The Removal of Arsenic and Its Inorganic Forms from Marine Algae—A Base for Inexpensive and Efficient Fertilizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Adsorbent
2.2. Adsorption Optimization
2.3. As Aqueous Extraction from Algae
2.4. Inorganic As Removal from the Aqueous Seaweed Extract
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Adsorbent Preparation
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
3.5. Inorganic As Extraction Procedure
3.6. Adsorption of Inorganic As from the Water Algal Extract
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cherry, P.; O’Hara, C.; Magee, P.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Allsopp, P.J. Risks and benefits of consuming edible seaweeds. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illera-Vives, M.; Seoane Labandeira, S.; Iglesias Loureiro, L.; López-Mosquera, M.E. Agronomic assessment of a compost consisting of seaweed and fish waste as an organic fertilizer for organic potato crops. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.A.T.; Duarte, A.C. Analytical methodologies for arsenic speciation in macroalgae: A critical review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, J.L.; Hoek-van den Hil, E.F.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Food safety hazards in the European seaweed chain. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 332–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camurati, J.R.; Salomone, V.N. Arsenic in edible macroalgae: An integrated approach. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2020, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górka, B.; Korzeniowska, K.; Lipok, J.; Wieczorek, P.P. The Biomass of Algae and Algal Extracts in Agricultural Production. In Algae Biomass: Characteristics and Applications; Developments in Applied Phycology; Chojnacka, K., Wieczorek, P., Schroeder, G., Michalak, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholssi, R.; Lougraimzi, H.; Grina, F.; Lorentz, J.F.; Silva, I.; Castaño-Sánchez, O.; Marks, E.A. Green agriculture: A review of the application of micro-and macroalgae and their impact on crop production on soil quality. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2022, 22, 4627–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camurati, J.R.; Londonio, A.; Smichowski, P.; Salomone, V.N. On-line speciation analysis of arsenic compounds in commercial edible seaweed by HPLC–UV-thermo-oxidation-HG-AFS. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.; Šmíd, B.; Johánek, V.; Khalakhan, I.; Yakovlev, Y.; Matolínová, I.; Matolín, V. Investigation of dextran adsorption on polycrystalline cerium oxide surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 544, 148890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercha, S.; Mali, G.; Khalakhan, I.; Skála, T.; Prince, K.C.; Matolín, V.; Tsud, N. Histidine adsorption on nanostructured cerium oxide. J. Electr. Spectr. Rel. Phenom. 2016, 212, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, K.; Khan, F.; Verma, D.K.; Agrawal, S. Effective removal of uranium from aqueous solution by using cerium oxide nanoparticles derived from citrus limon peel extract. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 332, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. A study of phosphate adsorption by different temperature treated hydrous cerium oxides. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupa, J.; Morlo, K.; Dobrowolski, R.; Legutko, P.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Kierys, A. Highly porous cerium oxide prepared via a one-step hard template method as an extremely effective adsorbent for arsenic species removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, A.; Chrzanowska, A.; Kierys, A. Highly Porous Ceria as an Adsorbent for Removing Artificial Dyes from Water. Environ. Process. 2024, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, A.E.; Smith, R.M. Protonation Values for Other Ligands. In Critical Stability Constants: First Supplement; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 425–453. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, J.J. Digitizing “The NBS Tables of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties: Selected Values for Inorganic and C1 and C2 Organic Substances in SI Units”. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2020, 125, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, Y.; Al-Lagtah, N.; Ahmad, M.N.M.; Allen, S.J.; Walker, G.M. Kinetic and thermodynamic investigations on arsenic adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lalhmunsiama, L.; Thanhmingliana, T.; Diwakar, T. Porous hybrid materials in the remediation of water contaminated with As(III) and As(V). Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasundara, L.; Ok, Y.-S.; Bundschuh, J. Selective removal of arsenic in water: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-H.; Nakajima, T.; Ohki, A. Adsorption and removal of arsenic(V) from drinking water by aluminum-loaded Shirasu-zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Zou, S.W.; Nanayakkara, K.N.; Matsuura, T.; Chen, J.P. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by a PVDF/zirconia blend flat sheet membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 374, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, S.; Kołodyńska, D. Arsenate removal on the ion exchanger modified with cerium(III) ions. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2022, 58, 147412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchieda, V.K.; D’Amato, E.; Chiavola, A.; Parisi, M.; Chianese, A.; Amamra, M.; Kanaev, A. Removal of Arsenic by Alumina: Effects of Material Size, Additives, and Water Contaminants. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Q.; Gao, S.; Shan, J.K. Exceptional arsenic adsorption performance of hydrous cerium oxide nanoparticles: Part A. Adsorption capacity and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinski, W.; Dziuba, J.; Rudzinski, W. Modeling of sorption kinetics: The pseudo-second order equation and the sorbate intraparticle diffusivity. Adsorption 2013, 19, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W.; Plazinska, A. Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface re-action mechanism: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Physical insights into kinetic models of adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S. Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.R.; Prelot, B. Chapter 7—Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: The perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. In Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 161–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakhova, T.V.; Romanchuk, A.Y.; Yakunin, S.N.; Dumas, T.; Demir, S.; Wang, S.; Minasian, S.G.; Shuh, D.K.; Tyliszczak, T.; Shiryaev, A.A.; et al. Solubility of Nanocrystalline Cerium Dioxide: Experimental Data and Thermodynamic Modeling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22615–22626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, T.S.; Das, S.; Pratt, C.J.; Seal, S. One-pot synthesis of a ceria–graphene oxide composite for the efficient removal of arsenic species. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3367–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunge, S.; Singh, S.; Sinha, A. Magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles from tea waste for arsenic removal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 356, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, Q.; Gao, S.; Shang, J.K. Strong adsorption of arsenic species by amorphous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Sheng, G.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, X.J. Enhanced arsenic removal from water by hierarchically porous CeO2–ZrO2 nanospheres: Role of surface- and structure-dependent properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Pu, H.; Li, H.; Deng, L.; Huang, S.; He, S.; Luo, Y. The optimization of As(V) removal over mesoporous alumina by using response surface methodology and adsorption mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CSN EN 15517:2008; Foodstuffs—Determination of Trace Elements—Determination of Inorganic Arsenic in Seaweed by Hydride Generation Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (HG AAS) after Acid Digestion. European Standard (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- Hsieh, Y.J.; Jiang, S.J. Application of HPLC-ICP-MS and HPLC-ESI-MS procedures for arsenic speciation in seaweed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Maher, W.; Krikowa, F.; Apte, S. A microwave-assisted sequential extraction of water and dilute acid soluble arsenic species from marine plant and animal tissues. Talanta 2007, 71, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pell, A.; Márquez, A.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Rubio, R.; Barbero, M.; Stegen, S.; Queirolo, F.; Díaz-Palma, P. Occurrence of arsenic species in algae and freshwater plants of an extreme arid region in northern Chile, the Loa River basin. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumette, G.; Koch, I.; Estrada, E.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic speciation in plankton organisms from contaminated lakes: Transformations at the base of the freshwater food chain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9917–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A.; Inamuddin Asiri, A.M. Exploring the reusability of synthetically contaminated wastewater containing crystal violet dye using tectona grandis sawdust as a very low-cost adsorbent. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, A.; Kierys, A. Polymer templated production of highly porous cerium oxide in direct temperature driven transformation of cerium(III) salt. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 318, 111032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yang, L.; Shao, P.; Shi, H.; Chang, Z.; Fang, D.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Proton Self-Enhanced Hydroxyl-Enriched Cerium Oxide for Effective Arsenic Extraction from Strongly Acidic Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10412–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.J. Solvothermal synthesis of nano-CeO2 aggregates and its application as a high-efficient arsenic adsorbent. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Zeng, C.; Westerhoff, P. Adsorption of Arsenic Ions Transforms Surface Reactivity of Engineered Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9437–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, P.; Ding, L.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; You, D.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, X. Lattice-Defect-Enhanced Adsorption of Arsenic on Zirconia Nanospheres: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29736–29745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Luo, X.; Hu, C.; Crittenden, J.C.; Qu, J. Zirconia (ZrO2) Embedded in Carbon Nanowires via Electrospinning for Efficient Arsenic Removal from Water Combined with DFT Studies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18912–18921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


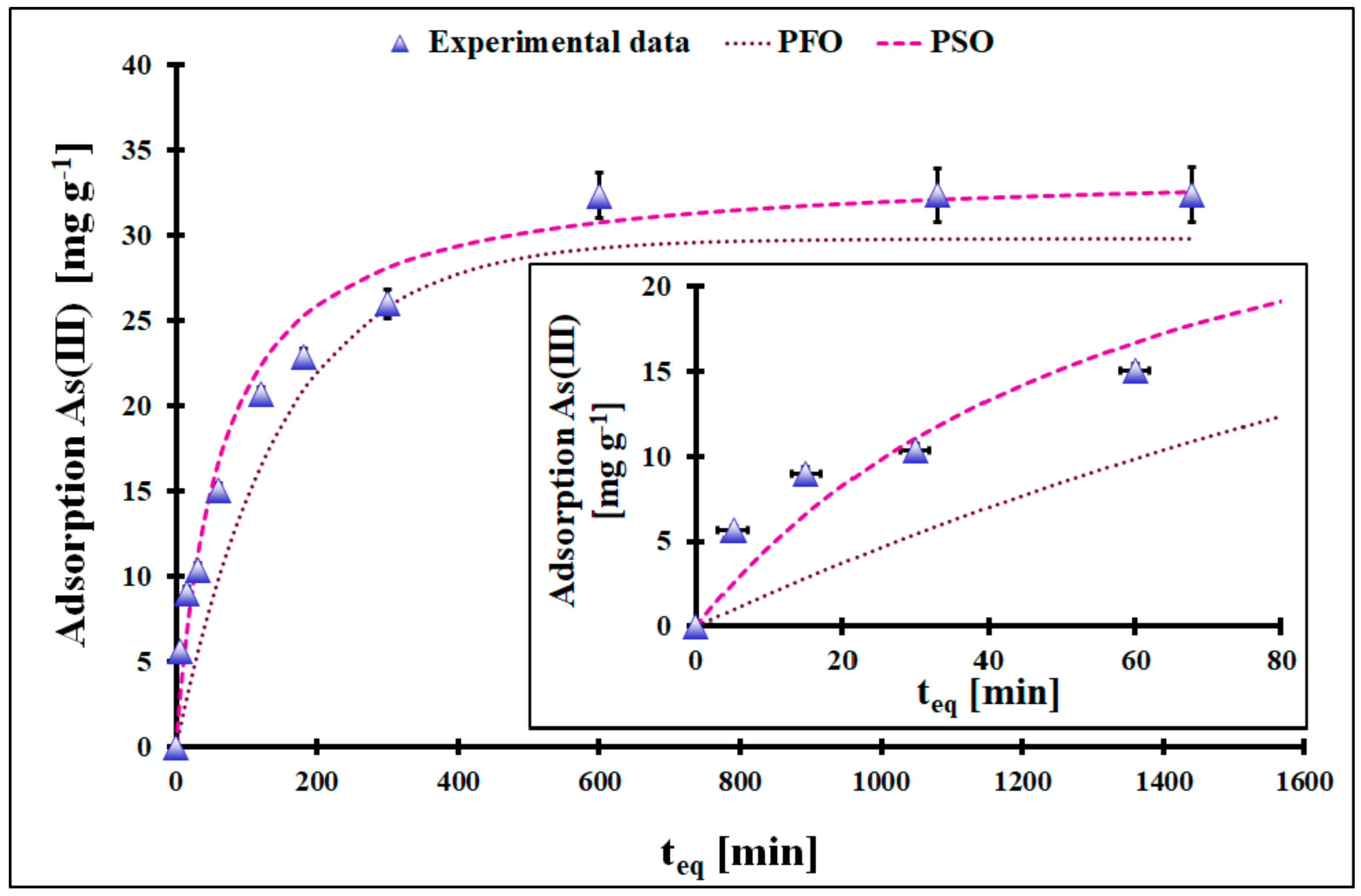
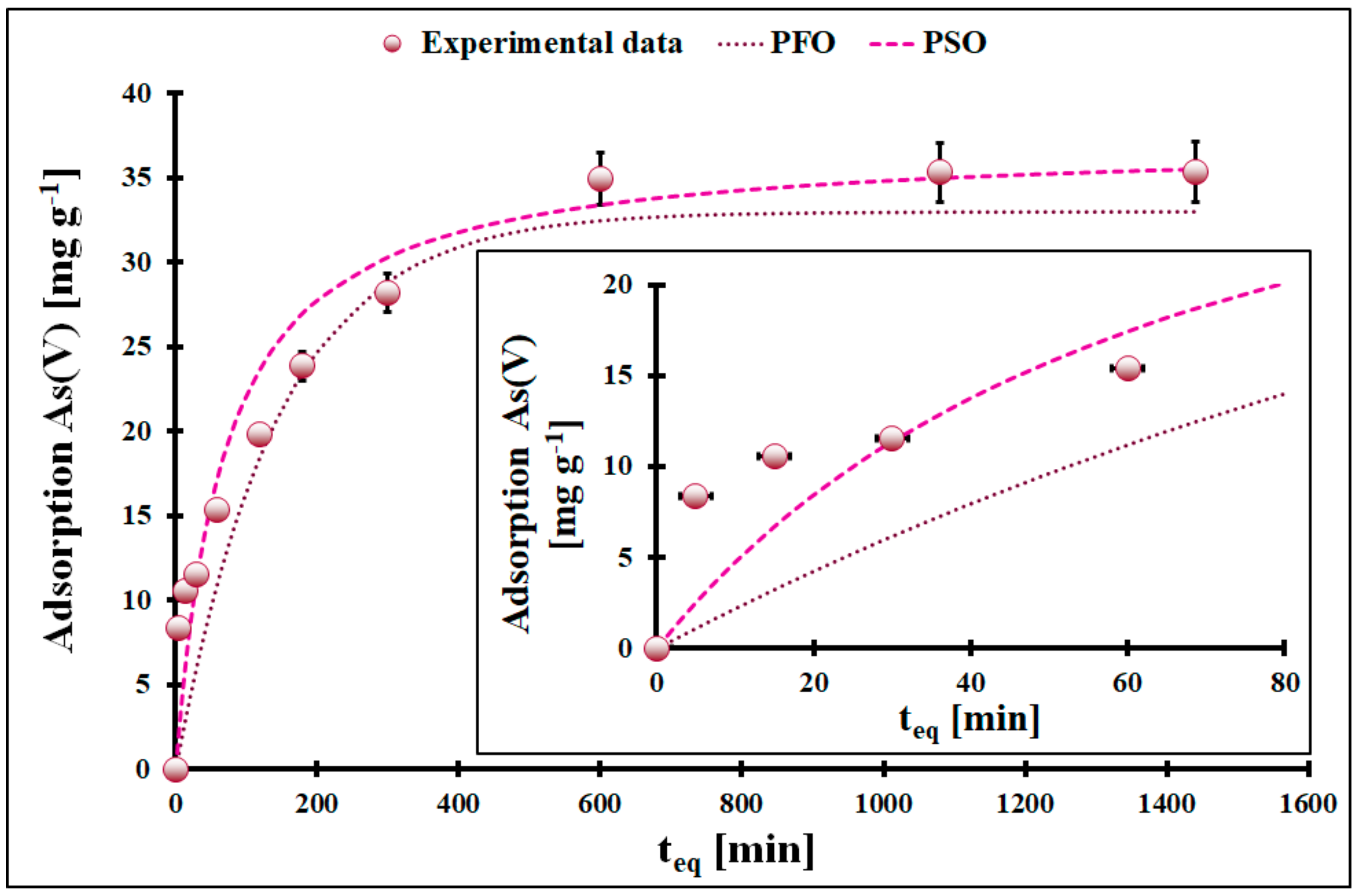
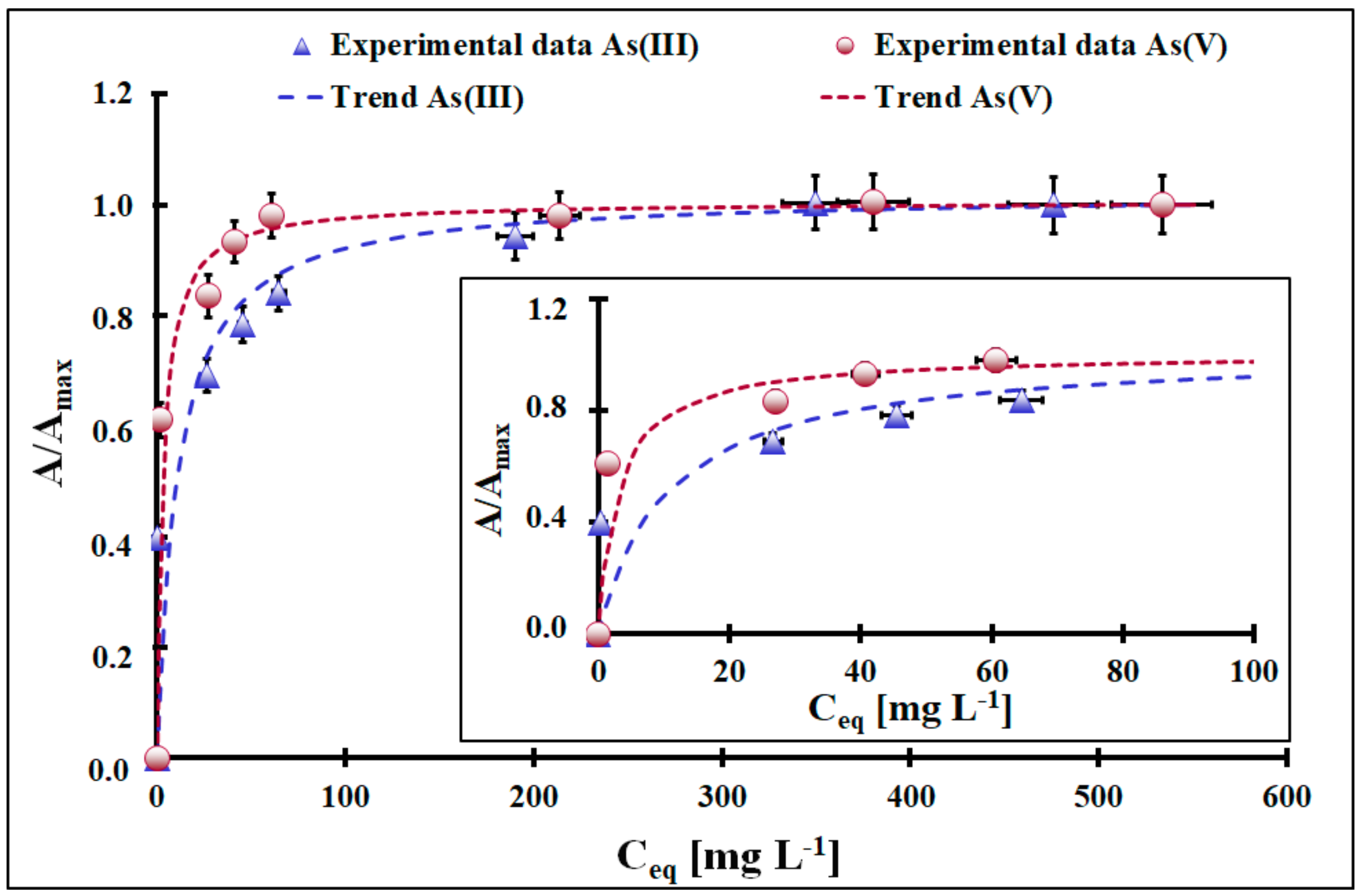


| Kinetic Model | PFO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic As Species | k1 [g mg−1 min−1] | Qeq [mg g−1] | R2 | |
| As(III) | 0.0067 *$ | 29.8 * ± 1.1 # | 0.9113 | |
| As(V) | 0.0069 *$ | 33.0 * ± 1.4 # | 0.9902 | |
| Kinetic Model | PSO | |||
| Inorganic As Species | k2 [g mg−1 min−1] | Qeq [mg g−1] | R2 | |
| As(III) | 0.00047 *$ | 34.0 * ± 1.5 # | 0.9979 | |
| As(V) | 0.00040 *$ | 37.2 * ± 1.7 # | 0.9965 | |
| Isotherm Model | Langmuir | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic As Species | kL [L mg−1] | qL [mg g−1] | R2 | |
| As(III) | 0.094 *$ | 96.1 * ± 3.8 # | 0.9991 | |
| As(V) | 0.324 * ± 0.012 # | 68.5 * ± 2.7 # | 0.9999 | |
| Isotherm Model | Freundlich | |||
| Inorganic As Species | nF [a. u.] | kF [mg1-nF LnF g−1] | R2 | |
| As(III) | 0.13 *$ | 42.9 * ± 1.9 # | 0.9898 | |
| As(V) | 0.083 *$ | 43.1 * ± 1.5 # | 0.8732 | |
| Literature | Content of Arsenic Species [mg kg−1] | Content of Total Arsenic [mg kg−1] | Type of Extract | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMA | MMA | Asinorg. | |||
| [39] | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.74 | 2.54 | methanol + ammonium carbonate |
| [40] | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 0.93 | methanol:water 1:1 |
| 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.20 | 1.51 | nitric acid 2% | |
| [8] | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.71 | 1.12 | nitric acid 1% |
| [41] | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.87 | aqueous |
| [42] | — | — | 0.70 | 1.30 | aqueous |
| Our work | — | — | 0.75 * ± 0.03 # | 3.10 * ± 0.12 # | aqueous |
| 0.891 * ± 0.037 # | 0.07 mol L−1 HCl | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ostrowski, J.; Drozd, A.; Olchowski, R.; Chałabis-Mazurek, A.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Kierys, A.; Morlo, K.; Dobrowolski, R. The Removal of Arsenic and Its Inorganic Forms from Marine Algae—A Base for Inexpensive and Efficient Fertilizers. Molecules 2024, 29, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061348
Ostrowski J, Drozd A, Olchowski R, Chałabis-Mazurek A, Sienkiewicz A, Kierys A, Morlo K, Dobrowolski R. The Removal of Arsenic and Its Inorganic Forms from Marine Algae—A Base for Inexpensive and Efficient Fertilizers. Molecules. 2024; 29(6):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061348
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstrowski, Jarosław, Alicja Drozd, Rafał Olchowski, Agnieszka Chałabis-Mazurek, Andrzej Sienkiewicz, Agnieszka Kierys, Kinga Morlo, and Ryszard Dobrowolski. 2024. "The Removal of Arsenic and Its Inorganic Forms from Marine Algae—A Base for Inexpensive and Efficient Fertilizers" Molecules 29, no. 6: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061348
APA StyleOstrowski, J., Drozd, A., Olchowski, R., Chałabis-Mazurek, A., Sienkiewicz, A., Kierys, A., Morlo, K., & Dobrowolski, R. (2024). The Removal of Arsenic and Its Inorganic Forms from Marine Algae—A Base for Inexpensive and Efficient Fertilizers. Molecules, 29(6), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29061348






