Abstract
To explore the composition of anthocyanins and expand their biological activities, anthocyanins were systematically isolated and purified from tubers of Solanum tuberosum L., and their tyrosinase inhibitory activity was investigated. In this study, two new anthocyanin degradation compounds, norpetanin (9) and 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose (10), along with 17 known anthocyanins and their derivatives, were isolated and purified from an acid-ethanolic extract of fresh purple potato tubers. Their structures were elucidated via 1D and 2D NMR and HR-ESI-MS and compared with those reported in the literature. The extracts were evaluated for anthocyanins and their derivatives using a tyrosinase inhibitor screening kit and molecular docking technology, and the results showed that petanin, norpetanin, 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E possessed tyrosinase inhibitory activity, with 50% inhibiting concentration (IC50) values of 122.37 ± 8.03, 115.53 ± 7.51, 335.03 ± 12.99, and 156.27 ± 11.22 μM (Mean ± SEM, n = 3), respectively. Furthermore, petanin was validated against melanogenesis in zebrafish; it was found that it could significantly inhibit melanin pigmentation (p < 0.001), and the inhibition rate of melanin was 17% compared with the normal group. This finding may provide potential treatments for diseases with abnormal melanin production, and high-quality raw materials for whitening cosmetics.
1. Introduction
The potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) is the fourth most important staple crop worldwide and originated from the highlands of the equatorial Andes in South America [1,2]. The potato is a diverse crop that includes varieties with white, yellow, and colored flesh (red, blue, and purple). These differences in flesh color result from significant differences in the phytochemical composition of crops [3,4]. Yellow-flesh potatoes are characterized by high levels of carotenoids, whereas red-, blue-, and purple-flesh potatoes contain large amounts of anthocyanins [5]. Therefore, potatoes rich in pigments are a good source of anthocyanins [6].
Colored potatoes are a rich source of anthocyanins, especially the acylated derivatives, which account for more than 98% of the total anthocyanins [7]. The red potato contains mainly the acylated side of pelargonidin, while the purple potato contains mainly the acylated side of petunidin and peonidin, whereas delphinidin and malvidin have fewer acylated glycosides. Red tubers contain mostly pelargonidin 3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside and lesser amounts of peonidin 3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside. Light to medium purple tubers contain petunidin 3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside (1.00~2.00 mg g−1, FW) and small amounts of malvidin 3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside, while dark purple–black tubers contained similar levels of petunidin 3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside, together with much higher concentrations of malvidin-3-O-(p-coumaroyl-rutinoside)-5-O-glucoside [8]. Caffeoyl anthocyanins were first identified in Norwegian potatoes, containing petunidin 3-O-[6-O-(4-O-E-caffeoyl-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-5-O-β-glucopyranoside (10%), peonidin 3-O-[6-O-(4-O-E-caffeoy1-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-5-O-β-glucopyranoside (6%), petunidin 3-O-[6-O-(4-O-E-p-coumaroyl-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-5-O-β-g1ucopyranoside (petanin, 37%), and peonidin 3-O-[6-O-(4-O-E-p-coumaroyl-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-5-O-β-glucopyranoside (25%) [9]. The study of polyphenol composition in colored potato skins found that the total anthocyanin content in purple potatoes was 0.863 ± 0.005–1.39 ± 0.01 mg g−1 (dry weight, DW), including acylated pelargonidin, peonidin, malvidin, and petunidin anthocyanins, as shown in Table 1 [7,10,11,12]. Thus, the types of anthocyanins contained in a crop are closely related to the variety of potato, and the content varies greatly among different varieties and regions.

Table 1.
The anthocyanins composition of purple potato skins.
Anthocyanins are a type of flavonoid and glycosidic water-soluble pigment that not only impart red, purple, and blue colors to many fruits, flowers, and tubers, but also confer physiological benefits, reflected in their antioxidant [13,14,15], anti-inflammatory [16,17], hypoglycaemic [18,19], and whitening properties [20,21,22]. In particular, tyrosinase inhibitors are gaining research interest as melanin pigmentation can be blocked by inhibiting tyrosinase, a rate-limiting enzyme in melanin production [23,24]. Extracts from the seed coat of black soya beans have been reported to possess anti-human tyrosinase activity, and a good correlation has been found between such anti-human tyrosinase activity and the cyanidin 3-O-glucoside content of coat extracts [25]. Radio frequency-assisted enzymatic extraction of anthocyanins from Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. flowers showed tyrosinase inhibitory activity (14.67 kojic acid equivalents/g extract) [26]. The IC50 value of anthocyanins from red rice bran, in which tyrosinase inhibitory activity was observed, was reported to be 4.26 μg mL−1 [27]. Anthocyanins purified from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. had inhibitory effects on tyrosinase monophenolase (IC50 = 1.483 ± 0.058 mg mL−1), and the type of inhibition was competitive (Ki = 39.83 ± 1.4 mg mL−1) [28]. Moreover, petunidin 3-O-glucoside may act as a tyrosinase inhibitor to block melanin production, and has inhibitory ratios exceeding 55% of the control value at 50 µM, showing dose-dependent inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 10.3 ± 1.0 µM [29]. Additionally, anthocyanins from Hibiscus syriacus L. inhibit melanogenesis by activating the extracellular regulated protein kinases signaling pathway [30]. Therefore, anthocyanins have good potential for tyrosinase inhibitory activity, and thus anti-melanogenesis.
In this study, anthocyanin components from Solanum tuberosum L. were isolated, purified, and prepared using chromatography, spectroscopy, and NMR techniques. Then, their tyrosinase inhibitory activities were evaluated using tyrosinase inhibitor screening kits, molecular docking, dynamic simulation, and through examination of their toxicity and anti-melanogenic effects in zebrafish. These results are expected to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the composition of anthocyanins in purple potato, their tyrosinase inhibitory activity, and potential for anti-melanogenic effects, and promote the wider use of purple potato in these contexts.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compounds Structure Identification
Anthocyanins and their novel degradation compounds (9 and 10) were extracted from fresh slices of potato tubers using acidic water-ethanol, enriched with macroporous resin, and purified via semi-preparative chromatography, as shown in Figure 1.
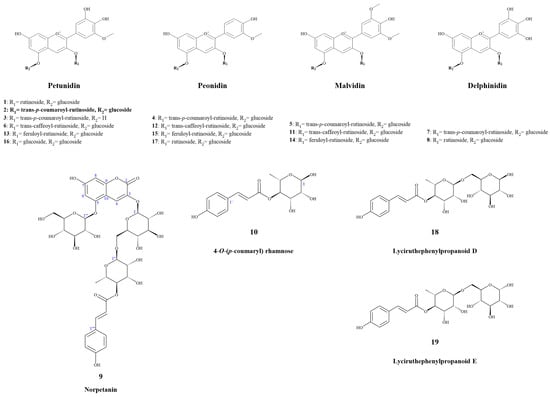
Figure 1.
Anthocyanins and their novel degradation compounds from Solanum tuberosum L.
2.1.1. Resolution and Identification of New Compounds
Compound 9 was obtained as a yellowish amorphous powder with a molecular formula of C36H42O21, as determined using HR-ESI-MS (m/z 833.2117 [M + Na]+, calcd. 833.2111). It had 16 degrees of unsaturation. The 1H NMR spectrum (Table 2) in CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1) of 9 exhibited a set of trans-p-coumaroyl signals at δH 7.48 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-2′′′′/H-6′′′′), 6.80 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-3′′′′/H-5′′′′), 7.60 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-7′′′′) and 6.34 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-8′′′′), one aromatic or olefinic proton singlet at δH 7.69 (1H, s, H-4), a set of 1,3,4,5-tetrasubstituted benzene ring signals at δH 6.60 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-6) and 6.37 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, H-8), two β-glucopyranosyl anomeric protons at δH 5.07 (1H, d, J = 7.0 Hz, H-1′) and 4.95 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1′′′), an α-rhamnopyranosyl anomeric proton at δH 4.76 (1H, br s, H-1′′), an acylated methine triplet at δH 4.94 (1H, t-like, J = 9.5 Hz, H-4′′), as well as a rhamnosyl methyl doublet in the up-field region. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 2) showed 36 carbon resonances, including a set of trans-p-coumaroyl carbons and 18 carbon signals assignable to three sugar moieties, whereas the remaining nine unsolved resonances originated from the aglycone core. The above NMR features were generally similar to those of petanin [31]; the main difference was that the ring B signals in the anthocyanin core were absent in 9, based on which the structure was inferred. It was inferred that the ring B moiety was oxidized and degraded to derive an unusual 3,5,7-trioxygen-substituted coumarin core. This inference was confirmed by the HMBC correlations (Figure 2) from H-4 to C-2 [δC 160.4 (s)], C-5 [δC 155.4 (s)], and C-9 [δC 153.3 (s)], H-6 and H-8 to C-10 [δC 104.4 (s)], and from H-1′ to C-3 [δC 139.0 (s)]. The resulting structure was further verified via careful analysis of the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HR-ESI-MS, HSQC, HMBC, and 1H,1H-COSY correlations shown in Figure 2 and Figures S1–S6. Therefore, the structure of compound 9 was established, as shown in Figure 1, and the compound was named norpetanin. To the best of our knowledge, compound 9 represents a rare class of ring B anthocyanins.

Table 2.
The 1H and 13C NMR spectral data for 9 in CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1).
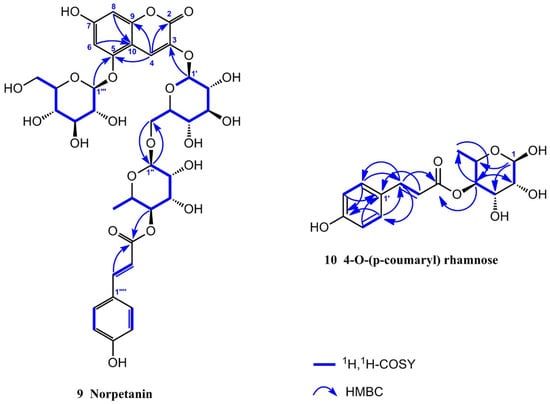
Figure 2.
Structures, key HMBC and 1H, 1H-COSY correlation of compounds 9 and 10.
Compound 10 was obtained as a yellowish amorphous powder with a molecular formula of C15H18O7 and seven degrees of unsaturation. The 1H and 13C NMR spectrum (Table 3) in CD3OD of 10 exhibited a set of trans-p-coumaroyl signals at δH 7.47 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-2′/H-6′), 6.80 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-3′/H-5′), 7.64 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-7′), and 6.36 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-8′), an α-rhamnopyranosyl anomeric proton at δH 5.04 (1H, br s, H-1), an acylated methine triplet at δH 5.02 (1H, t-like, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4), and a rhamnosyl methyl doublet in the up-field region. The inference was confirmed via the HMBC correlations from H-1 to C-3 [δC 70.3 (d)], C-5 [δC 67.3 (d)], from H-2 to C-3 and C-4 [δC 75.7 (d)], from H-3 to C-2 [δC 73.1 (d)], from H-4 to C-3, C-5, C-6 [δC 18.0 (q)], and C-9′ [δC 169.0 (s)], from H-6 to C-4 and C-5, from H-3′ and H-5′ to C-1′ [δC 127.2 (s)] and C-4′ [δC 161.3 (s)], from H-2′ and H-6′ to C-4′ and C-7′ [δC 146.8 (d)], from H-7′ to C-2′, 6′ [δC 131.2 (d)], C-8′ [δC 115.2 (d)], and C-9′ [δC 169.0 (s)], from H-8′ to C-1′ and C-9′. The resulting structure was further verified through careful analysis of the HSQC, HMBC, and 1H,1H-COSY correlations shown in Figure 2 and Figures S7–S11. Therefore, the structure of compound 10 was established (Figure 1) and it was named 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose.

Table 3.
The 1H and 13C NMR spectral data for 10 in CD3OD.
2.1.2. First Report of NMR Data for Known Compounds
Compound 3, which was obtained as an amorphous purple powder, possessed the molecular formula C37H39O18+ and had 19 degrees of unsaturation. The 1H-NMR spectrum (CD3OD:CF3COOD ≈ 9:1, 600 MHz) was as follows: δH 8.92 (1H, s, H-4), 7.93 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2′), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-6′), 7.56 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-7′′′′), 7.38 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-2′′′′, H-6′′′′), 6.83 (1H, br s, H-8), 6.80 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-3′′′′, H-5′′′′), 6.65 (1H, br s, H-6), 6.20 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-8′′′′), 5.35 (1H, d, J = 7.6 Hz, H-1′′), 4.94 (1H, t, J = 9.4 Hz, H-4′′′), 4.71 (1H, br s, H-1′′′), 3.97 (3H, s, 3′-OCH3), 0.98 (3H, d, J = 6.2 Hz, H-6′′′), as shown in Figure S12. Through comparison with research data [32], compound 3 was identified as petunidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside.
Compound 12, obtained as a purple amorphous powder, possessed the molecular formula C43H49O23+ and 19 degrees of unsaturation. The 1H-NMR spectrum (CD3OD:CF3COOD ≈ 9:1, 600 MHz) was as follows: δH 8.99 (1H, s, H-4), 8.28 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 1.9 Hz, H-6′), 8.20 (1H, d, J = 1.9 Hz, H-2′), 7.49 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-7′′′′′), 7.01–7.09 (4H, overlapped, H-6, H-8, H-5′, H-2′′′′′), 6.89 (1H, br d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-6′′′′′), 6.77 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-5′′′′′), 6.20 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-8′′′′′), 5.50 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-1′′), 5.19 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1′′′′), 4.90 (1H, t, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4′′′), 4.71 (1H, br s, H-1′′′), 4.00 (3H, s, 3′-OCH3), 0.99 (3H, d, J = 6.2 Hz, H-6′′′), as shown in Figure S13. It was named peonidin 3-O-trans-caffeoylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside [33].
Compound 15, obtained as a purple amorphous powder, possessed the molecular formula C44H51O23+ and 20 degrees of unsaturation. The 1H-NMR spectrum (CD3OD:CF3COOD ≈ 9:1, 600 MHz) was as follows: δH 9.00 (1H, s, H-4), 8.29 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 1.8 Hz, H-6′), 8.22 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, H-2′), 7.56 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-7′′′′′), 7.15 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2′′′′′), 7.01–7.10 (4H, overlapped, H-6, H-8, H-5′, H-6′′′′′), 6.80 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, H-5′′′′′), 6.30 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, H-8′′′′′), 5.47 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1′′), 5.18 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1′′′′), 4.90 (1H, t, J = 9.7 Hz, H-4′′′), 4.70 (1H, br s, H-1′′′), 4.00 (3H, s, 3′-OCH3), 3.87 (3H, s, 3′′′′′-OCH3), 0.98 (3H, d, J = 6.2 Hz, H-6′′′), as shown in Figure S14. Based on comparison and analysis of research data [33,34], 15 was identified as peonidin 3-O-feruloylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside.
2.1.3. Identification of Known Compounds
Compounds 1–8 and 11–19 were identified as petunidin 3-O-rutinoside-5-O-glucoside (1) [35], petanin (2), petunidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside (3) [32], peonidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (4) [33], malvidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (5) [35], petunidin 3-O-trans-caffeoylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (6) [35], delphinidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (7) [36], delphinidin 3-O-rutinoside-5-O-glucoside (8) [35], malvidin 3-O-trans-caffeoylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (11) [37], peonidin 3-O-trans-caffeoylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (12) [33], petunidin 3-O-feruloylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (13) [34], malvidin 3-O-feruloylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (14) [34], peonidin 3-O-feruloylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (15) [33,34], petunin (16) [38], peonidin 3-O-rutinoside-5-O-glucoside (17) [33], lyciruthephenylpropanoid D (18) [39], and lyciruthephenylpropanoid E (19) [39] via NMR, spectroscopic, mass spectrometric, and chromatographic analyses and comparison with compounds reported in the literature, as shown in Figures S16 and S17 and Table S1.
The anthocyanins in purple potato were found to be mainly petunidin anthocyanins, such as petunidin 3-O-rutinoside-5-O-glucoside, petanin, petunidin 3-O-trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside, petunidin 3-O-trans-caffeoylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside, petunidin 3-O-feruloylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside, and petunin [9,10,11]. However, there were slight differences in these results as compared to previous studies. For instance, in previous studies, the main anthocyanins of purple clones (UACH 0917, Shetland Black, and Violetta) were found to be malvidin, petunidin, and cyanidin, pelargonidin 3-O-p-coumaroylrutinoside-5-O-glucoside (0~0.0387 mg g−1), and petunidin 3-O-glucoside has also been identified in purple potatoes (Heijingang) [10,12,40]. Nevertheless, these differences may be related to potato varieties, analysis and identification methods, and producing areas.
Although lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E was first identified in Lycium ruthenicum Murr., lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E were first discovered and obtained in potato [39]. Interestingly, Solanum tuberosum L. and Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Belong to the Solanaceae Juss. in which the major anthocyanins are all petanin, and norpetanin also was purified from Lycium ruthenicum (Unpublished work from our research group). Consequently, these results may imply novel degradation or metabolic pathways of anthocyanins, such as from petanin to norpetanin to lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E to 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and need to be supported by more direct evidence.
2.2. Screening and Antimelanogenesis of Tyrosinase Inhibitors
Anthocyanins and their novel degradation compounds (1–19) were tested for tyrosinase inhibitory activity using a tyrosinase inhibitor screening kit. As shown in Table 4 and Figure 3A, petanin, norpetanin, 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E possessed tyrosinase inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 122.37 ± 8.03, 115.53 ± 7.51, 335.03 ± 12.99, and 156.27 ± 11.22 μM (Mean ± SEM, n = 3), respectively. However, the IC50 of kojic acid, which was lower than that of petanin and its degradation compounds, was 20.58 ± 1.62 μM. In addition, the tyrosinase inhibitory effect of other compounds (0.60 mM) were shown in Table S2.

Table 4.
Tyrosinase inhibitory activity (IC50), affinity, and amino acids of petanin and its degradation compounds.
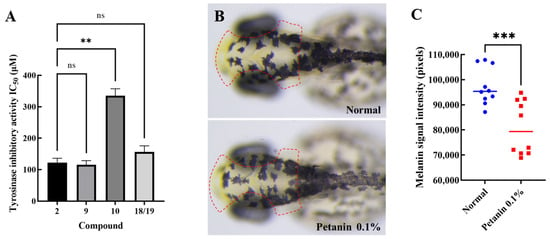
Figure 3.
Tyrosine inhibitory activity and anti-melanogenesis of anthocyanins and their novel degradation compounds (A) Tyrosine inhibits activity (**: p < 0.01, ns: not significant); (B) Melanin in zebrafish (Red box region is the characteristic site of melanin production in zebrafish); (C) Melanin signal intensity in zebrafish (***: p < 0.001).
Petanin, a major compound in purple potato, was tested for its safety and anti-melanogenic effects in zebrafish, as shown in Table S3 and Figure 3B,C.
Anthocyanins purified from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. had inhibitory effect on tyrosinase monophenolase (IC50 = 1.483 ± 0.058 mg mL−1), and the maximum inhibitory activity of the purified anthocyanins (3.00 mg mL−1) on tyrosinase diphenolase was 42.16% ± 0.77% [28]. Petunidin 3-O-glucoside may act as a tyrosinase inhibitor to block melanin production, and its IC50 value was 10.3 ± 1.0 µM [29]. As shown in Table 4 and Figure 3A, regarding the tyrosinase activity of petanin and its degradation compounds, petanin and 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose were shown to be significantly different (p < 0.01). However, there was no significant difference between petanin, norpetanin, and lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E (p > 0.05). Therefore, the acyl group containing two sugar groups may be the ‘key’ to the ‘lock’ for tyrosinase, whereas 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose may not have the same effect because the molecule is too small. In fact, according to the results of the evaluation of toxicity and anti-melanogenic effects in zebrafish, petanin not only had a very safe tolerated dose (MTC = 0.15%), but also showed a significant anti-melanogenic effect (17%, p < 0.05) at a concentration of 0.1% compared with the normal group, as shown in Figure 3B,C. Ultimately, petanin and its analogues inhibited tyrosinase activity, and its parent nucleus and acyl group may be important active groups.
2.3. Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation of Tyrosinase Inhibitors
Evaluation of petanin and its degradation compounds were performed against tyrosinase using AutoDock Vina. They depicted considerable docking energy and formation of intermolecular interactions with the essential residues of tyrosinase enzyme in the respective docked complexes (Figure 4 and Table 4). In addition, the ADMET of petanin was similar to that of norpetanin, as shown in Figure S18.
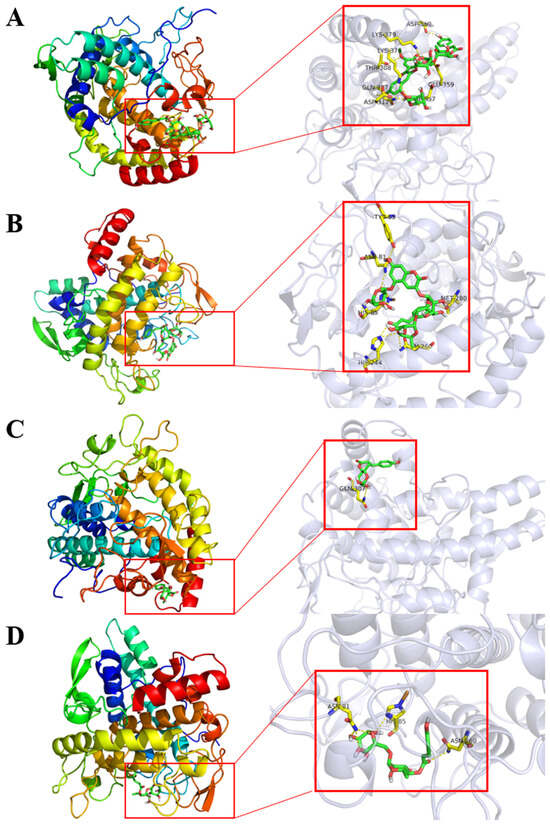
Figure 4.
The 3D intermolecular interactions for the docked complexes of tyrosinase with: (A) petanin, (B) norpetanin, (C) 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and (D) Lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E.
To further demonstrate the degree and stability of the binding between the compound and the protein, molecular dynamics simulations of 100 ns were performed for each set of docking results. The root mean square deviation (RMSD), root mean square fluctuation (RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), number of hydrogen bonds, and Gibbs free energy plots were analyzed in each set of molecular dynamics simulation trajectories (Figure 5).
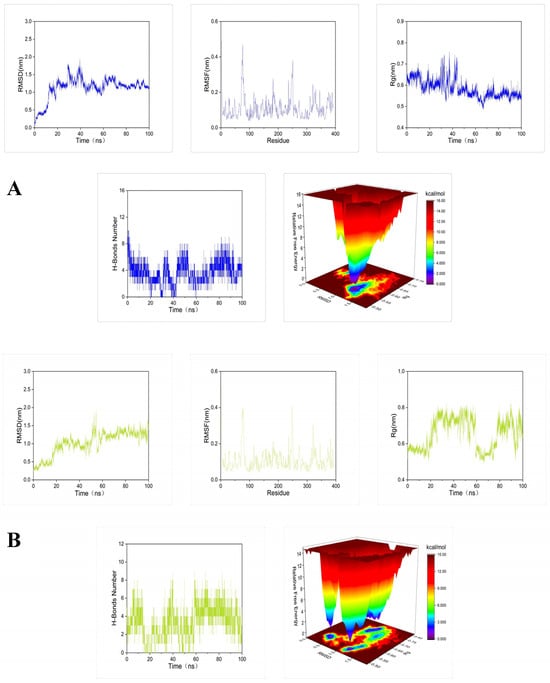
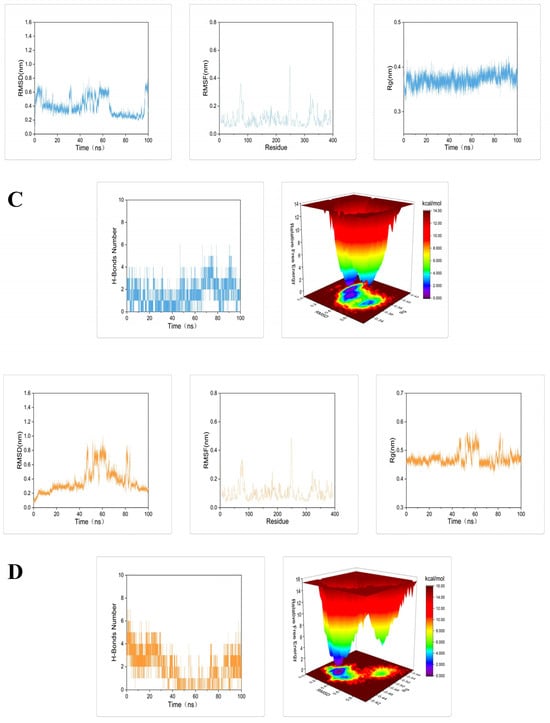
Figure 5.
Molecular dynamics simulations of 100 ns for tyrosinase docked with: (A) petanin, (B) norpetanin, (C) 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and (D) Lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E.
Molecular docking results showed that petanin and its degradation compounds had a huge binding energy with tyrosinase, but 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose had smaller binding energies and fewer hydrogen bonds than the other compounds, as shown in Table 4 and Figure 4. However, hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions are well established as essential factors in the stability of ligands at the active pocket of receptors [41]. Thus, the differences observed in the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of petanin and its degradation compounds may be related to the number and position of hydrogen bonds they form with tyrosinase.
Results of root mean square deviation (RMSD), root mean square fluctuation (RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), number of hydrogen bonds, and Gibbs free energy plots in the molecular dynamics simulation trajectories of the complex are shown in Figure 5. The RMSD fluctuation curve of molecular dynamics simulation reached a stable state without large fluctuations within 100 ns, and the fluctuation range was within 0–0.3 nm. This indicates that these compounds can form stable complexes with tyrosinase [42]. The RMSF showed that the amino acid residues in the complex all fluctuated around the amino acid residues at positions 80 and 250. This may be a normal fluctuation caused by the binding of the component small molecules to the protein [43]. The Rg curves all fluctuated in the range of 0.1–0.2 nm, indicating that each complex formed a tight and stable complex structure [44]. Calculation of the number of hydrogen bonds between the compound and the protein showed that petanin and norpetanin had four hydrogen bonds on average, lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E had three hydrogen bonds, and 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose had only two. The difference in the number of hydrogen bonds formed may be the main factor affecting the stability of the complex. Gibbs free energy plots showed that petanin formed the most stable complex with tyrosinase compared to its other compounds [45]. In conclusion, petanin and its degradation compounds formed stable complexes with tyrosinase, and this stability benefited from conformational fluctuations of the protein, fluctuations in the level of protein residues, protein folding, and the number of hydrogen bonds.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
Solanum tuberosum L. (Heijingang) fresh tubers were purchased from Yaodian Town, Dingxi City, Gansu Province, P. R. China (Latitude: 35°18′35″ N, Longitude: 104°03′23″ E, Altitude: approximately 2175 m) in June 2022, and were identified by Professor Baolong Liu of the Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NWIPB, CAS). A voucher specimen (Nwipb0335504) was deposited in the herbarium of the Key Laboratory of Tibetan Medicine Research (NWIPB, CAS).
3.2. General Experimental Procedures
The 1H (600 MHz/800 MHz) and 13C (600 MHz/800 MHz) NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AVANCE III 600 MHz Spectrometer (1H NMR spectra parameter configuration: NS = 4, DS = 2, DW = 41.6 usec. 13C NMR spectra parameter configuration: NS = 4/1024, DS = 2/4, DW = 41.6/13.8 usec.) and Bruker AV 800MHz Spectrometer (1H NMR spectra parameter configuration: NS = 4, DS = 0, DW = 31.2 usec. 2D NMR spectra parameter configuration: NS = 8/16, DS = 16/16, DW = 56.8/59.4 usec) (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) in a deuterated solvent. HR-ESI-MS and ESI-MS analyses were performed using a Shimadzu Corporation UPLC-IT-TOF spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Preparative high-performance liquid chromatography was performed on a DAC-HB50 separation module combined with a UV detector at 535 and 280 nm (Hanbon, Huai’an, China). A C18-ODS-A (300 mm × 50 mm, 5 μm, YMC, Kyoto, Japan) and XAqua C18 semi-preparative column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm, Acchrom, Wenling, China) were used for separation. UV spectra were acquired using a T6 New Century spectrophotometer (Persee, Beijing, China). Microscopic observation and photographs were taken using a SZX7 dissecting microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and a CCD camera (VertA1, Shanghai, China). All chemicals and solvents were of chromatographic grade.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
Fresh slices of potato tubers (100.00 kg) were subjected to extraction with 70% EtOH-Britton-Robinson buffer, and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum to obtain a crude extract (1.58 kg). The crude extract was partitioned with D101 macroporous adsorbent resin using an elution gradient of EtOH: water (0:100, 5 BV; 95:5, 4 BV) to obtain the potato extractum (100.50 g, a percentage yield of 0.10%, FW). The potato extract (40.00 g) was fractionated with DAC-HB50 using a water (0.60% trifluoroacetic acid)-acetonitrile gradient (0~55 min, 15%~35% acetonitrile; 50 mL, 535 nm) to obtain four fractions (Fr.1: 33.2~38.6 min, Fr.2: 40.6~43.5 min, Fr.3: 46.4~48.9 min, Fr.4: 52.8~54.6 min), as shown in Figure 6A. These fractions were separated using an XAqua C18 semi-preparative column with a water (0.6% trifluoroacetic acid)-acetonitrile elution system and various elution gradients in Fr.3, Fr.4, Fr.1, and Fr.2, as shown in Figure 6B–E.
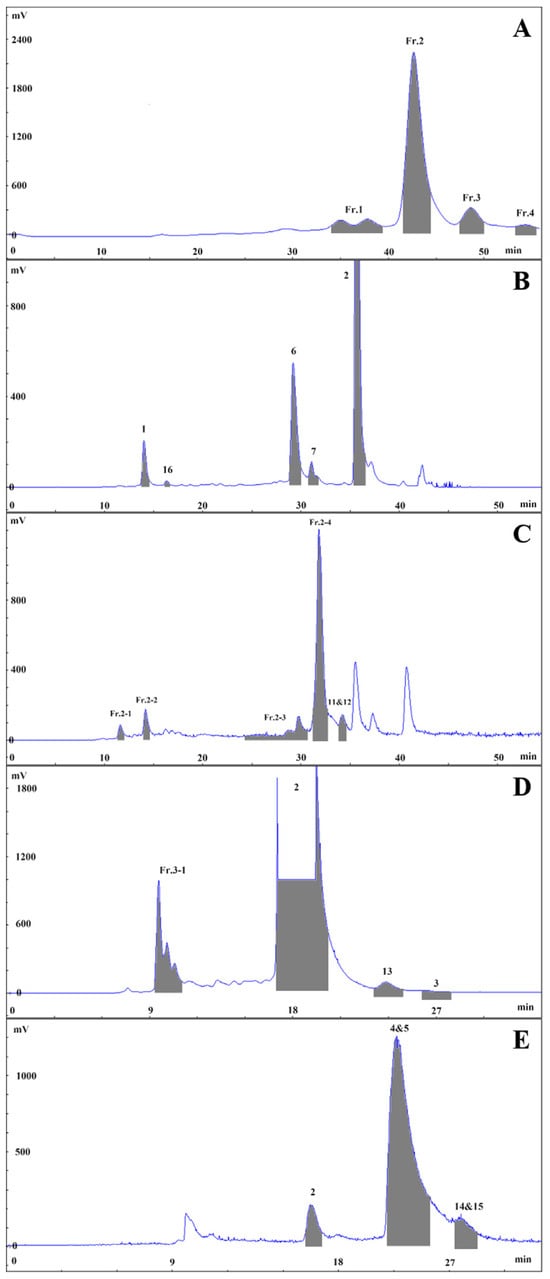
Figure 6.
Isolation and purification chromatography of Solanum tuberosum L. extract (A), Fr.1 (B), Fr.2 (C), Fr.3 (D) and Fr.4 (E).
3.3.1. Isolation and Purification of Fr.3
Fr.3 was eluted (0~35 min, 23%~23% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to give Fr.3-1 (9.2~11.1 min), 2 (16.9~20.2 min, 17.4 mg), 13 (23.1~25.0 min, 4.7 mg) and 3 (26.1~27.9 min, 5.2 mg). Then, Fr.3-1 was purified (0~40~45~55 min, 5%~20%~95%~95% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to yield 1 (33.2~34.2 min, 5.3 mg) and 16 (42.5~43.3 min, 2.6 mg).
3.3.2. Isolation and Purification of Fr.4
Fr.4 was eluted (0~30 min, 25~25% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to give 2 (16.1~16.9 min), 4, and 5 (20.5~22.7 min, 46.6 mg), along with 14 and 15 (24.1~25.3 min, 2.8 mg).
3.3.3. Isolation and Purification of Fr.1
Fr.1 was eluted (0~40~45~55 min, 15%~25%~95%~95% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to give 1 (13.9~14.9 min), 16 (16.4~16.9 min), 6 (28.9~30.2 min, 11.1 mg), 7 (31.0~32.1 min, 14.5 mg), and 2 (35.4~36.8 min).
3.3.4. Isolation and Purification of Fr.2
Fr.2 was eluted (0~50~55 min, 15%~27.5%~95% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to give Fr.2-1 (11.4~12.1 min), Fr.2-2 (13.9~14.6 min), Fr.2-3 (24.3~30.7 min), Fr.2-4 (31.4~32.8 min), and 11 and 12 (33.9~34.9 min, 4.9 mg). Then, Fr.2-1 was purified (0~20~40 min, 5%~11.5%~18% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to yield 8 (31.5~32.5 min, 2.4 mg). Fr.2-2 was purified (0~20~40~50 min, 5%~11.5%~18%~21.5% acetonitrile; 8 mL, 535 nm) to yield 1 (35.2~36.2 min). Fr.2-3 was purified (0~100 min, 16%~16% acetonitrile, 8 mL, 280 nm) to yield 18 and 19 (40.4~45.6 min, 44.3 mg), 10 (50.8~56.3 min, 2.1 mg), 9 (81.5~86.5 min, 29.4 mg), and 17 (89.9~93.7 min, 1.6 mg). Finally, Fr.2-4 was purified (0~40 min, 18%~18% acetonitrile, 8 mL, 535 nm) to yield 7 (23.7~27.2 min).
3.4. Screening and Validation of Inhibitory Tyrosinase Activity
3.4.1. Screening for Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity
Tyrosinase inhibitory activity was determined using a MAK257-1K tyrosinase inhibitor screening kit (Colorimetric; Sigma-Aldrich, Shanghai, China) (Lot: 7J08K05750), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were dissolved into the water (a 1.0 mM stock solution) and diluted to the proper test concentration with tyrosinase assay buffer before use. All tests were performed thrice independently, including inhibitor control (kojic acid) at an inhibitory ratio at 0.60 mM. The IC50 of petanin (2) and its derivatives (9 Norpetanin, 10 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and 18 and 19 Lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E) was calculated using GraphPad Prism (9.5.0, GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA).
3.4.2. Safety Evaluation and Verification of Anti-Melanogenic Effect
Wild-type AB strain zebrafish were used for safety evaluation in the experimental system. The age of zebrafish was 6 h after fertilization (6 hpf). The sample size of each group was 30 tails (n = 30). The adult fish were raised and bred according to the laboratory standards and in accordance with the requirements of the International AAALAC certification (Certification number: 001458). The experimental protocol was as follows: 1. The zebrafish were randomly selected in six-well plates, with 30 fish in each well. 2. Samples were dissolved in water, and the normal group and petanin 0.1% group were set up at the same time. The volume of each well was 3 mL. 3. The cells were incubated at 28 °C for 45 h in the dark. 4. The maximum tolerated concentration (MTC) of samples was determined for normal zebrafish based on zebrafish death count, death rate, and toxicity.
The anti-melanogenesis effect of petanin was also tested in zebrafish. The experimental protocol was as follows: 1. The zebrafish were randomly selected in six-well plates, with 30 fish in each well. 2. Samples were dissolved in water, and the normal group and petanin 0.1% group were set up at the same time. The volume of each well was 3 mL. 3. The cells were incubated at 28 °C for 45 h in the dark. 4. Ten zebrafish in each experimental group (n = 10) were randomly selected and photographed under a microscope, and the data were analyzed and collected by ImageJ. According to the Formula (1), the melanin inhibition rate of each sample was calculated and judged.
3.5. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation
3.5.1. Molecular Docking
Petanin and its derivatives (9 Norpetanin, 10 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, and 18 and 19 Lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E) were docked with tyrosinase (2y9x, from Protein Data Bank, www.rcsb.org) to analyze their binding affinities. The software packages used were as follows: ChemDraw (20.0.0.41) and Chem3D (20.0.0.41) for compounds structure, PyMOL (3.0.0) for ligands, and AutoDock Tools (1.5.6) and AutoDock Vina (1.2.5) for molecular docking. The ADMET of petanin and its derivatives were predicted by using the SwissADME (http://www.swissadme.ch/).
3.5.2. Dynamics Simulation
Gromacs (2020.3) software was used to simulate the molecular dynamics of the protein ligand complexes obtained via molecular docking. Charmm36 was selected as the protein force field, and Gaff2 was selected as the ligand force field. A TIP3P water model was used to add solvent to the protein ligand system, and a water box with a periodic boundary of 1.2 nm was established. Prior to formal dynamics simulations, the complex was subjected to energy minimization for 50,000 steps using conjugate gradient algorithms, followed by a further balancing system of 100 ps using an isothermal (310 K) system (NVT) and an isobaric (one standard atmosphere) system (NPT), and finally a molecular dynamics simulation at room temperature and pressure for 100 ns. The root mean square deviation (RMSD), root mean square fluctuation (RMSF), radius of gyration (Rg), number of hydrogen bonds, and Gibbs free energy plots for each set of molecular dynamics simulation trajectories were analyzed.
3.6. Statistical Analysis
The comparison of means between different groups of numerical variables was performed using a one-way ANOVA or t test. A p value less than 0.05 (p < 0.05) was considered to be statistically significant.
4. Conclusions
In this study, six petunidin anthocyanins were isolated and purified from fresh purple potato, together with four peonidin anthocyanins, three malvidin anthocyanin, and two delphinidin anthocyanins. These were mainly acylated anthocyanins. The novel compounds isolated and identified, norpetanin and 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, may indicate new metabolic pathways for anthocyanins: rearrangement or degradation at the B-ring, such as is seen in the pathway from petanin to norpetanin. However, more evidence is needed to support and elucidate the mechanism of the degradation or rearrangement reactions of anthocyanins. Moreover, petanin and its degradation compounds (such as norpetanin and lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E) showed promising potential as tyrosinase inhibitors based on both experimental and molecular docking and dynamic simulations. Hence, the chemical composition and biological activities of purple potato are now more widely recognized and understood, which facilitates the wider development and utilization of this crop, such as in the treatment of diseases related to melanin production and the development of cosmetic products with whitening efficacy. However, the evidence supporting the degradation pathway of petanin in purple potato is thus far very scarce and has not been clearly demonstrated, and transcriptomics and metabolomics should be investigated to provide more favorable evidence in future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules29071492/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1)) of 9; Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1)) of 9; Figure S3: HMBC spectrum and key HMBC correlations of 9; Figure S4: HSQC spectrum of 9; Figure S5: 1H, 1H-COSY spectrum and key 1H, 1H-COSY correlations of 9; Figure S6: HR-ESI-MS spectrum of 9; Figure S7: 1H NMR spectrum (800 MHz, CD3OD) of 10; Figure S8: 13C NMR spectrum (800 MHz, CD3OD) of 10; Figure S9: HMBC spectrum and key HMBC correlations of 10; Figure S10: HSQC spectrum of 10; Figure S11: 1H, 1H-COSY spectrum and key 1H, 1H-COSY correlations of 10; Figure S12: 1H NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1)) of 3; Figure S13: 1H NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1)) of 12; Figure S14: 1H NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CD3OD/CF3COOD (9:1)) of 15; Figure S15: HPLC chromatography of Solanum tuberosum L. extract (A) and Fr.1~Fr.4 (B~E); Figure S16: HPLC chromatography and spectrogram of 1~9; Figure S17: HPLC chromatography and spectrogram of 10~19; Figure S18: ADMET of (A) petanin, (B) norpetanin, (C) 4-O-(p-coumaryl) rhamnose, (D) Lyciruthephenylpropanoid D/E; Table S1: Retention time, purity and λmax of anthocyanins and their degradation products by HPLC; Table S2: Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of anthocyanins and their degradation products (0.60 mM); Table S3: Maximum tolerated concentration of petanin in zebrafish (n = 30).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.O. and H.W.; methodology, J.O. and N.H.; software, J.O.; validation, N.H. and H.W.; formal analysis, J.O.; investigation, J.O.; resources, H.W.; data curation, J.O.; writing—original draft preparation, J.O.; writing—review and editing, H.W. and N.H.; visualization, J.O.; supervision, H.W.; project administration, N.H.; funding acquisition, H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Innovation Platform for the Development and Construction of a Special Project of Qinghai Province (2021-ZJ-T05) and Qinghai “Kunlun Talents” programs.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and supplementary materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Wenna Zhou for their technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gutaker, R.M.; Weiß, C.L.; Ellis, D.; Anglin, N.L.; Knapp, S.; Luis Fernández-Alonso, J.; Prat, S.; Burbano, H.A. The origins and adaptation of European potatoes reconstructed from historical genomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gu, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Promoting potato as staple food can reduce the carbon–land–water impacts of crops in China. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, L.; Indukuri, V.V.; Charepalli, V.; Chrisfield, B.J.; Anantheswaran, R.C.; Lambert, J.D.; Vanamala, J.K. Comparative effects of vacuum or conventional frying on the polyphenol chemistry and in vitro colon cancer stem cell inhibitory activity of purple-flesh potatoes. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 3260–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Hayashi, K.; Ohara-Takada, A.; Watanuki, H.; Katahira, R.; Ono, H.; Terahara, N. Anthocyanins from Skins and Fleshes of Potato Varieties. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2010, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, A.; Matros, A.; Hartmann, A.; Arapitsas, P.; Dehmer, K.J.; Martens, S.; Mock, H.-P. Metabolite profiling of red and blue potatoes revealed cultivar and tissue specific patterns for anthocyanins and other polyphenols. Planta 2017, 246, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Niu, Y. A Comparative Study on Total Anthocyanin Content, Composition of Anthocyanidin, Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Pigmented Potato Peel and Flesh. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 22, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.; Winterhalter, P. Anthocyanins from pigmented potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.E.; Walker, J.R.; Lancaster, J.E.; Sutton, K.H. Determination of anthocyanins, flavonoids and phenolic acids in potatoes. I: Coloured cultivars of Solanum tuberosum L. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 77, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.; Øvstedal, D.O.; Slimestad, R.; Andersen, Ø.M. Anthocyanins from a Norwegian potato cultivar. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Dias, M.I.; Pereira, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, Â.; Leme, C.M.; Alexopoulos, A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C. Phenolic composition and cell-based biological activities of ten coloured potato peels (Solanum tuberosum L.). Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Lonchamp, J.; Dias, M.I.; Liddle, C.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Glamočlija, J.; Alexopoulos, A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L. Anthocyanin-rich extracts from purple and red potatoes as natural colourants: Bioactive properties, application in a soft drink formulation and sensory analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Niu, N.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Anthocyanin Profiles in Colored Potato Tubers at Different Altitudes by HPLC–MS Analysis with Optimized Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Foods 2023, 12, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Honmou, O.; Sasaki, M.; Haseda, A.; Kagami-Katsuyama, H.; Shoji, T.; Namioka, A.; Namioka, T.; Magota, H.; Oka, S. The impact of purple-flesh Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cv.“Shadow Queen” on minor health complaints in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strugała, P.; Urbaniak, A.; Kuryś, P.; Włoch, A.; Kral, T.; Ugorski, M.; Hof, M.; Gabrielska, J. Antitumor and antioxidant activities of purple potato ethanolic extract and its interaction with liposomes, albumin and plasmid DNA. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1271–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.; Blesso, C.N. Antioxidant properties of anthocyanins and their mechanism of action in atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Wu, B.; Fu, W.; Xu, B.; Pamuru, R.R.; Kennett, M.; Vanamala, J.K.; Reddivari, L. Anthocyanin-containing purple potatoes ameliorate DSS-induced colitis in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 93, 108616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokioja, J.; Yang, B.; Linderborg, K.M. Acylated anthocyanins: A review on their bioavailability and effects on postprandial carbohydrate metabolism and inflammation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5570–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Hong, S.-C.; Kim, S.M.; Pan, C.-H. Inhibitory effect of anthocyanin-enriched fractions from colored potatoes against lipase and α-glucosidase. LWT 2023, 184, 114952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Kortesniemi, M.K.; Linderborg, K.M.; Yang, B. Anthocyanins as promising molecules affecting energy homeostasis, inflammation, and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes with special reference to impact of acylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 71, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, F. Health benefits of anthocyanins and molecular mechanisms: Update from recent decade. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Jing, P. Anthocyanins in Brassicaceae: Composition, stability, bioavailability, and potential health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2205–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Chu, M.; Yu, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yan, N. Anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins: Chemical structures, food sources, bioactivities, and product development. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 4581–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şöhretoğlu, D.; Sari, S.; Barut, B.; Özel, A. Tyrosinase inhibition by some flavonoids: Inhibitory activity, mechanism by in vitro and in silico studies. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 81, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V. Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhan, J.K.; Chung, Y.C.; Chen, G.H.; Chang, C.H.; Lu, Y.C.; Hsu, C.K. Anthocyanin contents in the seed coat of black soya bean and their anti-human tyrosinase activity and antioxidative activity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Radio frequency-assisted enzymatic extraction of anthocyanins from Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. flowers: Process optimization, structure, and bioactivity determination. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 149, 112327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Shi, L.; Xue, P. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction by response surface methodology, antioxidant capacity, and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of anthocyanins from red rice bran. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Liu, K.; Liang, Y.; Liu, G.; Sang, J.; Li, C. Extraction optimization and purification of anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. and evaluation of tyrosinase inhibitory activity of the anthocyanins. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Su, X.; Kim, J.A. The Luteolinidin and Petunidin 3-O-Glucoside: A Competitive Inhibitor of Tyrosinase. Molecules 2022, 27, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathne, W.A.H.M.; Molagoda, I.M.N.; Park, S.R.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, O.-K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Oren, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.-R. Anthocyanins from Hibiscus syriacus L. inhibit melanogenesis by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, Ø.M.; Opheim, S.; Aksnes, D.W.; Frøystein, N.Å. Structure of petanin, an acylated anthocyanin isolated from Solanum tuberosum, using homo-and hetero-nuclear two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. Phytochem. Anal. 1991, 2, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempo, P.; Carafa, V.; Grassi, R.; Basile, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Formisano, C.; Rigano, D.; Altucci, L. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities of Solanum tuberosum L. var. Vitelotte. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Tatsuzawa, F.; Toya, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Hirayama, Y.; Shinoda, K.; Hara, R.; Seki, H. Acylated peonidin 3-rutinoside-5-glucosides from commercial petunia cultivars with pink flowers. Heterocycles 2004, 63, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.; Andersen, Ø.M. Anthocyanins from tubers and shoots of the purple potato, Solanum tuberosum. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Saito, N.; Tatsuzawa, F.; Kakefuda, T.; Yamakage, K.; Ohtani, E.; Koshi-ishi, M.; Matsusake, Y.; Kokubun, H.; Watanabe, H. Floral anthocyanins in wild taxa of Petunia (Solanaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1999, 27, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyanagi, T.; Kashiwada, Y.; Shida, Y.; Ikeshiro, Y.; Kaneyuki, T.; Konishi, T. Nasunin from Eggplant Consists of Cis–Trans Isomers of Delphinidin 3-[4-(p-Coumaroyl)-l-rhamnosyl (1→6) glucopyranoside]-5-glucopyranoside. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9472–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimestad, R.; Aaberg, A.; Andersen, O.M. Acylated anthocyanins from petunia flowers. Phytochemistry 1999, 50, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Sato, Y.; Okuno, R.; Kameda, K.; Isobe, M.; Kondo, T. Structural analysis and measurement of anthocyanins from colored seed coats of Vigna, Phaseolus, and Glycine legumes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-S.; Li, S.; Luo, Z.-H.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.-S.; Gao, H. Bioactive phenylpropanoid derivatives from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 116, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Han, H.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y. Anthocyanin Composition and Content in “Heijingang” Purple Potato. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, R.; Das, S.; Stanley, A.; Yadav, L.; Sudhakar, A.; Varma, A.K. Optimized hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding at the target-ligand interface leads the pathways of drug-designing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüschweiler, R. Efficient RMSD measures for the comparison of two molecular ensembles. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2003, 50, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, L.S. Electric conductance and pH measurements of isoionic salt-free bovine mercaptalbumin solutions. An evaluation of root-mean-square proton fluctuations. J. Phys. Chem. 1968, 72, 2958–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MIu, L.; Bogatyreva, N.; Galzitskaia, O. Radius of gyration is indicator of compactness of protein structure. Mol. Biol. 2008, 42, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bharatiy, S.K.; Hazra, M.; Paul, M.; Mohapatra, S.; Samantaray, D.; Dubey, R.C.; Sanyal, S.; Datta, S.; Hazra, S. In silico designing of an industrially sustainable carbonic anhydrase using molecular dynamics simulation. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 1081–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).