, A.; Kunicka-Styczyńska, A.; Siadura, A. Biological effects of various chemically characterized essential oils: Investigation of the mode of action against Candida albicans and HeLa cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97199–97207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertel, S.; Eichhorn, T.; Plinkert, P.K.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of Thymus vulgaris essential oil towards human oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- IARC International Agency for Research on Cancer. Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans, List of Classification, Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2021; Volume 129. [Google Scholar]
- IARC International Agency for Research on Cancer. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2006; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Polychlorinated Biphenyls Polybrominated Biphenyls—IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2016; Volume 107, pp. 9–500. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Cho, J. AIDM-Strat: Augmented Illegal Dumping Monitoring Strategy through Deep Neural Network-Based Spatial Separation Attention of Garbage. Sensors 2022, 22, 8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zuo, J.; Vanzo, J.; Chang, R.; Zillante, G. Assessing and predicting the illegal dumping risks in relation to road characteristics. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, D.; Rykala, W.; Nourani, V. Causes, Types and Consequences of Municipal Waste Landfill Fires—Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.C.; Farrell, G.; Tilley, N. Illegal waste fly-tipping in the COVID-19 pandemic: Enhanced compliance, temporal displacement, and urban–rural variation. Crime Sci. 2022, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA Guidance, Landfill Restoration General Guidance, WST-G-057, Version 1, Issued Oct 2018. Available online: https://www.sepa.org.uk/media/594440/sepa-guidance-wst-g-057-restoration.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Pusz, A.; Wiśniewska, M.P.; Rogalski, D.; Staśkiewicz, M. Assessment of the Impact of a Recultivated Landfill on the Soil Environment. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T.; Asakura, H. Treatment of landfill leachate with different techniques: An overview. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2021, 11, 66–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec-Grządziel, A.; Gałązka, A. Sequencing of the Whole Genome of a Bacterium of the Genus Achromobacter Reveals Its Potential for Xenobiotics Biodegradation. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funtikova, T.V.; Akhmetov, L.I.; Puntus, I.F.; Mikhailov, P.A.; Appazov, N.O.; Narmanova, R.A.; Filonov, A.E.; Solyanikova, I.P. Bioremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil of the Republic of Kazakhstan Using a New Biopreparation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat, N.A.; Benjamin, A.M.; Abdul-Rahman, S. A review on criteria and decision-making techniques in solving landfill site selection problems. J. Adv. Rev. Sci. Res. 2017, 37, 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Manyoma-Velásquez, P.C.; Vidal-Holguín, C.J.; Torres-Lozada, P. Methodology for locating regional landfills using multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1776451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supreme Audit Office. Post-Audit Presentation, Preventing Threats from Off-Site Landfills in the Łódź Voivodeship; Supreme Audit Office: Łódź, Poland, 2019. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Supreme Audit Office. Information on the Results of the Inspection, Preventing Threats from Off-Site Landfills in the Łódź Voivodeship; Supreme Audit Office: Warsaw, Poland, 2020. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- CEN EN 13098:2019; Workplace Exposure—Measurement of Airborne Microorganisms and Microbial Compounds—General Requirements. Slovenski Inštitut za Standardizacijo: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2019.
- Marczenko, Z.; Balcerzak, M. Spectrophotometric Methods in Inorganic Analysis; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- MassBank of North America (MoNA) Mass. Available online: https://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu/ (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- National Institute of Standards and Technology Mass Spectrometry Data Center. Available online: https://chemdata.nist.gov/ (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Nizioł, J.; Ossoliński, K.; Płaza-Altamer, A.; Kołodziej, A.; Ossolińska, A.; Ossoliński, T.; Ruman, T. Untargeted ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry metabolomic profiling of blood serum in bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossoliński, K.; Ruman, T.; Copié, V.; Tripet, B.P.; Kołodziej, A.; Płaza-Altamer, A.; Ossolińska, A.; Ossoliński, T.; Nieczaj, A.; Nizioł, J. Targeted and untargeted urinary metabolic profiling of bladder cancer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 233, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizioł, J.; Ossoliński, K.; Płaza-Altamer, A.; Kołodziej, A.; Ossolińska, A.; Ossoliński, T.; Nieczaj, A.; Ruman, T. Untargeted urinary metabolomics for bladder cancer biomarker screening with ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, M.J.; Muyzer, G.; Ward, D.M.; Spring, O. Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis Profiles of 16S rRNA-Defined Populations Inhabiting a Hot Spring Microbial Mat Community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, S.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- 16S-Metagenomic-Library-Prep-Guide-15044223-B 1–28. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Jensen, E.A.; Berryman, D.E.; Murphy, E.R.; Carroll, R.K.; Busken, J.; List, E.O.; Broach, W.H. Heterogeneity spacers in 16S rDNA primers improve analysis of mouse gut microbiomes via greater nucleotide diversity. Biotechniques 2019, 67, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Concentration | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | ng kg−1 | |||||||||
| Fe | Mn | Pb | Zn | Al | Hg | Cd | Cu | Cr | ||
| S1 | I | 700 ± 25.7 | 100 ± 5.24 | 38 ± 0.68 | 150 ± 6.02 | 89 ± 0.14 | 1.1 ± 0.15 | 4.5 ± 0.18 | below LOD | 4 ± 0.2 |
| II | 250 ± 0.85 | 39 ± 1.3 | 17 ± 1.1 | 50 ± 2.5 | 1.5 ± 0.031 | 3.6 ± 0.40 | 2.5 ± 0.093 | 2450 ± 92.02 | 3.8 ± 0.16 | |
| S2 | I | 435 ± 16.1 | 88 ± 4.6 | 16 ± 0.29 | 16 ± 0.64 | 8.2 ± 0.24 | 1.6 ± 0.22 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 4.3 ± 0.15 | 2.5 ± 0.096 |
| II | 195 ± 0.220 | 25 ± 1.0 | 8 ± 0.07 | 7 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.022 | 6.8 ± 0.45 | below LOD | below LOD | 3 ± 0.10 | |
| S3 | I | 611 ± 22.1 | 90 ± 4.7 | 21 ± 0.38 | 36 ± 1.3 | 4.0 ± 0.24 | 1.2 ± 0.35 | 2 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.29 | 4 ± 0.2 |
| II | 131 ± 4.90 | 18 ± 0.85 | 7 ± 0.15 | 11 ± 0.32 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.38 | below LOD | below LOD | 3.3 ± 0.11 | |
| S4 | I | 700 ± 26.4 | 200 ± 11.4 | 27 ± 0.48 | 100 ± 4.14 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.24 | 1.5 ± 0.065 | 10.5 ± 0.391 | 5 ± 0.2 |
| II | 67 ± 0.26 | 60 ± 1.5 | 7 ± 0.11 | 20 ± 0.40 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 7.4 ± 0.56 | below LOD | below LOD | 3 ± 0.09 | |
| S5 | I | 379 ± 14.3 | 300 ± 15.6 | 350 ± 0.632 | 1425 ± 52.24 | 3.1 ± 0.24 | 5.6 ± 0.35 | 4 ± 0.2 | 250.0 ± 9.499 | 12.5 ± 0.488 |
| II | 199 ± 0.221 | 48 ± 2.0 | 29 ± 0.12 | 150 ± 5.25 | 1.4 ± 0.21 | 8.9 ± 0.06 | 1.5 ± 0.078 | 150 ± 5.478 | 13.5 ± 0.479 | |
| S6 | I | 800 ± 29.2 | 400 ± 16.7 | 285 ± 0.511 | 1350 ± 50.08 | 13.7 ± 1.07 | 2.2 ± 0.16 | 4.5 ± 0.16 | 1200 ± 43.92 | 22.5 ± 1.12 |
| II | 134 ± 5.38 | 250 ± 0.248 | 1255 ± 46.04 | 1100 ± 40.49 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.754 | 4 ± 0.2 | 250 ± 9.26 | 16 ± 0.61 | |
| S7 | I | 970 ± 35.9 | 150 ± 8.71 | 11 ± 0.19 | 20 ± 0.70 | 8.9 ± 0.21 | 8.1 ± 0.45 | 0.5 ± 0.03 | 7 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.16 |
| II | 290 ± 0.353 | 28 ± 0.11 | 18 ± 0.15 | 16 ± 0.66 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 20.6 ± 1.11 | below LOD | 3.5 ± 0.13 | 3.5 ± 0.13 | |
| S8 | I | 815 ± 29.7 | 180 ± 0.914 | 15 ± 0.27 | 60 ± 2.3 | 9.0 ± 0.3 | 2.7 ±0.80 | 0.5 ± 0.03 | 5 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 0.12 |
| II | 112 ± 0.122 | 23 ± 0.072 | 6 ± 0.2 | 8 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.08 | 2.1 ± 0.10 | below LOD | below LOD | 3 ± 0.12 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szulc, J.; Okrasa, M.; Nowak, A.; Ryngajłło, M.; Nizioł, J.; Kuźniar, A.; Ruman, T.; Gutarowska, B. Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill—Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment—A Case Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071496
Szulc J, Okrasa M, Nowak A, Ryngajłło M, Nizioł J, Kuźniar A, Ruman T, Gutarowska B. Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill—Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment—A Case Study. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzulc, Justyna, Małgorzata Okrasa, Adriana Nowak, Małgorzata Ryngajłło, Joanna Nizioł, Anna Kuźniar, Tomasz Ruman, and Beata Gutarowska. 2024. "Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill—Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment—A Case Study" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071496
APA StyleSzulc, J., Okrasa, M., Nowak, A., Ryngajłło, M., Nizioł, J., Kuźniar, A., Ruman, T., & Gutarowska, B. (2024). Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill—Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment—A Case Study. Molecules, 29(7), 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071496